engine SSANGYONG KORANDO 2013 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2013, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 2013Pages: 1336, PDF Size: 92.18 MB
Page 251 of 1336
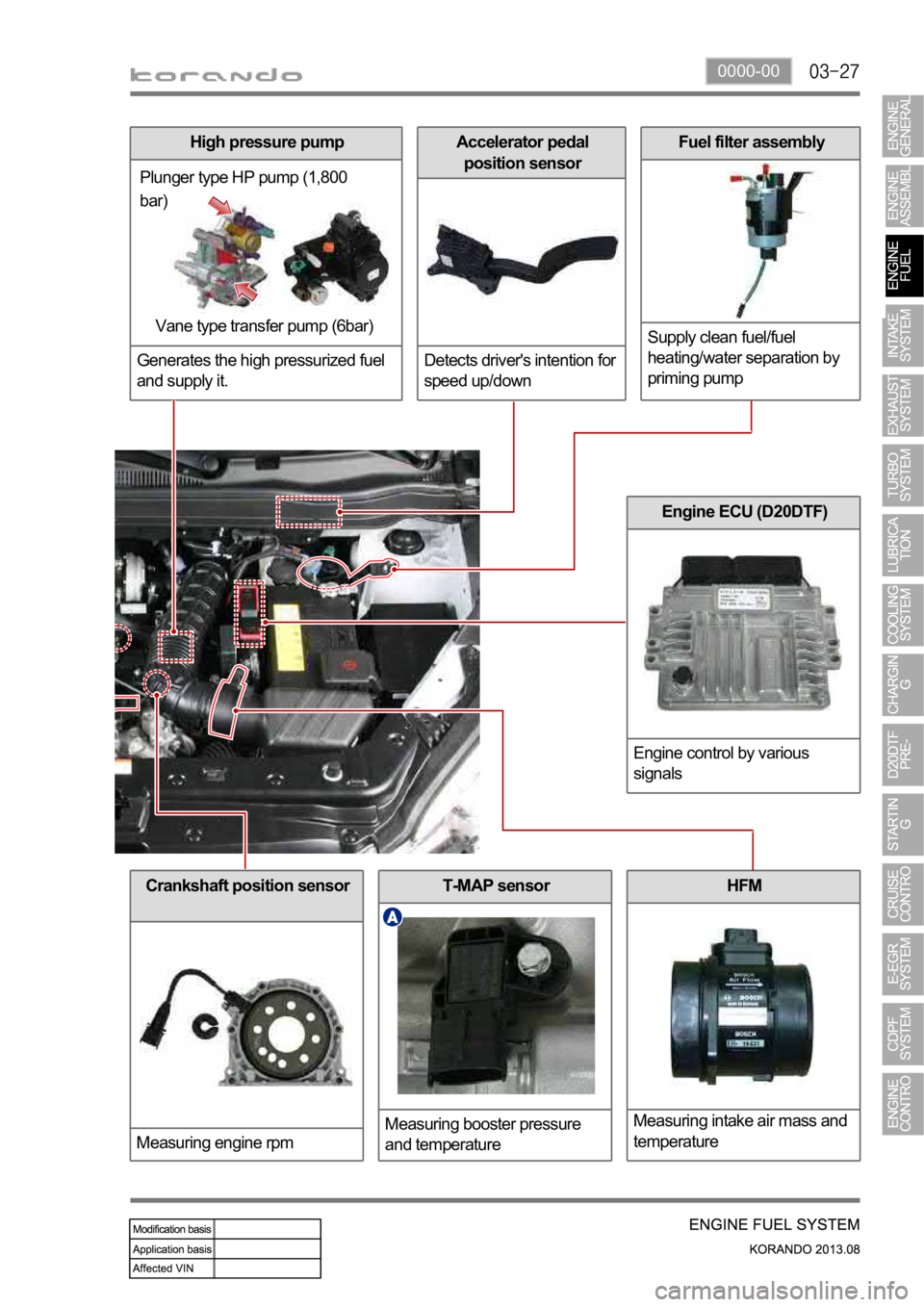
0000-00
Crankshaft position sensor
Measuring engine rpmT-MAP sensor
Measuring booster pressure
and temperatureHFM
Measuring intake air mass and
temperature
Engine ECU (D20DTF)
Engine control by various
signals
High pressure pump
Generates the high pressurized fuel
and supply it.
