SSANGYONG KORANDO 2013 Service Manual
Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2013, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 2013Pages: 1336, PDF Size: 92.18 MB
Page 1131 of 1336
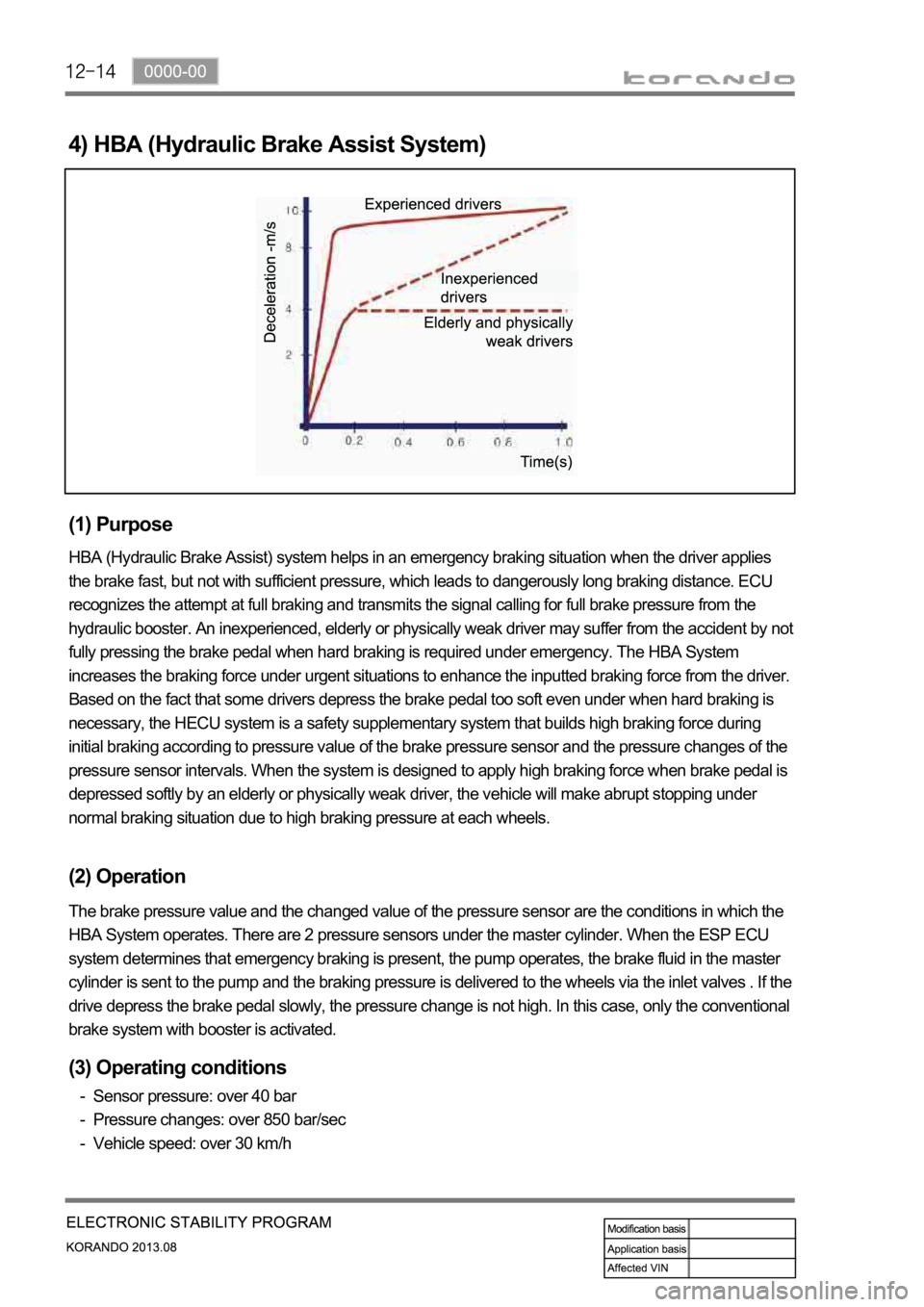
4) HBA (Hydraulic Brake Assist System)
(1) Purpose
HBA (Hydraulic Brake Assist) system helps in an emergency braking situation when the driver applies
the brake fast, but not with sufficient pressure, which leads to dangerously long braking distance. ECU
recognizes the attempt at full braking and transmits the signal calling for full brake pressure from the
hydraulic booster. An inexperienced, elderly or physically weak driver may suffer from the accident by not
fully pressing the brake pedal when hard braking is required under emergency. The HBA System
increases the braking force under urgent situations to enhance the inputted braking force from the driver.
Based on the fact that some drivers depress the brake pedal too soft even under when hard braking is
necessary, the HECU system is a safety supplementary system that builds high braking force during
initial braking according to pressure value of the brake pressure sensor and the pressure changes of the
