engine SKODA OCTAVIA TOUR 2009 1.G / (1U) Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SKODA, Model Year: 2009, Model line: OCTAVIA TOUR, Model: SKODA OCTAVIA TOUR 2009 1.G / (1U)Pages: 226, PDF Size: 13.11 MB
Page 134 of 226
Intelligent Technology133
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
Driving TipsIntelligent TechnologyElectronic stability programme (ESP)*GeneralGeneral
The ESP aids you maintain control of your vehicle in situations in borderline driving
situations such as when negotiating a curve too fast. The risk of skidding is reduced
and your car thus offers greater driving stability depending on the conditions of the
road surface. This occurs at all speeds.
The following systems are integrated into the electronic stability programme:•
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL),
•
Traction control system (TCS),
•
Antilock brake system (ABS),
•
Brake Assist. Operating principle
The ESP switches on automatically when the engine is started and then conducts a
self-test. The ESP control unit processes data from the individual systems. It also
processes additional measurement data which are supplied by highly sensitive
sensors: the rotational velocity of the vehi
cle about its vertical axis, the lateral accel-
eration of the vehicle, the brakin g pressure and the steering angle.
The direction which the driver wishes to ta ke is determined based on the steering
angle and the speed of the vehicle and is constantly compared with the actual
behaviour of the vehicle. If differences exis t, such as the car beginning to skid, the
ESP will automatically brake the appropriate wheel.
The car is stabilised again by the forces which take effect when the wheel is braked.
Intervention into the brake system takes place primarily on the outer front wheel of
a vehicle which tends to oversteer (tendency for the rear of the vehicle to break
away) while occurs this is on the inner re ar wheel of a vehicle which tends to under-
steer (tendency to shift out of the curve). This braking control cycle is accompanied
by noises.
The ESP operates in combination with the ABS ⇒page 137, “Antilock brake system
(ABS)*”. If there is a fault in the ABS system, the ESP also does not operate.
The ESP warning light ⇒page 33 lights up in the instrument cluster when there is a
fault on the ESP.
Switching off
You can switch the ESP off and on again as you wish, by pressing the button
⇒ fig. 141 . The ESP warning light ⇒page 33 lights up in the instrument cluster
when the ESP is switched off.
The ESP should normally always be switched on. It may be good practice in certain
exceptional cases, such as when you wish to have wheel slip, to switch off the
system.
Examples:
Fig. 141 ESP switch
s2ig.book Page 133 Monday, November 10, 2008 11:20 AM
Page 135 of 226

Intelligent Technology
134•
when driving with snow chains
•
when driving in deep snow or on a loose surface
•
when it is necessary to rock a ca r free when it has become stuck.
then you should switch on the ESP again.
WARNING
It is also not possible for the ESP to overcome the physical limits of the
vehicle. Even if a vehicle fitted with ESP you should still always adapt your
style of driving to the condition of the road surface and the traffic situation.
This particularly applies when driving on slippery and wet roads. The
increased safety offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than
otherwise - risk of an accident!
Note
•
All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres in order to achieve problem-
free operation of the ESP. Differing rollin g circumferences of the tyres can lead to
an undesirable reduction in the engine output.
•
Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or other assign-
ment of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the ESP ⇒page 181,
“Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)*
The electronic differential lock pr events an individual wheel from
slipping.Vehicles fitted with ABS* can be equipped with electron ic differential lock (EDL).
General
The EDL makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off, accelerate
and climb a steep hill when the conditio ns of the road surface are unfavourable. Operating principle
The EDL is activated automatically, that is
without any action on the part of the
driver. It monitors the speeds of the driven wheels with the aid of the ABS sensors.
Should only one drive wheel begin spinning on a slippery surface there will be an
appreciable difference in the speed of the driven wheels. The EDL function brakes
the slipping wheel and the differential transmits a greater driving force to the other
driven wheel. This control proces s is also accompanied by noises.
Overheating of the brakes
The EDL switches off automatically if unusually severe stresses exist in order to
avoid excessive heat generation in the disc brake on the wheel which is being
braked. The vehicle can continue to be dr iven and has the same characteristics as
a vehicle not fitted with EDL.
The EDL switches on again automatically as soon as the brake has cooled down.
WARNING
•
Depress the accelerator carefully when accelerating on uniformly slip-
pery road surfaces, such as ice and sn ow. The driven wheels might still spin
despite the EDL and affect the stability of the vehicle - risk of an accident!
