check engine light SKODA CITIGO 2013 1.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SKODA, Model Year: 2013, Model line: CITIGO, Model: SKODA CITIGO 2013 1.GPages: 176, PDF Size: 10.54 MB
Page 79 of 176
In vehicles not equipped with the START-STOP system, turn off the engine when
in a traffic jam, at a level crossing or traffic lights with longer wait times.
Even after just 30 – 40 seconds you will have saved more fuel than that is needed
when you start the engine up again.
If an engine is only idling it takes much longer for it to reach its normal operating
temperature. Wear-and-tear and pollutant emissions, though, are particularly
high in the warming-up phase. Therefore, start driving as soon as the engine has
started, High engine speeds should however be avoided.
Avoiding short distances
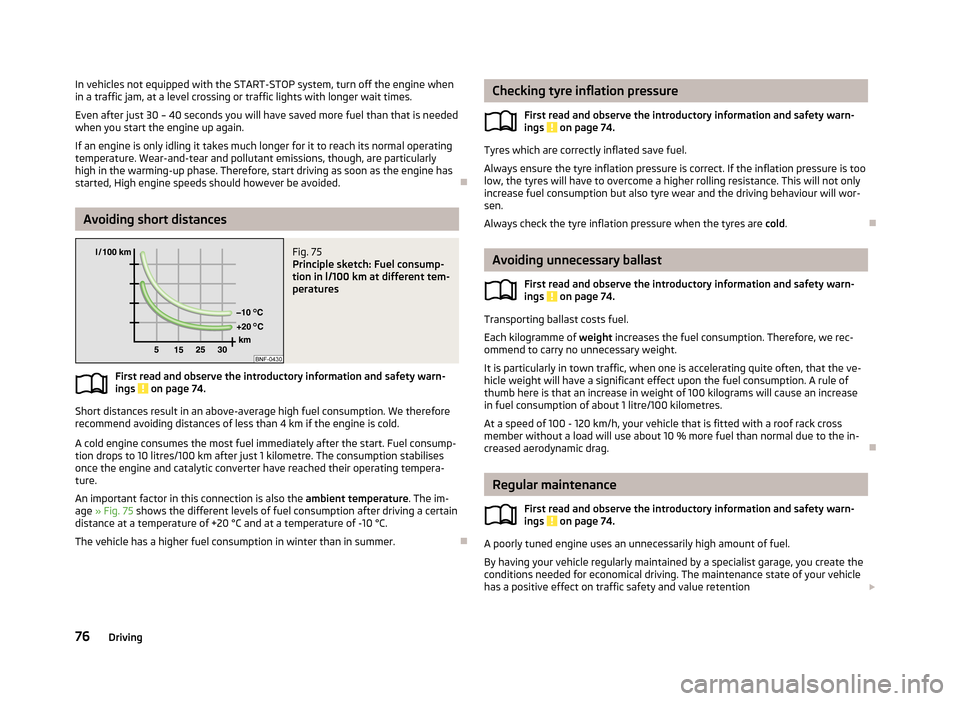
Fig. 75
Principle sketch: Fuel consump-
tion in l/100 km at different tem-
peratures
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 74.
Short distances result in an above-average high fuel consumption. We therefore
recommend avoiding distances of less than 4 km if the engine is cold.
A cold engine consumes the most fuel immediately after the start. Fuel consump-tion drops to 10 litres/100 km after just 1 kilometre. The consumption stabilises
once the engine and catalytic converter have reached their operating tempera- ture.
An important factor in this connection is also the ambient temperature. The im-
age » Fig. 75 shows the different levels of fuel consumption after driving a certain
distance at a temperature of +20 °C and at a temperature of -10 °C.
The vehicle has a higher fuel consumption in winter than in summer.
Checking tyre inflation pressure
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 74.
Tyres which are correctly inflated save fuel.
Always ensure the tyre inflation pressure is correct. If the inflation pressure is too
low, the tyres will have to overcome a higher rolling resistance. This will not only increase fuel consumption but also tyre wear and the driving behaviour will wor-
sen.
Always check the tyre inflation pressure when the tyres are cold.
Avoiding unnecessary ballast
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 74.
