Heat SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 2001 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2001, Model line: GRAND VITARA, Model: SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 2001 2.GPages: 656, PDF Size: 14.31 MB
Page 39 of 656
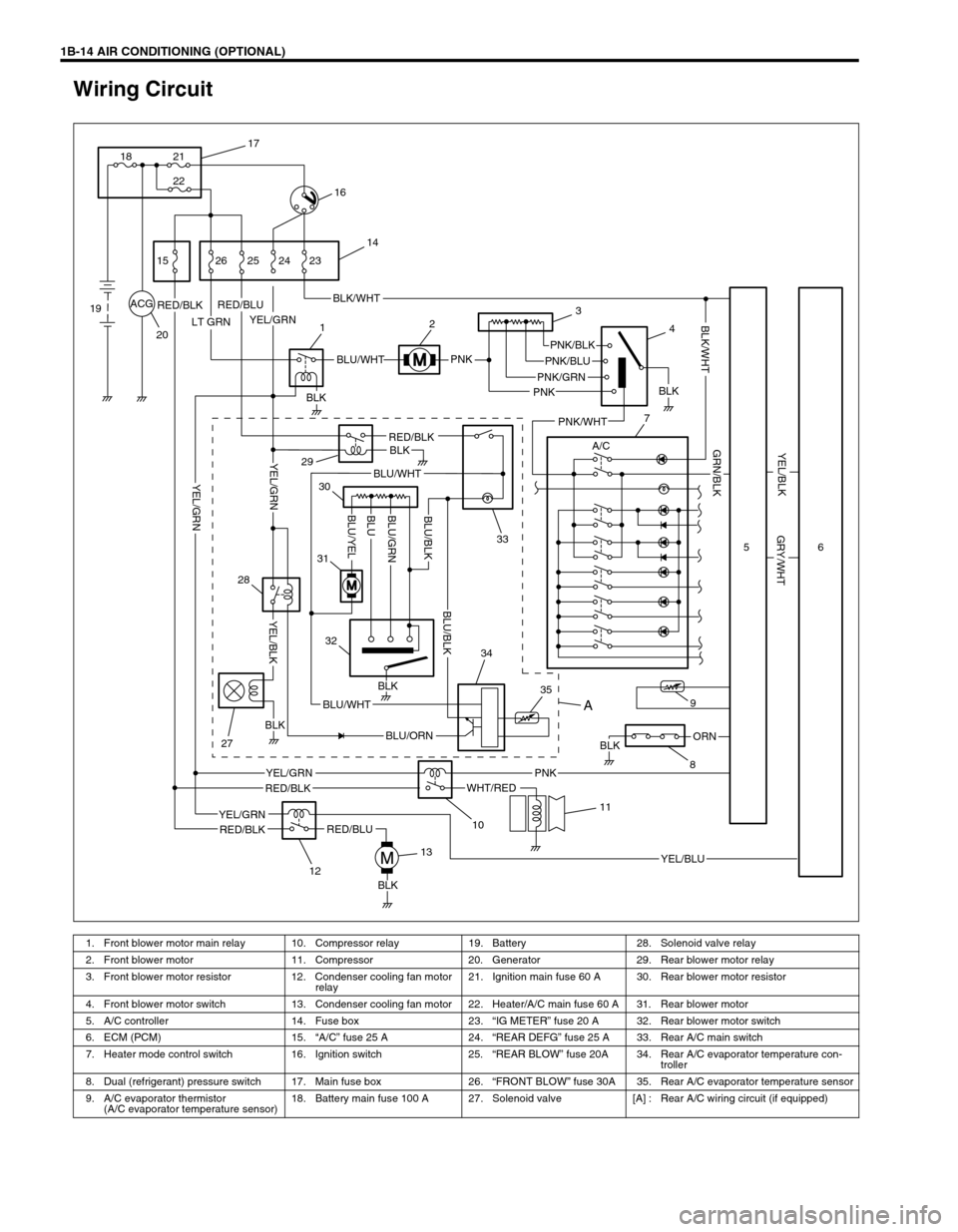
1B-14 AIR CONDITIONING (OPTIONAL)
Wiring Circuit
ACG
LT GRN
PNK
PNK
BLKORN
BLK
YEL/GRNRED/BLKBLK/WHT
BLU/WHTPNK/BLK
PNK/GRN
RED/BLK
WHT/RED
YEL/GRN
YEL/BLU
A/C
RED/BLU
RED/BLU
RED/BLKBLK
BLU/ORN
BLU/WHT
BLU/WHT
PNK
PNK/BLU
BLK
PNK/WHT
YEL/BLK
GRY/WHT
GRN/BLK
BLK/WHT
RED/BLK
YEL/GRN
BLK
BLK
BLK
YEL/BLK
YEL/GRN
YEL/GRNBLU/GRN
BLU/YELBLUBLU/BLK
BLU/BLK
17
21
22 18
16
15
19
2026 25 24 23
14
12
29
3
4
7
33 30
31
32
28
27
1213
10
11
35 349
856
A
1. Front blower motor main relay 10. Compressor relay 19. Battery 28. Solenoid valve relay
2. Front blower motor 11. Compressor 20. Generator 29. Rear blower motor relay
3. Front blower motor resistor 12. Condenser cooling fan motor
relay21. Ignition main fuse 60 A 30. Rear blower motor resistor
4. Front blower motor switch 13. Condenser cooling fan motor 22. Heater/A/C main fuse 60 A 31. Rear blower motor
5. A/C controller 14. Fuse box 23.“IG METER” fuse 20 A 32. Rear blower motor switch
6. ECM (PCM) 15.“A/C” fuse 25 A 24.“REAR DEFG” fuse 25 A 33. Rear A/C main switch
7. Heater mode control switch 16. Ignition switch 25.“REAR BLOW” fuse 20A 34. Rear A/C evaporator temperature con-
troller
8. Dual (refrigerant) pressure switch 17. Main fuse box 26.“FRONT BLOW” fuse 30A 35. Rear A/C evaporator temperature sensor
9. A/C evaporator thermistor
(A/C evaporator temperature sensor)18. Battery main fuse 100 A 27. Solenoid valve [A] : Rear A/C wiring circuit (if equipped)
Page 47 of 656

1B-22 AIR CONDITIONING (OPTIONAL)
Checking system for pressure leaks
After completing the evacuation, close manifold gauge high pres-
sure valve (HI) and low-pressure valve (LO) and wait 10 minutes.
Verify that low-pressure gauge reading has not changed.
Charging
CAUTION:
If the gauge reading moves closer to “0”, there is a leak
somewhere. Inspect the tubing connections, make nec-