•
You should always adapt your style of driving to the condition of road
surface and to the traffic situation even when your vehicle is fitted with EDL.
The increased safety offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than
otherwise - risk of an accident!Note
•
If the ABS warning light comes on, this ma y also indicate a fault in the EDL.
Please have the car inspected as soon as possible by a specialist garage.
•
Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or other assign-
ment of tyres and wheels) can in fluence the function of the EDL ⇒page 181,
“Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
s2ig.book Page 134 Monday, November 10, 2008 11:20 AM
Page 136 of 226
Intelligent Technology135
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
Traction control system (TCS)
The traction control system prevents the driven wheels from spinning
when accelerating.General
The TCS makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off, accelerate
and climb a steep hill when the conditio ns of the road surface are unfavourable.
Operating principle
The TCS switches on automatically when th e engine is started and then conducts a
self-test. The system monitors the speeds of the driven wheels with the aid of the
ABS sensors. If the wheels are spinning, the force transmitted to the road surface is
automatically adapted by redu cing the engine speed. This occurs at all speeds.
The TCS operates in combination with the ABS ⇒page 137, “Antilock brake system
(ABS)*”. The TCS will not function if a fault exists in the ABS system.
The TCS warning light ⇒page 33 lights up in the instrument cluster when there is a
fault on the TCS.
Switching off
You can switch the TCS off and on again as you wish by pressing the button
⇒ fig. 142 . The TCS warning light ⇒page 33 lights up in the instrument cluster
when the TCS is switched off. The TCS should normally always be switched on. It may be good practice in certain
exceptional cases, such as when you wish
to have wheel slip, to switch off the
system.
Examples:
•
when driving with snow chains
•
when driving in deep snow or on a loose surface
•
when it is necessary to rock a car free when it has become stuck.
then you should switch on the TCS again.
WARNING
You should always adjust your style of driving to the conditions of the road
surface and the traffic situation. The increased safety offered must not
tempt you to take greater risks than otherwise - risk of an accident!
Note
•
All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres in order to achieve problem-
free operation of the TCS. Differing rolling circumferences of the tyres can lead to
an undesirable reduction in the engine output.
•
Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or other assign-
ment of tyres and wheels) can in fluence the function of the TCS ⇒ page 181,
“Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
BrakesWhat has a negative effect on braking efficiency?Wear-and-tear
Wear-and-tear to the brake pads is greatly dependent on the operating conditions
of the vehicle and your style of driving. Particularly if you drive a great deal in towns
and over short distances or if you adopt a sporty style of driving, it may be neces-
sary to have the thickness of the brake pads inspected at a specialist garage
between the service inspections.
Fig. 142 TCS switch
s2ig.book Page 135 Monday, November 10, 2008 11:20 AM
Page 137 of 226

Intelligent Technology
136Wet roads or road salt
There may be a certain delay before the br akes take full effect under certain condi-
tions such as when driving through water, during heavy rain showers or after the
vehicle has been washed in an automatic vehicle wash, since the brake discs and
brake pads may be moist or even have a coating of ice on them in winter. You
should dry the brakes as soon as possib le (by applying and releasing the brakes
several times, if the road conditions and the traffic situation allows it).
There also may be a certain delay before the full braking efficiency is available when
driving on roads which have been treated wi th road salt if you have not used the
brakes for some considerable time beforeha nd. The layer of salt on the brake discs
and brake pads must first be rubb ed off when you apply the brakes.
Corrosion
Corrosion on the brake discs and dirt on th e bake pads occur if the vehicle has been
parked for a long period and if you do not make much use of the braking system.
We recommend cleaning the brake discs by firmly applying the brakes at a fairly
high speed if you do not make much use of the braking system or if surface corro-
sion is present ⇒.
Faults in the brake surface
If you notice that the braking distance has suddenly become longer and that the
brake pedal can be depressed further, it is possible that a brake circuit of the dual-
circuit brake system has failed. Drive, in such cases, to the nearest specialist garage
without delay in order to have the problem rectified. Drive at a reduced speed
while on your way to the dealer and adapt your style of driving to the higher brake
pedal pressure required.
Low brake fluid level
An insufficient level of brake fluid may result in problems in the brake system. The
level of the brake fluid is monitored electronically ⇒page 34, “Brake system ”.
