sensor SSANGYONG KORANDO 2012 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2012, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 2012Pages: 1082, PDF Size: 96.1 MB
Page 182 of 1082

06-50000-00
2) Inspection of Turbocharger
On-board Inspection 1.
Check the bolts and nuts foe looseness or missing
Check the intake and exhaust manifold for looseness or damage
Check the oil supply pipe and drain pipe for damages
Check the housing for crack and deterioration -
-
-
-
Inspection of turbine 2.
Remove the exhaust pipe at the opening of the turbine and check, with a lamp, the existence of
interference of housing and wheel, oil leakage and contamination (at blade edge) of foreign
materials.
Interference: In case where the oil leak sign exists, even the small traces of interferences on the
turbine wheel mean, most of times, that abrasion has occurred on the journal bearing. Must
inspect after overhauling the turbocharger.
Oil Leakage: Followings are the reasons for oil leakage condition -
-
Problems in engine: In case where the oil is smeared on inner wall section of the exhaust gas
opening.
Problems in turbocharger: In case where the oil is smeared on only at the exhaust gas
outlet section. *
* When problem occurs with the turbocharger, it could cause engine power decline,
excessive discharge of exhaust gas, outbreak of abnormal noise and excessive
consumption of oil.
Idling for long period of time can cause oil leakage to the turbine side due to low pressure of
exhaust gas and the rotation speed of turbine wheel. Please note this is not a turbocharger
problem.
Oil Drain Pipe Defect
In case where oil flow from the turbocharger sensor housing to the crank case is not smooth would
become the reason for leakage as oil builds up within the center housing. Also, oil thickens (sludge)
at high temperature and becomes the indirect reason of wheel hub section. In such case, clogging
