lock SKODA FABIA 2008 2.G / 5J Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SKODA, Model Year: 2008, Model line: FABIA, Model: SKODA FABIA 2008 2.G / 5JPages: 252, PDF Size: 40.88 MB
Page 105 of 252
Automatic gearbox104
In certain circumstances (e.g. when driving in mountainous regions or when towing a trailer) it may be beneficial to select the manual shift programme ⇒page 105 for a short time in order to adapt the gearbox ratios manually to the driving situations.
S - Position for sporty style of driving
Shifting up later into a higher gear makes it possible to fully exploit the power potential of the engine. The gearbox also then shifts down at higher engine speeds as in the position D.
The gearbox does not shift into the 6th gear in the position S, because the maximum speed is achieved with the 5th gear.
The Shiftlock on the selector lever grip must be pressed when moving the selector lever out of the position D into the position S.
WARNING
•Never move the selector lever into position R or P when driving - risk of an accident!
•When the engine is running and the vehicle is stationary, it is necessary to hold the car with the brake pedal in all the positions of the selector lever (except P and N) since the power transmission is never completely inter-rupted, also not when the engine is idling - the vehicle "creeps".
•You must on no account unintentionally operate the throttle (e.g. by hand from the engine compartment) if a drive position is engaged when the car is stationary. The vehicle would otherwise immediately start off - also when the handbrake is firmly applied - risk of an accident!
•You must move the selector lever into position P and firmly apply the handbrake first before you or any other person opens the bonnet and starts working on the engine when it is running - risk of accident! It is also essential to observe all warnings ⇒page 181, “Working in the engine compartment”.
Selector lever lock
Automatic selector lever lock
With the ignition on, the selector lever is locked when it is in the positions P and N. You must first of all depress the brake pedal in order to move the selector lever out of this position. The warning light ⇒page 27 lights up in the instrument cluster as a reminder for the driver when the selector lever is in position P and N:
A time delay element ensures that the selector lever is not blocked when rapidly switching over the position N (e.g. from R to D). This does, for example, allow one to seesaw out a stuck vehicle. The selector lever lock will click into place if the lever is in the N position for more than 2 seconds without the brake pedal being pressed.
The selector lever lock is only active if the vehicle is stationary or moving at speed of less than 5 km/hour. The lock is switched off automatically into position N when the car is travelling at a higher speed.
Shiftlock button
The Shiftlock button in the handle of selector lever prevents certain selector lever positions being engaged inadvertently. The selector lever lock is cancelled when you press the Shiftlock button.
Keylock - Ignition key withdrawal lock
You can only withdraw the ignition key after switching off the ignition if the selector lever is in position P. If the ignition key is withdrawn, the selector lever is blocked in position P.
This function is only valid for some countries.
Kickdown function
The kickdown function provides you with maximum acceleration
power.
Depressing the accelerator pedal allows the kickdown function to be activated in the desired driving program. This function has precedence over the driving programme and serves for maximum acceleration of the vehicle when exploiting the maximum power potential of the engine without taking into account the current selector lever position (D, S or Tiptronic). The gearbox shifts down to one
NKO A05F 20.book Page 104 Wednesday, April 2, 2008 1:02 PM
Page 111 of 252
Communication110
Caution
Taking the mobile phone out of the adapter during the call can lead to interruption of the connection. When taking out the mobile phone, the connection to the factory-fitted antenna is interrupted, this reduces the quality of the transmitting and receiving signal. This might result additionally in harmful radiation from the mobile phone in the interior of the vehicle and the charging of the telephone battery is interrupted.
Note
•Please also refer to the additional instructions ⇒page 117, “Mobile phones and two-way radio systems”.
•Please contact your Škoda Service Partner if there are any points which are not clear.
•The voice control of the telephone is only possible for adapters with PTT button. Suitable adapters are available at a Škoda Service Partner.
Inserting the mobile phone and adapter
Only one telephone mount is factory-fitted. An adapter for the mobile
phone can be purchased from Škoda original accessories.
