light SSANGYONG TURISMO 2013 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2013, Model line: TURISMO, Model: SSANGYONG TURISMO 2013Pages: 796, PDF Size: 78.99 MB
Page 497 of 796
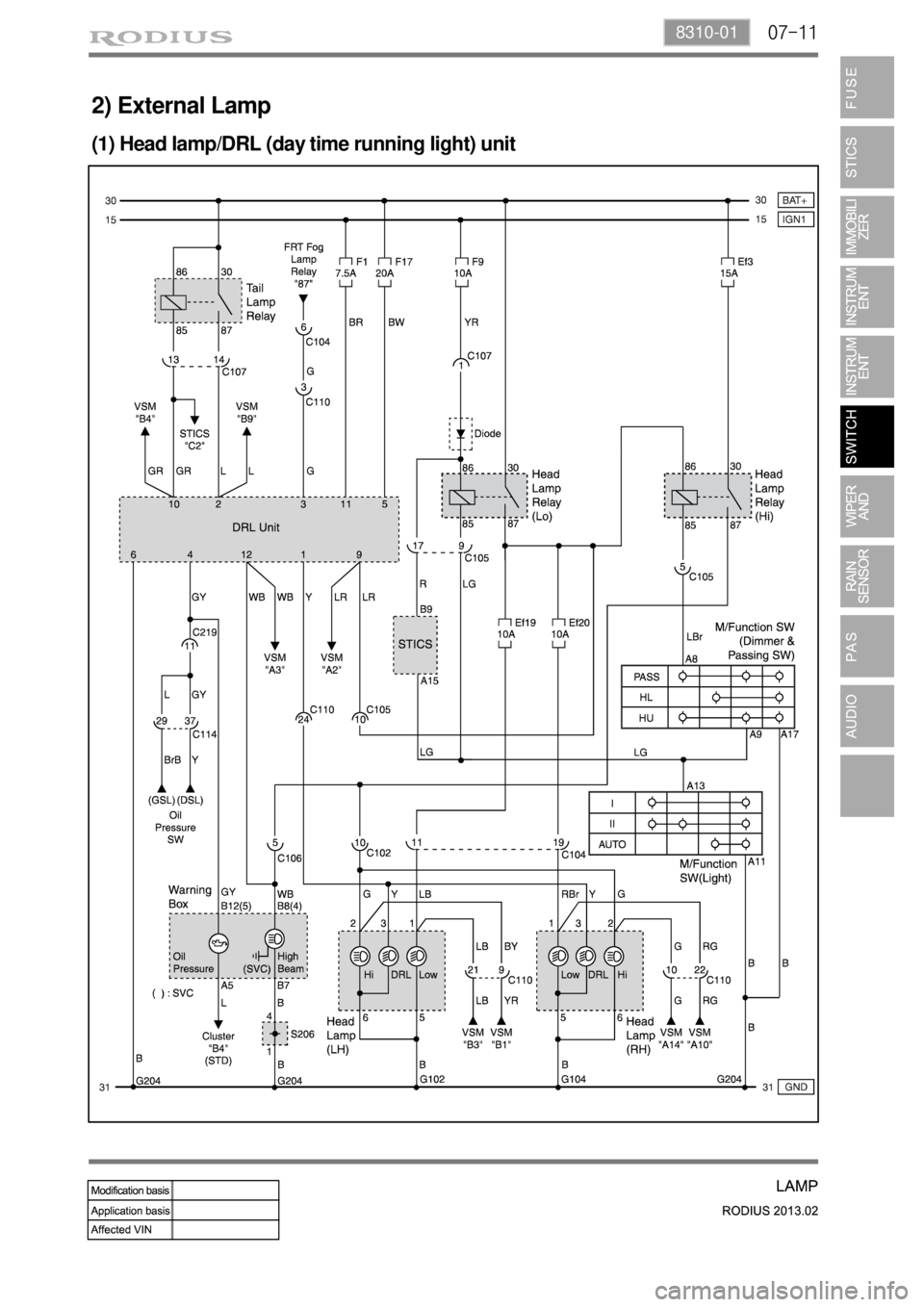
07-118310-01
2) External Lamp
(1) Head lamp/DRL (day time running light) unit
Page 504 of 796

06-4
4) Multifunction Switch
Description Description
Multifunction
switchRated voltage DC 12 V
Operating temperature-30℃~+80℃
Rated loadLight switch ON: 1A (Relay load)
Dimmer and passing switch High beam/low beam/passing:
0.3 A (Relay load)
Turn signal switch6.6±0.5 A (Lamp load)
Wiper switchLow: 5 A (Motor load)
High: 7 A (Motor load)
Auto: 0.22±0.05 A (Relay load)
Fixed: max. 28 A (Motor load)
Washer switch 4 A (Motor load)
