technical data Seat Altea Freetrack 2010 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SEAT, Model Year: 2010, Model line: Altea Freetrack, Model: Seat Altea Freetrack 2010Pages: 294, PDF Size: 7.71 MB
Page 25 of 294

Seat belts23
Safety First
Controls and equipment
Practical tips
Technical Data
Seat belts protection
Passengers not wearing seat belts risk severe injuries in the
event of an accident.Properly worn seat belts hold the vehicle occupants in the correct sitting posi-
tions and substantially reduce the kinetic energy in the event of an accident.
Seat belts also help to prevent uncontrolled movements that could lead to
severe injuries. In addition, properly worn seat belts reduce the danger of
being thrown from the car.
Passengers wearing their seat belts correctly benefit greatly from the ability
of the belts to absorb kinetic energy. The front part of your vehicle and other
passive safety features (such as the airbag system) are also designed to
absorb the kinetic energy released in a collision. Taken together, all these
features reduce the releasing kinetic energy and consequently, the risk of
injury.
Our examples describe frontal collisions. Of course, properly worn seat belts
substantially reduce the risk of injury in all other types of accidents. This is why it is so important to fasten seat belts before every trip, even when "just
driving around the corner".
Ensure that your passengers wear their seat belts as well. Accident statistics
have shown properly that wearing seat belts is an effective mean of substan-
tially reducing the risk of injury and improving the chances of survival in a
serious accident. Furthermore, properly worn seat belts improve the protec-
tion provided by airbags in the event of an accident. For this reason, wearing
a seat belt is required by law in most countries.
Although your vehicle is equipped with airbags, the seat belts must be
fastened and worn. The front airbags, for example, are only triggered in some
frontal accidents. The front airbags will
not be triggered during minor frontal
collisions, minor side collisions, rear collisions, rolls or accidents in which the
airbag trigger threshold value in the control unit is not exceeded.
Therefore, you should always wear your seat belt and ensure that your
passengers have fastened their seat belts properly before you drive off!
Safety instructions on using seat belts
If seat belts are used correctly, they can reduce the risk of
injury in an accident.– Always wear the seat belt as described in this booklet.
– Ensure that the seat belts can be fastened at all times and are not damaged.
WARNING
•If the seat belts are worn incorrectly or not at all, the risk of severe inju-
ries increases. The optimal protection from seat belts can be achieved only
if you use them properly.
Fig. 11 Driver wearing
the seat belt properly: is
secured by the belt in
sharp braking
Freetrack_EN.book Seite 23 Donnerstag, 10. September 2009 10:33 10
Page 27 of 294

Seat belts25
Safety First
Controls and equipment
Practical tips
Technical Data
– Adjust the seat and head restraint correctly.
– To fasten the belt, take hold of the latch plate and pull it slowly
across your chest and lap.
– Insert the latch plate into the buckle for the appropriate seat and push it down until it is securely locked with an audible click
⇒page 24, fig. 12 .
– Pull the belt to ensure that the latch plate is securely engaged in the buckle.The seat belts are equipped with an automatic retractor on the shoulder
strap. Full freedom of movement is permitted when the shoulder belt is pulled
slowly. However, during sudden braking, during travel in mountains or bends
and during acceleration, the automatic retractor on the shoulder belt is
locked.
The automatic belt retractors on the front seats are fitted with belt tension
devices ⇒page 28.
WARNING
•An incorrectly worn seat belt web can cause severe injuries in the event
of an accident.•The seat belts offer best protection only when the backrests are in an
upright position and the seat belts have been fastened properly.•Never put the latch plate in the buckle of another seat. If you do this, the
seat belt will not protect you properly and the risk of injury is increased.•I f a n o ccu p an t is i n co r re c t l y be l te d i n , t h e b e l t ca n n o t p ro te c t h i m o r h e r
properly. An incorrectly positioned belt web can cause extremely severe
injuries.•Always engage the retractor lock when you are securing a child seat in
group 0, 0+ or 1 ⇒page 46.
Seat belt position
Seat belts offer their maximum protection only when they are
properly positioned.
Fig. 13 Correct belt web
and head restraint posi-
tions, viewed from frontFig. 14 Correct belt web
and head restraint posi-
tions, viewed from side
Freetrack_EN.book Seite 25 Donnerstag, 10. September 2009 10:33 10
Page 29 of 294

