SSANGYONG NEW REXTON 2012 Service Manual
Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2012, Model line: NEW REXTON, Model: SSANGYONG NEW REXTON 2012Pages: 600, PDF Size: 73.29 MB
Page 371 of 600

3. INPUT/OUTPUT DEVICES
Page 372 of 600

1914-01
Control
rangeTurbocharger driving
mechanismControl method
EffectImproved
performance
At low
speedNarrows the flow
passage for the
exhaust gas by
folding the vanesThe flow rate is
increased as the
exhaust gas passes
the narrow passage
turbine & impeller
speed, Increased
compressive forceImproved
low speed torque
4. OPERATING PRINCIPLES
The E-VGT is designed to get more improved engine power in all ranges by controlling the turbine as
follows:
1) How it Works at Low Speed
Normal turbocharger cannot get the turbo effect because the amount of exhaust gas is not enough and
the flow speed is slow in a low speed zone, but VGT allows the flow passage of exhaust to narrow,
resulting in increasing the flow speed of exhaust gas and running the turbine quickly and powerfully.
Therefore, as VGT can intake more air than normal turbocharger, it can give the benefit of the increased
output even in a low speed zone.
Turbocharger lag
The turbocharger is at idle speed when there is no load or it is in the normal driving condition. During
this period, the amount of exhaust gas passing through the turbine is not enough to turn the
compressor wheel (impeller) fast. Therefore, the intake air is not compressed as needed.
Because of this, it takes time for turbocharger to supply the additional power after the accelerator
pedal is depressed. This is called "turbocharger lag". Basic principle at low speed
At low speed, it utilizes the principle of venturi.
For example, when air flows through the venturi
tube, the flow speed is faster and the pressure is
lower at the point "A". In this case, if the inner
diameter of venturi is more narrowed, the flow
speed is so much faster (refer to the equation).
Page 373 of 600