WARNING
•
Only apply the brakes for the purpose of drying and cleaning the brake
discs if the traffic conditions permit this. Do not place any other road users
in jeopardy.
•
When retrospectively mounting a front spoiler, solid wheel hubs etc. one
must ensure that the air supply to the front wheel brakes is not reduced
otherwise the braking sy stem could run too hot.
•
Allow for the fact that new brake pads do not achieve their full braking
efficiency until approximately 200 kilo metres. New brake pads must be first
“run in” before they develop their optimal friction force. You can, however,
compensate for this slightly reduced braking force by increasing the pres-
sure on the brake pedal. This guidelin e also applies to any new brake pads
installed at a future date.Caution
•
Never allow the brakes to ru b by applying slight pressure if you do not wish to
brake the vehicle. This causes the brakes to overheat and can also result in a longer
braking distance and excessive wear.
•
Before negotiating a steep downhill section, reduce your speed, shift down into
the next lower gear. This enables you to make full use of the braking power of the
vehicle and reduces the strain on the br akes. Any additional braking should be
done intermittently , not continuously.
Brake boosterThe brake booster boosts the pressure which you generate with the brake pedal.
The necessary pressure is only gene rated when the engine is running.
WARNING
•
Never switch off the engine before the vehicle is stationary.
•
The brake booster only operates when the engine is running. Greater
physical effort for braking is required when engine is swit ched off. Because
if you do not stop as normal, this can cause an accident and severe injuries.WARNING (continued)
s2ig.book Page 136 Monday, November 10, 2008 11:20 AM
Page 138 of 226

Intelligent Technology137
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
Antilock brake system (ABS)*ABS prevents the wheels locking when braking.General
The ABS contributes significan tly to enhancing the active safety of your vehicle.
Compared to a car not fitted with the ABS brake system, you are able to retain
optimal steering ability even during a fu ll brake application on a slippery road
surface because the wheels do not lock up.
You must not expect, however, that the br aking distance will be shorter under all
circumstances as a result of the ABS. Th e braking distance for example on gravel
and fresh snow, when you should anyway be driving slowly and cautiously, will be
longer.
Operating principle
The brake pressure will be reduced on a wheel which is rotating at a speed which is
too low for the speed of the vehicle and tend ing to lock. This control cycle is notice-
able from a pulsating movement of the brake pedal which is accompanied by
noises. This is consciously intended to provide the driver with the information that
the wheels are tending to lock (ABS control range). You must always keep the brake
pedal depressed to enable the ABS to optima lly control the brake application in this
braking range. Never interrupt the application of the brakes!
WARNING
•
The ABS can also not overcome the physic al limits of your vehicle. Please
do not forget this, particularly when driving on icy or wet road surfaces. If
the ABS is operating within the contro l range, adapt your speed immediately
to the conditions of the road surface and the traffic situation. The increased
safety offered by the ABS must not tempt you to take greater risks than
otherwise - risk of an accident!
•
The normal braking system is still fully functional if there is an ABS fault.
Visit a specialist garage as quickly as possible and adju st your style of driving
to take account of the ABS fault in the meantime since you will not know how
great the damage is.
Note
•
A warning light comes on if a fault occurs in the ABS system ⇒page 32.
•
Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or other assign-
ment of tyres and wheels) can in fluence the function of the ABS ⇒page 181,
“Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
Brake Assist*During a severe brake application (e.g. if a hazard exists), the Brake Assist increases
the braking force and thus makes it possible to rapidly produce the pressure
required in the brake system.
The majority of drivers do apply the brakes in good time in dangerous situations,
but do not depress the brake pedal with suff icient pressure. Consequently, it is not
possible for the car to achieve its maxi mum deceleration and the car covers a
greater distance than necessary.
The Brake Assist is activated by the very quick operation of the brake pedal. In such
cases, a much greater braking pressure ex ists than during a normal brake applica-
tion. This makes it possible, even with a relatively low resistance of the brake pedal,
to produce an adequate pressure in the brake system in the shortest possible time,
which is required for maximum deceleration of the car. You must apply the brake
pedal firmly and hold it in this position in order to achieve the shortest possible
braking distance.
The Brake Assist is able to help you achi eve a shorter braking distance in emergency
situations by rapidly producing the pressure required in the brake system. It fully
exploits the attributes of the ABS. After yo u release the brake pedal, the function of
the Brake Assist is automatically switched off and the brakes operate in the normal
way.
