engine SSANGYONG KORANDO 1997 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 1997, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 1997Pages: 2053, PDF Size: 88.33 MB
Page 180 of 2053
M162 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F1 -- 17
D AEW OO M Y_2000
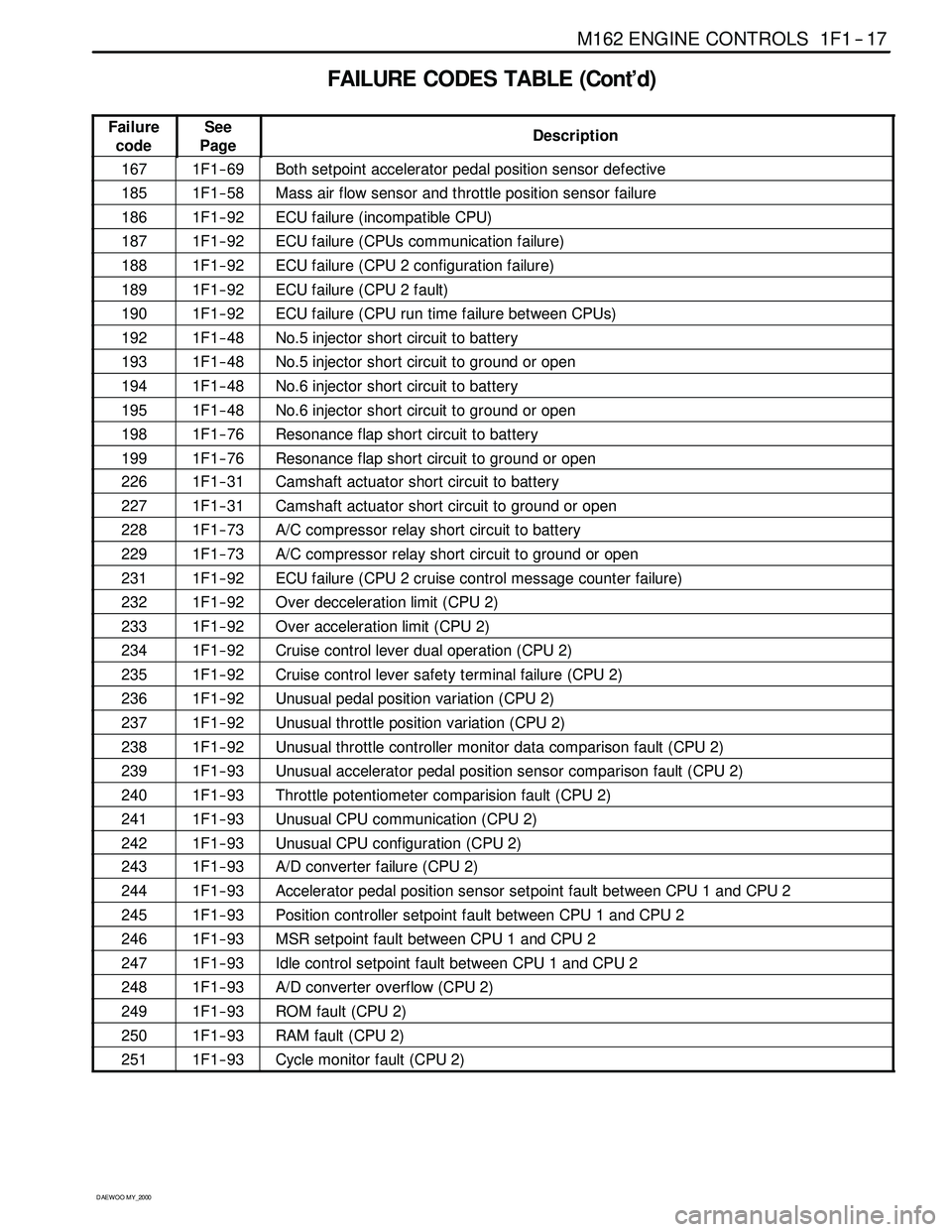
FAILURE CODES TABLE (Cont’d)
Failure
codeSee
PageDescription
1671F1 -- 69Both setpoint accelerator pedal position sensor defective
1851F1 -- 58Mass air flow sensor and throttle position sensor failure
1861F1 -- 92ECU failure (incompatible CPU)
1871F1 -- 92ECU failure (CPUs communication failure)
1881F1 -- 92ECU failure (CPU 2 configuration failure)
1891F1 -- 92ECU failure (CPU 2 fault)
1901F1 -- 92ECU failure (CPU run time failure between CPUs)
1921F1 -- 48No.5 injector short circuit to battery
1931F1 -- 48No.5 injector short circuit to ground or open
1941F1 -- 48No.6 injector short circuit to battery
1951F1 -- 48No.6 injector short circuit to ground or open
1981F1 -- 76Resonance flap short circuit to battery
1991F1 -- 76Resonance flap short circuit to ground or open
2261F1 -- 31Camshaft actuator short circuit to battery
2271F1 -- 31Camshaft actuator short circuit to ground or open
2281F1 -- 73A/C compressor relay short circuit to battery
2291F1 -- 73A/C compressor relay short circuit to ground or open
2311F1 -- 92ECU failure (CPU 2 cruise control message counter failure)
2321F1 -- 92Over decceleration limit (CPU 2)