Seat belts27
Safety First
Controls and equipment
Practical tips
Technical Data
WARNING
•An incorrectly worn seat belt web can cause severe injuries in the event
of an accident.•For pregnant women, the lap part of the seat belt must lie as low as
possible over the pelvis, never across the stomach, and always lie flat so
that no pressure is exerted on the abdomen.•Read and observe the warnings ⇒page 23.
Seat belt release
The seat belt must not be unfastened until the vehicle has
come to a standstill.– Press the red button on the belt buckle ⇒fig. 16 . The latch plate
is released and springs out ⇒ . – Guide the belt back by hand so that it rolls up easily and the trim
is not damaged.
WARNING
Never unbuckle a seat belt while the vehicle is in motion. If you do, you
increase the risk of sustaining severe or fatal injuries.Adjusting the seat belt height
Seat belt height adjusters can be used to adjust the position
of the seat belt at the shoulder.The seat belt adjuster for the front seats can be used to adjust the
proper belt position at the shoulder.
Fig. 16 Removing latch
plate from buckle
Fig. 17 Location of the
belt height adjuster
Freetrack_EN.book Seite 27 Donnerstag, 10. September 2009 10:33 10
Page 31 of 294

Seat belts29
Safety First
Controls and equipment
Practical tips
Technical Data
belt may be damaged. The consequence may be that, in the event of an acci-
dent, the belt tension devices function incorrectly or not at all.
So that the effectiveness of the belt tension device is not reduced and that
removed parts do not cause any injuries or environmental pollution, regula-
tions, which are known to the qualified workshops, must be observed.
WARNING
•If repairs are not carried out by a professional, or if the belt tension
devices are used incorrectly, the risk of severe or fatal injuries increases.
The belt tension devices may fail to trigger or may trigger in the wrong
circumstances.•Never attempt to repair, adjust, remove or install parts of the belt
tension devices or seat belts.•The belt tension device and seat belt including its automatic retractor
cannot be repaired.•Any work on the belt tension devices and seat belts, including the
removal and refitting of system parts in conjunction with other repair work,
must be performed by a qualified workshop only.•The belt tension devices will only provide protection for one accident
and must be changed it they have been activated.
Freetrack_EN.book Seite 29 Donnerstag, 10. September 2009 10:33 10
Page 33 of 294

Airbag system31
Safety First
Controls and equipment
Practical tips
Technical Data
•Always properly adjust the front seats.
The danger of fitting a child seat on the front passenger seat
Rear-facing child seats must never be used on the front
passenger seat when the front passenger airbag is enabled.An enabled front airbag on the front passenger side is potentially a major
danger to a child. The front passenger seat is life threatening to a child if
he/she is transported in a rear-facing child seat. You should always transport
all children up to 12 years of age on the rear seat.
If a rear-facing child seat is secured to the front passenger seat, an inflating
airbag can strike it with such great force that critical or fatal injuries may
result.
Therefore we strongly recommend you to transport children on the rear seats.
That is the safest place for children in the vehicle. Alternatively, the front
passenger airbag can be disabled with a key-operated switch ⇒page 44.
When transporting children, use a child seat appropriate to the age and size
of each child ⇒ page 46.
For those vehicles that do not include a key lock switch to turn the airbag off,
an Authorised Service Centre must be consulted.
WARNING
•If a child seat is secured to the front passenger seat, the risk to the child
of sustaining critical or fatal injuries in the event of an accident increases.•Never secure a rear-facing child seat to the front passenger seat if the
front passenger airbag is enabled. The child can suffer critical or fatal inju-
ries when the front passenger airbag is triggered.
•An inflating front passenger airbag can strike the rear-facing child seat
and hurl it with great force against the door, the roof or the backrest.•If, under special circumstances, it is necessary to transport a child in a
rear-facing child seat on the front passenger seat, it is absolutely essential
that you observe the following safety measures:
−Disable the front passenger airbag ⇒page 44, “Deactivating
airbags*”.
− The child seat must be approved by the child seat manufacturer for
use on a front passenger seat with front or side airbag.
− Follow the installation instructions given by the child seat manufac-
turer and observe the safety instructions ⇒page 46, “Child safety”.
− Before properly installing the child seat, push the front passenger
seat completely backwards so that the greatest possible distance to
the front passenger airbag is ensured.
− Ensure that no objects prevent the front passenger seat from being
pushed completely back.
− The backrest of the front passenger seat must be in an upright
position.
Warning lamp for airbag and belt tension device system
This warning lamp monitors the airbag and belt tension
device system.The warning lamp monitors all airbags and belt tension devices in the
vehicle, including control units and wiring connections.
WARNING (continued)
WARNING (continued)
Freetrack_EN.book Seite 31 Donnerstag, 10. September 2009 10:33 10
Page 35 of 294