Inserting the mobile phone and adapter
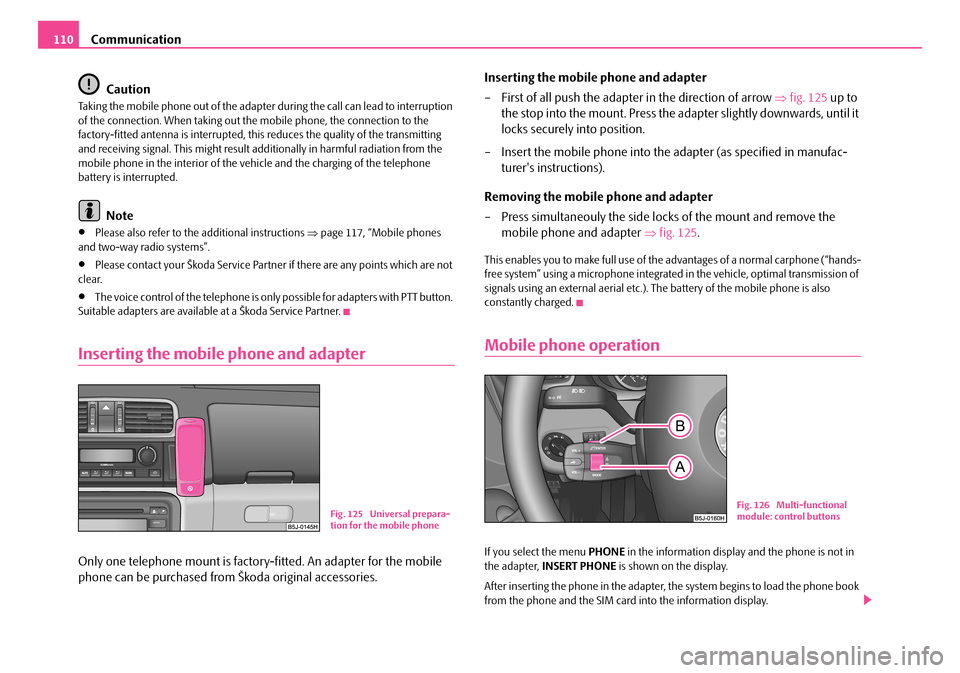
– First of all push the adapter in the direction of arrow ⇒fig. 125 up to
the stop into the mount. Press the adapter slightly downwards, until it
locks securely into position.
– Insert the mobile phone into the adapter (as specified in manufac-
turer's instructions).
Removing the mobile phone and adapter
– Press simultaneouly the side locks of the mount and remove the
mobile phone and adapter ⇒fig. 125.
This enables you to make full use of the advantages of a normal carphone (“hands-free system” using a microphone integrated in the vehicle, optimal transmission of signals using an external aerial etc.). The battery of the mobile phone is also constantly charged.
Mobile phone operation
If you select the menu PHONE in the information display and the phone is not in the adapter, INSERT PHONE is shown on the display.
After inserting the phone in the adapter, the system begins to load the phone book from the phone and the SIM card into the information display.
Fig. 125 Universal prepara-tion for the mobile phone
Fig. 126 Multi-functional module: control buttons
NKO A05F 20.book Page 110 Wednesday, April 2, 2008 1:02 PM
Page 114 of 252

Communication113
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
•When entering an incorrect PIN code, the system indicates “The PIN is incor-rect”.
•If the incorrect PIN code has been entered three times consecutively, the card is blocked. With the aid of the personal unblocking code PUK (Personal Unblock Key), the SIM card can be unblocked. The unblocking code can only be entered via the phone keypad and not through the voice control.
Example for entering the PIN code
You can interrupt the dialogue at any time by pressing the PTT button or with the voice command CANCEL.
Select number
– Press the PTT button.
– Give the command DIAL NUMBER after the signal tone.
After giving this command, the system requests the entry of a telephone number. The telephone number can be entered as an interconnected spoken row of digits (complete number), in the form of order of digits (separation through a brief voice pause) or through individually spoken digits. After each order of digits (separation through brief voice pause) the detected digits are repeated.
The digits zero to nine are permitted. The system detects no continuous digit combinations such as twenty-three, but only individually spoken digits (two, three).
If you enter more than 20 digits, the system announces: “The number is too long”.
Additionally for international calls a Plus (+) has to be entered in front of the 20 digits.
Example when entering a telephone number
You can interrupt the dialogue at any time by pressing the PTT button or with the voice command CANCEL.
Repeat last call
– Press the PTT button.
– Give the command REDIAL after the signal tone.
After giving this command, the last number selected via voice input is selected again.
Example of redial
Voice commandAnnouncement
ENTER PIN/PIN CODE“The PIN please”
e.g. ZERO ONE TWO THREE“Zero One Two Three”
If no entry is put in, the following announcement is made after about 5 seconds.
