SSANGYONG TURISMO 2013 Service Manual
Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2013, Model line: TURISMO, Model: SSANGYONG TURISMO 2013Pages: 796, PDF Size: 78.99 MB
Page 691 of 796
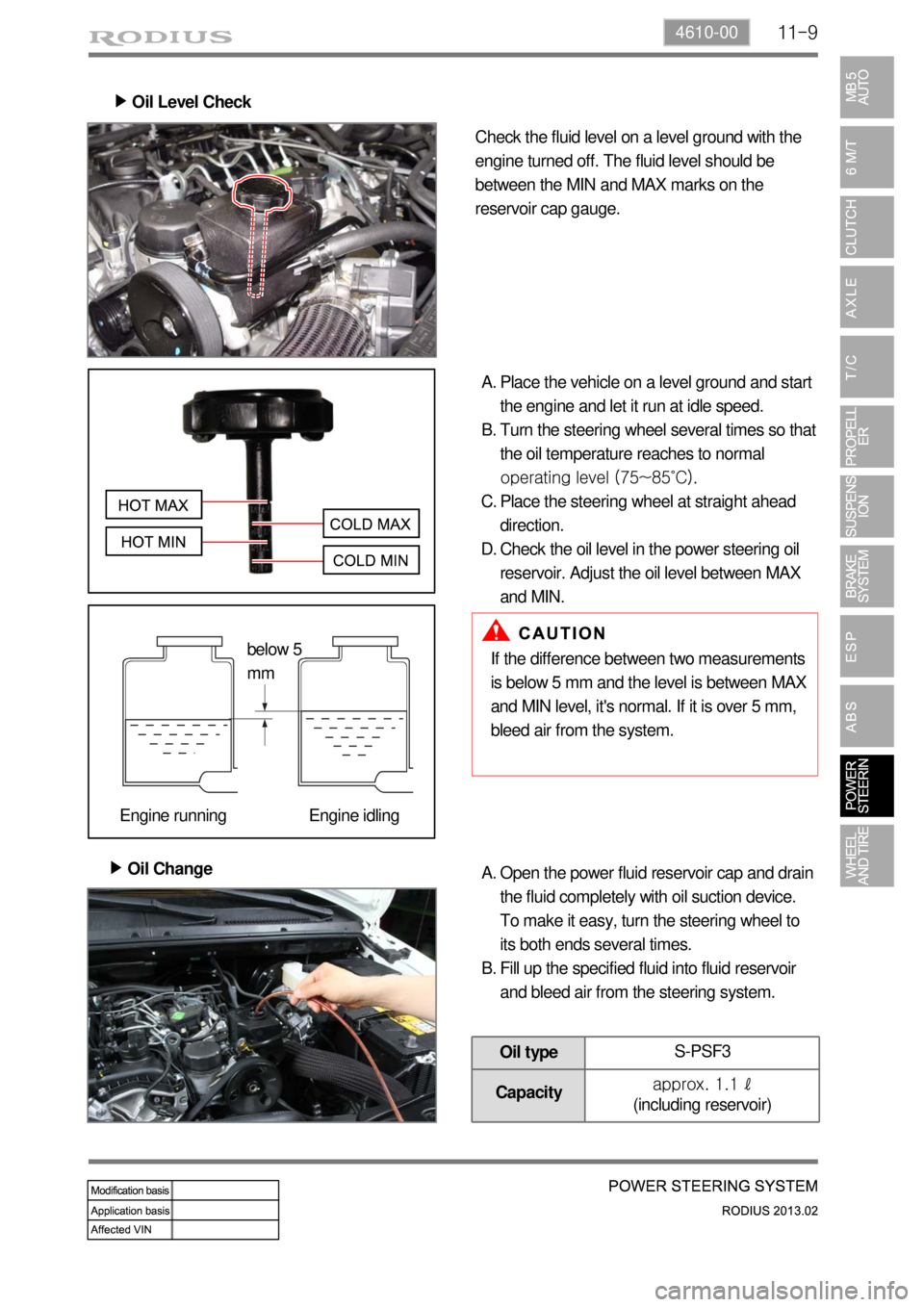
11-94610-00
Oil Level Check ▶
Check the fluid level on a level ground with the
engine turned off. The fluid level should be
between the MIN and MAX marks on the
reservoir cap gauge.
Place the vehicle on a level ground and start
the engine and let it run at idle speed.
Turn the steering wheel several times so that
the oil temperature reaches to normal
operating level (75~85˚C).
Place the steering wheel at straight ahead
direction.
Check the oil level in the power steering oil
reservoir. Adjust the oil level between MAX
and MIN. A.
B.
C.
D.
Oil Change ▶
If the difference between two measurements
is below 5 mm and the level is between MAX
and MIN level, it's normal. If it is over 5 mm,
bleed air from the system.
Open the power fluid reservoir cap and drain
the fluid completely with oil suction device.
To make it easy, turn the steering wheel to
its both ends several times.
Fill up the specified fluid into fluid reservoir
and bleed air from the steering system. A.
B.
Oil typeS-PSF3
Capacityapprox. 1.1 ℓ
(including reservoir)
below 5
mm
Engine running Engine idling
Page 692 of 796