Airbag system33
Safety First
Controls and equipment
Practical tips
Technical Data
•We strongly recommend you to go to a qualified workshop for all work
on the airbag system.•Never attempt to alter the front bumper or the body.•The airbags provide protection for just one accident; replace them once
they have deployed.WARNING (continued)
Freetrack_EN.book Seite 33 Donnerstag, 10. September 2009 10:33 10
Page 37 of 294
Airbag system35
Safety First
Controls and equipment
Practical tips
Technical Data
The front airbag system will not be triggered if:
•the ignition is switched off,•there is a minor frontal collision,•there is a side collision,•there is a rear-end collision,•the vehicle turns over.WARNING
•The seat belts and airbags can only provide maximum protection if the
occupants are seated correctly ⇒page 10, “Proper sitting position for
occupants”.•If a fault has occurred in the airbag system, have the system checked
immediately by a qualified workshop. Otherwise, during a frontal collision
the system may fail to trigger, or not trigger correctly.
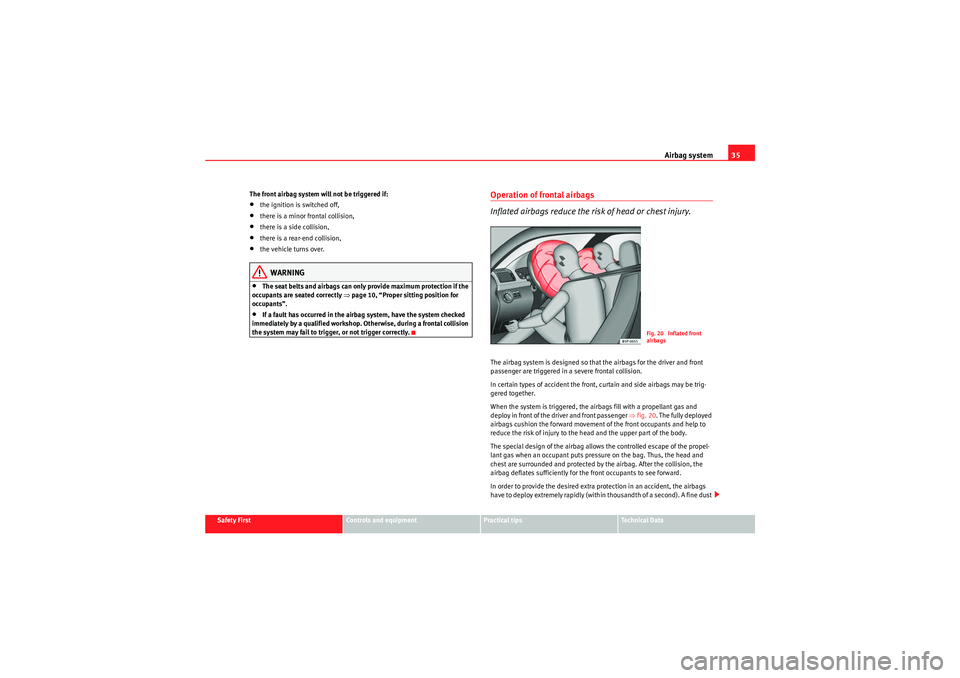
Operation of frontal airbags
Inflated airbags reduce the risk of head or chest injury.The airbag system is designed so that the airbags for the driver and front
passenger are triggered in a severe frontal collision.
In certain types of accident the front, curtain and side airbags may be trig-
gered together.
When the system is triggered, the airbags fill with a propellant gas and
deploy in front of the driver and front passenger ⇒ fig. 20. The fully deployed
airbags cushion the forward movement of the front occupants and help to
reduce the risk of injury to the head and the upper part of the body.
The special design of the airbag allows the controlled escape of the propel-
lant gas when an occupant puts pressure on the bag. Thus, the head and
chest are surrounded and protected by the airbag. After the collision, the
airbag deflates sufficiently for the front occupants to see forward.
In order to provide the desired extra protection in an accident, the airbags
have to deploy extremely rapidly (within thousandth of a second). A fine dust
Fig. 20 Inflated front
airbags
Freetrack_EN.book Seite 35 Donnerstag, 10. September 2009 10:33 10
Page 39 of 294

