ABS Seat Ibiza ST 2011 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SEAT, Model Year: 2011, Model line: Ibiza ST, Model: Seat Ibiza ST 2011Pages: 280, PDF Size: 4.01 MB
Page 169 of 280

167
Intelligent technology
Practical Tips Intelligent technology
Brakes Brake servo
The brake servo increases the pressure you apply to the brake pedal. It
works only when the engine is running .
If the brake servo is not functioning due to a malfunction, or if the vehicle
has to be towed, you will have to press the brake pedal considerably harder
to make up for the lack of servo assistance.
WARNING
The braking distance can also be affected by external factors.
● Never let the vehicle coast with the engine switched off. Failure to do
so could result in an accident. The braking distance is increased consid-
erably when the brake servo is not active.
● If the brake servo is not working, for example when the vehicle is be-
ing towed, you will have to press the brake pedal considerably harder
than normal.
Hydraulic Brake Assist (HBA)*
The Hydraulic Brake Assist function (HBA) is only included in
vehicles with ESP.
In an emergency, most drivers brake in time, but not with maximum force.
This results in unnecessarily long braking distances.
This is when the brake assist system comes into action. When pressing the
brake pedal rapidly, the assistant interprets it as an emergency. It then very
quickly builds up the full brake pressure so that the ABS can be activated
more quickly and efficiently, thus reducing the braking distance.
Do not reduce the pressure on the brake pedal. The brake assist system
switches off automatically as soon as you release the brake.
Automatic hazard warning lights activation
The brake lights flash automatically to indicate that the vehicle is braking
suddenly or in an emergency situation. If the emergency braking continues
until the vehicle comes to a standstill, the hazard warning lights will then
come on and the brake lights will remain on permanently from that moment.
The warning lights will automatically switch off when the vehicle begins to
move again or when the "warning" light button is pressed.
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications
Page 170 of 280
168Intelligent technology
WARNING
● The risk of accident is higher if you drive too fast, if you do not keep
your distance to the vehicle in front, and when the road surface is slip-
pery or wet. The increased accident risk cannot be reduced by the brake
assist system.
● The brake assist system cannot defy the laws of physics. Slippery
and wet roads are dangerous even with the brake assist system! There-
fore, it is essential that you adjust your speed to suit the road and traffic
conditions. Do not let the extra safety features tempt you into taking any
risks when driving.
Anti-lock brake system and traction control
ABS Anti-lock brake system (ABS)
The anti-lock brake system prevents the wheels locking dur-
ing braking.
The anti-lock brake system (ABS) is an important part of the vehicle's active
safety system.
How the ABS works
If one of the wheels is turns too slowly in relation to the road speed, and is
close to locking, the system will reduce the braking pressure for this wheel.
The driver is made aware of this control process by a pulsating of the brake
pedal and audible noise. This is a deliberate warning to the driver that one
or more of the wheels is tending to lock and the ABS control function has
intervened. In this situation it is important to keep the brake pedal fully de-
pressed so the ABS can regulate the brake application. Do not “pump”. If you brake hard on a slippery road surface, the best possible control is re-
tained as the wheels do not lock.
However, ABS will not necessarily guarantee shorter braking distances in
all
conditions. The braking distance could even be longer if you brake on gravel
or on fresh snow covering a slippery surface.
WARNING
● The anti-lock brake system cannot defy the laws of physics. Slippery
and wet roads are dangerous even with ABS! If you notice that the ABS is
working (to counteract locked wheels under braking), you should reduce
speed immediately to suit the road and traffic conditions. Do not let the
extra safety features tempt you into taking any risks when driving.
● The effectiveness of ABS is also determined by the tyres fitted
⇒ page 215.
● If the running gear or brakes are modified, the effectiveness of the
ABS could be severely limited.
Traction control system (TCS)*
The traction control system prevents the drive wheels from
spinning when the vehicle is accelerating. The system al-
ways includes ABS
Description and operation of the traction control system during
acceleration (TCS)
TCS reduces engine power to help prevent the drive wheels of front-wheel
drive vehicles losing traction during acceleration. The system works in the
entire speed range in conjunction with ABS. If a malfunction occurs in the
ABS, the TCS will also be inoperative.