2331F1 -- 92Over acceleration limit (CPU 2)
2341F1 -- 92Cruise control lever dual operation (CPU 2)
2351F1 -- 92Cruise control lever safety terminal failure (CPU 2)
2361F1 -- 92Unusual pedal position variation (CPU 2)
2371F1 -- 92Unusual throttle position variation (CPU 2)
2381F1 -- 92Unusual throttle controller monitor data comparison fault (CPU 2)
2391F1 -- 93Unusual accelerator pedal position sensor comparison fault (CPU 2)
2401F1 -- 93Throttle potentiometer comparision fault (CPU 2)
2411F1 -- 93Unusual CPU communication (CPU 2)
2421F1 -- 93Unusual CPU configuration (CPU 2)
2431F1 -- 93A/D converter failure (CPU 2)
2441F1 -- 93Accelerator pedal position sensor setpoint fault between CPU 1 and CPU 2
2451F1 -- 93Position controller setpoint fault between CPU 1 and CPU 2
2461F1 -- 93MSR setpoint fault between CPU 1 and CPU 2
2471F1 -- 93Idle control setpoint fault between CPU 1 and CPU 2
2481F1 -- 93A/Dconverteroverflow(CPU2)
2491F1 -- 93ROM fault (CPU 2)
2501F1 -- 93RAM fault (CPU 2)
2511F1 -- 93Cycle monitor fault (CPU 2)
Page 181 of 2053
1F1 -- 18 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
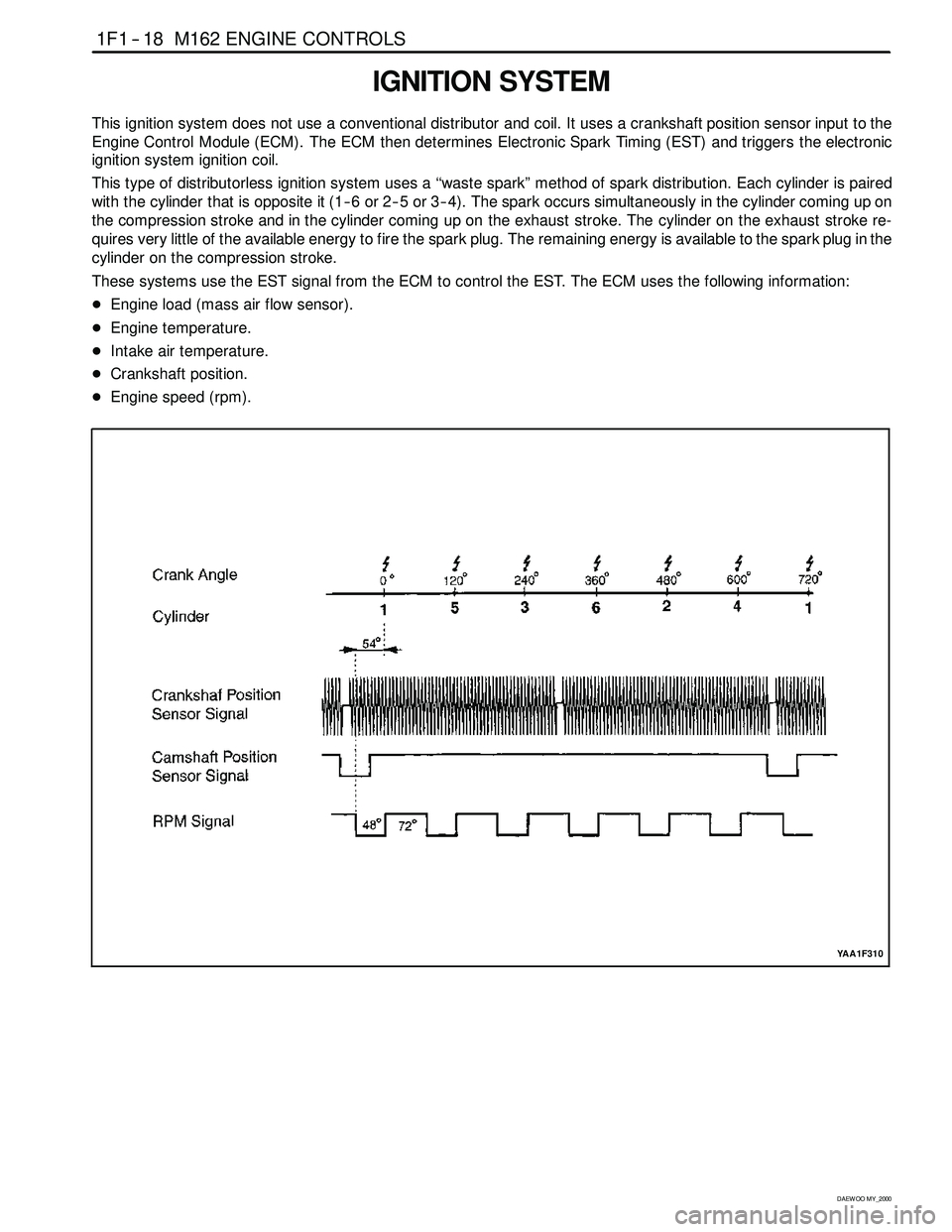
IGNITION SYSTEM
This ignition system does not use a conventional distributor andcoil. It uses a crankshaft position sensor input to the
Engine Control Module (ECM). The ECM then determines Electronic Spark Timing (EST) and triggers the electronic
ignition system ignition coil.