“Possible commands are: store, repeat, back, delete or more digits”
STORE“The PIN is saved”(end of dialogue)
Voice commandAnnouncement
DIAL NUMBER“The number please”
e.g. ZERO SIX ZERO THREE“Zero Six Zero Three”
If no entry is put in, the following announcement is made after about 5 seconds.
“Possible commands are: dial, repeat, back, delete or more digits”
FIVE SEVEN TWO“Five Seven Two”
DIAL“The number is being dialed”
Voice commandAnnouncement
REDIAL“The number is being dialed”
NKO A05F 20.book Page 113 Wednesday, April 2, 2008 1:02 PM
Page 124 of 252
Passive Safety123
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
For your own safety and to reduce the risk of injury in the event of an accident, we recommend the following setting.
•Adjust the steering wheel so that the distance between the steering wheel and your chest is at least 25 cm ⇒page 122, fig. 128.
•Position the driver seat in the forward/back direction so that you are able to press the pedals with your legs at a slight angle .
•Adjust the backrest so that you are able to reach the highest point of the steering wheel with your arms at a slight angle.
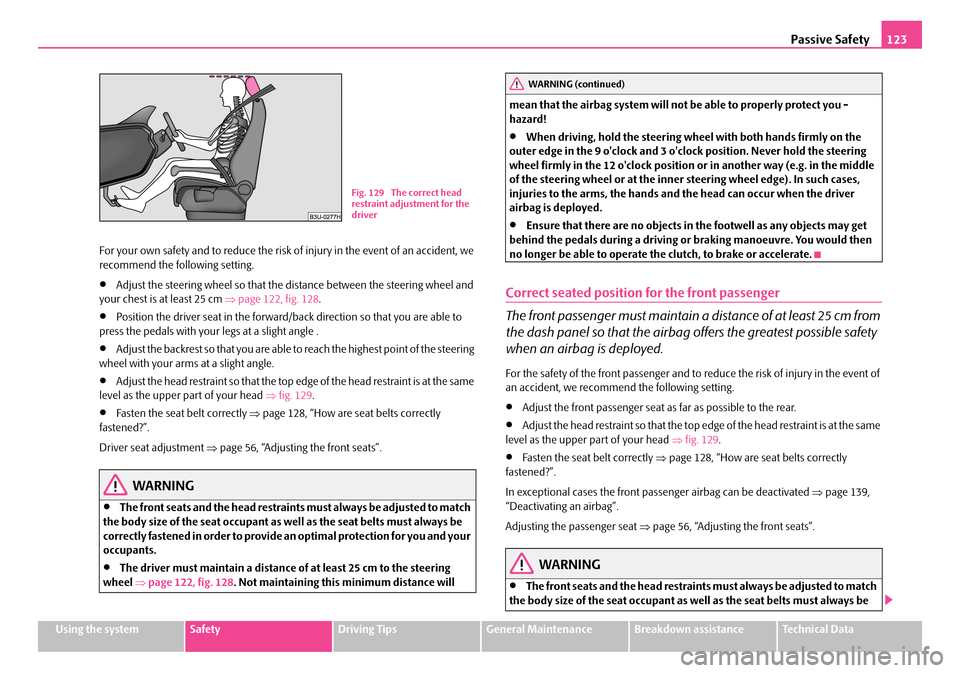
•Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at the same level as the upper part of your head ⇒fig. 129.
•Fasten the seat belt correctly ⇒page 128, “How are seat belts correctly fastened?”.
Driver seat adjustment ⇒page 56, “Adjusting the front seats”.
WARNING
•The front seats and the head restraints must always be adjusted to match the body size of the seat occupant as well as the seat belts must always be correctly fastened in order to provide an optimal protection for you and your occupants.
•The driver must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the steering wheel ⇒page 122, fig. 128. Not maintaining this minimum distance will
mean that the airbag system will not be able to properly protect you - hazard!
•When driving, hold the steering wheel with both hands firmly on the outer edge in the 9 o'clock and 3 o'clock position. Never hold the steering wheel firmly in the 12 o'clock position or in another way (e.g. in the middle of the steering wheel or at the inner steering wheel edge). In such cases, injuries to the arms, the hands and the head can occur when the driver airbag is deployed.
•Ensure that there are no objects in the footwell as any objects may get behind the pedals during a driving or braking manoeuvre. You would then no longer be able to operate the clutch, to brake or accelerate.
Correct seated position for the front passenger
The front passenger must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm from
the dash panel so that the airbag offers the greatest possible safety
when an airbag is deployed.
For the safety of the front passenger and to reduce the risk of injury in the event of an accident, we recommend the following setting.
