brake sensor SKODA SUPERB 2006 1.G / (B5/3U) Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SKODA, Model Year: 2006, Model line: SUPERB, Model: SKODA SUPERB 2006 1.G / (B5/3U)Pages: 281, PDF Size: 12.67 MB
Page 27 of 281
Instruments and Indicator/Warning Lights
26
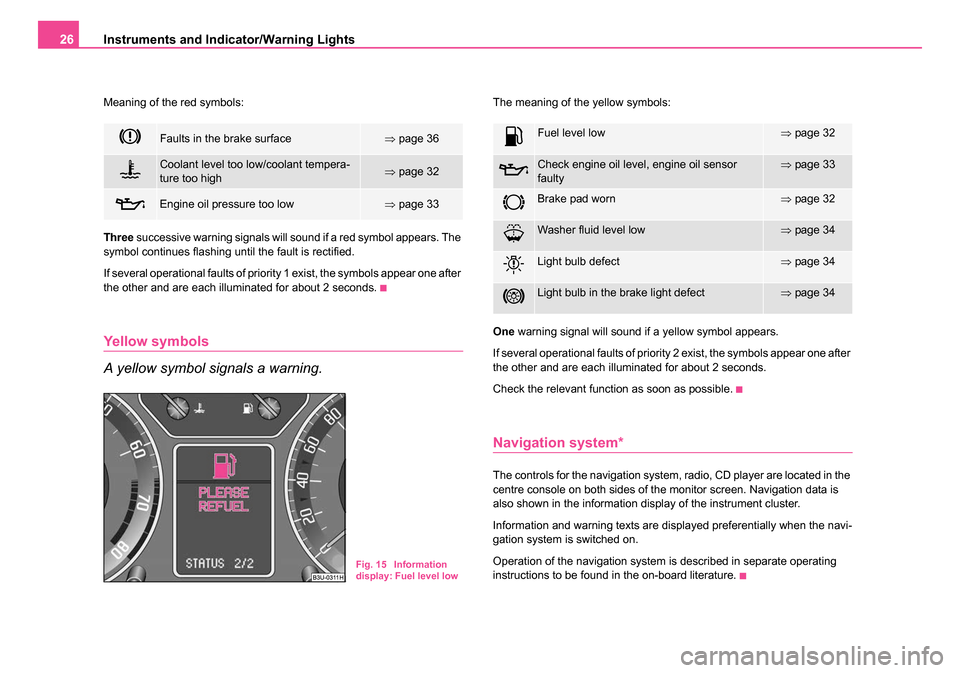
Meaning of the red symbols:
Three successive warning signals will sound if a red symbol appears. The
symbol continues flashing until the fault is rectified.
If several operational faults of priority 1 exist, the symbols appear one after
the other and are each illuminated for about 2 seconds.
Yellow symbols
A yellow symbol signals a warning.
The meaning of the yellow symbols:
One warning signal will sound if a yellow symbol appears.
If several operational faults of priority 2 exist, the symbols appear one after
the other and are each illuminated for about 2 seconds.
Check the relevant function as soon as possible.
Navigation system*
The controls for the navigation system, radio, CD player are located in the
centre console on both sides of the monitor screen. Navigation data is
also shown in the information display of the instrument cluster.
Information and warning texts are displayed preferentially when the navi-
gation system is switched on.
Operation of the navigation system is described in separate operating
instructions to be found in the on-board literature.
Faults in the brake surface⇒ page 36
Coolant level too low/coolant tempera-
ture too high⇒page 32
Engine oil pressure too low⇒page 33
Fig. 15 Information
display: Fuel level low
Fuel level low⇒page 32
Check engine oil level, engine oil sensor
faulty⇒page 33
Brake pad worn⇒page 32
Washer fluid level low⇒page 34
Light bulb defect⇒page 34
Light bulb in the brake light defect⇒page 34
NKO B5 20.book Page 26 Monday, July 3, 2006 2:09 PM
Page 127 of 281