This type of distributorless ignition system uses a‘‘waste spark” method of spark distribution. Each cylinder is paired
with the cylinder that is opposite it (1 -- 6 or 2 -- 5 or 3 -- 4). The spark occurs simultaneously in the cylinder coming up on
the compression stroke and in the cylinder coming up on the exhaust stroke. The cylinder on the exhaust stroke re-
quires very little of the available energy to fire the spark plug. The remaining energy is available to the spark plug in the
cylinder on the compression stroke.
These systems use the EST signal from the ECM to control the EST. The ECM uses the following information:
DEngine load (mass air flow sensor).
DEngine temperature.
DIntake air temperature.
DCrankshaft position.
DEngine speed (rpm).
YAA1F310
Page 182 of 2053

M162 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F1 -- 19
D AEW OO M Y_2000
BLANK
Page 183 of 2053
1F1 -- 20 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
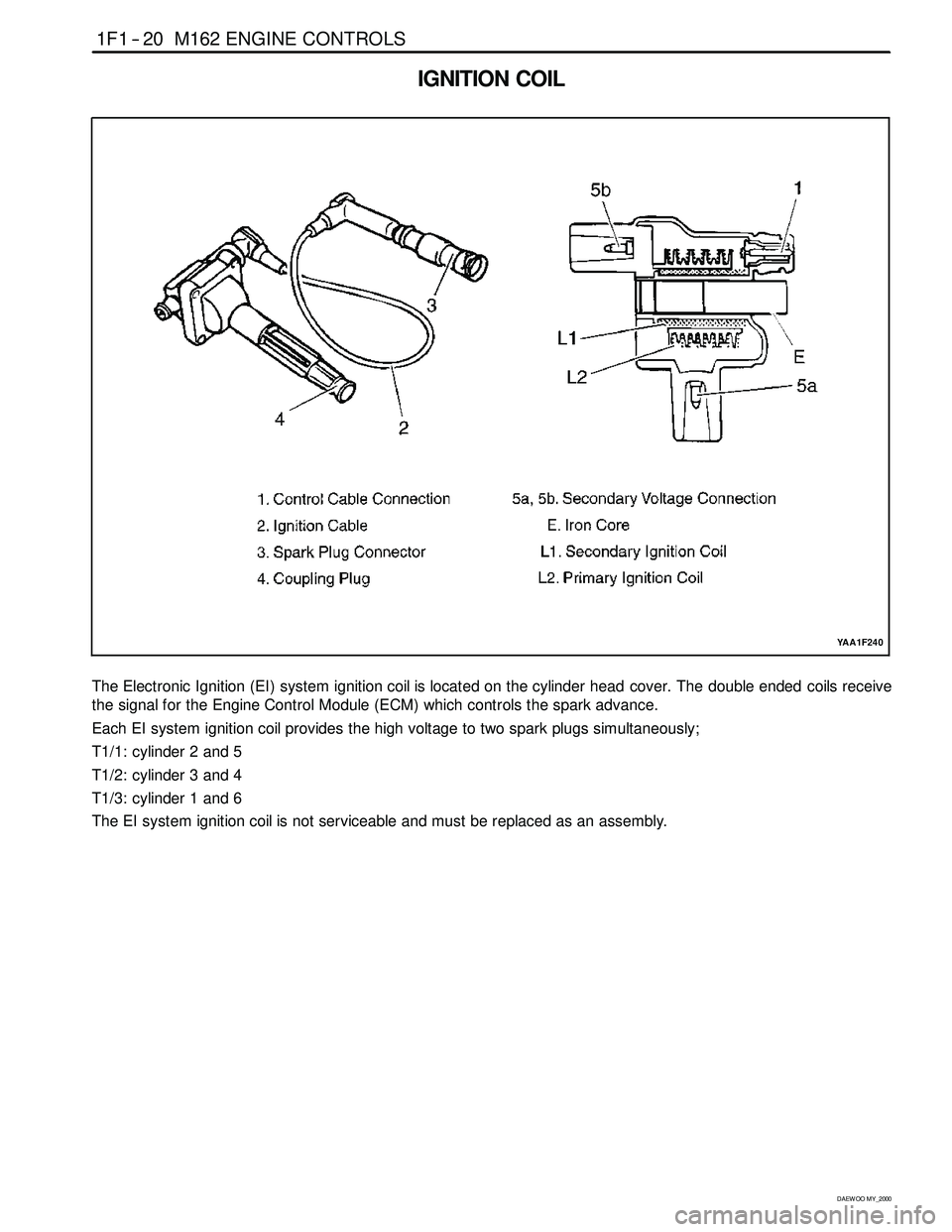
IGNITION COIL
YAA1F240
The Electronic Ignition (EI) system ignition coil is located on the cylinder head cover. The double ended coils receive
the signal for the Engine Control Module (ECM) which controls the spark advance.