Page 171 of 280

169
Intelligent technology
TCS helps the vehicle to start moving, accelerate and climb a gradient in
slippery conditions where this may otherwise be difficult or even impossi-
ble.
The TCS is switched on automatically when the engine is started. If necessa-
ry, it may be turned on or off by briefly pushing the ESP button on the centre
console.
When the TCS is off, the warning lamp is lit. The TCS should normally be
left on. Only in exceptional circumstances, when the slipping of the wheels
is required, can they be disconnected using the ESP button, for example.
● With compact temporary spare wheel.
● When using the snow chains.
● When driving in deep snow or on loose surfaces
● When the vehicle is bogged-down, to free it by rocking.
The TCS should be switched on again as soon as possible.
WARNING
● It must be remembered that TCS cannot defy the laws of physics. This
should be kept in mind, particularly on slippery and wet roads and when
towing a trailer.
● Always adapt your driving style to suit the condition of the roads and
the traffic situation. Do not let the extra safety afforded by TCS tempt you
into taking any risks when driving, this can cause accidents.
CAUTION
● In order to ensure that TCS function correctly, all four wheels must be fit-
ted with the same tyres. Any differences in the rolling radius of the tyres can
cause the system to reduce engine power when this is not desired.
● Modifications to the vehicle (e.g. to the engine, the brake system, run-
ning gear or any components affecting the wheels and tyres) could affect
the efficiency of the ABS and TCS. XDS*
Driveshaft differential
When taking a bend, the driveshaft differential mechanism allows the outer
wheel to turn at a higher speed than the inner wheel. In this way, the wheel
that is turning faster (outer wheel) receives less drive torque than the inner
wheel. This may mean that in certain situations the torque delivered to the
inner wheel is too high, causing the wheels to spin. On the other hand, the
outer wheel is receiving a lower drive torque than it could transmit. This
causes an overall loss of lateral grip on the front axle, resulting in under-
steer or “lengthening” of the trajectory.
By using the ESP sensors and signals, the XDS system is able to detect and
correct this effect.
Through the ESP, the XDS brakes the inner wheel, thereby counteracting the
excess drive torque in this wheel. This means that the driver's desired tra-
jectory is much more precise,
The XDS system operates in combination with the ESP and is always active,
even when the traction control, TCS, is disconnected.
Electronic Stability Programme (ESP)* General notes
The Electronic Stability Programme increases the vehicle's
stability on the road.
The Electronic Stability Programme helps reduce the danger of skidding.
The Electronic Stability Programme (ESP) consists of ABS, EDL and TCS.
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications
Page 172 of 280

170Intelligent technology
Electronic Stability Programme (ESP)*
ESP reduces the danger of skidding by braking the wheels individually.
The system uses the steering wheel angle and road speed to calculate the
changes of direction desired by the driver, and constantly compares them
with the actual behaviour of the vehicle. If the desired course is not being
maintained (for instance, if the vehicle is starting to skid), then the ESP
compensates automatically by braking the appropriate wheel.
The forces acting on the braked wheel bring the vehicle back to a stable
condition. If the vehicle tends to oversteer, the system will act on the front
wheel on the outside of the turn.
WARNING
● It must be remembered that ESP cannot defy the laws of physics. This
should be kept in mind, particularly on slippery and wet roads and when
towing a trailer.
● Always adapt your driving style to suit the condition of the roads and
the traffic situation. Do not let the extra safety afforded by ESP tempt you
into taking any risks when driving, as this can cause accidents.
CAUTION
● In order to ensure that ESP functions correctly, all four wheels must be
fitted with the same tyres. Any differences in the rolling radius of the tyres
can cause the system to reduce engine power when this is not desired.
● Modifications to the vehicle (e.g. to the engine, the brake system, run-
ning gear or any components affecting the wheels and tyres) could affect
the efficiency of the ABS, EDL, ESP and TCS. Anti-lock brake system (ABS)
The anti-lock brake system prevents the wheels locking during braking
⇒ page 168.
Electronic differential lock (EDL)*
The electronic differential lock helps prevent the loss of trac-
tion caused if one of the driven wheels starts spinning.
