differential SSANGYONG KORANDO 2013 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2013, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 2013Pages: 1336, PDF Size: 92.18 MB
Page 415 of 1336

Rear temp.
sensor
Front temp.
sensorCDPF (DOC+DPF)
Throttle valveD20DTF ECUDifferential pres.
sensor
Oxygen sensor
(11) CDPF control
a. Overview
As the solution for environmental regulations and PM Particle Material) of diesel engine, the low emission
vehicle is getting popular. This vehicle is equipped with an extra filter to collect the soot and burn it again
so that the amount of PM in the exhaust gas passed through the DOC (Diesel Oxidation Catalyst) is
reduced. The CDPF (Catalyst & Diesel Particulate Filter) is an integrated filter including DOC (Diesel
Oxidation Catalyst) and DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter).
For details, refer to Chapter "CDPF".
b. Components
Page 417 of 1336

Rear temp. sensor:
Measure DPF
temp.DPF performs
recycling
(combustion)
process at 600C,
and rear
temperature sensor
monitors the
temperature of DPF.
Differential pressure
sensor measures the
pressure difference
between pre-CDPF
and post-CDPF (If
PM has been
accumulated, the
measured value is
over the specified
value).Diff. pres. sensor:
Measure
pressure between
front side and
rear side of CDPF
Injector: Control
post injection
Front temp.
sensor: Measure
DOC temp.DOC performs
oxidation and
reduction process at
front temperature
sensor monitors the
temperature of
DOC.
Electronic
throttle body:
Control intake ai
r
mass
ECU (DCM 3.7)
d. Operation process
When the differential pressure sensor detects the pressure difference between the front and the rear
side of CDPF, the sensor sends signal indicating the soot is accumulated and the post injection is
performed to raise the temperature of exhaust gas. The amount of fuel injected is determined according