Each EI system ignition coil provides the high voltage to two spark plugs simultaneously;
T1/1: cylinder 2 and 5
T1/2: cylinder 3 and 4
T1/3: cylinder 1 and 6
The EI system ignition coil is not serviceable and must be replaced as an assembly.
Page 184 of 2053
M162 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F1 -- 21
D AEW OO M Y_2000
KAB1F140
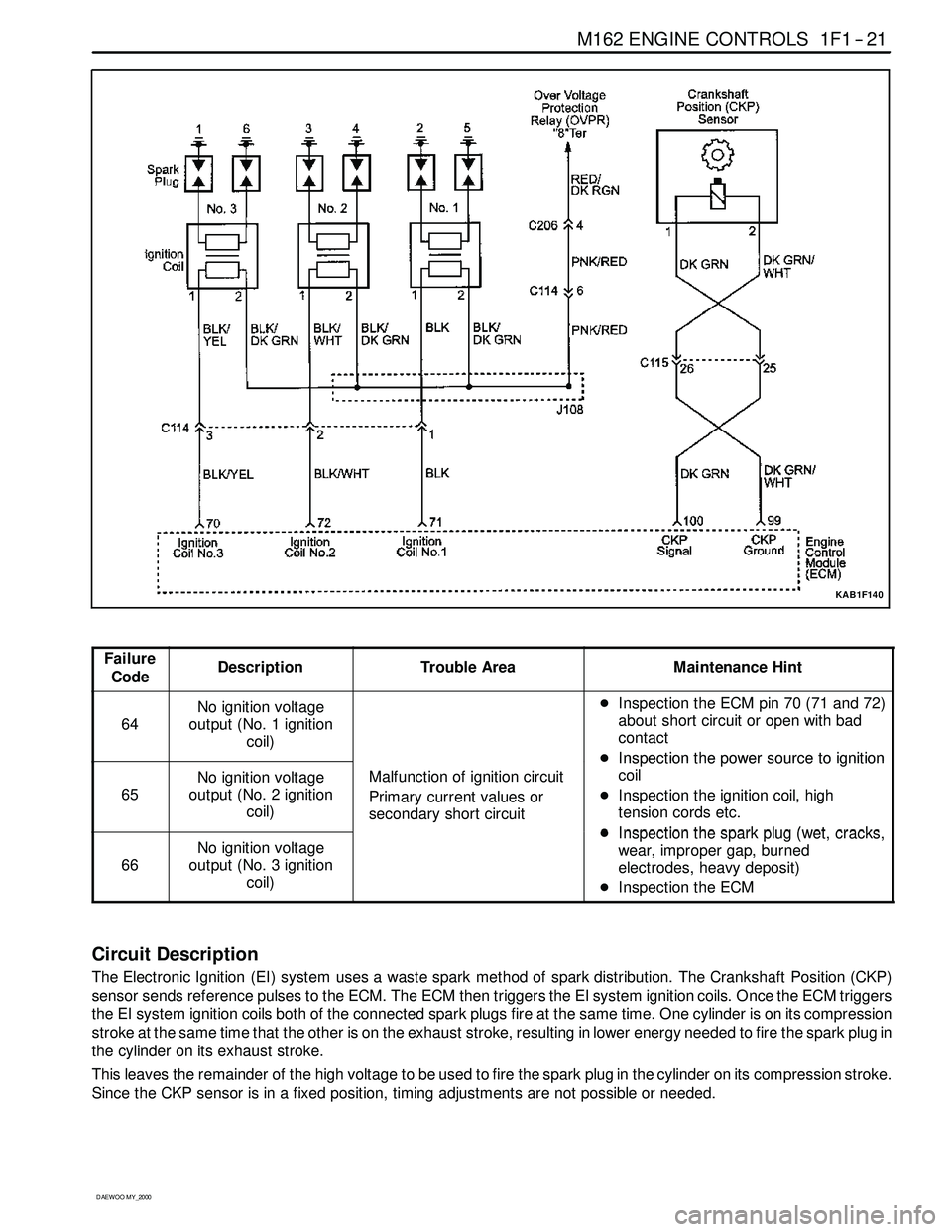
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
64
No ignition voltage
output (No. 1 ignition
coil)DInspectiontheECMpin70(71and72)
about short circuit or open with bad
contact
DInspectionthepowersourcetoignition
65
No ignition voltage
output (No. 2 ignition
coil)Malfunction of ignition circuit
Primary current values or
secondary short circuit
DInspectionthepowersourcetoignition
coil
DInspection the ignition coil, high
tension cords etc.