2) How it Works at High Speed
In a high speed zone, the amount of exhaust gas increases and it is accompanied with a great force.
Therefore, if the inner diameter of venturi is more widened, the turbine in the turbocharger by the
releasing force of abundant exhaust gas can deliver a more increased energy to the compressor. The
output will increase in submission to the increase of intake air volume.
Control
rangeTurbocharger driving
mechanismControl
methodEffectImproved
performance
At high
speedExpands the
flow passage for
the exhaust gas
by unfolding the
vanesThe flow rate is
increased due to the
expanded
Increased turbine &
impeller speed,
Increased
compressive forceImproved
maximum
power
Page 374 of 600
1543-00
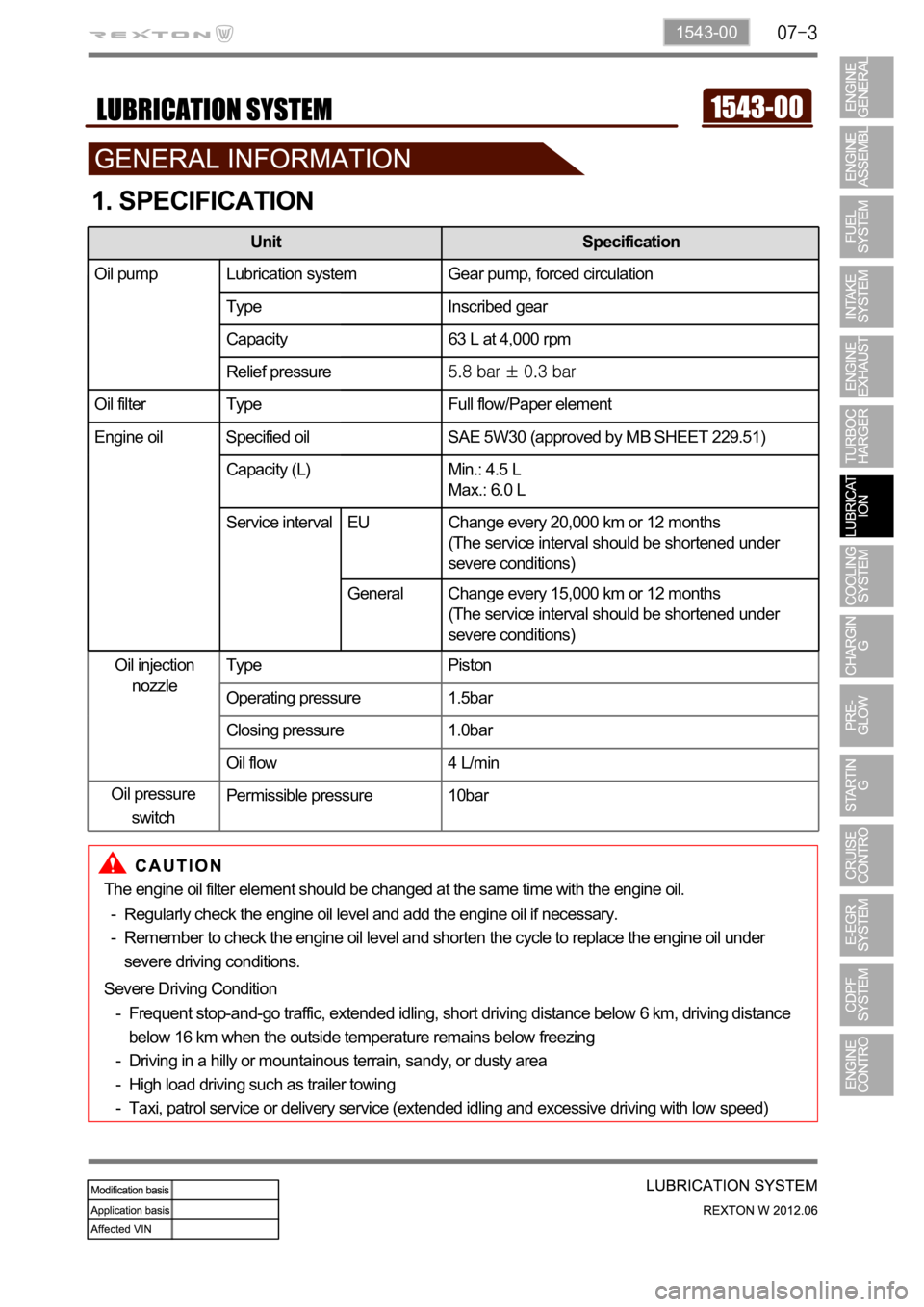
1. SPECIFICATION
The engine oil filter element should be changed at the same time with the engine oil.
Regularly check the engine oil level and add the engine oil if necessary.
Remember to check the engine oil level and shorten the cycle to replace the engine oil under
severe driving conditions. -
-
Severe Driving Condition
Frequent stop-and-go traffic, extended idling, short driving distance below 6 km, driving distance
below 16 km when the outside temperature remains below freezing
Driving in a hilly or mountainous terrain, sandy, or dusty area
High load driving such as trailer towing
Taxi, patrol service or delivery service (extended idling and excessive driving with low speed) -
-
-
-
Unit Specification
Oil pump Lubrication system Gear pump, forced circulation
Type Inscribed gear
Capacity 63 L at 4,000 rpm
Relief pressure
Oil filter Type Full flow/Paper element
Engine oil Specified oil SAE 5W30 (approved by MB SHEET 229.51)
Capacity (L) Min.: 4.5 L
Max.: 6.0 L
Service interval Change every 15,000 km or 12 months (But, shorten
the service interval under severe condition)
Oil injection
nozzleType Piston
Operating pressure 1.5bar
Closing pressure 1.0bar
Oil flow 4 L/min
Permissible pressure 10bar
Unit Specification
Oil pump Lubrication system Gear pump, forced circulation
Type Inscribed gear
Capacity 63 L at 4,000 rpm
Relief pressure
Oil filter Type Full flow/Paper element
Engine oil Specified oil SAE 5W30 (approved by MB SHEET 229.51)
Capacity (L) Min.: 4.5 L
Max.: 6.0 L
Service interval EU Change every 20,000 km or 12 months
(The service interval should be shortened under
severe conditions)
General Change every 15,000 km or 12 months
(The service interval should be shortened under
severe conditions)
Oil pressure
switch
Page 375 of 600

2. MAINTENANCE
1) Level Check
Park the vehicle on a level ground and apply the parking brake. Stop the engine and wait more than 5
minutes.
Pull out the dipstick and wipe it with a clean cloth. Reinsert it all the way.
Pull out it again and check the oil level.
The oil level should be between the maximum (Max) mark and minimum (Min) mark on the oil dipstick.
Oil should be replenished before the level goes below the minimum mark. -
-
-
Operating vehicle with insufficient amount of oil can damage the engine. Make sure the engine oil
level is correct and add oil if necessary.
2) Replenishment
If the level gets to the lower point, open the filler cap on top of the cylinder block and add the genuine oil
without exceeding the level of the upper mark.
Recheck the oil level after 5 minutes.
Regularly check the engine oil level and add Ssangyong genuine engine oil if necessary.
Clean the dipstick with clean cloth so that any foreign materials cannot get into the engine.
The oil should not go above the upper mark on the dipstick.
The engine oil may be consumed more if the engine is new. -
-
-
-
Engine oil dipstickEngine oil filler
Page 376 of 600

