oil type SSANGYONG KORANDO 2012 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2012, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 2012Pages: 1082, PDF Size: 96.1 MB
Page 916 of 1082

08-30000-00
System Description Specification
Front
suspensionSuspension type Macperson strut type
Spring type Coil spring
Stabilizer type Torsion bar type
Shock absorber Type Cylindrical reciprocation type
Max. length (extended)
554 mm
Min. length
(compressed)372 mm
Min. length
(compressed)Inner diameter (A) Upper: 84.0 mm
Lower: 100.0 mm
Outer diameter (B) 163.1 mm
Free length (C) 356.1 mm
Installed length (D) 276.0 mm
Coil windings 5.32 turns
Winding direction Right direction
Rear
suspensionDriving type AWD 2WD
Suspension type (trailing, upper, lower & track
rod)Multi-link type←
Spring type Coil spring←
Stabilizer type Torsion bar type←
Shock absorber Type Cylindrical
reciprocation type←
Max. length (extended) 551 mm←
Min. length
(compressed)361 mm←
Coil spring Diameter (A) 12.8 mm 12.6 mm
Free length (B) 287.1 mm 291.7 mm
Coil windings 6.64 turns 6.32
Winding direction Right direction←
1. SPECIFICATION
Page 922 of 1082
08-90000-00
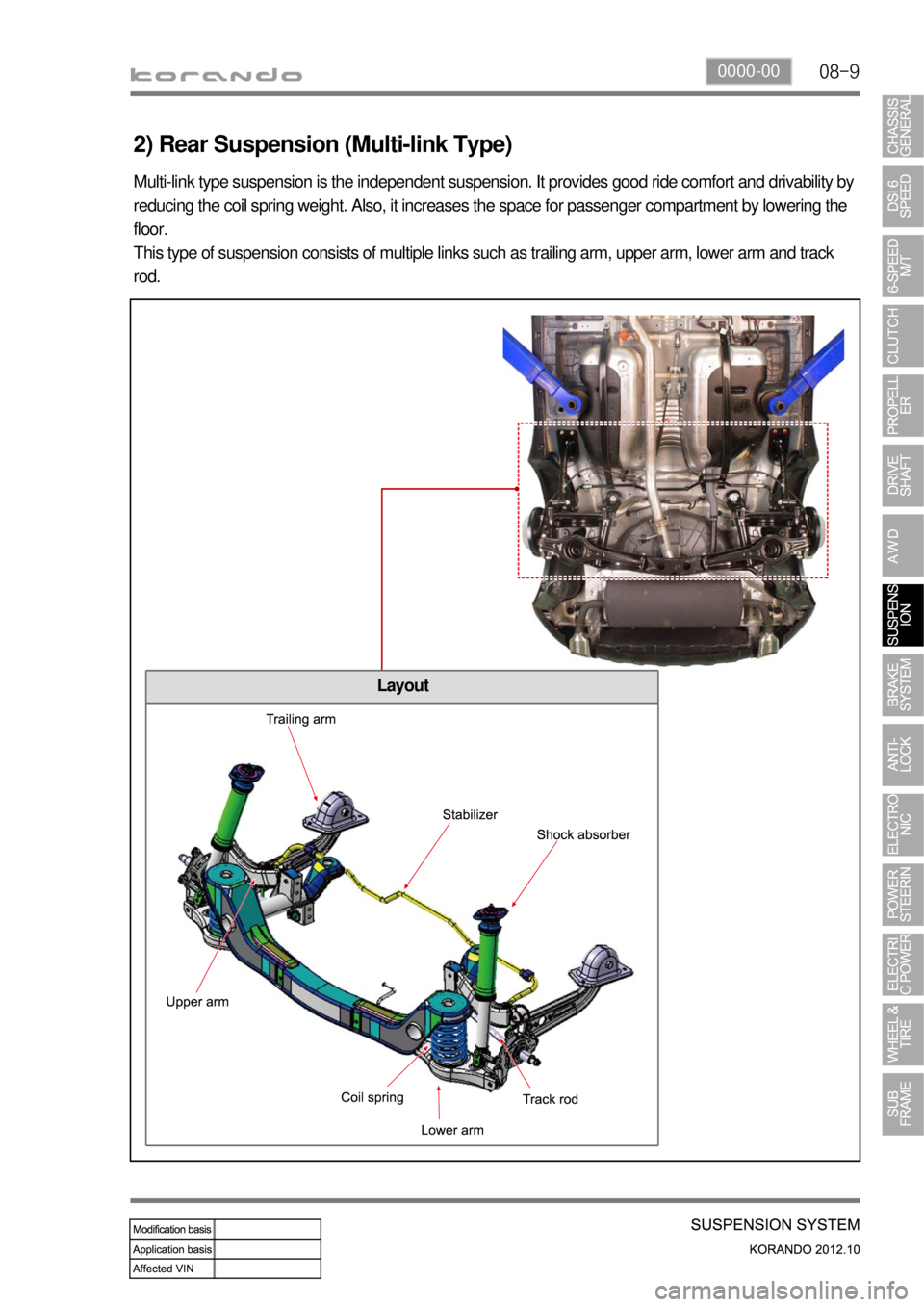
2) Rear Suspension (Multi-link Type)
Multi-link type suspension is the independent suspension. It provides good ride comfort and drivability by
reducing the coil spring weight. Also, it increases the space for passenger compartment by lowering the
floor.
This type of suspension consists of multiple links such as trailing arm, upper arm, lower arm and track
rod.
Layout
Page 926 of 1082
09-6
2. SPECIFICATION (DSL ONLY)
Unit Description Specification
Front brake Type Ventilated disc
Outer diameter of discØ298 mm
Inner diameter of caliper cylinderØ43.0 x 2 mm
Thickness of disc 26 mm (wear limit: 24 mm)
Thickness of brake pad 10.5 mm (wear limit: 2 mm)
Pad wear indicator Mechanical type
Rear brake Type Solid disc
Outer diameter of disc2WD: Ø262 mm, 4WD: Ø284 mm
Thickness of disc 10 mm (wear limit: 8.4 mm)
Thickness of brake pad 10 mm (wear limit: 2 mm)
Pad wear indicator Mechanical type
Brake booster Type Vacuum assist type
Size8” + 9” (Tandem)
Master cylinder Type Tandem (level sensor installed)
Inner diameter of cylinderØ25.4 mm
Brake pedal Maximum operating stroke140 ± 3 mm
Pedal ratio 3.8 : 1
Free play 3 to 10 mm
Parking brake Type Mechanically expanded rear lining
Operating type Hand operated type
Inner diameter of drum2WD: Ø168 mm, 4WD: Ø190 mm
Brake oil Specification DOT 4
Capacity 0.7 to 0.8 liters
Service interval for brake fluid: Change every other year.
Page 980 of 1082