essary corrections, and evacuate system once again,
making sure that there are no leaks.
CAUTION:
ALWAYS CHARGE THROUGH LOW PRESSURE-SIDE of A/C system at after the initial charging is
performed from the high-pressure side with the engine stopped.
NEVER CHARGE TO HIGH PRESSURE-SIDE of A/C system with engine running.
Do not charge while compressor is hot.
When installing tap valve to refrigerant container to make a hole there through, carefully follow
directions given by manufacturer.
A pressure gauge should always be used before and during charging.
The refrigerant container should be emptied of refrigerant when discarding it.
The refrigerant container should not be heated up to 40 °C (104 °F) or over.
Refrigerant container should not be reversed in direction during charging. Reversing in direction
causes liquid refrigerant to enter compressor, causing troubles, such as compression of liquid
refrigerant and the like.
NOTE:
The air conditioning system contains HFC-134a (R-134a).
Described here is a method to charge the air conditioning system with refrigerant from the refrigerant
service container.
When charging refrigerant recovered by using the refrigerant and recycling equipment (when recy-
cling refrigerant), follow the procedure described in the equipment manufacturer’s instruction manual.
Page 51 of 656

1B-26 AIR CONDITIONING (OPTIONAL)
Never use heat for bending pipes. When bending a pipe, try to make its bending radius as slight as possible.
Keep internal parts of air conditioning free from moisture and dirt. When disconnecting any line from system,
install a blind plug or cap to the fitting immediately.
When tightening or loosening a fitting, use two wrenches, one for turning and the other for support.
Tighten flared nuts to specified torque.
Tightening torque
8 mm (0.31 in.) pipe : 13 N·m (1.3 kg-m, 9.5 lb-ft)
12.7 mm (0.5 in.) pipe : 22 N·m (2.2 kg-m, 16.0 lb-ft)
16 mm (0.63 in.) pipe : 33 N·m (3.3 kg-m, 24.0 lb-ft)
Route drain hose so that drained water does not make any contact to vehicle components.
Handling refrigerant HFC-134a (R-134a)
When handling refrigerant, always wear goggles to protect your eyes.
