air condition SSANGYONG RODIUS 2012 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2012, Model line: RODIUS, Model: SSANGYONG RODIUS 2012Pages: 715, PDF Size: 79.36 MB
Page 512 of 715

09-58790-01
2. CAUTIONS
The parking aid system is just a supplemental device to help your parking.
Always keep the safety precautions.
Do not press or shock the sensors by hitting or using a high-pressure water gun while
washing, since it may damage the sensors.
If the system is in normal operating condition, a short beep sounds when the shift lever is
moved into "R" position with the ignition key "ON".
If the system is defective, the warning buzzer sounds for 3 seconds when moving the gear
<009a008f0090008d009b00470093008c009d008c00990047009b0096004702c8007902c9004700970096009a0090009b0090009600950047009e0090009b008f0047009b008f008c00470090008e00950090009b0090009600950047007600750055004700
69008c0047008a00880099008c008d009c0093004700950096>t to confuse this and the parking
aid alarm (in 50 cm). 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
· Note that the display does not show everything in the rear area. Always check
nobody, especially animals and children, is behind the vehicle when parking or
reversing.
· If you can not properly check the vehicle behind, get out of the vehicle and then
visually check it.
The parking aid system will not work or improperly work under following cases: ▶
1) Certain obstacles that sensors can not detect
Thin and narrow objects, such as wires, ropes, chains
Cotton, sponge, clothes, snow; that absorb ultrasonic waves
Obstacles lower than the bumper (ex. drain ditch or mud puddle) -
-
-
2) Not defective but improperly working
When the sensing portion is frozen (operates normally after thawed)
When the sensing portion is covered by rain, water drops, snow or mud (operates normally
after cleaned)
When receiving other ultrasonic signals (metal sound or air braking noises from heavy
commercial vehicles)
When a high-power radio is turned on -
-
-
-
3) Narrowed sensing area
When the sensing portion is partially covered by snow or mud (operates normally after cleaned)
<007a009c009900990096009c0095008b00900095008e0047009b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c00470096008d0047009a008c0095009a0096009900470090009a0047009b009600960047008f0090008e008f0047004f00880097009700
990096009f005500470096009d008c00990047005f005700b6>C) or too low
(approx. below -30°C) -
-
4) Not defective but may cause malfunction
When driving on the rough roads, gravel road, hill and grass
When the bumper height is changed due to heavy load
When the sensing portion is frozen
When the sensing portion is covered by rain, water drops, snow or mud
When receiving other ultrasonic signals (metal sound or air braking noises from heavy
commercial vehicles)
When a high-power radio is turned on
When some accessories are attached in detecting ranges -
-
-
-
-
-
-
Page 636 of 715

10-74891-01
2) EBD (Electronic Brake Force Distribution) System
▶System description
As an add-on logic to the ABS base algorithm, EBD works in a range in which the intervention
thresholds for ABS control are not reached yet.
EBD ensures that the rear wheels are sensitively monitored for slip with respect to the front axle. If slip is
detected, the inlet valves for the rear wheels are switched to pressure hold to prevent a further increase
in pressure at the rear-wheel breaks, thus electronically reproducing
a pressure-reduction function at the rear-wheel brakes.
ABS features an enhanced algorithm which includes control of the brake force distribution between the
front and rear axles. This is called Electronic Brake Distribution. In an unloading car condition the brake
efficiency is comparable to the conventional system but for a fully loaded vehicle the efficiency of the
EBD system is higher due to the better use of rear axle braking capability.
▶Advantages
Elimination of conventional proportioning valve EBD utilizes the existing rear axle wheel speed
sensor to monitor rear wheel slip.
Based on many variables in algorithm a pressure hold, increase and/or decrease pulsetrain may be
triggered at the rear wheels insuring vehicle stability.
Vehicle approaches the ideal brake force distribution (front to rear).
Constant brake force distribution during vehicle lifetime.
EBD function is monitored via ABS safety logic (conventional proportioning valves are not
monitorable). ·
·
·
·
·
3) Important Notice
The modulators for production line are not filled with the brake fluid (dry type). But, for after service, they
are filled with the brake fluid (wet type).
Make sure to keep the procedures in service manual when bleeding the air from the brake lines.
Be familiar with the lamp ON conditions to provide the correct information and reliability to customers.
ECU monitors the valve and motor for ABS when the vehicle speed approaches 5 km/h. At this time, you
can hear the clattering noise. 1.
2.
3.
Page 657 of 715

01-2
Front air conditioner module assembly - inside instrument panel
Compressor - engine rightAQS/Air source selection
switch
Sun load sensor - instrument
panel upper left
1. SYSTEM LAYOUT AND COMPONENTS
Type Air cindotioner controller
FATC
Manual air
conditioner
It change sun load coming through
front windshield into current to input to
FATC controller. *
Air mix door
actuator
PTC (If equipped)
Duct temperature
sensor
Mode door
actuator
Air conditioner wiring
Thermo AMP
Air source door
actuator
Air conditioner
filter
Bloewr motor
Blower high speed relayPower transistor
Page 658 of 715