Plunger type HP pump (1,800
bar)
Vane type transfer pump (6bar)
Accelerator pedal
position sensor
Detects driver's intention for
speed up/downFuel filter assembly
Supply clean fuel/fuel
heating/water separation by
priming pump
Page 254 of 1336

The engine ECU calculates the accelerator pedal based on the input signals from various sensors, and
controls the overall operation of the vehicle.
The ECU receives the signals from various sensor through data line, and performs effective air-fuel ratio
control based on these signals.
The crankshaft speed (position) sensor measures the engine speed, and the camshaft speed (position)
sensor determines the order of injections, and the ECU detects the amount of the accelerator pedal
depressed (driver's will) by receiving the electrical signals from the accelerator pedal sensor.
The mass air flow sensor detects the volume of intake air and sends the value to the ECU.
The major function of the ECU is controlling air-fuel ratio to reduce the emission level (EGR valve control)
by detecting instantaneous air flow change with the signals from the mass air flow sensor.
Also, the ECU uses the signals from the coolant temperature & air temperature sensors, booster pressure
sensor, atmospheric pressure sensor to: a) determine injection starting point and set value for pilot
injection, and b) deal with various operations and variable conditions.
Page 258 of 1336

2. INSPECTION
1) Troubleshooting
When Abnormal Noises are Heard from the Engine Room
For the vehicle equipped with DI engine, if a learning noise occurs in each range or other noises occur,
the major cause of it is a faulty turbocharger assembly. But an interference issue, poor tightness or
