belt SSANGYONG NEW ACTYON SPORTS 2012 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2012, Model line: NEW ACTYON SPORTS, Model: SSANGYONG NEW ACTYON SPORTS 2012Pages: 828, PDF Size: 91.28 MB
Page 511 of 828
04-20
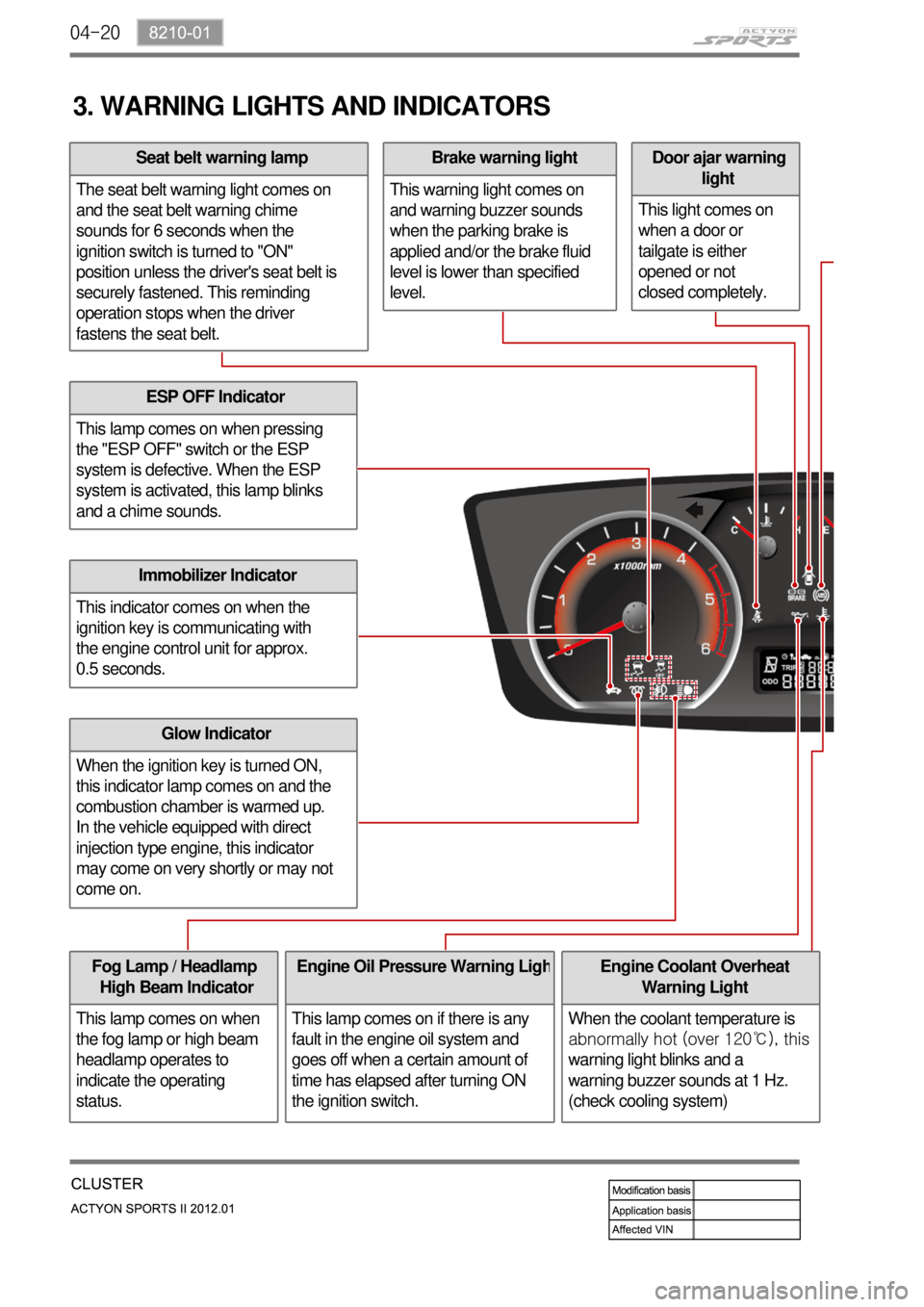
3. WARNING LIGHTS AND INDICATORS
ESP OFF Indicator
This lamp comes on when pressing
the "ESP OFF" switch or the ESP
system is defective. When the ESP
system is activated, this lamp blinks
and a chime sounds.
Immobilizer Indicator
This indicator comes on when the
ignition key is communicating with
the engine control unit for approx.
0.5 seconds.
Glow Indicator
When the ignition key is turned ON,
this indicator lamp comes on and the
combustion chamber is warmed up.
In the vehicle equipped with direct
injection type engine, this indicator
may come on very shortly or may not
come on.
Fog Lamp / Headlamp
High Beam Indicator
This lamp comes on when
the fog lamp or high beam
headlamp operates to
indicate the operating
status.Engine Oil Pressure Warning Ligh
This lamp comes on if there is any
fault in the engine oil system and
goes off when a certain amount of
time has elapsed after turning ON
the ignition switch.
Door ajar warning
light
This light comes on
when a door or
tailgate is either
opened or not
closed completely.Brake warning light
This warning light comes on
and warning buzzer sounds
when the parking brake is
applied and/or the brake fluid
level is lower than specified
level.Seat belt warning lamp
The seat belt warning light comes on
and the seat belt warning chime
sounds for 6 seconds when the
ignition switch is turned to "ON"
position unless the driver's seat belt is
securely fastened. This reminding
operation stops when the driver
fastens the seat belt.
Engine Coolant Overheat
Warning Light
When the coolant temperature is
abnormally hot (over 120℃), this
warning light blinks and a
warning buzzer sounds at 1 Hz.
(check cooling system)
Page 733 of 828

