clutch SSANGYONG KORANDO 2012 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2012, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 2012Pages: 1082, PDF Size: 96.1 MB
Page 873 of 1082

03-133660-01
2) Transaxle Cooling
The transaxle cooling system ensures rapid warm-up and constant operating temperature resulting in
reduced fuel consumption and refined shift quality.
It also includes a cooler by-pass within the hydraulic system to allow sufficient lubrication to the transaxle
drivetrain in the event of a blockage in the transaxle cooler.
3) Shift Strategy
Gear Change ▶
Transaxle gear change is controlled by the
TCU. The TCU receives inputs from various
engine and vehicle sensors to select shift
schedules and to control the shift feel and
torque converter clutch (TCC) operation at each
gear change.
Coast down ▶
Coast down down shifts occur at 0% pedal
when the vehicle is coasting down to a stop.
Torque Demand ▶
Torque demand down shifts occur
(automatically) when the driver demand for
torque is greater than the engine can provide at
that gear ratio. If applied, the transaxle will
disengage the TCC to provide added
acceleration.
Page 876 of 1082

03-16
4. LIMP HOME MODE
When the transaxle is defective ▶
In the event of a system fault, the TCU also provides for failure mode effect control (FMEC) to maintain
maximum functional operation of the transaxle. (There are 3 FMEC modes, mechanical limp-home
mode, electrical limp-home mode, limp-home mode C.)
In the event of a total loss of control or electrical power, the basic transaxle functions (Park, Reverse,
Neutral and Drive) are retained. The 4th and reverse gear ratios with the torque converter clutch in the
unlocked state are the retained gear states the hydraulic system supports without any electrical
assistance. (Mechanical limp-home)
If the speed sensor circuit is failed, the gear is fixed to 4th gear, but manual shifting
<004f00590095008b02e9005a0099008b02e9005b009b008f005000470090009a00470088009d008800900093008800890093008c0055004f006c0093008c008a009b00990090008a00880093004700930090009400970047008f00960094008c0047009400
96008b008c0050>
If the inhibitor switch signals are invalid, shifting to1st and 2nd gear is forbidden. (Limp-home C)
The TCU communicates with other vehicle electronic control modules by the controller area network
(CAN). If a major fault is developed, the transaxle may not accomplish the intelligent shift control. The
TCU controls the transaxle with preset values.
The TCU also provides for transaxle diagnostics, which meet the requirements of OBD II regulation,
monitoring all components which may effect vehicle emissions. 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Towing the automatic transaxle equipped vehicle ▶
Flat-bed equipment is the best method of moving a disabled vehicle to avoid any damages.
For AWD vehicle: The vehicle must be towed with a wheel lift and dollies or flatbed equipment with
all the wheels off the ground.
For 2WD vehicles: It is acceptable to tow the vehicle with the rear wheels on the ground without
dollies and the front wheels off the ground. When being towed by a commercial towtruck and
wheel dollies are not available, the front of the vehicle should be lifted, not the rear. -
-
Page 877 of 1082

03-173660-01
5. TRANSAXLE ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM
1) General Information
The transmission control unit (TCU) and its input/output network control the following transmission
operations:
Shift timing
Line pressure
Clutch pressure (shift feel)
Torque converter clutch -
-
-
-
also uses these signals when determining transaxle operating strategy. Using all of these input signals,
the TCU can determine when the time and conditions are right for a shift, or when to apply or release the
torque converter clutch. It will also determine the pressure needed to optimise shift feel.
2) TCU (Transmission Control Unit)
The transaxle control unit (TCU) is mounted
under the driver's seat and controls the operation
of the transaxle.
Internal sensors and signals received across the
CAN bus in analogue and digital forms such as:
Transaxle input speed
Transaxle output speed
Accelerator pedal position
Gear selector position
Engine torque
Engine speed
Transaxle fluid temperature
Brake pedal status
Engine oil temperature
Engine coolant temperature
Ambient air temperature
Barometric pressure -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
The TCU monitors all TCU inputs and outputs to confirm correct system operation. If a fault occurs the
TCU is able to perform default action and inform the driver of the problem through the instrument cluster
warning lights. Detailed information is available via trouble codes which can be read with the service tool.
Page 879 of 1082

03-193660-01
7. POWER TRANSFER
Power transfer modes are as follow:
Manual: 1st gear (position M)
Drive: 1st gear
Drive: 2nd gear
Drive: 3rd gear
Drive: 4th gear - limp home mode
Drive: 5th gear
Drive: 6th gear -
-
-
-
-
-
-
1) Overview
Name Component
C1 OVER DRIVE CLUTCH
C2 35R CLUTCH
B1 LOW & REVERSE BRAKE
B2 2/6 BRAKE
B3 UNDER DRIVE BRAKE
1F 1-2 ONE WAY CLUTCH
GEARCLUTCH BRAKE
OWC Gear Ratio
OD 35R 26 LR UD
1ST△*O O 4.212
2ND O O 2.637
3RD O O 1.800
4TH O O 1.386
5TH O O 1.000
6TH O O 0.772
REV O O 3.385
N.P O
(1) Gear Selection and Engagement Element
Operation when vehicle speed under 5kph *
Page 880 of 1082