DInspectionthesparkplug(wetcracks
66
No ignition voltage
output (No. 3 ignition
coil)DInspection the spark plug (wet, cracks,
wear, improper gap, burned
electrodes, heavy deposit)
DInspection the ECM
Circuit Description
The Electronic Ignition (EI) system uses a waste spark method of spark distribution. The Crankshaft Position (CKP)
sensor sends reference pulses to the ECM. The ECM then triggers the EI system ignition coils. Once the ECM triggers
the EI system ignition coils both of the connected spark plugs fire at the same time. One cylinder is on its compression
stroke at the same time that the other is on the exhaust stroke, resulting in lower energy needed to fire the spark plug in
the cylinder on its exhaust stroke.
This leaves the remainder of the high voltage to be used to fire the spark plug in the cylinder on its compression stroke.
Since the CKP sensor is in a fixed position, timing adjustments are not possible or needed.
Page 185 of 2053
1F1 -- 22 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
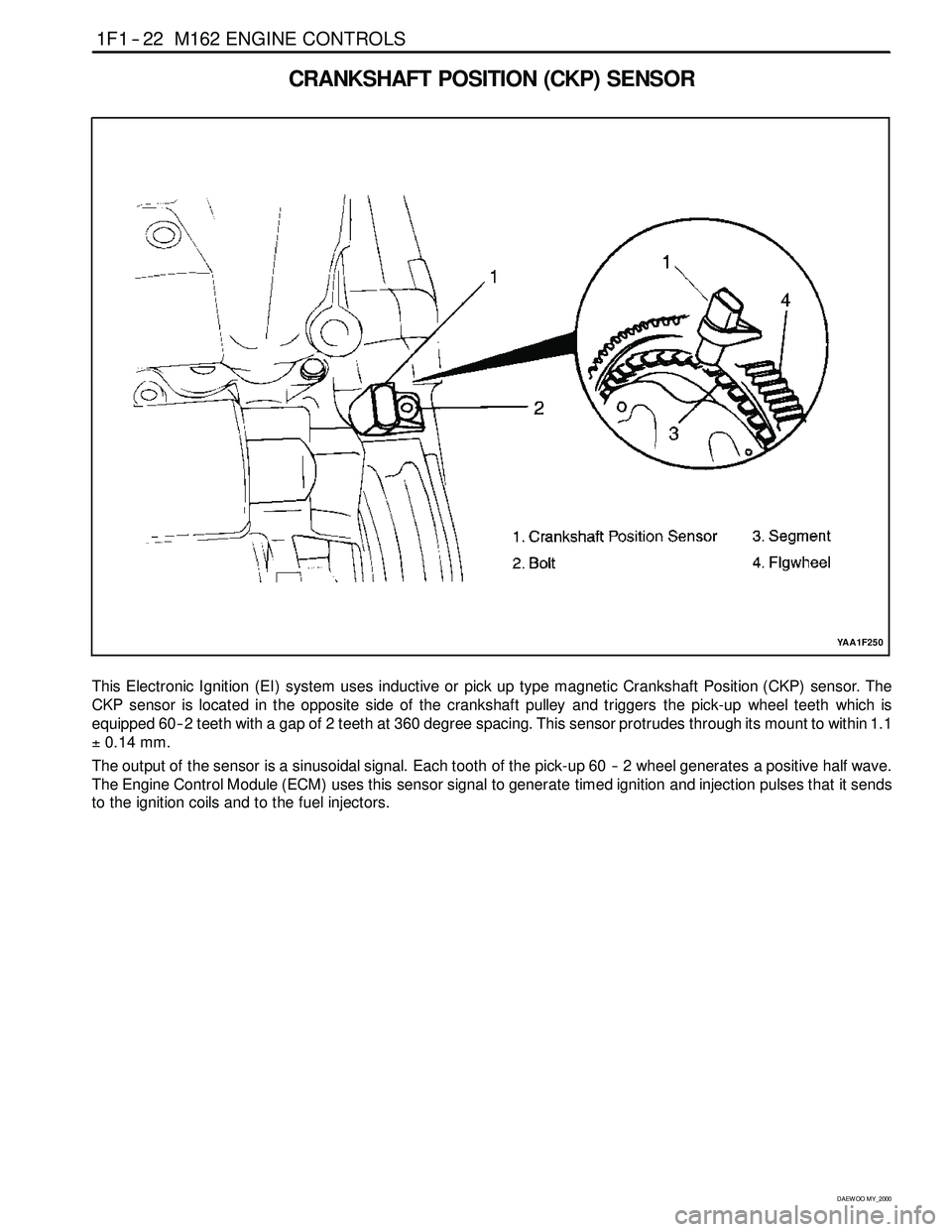
CRANKSHAFT POSITION (CKP) SENSOR
YAA1F250
This Electronic Ignition (EI) system uses inductive or pickup type magnetic Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor. The
CKP sensor is located in the opposite side of the crankshaft pulley and triggers the pick-up wheel teeth which is
equipped 60 -- 2 teeth with a gap of 2 teeth at 360 degree spacing. This sensor protrudes through its mount to within 1.1
±0.14 mm.