Starting-off and Driving
126
Caution
After the car has come to a stop, always first of all apply the handbrake
firmly before then additionally engaging a gear (manual gearbox) or
moving the selector lever into position P (automatic gearbox).
Parking aid*
The parking aid provides a warning of obstacles behind
the vehicle.
The audible parking aid determines the distance between the rear bumper
and an obstacle located behind the vehicle with the aid of ultrasound
sensors. The sensors are integrated in the rear bumper. Range of sensors
The clearance warning begins at a distance of about 160 cm from the
obstacle (area
⇒fig. 119 ). The interval between the warning signals
becomes shorter as the clearance is reduced.
A continuous tone sounds from a clearance of just 30 cm (Bereich ) -
danger area. From this moment on do not continue driving in the
selected direction or the direction from where the obstacle is
reported!
Activating
The parking aid is activated automatically when reverse gear is engaged
and the ignition is turned on. This is confirmed by a brief acknowledge-
ment signal.
Deactivating
The parking aid is deactivated by removing the reverse gear.
WARNING
•The parking aid is not a substitute for the driver paying proper
attention and it is always the driver's responsibility to take care
when parking the vehicle or carrying out similar manoeuvres.
•You should therefore satisfy yourself, before reversing, that
there is no small obstacle, such as a rock, thin post, trailer drawbar
etc., behind your vehicle. Such an obstacle might not be within the
range detected by the sensors.
Note
•The parking aid does not operate if you are towing a trailer (applies to
models which feature a factory-fitted towing device*).
•If a warning signal sounds for about 3 seconds after switching the igni-
tion on and engaging reverse gear, and there is no obstacle close to your
Fig. 119 Parking aid:
Detection range of rear
sensors
AA
AB
NKO B5 20.book Page 126 Monday, July 3, 2006 2:09 PM
Page 129 of 281

Starting-off and Driving
128
lights up in the button. The activation is confirmed by a brief acknowledge-
ment signal.
Deactivating
The parking aid is deactivated after pressing the button
⇒ page 127,
fig. 120 or at a speed of more than 15 km/h - the symbol in the button
is no longer illuminated.
WARNING
•The parking aid is not a substitute for the driver paying proper
attention and it is always the driver's responsibility to take care
when reversing the vehicle or carrying out similar manoeuvres.
•You should therefore satisfy yourself, before reversing, that
there is no small obstacle, such as a rock, thin post, trailer drawbar
etc., in front or behind your vehicle. Such an obstacle might not be
within the range detected by the sensors.
Note
•Only the front parking aid operates if you are towing a trailer (applies
only to models which feature a factory-fitted towing device*).
•If a warning signal sounds for about 3 seconds after activating the
system and there is no obstacle close to your car, this indicates a system
fault. The fault is confirmed additionally when the symbol
flashes in the
button ⇒page 127, fig. 120 . Have the fault rectified by a specialist work-
shop.
•The sensors must be kept clean and free of ice to enable the parking
aid to operate properly.
Cruise control system (CCS)*
Introduction
The cruise control system (CCS) maintains a constant speed, more than
30 km/h (20 mph), once it has been set, without you having to depress the
accelerator pedal. This is only possible within the range which is permitted
by the power output and braking power of the engine. The cruise control
system makes it possible - particularly on long journeys - for you to rest
your “accelerator foot”.
WARNING
•The cruise control system must not, for safety reasons, be used
in dense traffic or on unfavourable road surfaces (such as icy
roads, slippery roads or loose chippings) - risk of accident!
•In order to prevent unintentional use of the cruise control
system, always switch off the system after use.
Note
•Models fitted with a manual gearbox: Always depress the clutch pedal
if you switch on the cruise control system when the gearbox is in Neutral.
Otherwise the engine can rev up unintentionally.
•The cruise control system is not able to maintain a constant speed
when driving on steep downhill sections. The weight of the vehicle
increases the speed at which it travels. One should shift down in good time
to a lower gear or slow the vehicle down by applying the foot brake.
•It is not possible on vehicles fitted with an automatic gearbox to switch
on the cruise control system if the selector lever is in the position P, N , R
or 2.
NKO B5 20.book Page 128 Monday, July 3, 2006 2:09 PM
Page 186 of 281

Intelligent Technology185
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
Driving Tips
Intelligent Technology
Electronic stability programme (ESP)*
General
General
The ESP aids you maintain control of your vehicle in situations in border-
line driving situations such as when negotiating a curve too fast. The risk
of skidding is reduced and your car thus offers greater driving stability
depending on the conditions of the road surface. This occurs at all speeds.
The following systems are integrated into the electronic stability
programme:
•Electronic Differential Lock (EDL),
•Traction control system (TCS),
•Antilock brake system ABS,
•Brake Assist.
Operating principle
The ESP switches on automatically when the engine is started and then
conducts a self-test. The ESP control unit processes data from the indi-
vidual systems. It also processes additional measurement data which are
supplied by highly sensitive sensors: the rotational velocity of the vehicle
about its vertical axis, the lateral acceleration of the vehicle, the braking
pressure and the steering angle.
The direction which the driver wishes to take is determined based on the
steering angle and the speed of the vehicle and is constantly compared
with the actual behaviour of the vehicle. If differences exist, such as the
car beginning to skid, the ESP will automatically brake the appropriate
wheel.
The car is stabilised again by the forces which take effect when the wheel
is braked. Intervention into the brake system takes place primarily on the
outer front wheel of a vehicle which tends to oversteer (tendency for the
rear of the vehicle to break away) while occurs this is on the inner rear
wheel of a vehicle which tends to understeer (tendency to shift out of the
curve). This braking control cycle is accompanied by noises.
The ESP operates in combination with the ABS ⇒page 189, “Antilock
brake system (ABS)”. If there is a fault in the ABS system, the ESP also
does not operate.
Fig. 164 ESP switch
NKO B5 20.book Page 185 Monday, July 3, 2006 2:09 PM
Page 187 of 281