1543-00
1. SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
1) Overview
The lubrication system supplies oil to each lubrication section to prevent friction and wear and to remove
heat from the friction part. As the engine runs, frictional heat is generated on each lubrication section. If
this condition persists, the bearing can be burned and stuck.
In other words, it creates an oil film on each sliding surface to convert solid friction to liquid friction in order
to minimize wear and prevent temperature increasing on the friction part.
For the D20DTF engine with no oil pressure switch, the engine ECU receives the low engine oil level
signal from the oil level sensor and communicates with the instrument cluster through the CAN
communication to turn on the warning lamp.
2) Components
Oil coolerOil dipstick gaugeOil pump
Oil filter moduleOil pressure switchOil pan
Page 377 of 600

2. FUNCTIONS OF LUBRICATION
1) Lubrication
It creates a viscous barrier between moving parts that reduces friction, which means less heat and
longer life for those parts. As a lubricant, oil must maintain a protective film to prevent metal-to-metal
contact. It must be fluid enough to allow easy starting and to circulate quickly through the engine, yet
remain thick enough at higher operating temperatures and speeds to provide adequate lubrication.
2) Cooling
Combustion heat and friction energy must be removed from the engine in order to prevent its
overheating. Most of heat energy is taken by the engine oil.
Clean oil passages, proper viscosity and low contamination provide sufficient flow rate of the engine oil
and effective cooling.
3) Sealing
It helps to seal the space between the pistons and the cylinder walls so that compression is more
effective and power is not lost during combustion.
4) Anti-corrosion
As a corrosion inhibitor, oil coats internal engine parts to prevent surface rust on the inside of the engine
which can be caused by blow-by products and water formed in combustion. It must also be capable of
neutralizing the acids that are formed by combustion blow-by and oil oxidation at high temperatures.
5) Cleaning
The small particles of dirt or other contaminants are suspended in oil and carried away to be filtered out.
As a detergent, engine oil must be able to gather and suspend dirt and other contaminants until the oil
can leave them as it passes through the filter and returns to the internal engine environment.
Page 378 of 600