to the temperature of exhaust gas detected by the rear temperature sensor. If the temperature is below
low load range, the amount of post injection and the amount of intake air are controlled. It is to raise the
temperature by increasing the amount of fuel while decreasing the amount of intake air.
T-MAP sensor
Intake air
mass
Exceed PM
limitBooster
pressure/
temperaturePost injection
Control intake air
mass
Page 986 of 1336
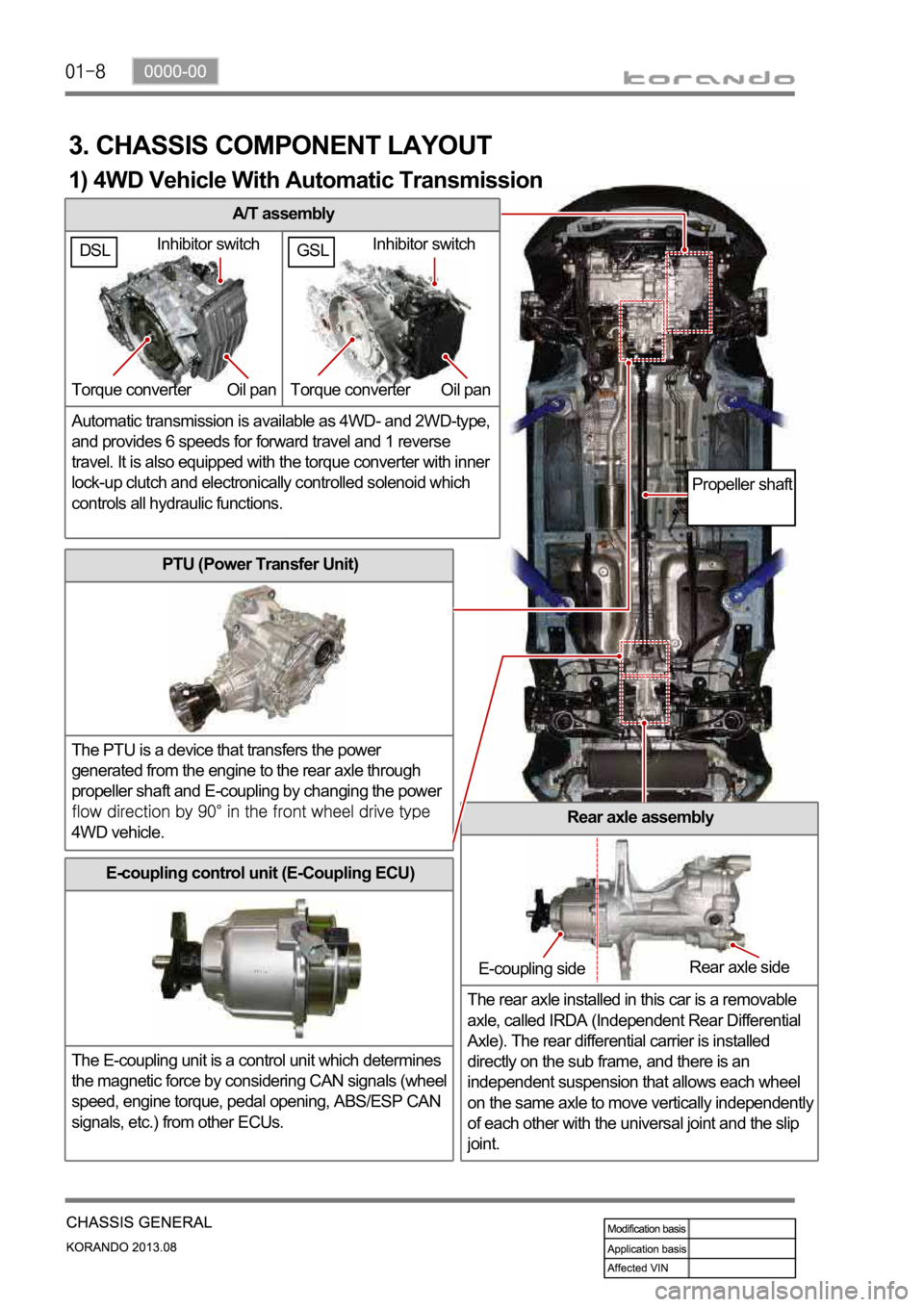
A/T assembly
Automatic transmission is available as 4WD- and 2WD-type,
and provides 6 speeds for forward travel and 1 reverse
travel. It is also equipped with the torque converter with inner
lock-up clutch and electronically controlled solenoid which
controls all hydraulic functions.
3. CHASSIS COMPONENT LAYOUT
PTU (Power Transfer Unit)
The PTU is a device that transfers the power
generated from the engine to the rear axle through
propeller shaft and E-coupling by changing the power
4WD vehicle.Rear axle assembly
The rear axle installed in this car is a removable
axle, called IRDA (Independent Rear Differential
Axle). The rear differential carrier is installed
directly on the sub frame, and there is an
independent suspension that allows each wheel
on the same axle to move vertically independentl
y
of each other with the universal joint and the slip
joint.
E-coupling control unit (E-Coupling ECU)
The E-coupling unit is a control unit which determines
the magnetic force by considering CAN signals (wheel
speed, engine torque, pedal opening, ABS/ESP CAN
signals, etc.) from other ECUs.
Inhibitor switch
Torque converter Oil pan
E-coupling sideRear axle side
Propeller shaft
1) 4WD Vehicle With Automatic Transmission
GSLDSLInhibitor switch
Torque converter Oil pan
Page 1006 of 1336

2) Sectional Diagram
Double planetary gear-set
Clutch packSingle planetary gear-set
Oil pump
Torque converter
Input shaft
Intermediate shaft
Differential assembly
Page 1019 of 1336