Transporting ballast costs fuel.
Each kilogramme of weight increases the fuel consumption. Therefore, we rec-
ommend to carry no unnecessary weight.
It is particularly in town traffic, when one is accelerating quite often, that the ve-
hicle weight will have a significant effect upon the fuel consumption. A rule of
thumb here is that an increase in weight of 100 kilograms will cause an increase in fuel consumption of about 1 litre/100 kilometres.
At a speed of 100 - 120 km/h, your vehicle that is fitted with a roof rack crossmember without a load will use about 10 % more fuel than normal due to the in-
creased aerodynamic drag.
Regular maintenance
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 74.
A poorly tuned engine uses an unnecessarily high amount of fuel.
By having your vehicle regularly maintained by a specialist garage, you create the conditions needed for economical driving. The maintenance state of your vehicle has a positive effect on traffic safety and value retention
76Driving
Page 82 of 176
NoteAfter driving through water, we recommend having the vehicle checked by a spe-
cialist garage.
Driving abroad
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Unleaded petrol
79
Headlights
79
In certain countries, it may be possible that the ŠKODA Partner network is limited
or has not been established. This is the reason why procuring certain spare parts
may be somewhat complicated and specialist garages may only be able to make
limited repairs.
Unleaded petrol
First read and observe the introductory information given on page 79.
A vehicle fitted with a petrol engine must always be refuelled with unleaded pet-rol » page 123 , Unleaded petrol . Information regarding the locations of filling sta-
tions that offer unleaded petrol is, for example, provided by the automobile asso-
ciations.
Headlights
First read and observe the introductory information given on page 79.
The low beam of your headlights is set asymmetrically. It illuminates the side of
the road on which the vehicle is being driven to a greater extent.
When driving in countries in which the traffic drives on the other side of the roadthan in your home country, the asymmetrical low beam may dazzle oncoming
drivers. In order to avoid this, the headlights must be adjusted at a specialist ga-
rage.
NoteYou can find out more information on adjusting the headlights at a specialist ga-
rage.
79Starting-off and Driving
Page 88 of 176
START-STOP
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Starting/shutting down the engine
85
Operating conditions of the system
85
Manually activating/deactivating the system
86
The START-STOP system helps you to save fuel while at the same time reducing
harmful exhaust emissions and CO 2 emissions.
The function is automatically activated each time the ignition is switched on. In the start-stop mode, the engine automatically switches to the vehicle's idle phase, e.g. when stopped at traffic lights. The engine restarts automatically
where necessary.
The system can work only if the following basic conditions are met.
The driver's door is closed.
The driver has fastened the seat belt.
The bonnet is closed.The driving speed was higher than 4 km/h after the last stop.
WARNING■ The brake servo unit and power steering only operate if the engine is run-
ning.■
Never let the vehicle roll with the engine switched off.
CAUTION
Always deactivate the START-STOP system before driving through wa-
ter » page 78 .Note■
If the driver's seat belt is removed for more than 30 seconds or the driver's door
is opened during stop mode, the engine must be started manually with the key.■
After manually starting the engine on vehicles with manual transmission, auto-
matic engine shut down is not possible until the vehicle has travelled the re- quired minimum distance for START-STOPmode.
■
Changes to the outdoor temperature can have an effect on the internal temper-
ature of the vehicle battery even after several hours. If the vehicle remains out-
doors for a long time in minus temperatures or in direct sunlight, it can take sev-
eral hours until the internal temperature of the vehicle battery reaches a suitable temperature for proper operation of the START STOP system.
Starting/shutting down the engine
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 85.
›
Stop the vehicle (where necessary, apply the handbrake).
›
Put the gear stick into Neutral.
›
Release the clutch pedal.
Automatic engine shut down (STOP phase) takes place. The warning symbol
appears in the instrument cluster display.
›
Depress the clutch pedal.
The automatic start procedure takes place again (START phase). The warning
symbol
goes out.
Operating conditions of the system
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 85.
The START-STOP system is very complex. Some of the procedures are hard tocheck without servicing.
No engine shut down is carried out
Before each STOP phase, the system checks whether certain conditions have
been met. No engine shut down takes place in the following situations.