12-74610-01
3. TROUBLESHOOTING
Problem Possible Cause Action
Movements of steering
feels heavyUnregular wear or binding of steering ball joint
due to lack of lubrication or foreign material
insertionLubricate or replace
Damaged or defective steering gear Replace the steering
gear assembly
Incorrect steering pinion preload Adjust
Defective steering shaft joint Replace
leakage of steering fluid Repair or replace
Insuffcient steering fluid or air insertion Fill up fluid or bleed air
Defective steering oil pump Replace
Damaged or loosened pump drive belt Adjust or replace
Clogging of fluid line Repair or replace
Damaged wheel or tire Repair or replace
Defective suspension Repair or replace
Steering wheel pulls to
one sideDamaged steering linkage Replace
Damaged wheel or tire Repair or replace
Defective suspension Repair or replace
Defective brake system Repair or replace
Excessive free play of
steering wheelWorn steering gear Replace the steering
gear assembly
Worn or damaged steering ball joint Replace
Looseness of steering gear box Retighten
Poor returning of
steering wheelBroken or binding of steering ball joint Replace
Improper correct steering pinion preload Replace the steering
gear assembly
Damaged wheel or tire Repair or replace
Defective suspension Repair or replace
Page 734 of 828

12-8
Problem Possible Cause Action
Excessive vibration of
steering wheel
(shimming)Broken steering linkage Replace
Looseness of steering gear box Retighten
Broken or binding of steering ball joint Replace
Worn or damaged front wheel bearing Replace
Damaged wheel or tire Repair or replace
Defective suspension Repair or replace
Abnormal noise from
steering systemLooseness of steering gear box Retighten
Defective steering gear Replace the gear
assembly
Interference between steering column and
partsRepair
Looseness of steering linkage Retighten
Loosened or damaged oil pump drive belt Adjust or replace
Looseness of oil pump bracket Replace
Looseness of oil pump Replace
Air insertion into system Bleed air
Defective oil pump Replace
Abnormal noise when
turning steering wheelLooseness of steering column Retighten
Worn or damaged steering shaft bearing Replace the steering
column
Looseness of intermediate shaft Retighten
Too heavy steering wheel Worn or damaged steering shaft bearing Replace the steering
column
Page 739 of 828