The output of the sensor is a sinusoidal signal. Each tooth of the pick-up 60 -- 2 wheel generates a positive half wave.
The Engine Control Module (ECM) uses this sensor signal to generate timed ignition and injection pulses that it sends
to the ignition coils and to the fuel injectors.
Page 186 of 2053
M162 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F1 -- 23
D AEW OO M Y_2000
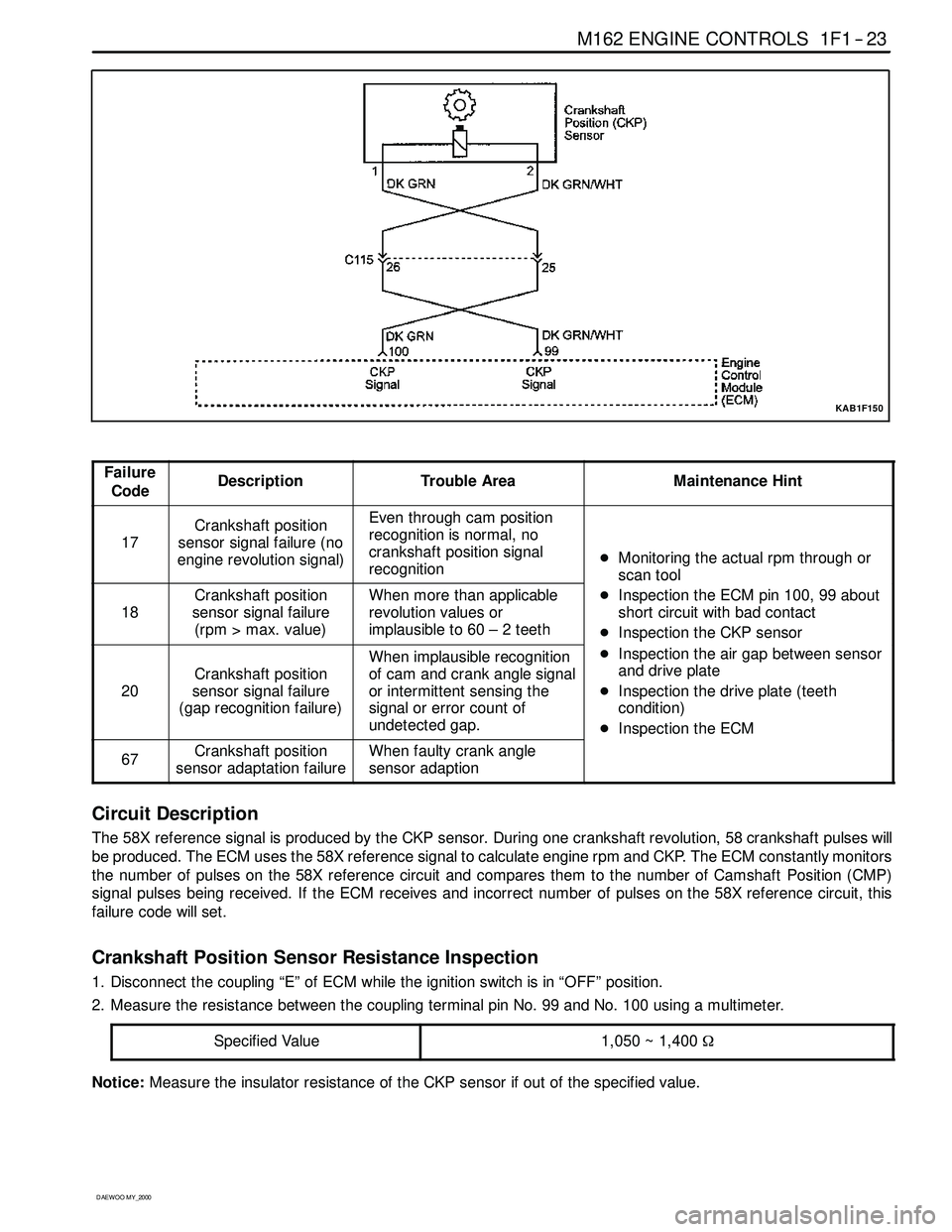
KAB1F150
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
17
Crankshaft position
sensor signal failure (no
engine revolution signal)Even through cam position
recognition is normal, no
crankshaft position signal
recognition
DMonitoring the actual rpm through or
scan tool
18
Crankshaft position
sensor signal failure
(rpm > max. value)When more than applicable
revolution values or
implausibleto60–2teeth
scantool
DInspection the ECM pin 100, 99 about
short circuit with bad contact
DInspection the CKP sensor
20
Crankshaft position
sensor signal failure
(gap recognition failure)
When implausible recognition
of cam and crank angle signal
or intermittent sensing the
signal or error count of
undetected gap.