•Adjust the front passenger seat as far as possible to the rear.
•Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at the same level as the upper part of your head ⇒fig. 129.
•Fasten the seat belt correctly ⇒page 128, “How are seat belts correctly fastened?”.
In exceptional cases the front passenger airbag can be deactivated ⇒page 139, “Deactivating an airbag”.
Adjusting the passenger seat ⇒page 56, “Adjusting the front seats”.
WARNING
•The front seats and the head restraints must always be adjusted to match the body size of the seat occupant as well as the seat belts must always be
Fig. 129 The correct head restraint adjustment for the driver
WARNING (continued)
NKO A05F 20.book Page 123 Wednesday, April 2, 2008 1:02 PM
Page 129 of 252
Seat belts128
•No two persons (also not children) should ever use a single seat belt together.
•The maximum protection which seat belts can offer is only achieved if you are correctly seated ⇒page 122, “Correct seated position”.
•The belt webbing must not run across solid or fragile objects (e.g. spec-tacles, ball-point pens, keys etc.) as this may be a cause of injuries.
•Bulky, loose clothing (e.g. a winter coat over a jacket) does not allow you to be correctly seated and impairs proper operation of the seat belts.
•It is prohibited to use clamps or other objects to adjust seat belts (e.g. for shortening the belts for smaller persons).
•The lock tongue should only be inserted into the lock which is the correct one for your seat. Wrong use of the safety belt will reduce its capacity to protect and the risk of injury increases.
•The backrests must not be tilted too far to the rear otherwise the seat-belts can lose their effectiveness.
•The belt webbing must always be kept clean. Soiled belt webbing may impair proper operation of the inertia reel ⇒page 175, “Seat belts”.
•The slot of the belt tongue must not be blocked by paper or similar objects otherwise the belt tongue will not lock in place properly.
•Inspect the seat belts regularly to ensure they are in good condition. If you find seat belts which have damage to the seat belt webbing, seat belt connections, to the inertia reels or to the lock, the relevant safety belt must be replaced by a specialist garage.
•The seat belts must not be removed or changed in any way. Do not make an attempt to repair the seat belts yourself.
•Damaged seat belts which have been subjected to stress in an accident and were therefore stretched, must be replaced - this is best done by a specialist garage. The anchorage points of the belts must also be inspected. The anchorage points for the belts should also be checked.
•In certain countries it is possible to use seat belts which differ in terms of their operation from the seat belts which are described on the pages which follow.
How are seat belts correctly fastened?
Fastening three-point seat belts
Fasten your seat belt before starting!
– Correctly adjust the seat and the head restraint before fastening your
seat belt ⇒page 122, “Correct seated position”.
WARNING (continued)
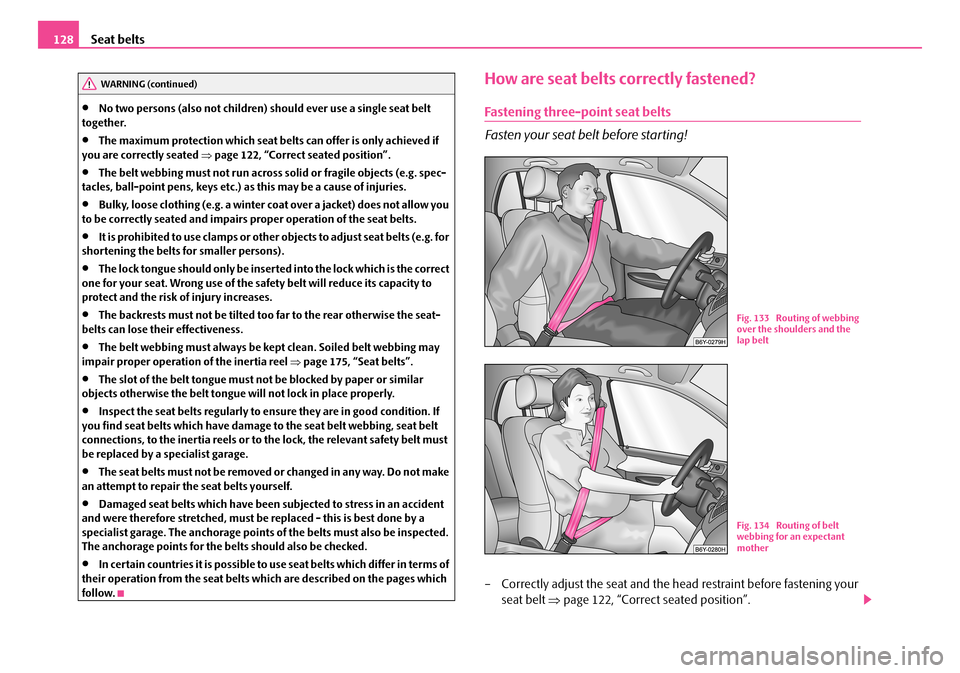
Fig. 133 Routing of webbing over the shoulders and the lap belt
Fig. 134 Routing of belt webbing for an expectant mother
NKO A05F 20.book Page 128 Wednesday, April 2, 2008 1:02 PM
Page 130 of 252
Seat belts129
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
– Slowly pull the belt webbing at the tongue of the lock over your chest
and pelvis ⇒.