and damage of the oil drain pipe and the pressure of blow-by gas within the crank case must be
inspected.
Damages due to Foreign Materials
When the foreign materials get into the system, it could induce inner damage as rotating balance of
the turbocharger gets out of alignment. -
-
Page 196 of 1082
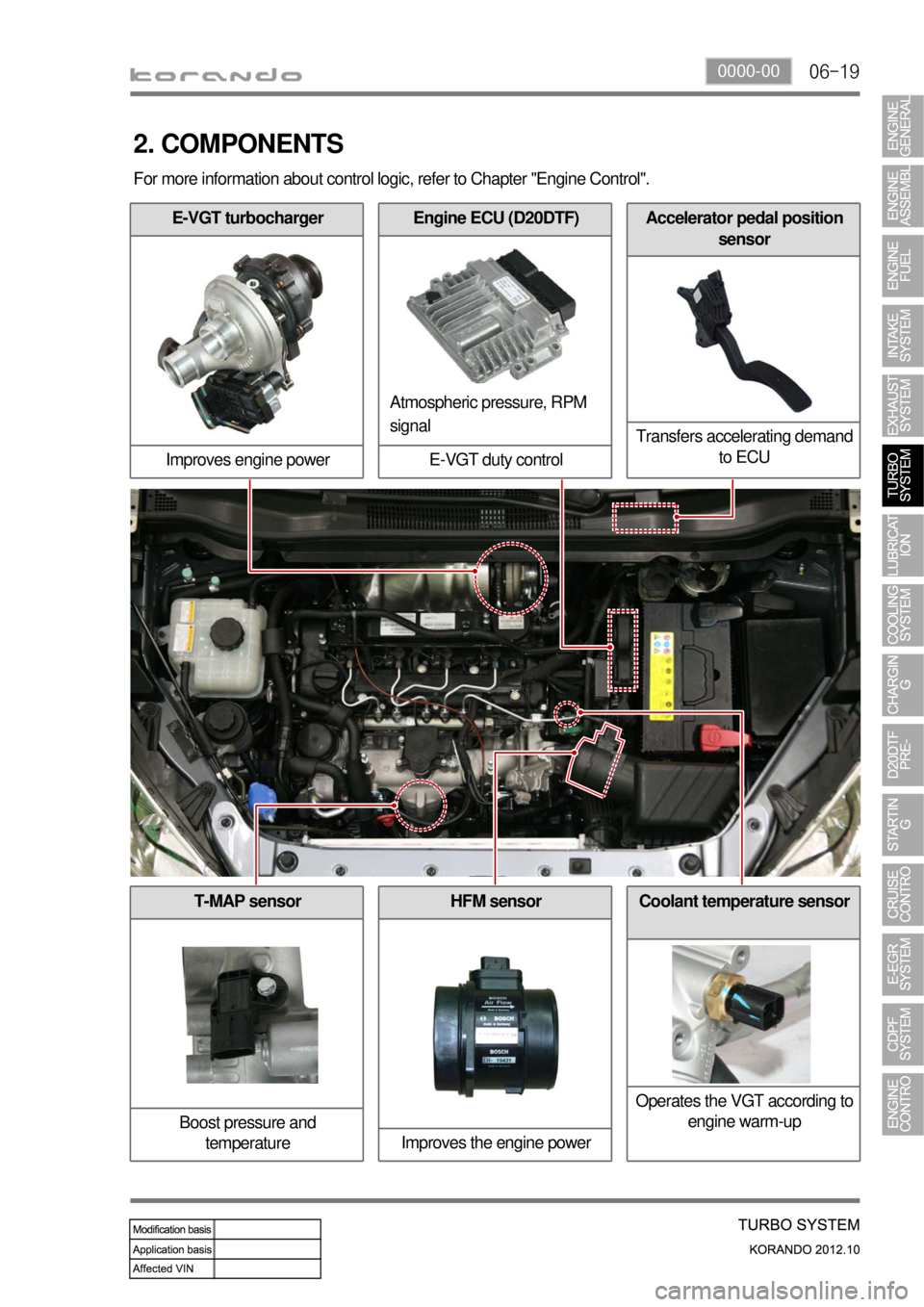
06-190000-00
T-MAP sensor
Boost pressure and
temperature
E-VGT turbocharger
Improves engine power
2. COMPONENTS
Engine ECU (D20DTF)
E-VGT duty controlAccelerator pedal position
sensor
Transfers accelerating demand
to ECU
Atmospheric pressure, RPM
signal
HFM sensor
Improves the engine powerCoolant temperature sensor
Operates the VGT according to
engine warm-up
For more information about control logic, refer to Chapter "Engine Control".
Page 202 of 1082

07-50000-00
1. SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
1) Overview
The lubrication system supplies oil to each lubrication section to prevent friction and wear and to remove
heat from the friction part. As the engine runs, frictional heat is generated on each lubrication section. If
this condition persists, the bearing can be burned and stuck.
In other words, it creates an oil film on each sliding surface to convert solid friction to liquid friction in
order to minimize wear and prevent temperature increasing on the friction part.
For the D20DTF engine with no oil pressure switch, the engine ECU receives the low engine oil level
signal from the oil level sensor and communicates with the instrument cluster through the CAN
communication to turn on the warning lamp.
2) Component
Oil level sensorEngine oil dipstick
Oil panOil pumpOil filter module
Oil cooler
Page 207 of 1082
08-4
2. INSPECTION
Possible Cause Action
Coolant level
is too low- Leak from the radiator
- Leak from the auxiliary reservoir
- Leak from the heater core- Replace the radiator