3680-01
2) Power Flowing Sequence
Torque converter Input shaft Front planetary gear
C2 clutch Forwarding sun gear Rear planetary gear
C1 clutch Center support Intermediate shaft
assembly
inal reduction and
differential gearThis is a fluid clutch.
Transfers the power from
engine to transaxle and
amplifies the torque.Transfers the power
from torque converter
to front planetary
gear.Generates the gear
ratio and transfers the
power.
Engaged by hydraulic
pressure and transfers the
power to C1 clutch.Transfers the power from
torque converter to rear
planetary gear.Generates the gear ratio
and transfers the power.
Engaged by hydraulic
pressure and transfers the
power to C1 clutch.Transfers the power from
input shaft to intermediate
shaft.Changes the rotating direction
and generates the final
reduction rear ratio.
Generates the final reduction gear ratio and performs
the differential function.
Transfers the power to constant velocity shaft.
Page 1020 of 1336

3) Power Flow
Front planetary gear
Front sun gear (FSG)
Planetary hear pinion (PP)
Ring gear (Internal) 1.
2.
3.
Rear planetary gear
Forward sun gear (FSG)
Reverse sun gear (RSG)
Short pinion (SPP)
Long oinion (LPP)
Ring gear (RG) 4.
5.
6.
7.
8.Intermediate gearDrive gear
Driven gear 9.
10.
Differential gear
Pinion
Differential 11.
12.
Page 1056 of 1336

3190-01
2. TIGHTENING TORQUE
Part name Tightening torque Remark
1. Drive gear mounting bolt of differential carrier 166.6 to 176.4 Nm 10 EA
2. Reverse shaft mounting bolt 74.5 to 89.2 Nm
3. Transmission case mounting bolt 19.6 to 26.5 Nm 22 EA
4. Concentric slave cylinder mounting bolt 11.8 to 14.7 Nm 3 EA
5. Backup lamp switch 29.4 to 34.3 Nm
6. Neutral switch 29.4 to 34.3 Nm
7. Oil filler plug 58.8 to 78.4 Nm
8. Oil drain plug 58.8 to 78.4 Nm
9. Oil plug 58.8 to 78.4 Nm
10. Shift lever mounting nut 42.2 to 53.9 Nm
11. Selector lever mounting nut 42.2 to 53.9 Nm
12. Control shaft assembly mounting bolt 9.8 to 11.8 Nm 7 EA
13. Guide bolt 42.2 to 53.9 Nm
Page 1074 of 1336

4110-01
1. SPECIFICATION
Component Item Specifications
2WD,
4WDFront drive
shaftJoint type Inside: Tripod joint
Outside: Ball joint
Max. allowed angle
To compensate the bending
angleInstallation of equivalent
length shaft
Rear drive
shaftJoint type Inside: Cross groove joint
Outside: Ball joint
Max. allowed angle
Rear differential
carrierType Independent Rear Drive Axle
(IRDA)
Reduction gear type Hypoid gear
Gear reduction ratio 2.93
Diameter of gear
Oil type Hypoid gear oil
(SAE 75W/90)
Final drive gear backlash 0.10 to 0.15 mm
Differential gear backlash 0 to 0.076 mm
Propeller shaft Joint type PTU side: CV joint
Rear axle side: Rubber coupling
Sliding distance
Unbalance 80 g.mm or less at 3,000 rpm
Total runout 0.3 mm or less
4WD
only
Page 1075 of 1336