11-10
Air Bleeding ▶
The air bleeding should be done after servicing
the power steering system and when the
difference between two measurements (cooled
and normal temperature) is prominent.
Normal
AbnormalLift up the vehicle very carefully.
Turn the steering wheel to its both ends
several times and add the oil up to MAX line
in the steering oil reservoir.
Periodically crank the starting motor and turn
the steering wheel to its both ends without
any interruption.
Check the oil level again. If the oil level is
fluctuated, repeat the procedures from step
3 to step 5.
Start the engine.
Turn the steering wheel to its both ends until
any bubble can be found in the steering oil
reservoir.
Perform the test drive and check the
steering wheel for normal operation and
noise.
If the oil level abruptly goes up, bleed the air
from the system again. A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
F.
G.
H.
If the air bleeding is not properly performed,
the life span of the power steering pump
may be shortened. -
Page 693 of 796

11-114610-00
Oil Pump Pressure Check ▶
Check the oil pump pressure to locate any
defect in oil pump.
Before checking the pressure, check the oil
level and belt tension. Prepare the empty
container to collect the spilled oil during the
service.
Unscrew the pressure line fitting in power
steering pump.
Install the pressure gauge between the
power steering pump and the power steering
oil pressure line.
Place the shift lever to neutral position. Apply
the parking brake.
Open the valve in pressure gauge. Start the
engine and let it run at idle speed.
Turn the steering wheel several times so that
the oil temperature reaches to normal
operating level. A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Fully close the valve in pressure gauge and
measure the oil pressure. F.
To prevent internal damage, do not close the
gauge valve over 10 seconds.
Keep the oil temperature at proper range. -
-
Relief pressure93.3 ~ 100.4 kgf/cm²
Page 694 of 796

11-12
Measure the oil pressure with the gauge
valve fully open. G.
Pressure at no load3 ~ 5 bar
If the pump pressure is in specified range,
the pump is normal. If not, replace the power
steering pump H.
Turn the steering wheel right or left until it
stops with the engine idling and valve fully
open. I.
Oil pressure78 ~ 83 bar
Page 695 of 796