- Replace the auxiliary reservoir
- Replace the heater
- Leak from the coolant hose connections
- Damaged coolant hose- Reconnect the hose or replace
the clamp
- Replace the hose
- Leak from the water pump gasket
- Leak from the water pump internal seal- Replace the gasket
- Replace the water pump
- Leak from the water inlet cap
- Leak from the thermostat housing- Replace the water inlet cap
gasket
- Replace the thermostat sealing
- Incorrect tightening torque of the
cylinder head bolts
- Damaged cylinder head gasket- Tighten the bolts to the specified
torque
- Replace the cylinder head
gasket
Coolant
temperature is
too high- Coolant leakage (Coolant level is low)
- Improper coolant mixture ratio
- Kinked coolant hose- Add coolant
- Check the coolant concentration
(Anti-freeze)
- Repair or replace the hose
- Defective thermostat
- Defective water pump
- Defective radiator
- Defective auxiliary reservoir or tank cap- Replace the thermostat
- Replace the water pump
- Replace the radiator
- Replace the auxiliary reservoir
or tank cap
- Cracks on the cylinder block or cylinder
head
- Clogged coolant passages in the
cylinder block or cylinder head- Replace cylinder block or
cylinder head
- Clean the coolant passage
- Clogged radiator core - Clean the radiator core
- Improper operation of cooling fan - Replace the cooling fan or repair
the related circuit
- Defective temperature sensor or faulty
wiring- Replace the sensor or repair the
related wiring
Coolant
temperature is
too low- Thermostat is stuck open - Replace the thermostat
- Improper operation of cooling fan - Replace the cooling fan or repair
the related circuit
- Defective temperature sensor or faulty
wiring- Replace the sensor or repair the
related wiring
Page 212 of 1082
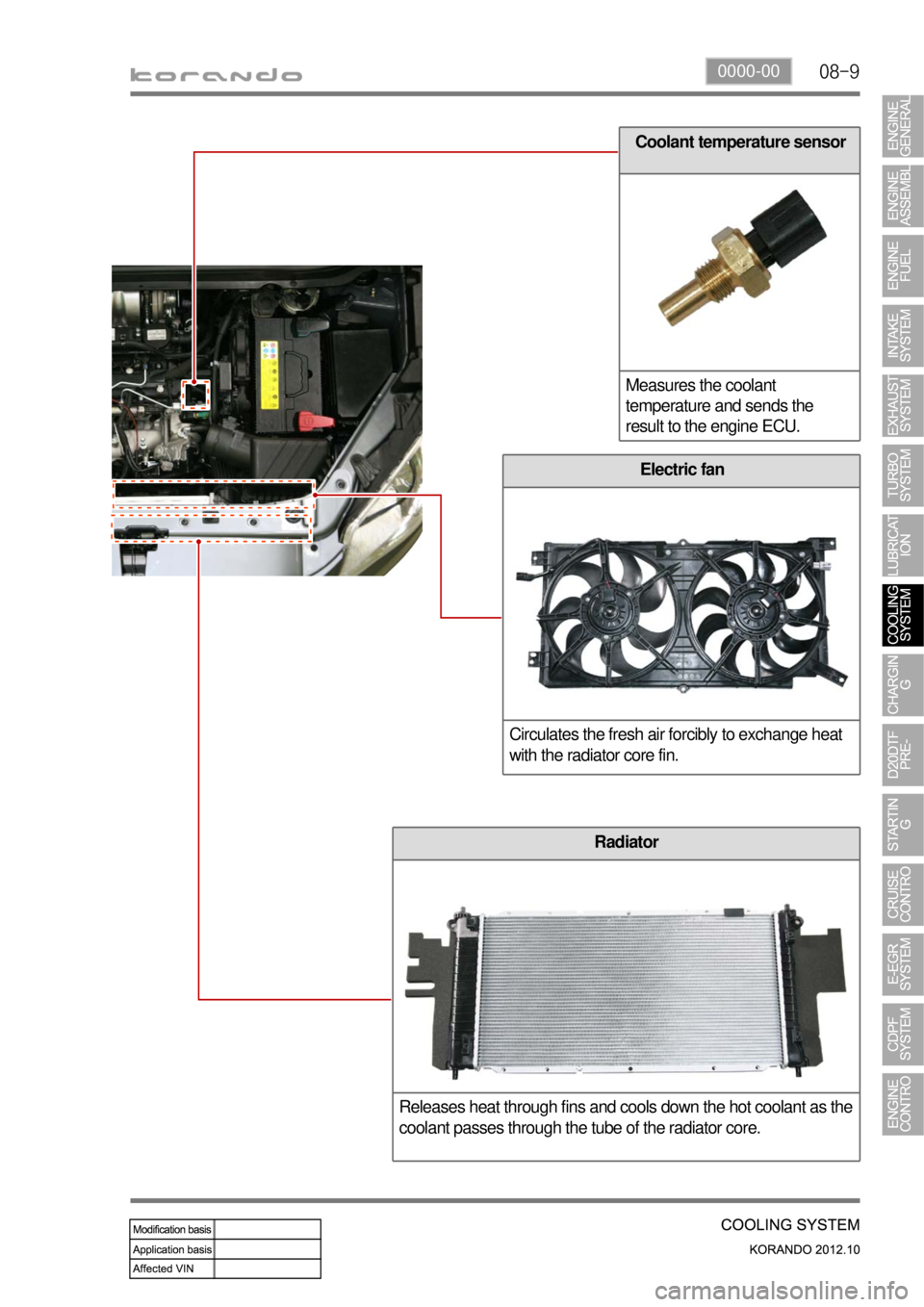
08-90000-00
Coolant temperature sensor
Measures the coolant
temperature and sends the
result to the engine ECU.
