SUBARU IMPREZA WRX 2014 4.G Owners Manual
Manufacturer: SUBARU, Model Year: 2014, Model line: IMPREZA WRX, Model: SUBARU IMPREZA WRX 2014 4.GPages: 414, PDF Size: 14.22 MB
Page 381 of 414
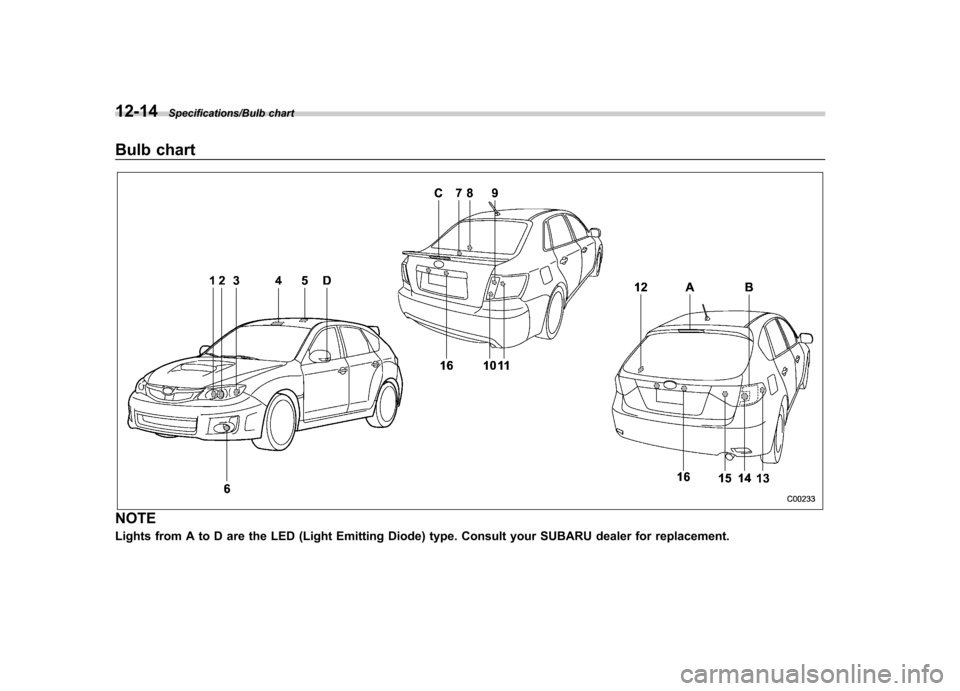
12-14Specifications/Bulb chart
Bulb chart
NOTE
Lights from A to D are the LED (Light Emitting Diode) type. Consult your SUBARU dealer for replacement.
Page 382 of 414

Wattage Bulb No.
1) High beam headlight 12V-60W 9005 (HB3)
2) Low beam headlight
Models with HID light 12V-35W D2S
Models with halogen light 12V-55W H11
3) Front turn signal light/Front side marker light 12V-27/8W 1157NA
4) Map light 12V-8W–
5) Dome light 12V-8W–
6) Front fog light 12V-51W 9006 (HB4)
7) Trunk light (4-door) 12V-5W 168 (W5W)
8) High-mounted stop light (4-door, if equipped) 12V-21W (P21W)
9) Rear turn signal light (4-door) 12V-21W (WY21W)
10) Backup light (4-door) 12V-16W 921
11) Stop light/Tail and rear side marker light (4-door) 12V-21/5W 7443 (W21/5W)
12) Cargo area light (5-door) 12V-5W–
13) Rear side marker light (5-door) 12V-5W 168 (W5W)
14) Rear turn signal light (5-door) 12V-21W (WY21W)
15) Backup light (5-door) 12V-21W 7440
16) Licence plate light 12V-5W 168 (W5W)
A) High-mounted stop light (5-door) ––
B) Stop light/Tail light (5-door) ––
C) High-mounted stop light (4-door, if equipped) ––
D) Side turn signal light (if equipped) ––WARNING
. Bulbs may become very hot while
illuminated. Before replacing
bulbs, turn off the lights and wait
until the bulbs cool down. Other-
wise, there is a risk of sustaining
a burn injury.
. For models with HID low beam
headlights, observe the following
precautions. Not doing so carries
the risk of an electric shock that
could result in serious injury
because the HID bulbs use an
extremely high voltage. – Do not replace any headlight
bulbs (both low beam and
high beam) by yourself.
– Do not remove/restore the
headlight assemblies by your-self.
– Do not remove any headlight-
assembly components byyourself.
For replacement, contact your SUBARU dealer.
Specifications/Bulb chart12-15
– CONTINUED –
Page 383 of 414