Intelligent Technology
186
The ESP warning light ⇒page 34 lights up in the instrument cluster when
there is a fault on the ESP.
Switching off
You can switch the ESP off and on again as you wish, by pressing the
button ⇒page 185, fig. 164 . The ESP warning light ⇒ page 34 lights up
in the instrument cluster when the ESP is switched off.
The ESP should normally always be switched on. It may be good practice
to switch the system off only in particular exceptional situations if you
desire wheel slip.
Examples:
•when driving with snow chains,
•when driving in deep snow or on a loose surface,
•when it is necessary to rock a car free when it has become stuck.
then you should switch on the ESP again.
WARNING
It is also not possible for the E SP to overcome the physical limits
of the vehicle. Even if a vehicle fitted with ESP you should still
always adapt your style of driving to the condition of the road
surface and the traffic situation. This particularly applies when
driving on slippery and wet roads. The increased safety offered
must not tempt you to take greater risks than otherwise - risk of an
accident!
Note
•All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres in order to achieve
problem-free operation of the ESP. Differing rolling circumferences of the
tyres can lead to an undesirable reduction in the engine output.
•Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or other
assignment of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the ESP
⇒ page 242.
Traction control system (TCS)*
The traction control system prevents the driven wheels
from spinning when accelerating.
General
The TCS makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off,
accelerate and climb a steep hill when the conditions of the road surface
are unfavourable.
Operating principle
The TCS switches on automatically when the engine is started and then
conducts a self-test. The system monitors the speeds of the driven wheels
with the aid of the ABS sensors. If the wheels are spinning, the force trans-
Fig. 165 TCS switch
NKO B5 20.book Page 186 Monday, July 3, 2006 2:09 PM
Page 188 of 281

Intelligent Technology187
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
mitted to the road surface is automatically adapted by reducing the engine
speed. This occurs at all speeds.
The TCS operates in combination with the ABS
⇒page 189, “Antilock
brake system (ABS)”. The TCS will not function if a fault exists in the ABS
system.
The TCS warning light ⇒page 35 lights up in the instrument cluster when
there is a fault on the TCS.
Switching off
You can switch the TCS off and on again as you wish by pressing the
button ⇒page 186, fig. 165 . The TCS warning light ⇒page 35 lights up
in the instrument cluster when the TCS is switched off.
The TCS should normally always be switched on. It may be good practice
to switch the system off only in particular exceptional situations if you
desire wheel slip.
Examples:
•when driving with snow chains,
•when driving in deep snow or on a loose surface,
•when it is necessary to rock a car free when it has become stuck.
then you should switch on the TCS again.
The EDL ⇒page 187, “Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)” is a part of the
TCS. THE EDL operates independently of the TCS (also when the TCS
has been switched off using the TCS button).
WARNING
You should always adjust your style of driving to the conditions of
the road surface and the traffic situation. The increased safety
offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than otherwise -
risk of an accident!
Note
•All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres in order to achieve
problem-free operation of the TCS. Differing rolling circumferences of the
tyres can lead to an undesirable reduction in the engine output.
•Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or other
assignment of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the TCS
⇒ page 242, “Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)
The electronic differential lock prevents an individual
wheel from slipping.
General
The EDL makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off,
accelerate and climb a steep hill when the conditions of the road surface
are unfavourable.
Operating principle
The EDL is activated automatically, that is without any action on the part
of the driver. It monitors the speeds of the driven wheels with the aid of the
ABS sensors. Should only one drive wheel begin spinning on a slippery
surface there will be an appreciable difference in the speed of the driven
wheels. The EDL function brakes the slipping wheel and the differential
transmits a greater driving force to the other driven wheel. This control
process is also accompanied by noises.
Overheating of the brakes
The EDL switches off automatically if unusually severe stresses exist in
order to avoid excessive heat generation in the disc brake on the wheel
which is being braked. The vehicle can continue to be driven and has the
same characteristics as a vehicle not fitted with EDL.
NKO B5 20.book Page 187 Monday, July 3, 2006 2:09 PM