WARNING
•
The Brake Assist is also not able to overcome the physical limits of your
car in terms of the braking distance required.
s2ig.book Page 137 Monday, November 10, 2008 11:20 AM
Page 140 of 226

Driving and the Environment139
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
Driving and the EnvironmentThe first 1 500 kilometres and then afterwardsA new engine
The engine has to be run in during the first 1 500 kilometres.Up to 1 000 kilometres
– Do not drive faster than 3/4 of the mamimum speed of the gear in use,
that is 3/4 of the maximum permissible engine speed.
– Do not use full throttle.
– Avoid high engine revolutions.
– Do not tow a trailer.
From 1 000 up to 1 500 kilometres
– Increase the power output of the engine gradually up to the full
speed of the gear engaged, that is up to the maximum permissible
engine revolutions.During the first operating hours the engine has higher internal friction than later
until all of the moving parts have harmonized. The driving style which you adopt
during the first approx.1 500 kilometres plays a decisive part in the success of
running in your car.
You should not drive at unnecessarily high engine revolutions even after the
running-in period is complete. The maximum permissib le engine speed is marked
by the beginning of the red zone on the scale of the revolutions counter. Shift up
into the next higher gear on a vehicle fitted with manual gearbox before the red
zone is reached. Extremely high engine revolutions are automatically governed, by
the way.
For a vehicle fitted with a manual gearbox the converse situation also applies: Do
not drive at engine revolutions which are too low. Shift down as soon as the engine
is no longer running smoothly.
Caution
All the speed and engine revolution figure s apply only when the engine is at its
normal operating temperature. Never rev up an engine which is cold, neither when
the vehicle is stationary nor when driving in individual gears.
For the sake of the environment
Not driving at unnecessarily high engine revolutions and shifting to a higher gear as
early as possible are ways to minimise fuel consumption and operating noise levels
and protects the environment.New tyresNew tyres have to be “run in” since they do not offer optimal grip at first. You should
take account of this fact for the firs t 500 kilometres and drive particularly
carefully.New brake padsAllow for the fact that new brake pads do not achieve their full braking efficiency
until approximately 200 kilometres. New brake pads must be first “run in” before
they develop their optimal friction force. You can, however, compensate for this
slightly reduced braking force by increasing the pressure on the brake pedal.
This guideline also applies to any new brake pads installed at a future date.
During the running-in period, you should avoid excessive stresses on the brakes.
This includes, for example, violent braking, particularly from very high speeds, and
also when crossing mountain passes.
s2ig.book Page 139 Monday, November 10, 2008 11:20 AM
Page 141 of 226

Driving and the Environment
140Catalytic converterProper operation of the emission co ntrol system (catalytic converter)
is of major significance for drivin g your vehicle in an environmen-
tally conscious way.Please refer to the following guidelines:
– For vehicles with petrol engine only refuel with unleaded petrol
⇒ page 157, “Grades of petrol”.
– Never run the fuel tank completely empty.
– Do not switch off the ignition while you are driving the vehicle.
– Do not pour too much oil into the engine ⇒page 165, “Replenishing
engine oil”.
– Do not tow-start the vehicle over a distance of more than 50 metres
⇒ page 193, “Tow-starting a vehicle”.If you drive your vehi cle in a country in which unleaded petrol is not available, you
must have the catalytic converter replaced later when driving the vehicle into a
country in which use of a cata lytic converter is mandatory.
WARNING
•
In view of the high temperatures which may be produced in the catalytic
converter, one should always park a vehicle in such a way that the catalytic
converter cannot come into contact with easily flammable materials below
the vehicle - a risk of fire!
•
Never use additional underbody protection or corrosion-protection
agents for the exhaust pipes, catalyti c converters or heat shields. Such
substances might ignite when driving - risk of fire!Caution
•
Vehicles fitted with catalytic converter should neve r be allowed to let the fuel
tank to run completely empty. An irregular fuel supply can result in poor ignition or misfiring. Unburnt fuel may get into the exhaust system and damage the catalytic
converter.
•
Filling the tank even only once with le
aded petrol will result in the catalytic
converter being destroyed.