loose in the intake and exhaust system also can cause those noises. This is mainly because the
operator didn't follow the instruction exactly when reconnecting the intake hoses and pipes which were
disconnected to check the system or replace the air cleaner. If the intake system is free of any faults,
check the EGR and PCV oil separator connected to the intake system.
The figure may be different from the actual engine. Therefore, read thoroughly below before replacing
the parts.
2) Abnormal Noise Caused by Poor Tightness of Intake System
When the DI engine is running, the air entered into the engine flows in the sequence as shown above. If
high intake pressure is applied to the loose or damaged part, a whistling noise may occur, the intake air
volume is measured incorrectly or the engine power is derated.
Page 259 of 1336
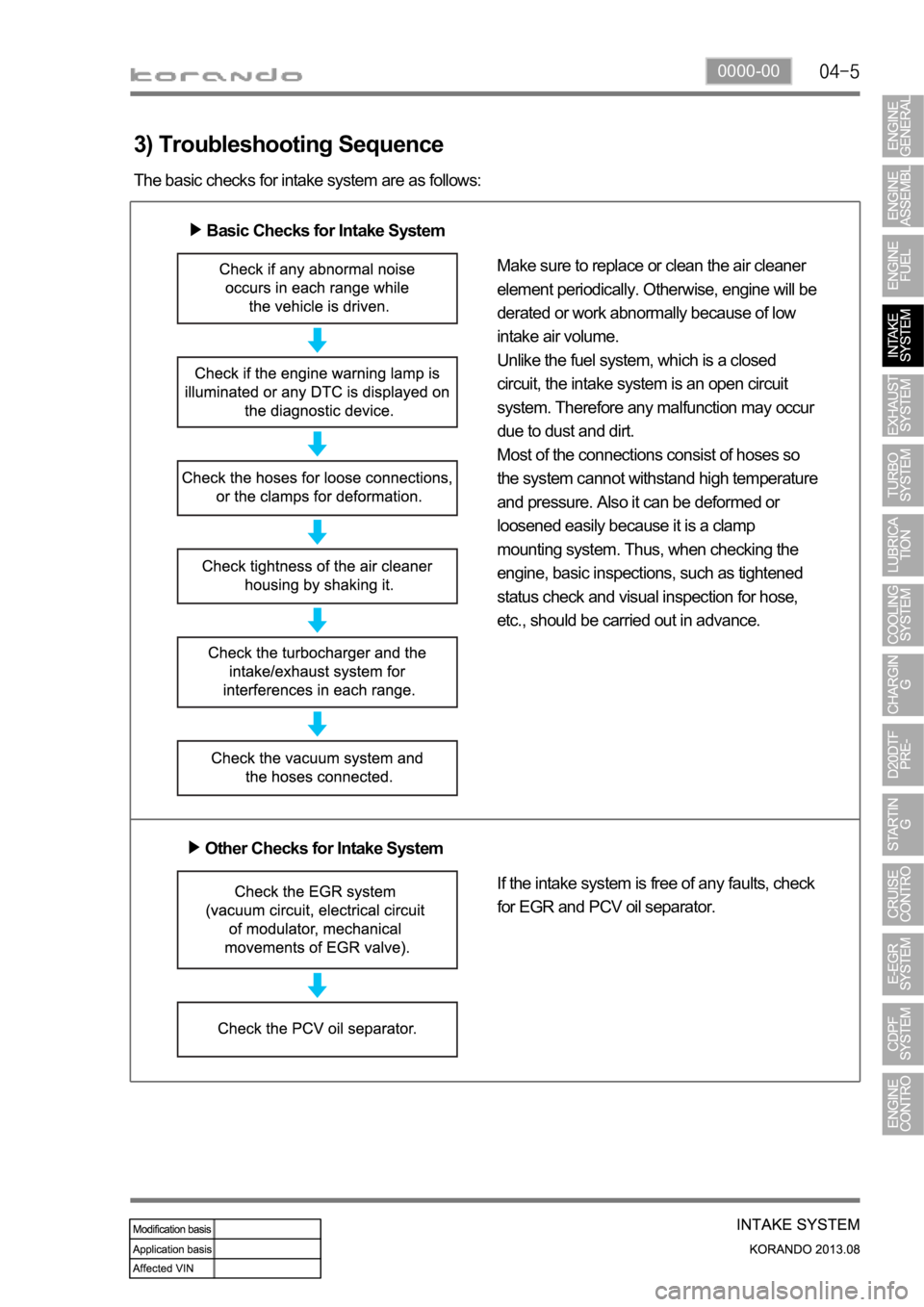
0000-00
3) Troubleshooting Sequence
The basic checks for intake system are as follows:
Basic Checks for Intake System
Make sure to replace or clean the air cleaner
element periodically. Otherwise, engine will be
derated or work abnormally because of low
intake air volume.
Unlike the fuel system, which is a closed
circuit, the intake system is an open circuit
system. Therefore any malfunction may occur
due to dust and dirt.
Most of the connections consist of hoses so
the system cannot withstand high temperature
and pressure. Also it can be deformed or
loosened easily because it is a clamp
mounting system. Thus, when checking the
engine, basic inspections, such as tightened
status check and visual inspection for hose,
etc., should be carried out in advance.
Other Checks for Intake System
If the intake system is free of any faults, check
for EGR and PCV oil separator.