pressure sensor intervals. When the system is designed to apply high braking force when brake pedal is
depressed softly by an elderly or physically weak driver, the vehicle will make abrupt stopping under
normal braking situation due to high braking pressure at each wheels.
(2) Operation
The brake pressure value and the changed value of the pressure sensor are the conditions in which the
HBA System operates. There are 2 pressure sensors under the master cylinder. When the ESP ECU
system determines that emergency braking is present, the pump operates, the brake fluid in the master
cylinder is sent to the pump and the braking pressure is delivered to the wheels via the inlet valves . If the
drive depress the brake pedal slowly, the pressure change is not high. In this case, only the conventional
brake system with booster is activated.
(3) Operating conditions
Sensor pressure: over 40 bar
Pressure changes: over 850 bar/sec
Vehicle speed: over 30 km/h -
-
-
Page 1132 of 1336
0000-00
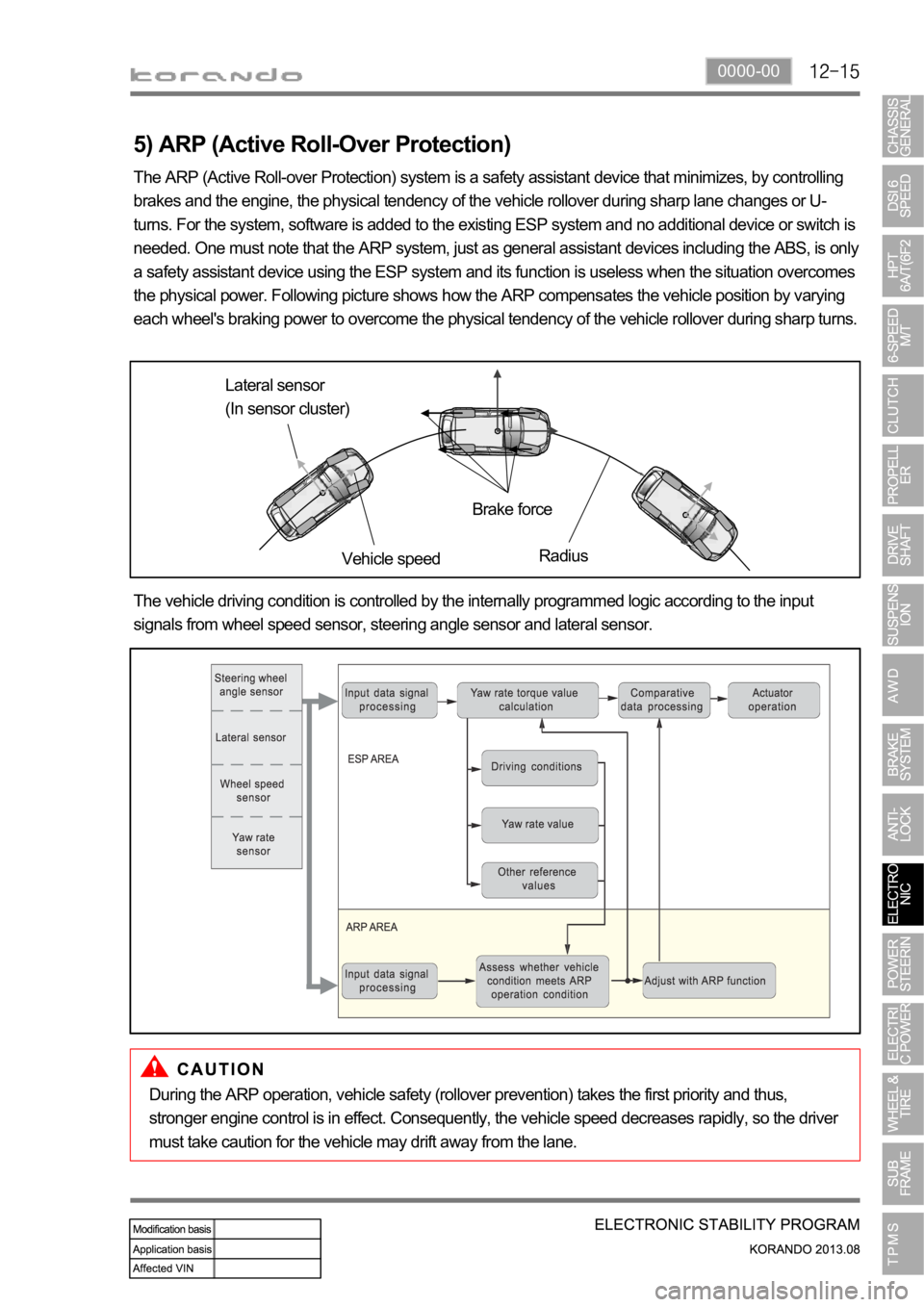
5) ARP (Active Roll-Over Protection)
The ARP (Active Roll-over Protection) system is a safety assistant device that minimizes, by controlling
brakes and the engine, the physical tendency of the vehicle rollover during sharp lane changes or U-
turns. For the system, software is added to the existing ESP system and no additional device or switch is
needed. One must note that the ARP system, just as general assistant devices including the ABS, is only
a safety assistant device using the ESP system and its function is useless when the situation overcomes
the physical power. Following picture shows how the ARP compensates the vehicle position by varying
each wheel's braking power to overcome the physical tendency of the vehicle rollover during sharp turns.
Lateral sensor
(In sensor cluster)
Vehicle speedBrake force
Radius
The vehicle driving condition is controlled by the internally programmed logic according to the input
signals from wheel speed sensor, steering angle sensor and lateral sensor.
During the ARP operation, vehicle safety (rollover prevention) takes the first priority and thus,
stronger engine control is in effect. Consequently, the vehicle speed decreases rapidly, so the driver
must take caution for the vehicle may drift away from the lane.
Page 1133 of 1336