•
If you detect misfiring, a drop in performance or irregular engine running when
driving, reduce your speed immediately and have the vehicle inspected by the
nearest specialist garage. The symptoms described may be caused by a fault in the
ignition system. Unburnt fuel may get in to the exhaust system and damage the
catalytic converter.For the sake of the environment
Even if the exhaust system is operating properly, a sulphur-like exhaust odour may
be produced under certain op erating conditions of the engine. This depends on the
sulphur content of the fuel. It is often su fficient to refuel with unleaded premium-
grade petrol of a different brand or at a different filling station.Driving in an economical and environmentally
conscious mannerGeneral
Your personal style of driving is a major factor.Your fuel consumption, any pollution of the environmental and the wear-and-tear
to the engine, brakes and tyres, depend essentially on three factors:•
your personal style of driving,
•
the conditions under which your vehicle is operated,
•
technical aspects.
You can easily improve your fuel economy by 10 - 15 percent by driving in an
economical way with foresight. This section is intended to provide you with a
number of tips on how to protect the en vironment and at the same time save
money.
s2ig.book Page 140 Monday, November 10, 2008 11:20 AM
Page 142 of 226
Driving and the Environment141
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
The fuel consumption can naturally also be
influenced by factors which are beyond
the driver's control. It is, for example, normal for the fu el consumption to increase
in winter and under worsened conditions such as poor road conditions, towing a
trailer, etc.
The technical requirements for low fuel usage and economic efficiency of the
vehicle have already been built into the ve hicle at the works. Special attention has
been given to minimising ne gative effects on the environment. It is necessary to
take note of the guidelines given in this chapter in order to make best use of these
characteristics and to maintain their effectiveness.
The optimal engine speed should be obtained when accelerating, in order to avoid
a high fuel consumption an d resonance of the vehicle.
Looking ahead when driving
A vehicle's highest fuel consumption occurs it accelerates.Avoid accelerating and brakin g unnecessarily. If you drive with forsight you will not
need to brake so often and will also then not have to accelerate so much. Let your
vehicle coast to a stop, for example, if this is possible, when you see that the next
set of traffic lights is at red.Shifting gears and saving energy
Shifting up early saves on fuel.
Manual gearbox
– Drive no more than about one length of your vehicle in first gear.
– Always shift up into the next higher gear at approx. 2 000 to 2 500 revs.An effective way of achieving good fuel economy is to shift up early. You will
consume more fuel if you drive at unnecessa rily high revolutions in any given gear.
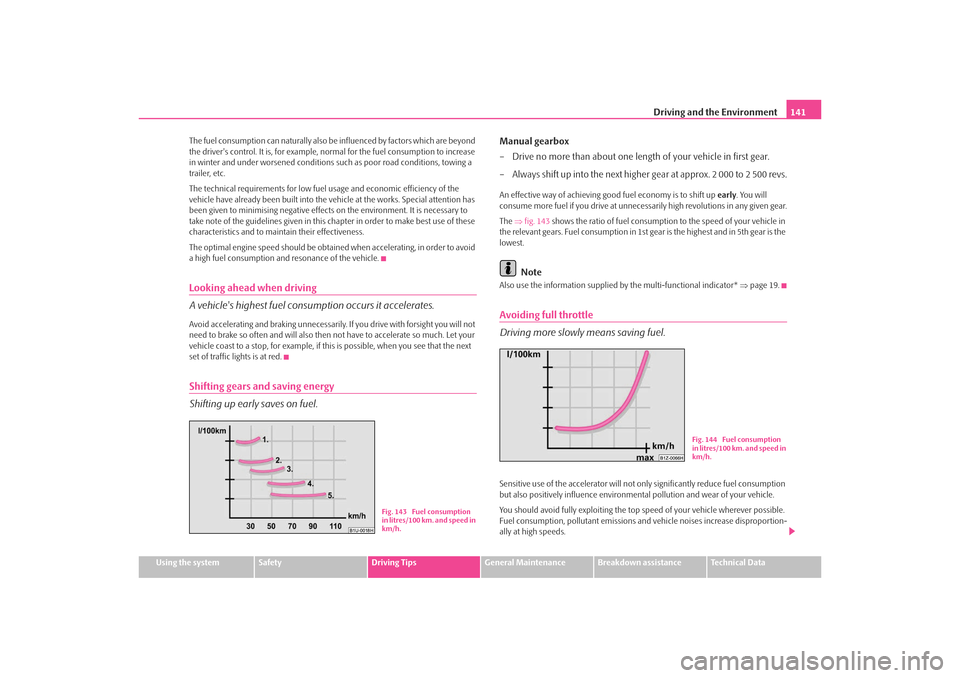
The ⇒fig. 143 shows the ratio of fuel consumption to the speed of your vehicle in
the relevant gears. Fuel consumption in 1st gear is the highest and in 5th gear is the
lowest.
