rear wheel SSANGYONG KORANDO 2012 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2012, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 2012Pages: 1082, PDF Size: 96.1 MB
Page 938 of 1082

10-74890-00
4WD - Front/Rear wheel speed
sensor
2WD - Front wheel speed sensor
2WD - Rear wheel speed sensor
ECU (Electronic Control Unit) 1.
ECU calculates the wheel speed, acceleration and
deceleration with the information from wheel
speed sensor, and determines the wheel slip to
control the valve and motor.
HU (Hydraulic Unit) 2.
The hydraulic circuit contains the primary circuit
and secondary circuit for ABS operation. This unit
controls the hydraulic pressure to each wheel. If
the system needs ABS operation, the valves in
the unit operate to control HOLD, RISE and
DUMP according to ECU control logic.
Motor 3.
The motor is operated when ABS is activated. The
cam-shaped output shaft of the motor enables the
brake system to receive and supply the brake fluid
during the motor operation.
Wheel speed sensor ▶
Wheel speed sensor sends the data detected by
tone wheel to HECU.
HECU ▶
Rear wheel speed sensor in 2WD vehicle is
different from that in 4WD vehicle.
Location of rear tone wheel (A) and wheel
sensor (B) in 2WD vehicle
Page 939 of 1082

10-8
G-sensor (only for 4WD) ▶
For the vehicle with the ABS, a speed difference
between the wheels is not noticeable as all the
wheels are slipping during abrupt braking.
Therefore, the vehicle needs the speed
information from other sensors other than the
wheel speed sensor. On the 2WD vehicle, there
is not large difference between the vehicle speed
reduction and actual wheel speed reduction in
the event of braking since the driving wheels are
in the front. So, the ABS HECU can control the
vehicle, based on a calculation value. But, on the
4WD vehicle, if a speed reduction occurs in the
front or rear of the vehicle, it affects the other side
wheel. In other words, braking the rear wheels
induces also a large speed reduction in the front
wheels. The longitudinal acceleration sensor is
used for this case. It controls the ABS by using
the signals from the sensor during abrupt braking
and acceleration.G-sensor
Page 949 of 1082
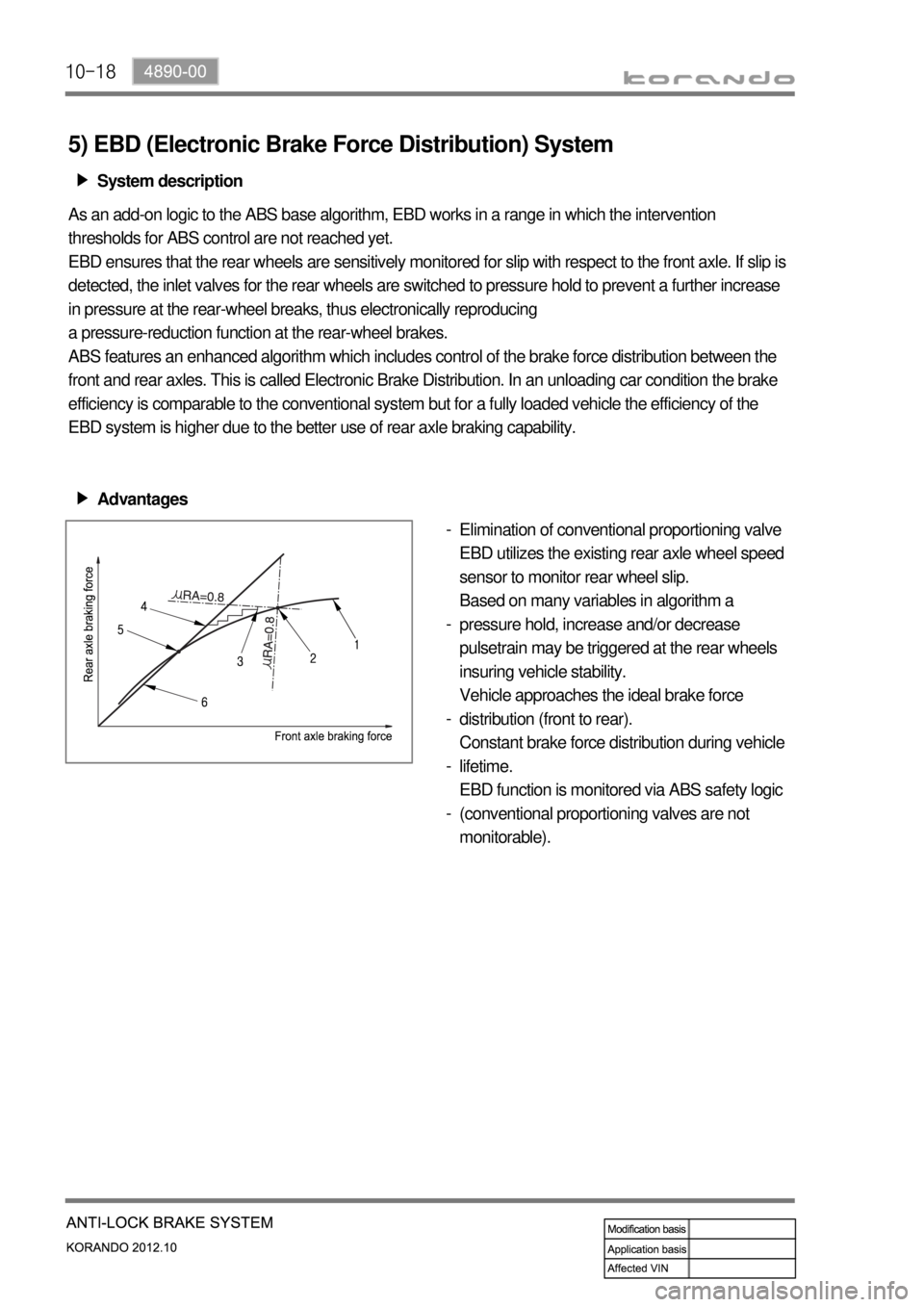
10-18
5) EBD (Electronic Brake Force Distribution) System
System description ▶
As an add-on logic to the ABS base algorithm, EBD works in a range in which the intervention
thresholds for ABS control are not reached yet.
EBD ensures that the rear wheels are sensitively monitored for slip with respect to the front axle. If slip is
detected, the inlet valves for the rear wheels are switched to pressure hold to prevent a further increase
in pressure at the rear-wheel breaks, thus electronically reproducing
a pressure-reduction function at the rear-wheel brakes.
ABS features an enhanced algorithm which includes control of the brake force distribution between the
front and rear axles. This is called Electronic Brake Distribution. In an unloading car condition the brake
efficiency is comparable to the conventional system but for a fully loaded vehicle the efficiency of the
EBD system is higher due to the better use of rear axle braking capability.
Advantages ▶
Elimination of conventional proportioning valve
EBD utilizes the existing rear axle wheel speed
sensor to monitor rear wheel slip.
Based on many variables in algorithm a
pressure hold, increase and/or decrease
pulsetrain may be triggered at the rear wheels
insuring vehicle stability.
Vehicle approaches the ideal brake force
distribution (front to rear).
Constant brake force distribution during vehicle
lifetime.
EBD function is monitored via ABS safety logic
(conventional proportioning valves are not
monitorable). -
-
-
-
-
Page 955 of 1082