6) HSA (Hill Start Assist)
The HSA (Hill Start Assist) prevents the vehicle from rolling backward by supplying the hydraulic
pressure to the wheels by the HECU after the brake pedal is released when starting off on uphill.
Page 1134 of 1336

0000-00
7) Emergency Hazard Flasher Control (Coupled with ABS)
(1) System layout
(2) Emergency stop signal function
When ABS system is operating (or sudden braking), the hazard warning flashers will blink for 10
seconds to inform the emergency situation to the vehicles behind.
(3) Operating process
When receiving the emergency stop signal through PCAN communication it blinks with the interval of 4
Hz and when receiving the emergency stop OFF signal through PCAN communication it blinks with the
interval of 1.25 Hz, normal operating speed.
However, the manual operation of the switch has a priority over this function.
flasher
Page 1135 of 1336

The BCM flashes the emergency auto hazard flasher with interval of 1.25 times/sec.:
The emergency hazard flasher does not operate if the vehicle speed is over 50 km/h when the
emergency stop signal is received.
The emergency hazard flasher operates if the vehicle speed is 50 km/h or lower when the
emergency stop signal is received.
When vehicle speed increases more than 10 km/h above the speed when the signal is received
during operation by emergency braking signal, the emergency hazard flasher stops operation.
When turning emergency hazard flasher switch OFF during operation by emergency braking signal,
it stops operation.
It is deactivated automatically 10 seconds after if items 2) and 3) above are not met during operation
by emergency braking signal.
If multi-function automatic hazard flasher signal is received during operation by emergency braking
signal, it will be overridden. -
-
-
-
-
-
Page 1136 of 1336

0000-00
6. HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT OF ESP
MCP: Master Cylinder Primary
MSP: Master Cylinder Secondary
ESV: Electric Shuttle Valve
NO: Normal Open
NC: Normal Close
LPA: Low Pressure Accumulator
Page 1137 of 1336

Circuit description
When compared to the vehicle equipped with ABS/EBD only, the internal hydraulic circuit has a
normally-open separation valve and a shuttle valve in primary circuit and in secondary circuit.
When the vehicle brakes are not applied during engine running or when applying the non-ABS operating
brakes, the normally-open separation valve and the inlet valve are open, whereas the normally-closed
shuttle valve and the outlet valve are closed.
When the ESP system is operating, the normally-open separation valve will be closed by the solenoid
valve operation and the hydraulic circuit will be established by the shuttle valve. Then, the inlet and outlet
valves will be closed or open depending on the braking pressure RISE, HOLD or DUMP conditions.
Flashing warning lamp and warning sound during ESP operation
When the ESP operates while the vehicle is moving, the ESP warning lamp on the instrument panel
flickers and the buzzer sounds at every 0.1 second. The ESP lamp operation is to inform a driver that the
vehicle is extremely unstable.
The ESP system is just a supplementary system for the vehicle and it cannot control the vehicle over the
physical limit. Do not solely rely on the system but be advised to drive the vehicle safely.
Drive feeling during ESP operation
When the ESP system activates, the driving feeling can be different depending on vehicle driving
conditions. For example, it will feel different when the ESP system is activated while the ABS is operated
by depressing the brake pedal and when the ESP system is in control without the brake pedal
depressed on the same curve.
If the ESP system operates with the brake applied, the brake pressure will be increased on the
corresponding wheel which already has braking pressure for the ESP controls. In other words, the ESP
system would make the driver feel more abruptly braked compared to the situation that the braking
pressure is applied to wheel which had no braking force.
Noise and vibration that driver senses during ESP operation
The ESP system may transfer noise and vibration to a driver due to the pressure changes caused by the
motor and valve operations in a very short period of time.
Extreme cornering will trigger the ESP operation and this will make the driver sense noise and vibration
due to sudden brake application.
Also, the ESP system controls the engine power. Therefore, the driver may notice the engine power
decreases even when the accelerator pedal is depressed.
Page 1138 of 1336

0000-00
1) Idling and Normal Braking Condition
In this position, the separation valve and the inlet valve are open (normal open), the electrically operated
shuttle valve and the outlet valve are closed.
When the brake is applied under these conditions, the brake fluid will be sent to each wheel via the
separation valve and inlet valve.
Page 1139 of 1336

2) DUMP (ESP is working) Mode
The pressure decreases just before the wheel speed drops and the wheels are locked.
The inlet valve closes and the outlet valve opens as in the ABS HECU and the oil is gathered at the low
pressure chamber while no additional oil is being supplied. Then the pump operates to allow fast oil
drainage. The shuttle valve and the separation valve do not operate while decompression.
Page 1140 of 1336

0000-00
3) HOLD (ESP is working) Mode
The Inlet valve and outlet valve will be closed to maintain the pressure in the hydraulic circuit applied at
the wheels. By closing the valves, the hydraulic pressure at the wheels will not be lost or supplied any
more. During ESP operation, the separation valve closes and only the shuttle valve at the pump opens.