85Assist systems
Page 121 of 176
This wax protection does not need to be inspected or re-applied.If any small amount of wax flow out of the cavities at high temperatures, thesemust be removed with a plastic scraper and the stains cleaned using a petroleum cleaner.WARNINGSafety regulations should be observed when using petroleum cleaner to re-
move wax – risk of fire!
Wheels
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 115.
Wheel rims
Also thoroughly wash the wheel rims when washing the vehicle on a regular ba- sis.
Regularly remove salt and brake abrasion, otherwise the rim material will be cor-
roded.
Damage to the paint layer on the wheel rims must be touched up immediately.
Light alloy wheels
After washing thoroughly and treat the wheel rims with a protective product for
light alloy wheels. Products which cause abrasion must not be used to treat the
wheel rims.
CAUTION
Severe layers of dirt on the wheels can also result in wheel imbalance. This may
show itself in the form of a wheel vibration which is transmitted to the steering
wheel which, in certain circumstances, can cause premature wear of the steering.
This means it is necessary to remove the dirt.
Underbody protection
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 115.
The underside of your vehicle is protected for life against chemical and mechani-
cal influences.
When driving, it cannot be guaranteed that no damage to the protective layer will
occur.
We recommend having the protective layer underneath the vehicle and the chas-
sis checked — preferably before the beginning of winter and at the end of winter.
WARNINGNever use additional underbody protection or anti-corrosion agents for ex-
haust pipes, catalytic converters or heat shields. When the engine reaches its
operating temperature, these substances may ignite - risk of fire!
Taking care of the interior
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Natural leather
119
Artificial leather, cloths and Alcantara ®
120
Seat covers
120
Seat belts
121
Regular and proper care helps to ensure efficiency and maintain the
value of your
vehicle.
We recommend using vehicle care products from ŠKODA Original Accessories. These are available from ŠKODA Partners. The usage instructions on the packagemust be observed.
118General Maintenance
Page 128 of 176

In the following situation, it is possible that the tank cannot be fully filled with
natural gas.
› At very high ambient temperatures. The natural gas refuelling systems have
overheating protection. When the ambient temperature reaches a predefined value, the refuelling system automatically switches off.
› If the refuelling system has been in operation for a longer period, the filling
pressure of the natural gas refuelling system slightly drops.WARNING■ Stop the engine before refuelling.■Always switch off your mobile phone, do not smoke and do not use open
flames when refuelling with natural gas – risk of explosion!■
When refuelling, never get into the vehicle. If you have to get into your vehi-
cle in exceptional cases, close the door and touch a metal surface before you
touch the filling coupling again. This will avoid electrostatic discharges, which
may generate sparks. Sparks can cause a fire during refuelling.
■
Natural gas is highly explosive and flammable. Incorrect refuelling or improp-
er handling of natural gas can cause a fire, an explosion and injuries.
Note
■ The natural gas system of your vehicle is suitable both for fuelling from small
compressors (slow fuelling) and for fuelling from natural gas stations with large
compressors (quick fuelling).■
Noises that occur during refuelling represent no risk.
■
If the vehicle is parked for a longer period of time immediately after refuelling,
the situation may arise in which the pointer of the fuel tank gauge does not indi- cate exactly the same level as was the case immediately after refuelling when theengine is restarted. This is not due to any system leakages but a drop in pressurein the natural gas fuel tank due to technical reasons after a cooling phase directly
after refuelling.
■
For frequent short-haul traffic, especially at low outside temperatures, the vehi-
cle is driven more frequently in petrol mode than in natural gas mode. This is why the petrol tank runs empty faster than the natural gas tank.
■
The capacity of the natural gas tank is about 11 kg, of which about 1.5 kg are a
reserve.
■
The capacity of the petrol tank is about 10 l, of which about 5 l are a reserve.
Automatic switching from CNG to petrol mode
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 123.
The vehicle automatically switches over from CNG mode to petrol mode when the following conditions are met:
› when starting the engine, if the coolant temperature is below 15 °C,
› when the natural gas tank is empty,
› after refuelling with natural gas.
Natural gas as fuel
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 123.