EDL helps the vehicle to start moving, accelerate and climb a gradient in
slippery conditions where this may otherwise be difficult or even impossi-
ble.
The system will control the revolutions of the drive wheels using the ABS
sensors (in case of an EDL fault the warning lamp for ABS lights up)
⇒ page 69.
At speeds of up to approximately 80 km/h, it is able to balance out differen-
ces in the speed of the driven wheels of approximately 100 rpm caused by a
slippery road surface on one side of the vehicle. It does this by braking the
wheel which has lost traction and distributing more driving force to the oth-
er driven wheel via the differential.
To prevent the disc brake of the braking wheel from overheating, the EDL
cuts out automatically if subjected to excessive loads. The vehicle will con-
tinue to function normally without EDL. For this reason, the driver is not in-
formed that the EDL has been switched off.
The EDL will switch on again automatically when the brake has cooled
down.
Page 198 of 280
196Checking and refilling levels
The LPG tank ⇒ fig. 129 in the spare wheel well has a capacity of 52.8 litres.
If the outside temperatures are very low, it may not be possible to complete-
ly fill the LPG tank.
Pump attachments
There are a variety of types of LPG pump, and the methods of use may vary.
Therefore, let the pump operator fill the tank when refuelling for the first
time or fill from another pump.
Noises when refuelling with LPG
When refuelling with LPG, noises may be heard. These noises are insignifi-
cant.
WARNING
Failure to refuel or handle LPG in the correct way could result in a fire,
cause an explosion or lead to injuries.
● LPG is a highly explosive and inflammable substance. It may cause
severe burns and other injury.
● Switch off the engine before refuelling.
● Always disconnect mobile phones and any other radiophony applian-
ces, as electromagnetic waves may produce sparks and cause a fire.
● Do not remain in the vehicle while refuelling. If it is absolutely neces-
sary to enter the vehicle, close the door and touch a metal surface before
touching the attachment again. This will prevent the generation of static
electricity and any possible fires while refuelling.
● Small quantities of LPG may leak out after refuelling. If LPG comes in-
to contact with skin, there is a risk of freezing.
● Do not smoke and always keep bare flames away from the tank during
refuelling. Failure to do so may lead to an explosion.
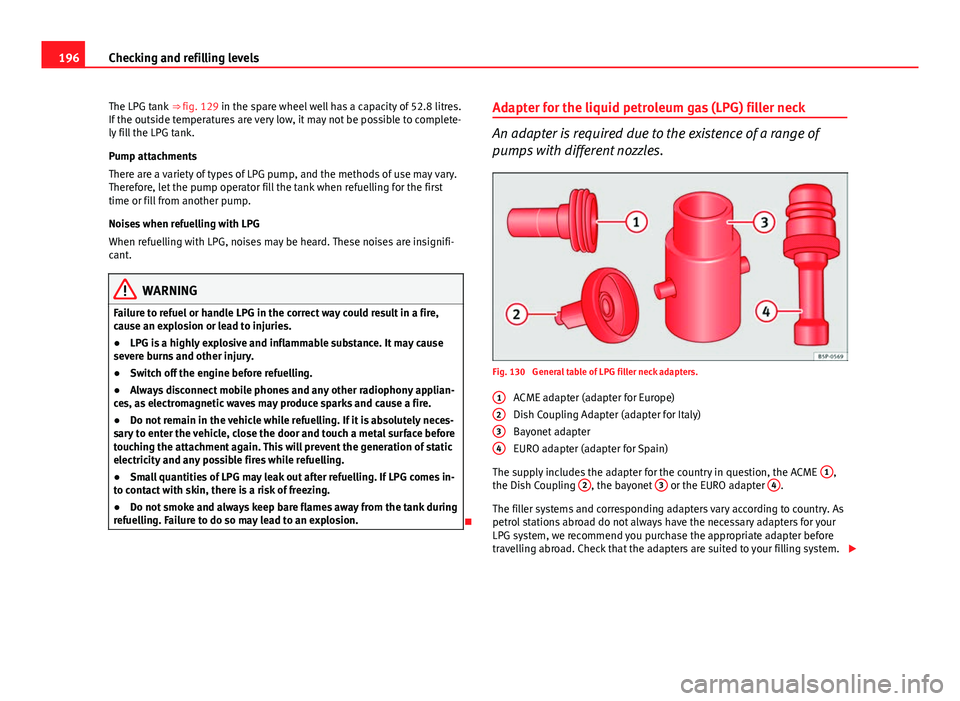
Adapter for the liquid petroleum gas (LPG) filler neck
An adapter is required due to the existence of a range of
pumps with different nozzles.