Note
Also use the information supplied by the multi-functional indicator* ⇒page 19.Avoiding full throttle
Driving more slowly means saving fuel.Sensitive use of the accelerator will not only significantly reduce fuel consumption
but also positively influe nce environmental pollution and wear of your vehicle.
You should avoid fully exploiting the top speed of your vehicle wherever possible.
Fuel consumption, pollutant emissions an d vehicle noises increase disproportion-
ally at high speeds.
Fig. 143 Fuel consumption
in litres/100 km. and speed in
km/h.
Fig. 144 Fuel consumption
in litres/100 km. and speed in
km/h.
s2ig.book Page 141 Monday, November 10, 2008 11:20 AM
Page 143 of 226
Driving and the Environment
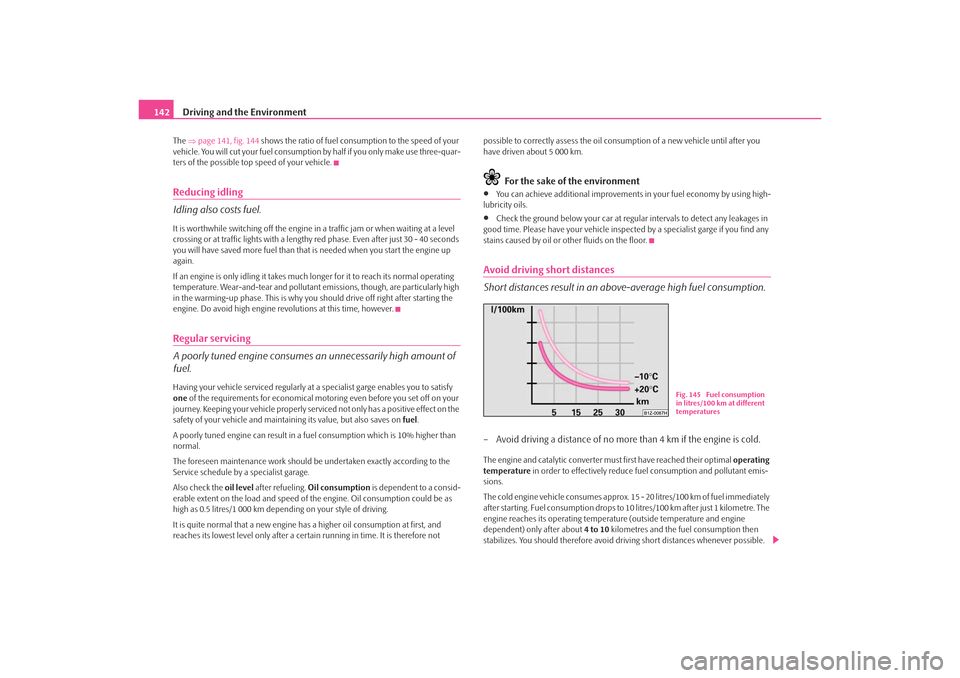
142The ⇒page 141, fig. 144 shows the ratio of fuel consumption to the speed of your
vehicle. You will cut your fuel consumption by half if you only make use three-quar-
ters of the possible top speed of your vehicle.Reducing idling
Idling also costs fuel.It is worthwhile switching off the engine in a traffic jam or when waiting at a level
crossing or at traffic lights with a length y red phase. Even after just 30 - 40 seconds
you will have saved more fuel than that is needed when you start the engine up
again.
If an engine is only idling it takes much longer for it to reach its normal operating
temperature. Wear-and-tear and pollutant em issions, though, are particularly high
in the warming-up phase. This is why you should drive off right after starting the
engine. Do avoid high engine revolutions at this time, however.Regular servicing
A poorly tuned engine consumes an unnecessarily high amount of
fuel.Having your vehicle serviced regularly at a specialist garge enables you to satisfy
one of the requirements for economical motoring even before you set off on your
journey. Keeping your vehicle properly servic ed not only has a positive effect on the
safety of your vehicle and maintaining its value, but also saves on fuel.
A poorly tuned engine can result in a fu el consumption which is 10% higher than
normal.