Page 260 of 1336
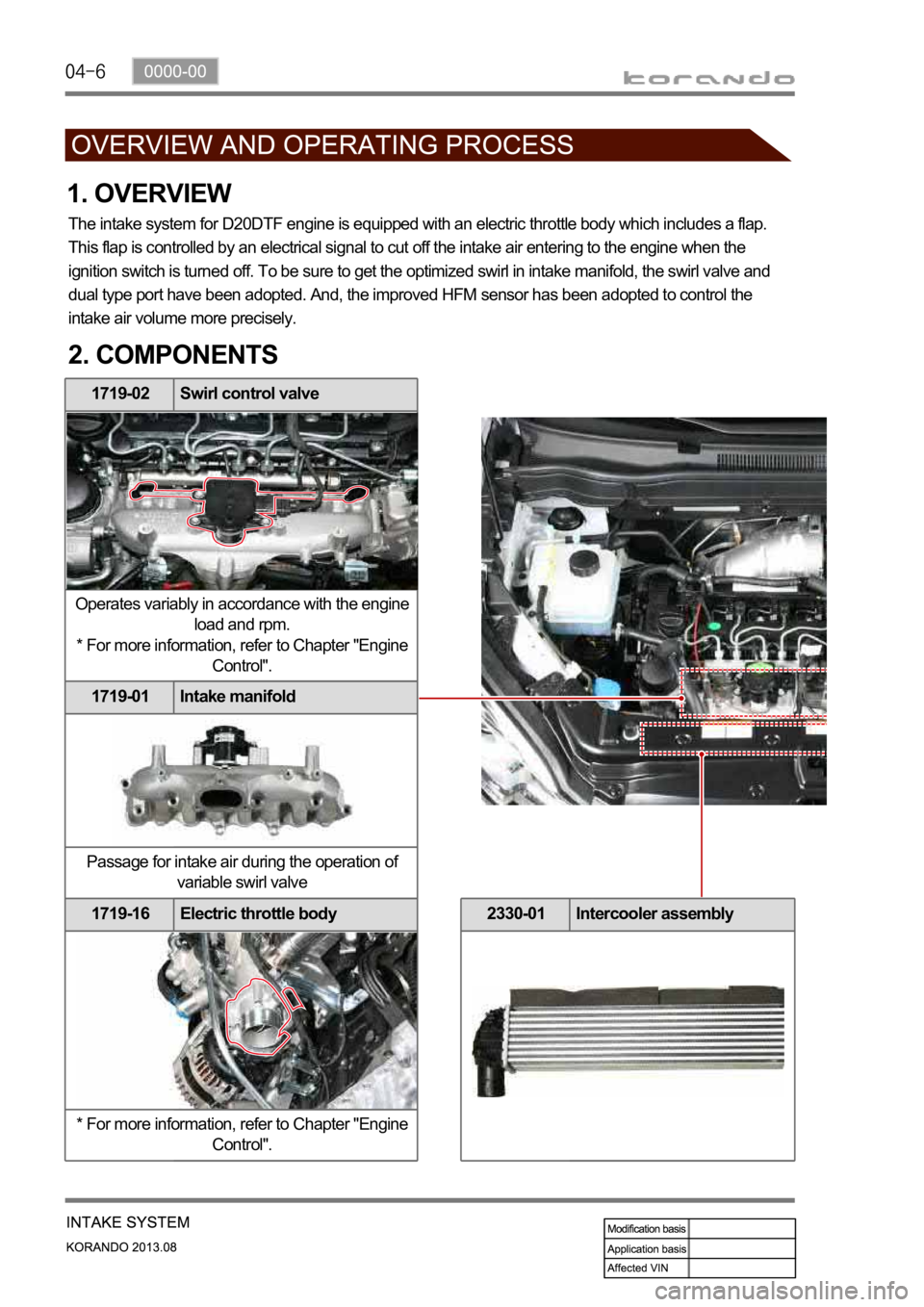
1719-02 Swirl control valve
Operates variably in accordance with the engine
load and rpm.
* For more information, refer to Chapter "Engine
Control".
1719-01 Intake manifold
Passage for intake air during the operation of
variable swirl valve
1719-16 Electric throttle body
* For more information, refer to Chapter "Engine
Control".
1. OVERVIEW
The intake system for D20DTF engine is equipped with an electric throttle body which includes a flap.
This flap is controlled by an electrical signal to cut off the intake air entering to the engine when the
ignition switch is turned off. To be sure to get the optimized swirl in intake manifold, the swirl valve and
dual type port have been adopted. And, the improved HFM sensor has been adopted to control the
intake air volume more precisely.
2. COMPONENTS
2330-01 Intercooler assembly
Page 261 of 1336

0000-00
2313-15 HFM (Hot Film Air-Mass) sensor
HFM sensor, version 6
* For more information, refer to Chapter "Engine
Control".