Natural gas is an alternative fuel for motor vehicles. Its main component is meth-
ane (CH 4). The rest is carbon dioxide and lower hydrocarbons.
The strict legal requirements for exhaust emissions of motor vehicles are decisive for the current significance of natural gas. In direct comparison to all other fossil
fuels, natural gas is one of the fuels which cause the lowest emissions.
Natural gas is odourless and lighter than air. For safety reasons, it is saturated
with odorous substances, so that is perceived even in very small amounts.
Regular gas system checks
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 123.
Every two years, the following inspections must be carried out:
› Check the condition of the fuel filler cap, filler neck and sealing ring, and clean
sealing ring if necessary.
› Check gas system for leaks.
The following checks must be carried out every four years: › Check gas tank mounting for secure attachment and possible damage.
The gas tank must be filled prior to the regular gas system check.
125Inspecting and replenishing
Page 132 of 176
›Take the bonnet support out of its holder 3
» Fig. 104 in the direction if the
arrow and secure the opened bonnet by inserting the end of the support in the
opening 4
designed for it.
Closing
›
Lift the bonnet slightly and unhook the bonnet support. Insert the bonnet sup-
port into the holder
3
designed for this purpose » Fig. 104.
›
Let the bonnet drop into the lock carrier lock from a height of around 20 cm – do
not push it in .
WARNINGCheck that the bonnet is closed properly.
CAUTION
Never open the bonnet using the locking lever » Fig. 103.
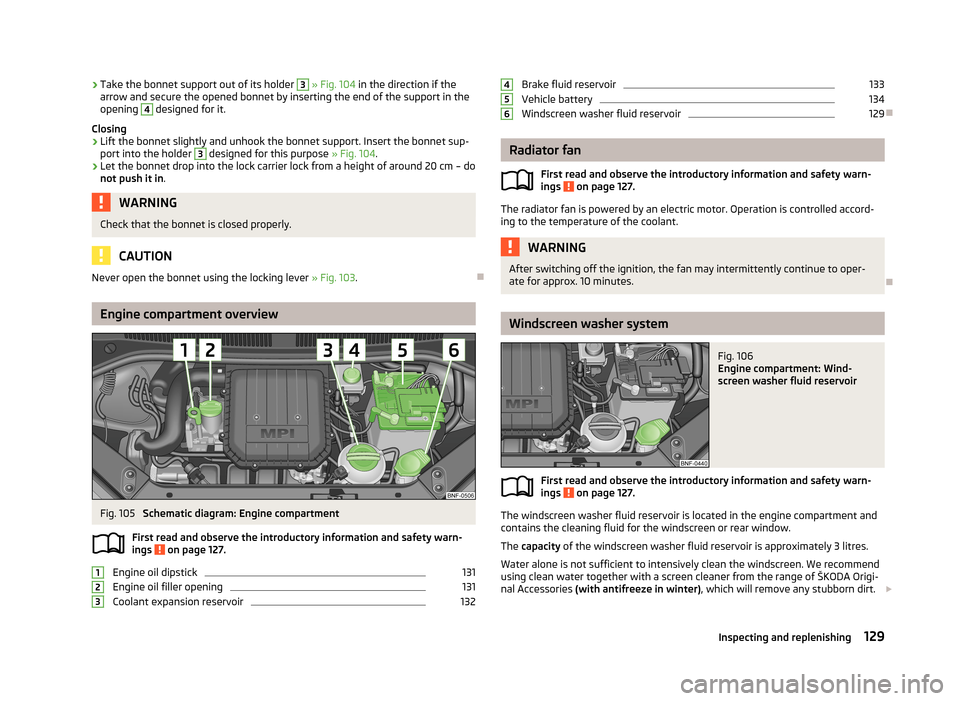
Engine compartment overview
Fig. 105
Schematic diagram: Engine compartment
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn- ings
on page 127.
Engine oil dipstick
131
Engine oil filler opening
131
Coolant expansion reservoir
132123Brake fluid reservoir133Vehicle battery134
Windscreen washer fluid reservoir
129
Radiator fan
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 127.
The radiator fan is powered by an electric motor. Operation is controlled accord-
ing to the temperature of the coolant.