03-20
2) Operation in Each Gear Position
(1) Neutral/Park
Lower & reverse brake (LR/B) op<008c00990088009b008c008b004702e700470076009d008c0099008b00990090009d008c0047004f00760056006b00500047008f009c0089004700930096008a0092008c008b004702e7004700740090008b008b0093008c0047004d00470099008c008800
9900470047004f00740070006b0047004d0047>
REAR) P/C locked
<007000950097009c009b0047009a008f0088008d009b004700990096009b0088009b008c008b004702e700470079008c008800990047009a009c00950047008e008c00880099004700990096009b0088009b008c008b004702e700470079008c0088009900
47009000950095008c00990047009700900095009000960095> reverse rotated → Rear outer
<009700900095009000960095004700990096009b0088009b008c008b004702e700470079008c008800990047008800950095009c0093009c009a0047008e008c00880099004700990096009b0088009b008c008b004702e70047006d009900960095009b00
47008800950095009c0093009c009a0047008e008c00880099> rotated → Front pinion
<00990096009b0088009b008c008b004702e70047006d009900960095009b0047009a009c00950047008e008c0088009900470099008c009d008c0099009a008c004700990096009b0088009b008c008b004702e70047007c0095008b008c0099008b009900
90009d008c0047004f007c0056006b00500047008f009c0089> reverse rotated
Input shaft rotated → Overdrive clutch (OD/C) retainer rotated
Input shaft rotated → 35R clutch rotated -
-
-
-
Power flow ▶
Description 35R C OD C 26 B UD B LR B O.W.C
P.N●
Page 885 of 1082

03-253660-01
(6) 4th Drive Gear (1.386)
Front sun gear locked, rear planetary gear and rear sun gear rotated
When the overdrive clutch (OD/C) operates, the carrier is engaged with sun gear in rear planetary
gear set and the power with 1:1 ratio flows to the front planetary gear locked with sun gear after
passing through the rear & front annulus gears.
At this moment, by operation of speed-reduced annulus gears and carrier in 1:1 ratio, the middle sun
gear in middle planetary gear set increases its speed without load (idling). -
-
-
Power flow ▶
Description 35R C OD C 26 B UD B LR B O.W.C
4th●●
Page 893 of 1082