11-30000-00
1. SPECIFICATION
1) Specification of Active Wheel Sensor
Description Specification
Supplying voltage DC 12 V
Output current (at 2.75 km/h of vehicle speed) 7 mA (Lo) ~ 14 mA (Hi) +20%/-16%
Tightening torque Front: 7.8 to 11.8 Nm
Rear: 7.8 to 11.8 Nm
Operating temperature-40 ~ 150 ℃
Operating frequency 1 ~ 2,500 Hz
UnitDescription
ABS ESP
HECU Clock frequency: 32 MHz Clock frequency: 50 MHz
Memory: 128 KB Memory: 512 KB
Switch orifice Switch orifice
Wheel speed sensor Active type Active type
Steering wheel angle
sensorNone Max. detection angle speed:
1500 °/Sec
Operating voltage: 9 to 12 V
Sensor cluster None Yaw rate sensor + lateral G sensor +
longitudinal G sensor (4WD)
Longitudinal G sensor 4WD only None
Pressure sensor None HECU integrated
Page 959 of 1082

11-70000-00
3. ESP OFF switch
Located on the left side of
instrument panel.2. Steering wheel angle
sensor
Located on column shaft with
contact coil.1. HECU assembly
Located under the power
steering fluid reservoir and
contains the pressure sensor.
2. COMPONENTS
4. Sensor cluster
Located on the floor under front
passenger seat.5. Wheel speed sensor
(4WD/2WD-front)
Located on knuckle. the
appearance of front sensor is
same with rear sensor.6. Rear wheel speed sensor
(2WD)
Located on knuckle. The
appearance is different from
that for 4WD.
Page 965 of 1082