WARNINGAfter switching off the ignition, the fan may intermittently continue to oper-
ate for approx. 10 minutes.
Windscreen washer system
Fig. 106
Engine compartment: Wind-
screen washer fluid reservoir
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn- ings on page 127.
The windscreen washer fluid reservoir is located in the engine compartment and
contains the cleaning fluid for the windscreen or rear window.
The capacity of the windscreen washer fluid reservoir is approximately 3 litres.
Water alone is not sufficient to intensively clean the windscreen. We recommend using clean water together with a screen cleaner from the range of ŠKODA Origi-
nal Accessories (with antifreeze in winter) , which will remove any stubborn dirt.
456129Inspecting and replenishing
Page 134 of 176
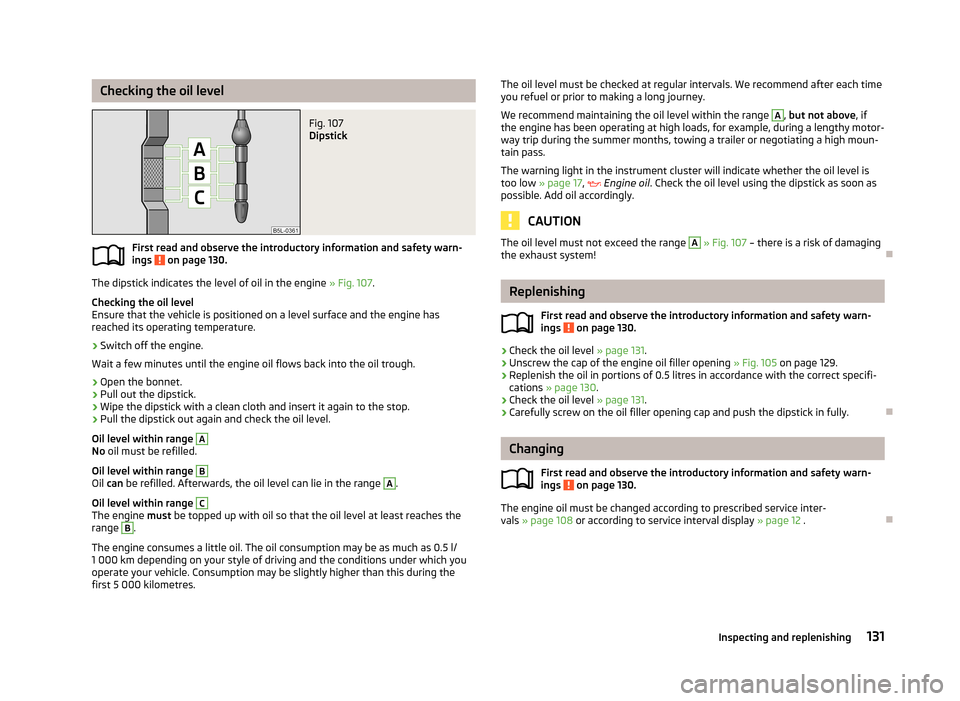
Checking the oil levelFig. 107
Dipstick
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 130.
The dipstick indicates the level of oil in the engine » Fig. 107.
Checking the oil level
Ensure that the vehicle is positioned on a level surface and the engine has reached its operating temperature.
›
Switch off the engine.
Wait a few minutes until the engine oil flows back into the oil trough.
›
Open the bonnet.
›
Pull out the dipstick.
›
Wipe the dipstick with a clean cloth and insert it again to the stop.
›
Pull the dipstick out again and check the oil level.
Oil level within range
A
No oil must be refilled.
Oil level within range
B
Oil can be refilled. Afterwards, the oil level can lie in the range
A
.
Oil level within range
C
The engine must be topped up with oil so that the oil level at least reaches the
range
B
.
The engine consumes a little oil. The oil consumption may be as much as 0.5 l/
1 000 km depending on your style of driving and the conditions under which you
operate your vehicle. Consumption may be slightly higher than this during the
first 5 000 kilometres.
The oil level must be checked at regular intervals. We recommend after each time
you refuel or prior to making a long journey.