– Insert the tongue of the lock into the seat belt buckle belonging to the
seat until it is heard to lock in place.
– Pull on the belt to check that it has also reliably engaged in the lock.
Each three-point seat belt is equipped with an inertia reel. This inertia reel offers you complete freedom of movement if the belt is unreeled slowly. If the brakes are applied suddenly, the inertia reel will block. It also blocks the belts when the car accelerates, when driving downhill and when cornering.
Expectant mothers must also wear the seat belt ⇒.
WARNING
•The shoulder part of the seat belt must never run across your neck but must run approximately over the middle of the shoulder and fit snugly against the chest. The lap part of the belt must run across the hip and must never be routed across the stomach. It must always fit snugly ⇒page 128, fig. 133. Adjust the belt webbing as required.
•The lap part of the belt should be positioned as low as possible at the pelvis of an expectant mother in order to avoid exerting any pressure on the lower abdomen.
•Always ensure that the webbing of the seat belts is properly routed. Seat belts which are not correctly adjusted can themselves cause injuries even in minor accidents.
•A seat belt which is hanging too loose can result in injuries as your body is moved forward by the kinetic energy produced in an accident and is then suddenly held firm by the belt.
•Only insert the lock tongue into the lock which is the correct one for your seat. This will affect the protection which the belt offers and increase the risk of an injury.
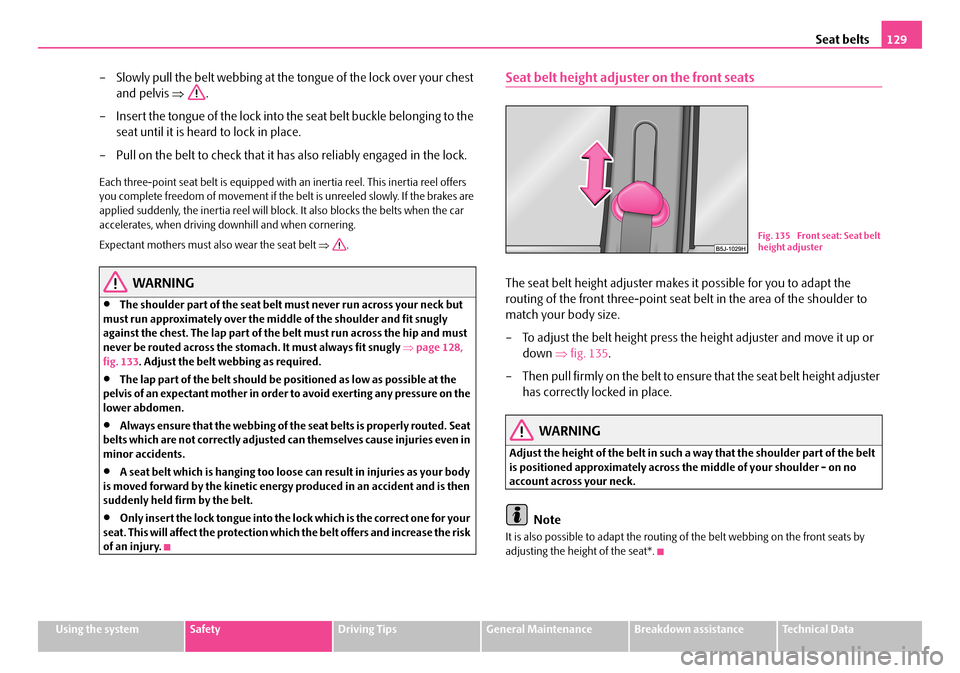
Seat belt height adjuster on the front seats
The seat belt height adjuster makes it possible for you to adapt the
routing of the front three-point seat belt in the area of the shoulder to
match your body size.