11-134610-00
1. OVERVIEW
The power steering has been designed to make the wheel move more easily than in a manual steering
system. The hydraulic power assists the process utilizing hydraulic fluid. The fluid increases pressure
in the power steering pump and aids the movement of the steering mechanism. The power steering
system consists of pump, oil reservoir, rack and gear box. The power steering pump is a vane type
and delivers hydraulic pressure to operate the power steering system. The pressure relief valve in the
pump controls the discharging pressure. The rotary valve in the rack and the pinion gear directs the oil
from the power steering pump to one side of the rack piston. The integrated rack piston converts the
hydraulic pressure to linear movement. The operating force of the rack moves the wheels through the
tie rod, the tie rod end and the steering knuckle. Even though the hydraulic pressure cannot be
generated, a driver can steer the vehicle without power assist but it needs very high steering force. In
this case, the operating force of the steering wheel is conveyed to the pinion, and the movement of the
pinion moves the rack through the pinion gear combined to the rack gear.
Page 696 of 796
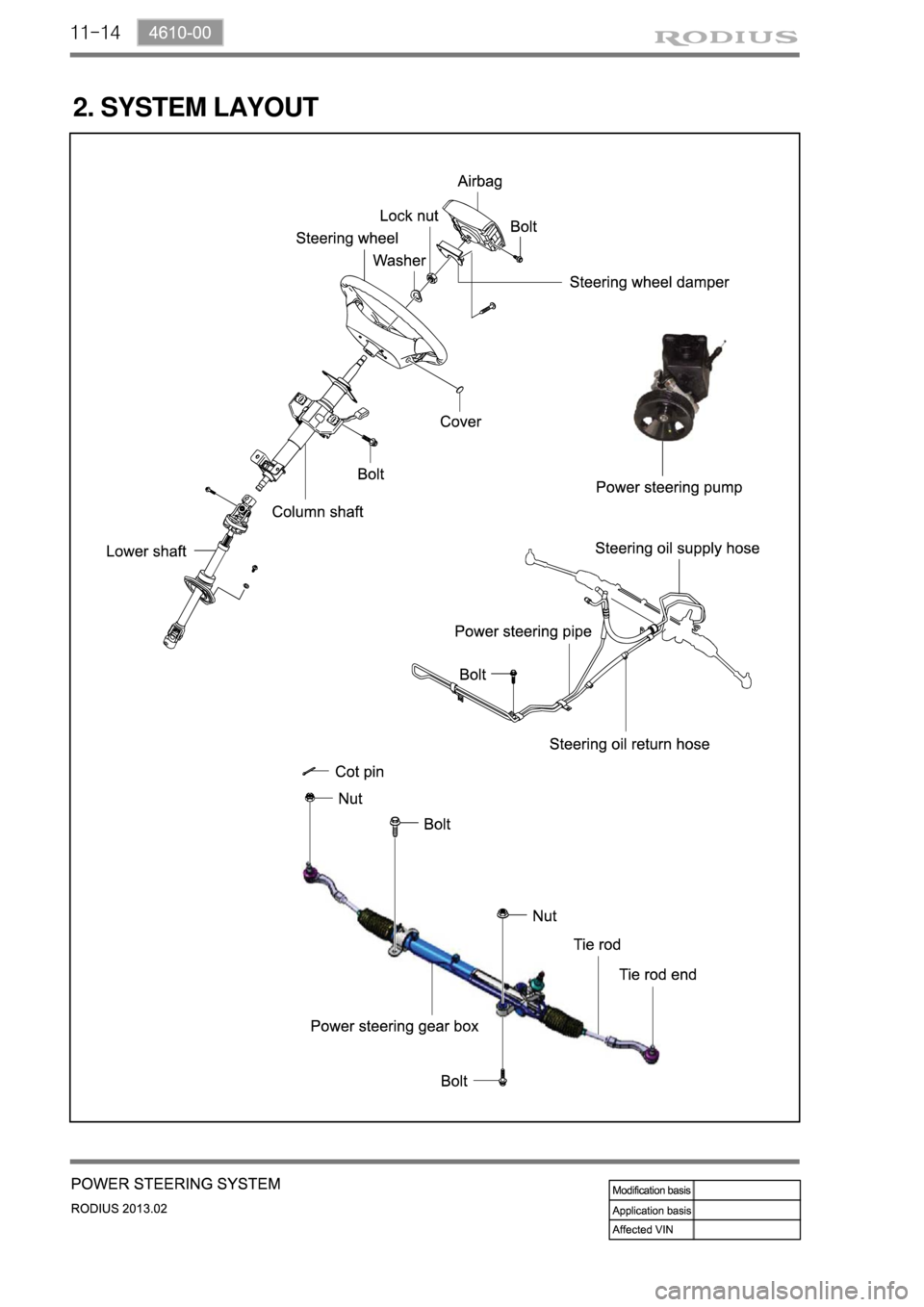
11-14
2. SYSTEM LAYOUT
Page 697 of 796