2313-01 Air cleaner assembly and
resonator
Page 264 of 1336
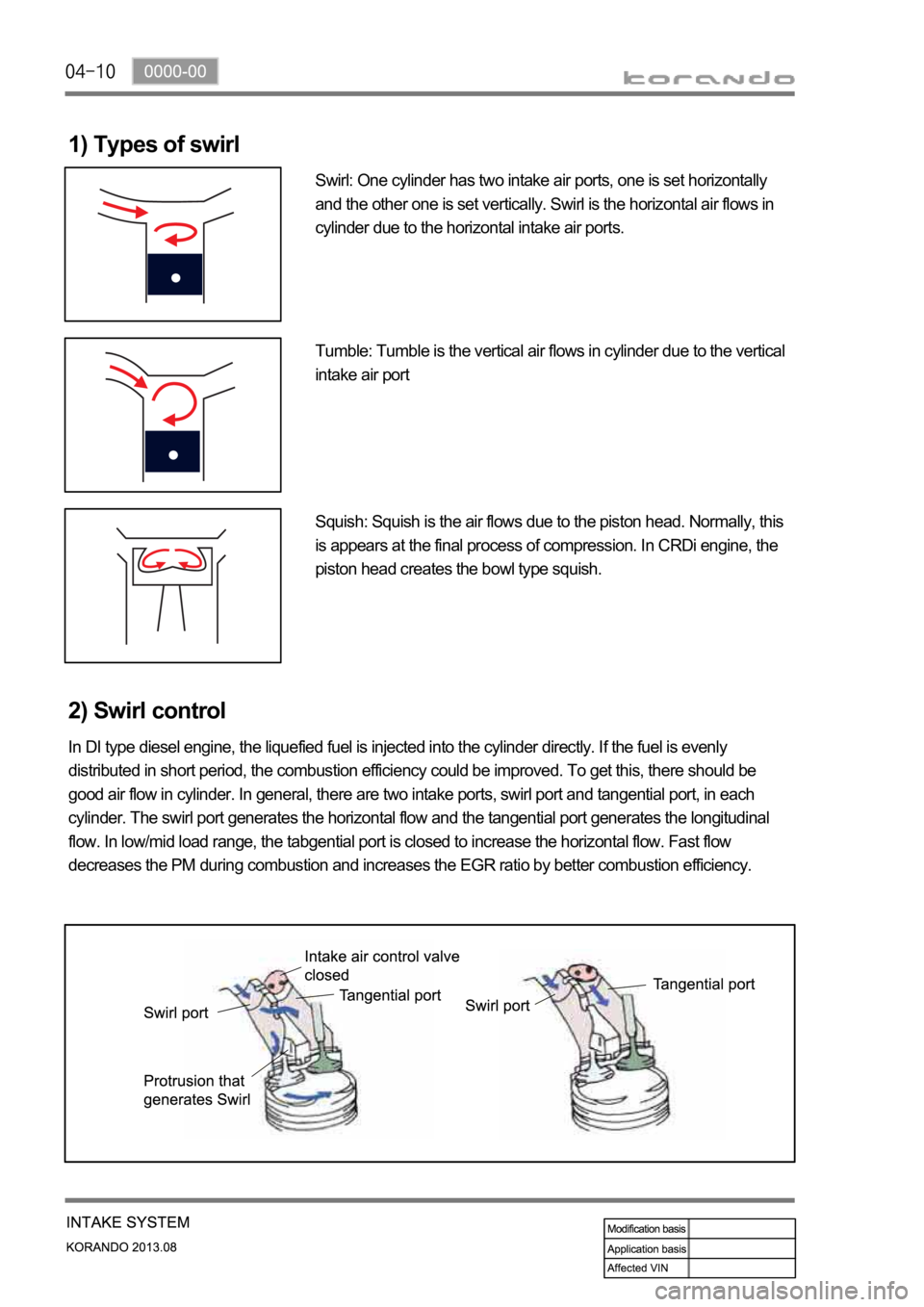
1) Types of swirl
Swirl: One cylinder has two intake air ports, one is set horizontally
and the other one is set vertically. Swirl is the horizontal air flows in
cylinder due to the horizontal intake air ports.