1. COMPONENT
For AWD vehicle For 2WD vehicle
Front drive shaft (LH)
Front drive shaft (RH)
Intermediate shaft
Power transfer unit(PTU) - 4WD
Propeller shaft - 4WD 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.E-coupling - 4WD
Rear differential carrier - 4WD
Rear drive shaft (LH) - 4WD
Rear drive shaft (RH) - 4WD 6.
7.
8.
9.
Page 1077 of 1336
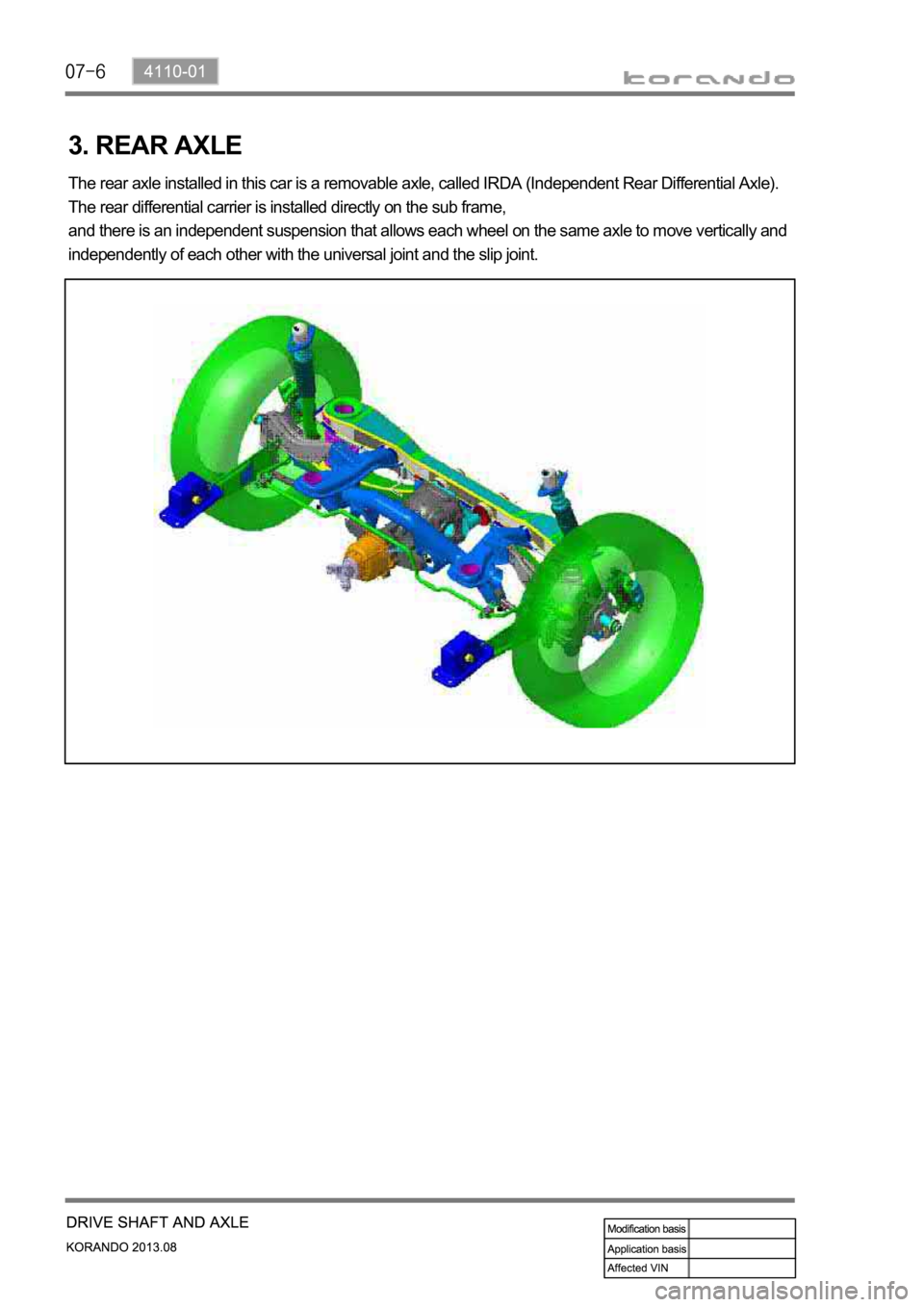
3. REAR AXLE
The rear axle installed in this car is a removable axle, called IRDA (Independent Rear Differential Axle).
The rear differential carrier is installed directly on the sub frame,
and there is an independent suspension that allows each wheel on the same axle to move vertically and
independently of each other with the universal joint and the slip joint.