01-36810-30
Rear air conditioner module assembly - bottom of rear left
Engine ECU - passenger's
footstep
CondenserRecevier driver-condenser
right
Rear fan speed dial
Sub-condenser - right wheel
front
Absorbs moisture in the
refrigerant and reserves
refrigerant to supply
smoothly. *Instslled in front of vehicle and
condenses vapor refrigerant into
low temperature and high
pressure liquid refrigerant *
Condenses high temperature and
high pressure vapor refrigerant into
low-temperature-high-pressure
liquid refrigerant. *
Detects A/C AUTO switch position,
coolant temperature, engine
condition and driving condition to
control the air conditioner *
A sensor that detects coolant
temperature and transmits to
engine ECU *
Blower motor
Power transistor
Air conditoner high
pressure/low
pressure pipe
Air mix door
actuator
Front
Rear
A switch that controls the rear air
conditioner module. *
Collant temperature sensor -
on engine
Page 660 of 715

01-56810-30
(2) Ventilation Modes
Vent mode * Bi-level mode*
Floor mode * Defrost and floor mode*
Defrost mode * Rear air conditioning mode*
Page 661 of 715

01-6
2) AIR CONDITIONER MODULE WIRING AND LAYOUT
(1) Front Air Conditioner Module
Air source selection
door actuator
Air conditioner
filterEvaporator
Blower motor
Blower high
speed relay
Heater core
Wiring layout
Components
Page 662 of 715

01-76810-30
(2) Rear Air Conditioner Module
Roof air conditioner duct
Blower motor
Evaporator
Mixer door
Heater core
Air mixer door actuator
Rear floor
heater duct
Heater &
air conditioner
pipes
Wiring layout
Components
Page 667 of 715
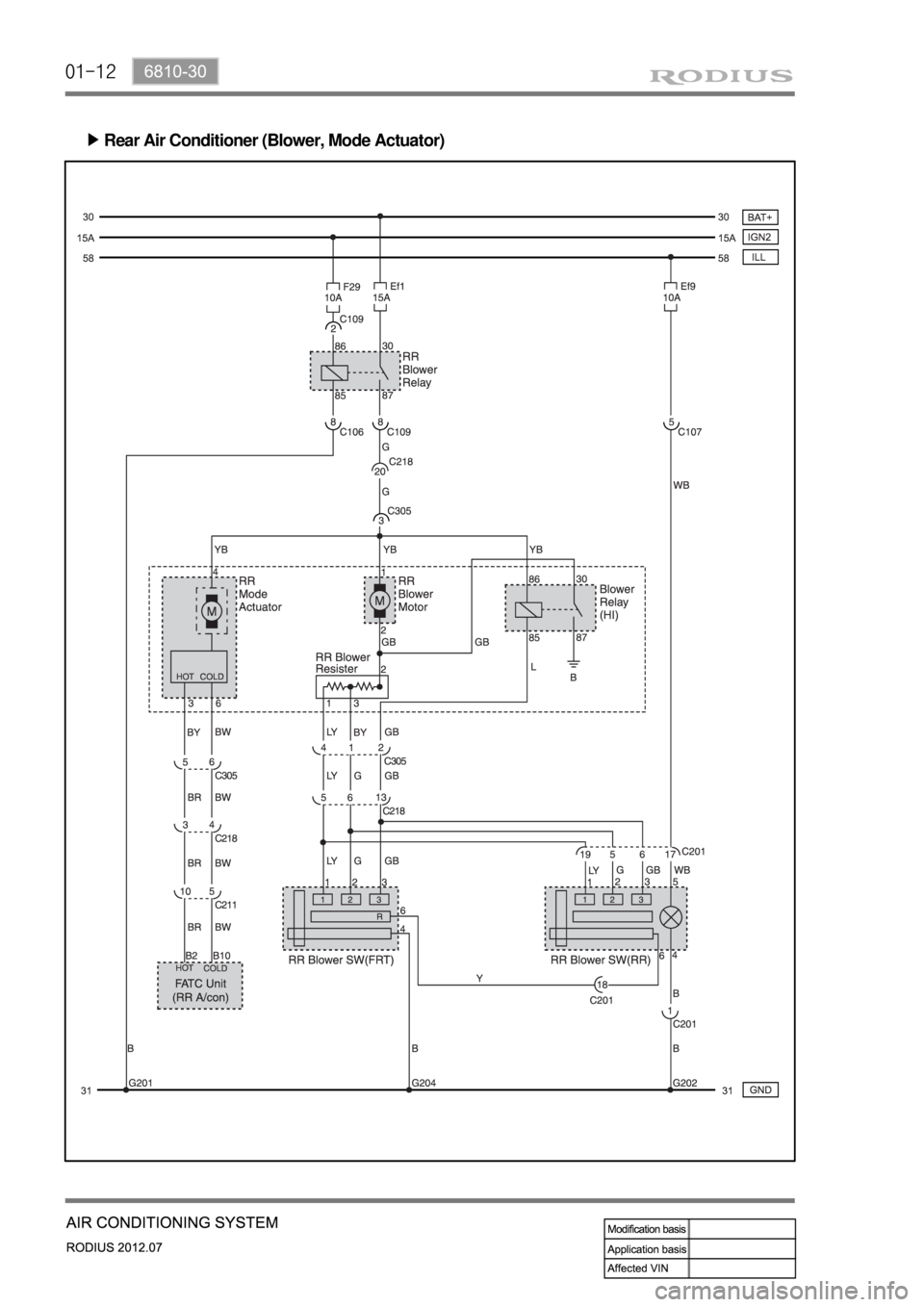
01-12
Rear Air Conditioner (Blower, Mode Actuator) ▶
Page 668 of 715

01-136810-30
2) Manual Air Conditioner
D20DTR, Motor (Mode, Intake, Air Mix, PWM) ▶