We recommend maintaining the oil level within the range A
, but not above , if
the engine has been operating at high loads, for example, during a lengthy motor-
way trip during the summer months, towing a trailer or negotiating a high moun- tain pass.
The warning light in the instrument cluster will indicate whether the oil level is too low » page 17 , Engine oil . Check the oil level using the dipstick as soon as
possible. Add oil accordingly.
CAUTION
The oil level must not exceed the range A » Fig. 107 – there is a risk of damaging
the exhaust system!
Replenishing
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 130.
›
Check the oil level » page 131.
›
Unscrew the cap of the engine oil filler opening » Fig. 105 on page 129.
›
Replenish the oil in portions of 0.5 litres in accordance with the correct specifi-
cations » page 130 .
›
Check the oil level » page 131.
›
Carefully screw on the oil filler opening cap and push the dipstick in fully.
Changing
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 130.
The engine oil must be changed according to prescribed service inter-
vals » page 108 or according to service interval display » page 12 .
131Inspecting and replenishing
Page 136 of 176

›Check the level of coolant in the coolant expansion bottle
» Fig. 108. The cool-
ant level when the engine is cold must lie between the “MIN” and “MAX” mark-
ings. The level may also rise slightly above the “MAX” marking when the engine is warm.
If the coolant level in the coolant expansion tank is too low, this is indicated by
the warning light lighting up in the instrument cluster » page 18, Coolant .
We still recommend inspecting the coolant level directly at the reservoir from
time to time.
Loss of coolant
A loss of coolant is first and foremost an indication of a leak in the system. Do
not merely top up the coolant. Have the cooling system checked by a specialist
garage.
Replenishing
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 132.
Only top up with new coolant.
›
Switch off the engine.
›
Allow the engine to cool.
›
Place a cloth over the cap of the coolant expansion tank and unscrew the cap carefully .
›
Replenish the coolant.
›
Turn the cap until it clicks into place.
Do not use an alternative additive if the specified coolant is not available in an emergency. In this case, use just water and have the correct mixing ratio of water
and coolant additive restored by a specialist garage as soon as possible.
Brake fluid
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Checking the brake fluid level
133
Changing
134WARNING■ The engine compartment of your car is a hazardous area. The following
warning instructions must be followed at all times when working in the en-
gine compartment » page 127.■
If the fluid level has dropped below the MIN marking » Fig. 108 on page 132,
do not continue your journey - there is the risk of an accident! Seek help
from a specialist garage.
■
Do not use used brake fluid - the function of the brake system may be im-
paired – risk of accident!
CAUTION
Brake fluid damages the paintwork of the vehicle.
Note
The brake fluid is changed as part of a compulsory inspection service.
Checking the brake fluid level
Fig. 109
Engine compartment: Brake fluid
reservoir
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 133.
The brake fluid reservoir is located in the engine compartment.
›
Switch off the engine.
›
Open the bonnet.
›
Check the level of brake fluid in the reservoir » Fig. 109.
The level must be between the “MIN” and “MAX” markings.
133Inspecting and replenishing
Page 138 of 176

WARNING■It is prohibited to work with naked flames or lights.■It is prohibited to smoke or carry out any activities that produce sparks.■
Never use a damaged vehicle battery – risk of explosion!
■
Never charge a frozen or thawed vehicle battery – risk of explosion and
chemical burns!
■
Replace a frozen vehicle battery.
■
Never jump-start vehicle batteries with insufficient acid levels – risk of ex-
plosion and chemical burns.
WARNING■ When you charge a battery, hydrogen is released, and a highly explosive gas
mixture is also produced. An explosion can be caused through sparkling over during unclamping or loosening of the cable plug while the ignition is on.■
Creating a bridge between the poles on the battery (e.g. with a metal object
or cable) creates a short circuit - risk of melting the lead bars, and risk of ex-
plosion, battery fire and acid splashes.
■
Avoid creating sparks when working with cables and electrical devices.
Strong sparking represents a risk of injury.
■
Before carrying out any work on the electrical system, switch off the engine,
the ignition and all of the electrical components and disconnect the negative
terminal ( ) of the battery.
CAUTION
Improper handling of the battery can lead to damage. We recommend having all
work on the vehicle battery carried out by a specialist garage.