p
DInspection the air gap between sensor
and drive plate
DInspection the drive plate (teeth
condition)
DInspection the ECM
67Crankshaft position
sensor adaptation failureWhen faulty crank angle
sensor adaption
p
Circuit Description
The 58X reference signal is produced by the CKP sensor. During one crankshaft revolution, 58 crankshaft pulseswill
be produced. The ECM uses the 58X reference signal to calculate engine rpm and CKP. The ECM constantly monitors
the number of pulses on the 58X reference circuit and compares them to the number of Camshaft Position (CMP)
signal pulses being received. If the ECM receives and incorrect number of pulses on the 58X reference circuit, this
failure code will set.
Crankshaft Position Sensor Resistance Inspection
1. Disconnect the coupling “E” of ECM while the ignition switch is in “OFF” position.
2. Measure the resistance between the coupling terminal pin No. 99 and No. 100 using a multimeter.
Specified Value
1,050 ~ 1,400Ω
Notice:Measure the insulator resistance of the CKP sensor if out of the specified value.
Page 187 of 2053
1F1 -- 24 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
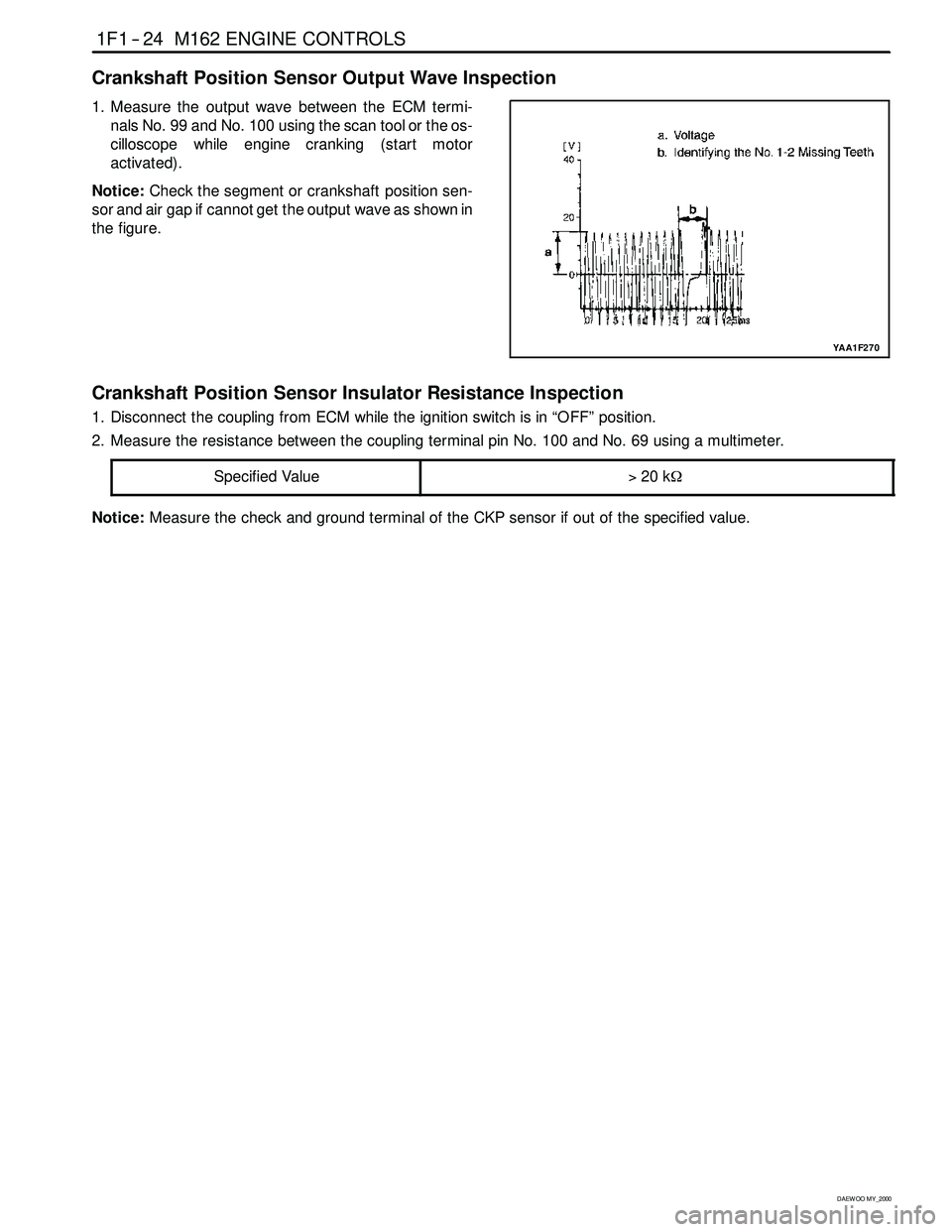
Crankshaft Position Sensor Output Wave Inspection
1. Measure the output wave between the ECM termi-
nals No. 99 and No. 100 using the scan tool or the os-
cilloscope whileengine cranking (start motor
activated).
