fuel SSANGYONG RODIUS 2006 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2006, Model line: RODIUS, Model: SSANGYONG RODIUS 2006Pages: 444, PDF Size: 56.32 MB
Page 157 of 444

0-12
RODIUS 2007.07
0000-00
CDEF(Catalytic Disel Particulate Filter)
6) CDPF Over Load (Notice of Beginning CPF Regeneration Mode
- P1430)
The CDPF system enters the regeneration mode when the mileage is around 600 ~ 1,200
km, depending on the driving condition and driving habits. At this moment, the ECU
performs the CDPF regeneration process; however, the driver may not notice anything
because there is no engine warning or other signals indicating such process.
The control logic in the regeneration process is to increase the exhaust gas temperature by
increasing the fuel injection during post injection process and controlling the intake ai
r
amount(throttle body), and no significant change can be noticed in the vehicle condition.
The engine CHECK lamp flashes but there is no decrease in engine torque.
The engine CHECK lamp flashes to inform the driver when there is an over load due to soot
accumulation because the regeneration temperature cannot be reached due to low speed,
even though CDPF regeneration is in process.
The CDPF regeneration process must be completed by driving for 15-20 minutes at a speed
higher than 80 km/h to solve this problem.
The engine CHECK lamp flashes when CDPF is over loaded; therefore, 4) above must be
performed in this case. 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
7) CDPF's Excessive Soot Accumulation (P0432)
When the vehicle is driven at a low speed (5-10 km/h) for a long time or long distance, the
soot over accumulates inside the CDPF and the combustion temperature cannot be reached
even by performing the soot combustion process. In this case, this DTC is generated.
This is more serious situation than the CDPF over load condition. Therefore, the engine
power is decreased to protect the system and the engine CHECK lamp is turned on.
Blow the soot between the engine and the exhaust system several times and clear the DTC
to solve this problem. If the same DTC is generated again, check the system according to
the DTC description related to the differential pressure sensor.
* This DTC is actually generated mostly due to the related system malfunction, such as
differential pressure sensor malfunction. 1.
2.
3.
Page 216 of 444

0-4
RODIUS 2007.07
8010-10
CLUSTER
2. DESCRIPTIONS OF INDICATOR DISPLAY
1. Immobilizer indicator
2. Glow indicator
3. Winter mode indicator
4. Left turn signal indicator
5. Auto shift indicator (for automatic transmission)
6. Right turn signal indicator
7. Harzard indicator*
8. Engine check warning light
9. Cruise control indicator*
10. 4WD CHECK warning light
11. 4WD HIGH indicator
12. 4WD LOW indicator
13. Brake warning light14. Battery charge warning light
15. Seat belt reminder
16. Low fuel level warning light
17. Heated glass indicator
18. Door open warning light
19. High beam indicator
20. Engine oil pressure warning light
21. Air bag warning light
22. Water separator warning light
23. ABS warning light
24. EBD warning light
25. ESP warning light
Page 222 of 444
0-10
RODIUS 2007.07
8010-10
CLUSTER
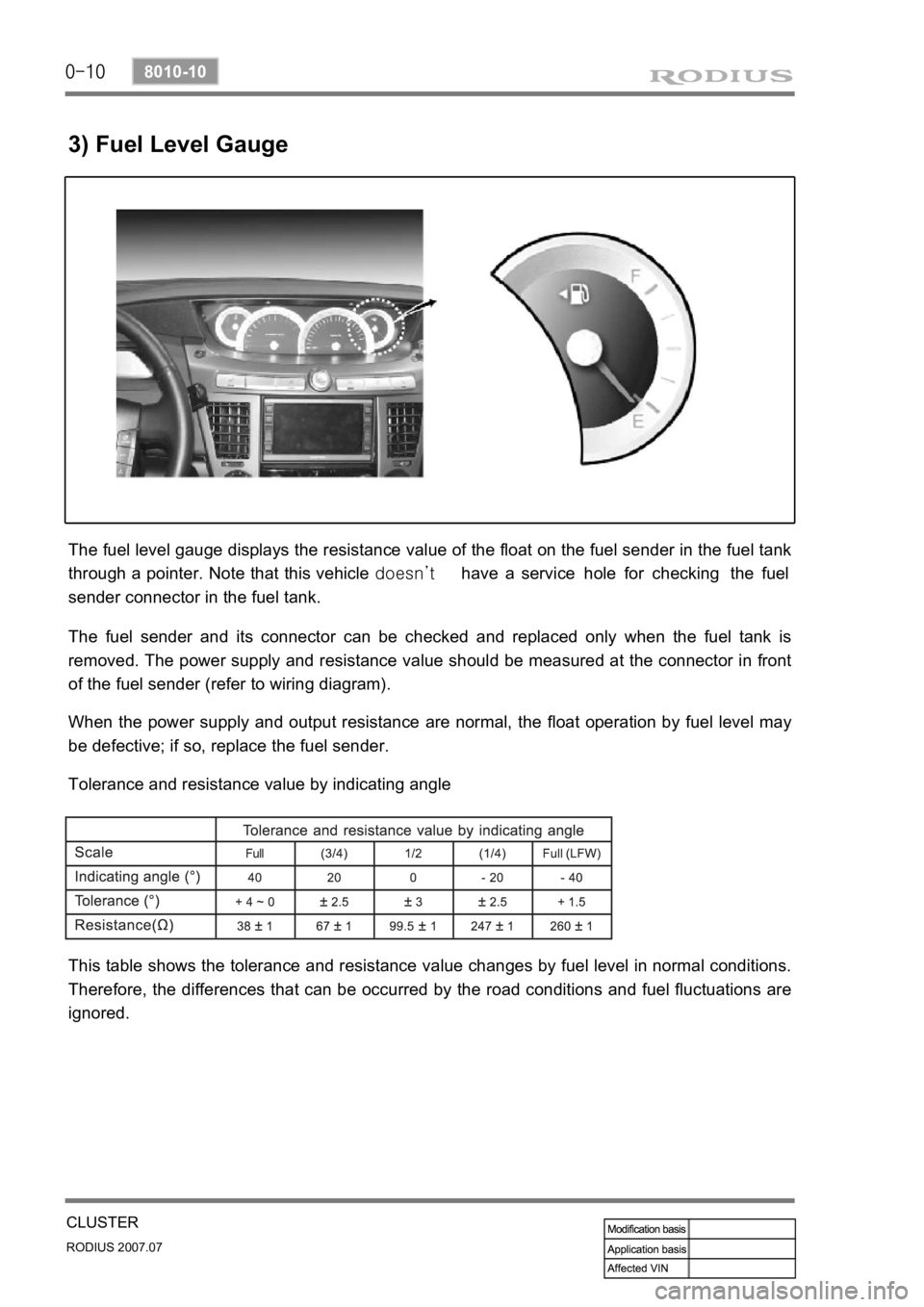
3) Fuel Level Gauge
The fuel level gauge displays the resistance value of the float on the fuel sender in the fuel tank
through a pointer. Note that this vehicle doesn’t have a service hole for checking the fuel
sender connector in the fuel tank.
The fuel sender and its connector can be checked and replaced only when the fuel tank is
removed. The power supply and resistance value should be measured at the connector in front
of the fuel sender (refer to wiring diagram).
When the power supply and output resistance are normal, the float operation by fuel level may
be defective; if so, replace the fuel sender.
Tolerance and resistance value by indicating angle
This table shows the tolerance and resistance value changes by fuel level in normal conditions.
Therefore, the differences that can be occurred by the road conditions and fuel fluctuations are
ignored.
Page 352 of 444