11-154610-00
The steering pump is driven by the engine power through a belt. This pump circulates the power
steering oil from the reservoir -> steering pump -> oil supply pipe -> steering gear box -> oil return pipe
-> reservoir to perform steering operations
Return hose & tube
Lower shaft Column & shaft
Steering wheel
Power steering gear boxHigh pressure hosePower steering
pump & tank
Return line
High pressure line
Steering pump Steering return pipe Steering cylinder
Page 698 of 796

12-34170-01
1. SPECIFICATION
Description Specification
Tire 16 inch 225/65R16
17 inch 235/60R17
Tire inflation pressure 35 psi
Wheel 16 inch 6.5JX16
17 inch 7.0JX17
Balance weight Inner: Clip-on type
Outer: Tape type
Tightening torques of wheel bolt 127.4 to 156.8 Nm
Wheel offset 2WD 38 mm
4WD 50 mm
Page 699 of 796

12-4
Spare Tire & Winch Assembly
- Spare tire specification added (same as one fitted to vehicle with standard wheel and tire)
Wheel assembly
16 inch (6.5JX16) 17 inch (7.0JX17)
2WD 4WD 2WD 4WD
225/65R16 235/60R17
- 16 inch wheel design changed (same as before for tire size)
- 17 inch wheel specification added (235/60R17 tire)
2. CHANGES
Wheel tire design changed and specification added ▶
With spare tire ▶
Spare tire
Winch assembly
Page 700 of 796

12-54170-01
1. OVERVIEW
A radial tire uses a cord angle of 90 degrees. That is, the cord material runs in a radial or direct line
from one bead to the other across the tread. In addition, a radial tire has a belt overwrap under the
tread surface to provide greater structural stability. The belt overwrap of a radial tire distortion while the
radial structure enables high speed driving.
Tire supports the weight of the vehicle, reduces the impact from the road and at the same time,
transmits the power to propel, brake and steer on the road. It also functions to maintain a
vehicle’s movement. In order to complete such tasks, a tire must be structured to be a resilient
vessel of air.
There is wear limit mark on the tire, which protrudes as a strip shape located approximately 1.6 mm
from the groove bottom. This wear limit mark is not seen from the outside so there is additional
"▲" mark on the shoulder to let the driver find the wear mark easily. To measure the tire groove
depth, measure at any point other than the point which has a wear limit mark.
The tire is worn unevenly according to the driver's driving habit, improper servicing, low tire inflation
pressure, changed tire location, etc.
1) Structure of Tire
Tread
This thick layer of rubber provides the interface
between the tire and the road. Wear-resistant
rubber is used to protect the carcass and belt
against fractures and impacts and to deliver a
long driving life.
Shoulder
Located between the tread and sidewall, the
shoulder rubber is the thickest so that the
design must allow for the easy diffusion of heat
generated within the tire while driving.
Sidewall
The part between the shoulder and bead, the
flexible sidewall protects the carcass and
enhances the ride. A tire’s type, size,
structure, pattern, manufacturing company,
product name and various characters are
indicated here. Bead
The bead attaches the tire to the rim and wraps
the end of the cord fabric. Comprised of the bead
wire, core, flipper and other parts, the bead is
generally designed to be slightly tight around the
rim so that in the case of a sudden drop in
inflation pressure, the tire will not fall off the rim.
Carcass
As the most important framework of a tire, the
entire inner layer of cord fabric is called the
carcass. The carcass acts to support air
pressure, vertical load and absorb shocks.
Valve
Belt
Bead core