03-8
1) Characteristics of WM6F1 M/T
Both Forward and Reverse gears use the helical gear and are made of high-strength material.
Drives the clutch with a concentric slave cylinder mounting bolt.
Shifting the transmission gears is performed through the remote control cable.
A pull type clutch is used for Reverse gear shifting.
Features triple/double/single synchronization. -
-
-
-
-
Clutch housing
Transmission case
Input shaft
Concentric slave cylinder
Shift lever
Selector lever
Wiring bracket
Neutral switch
Backup lamp switch
Reverse idle shaft mounting bolt 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.Control guide bolt
Oil filler plug (for servicing)
Oil drain plug
Oil filler plug (for manufacturing)
Air breather
Detent pin (for securing shift fork)
Oil seal (RH)
Oil seal (LH)
Control housing 11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
Page 899 of 1082
04-30000-00
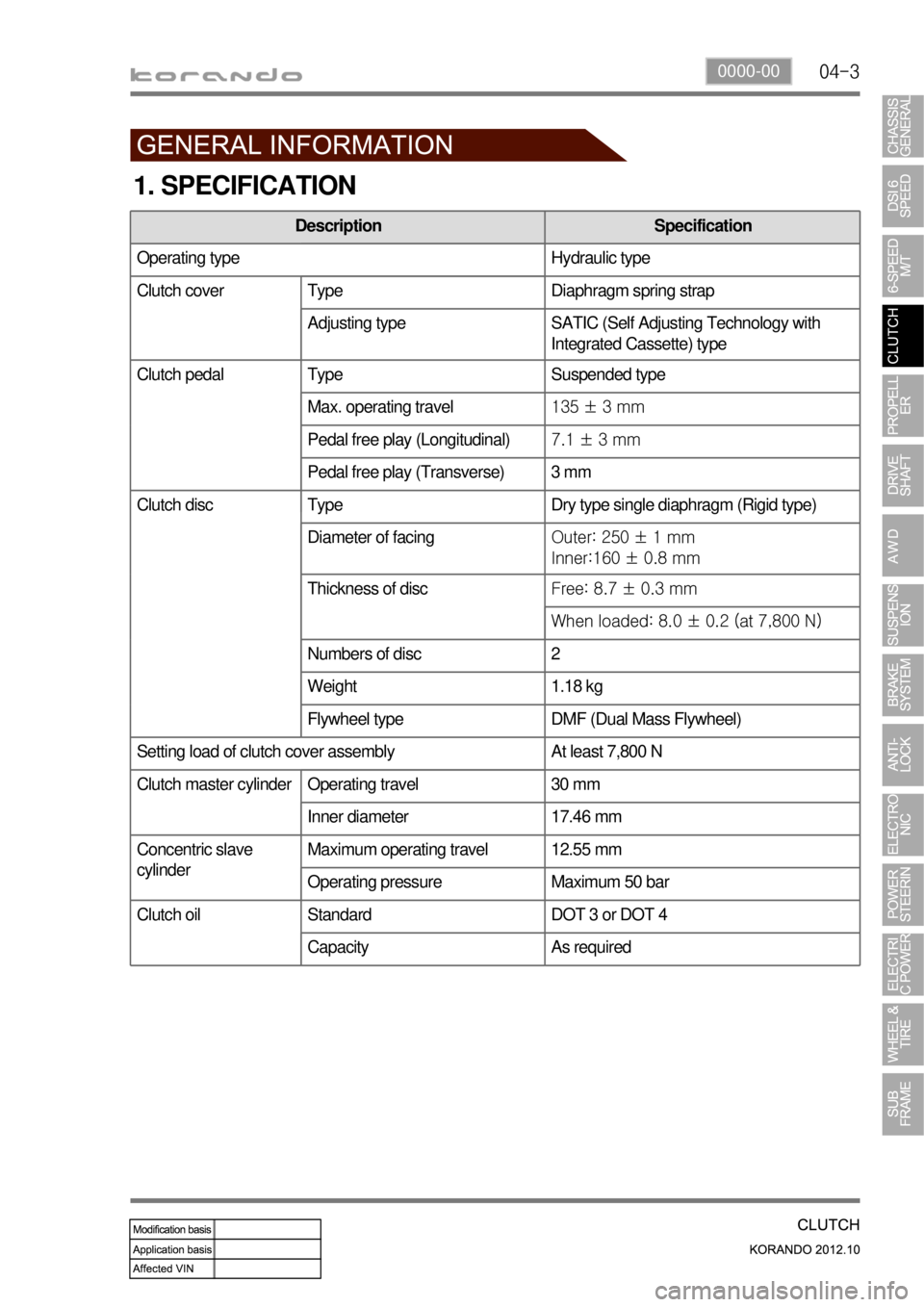
1. SPECIFICATION
Description Specification
Operating type Hydraulic type
Clutch cover Type Diaphragm spring strap
Adjusting type SATIC (Self Adjusting Technology with
Integrated Cassette) type
Clutch pedal Type Suspended type
Max. operating travel135 ± 3 mm
Pedal free play (Longitudinal)7.1 ± 3 mm
Pedal free play (Transverse) 3 mm
Clutch disc Type Dry type single diaphragm (Rigid type)
Diameter of facingOuter: 250 ± 1 mm
Inner:160 ± 0.8 mm
Thickness of discFree: 8.7 ± 0.3 mm
When loaded: 8.0 ± 0.2 (at 7,800 N)
Numbers of disc 2
Weight 1.18 kg
Flywheel type DMF (Dual Mass Flywheel)
Setting load of clutch cover assembly At least 7,800 N
Clutch master cylinder Operating travel 30 mm
Inner diameter 17.46 mm
Concentric slave
cylinderMaximum operating travel 12.55 mm
Operating pressure Maximum 50 bar
Standard DOT 3 or DOT 4
Capacity As required
Clutch oil
Page 900 of 1082

04-4
2. TIGHTENING TORQUE
DescriptionTightening torque
Amount
Clutch housing boltUpper (17 mm) 85.0 to 100 Nm 2
Front (14 mm)54.0 Nm + 20°1
Rear (14 mm) 51.3 to 56.7 Nm 2
Lower (14 mm) 56.0 to 62.0 Nm 4
Pressure plate assembly bolt (Hexagon 6 mm) 21.0 to 27.0 Nm 6
Concentric slave cylinder bolt (Hexagon 5 mm) 10 to 16 Nm 3
Concentric slave cylinder oil pipe nut 24.5 to 28.4 Nm Remove the nut if it is
necessary. (Once
removed, apply the
Loctite on the thread
before installation.)
Master cylinder nut (12 mm) 7.8 to 17.6 Nm
Master cylinder oil pipe nut (10 mm) 14.7 to 17.6 Nm
Master cylinder push rod lock nut 8.8 to 13.7 Nm
Clutch oil chamber screw and bolt (10 mm) 3.9 to 7.8 Nm
Oil pipe nut (10 mm) 14.7 to 17.6 Nm
Clutch pedal mounting nut (12 mm) 7.8 to 17.6 Nm
Stopper bolt 16 to 22 Nm
Page 901 of 1082

04-50000-00
1. OVERVIEW
The hydraulic clutch transmits the force required to operate the clutch pedal to the concentric slave
cylinder fitted to the clutch housing as a hydraulic pressure.
(The hydraulic pressure is transmitted in the following order: Clutch pedal - Clutch master cylinder -
Clutch pipe - Clutch damper - Clutch pipe and hose - Concentric slave cylinder - Pressure plate -
Flywheel.)
If a driver depress the clutch pedal, the hydraulic pressure is generated in the master cylinder. It is
transmitted to the concentric slave cylinder through the pipe, resulting in the cylinder being forced out. At
this time, the clutch disc is forced against the cylinder by pushing the cover. This, in turn, remove the
flywheel from the pressure plate. As a consequence, the power from the engine will be cut off and the
gear change can be carried out.