12-30000-00
1. SPECIFICATION (HPS)
Component Item Specification
Steering wheel Type 3-spoke
Outside diameterΦ 380 mm
Number of revolutions 3.11 rotations
Heated wire Simple ON/OFF
Gear box Type Rack and pinion
Gear ratio 46.94
Rack stroke± 73 mm
Steering angle Inner39°
Outer31.24°
Wheel alignment Toe-in2 ± 2 mm
Oil pump Type Vane (removable pump and reservoir)
Maximum pressure100 ± 3 bar
Displacement6.0 to 9.75 ℓ/min
Pulley diameterΦ 115 mm
Steering column Tilting angle Up + 2.0
Down - 30
Lower shaft Type Ball slip
Steering oil Oil typeATF Dexron Ⅱ or Ⅲ
Oil reservoir capacity1 ℓ
Change interval EU (Diesel): Check and add at every 20,000
km
GEN (Diesel, Gasoline): Check and add at
every 15,000 km
Turning capability Min. turning radius 5.4 m
Page 984 of 1082

12-70000-00
1. SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The power steering has been designed to make the wheel move more easily than in a manual steering
system. The hydraulic power assists the process utilizing hydraulic fluid. The fluid increases pressure in
the power steering pump and aids the movement of the steering mechanism.
The power steering system consists of pump, oil reservoir, rack and gear box.
The power steering pump is a vane type and delivers hydraulic pressure to operate the power steering
system.
The pressure relief valve in the pump controls the discharging pressure.
The rotary valve in the rack and the pinion gear directs the oil from the power steering pump to one side
of the rack piston. The integrated rack piston converts the hydraulic pressure to linear movement. The
operating force of the rack moves the wheels through the tie rod, the tie rod end and the steering knuckle.
Even though the hydraulic pressure cannot be generated, a driver can steer the vehicle without power
assist but it needs very high steering force.
In this case, the operating force of the steering wheel is conveyed to the pinion, and the movement of the
pinion moves the rack through the pinion gear combined to the rack gear.