0-8
RODIUS 2007.07
4710-09
WHEEL
3. WHEEL ALIGNMENT
The first responsibility of engineering is to design safe steering and suspension systems. Each
component must be strong enough to with stand and absorb extreme punishment.
Both the steering system and the front and the rear suspension must function geometrically
with the body mass.
The steering and suspension systems require that the front wheels self-return and that the tire
rolling effort and the road friction be held to a negligible force in order to allow the customer to
direct the vehicle with the least effort and the most comfort.
A complete wheel alignment check should include measurements of the rear toe and camber.
1) Toe-in
2) Camber
Toe-in is the turning in of the tires, while toe-
out is the turning out of the tires from the
geometric centerline or thrust line. The toe
ensures parallel rolling of the wheels.
The toe serves to offset the small deflections
of the wheel support system which occu
r
when the vehicle is rolling forward.
The specified toe angle is the setting which
achieves-degrees “0°” of toe when the
vehicle is moving.
Incorrect toe-in or toe-out will cause tire
wear and reduced fuel economy. As the
individual steering and suspension
components wear from vehicle mileage,
additional toe will be needed to compensate
for the wear. Always correct the toe
dimension last.
Camber is the tilting of the top of the tire
from the vertical when viewed from the front
of the vehicle. When the tires tilt outward,
the camber is positive. When the tires tilt
inward, the camber is negative. The cambe
r
angle is measured in degrees from the
vertical. Camber influnces both directional
control and tire wear.
If the vehicle has too much positive camber,
the outside shoulder of the tire will wear. I
f
the vehicle has too much negative camber,
the inside shoulder of the tire will wear.
Camber is measured in degrees and is not
adjustable.
Page 357 of 444

0-6
RODIUS 2007.07
6810-20
AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM
3. FFF GENERAL INFORMATION
The system is to increase the coolant temperature quickly by firing diesel fuel in the burner that
is installed in engine cooling system when in winter time the ambient temperature and engine
coolant temperature is low. (Option)
FFH System consists of independent fuel lines, fuel pump, coolant circuit, coolant ciculation
pump, electrical glow plug and exhaust system by driver’s intention because FFH system
is automatically.
Operated according to the coolant temperature and the ambient temperature.
FFH system operates up to more than 2 minutes to burn the residual fuel inside the system
when driver stop the engine during its operation. Therefore, a certain period of FFH operation
after stopping the engine is not a malfunction.