12-16Specifications/Bulb chart
CAUTION
Replace any bulb only with a new
bulb of the specified wattage. Using
a bulb of different wattage could
result in a fire.
Page 384 of 414
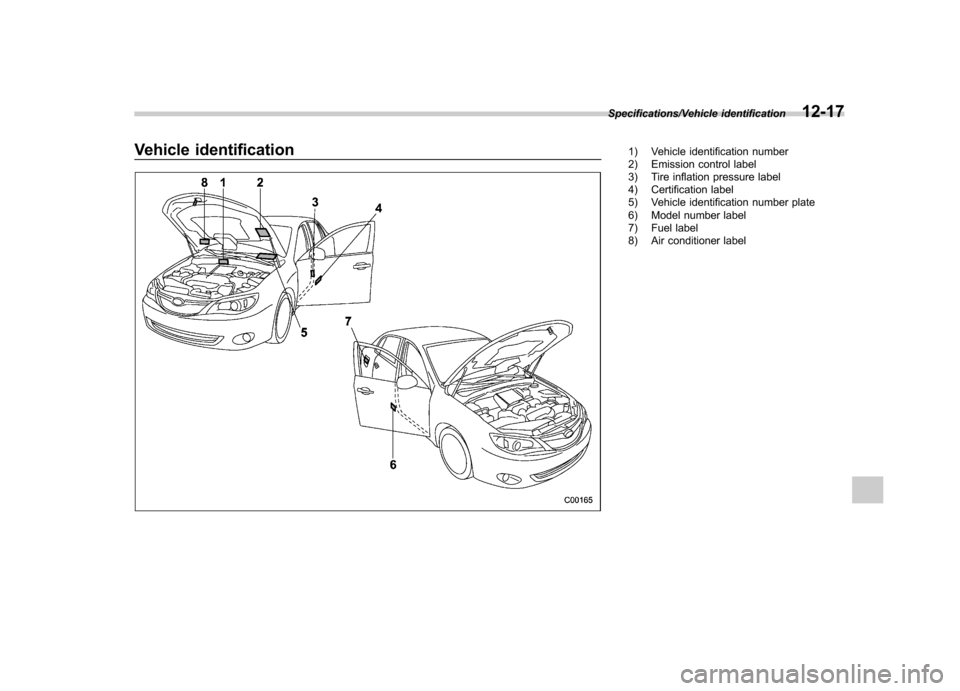
Vehicle identification1) Vehicle identification number
2) Emission control label
3) Tire inflation pressure label
4) Certification label
5) Vehicle identification number plate
6) Model number label
7) Fuel label
8) Air conditioner label
Specifications/Vehicle identification12-17
Page 385 of 414

————————————————————————————————————————
————————————————————————————————————————
————————————————————————————————————————
————————————————————————————————————————
————————————————————————————————————————
————————————————————————————————————————
————————————————————————————————————————
————————————————————————————————————————
————————————————————————————————————————
————————————————————————————————————————
————————————————————————————————————————
————————————————————————————————————————
————————————————————————————————————————
Page 386 of 414