Avoid you direct contact to liquid refrigerant.
Do not heat refrigerant container higher than 40 °C (104 °F).
Do not discharge refrigerant into atmosphere.
Do not allow liquid refrigerant to touch bright metals. Refrigerant combined with moisture is corrosive and
will tarnish surfaces of bright metals including chrome.
After recovering refrigerant from system, the amount of compressor oil removed must be measured and the
same amount added to the system.
Refrigerant recovery
When discharging refrigerant out of A/C system, always recover it by using refrigerant recovery and recycling
equipment. Discharging refrigerant HFC-134a (R-134a) into atmosphere would cause adverse effect to environ-
ments.
Refrigerant charge
Charge a proper amount of refrigerant to A/C system according to charging procedure described in recovery,
evacuation and charging.NOTE:
When handling recovery and recycling equipment, be sure to follow the instruction manual for the
equipment.
CAUTION:
Do not perform an additional refrigerant charging to A/C system. This cause it to overcharge.
Page 88 of 656
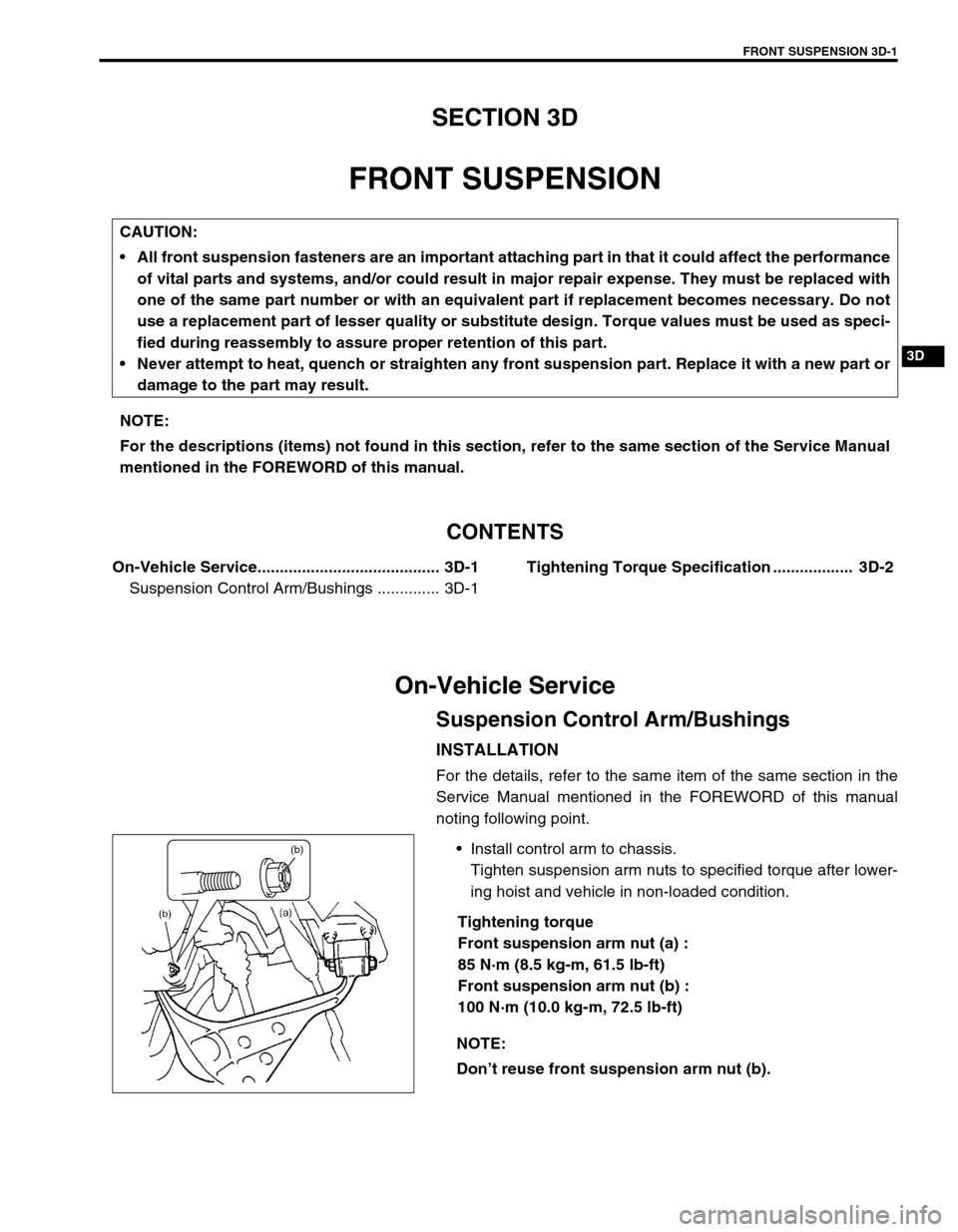
FRONT SUSPENSION 3D-1
3D
SECTION 3D
FRONT SUSPENSION
CONTENTS
On-Vehicle Service......................................... 3D-1
Suspension Control Arm/Bushings .............. 3D-1Tightening Torque Specification .................. 3D-2
On-Vehicle Service
Suspension Control Arm/Bushings
INSTALLATION
For the details, refer to the same item of the same section in the
Service Manual mentioned in the FOREWORD of this manual
noting following point.