Airbag system37
Safety First
Controls and equipment
Practical tips
Technical Data
Safety notes on the frontal airbag system
If you use airbags correctly, they can considerably reduce the
risk of injury in many kinds of accident.
WARNING
•It is important for the driver and front passenger to keep a distance of
at least 25 cm from the steering wh eel or dash panel. If the minimum
distance is not observed then the airbags do not correctly protect the
vehicle occupants; risk of fatal injuries! In addition, the front seats and
head restraints must always be positioned correctly for the height of the
occupant.•If you are not wearing a seat belt, if you lean forward or to the side while
travelling or assume an incorrect sitting position, there is a substantially
increased risk of injury. This increased risk of injury will be further
increased if you are struck by an inflating airbag.•Never let a child travel on the front seat without an appropriate restraint
system. If the airbag is triggered in an accident, children can sustain
serious or fatal injuries from the airbag as it inflates ⇒page 46, “Child
safety”.•The deployment space between the front passengers and the airbags
must not in any case be occupied by other passenger, pets and objects.•The airbags provide protection for just one accident; replace them once
they have deployed.•It is also important not to attach any objects such as cup holders or
telephone mountings to the surfaces covering the airbag units.•Do not attempt to modify components of the airbag system in any
way.
Side airbags*Description of side airbags
The airbag system is not a substitute for the seat belts.The front side airbags are located in the driver seat and front passenger seat
backrests ⇒fig. 22. The rear side airbags are located in the rear wheel
housing lining. The locations are identified by the text “AIRBAG” in the upper
region of the backrests and in the rear wheel housing lining.
Together with the seat belts, the side airbag system gives the front seat occu-
pants additional protection for the upper body in the event of a severe side
collision ⇒page 40, “Safety notes on the operation of the side airbag
system”.
In a side collision, the side airbags reduce the risk of injury to passengers on
the front seats to the areas of the body facing the impact. In addition to their
normal function of protecting the occupants in a collision, the seat belts also
Fig. 22 Side airbag in
driver seat
Freetrack_EN.book Seite 37 Donnerstag, 10. September 2009 10:33 10
Page 41 of 294

Airbag system39
Safety First
Controls and equipment
Practical tips
Technical Data
Function of side airbags
Inflated airbags can reduce the risk of head or chest injury in
many side impact collisions.In some side collisions the side airbag is triggered on the impact side of the
vehicle ⇒fig. 23 .
In certain types of accident the front, curtain and side airbags may be trig-
gered together.
When the system is triggered, the airbag is filled with propellant gas.
In order to provide the desired extra pr otection in an accident, the airbags
have to deploy extremely rapidly (within thousandth of a second). A fine dust
may develop when the airbag deploys. This is normal and it is not an indica-
tion of fire in the vehicle.
The fully deployed airbags cushion the movement of the occupants of the
front seats and the outer rear seats and help to reduce the risk of injury to the
upper body. The special design of the airbag allows the controlled escape of the propel-
lant gas when an occupant puts pressure on the bag. Thus, the head and
chest are surrounded and protected by the airbag.
Fig. 23 Inflated side
airbag on left side of
vehicle
Freetrack_EN.book Seite 39 Donnerstag, 10. September 2009 10:33 10
Page 43 of 294

Airbag system41
Safety First
Controls and equipment
Practical tips
Technical Data
Curtain airbagsDescription of curtain airbags
The airbag system is not a substitute for the seat belts.The curtain airbags are located on both sides in the interior above the doors
⇒fig. 24 and are identified with the text “AIRBAG”.
In conjunction with the seat belts, the curtain airbag system gives the occu-
pants additional protection for the head and upper body in the event of a
severe side collision ⇒ page 42, “Safety notes on the operation of the
curtain airbag system”.
The airbag system is not a substitute for seat belts, but it is an integral part
of the vehicle's overall passive safety system. Please bear in mind that the
airbag system can only work effectively when the occupants are wearing their
seat belts correctly and have adjusted the head restraints properly. Therefore,
it is most important to wear the seat belts at all times, not only because this is required by law in most countries, but also for your safety
⇒page 19,
“Brief introduction”.
The main parts of the curtain airbag system are:
•an electronic control and monitoring system (control unit),•the curtain airbags (airbags with ga s generator) for the driver, front
passenger and passengers on the rear seats,•a warning lamp
in the dash panel insert ⇒page 31.
The airbag system operation is monitored electronically.
The curtain airbag system will not be triggered
•the ignition is switched off,
Fig. 24 Location of left curtain airbag
Freetrack_EN.book Seite 41 Donnerstag, 10. September 2009 10:33 10