For U.S.A............................................................ 13-2
Tire information .................................................. 13-2
Tire labeling ....................................................... 13-2
Recommended tire inflation pressure .................. 13-4
Glossary of tire terminology ............................... 13-5
Tire care –maintenance and safety
practices ........................................................ 13-10
Vehicle load limit –how to determine ................ 13-10 Determining compatibility of tire and vehicle
load capacities .............................................. 13-13
Adverse safety consequences of overloading on handling and stopping and on tires ........... 13-14
Steps for Determining Correct Load Limit ......... 13-14
Uniform tire quality grading standards .......... 13-15
Treadwear ....................................................... 13-15
Traction AA, A, B, C ......................................... 13-15
Temperature A, B, C ......................................... 13-15
Reporting safety defects (U.S.A.) ................... 13-16
Consumer information and Reporting safety defects
13
Page 387 of 414

13-2Consumer information and Reporting safety defects/For U.S.A.
For U.S.A.
The following information has been
compiled according to Code of
Federal Regulations“Title 49, Part
575 ”. Tire information &
Tire labeling
Many markings (e.g. Tire size, Tire
Identification Number or TIN) are
placed on the sidewall of a tire by
tire manufacturers. These markings
can provide you with useful infor-
mation on the tire. ! Tire size
Your vehicle comes equipped with
P-Metric tire size. It is important to
understand the sizing system in
selecting the proper tire for your
vehicles. Here is a brief review of
the tire sizing system with a break-
down of its individual elements.
!P Metric
With the P-Metric system, Section
Width is measured in millimeters.
To convert millimeters into inches,
divide by 25.4. The Aspect Ratio
(Section Height divided by Section
Width) helps provide more dimen-
sional information about the tiresize. Example:
(1) P = Certain tire type used on
light duty vehicles such as passen-
ger cars
(2) Section Width in millimeters
(3) Aspect Ratio (= section height 7
section width).
(4) R = Radial Construction
(5) Rim diameter in inches
! Load and Speed Rating De-
scriptions
The load and speed rating descrip-
tions will appear following the size designation.
They provide two important facts
about the tire. First, the number
designation is its load index. Sec-
ond, the letter designation indicates
the tire ’s speed rating.
Page 388 of 414