Install control arm to chassis.
Tighten suspension arm nuts to specified torque after lower-
ing hoist and vehicle in non-loaded condition.
Tightening torque
Front suspension arm nut (a) :
85 N·m (8.5 kg-m, 61.5 lb-ft)
Front suspension arm nut (b) :
100 N·m (10.0 kg-m, 72.5 lb-ft) CAUTION:
All front suspension fasteners are an important attaching part in that it could affect the performance
of vital parts and systems, and/or could result in major repair expense. They must be replaced with
one of the same part number or with an equivalent part if replacement becomes necessary. Do not
use a replacement part of lesser quality or substitute design. Torque values must be used as speci-
fied during reassembly to assure proper retention of this part.
Never attempt to heat, quench or straighten any front suspension part. Replace it with a new part or
damage to the part may result.
NOTE:
For the descriptions (items) not found in this section, refer to the same section of the Service Manual
mentioned in the FOREWORD of this manual.
NOTE:
Don’t reuse front suspension arm nut (b).
(b)
Page 90 of 656

REAR SUSPENSION 3E-1
3E
SECTION 3E
REAR SUSPENSION
CONTENTS
On-Vehicle Service......................................... 3E-1
Rear Axle Shaft and Wheel Bearing ............ 3E-1
Rear Axle Shaft Inner Oil Seal ..................... 3E-5
Rear Axle Housing ....................................... 3E-5Tightening Torque Specification .................. 3E-6
Required Service Material ............................. 3E-6
Special Tool .................................................... 3E-7
On-Vehicle Service
Rear Axle Shaft and Wheel Bearing
REMOVAL
1) Remove axle shaft from axle housing according to Step1) to
6) in the same section in the service manual mentioned in
the FOREWORD of this manual noting following points. NOTE:
For the descriptions (items) not found in this section, refer to the same section of the Service Man-
ual mentioned in the FOREWORD of this manual.
All suspension fasteners are an important attaching part in that it could affect the performance of
vital parts and systems, and/or could result in major repair expense. They must be replaced with
one of the same part number or with an equivalent part if replacement becomes necessary. Do not
use a replacement part of lesser quality or substitute design. Torque values must be used as speci-
fied during reassembly to assure proper retention of this part.
Never attempt to heat, quench or straighten any suspension part. Replace it with a new part, or
damage to the part may result.