12-134610-01
Oil Pump Pressure Check ▶
Unscrew the pressure line fitting in power
steering pump.
Install the pressure gauge between the
power steering pump and the power
steering oil pressure line.
Place the shift lever to neutral position.
Apply the parking brake.
Open the valve in pressure gauge. Start
the engine and let it run at idle speed.
Turn the steering wheel several times so
that the oil temperature reaches to normal
operating level. 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Before checking the pressure, check the oil
level and belt tension. Prepare the empty
container to collect the spilled oil during the
service. Check the oil pump pressure to locate any
defect in oil pump.
Fully close the valve in pressure gauge and
measure the oil pressure. 6.
Relief pressure
90 ± 3 bar
Oil pump
Steering gear box
To prevent internal damage, do not close
the gauge valve over 10 seconds.
Keep the oil temperature at proper range. -
-
Page 742 of 828

12-16
2. SYSTEM LAYOUT
The steering pump is driven by the engine power through a belt. This pump circulates the power
steering oil from the reservoir -> steering pump -> oil supply pipe -> steering gear box -> oil
return pipe -> reservoir to perform steering operations
Steering pump Steering return pipe Steering cylinder
Return line
High pressure line
Return hose & tube
Steering pump &
reservoir
High pressure hose
Linkage gear box Steering wheel
Lower shaft Column & shaft
Page 752 of 828

13-114170-09
1. OVERVIEW
A radial tire uses a cord angle of 90 degrees. That is, the cord material runs in a radial or direct
line from one bead to the other across the tread. In addition, a radial tire has a belt overwrap
under the tread surface to provide greater structural stability. The belt overwrap of a radial tire
distortion while the radial structure enables high speed driving.
Tire supports the weight of the vehicle, reduces the impact from the road and at the same time,
transmits the power to propel, brake and steer on the road. It also functions to maintain a
<009d008c008f0090008a0093008c02c5009a004700940096009d008c0094008c0095009b0055004700700095004700960099008b008c00990047009b00960047008a0096009400970093008c009b008c0047009a009c008a008f0047009b0088009a009200
9a0053004700880047009b00900099008c00470094009c009a>t be structured to be a resilient
vessel of air.
There is wear limit mark on the tire, which protrudes as a strip shape located approximately 1.6
mm from the groove bottom. This wear limit mark is not seen from the outside so there is
additional "▲" mark on the shoulder to let the driver find the wear mark easily. To measure the tire
groove depth, measure at any point other than the point which has a wear limit mark.
The tire is worn unevenly according to the driver's driving habit, improper servicing, low tire
inflation pressure, changed tire location, etc.
Page 754 of 828

13-134170-09
Structure of Tire ▶
Tread
This thick layer of rubber provides the interface between the tire and the road. Wear-resistant
rubber is used to protect the carcass and belt against fractures and impacts and to deliver a long
driving life.
Shoulder
Located between the tread and sidewall, the shoulder rubber is the thickest so that the design
must allow for the easy diffusion of heat generated within the tire while driving.
Sidewall
The part between the shoulder and bead, the flexible sidewall protects the carcass and enhances
the ride. A tire’s ty
pe, size, structure, pattern, manufacturing company, product name and various
characters are indicated here.
Bead
The bead attaches the tire to the rim and wraps the end of the cord fabric. Comprised of the
bead wire, core, flipper and other parts, the bead is generally designed to be slightly tight around
the rim so that in the case of a sudden drop in inflation pressure, the tire will not fall off the rim.
Carcass
As the most important framework of a tire, the entire inner layer of cord fabric is called the
carcass. The carcass acts to support air pressure, vertical load and absorb shocks.
Page 785 of 828

02-38810-01
1. CAUTIONS FOR AIR BAG OPERATION
When there is any deployed air bag (including seat belt pretensioner), the air bag unit should
be replaced. Any DTC (Diagnostic Trouble Code) in the air bag unit should not be cleared
since the unit has data for status when the air bag was deployed as well as information
related to the air bag deployment.
Note that the used components related to the air bag, especially the air bag unit, should be
packaged in an air tight container to prevent any damage.
Do not connect a tester to any connector or component to check supply voltage or
resistance of air bag related components. The detonator may explode due to a sudden extra
power supplied by the tester.
Before removing or installing any air bag related components, disconnect the negative battery
cable. 1.
2.
3.
4.
Collision sensors, a kind of impact G (acceleration) sensor, detect the lateral and longitudinal
collisions and determine whether or not to deploy air bags. The roles of each collision sensor are
as follows:
Front G sensors (inside the air bag unit)
Send signals to the front air bags (driver and passenger air bags) and the driver's and front
passenger's seat belt pretensioners. When the front collision G sensor sends out only the air
bag deployment signal, the signal deploys the two front air bags and activates their seat belt
pretensioners.
Once an air bag deploys, its repair parts vary according to the deployment situation and damage
to the vehicle from collision. Needed repairs also slightly vary between the front air bags and the
curtain air bags. The following are the differences:
Replacement parts when the front air bags deploy:
Air bag unit and its wiring (including connector), seat belt pretensioner and its wiring
(including connector), whole front air bags, instrument panel (IP)
Page 786 of 828