Example:
(6) Load Index: A numerical code
which specifies the maximum load
a tire can carry at the speed
indicated by its speed symbol, at
maximum inflation pressure.
For example,“90 ”means 1,323 lbs
(600 kg), “89 ”means 1,278 lbs (580
kg).
WARNING
Load indices apply only to the
tire, not to the vehicle. Putting
a load rated tire on any vehicle
does not mean the vehicle can
be loaded up to the tire ’s rated
load.
(7) Speed Rating: An alphabetical
system describing a tire ’s capability
to travel at established and prede-
termined speeds.
For example, “V ” means 149 mph
(240 km/h)
WARNING
. Speed ratings apply only to
the tire, not to the vehicle.
Putting a speed rated tire on
any vehicle does not mean
the vehicle can be operated
at the tire ’s rated speed.
. The speed rating is void if
the tires are worn out, da-
maged, repaired, retreaded,
or otherwise altered from
their original condition. If
tires are repaired, re-
treaded, or otherwise al-
tered, they may not be sui-
table for original equipment
tire designed loads andspeeds.
! Tire Identification Number (TIN)
Tire Identification Number (TIN) is
marked on the intended outboard
sidewall. The TIN is composed of
four groups. Here is a brief review
of the TIN with a breakdown of its
individual elements.
(1) Manufacturer ’s Identification
Mark
(2) Tire Size
(3) Tire Type Code
(4) Date of Manufacture
The first two figures identify the
week, starting with “01 ”to represent
the first full week of the calendar
year; the second two figures repre-
sent the year. For example, 0101
means the 1st week of 2001.
! Other markings
The following makings are also
placed on the sidewall.
! Maximum permissible infla-
tion pressure
The maximum cold inflation pres-
sure to which this tire may be
inflated. For example, “300 kPa
(44 PSI) MAX. PRESS ”
Consumer information and Reporting safety defects/Tire information13-3
– CONTINUED –
Page 389 of 414
13-4Consumer information and Reporting safety defects/Tire information
!Maximum load rating
The load rating at the maximum
permissible weight load for this tire.
For example, “MAX. LOAD 580 kg
(1279 LBS) @ 300 kPa (44 PSI)
MAX. PRESS. ”
WARNING
Maximum load rating applies
only to the tire, not to the
vehicle. Putting a load rated
tire on any vehicle does not
mean the vehicle can be
loaded up to the tire ’s rated
load.
! Construction type
Applicable construction of this tire.
For example, “TUBELESS STEEL
BELTED RADIAL ”
! Construction
The generic name of each cord
material used in the plies (both
sidewall and tread area) of this tire.
For example, “PLIES: TREAD 2 STEEL + 2 POLYESTER SIDE-
WALL 2 POLYESTER
”
! Uniform Tire Quality Grading
(UTQG)
For details, refer to “Uniform tire
quality grading standards ”F 13-15 .
& Recommended tire inflation pressure
! Recommended cold tire infla-
tion pressure
For recommended cold tire inflation
pressure for your vehicle ’s tires,
refer to “Tires ”F 12-9 .
! Vehicle placard
The vehicle placard is affixed to the driver ’s side B-pillar.
Example:
The vehicle placard shows original
tire size, recommended cold tire
inflation pressure on each tire at
maximum loaded vehicle weight,
seating capacity and loading infor-mation. ! Adverse safety consequences
of under-inflation
Driving at high speeds with exces-
sively low tire pressures can cause
the tires to flex severely and to
rapidly become hot. A sharp in-
Page 390 of 414

crease in temperature could cause
tread separation, and failure of the
tire(s). Possible resulting loss of
vehicle control could lead to anaccident. !Measuring and adjusting air
pressure to achieve proper in-
flation
Check and, if necessary, adjust the
pressure of each tire (including the
spare) at least once a month and
before any long journey. Check the
tire pressures when the tires are
cold. Use a pressure gauge to
adjust the tire pressures to the
specific values. Driving even a
short distance warms up the tires
and increases the tire pressures.
Also, the tire pressures are affected
by the outside temperature. It is
best to check tire pressure out-
doors before driving the vehicle.
When a tire becomes warm, the air
inside it expands, causing the tire
pressure to increase. Be careful not
to mistakenly release air from a
warm tire to reduce its pressure. &
Glossary of tire terminology
. Accessory weight
The combined weight (in excess of
those standard items which may be
replaced) of automatic transmis-
sion, power steering, power brakes,
power windows, power seats, radio,
and heater, to the extent that these
items are available as factory-in-
stalled equipment (whether in-
stalled or not). . Bead
The part of the tire that is made of
steel wires, wrapped or reinforced
by ply cords and that is shaped to fit
the rim.. Bead separation
A breakdown of the bond between
components in the bead.. Bias ply tire
A pneumatic tire in which the ply
cords that extend to the beads are
laid at alternate angles substantially
less than 90 degrees to the center-
line of the tread. . Carcass
The tire structure, except tread and sidewall rubber which, when in-
flated, bears the load. .
Chunking
The breaking away of pieces of the
tread or sidewall.. Cold tire pressure
The pressure in a tire that has been
driven less than 1 mile or has been
standing for three hours or more.. Cord
The strands forming the plies in the tire. . Cord separation
The parting of cords from adjacent
rubber compounds.. Cracking
Any parting within the tread, side-
wall, or inner liner of the tire
extending to cord material. . Curb weight
The weight of a motor vehicle with
standard equipment including the
maximum capacity of fuel, oil and
coolant, and if so equipped, air
conditioning and additional weight
optional engine.
Consumer information and Reporting safety defects/Tire information13-5
– CONTINUED –