Page 162 of 656

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-1
6-1
SECTION 6-1
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND
DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
CONTENTS
General Information ...................................... 6-1-3
Statement of Cleanliness and Care ............ 6-1-3
General Information on Engine Service ...... 6-1-3
Precaution on Fuel System Service ............ 6-1-4
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure .................. 6-1-5
Fuel Leakage Check Procedure .................. 6-1-5
Engine Diagnosis .......................................... 6-1-6
General Description .................................... 6-1-6
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle
without Monitor Connector) ......................... 6-1-6
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle with
Monitor Connector) ..................................... 6-1-9
Precaution in Diagnosing Trouble ............. 6-1-10
Engine Diagnostic Flow Table ................... 6-1-11
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Check... 6-1-16
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Check ..... 6-1-16
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Clearance 6-1-17
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Table ...... 6-1-18For A/T system (Refer to Section 7B1
for diagnosis)......................................... 6-1-21
For immobilizer control system (Refer to
Section 8G for diagnosis) ...................... 6-1-22
Fail-Safe Table.......................................... 6-1-23
Scan Tool Data ......................................... 6-1-24
Scan tool data definitions ...................... 6-1-27
Engine Diagnosis Table ............................ 6-1-31
Inspection of PCM (ECM) and its Circuits. 6-1-36
Table A-1 Malfunction Indicator Lamp
Circuit Check – Lamp Does Not Come
“ON” or Dims at Ignition Switch ON
(But Engine at Stop).................................. 6-1-43
Table A-2 Malfunction Indicator Lamp
Circuit Check – Lamp Remains “ON” after
Engine Starts ............................................ 6-1-44
Table A-3 Malfunction Indicator Lamp
Check – MIL Flashes at Ignition Switch
ON (Vehicle with Monitor Connector) ....... 6-1-45 WARNING:
For vehicles equipped with Supplemental Restraint (Air Bag) System:
Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed only by an
authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer to “Air Bag System Components and Wiring Location View” under
“General Description” in air bag system section in order to confirm whether you are performing ser-
vice on or near the air bag system components or wiring. Please observe all WARNINGS and “Ser-
vice Precautions” under “On-Vehicle Service” in air bag system section before performing service
on or around the air bag system components or wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could result in
unintentional activation of the system or could render the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
Technical service work must be started at least 90 seconds after the ignition switch is turned to the
“LOCK” position and the negative cable is disconnected from the battery. Otherwise, the system
may be activated by reserve energy in the Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM).
NOTE:
Whether following systems (parts) are used in the particular vehicle or not depends on specifications.
Be sure to bear this in mind when performing service work.
Monitor connector
CKP sensor
MAP sensor
EGR valve
Heated oxygen sensor or CO adjusting resistor
Three way catalytic converter, Warm-up three way catalytic converter
Page 163 of 656

6-1-2 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
Table A-4 Malfunction Indicator Lamp
Check – MIL Does Not Flash or Just
Remains ON Even with Grounding
Diagnosis Switch Terminal (Vehicle with
Monitor Connector) ................................... 6-1-45
Table A-5 ECM (PCM) Power and Ground
Circuit Check – MIL Doesn’t Light at
Ignition Switch ON and Engine Doesn’t
Start Though It Is Cranked Up .................. 6-1-46
DTC P0100 (DTC No.33, 34) Mass Air
Flow Circuit Malfunction ............................ 6-1-48
DTC P0110 (DTC No.23, 25) Intake Air
Temp. (IAT) Circuit Malfunction ................ 6-1-50
DTC P0115 (DTC No.14, 15) Engine
Coolant Temp. Circuit Malfunction ............ 6-1-52
DTC P0120 (DTC No.21, 22) Throttle
Position Circuit Malfunction....................... 6-1-54
DTC P0121 Throttle Position Circuit
Range/Performance Problem ................... 6-1-56
DTC P0130 (DTC No.13) HO2S-1 (Bank 1)
Circuit Malfunction or No Activity
Detected.................................................... 6-1-58
DTC P0133 HO2S-1 (Bank 1) Circuit Slow
Response .................................................. 6-1-60
DTC P0135 HO2S-1 (Bank 1) Heater
Circuit Malfunction .................................... 6-1-61
DTC P0136 HO2S-2 (Bank 1) Circuit
Malfunction................................................ 6-1-63
DTC P0141 HO2S-2 (Bank 1) Heater
Circuit Malfunction .................................... 6-1-65
DTC P0150 (DTC No.26) HO2S-1 (Bank 2)
Circuit Malfunction or No Activity
Detected.................................................... 6-1-67
DTC P0153 HO2S-1 (Bank 2) Circuit Slow
Response .................................................. 6-1-69
DTC P0155 HO2S-1 (Bank 2) Heater