Intermittent wiper switch max. 25 mA
Mist switch 5 A (Motor load)
Page 509 of 796
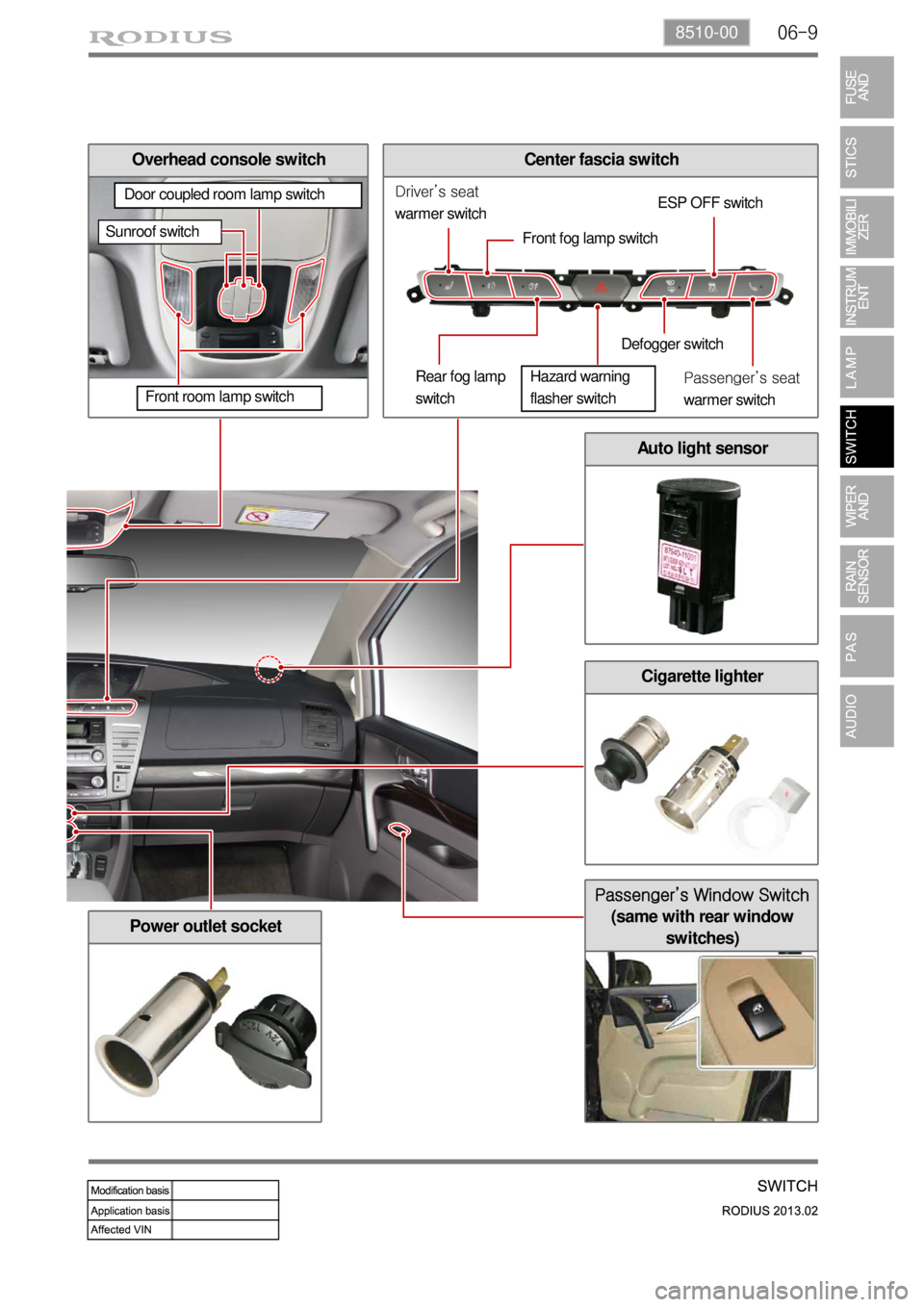
06-98510-00
Center fascia switch
Passenger’s Window Switch
(same with rear window
switches)
Overhead console switch
Auto light sensor
Cigarette lighter
Power outlet socket
Driver’s seat
warmer switch
Rear fog lamp
switchESP OFF switch
Defogger switch
Passenger’s seat
warmer switch Front fog lamp switch
Front room lamp switch
Sunroof switch
Door coupled room lamp switch
Hazard warning
flasher switch
Page 515 of 796

08-38610-11
The rain sensing wiper unit in this vehicle doesn’t control the wiper directly.
The rain sensing unit detects the amount of rain drops and sends the operating signal to STICS, and
STICS drives the wiper directly.