Fig. 130 General table of LPG filler neck adapters.
ACME adapter (adapter for Europe)
Dish Coupling Adapter (adapter for Italy)
Bayonet adapter
EURO adapter (adapter for Spain)
The supply includes the adapter for the country in question, the ACME 1
,
the Dish Coupling 2, the bayonet 3 or the EURO adapter 4.
The filler systems and corresponding adapters vary according to country. As
petrol stations abroad do not always have the necessary adapters for your
LPG system, we recommend you purchase the appropriate adapter before
travelling abroad. Check that the adapters are suited to your filling system.
1
234
Page 214 of 280
212Checking and refilling levels
WARNING
Before opening the bonnet to check the brake fluid level, read and ob-
serve the warnings ⇒ page 199.
Changing the brake fluid
The Maintenance Programme indicates the brake fluid
change intervals. We recommend that you have the brake fluid changed by an Authorised
Service Centre.
Before opening the bonnet, please read and follow the warnings ⇒
in
Safety instructions on working in the engine compartment on page 199 in
section “Safety notes for working in the engine compartment”.
Brake fluid absorbs moisture. In the course of time, it will absorb water from
the ambient air. If the water content in the brake fluid is too high, the brake
system could corrode. This also considerably reduces the boiling point of
the brake fluid. Heavy use of the brakes may then cause a vapour lock
which could impair the braking effect.
It is important that you use only brake fluid compliant with US standard
FMVSS 116 DOT 4. We recommend the use of Genuine SEAT brake fluid.
WARNING
Brake fluid is poisonous. Old brake fluid impairs the braking effect.
● Before opening the bonnet to check the brake fluid level, read and ob-
serve the warnings ⇒ page 199.
WARNING (Continued)
● Brake fluid should be stored in the closed original container in a safe
place out of reach of children. There is a toxic risk.
● Complete the brake fluid change according to the Maintenance Pro-
gramme. Heavy use of the brakes may cause a vapour lock if the brake
fluid is left in the system for too long. This would seriously affect the effi-
ciency of the brakes and the safety of the vehicle. This may cause an ac-
cident.
CAUTION
Brake fluid could damage the paintwork. Wipe off any brake fluid from the
paintwork immediately.
For the sake of the environment
The brake pads and fluid must be collected and disposed of according the
applicable regulations. The SEAT Technical Service network has the neces-
sary equipment and qualified personnel for collecting and disposing of this
waste material.
Page 232 of 280
230If and when
Note
● If a newly replaced fuse blows again after a short time, the electrical sys-
tem must be checked by a specialised workshop as soon as possible.
● If you replace a fuse with higher-rating fuse, you could cause damage to
another location in the electrical system.
● Always keep some spare fuses in the vehicle. These are available from
SEAT dealers.