02-4
2. OPERATING RANGE
In the event of the collision, the air bag will be deployed when the G value detected by the G
sensor in the SDM is beyond the impact limit. ▶
Seat Belt Status Air Bag OperationSeat Belt Pretensioner Operation
Fastened Over reference speed Below reference speed
Unfastened Below reference speed Inoperative
Failure, during initial
diagnosisBelow reference speed Below reference speed
No sensor Below reference speed Below reference speed
This is based on frontal collision and reference speed is between approx. 4 and 24 km/h. *
The air bag is deployed in the event of frontal collisions while drving.
But, there are exceptional cases as follows: ▶
Situation Condition
May operate or not
Never operate
Seldom oeprate
Underbody impact from the road surface, impact against the
curb at a very high speed, or dropping impact onto the road
surface with a large angle occurs.
The vehicle rolls over or tips over sideward by severe impact. -
-
A collision with oblique impact to the front seat direction or a front
collision to the diagonal direction occurs.
A front/rear collision occurs.
The vehicle rolls over or tips over sideward with minor impact.
The air bag warning lamp is on. -
-
-
-The vehicle is stationary or a front collision occurs with low speed.
A rear collision occurs.
A minor collision occurs. -
-
-
Page 787 of 828

02-58810-01
3. GENERAL WARNINGS
Do not diagnose the circuit with a circuit tester or attempt to modify any air bag components
including the steering wheel, air bag mounting area and harness.
Incorrect inspection could cause a problem with an air bag and seat belt pretensioner, and
they cannot protect occupants properly. Inspection and repair service should be done only by
a qualified technician.
An infant or a child should not be seated on the front seat alone or on an adult's lap. An infant
or a child could be severely injured by air bag deployed.
A child restraint system should be placed on the rear seat which has the 3-point type seat belt.
Never install a child restraint system on the front seat. Impact by the air bag inflation might
cause severe injury or even death.
When an occupant fastens the seat belt with unstable or inclined posture, the air bag cannot
protect the occupant properly. Moreover, the occupant may be injured by the air bag.
Do not incline toward the steering wheel while driving. If you hit the air bag before it is fully
inflated, brain or neck injury, or even death can occur.
Be careful not to strike the steering wheel, air bag mounting area, any air bag related
component (including wiring) and seat belt pretensioner. You might get severely injured by
sudden deployment of the air bag.
The air bag contains explosive materials, so handle it carefully when disposing or replacing it.
The air bag components will be very hot immediately after deployment. Do not touch them until
they cool down.
Once the air bag/seat belt pretentioner is triggered, it will not deploy again even if an additional
impact is applied to it. Once triggered air bag/seat belt pretensioner related components
cannot be reused, so they should be removed from the vehicle and the whole system should
be replaced with a new one.
Do not place any object or sticker on the air bag mounting area for correct and safe activation
of the air bag.
Do not bang the door. Otherwise, an air bag might operate erroneously.
Hold the outer rim of the steering so that the air bag can inflate without any hindrance.
Do not incline toward the steering wheel or hold the steering wheel with your hands crossed. It
will cause a problem with the air bag activation or severe injury when the air bag inflates.
Never put your hands or feet on the dash board. You can severely injured when the air bag
inflates.
It is normal that a loud noise, dust and smoke occur when the air bag and seat belt
pretensioner operate.
The gas come out of air bag/seat belt pretensioner activation is non-toxic nitrogen gas.
However, if this gas occurs irritation to your skin, eyes, nose, and so on, wash it out with clean
water. Seek medical help if symptoms develop. -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-