1. SYSTEM LAYOUT AND OVERVIEW
Rain sensing unitMultifunction wiper switch:
AUTO and sensitivity control
A sensor that emits infrared rays through LED
and then detects the amount of rain drops by
receiving reflected rays against sensing
section(rain sensor mounting section on the
windshield)with photodiode. AUTO
: Wiper operates automatically by rain sensor
FAST <-------> SLOW
: Auto delay/Auto speed control. A position
that can control sensitivity against rains on
the windshield and transmits wiping demand
signal accordingly.
Emitter lens
The LED which is located
at bottom emits the
infrared rays and the lens
guides the infrared rays to
target point.
Enlarged auto light
sensor section
Auto light sensor
Auto light sensor (Horizon)
Auto light sensor (Vertical)
Page 551 of 796
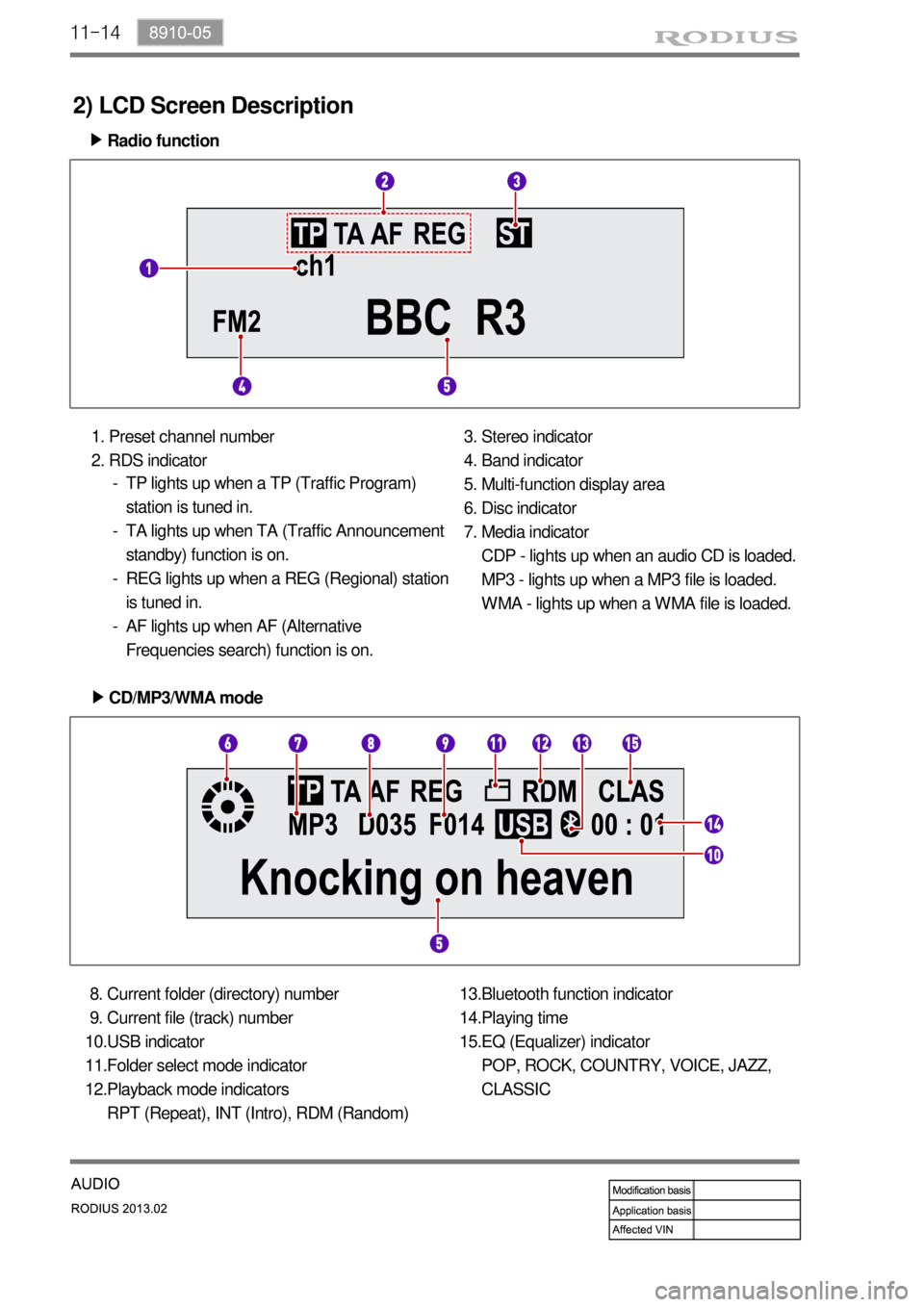
11-14
2) LCD Screen Description
Radio function ▶
Preset channel number
RDS indicator 1.