Electric fan
Circulates the fresh air forcibly to exchange heat
with the radiator core fin.
Radiator
Releases heat through fins and cools down the hot coolant as the
coolant passes through the tube of the radiator core.
Page 261 of 1082

13-31793-01
E-EGR bypass valve Solenoid valve Drivien byVacuum
(Solenoid valve)
1. SPECIFICATION
Item
E-EGR valve Motor EGR response time 50 mS
Driven by DC motor
Valve EGR gas flow rate 120 Kg/h
Position sensor Sensing type Hall sensor
Supply voltage 5V ± 10%
Signal range 5% ~ 95%
Max. current consumption<15mA
E-EGR cooler Cooling capacity 8.3 kW or more
Coolin fin type Wavy fin
Coller type U-shaped
Page 262 of 1082

13-4
1. SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
1) Overview
The EGR (Electric-Exhaust Gas Recirculation) valve reduces the NOx emission level by recirculating
some of the exhaust gas to the intake system.
To meet Euro-V regulation, the capacity and response rate of E-EGR valve in D20DTF engine have
been greatly improved. The EGR cooler with high capacity reduces the Nox, and the bypass valve
reduces the CO and HC due to EGR gas before warming up.
Also, the engine ECU adjusts the E-EGR opening by using the air mass signal through HFM sensor. If
the exhaust gas gets into the intake manifold when the EGR valve is open, the amount of fresh air
through HFM sensor should be decreased.
Benefits of E-EGR valve ▶
Improved accuracy and response through electric control
Feedback function (Potentiometer)
Preventing chattering of EGR valve and improved durability
Self-cleaning function -
-
-
-
Page 263 of 1082
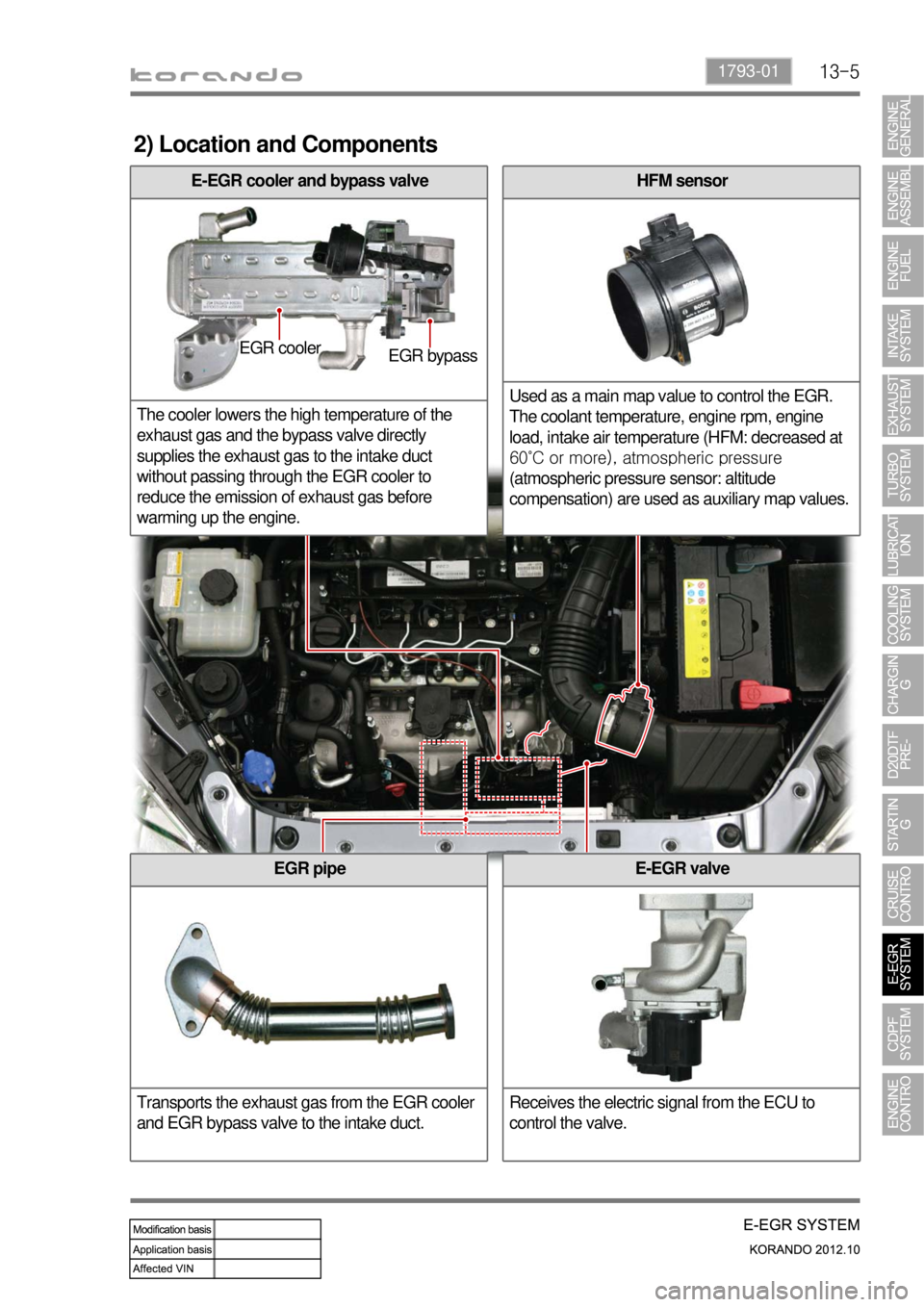
13-51793-01
2) Location and Components
HFM sensor
Used as a main map value to control the EGR.
The coolant temperature, engine rpm, engine