Fuses on left side of dash panel
Fuses
NumberConsumerAmps1Power steering/Engine operation/Flow meter7,5
2
Diagnostics/Heater/Autoclimate/Climatronic/
Electric anti-dazzle mirror/Navigator/Air condi-
tioning pressure switch/ Climate fan/AFS Control
unit/Coming home relay/Soundaktor/CCS
10
3Petrol engine control unit/Diesel engine control
unit/Relay coils/Engine operation/Bi-turbo fuel
control unit5
4ABS-ESP Control unit/RKA Switch/Gateway con-
trol unit/ESP Relay/Rotation sensor10
5Reverse light/Heating nozzles106Instrument panel57Retro fog light/Start-Stop relays7,5
8Paddle levers on steering wheel for automatic
gearbox2
9Headlight lever/Windscreen wiper switch1010BCM Electronic control unit power supply511Airbag control unit5
NumberConsumerAmps12Automatic gearbox/ LPG system1013Exterior mirror control514Left-hand AFS headlights1515Right-hand AFS headlights1516Vacant 17Number plate light518Clean pump7,519Electronic control unit520Indicators/Brake lights1521Lights control, instrument panel522Heated mirrors5
23Engine injection module/ Rain sensor/ Automat-
ic gear lever/ Main petrol relay7,5
24Luggage compartment light, interior light, glove
compartment light10
25Parking aid526Towing hook 27Headlight control528Lambda probe1029Vacuum pump/LPG power supply15, 20 a)
30Engine solenoid coils/Additional heating relay/
Pressure sensor/AKF Valve15
31Petrol engine operation/Glow plugs/Relay coil/
Electric fan/Secondary water pump relay10
32Engine control unit15, 20,
30 b)
33Clutch switch sensor/Additional heating relay
coil/ Servo sensor5
34Fuel control unit / Vacuum pump1535Vacant
Page 234 of 280

232If and when
Fuses in engine compartment above battery
Fig. 150 Fuses in engine
compartment
Non-metal fuses
NumberConsumerAmpsS1ABS ESP Control unit25S2Electroblower climate heater/fan30S3Automatic gearbox control unit30S4ABS ESP Control unit10S5Electronic control unit5S6Injection module30
Some of the electrical items listed in the table are only fitted on certain
models or are optional extras.
Please note that the above list contains all data at the time of going to
press, so it is subject to modifications. Bulb change
General notes
Before changing any bulb, first turn off the failed component.
Do not touch the bulb glass. Fingerprints vaporise in the heat, causing a re-
duction in the bulb life and condensation on the mirror surface, thus reduc-
ing efficiency.
A bulb should only be replaced by one of the same type. The type is inscri-
bed on the bulb, either on the glass part or on the base.
Below, the light source used for all functions is detailed.
Double headlights - H7 Long Life
- H7
- W5W Long Life - PY 21W
Single headlight - H4 Long Life
- W5W Long Life - PY 21W
Dipped beam
Main beam
Position
Turn signal
Dipped/Main
Position
Turn signal
Page 246 of 280
244If and when
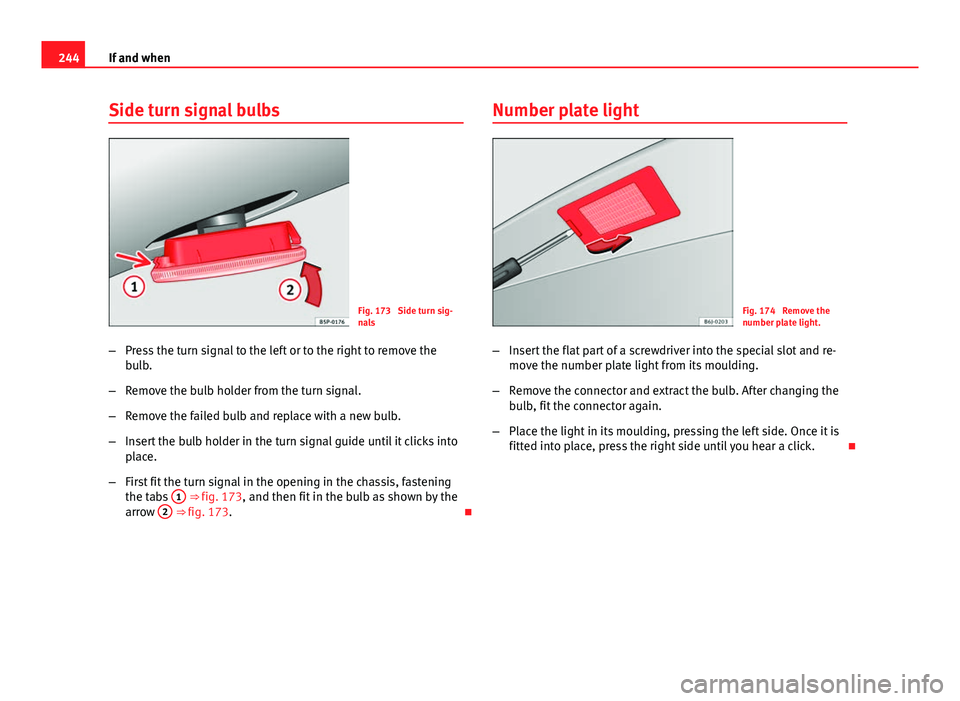
Side turn signal bulbs
Fig. 173 Side turn sig-
nals
– Press the turn signal to the left or to the right to remove the
bulb.