– To adjust the belt height press the height adjuster and move it up or
down ⇒fig. 135.
– Then pull firmly on the belt to ensure that the seat belt height adjuster
has correctly locked in place.
WARNING
Adjust the height of the belt in such a way that the shoulder part of the belt is positioned approximately across the middle of your shoulder - on no account across your neck.
Note
It is also possible to adapt the routing of the belt webbing on the front seats by adjusting the height of the seat*.
Fig. 135 Front seat: Seat belt height adjuster
NKO A05F 20.book Page 129 Wednesday, April 2, 2008 1:02 PM
Page 131 of 252
Seat belts130
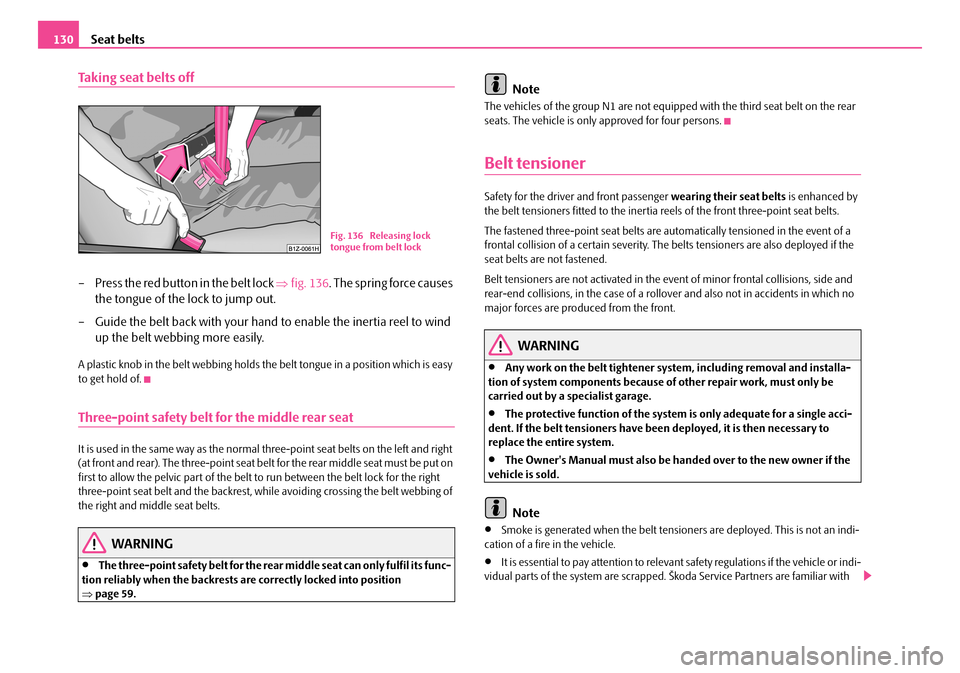
Taking seat belts off
– Press the red button in the belt lock ⇒fig. 136. The spring force causes
the tongue of the lock to jump out.
– Guide the belt back with your hand to enable the inertia reel to wind
up the belt webbing more easily.
A plastic knob in the belt webbing holds the belt tongue in a position which is easy to get hold of.
Three-point safety belt for the middle rear seat
It is used in the same way as the normal three-point seat belts on the left and right (at front and rear). The three-point seat belt for the rear middle seat must be put on first to allow the pelvic part of the belt to run between the belt lock for the right three-point seat belt and the backrest, while avoiding crossing the belt webbing of the right and middle seat belts.
WARNING
•The three-point safety belt for the rear middle seat can only fulfil its func-tion reliably when the backrests are correctly locked into position ⇒page 59.
Note
The vehicles of the group N1 are not equipped with the third seat belt on the rear seats. The vehicle is only approved for four persons.
Belt tensioner
Safety for the driver and front passenger wearing their seat belts is enhanced by the belt tensioners fitted to the inertia reels of the front three-point seat belts.
The fastened three-point seat belts are automatically tensioned in the event of a frontal collision of a certain severity. The belts tensioners are also deployed if the seat belts are not fastened.
Belt tensioners are not activated in the event of minor frontal collisions, side and rear-end collisions, in the case of a rollover and also not in accidents in which no major forces are produced from the front.
WARNING
•Any work on the belt tightener system, including removal and installa-tion of system components because of other repair work, must only be carried out by a specialist garage.
•The protective function of the system is only adequate for a single acci-dent. If the belt tensioners have been deployed, it is then necessary to replace the entire system.