The foreseen maintenance work should be undertaken exactly according to the
Service schedule by a specialist garage.
Also check the oil level after refueling. Oil consumption is dependent to a consid-
erable extent on the load and speed of the engine. Oil consumption could be as
high as 0.5 litres/1 000 km depending on your style of driving.
It is quite normal that a new engine ha s a higher oil consumption at first, and
reaches its lowest level only after a cert ain running in time. It is therefore not possible to correctly assess the oil cons
umption of a new vehicle until after you
have driven about 5 000 km.
For the sake of the environment
•
You can achieve additional improvements in your fuel economy by using high-
lubricity oils.
•
Check the ground below your car at regula r intervals to detect any leakages in
good time. Please have your vehicle inspected by a specialist garge if you find any
stains caused by oil or other fluids on the floor.
Avoid driving short distances
Short distances result in an above-average high fuel consumption.– Avoid driving a distance of no more than 4 km if the engine is cold.The engine and catalytic converter mu st first have reached their optimal operating
temperature in order to effectively reduce fuel consumption and pollutant emis-
sions.
The cold engine vehicle consumes approx. 15 - 20 litres/100 km of fuel immediately
after starting. Fuel consumption drops to 10 litres/100 km after just 1 kilometre. The
engine reaches its operating temperat ure (outside temperature and engine
dependent) only after about 4 to 10 kilometres and the fuel consumption then
stabilizes. You should therefore avoid driving short distances whenever possible.
Fig. 145 Fuel consumption
in litres/100 km at different
temperatures
s2ig.book Page 142 Monday, November 10, 2008 11:20 AM
Page 144 of 226

Driving and the Environment143
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
An important factor in this connection is also the
ambient temperature. The
⇒ page 142, fig. 145 shows the different fuel consum ptions for the same distance,
on the one hand at +20°C and on the other hand at -10°C. Your vehicle has a higher
fuel consumption in winter than in summer.
Checking tyre inflation pressures
Tyres which are correctly inflated save fuel.Always ensure that your tyres are inflated to the correct pressure at all times. The
rolling resistance will be increased if the tyre filling pressure is too low. This will not
only increase fuel consumption but also tyre wear and the driving behaviour will
worsen.
Always check the inflation pressure of the tyres when cold.
Do not drive with winter tyres all year round for this costs about 10 % more fuel.
Winter tyres are also louder.No unnecessary ballast
Transporting balla st costs fuel.The fact that every kilogram of extra weight increases your fuel consumption
means that it is worth taking a look in the luggage compartment to avoid trans-
porting any unnecessary ballast.
It is par ticularly i n town tra ffi c, whe n one is accelerating quite often, that the vehicle
weight will have a significant effect upon the fuel consumption. A rule of thumb
here is that an increase in weight of 100 kilograms will cause an increase in fuel
consumption of about 1 litre/100 kilometres.
You may frequently also leave a roof rack fitted on just out of convenience,
although you no longer need it. The incr eased aerodynamic drag of your vehicle
causes it to use about 10% more fuel than normal at a speed of 100 - 120 km/h,
even when you are not carr ying a load on the roof.
Saving electricity
Generating electricity costs fuel.– Switch off electrical components as soon as you no longer need them.When the engine is running, the alternator generates and supplies electrical power.
The greater the load on the alternator as a result of having a large number of elec-
trical components switched on, the more fuel will be consumed for operating the
alternator.Keeping a log of your fuel consumptionIf you really wish to keep a close check on your fuel consumption, it is best to enter
the figures in a logbook. This does not take much time but is a very worthwhile exer-
cise. It enables you to detect any change (positive and negative) at an early stage
and to take any appropriate action.
If you find that your fuel consumption is too high, you sh ould reflect on how, where
and in what conditions you have driven the vehicle since you last refuelled.Environmental compatibilityEnvironmental protection has played a majo r role in the design, selection of mate-
rials and manufacture of your new Škoda. Particular emphasis has been paid to a
number of aspects, including:
Design measures•
joints designed to be easily detached;
•
simplified disassembly due to the modular structure system;
•
improved purity of differ ent classes of materials;
•
Identification of all plastic parts in accordance with VDA Recommendation 260;
•
Reduced fuel consumption and exhaust emission CO
2;
•
Minimum fuel leakage during accidents;
•
Reduced noise.
s2ig.book Page 143 Monday, November 10, 2008 11:20 AM