2.Stereo indicator
Band indicator
Multi-function display area
Disc indicator
Media indicator
CDP - lights up when an audio CD is loaded.
MP3 - lights up when a MP3 file is loaded.
WMA - lights up when a WMA file is loaded. 3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
CD/MP3/WMA mode ▶
Current folder (directory) number
Current file (track) number
USB indicator
Folder select mode indicator
Playback mode indicators
RPT (Repeat), INT (Intro), RDM (Random) 8.
9.
10.
11.
12.Bluetooth function indicator
Playing time
EQ (Equalizer) indicator
POP, ROCK, COUNTRY, VOICE, JAZZ,
CLASSIC 13.
14.
15.
TP lights up when a TP (Traffic Program)
station is tuned in.
TA lights up when TA (Traffic Announcement
standby) function is on.
REG lights up when a REG (Regional) station
is tuned in.
AF lights up when AF (Alternative
Frequencies search) function is on. -
-
-
-
Page 592 of 796

03-6
Pedal free play ▶
Pedal free play (A) A.
Stop the engine.
Measure the current pedal position.
Lightly depress the clutch pedal until you feel
the resistance from the pedal and measure
the distance. 1)
2)
3)
Free play (A)5 ~ 15 mm
Adjustment-
Release the lock nut (B) from the master
cylinder.
Turn the push rod (C) to adjust the pedal
free play.
Tighten the lock nut to the specified
tightening torque. 1)
2)
3)
Page 700 of 796

12-54170-01
1. OVERVIEW
A radial tire uses a cord angle of 90 degrees. That is, the cord material runs in a radial or direct line
from one bead to the other across the tread. In addition, a radial tire has a belt overwrap under the
tread surface to provide greater structural stability. The belt overwrap of a radial tire distortion while the
radial structure enables high speed driving.
Tire supports the weight of the vehicle, reduces the impact from the road and at the same time,
transmits the power to propel, brake and steer on the road. It also functions to maintain a
vehicle’s movement. In order to complete such tasks, a tire must be structured to be a resilient
vessel of air.
There is wear limit mark on the tire, which protrudes as a strip shape located approximately 1.6 mm
from the groove bottom. This wear limit mark is not seen from the outside so there is additional
"▲" mark on the shoulder to let the driver find the wear mark easily. To measure the tire groove
depth, measure at any point other than the point which has a wear limit mark.
The tire is worn unevenly according to the driver's driving habit, improper servicing, low tire inflation
pressure, changed tire location, etc.
1) Structure of Tire
Tread
This thick layer of rubber provides the interface
between the tire and the road. Wear-resistant
rubber is used to protect the carcass and belt
against fractures and impacts and to deliver a
long driving life.
Shoulder
Located between the tread and sidewall, the
shoulder rubber is the thickest so that the
design must allow for the easy diffusion of heat
generated within the tire while driving.
Sidewall
The part between the shoulder and bead, the
flexible sidewall protects the carcass and
enhances the ride. A tire’s type, size,
structure, pattern, manufacturing company,
product name and various characters are
indicated here. Bead
The bead attaches the tire to the rim and wraps
the end of the cord fabric. Comprised of the bead
wire, core, flipper and other parts, the bead is
generally designed to be slightly tight around the
rim so that in the case of a sudden drop in
inflation pressure, the tire will not fall off the rim.
Carcass
As the most important framework of a tire, the
entire inner layer of cord fabric is called the
carcass. The carcass acts to support air
pressure, vertical load and absorb shocks.
Valve
Belt
Bead core
Page 732 of 796

02-4
2. OPERATION
1) Air Bag
▶Air bag inflates when:
In response to a severe frontal impact, the driver’s and front passenger’s air bags
deploy at the same time to supplement the seat belts to prevent or reduce any personal
injuries. -
▶Air bag can inflate when:
Underbody impact from the road surface; impact against the curb at a very high speed;
dropping impact onto the road surface with a large angle -
▶Air bag does not inflate when:
Rollover, side impact or rear impact
If the severity of impact to the vehicle is not significant and the seat belts are enough to protect
occupants. -
-
Air bag seldom inflates when: ▶
Oblique impact, rollover
Weak impact in which the sensor is unable to detect (under the inflation requirements)
Impact against narrow objects such as a utility pole or a tree
The vehicle falls into a drainage or a puddle
The front of the vehicle crashes into a high impact point vehicle such as a truck
Impact on the hood by falling stones
The air bag warning light is on
Moderate or severe impact to the middle of the vehicle body’s side structure. In that case,
only the side curtain air bags deploy. -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Page 740 of 796

02-12
4. OPERATION PROCESS
1) Air Bag System Block Diagram
The overall air bag operation process and its functions and roles are broadly explained in this block
diagram. This diagram summarizes and highlights the functions adopted by Ssangyong Motors. -