•The Owner's Manual must also be handed over to the new owner if the vehicle is sold.
Note
•Smoke is generated when the belt tensioners are deployed. This is not an indi-cation of a fire in the vehicle.
•It is essential to pay attention to relevant safety regulations if the vehicle or indi-vidual parts of the system are scrapped. Škoda Service Partners are familiar with
Fig. 136 Releasing lock tongue from belt lock
NKO A05F 20.book Page 130 Wednesday, April 2, 2008 1:02 PM
Page 134 of 252

Airbag system133
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
When are the airbags deployed?
The airbag system is designed in such a way that the driver and the front passenger airbag* are deployed in the event of a frontal collision of major severity.
In the case of a violent side crash, the side airbag* in the front seat and the head airbag* on the side of the car at which the collision occurs are deployed.
It is also possible under certain special accident situations that the front as well as the side airbags and head airbags* are deployed.
The airbags are not deployed in the case of minor frontal and side collisions, in the case of rear-end collisions and vehicle rollover.
Deployment factors
It is not possible to state globally which deployment conditions apply to the airbag system in every situation as the circumstances which exist in the case of accidents vary greatly. An important role in this case, for example, is played by factors such as the type of object against which the vehicle impacts (hard, soft), the angle of impact, the vehicle speed etc.
A decisive factor for the deployment of the airbags is the deceleration which occurs during a collision. The control unit analyses the nature of the collision and activates the relevant restraint system. If the vehicle deceleration which occurs and is meas-ured during the collision remains below the prescribed reference values specified in the control unit, the airbags are not deployed although the vehicle may well suffer severe damage to the bodywork as a consequence of the accident.
The airbags are not deployed if:
•ignition off,
•a minor frontal collision,
•a minor side collision,
•a rear-end collision,
•rollover.
Caution
The dash panel must be replaced after the front passenger airbag has been deployed.
Note
•A grey white or red, non harmful gas is released when airbag is inflated. This is perfectly normal and is not an indication of a fire in the vehicle.
•In the event of an accident in which the airbags are deployed:
−The interior lighting comes on (if the switch for the interior light is in the door contact position),
−The hazard warning light is switched on,
−All the doors are unlocked.
Front airbags
Description of the front airbags
The airbag system is not a substitute for the seat belt!
Fig. 137 Driver airbag in the steering wheel
NKO A05F 20.book Page 133 Wednesday, April 2, 2008 1:02 PM
Page 149 of 252
Transporting children safely148
run across the neck. The lap part of the seat belt must run across the pelvis and fits snugly; it must not run over the belly. Tighten the belt webbing over your hip if necessary.
•Please comply with any differing national legal regulations regarding the use of child safety seats.
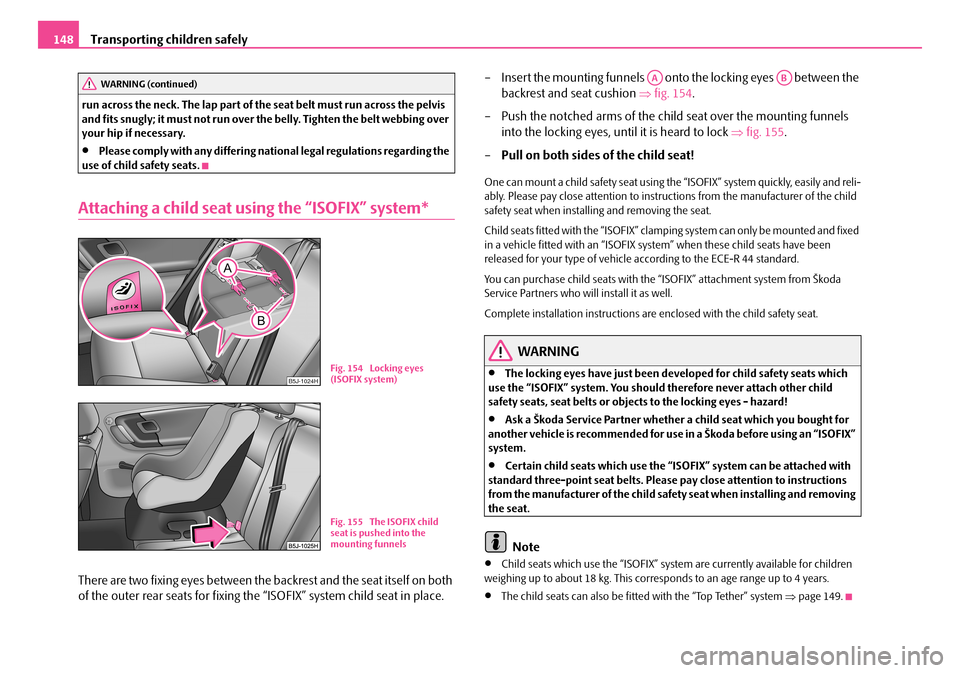
Attaching a child seat using the “ISOFIX” system*
There are two fixing eyes between the backrest and the seat itself on both
of the outer rear seats for fixing the “ISOFIX” system child seat in place.