11-130000-00
ESP controls during understeer ▶
The ESP system recognizes the directional angle with the steering wheel angle sensor and senses the
slipping route that occurs reversely against the vehicle cornering direction during understeer with the ya
w
rate sensor and lateral sensor. Then, the ESP system applies the braking force to the rear inner wheel to
compensate the yaw moment value. In this way, the vehicle does not lose its driving direction and the
driver can steer the vehicle as intended.
(2) Over steering
What is oversteering? ▶
Oversteer is a term of a condition in which the steering wheel is steered to a certain angle during driving
and the rear tires slip outward losing traction.
Compared to understeering vehicles, it is hard to control the vehicle during cornering and the vehicle can
spin due to rear wheel moment when the rear tires lose traction and the vehicle speed increases.
ESP controls during oversteer ▶
The ESP system recognizes the directional angle with the steering wheel angle sensor and senses the
slipping route that occurs towards the vehicle cornering direction during oversteer with the yaw rate
sensor and lateral sensor. Then the ESP system applies the braking force to the front outer wheel to
compensate the yaw moment value. In this way, the vehicle does not lose its driving direction and the
driver can steer the vehicle as intended.
Page 978 of 1082
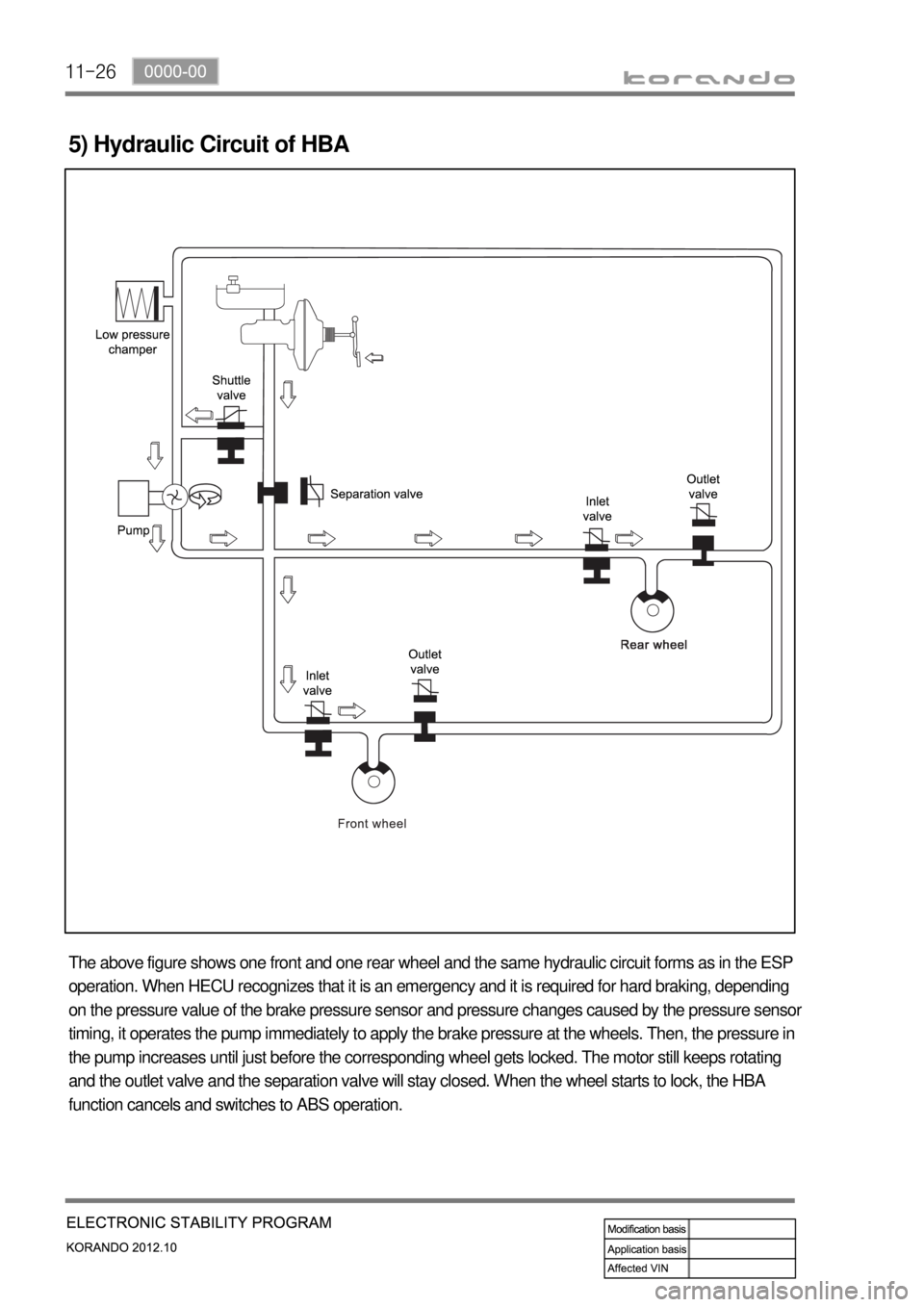
11-26
5) Hydraulic Circuit of HBA
The above figure shows one front and one rear wheel and the same hydraulic circuit forms as in the ESP
operation. When HECU recognizes that it is an emergency and it is required for hard braking, depending
on the pressure value of the brake pressure sensor and pressure changes caused by the pressure sensor
timing, it operates the pump immediately to apply the brake pressure at the wheels. Then, the pressure in
the pump increases until just before the corresponding wheel gets locked. The motor still keeps rotating
and the outlet valve and the separation valve will stay closed. When the wheel starts to lock, the HBA
function cancels and switches to ABS operation.
Page 1022 of 1082