Tumble: Tumble is the vertical air flows in cylinder due to the vertical
intake air port
Squish: Squish is the air flows due to the piston head. Normally, this
is appears at the final process of compression. In CRDi engine, the
piston head creates the bowl type squish.
2) Swirl control
In DI type diesel engine, the liquefied fuel is injected into the cylinder directly. If the fuel is evenly
distributed in short period, the combustion efficiency could be improved. To get this, there should be
good air flow in cylinder. In general, there are two intake ports, swirl port and tangential port, in each
cylinder. The swirl port generates the horizontal flow and the tangential port generates the longitudinal
flow. In low/mid load range, the tabgential port is closed to increase the horizontal flow. Fast flow
decreases the PM during combustion and increases the EGR ratio by better combustion efficiency.
Page 265 of 1336

0000-00
Load Engine speed Swirl
valveAmount of
swirlRemarks
Low speed,
Low loadbelow 3,000 rpm Closed HeavyIncreased EGR ratio, better air-fuel
mixture (reduce exhaust gas)
High speed,
High loadover 3,000 rpm Open LightIncrease charge efficiency, higher
engine power
The variable swirl valve actuator operates when
turning the ignition switch ON/OFF position to
open/close the swirl valve. In this period, the soot
will be removed and the learning for swirl valve
position is performed.
Swirl valve
Swirl: This is the twisted (radial) air flow along the cylinder wall during the intake stroke. This
stabilizes the combustion even in lean air-fuel mixture condition.
3) Features
Swirl and air intake efficiency
To generate the swirl, the intake port should be serpentine design. This makes the resistance in air
flow. The resistance in air flow in engine high speed decreases the intake efficiency. Eventually, the
engine power is also decreased, Thus, the swirl operation is deactivated in high speed range to
increase the intake efficiency.
Relationship between swirl and EGR
To reduce Nox, it is essential to increase EGR ratio. However, if EGR ratio is too high, the PM also
could be very higher. And, the exhaust gas should be evenly mixed with newly aspired air. Otherwise,
PM and CO are dramatically increased in highly concentrated exhaust gas range and EGR ratio
could not be increased beyond a certain limit. If the swirl valve operates in this moment, the limit of
EGR ratio will be higher. -
-
4) Relationship between swirl and fuel injection pressure
The injector for DI engine uses the multi hole design. For this vehicle, there are 8 holes in injector. If the
swirl is too strong, the injection angles might be overlapped and may cause the increased PM and
insufficient engine power. Also, if the injection pressure is too high during strong swirl, the injection angles
might be overlapped. Therefore, the system may decreases the fuel injection pressure when the swirl is
too strong.
Page 268 of 1336

2. CAUTIONS
Do not park the vehicle on flammable materials, such as grass, leaves and carpet.
Do not touch the catalyst or the exhaust gas ignition system when the engine is running.
If a misfire occurs in the combustion chamber or the emission of pollutant exceeds the specified
level, the catalyst can be damaged.
When servicing or replacing components of the exhaust system, makes sure that the components
are positioned at regular intervals from all other parts of the under body.
Be careful not to damage the exhaust system when lifting the vehicle from its side.
All components and body parts of the engine exhaust system should be inspected for crack,
damage, air hole, part loss and incorrect mounting location. Also check for any deformation which
can result in exhaust gas drawn into the vehicle.
Make sure that the exhaust pipe is cooled down sufficiently before working on it because it is still hot
right after the engine is stopped.
Wear protective gloves when removing the exhaust pipe. -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Page 269 of 1336

0000-00
Exhaust manifoldCDPF assembly
No. 1 exhaust pipe
No. 2 exhaust pipe
No.3 muffler pipe
1. OVERVIEW
This system purifies the exhaust gas generated by the combustion in the engine to reduce the pollutants
and noise during that arise during combustion.
2. COMPONENT
Fore details about the CDPF
assembly, refer to Chapter
"CDPF System".