– Insert the mounting funnels onto the locking eyes between the
backrest and seat cushion ⇒fig. 154.
– Push the notched arms of the child seat over the mounting funnels
into the locking eyes, until it is heard to lock ⇒fig. 155.
–Pull on both sides of the child seat!
One can mount a child safety seat using the “ISOFIX” system quickly, easily and reli-ably. Please pay close attention to instructions from the manufacturer of the child safety seat when installing and removing the seat.
Child seats fitted with the “ISOFIX” clamping system can only be mounted and fixed in a vehicle fitted with an “ISOFIX system” when these child seats have been released for your type of vehicle according to the ECE-R 44 standard.
You can purchase child seats with the “ISOFIX” attachment system from Škoda Service Partners who will install it as well.
Complete installation instructions are enclosed with the child safety seat.
WARNING
•The locking eyes have just been developed for child safety seats which use the “ISOFIX” system. You should therefore never attach other child safety seats, seat belts or objects to the locking eyes - hazard!
•Ask a Škoda Service Partner whether a child seat which you bought for another vehicle is recommended for use in a Škoda before using an “ISOFIX” system.
•Certain child seats which use the “ISOFIX” system can be attached with standard three-point seat belts. Please pay close attention to instructions from the manufacturer of the child safety seat when installing and removing the seat.
Note
•Child seats which use the “ISOFIX” system are currently available for children weighing up to about 18 kg. This corresponds to an age range up to 4 years.
•The child seats can also be fitted with the “Top Tether” system ⇒page 149.
WARNING (continued)
B5J-1024HFig. 154 Locking eyes (ISOFIX system)
Fig. 155 The ISOFIX child seat is pushed into the mounting funnels
AAAB
NKO A05F 20.book Page 148 Wednesday, April 2, 2008 1:02 PM
Page 152 of 252

Intelligent Technology151
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
Driving Tips
Intelligent Technology
Electronic stability programme (ESP)*
General
General
The ESP aids you maintain control of your vehicle in situations in borderline driving situations such as when negotiating a curve too fast. The risk of skidding is reduced and your car thus offers greater driving stability depending on the conditions of the road surface. This occurs at all speeds.
The following systems are integrated into the electronic stability programme:
•Electronic Differential Lock (EDL),
•Traction control system (TCS),
•Antilock brake system (ABS),
•Brake Assist.
Operating principle
The ESP switches on automatically when the engine is started and then conducts a self-test. The ESP control unit processes data from the individual systems. It also processes additional measurement data which are supplied by highly sensitive sensors: the rotational velocity of the vehicle about its vertical axis, the lateral accel-eration of the vehicle, the braking pressure and the steering angle.
The direction which the driver wishes to take is determined based on the steering angle and the speed of the vehicle and is constantly compared with the actual behaviour of the vehicle. If differences exist, such as the car beginning to skid, the ESP will automatically brake the appropriate wheel.
The car is stabilised again by the forces which take effect when the wheel is braked. Intervention into the brake system takes place primarily on the outer front wheel of a vehicle which tends to oversteer (tendency for the rear of the vehicle to break away) while occurs this is on the inner rear wheel of a vehicle which tends to under-steer (tendency to shift out of the curve). This braking control cycle is accompanied by noises.
The ESP operates in combination with the ABS ⇒page 155, “Antilock brake system (ABS)*”. If there is a fault in the ABS system, the ESP also does not operate.
The ESP warning light ⇒page 27 lights up in the instrument cluster when there is a fault on the ESP.
Switching off
You can switch the ESP off and on again as you wish, by pressing the button ⇒fig. 158. The ESP warning light ⇒page 27 lights up in the instrument cluster when the ESP is switched off.
The ESP should normally always be switched on. It may be good practice in certain exceptional cases, such as when you wish to have wheel slip, to switch off the system.
Examples:
Fig. 158 ESP switch
NKO A05F 20.book Page 151 Wednesday, April 2, 2008 1:02 PM