02-6
Seldom oeprate ▶The air bag deploys when: ▶
The air bag can deploy when: ▶a severe oblique collision occurs with a specific severity, angle, speed, and position. -
A collision with oblique impact to the front seat direction or a front collision to the diagonal
direction occurs.
a frontal or rear collision occurs.
The vehicle rolls over or tips over sideward with minor impact.
The air bag warning lamp is on. -
-
-
-the vehicle rolls over or tips over sideward with a severe impact.
The vehicle is stationary or a front collision occurs with low speed.
A rear collision occurs.
The impact of the collision is low enough for the seat belt to protect the occupant properly. -
-
-
-
Seldom oeprate ▶The air bag deploys when: ▶
The air bag can deploy when: ▶
The air bag does not deploy when: ▶
The vehicle is stationary or a front collision occurs with low speed.
A rear collision occurs.
The impact of the collision is low enough for the seat belt to protect the occupant properly. -
-
-
C. General Warnings for Air Bag
Do not check the circuits with a circuit tester. Do not attempt to modify any air bag component
including the steering wheel, air bag mountings and related wirings.
Do not subject any air bag component, such as the steering wheel, air bag mountings, wirings, to
impacts. You might get severely injured by sudden deployment of the air bag.
As the air bag/seat belt pretensioner parts are very hot after being deployed. Allow them to cool
down sufficiently before touching them.
The deployed air bag/seat belt pretensioner cannot deploy again. It will work when an additional
impact is applied. The components of the deployed air bag/seat belt pretensioner are non-reusable
parts. Therefore, remove or replace them as a unit.
The air bag and seat belt pretensioner systems contain explosive charges, so handle carefully when
disposing or replacing them.
Incorrect inspection can result in serious injuries or malfunctions in the air bag and seat belt
pretensioner system.
The air bag warning lamp is illuminated for 3 to 7 sec. after the engine is started to check the system.
Drive the vehicle after this warning lamp is turned off. If this warning lamp stays ON, the system may
be defective. Have the air bag system checked immediately by Ssangyong Dealer or Ssangyong
Authorized Service Center. -
-
-
-
-
-
-
Page 1023 of 1082

02-78810-00
As the air bag system is very hot after being deployed, allow at least 30 minutes for the system to cool
down sufficiently before touching it. It can cause serious burns.
When an occupant fastens the seat belt in an unstable or inclined posture, the air bag system cannot
protect the occupant properly. Moreover, the occupant can be injured by the air bag.
Children and infants should ride in a rear seat. Seating in the passenger's seat with carrying a child or
infant is strictly prohibited. An infant or a child could be severely injured by air bag deployed.
A child restraint system must be placed in a rear seat.
A child restraint system must not be placed in the passenger's seat. An infant or a child could be
severely injured by the air bag deployment.
Do not cover, place any object or affix any stickers on the air bag inflation location.
Do not cover the front seat. The side air bag will not work properly.
Never put your arms around the front seat from behind, lean on the front seatback, or put your arms
out of the window. You can severely injured when the side air bag deploys.
Never lean on the door since it becomes very dangerous when the side air bag deploys.
Do not put any object such as an umbrella or bags between the door and side air bag mounting.
The side air bag deploys when there is a severe side collision.
Do not put any object such as an umbrella or bags between the door and side air bag mounting.
Do not slam the front door to close it. The side air bag may deploy unexpectedly.
Do not move your seat too close to the steering wheel or dashboard. Being too close to the steering
wheel or instrument panel during the air bag deployment could cause serious injury, including death
Move back as far as practical to allow the air bag room to inflate when driving.
Do not incline toward the steering wheel or hold the steering wheel with your hands crossed. Never
allow the front passenger to put hands or feet on the dash board. It can cause severe injures when
the air bag inflates.
Never put your feet on the dash board. You can severely injured when the air bag inflates.
It is normal that a loud noise, dust and smoke occur when the air bag and seat belt pretensioner
operate.
A large quantity of non-toxic gas is generated when the air bag or seat belt pretensioner deploys. If
these airborne particles irritate your skin, eyes, nose, or throat, rinse the area with cool water. If the
irritation continues, see your doctor.
The windshield glass may be broken when the passenger air bag deploys.
The air bag is a unit to save an occupant's life from sudden accident and it inflates at a very fast speed
by gas with high temperature, which might cause injury, such as an abrasion, bruise and burn
depending on the accident conditions.
A loud noise and non-toxic smoke-like particles are generated when air bags deploy. -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-