1520-00
1. SPECIFICATION
Unit Description Specification
Cooling system Type Water cooling, forced circulation
Coolant Capacity approx. 8.5 L
Radiator Core size 662.1W x 510H x 27T
Flow type Cross flow
Min. cooling capacity over 72,000 kcal/h
Antifreeze Type Long life coolant
Mixing ratio
(water:antifreeze)50 : 50
Cooling fan module Type Electric
Capacity
Control type PWM type
Coolant reservoir Capacity over 1.5 L
Circulation Closed roof type
Pressure cap Screw type, 1.4bar
Vacuum valve Screw type, 1.4bar
Thermostat Type Wax pallet type
Opening temperature
Fully open temperature
Valve lift 8 mm
Page 379 of 600
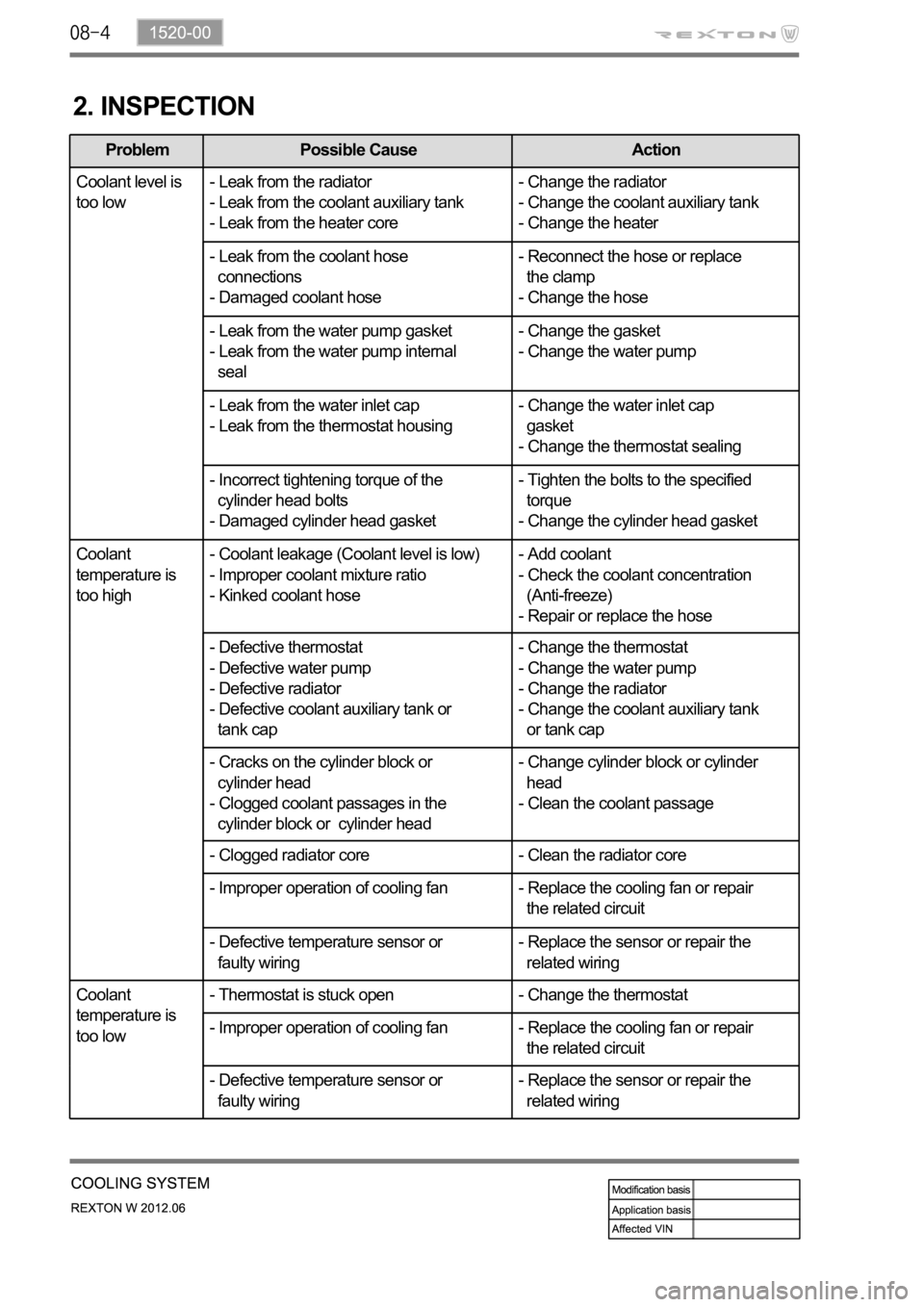
2. INSPECTION
Problem Possible Cause Action
Coolant level is
too low- Leak from the radiator
- Leak from the coolant auxiliary tank
- Leak from the heater core- Change the radiator
- Change the coolant auxiliary tank
- Change the heater
- Leak from the coolant hose
connections
- Damaged coolant hose- Reconnect the hose or replace
the clamp
- Change the hose
- Leak from the water pump gasket
- Leak from the water pump internal
seal- Change the gasket
- Change the water pump
- Leak from the water inlet cap
- Leak from the thermostat housing- Change the water inlet cap
gasket
- Change the thermostat sealing
- Incorrect tightening torque of the
cylinder head bolts
- Damaged cylinder head gasket- Tighten the bolts to the specified
torque
- Change the cylinder head gasket
Coolant
temperature is
too high- Coolant leakage (Coolant level is low)
- Improper coolant mixture ratio
- Kinked coolant hose- Add coolant
- Check the coolant concentration
(Anti-freeze)
- Repair or replace the hose
- Defective thermostat
- Defective water pump
- Defective radiator
- Defective coolant auxiliary tank or
tank cap- Change the thermostat
- Change the water pump
- Change the radiator
- Change the coolant auxiliary tank
or tank cap
- Cracks on the cylinder block or
cylinder head
- Clogged coolant passages in the
cylinder block or cylinder head- Change cylinder block or cylinder
head
- Clean the coolant passage
- Clogged radiator core - Clean the radiator core
- Improper operation of cooling fan - Replace the cooling fan or repair
the related circuit
- Defective temperature sensor or
faulty wiring- Replace the sensor or repair the
related wiring
Coolant
temperature is
too low- Thermostat is stuck open - Change the thermostat
- Improper operation of cooling fan - Replace the cooling fan or repair
the related circuit
- Defective temperature sensor or
faulty wiring- Replace the sensor or repair the
related wiring
Page 380 of 600

1520-00
1) Coolant Level Check
Park the vehicle on level ground and apply the parking brake. Stop the engine and wait until it is
cooled down.
The coolant level should be between the MAX and MIN mark on the coolant reservoir.1.
2.
Scalding hot coolant and steam could be blown out under pressure, which could cause serious
injury. Never remove the coolant reservoir cap when the engine and radiator are hot.
Avoid any direct contact of the coolant to the painted body of the vehicle. -
-