Notice:Check the segment or crankshaft position sen-
sor and air gap if cannot get the output wave as shown in
the figure.
YAA1F270
Crankshaft Position Sensor Insulator Resistance Inspection
1. Disconnect the coupling from ECM while the ignition switch is in “OFF” position.
2. Measure the resistance between the coupling terminal pin No. 100 and No. 69 using a multimeter.
Specified Value
>20 kΩ
Notice:Measure the check and ground terminal of the CKP sensor if out of the specified value.
Page 188 of 2053

M162 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F1 -- 25
D AEW OO M Y_2000
BLANK
Page 189 of 2053
1F1 -- 26 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
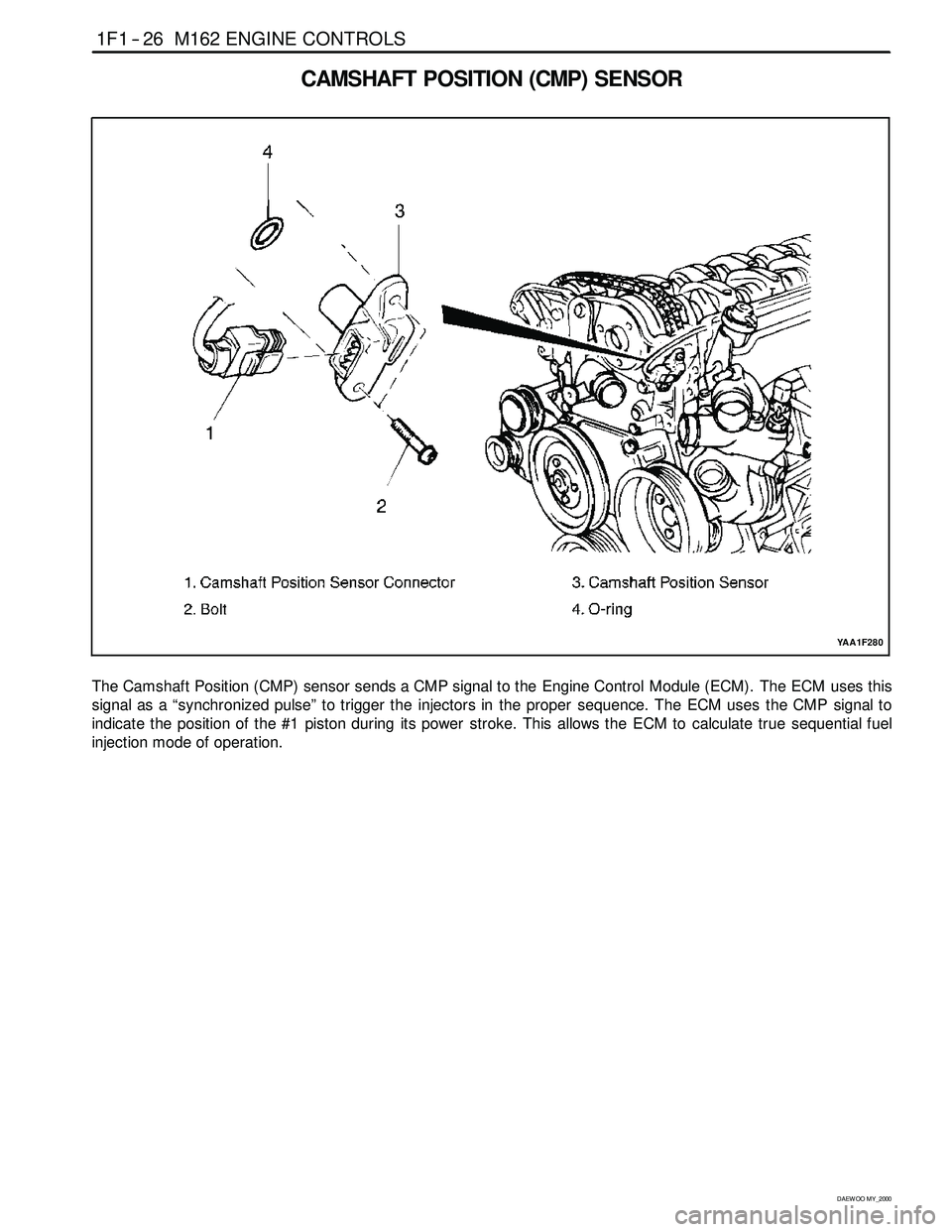
CAMSHAFT POSITION (CMP) SENSOR
YAA1F280
The Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor sends a CMP signal to the Engine Control Module (ECM). The ECM uses this
signal as a “synchronized pulse” to trigger the injectors in the proper sequence. The ECM uses the CMP signal to
indicate the position of the #1 piston during its power stroke. This allows the ECM to calculate true sequential fuel
injection mode of operation.