load, intake air temperature (HFM: decreased at
60˚C or more), atmospheric pressure
(atmospheric pressure sensor: altitude
compensation) are used as auxiliary map values.
EGR pipe
Transports the exhaust gas from the EGR cooler
and EGR bypass valve to the intake duct.
E-EGR cooler and bypass valve
The cooler lowers the high temperature of the
exhaust gas and the bypass valve directly
supplies the exhaust gas to the intake duct
without passing through the EGR cooler to
reduce the emission of exhaust gas before
warming up the engine.
E-EGR valve
Receives the electric signal from the ECU to
control the valve.
EGR cooler
EGR bypass
Page 269 of 1082

14-6
Excessive overload of CDPF (warning lamp illuminated) ▶
If the vehicle is driven at a speed of 5 to 10
km/h for an extended period of time, the soot
accumulated in the CDPF cannot be burned
as the CDPF cannot reach the regeneration
temperature. Then, an excessive amount of
soot can be accumulated in the CDPF.
This case is much worse than the simple over-
load of the CDPF. To inform this to the driver,
the engine warning lamp comes on and the
engine power is decreased to protect the
system.
To solve this problem, blow soot between the
engine and exhaust system several times and
erase the related DTC. Then, check if the
same DTC is regenerated again. If so, check
the DTC related to the differential pressure
sensor. 1.
2.
3.
Page 271 of 1082

14-8
Engine ECU (D20DTF)
Post-injectionDifferential pressure sensor
Calculates the amount of PM
collected by reading the pressure
difference between before and
after the CDPF.Electric throttle body
Regulates the rate of air
intake.
CDPF
(DOC + DPF)Front temperature
sensor
Protects the
turbocharger.Rear temperature
sensor
Measures the
temperature of fuel
combustion.
2. COMPONENT
Oxygen sensor