CAUTION
■ The vehicle battery must only be disconnected if the ignition is switched off,
otherwise the vehicle's electrical system (electronic components) can be dam-
aged. When disconnecting the battery from the vehicle first disconnect the nega- tive terminal ( ) and only then the positive terminal ( ) of the battery.■
When connecting the battery to the electrical system, connect the positive ter-
minal ( ) first and then the negative terminal ( ) of the battery. Under no circum-
stances must the battery cables be connected incorrectly – risk of a cable fire.
■
Ensure that battery acid does not come into contact with the bodywork – risk of
damage to the paintwork.
■ Do not place the battery in direct daylight in order to protect the vehicle battery
housing from the effects of ultra-violet light.■
If the vehicle has not been driven for more than 3 to 4 weeks, the battery will
discharge. This is because certain electrical components consume electricity (e. g.
control units) also in idle state. The battery discharge can be prevented by discon-
necting the negative terminal ( ) of the battery or by ensuring the battery is con-
tinuously charged with very low charging current.
■
If the vehicle is frequently used for making short trips, the vehicle battery will
not have time to charge up sufficiently and may discharge.
For the sake of the environment
A vehicle battery that has been removed is a special type of hazardous waste.
These must be disposed of in accordance with national legal regulations.
Note
You should replace batteries older than 5 years.
Checking the battery electrolyte level
Fig. 110
Vehicle battery: Electrolyte level
indicator
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 134.
On vehicles with a vehicle battery fitted with a colour indicator, the so-called
magic eye » Fig. 110 , the electrolyte level can be determined by looking at the
change in colour.
135Inspecting and replenishing
Page 139 of 176

Air bubbles can influence the colour of the indicator. For this reason carefully
knock on the indicator before carrying out the check.
› Black colour – electrolyte level is correct.
› Colourless or light yellow colour – electrolyte level too low, the battery must be
replaced.
Vehicles with a START-STOP system are fitted with a battery control unit for checking the energy level for the recurring engine start.
We recommend that you have the acid level checked regularly by a specialist ga-
rage, especially in the following cases.
› High external temperatures.
› Longer day trips.
› After each charge.
CAUTION
For technical reasons, on vehicles with the description “AGM”, the electrolyte lev-
el cannot be checked.
Note
The battery acid level is also checked regularly by a specialist garage as part of
the inspection service.
Operation in winter
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 134.
The vehicle battery only has a proportion of the starting power in lower tempera-
tures. A discharged vehicle battery may already freeze at temperatures just be-
low 0 °C .
We therefore recommend that you have the battery checked and, if necessary, re-
charged by a specialist garage before the start of the winter.
Charging
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 134.
A properly charged vehicle battery is essential for reliably starting the engine.
› Switch off the ignition and all of the electrical components.›Only when performing a “quick-charge”, disconnect both battery cables (first
“negative”, then “positive”).›
Attach the terminal clamps of the charger to the battery terminals (red = “posi- tive”, black = “negative”).
›
Plug the mains cable of the charger into the power socket and switch on thedevice.
›
After charging has been successful: Switch off the charger and remove themains cable from the power socket.
›
Only then disconnect the charger's terminal clamps.
›
Reconnect the cables to the battery (first “positive”, then “negative”).
It is not necessary to disconnect the cables of the battery if you recharge the ve-
hicle battery using low amperages (for example from a mini-charger). Refer to the
instructions of the charger manufacturer .
A charging current of 0.1 multiple of the total vehicle battery capacity (or lower) must be used until full charging is achieved.
It is necessary to disconnect both cables before charging the battery with high
amperages, known as “ rapid charging”.
The vent plugs of the vehicle battery should not be opened for charging.
WARNING“Quick-charging” the vehicle battery is dangerous and requires a special
charger and specialist knowledge.
CAUTION
On vehicles with the START/STOP system, the pole terminal of the charger must
not be connected directly to the negative terminal of the vehicle battery, but only
to the engine earth » page 152, Jump-starting in vehicles with the START-STOP
system .
Note
We therefore recommend that vehicle batteries be rapid charged by a specialist
garage.
136General Maintenance