– Remove the bulb holder from the turn signal.
– Remove the failed bulb and replace with a new bulb.
– Insert the bulb holder in the turn signal guide until it clicks into
place.
– First fit the turn signal in the opening in the chassis, fastening
the tabs 1
⇒ fig. 173, and then fit in the bulb as shown by the
arrow 2 ⇒ fig. 173. Number plate light
Fig. 174 Remove the
number plate light.
– Insert the flat part of a screwdriver into the special slot and re-
move the number plate light from its moulding.
– Remove the connector and extract the bulb. After changing the
bulb, fit the connector again.
– Place the light in its moulding, pressing the left side. Once it is
fitted into place, press the right side until you hear a click.
Page 247 of 280
245
If and when
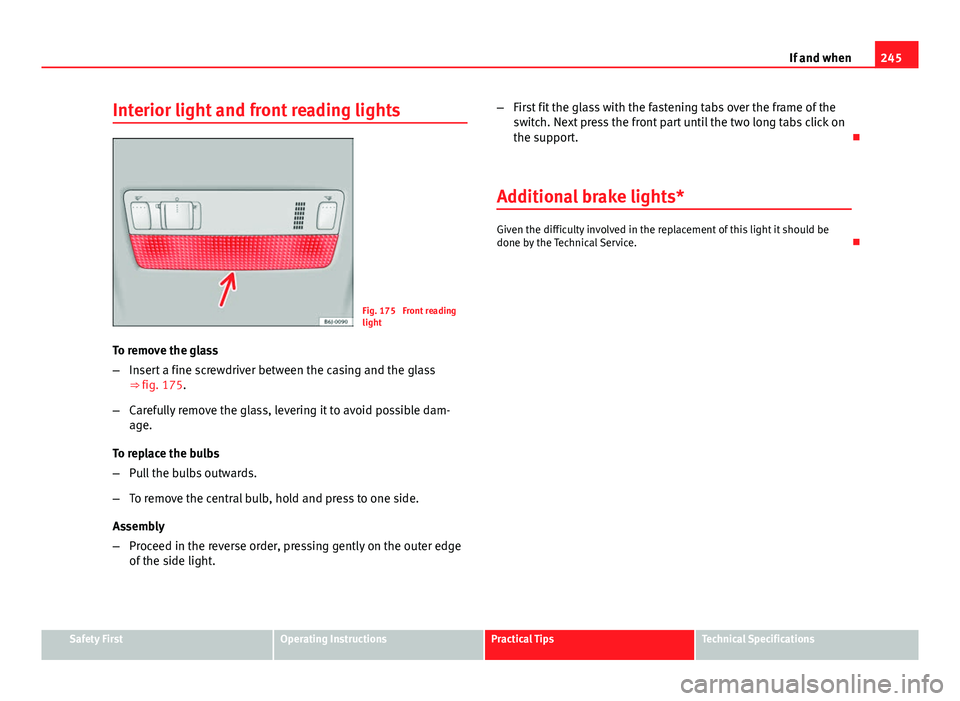
Interior light and front reading lights
Fig. 175 Front reading
light
To remove the glass
– Insert a fine screwdriver between the casing and the glass
⇒ fig. 175.
– Carefully remove the glass, levering it to avoid possible dam-
age.
To replace the bulbs
– Pull the bulbs outwards.
– To remove the central bulb, hold and press to one side.
Assembly
– Proceed in the reverse order, pressing gently on the outer edge
of the side light. –
First fit the glass with the fastening tabs over the frame of the
switch. Next press the front part until the two long tabs click on
the support.
Additional brake lights*
Given the difficulty involved in the replacement of this light it should be
done by the Technical Service.
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications