transmission SSANGYONG NEW ACTYON SPORTS 2013 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2013, Model line: NEW ACTYON SPORTS, Model: SSANGYONG NEW ACTYON SPORTS 2013Pages: 751, PDF Size: 72.63 MB
Page 522 of 751

04-6
2) Overview
Driving elements ▶
The driving elements consist of two flat surfaces machined to a smooth finish.
One of these is the rear face of the engine flywheel and the other is the clutch pressure plate. The clutch
pressure plate is fitted into a clutch steel cover, which is bolted to the flywheel.
Driven elements ▶
The driven element is the clutch disc with a splined hub which is free to slide lengthwise along the splines
of the input shaft.
The driving and driven elements are held in contact by spring pressure. This pressure is exerted by a
diaphragm spring in the clutch cover pressure plate assembly.
Operating Elements ▶
The clutch "release" system consists of the clutch pedal and clutch release cylinder.
This system directly releases the clutch by using hydraulic pressure while the conventional clutch system
releases the clutch by using release lever and release fork. This system provides higher efficiency than
conventional clutch system, and its durability is superior.
Clutch master cylinder (mounted on clutch pedal)
Concentric slave cylinder pipe (mounted inside of transmission) -
-
Page 524 of 751
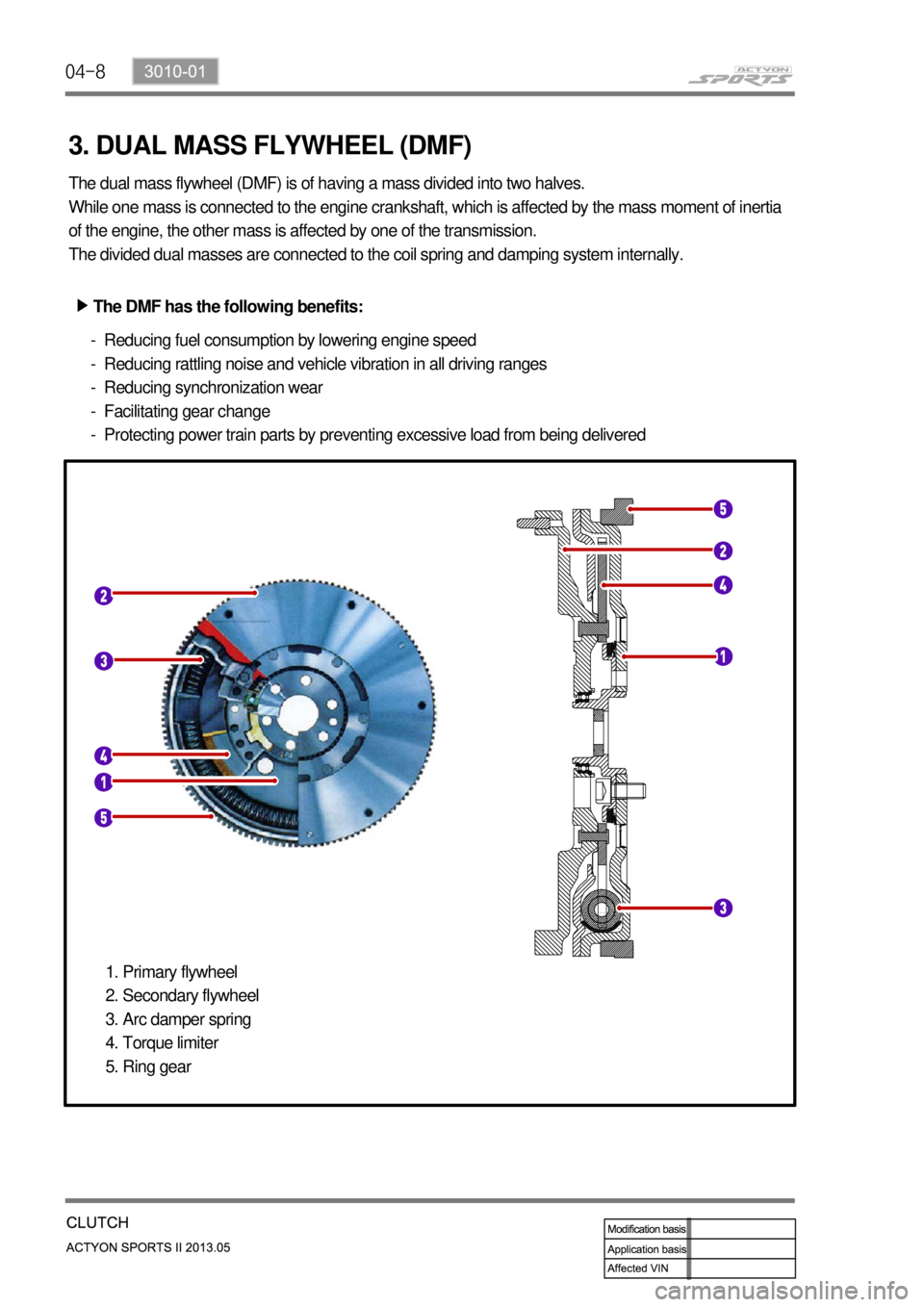
04-8
3. DUAL MASS FLYWHEEL (DMF)
The dual mass flywheel (DMF) is of having a mass divided into two halves.
While one mass is connected to the engine crankshaft, which is affected by the mass moment of inertia
of the engine, the other mass is affected by one of the transmission.
The divided dual masses are connected to the coil spring and damping system internally.
The DMF has the following benefits: ▶
Reducing fuel consumption by lowering engine speed
Reducing rattling noise and vehicle vibration in all driving ranges
Reducing synchronization wear
Facilitating gear change
Protecting power train parts by preventing excessive load from being delivered -
-
-
-
-
Primary flywheel
Secondary flywheel
Arc damper spring
Torque limiter
Ring gear 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Page 526 of 751

05-4
1. OVERVIEW
The propeller shaft transfers the power through the transmission and transfer case to the front/rear axle
differential carrier (final reduction gear).
It is manufactured by a thin rounded steel pipe to have the strong resisting force against the torsion and
bending.
Both ends of propeller shaft are connected to the spider and the center of propeller shaft is connected to
the spline to accommodate the changes of the height and length.
The rubber bushing that covers the intermediate bearing keeps the balance of rear propeller shaft and
absorbs its vibration.
Function of propeller shaft ▶
Transmits driving torque.
Compensates the angle change (universal joint / CV joint).
Compensates the axial length change (splines for the slip joint). -
-
-
Front propeller shaft
Rear propeller shaft
Page 530 of 751

07-53240-01
Operation ▶
Description Mode Conditions
Driving
mode2H 2 Wheel drive
(rear wheel)Rear-wheel drive mode. This is used under
normal or high-speed driving conditions on
public roads or highways.
4H 4 Wheel drive
(high speed)This is used under sandy, muddy or snow-
covered road conditions
4L 4 Wheel drive
(low speed)This is used for maximum traction.
When cornering with low speed in 4WD
condition, there could be tire dragging, some
mechanical shocks and resistances in
vehicle’s drive train. These are normal
conditions due to internal resistance in the drive
train when the 4WD system is properly working
Mode change2H←4H2 Wheel drive
↔4 Wheel driveShifting is possible while driving at the speed of
70 km/h or less
2H,
4H↔4L2 Wheel drive,
4 Wheel drive (high
speed)
↔4 Wheel drive
(low speed)For Automatic Transmission:
For Manual Transmission:
Stop the vehicle on level ground and
move the gear selector lever into the
“N” position. Turn the switch to the
desired position. ·
Stop the vehicle on level ground and
move the gear selector lever into the
“N” position. Then turn the switch to
the desired position while depressing the
clutch pedal. ·
To make the mode change easily, stop the
vehicle on level ground and turn the mode
switch to the desired position and move the
shift lever to "N"-"R"-"N" while depressing
the brake pedal.
Page 531 of 751

07-6
2. LAYOUT
Front axle
Front locking hub system (IWE)
Front propeller shaft
DSI 6-speed automatic
transmission
Part-time transfer case
Rear propeller shaft
Rear axle
Page 537 of 751

07-12
1) 2H Mode (2 Wheel Drive)
Power Flow ▶
Output shaft of
transmission
Rear propeller shaftRear wheel
Rear axle
Rear wheel
Input shaft of transfer case
↓
Output shaft of transfer
case
The driving force is directly engaged(1:1) to rear axle and is transferred only to the rear wheels.
Page 546 of 751

08-94411-01
Under View (4WD, Automatic Transmission)
Rear suspension
1. SUSPENSION
The suspension is the device to connect the axle and vehicle. It absorbs the vibrations and impacts from
road surface, which enhances the comforts, driving force, braking force and drivability.
Front suspension
Page 559 of 751

09-10
This section describes the noise phenomena occurred possibly in the brake system operation.
Distinguish between the information given below and the actual problems and then, inspect the vehicle
and take appropriate measures.
Noise symptoms and Causes -
Symptom 1. If depressing the brake pedal when the engine is cold, "screeching" sound always
occurs and, after driving for a while, the sound disappears..
This usually occurs in the morning. When the temperature goes down, the dew condensation
phenomenon sets moisture on the brake disc as the window frost forms. Due to this moisture, the iron
within the brake disc and pad oxidizes, forming undetectable micro-rusts on the disc surface. When
starting the engine under this condition, noise may sound due to the friction of micro-rusts. When
operating the brake several times, the disc temperature goes up and the micro-rusts come off and the
noise goes away. Depending on the driving conditions, noise gets louder when slightly depressing the
brake pedal and oppositely, noise is smaller when deeply depressing the brake pedal. This is simply a
physical phenomenon, called "morning effect" in professional terms, and does not imply any problems
with the brake system.
Symptom 2. Slip or screech after the brake pad replacement.
This usually occurs when the bed-in is not made between the disc and the pad's friction material. The
bed-in is a state that the brake system normally works and gives no noise out, when, after about 300 km
city driving, the contact area of the pad friction material is enlarged and the disk is in complete contact
with the pad's friction material. Therefore, for some time after the brake disk/pad replacement, the brake
system poorly operates or noise (abnormal sound) occurs due to the partial contact.
Symptom 3. "Groaning" sound occurs in the automatic transmission vehicle when slightly taking the foot
off the brake pedal to slowly start after waiting for the signal, or slightly depressing the brake pedal.
This is the noise "Creep groan" that occurs when, in both the automatic and manual transmission,
slightly releasing the brake pedal in the neutral gear at downhill roads.
It frequently occurs at the low braking power and low speed, through the following process. When
operating the brake system at low speed and low pressure, adhesion and slip repeatedly take place
between the brake disk and the friction material, and this makes the braking power inconstant, instantly
increasing or decreasing, and gives out the brake noise.
It is also a physical phenomenon and has no relation with the brake performance.BRAKE OPERATION AND NOISE ▶
Page 703 of 751

01-24
5. A/C INPUT/OUTPUT DIAGRAM
Below diagram shows the input/output mapping between the components of FATC A/C and A/C
controller briefly.
▶ A/C compressor control by engine ECU
In case of current vehicle models, the system turns ON or OFF the compressor switch according to the
refrigerant pressure, ambient temperature and condenser temperature to protect the A/C circuits.
However, for the vehicles equipped with DI engine, the engine ECU turns off the A/C compressor unde
r
below conditions, including those above.
Coolant temperature: 20℃ or less
Coolant temperature: 115℃ or more
For approx. 4 sec. after starting the engine
Engine speed: 650 rpm or less
Engine speed: 4,500 rpm or more
During abrupt acceleration for the vehicle equipped with manual transmission 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.