Circuit Malfunction .................................... 6-1-70
DTC P0156 HO2S-2 (Bank 2) Circuit
Malfunction................................................ 6-1-72
DTC P0161 HO2S-2 (Bank 2) Heater
Circuit Malfunction .................................... 6-1-74
DTC P0171/P0172 Fuel System Too
Lean/Rich (Bank 1) ................................... 6-1-76
DTC P0174/P0175 Fuel System Too
Lean/Rich (Bank 2) ................................... 6-1-78
DTC P0300/P0301/P0302/P0303/P0304/
P0305/P0306 Random Misfire/Cylinder 1
Misfire/Cylinder 2 Misfire/Cylinder 3 Misfire/
Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected/Cylinder 5
Misfire Detected/Cylinder 6 Misfire
Detected.................................................... 6-1-80
DTC P0325 (DTC No.43) Knock Sensor Circuit Malfunction ..................................... 6-1-82
DTC P0335 Crankshaft Position Sensor
Circuit Malfunction ..................................... 6-1-84
DTC P0340 (DTC No.42) Camshaft
Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction ........... 6-1-86
DTC P0400 Exhaust Gas Recirculation
Flow Malfunction ........................................ 6-1-89
DTC P0403 (DTC No.51) Exhaust Gas
Recirculation Circuit Malfunction ............... 6-1-92
DTC P0420 Catalyst System Efficiency
Below Threshold (Bank 1) ......................... 6-1-94
DTC P0430 Catalyst System Efficiency
Below Threshold (Bank 2) ......................... 6-1-96
DTC P0443 Evap Control System Purge
Control Valve Circuit Malfunction............... 6-1-98
Evap canister purge system
inspection ............................................. 6-1-100
Vacuum passage inspection ................ 6-1-100
Vacuum hose inspection ...................... 6-1-101
Evap canister purge valve and its
circuit inspection .................................. 6-1-101
Evap canister purge valve inspection .. 6-1-101
DTC P0460 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit
High Input ................................................ 6-1-103
DTC P0500 (DTC No.24) Vehicle Speed
Sensor Malfunction .................................. 6-1-105
DTC P0505 Idle Air Control System
Malfunction .............................................. 6-1-108
DTC P0601 (DTC No.71) Internal Control
Module Memory Check Sum Error .......... 6-1-110
DTC P1408 Manifold Absolute Pressure
Sensor Circuit Malfunction ....................... 6-1-111
DTC P1450/P1451 Barometric Pressure
Sensor Circuit Malfunction/Performance
Problem ................................................... 6-1-113
DTC P1500 Engine Starter Signal Circuit
Malfunction .............................................. 6-1-114
DTC P1510 Ecm Back-Up Power Supply
Malfunction .............................................. 6-1-115
Table B-1 Fuel Pump Circuit Inspection .. 6-1-116
Table B-2 Fuel Injectors and Circuit
Inspection ................................................ 6-1-117
Table B-3 Fuel Pressure Inspection ........ 6-1-119
Table B-4 Idle Air Control System
Inspection ................................................ 6-1-121
Table B-5 A/C Signal Circuits Inspection
(If Equipped) ............................................ 6-1-123
Table B-6 A/C Condenser Fan Motor
Relay Control System Inspection
(If Equipped) ............................................ 6-1-124
Special Tool ............................................... 6-1-125
Page 170 of 656

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-9
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle with
Monitor Connector)
ECM diagnosis troubles which may occur in the area including the
following parts when the ignition switch is ON and the engine is
running, and indicates the result by turning on of flashing mal-
function indicator lamp (1).
• Heated oxygen sensor (if equipped)
•ECT sensor
•TP sensor
• IAT sensor
• CMP sensor
•MAF sensor
• Knock sensor
• EGR (if equipped)
•VSS
• CPU (Central Processing Unit) of ECM
ECM and malfunction indicator lamp (1) operate as follows.
• Malfunction indicator lamp (1) light when the ignition switch
is turned ON (but the engine at stop) with the diagnosis
switch terminal ungrounded regardless of the condition of
Engine and Emission control system. This is only to check
the malfunction indicator lamp (1) bulb and its circuit.
• If the above areas of Engine and Emission control system is
free from any trouble after the engine start (while engine is
running), malfunction indicator lamp (1) turns OFF.
• When ECM detects a trouble which has occurred in the
above areas, it makes malfunction indicator lamp (1) turn ON
while the engine is running to warn the driver of such occur-
rence of trouble and at the same time it stores the trouble
area in ECM back-up memory. (The memory is kept as it is
even if the trouble was only temporary and disappeared
immediately. And it is not erased unless the power to ECM is
shut off for specified time.)
ECM also indicates trouble area in memory by means of
flashing of malfunction indicator lamp (1) at the time of
inspection. (i.e. when diagnosis switch terminal (2) is con-
nected to ground terminal (3) with a service wire and ignition
switch is turned ON.)
NOTE:
When a trouble occurs in the above areas and disappears
soon while the diagnosis switch terminal is ungrounded
and the engine is running, malfunction indicator lamp (1)
lights and remains ON as the trouble exists but it turns
OFF when the normal condition is restored.
Page 180 of 656
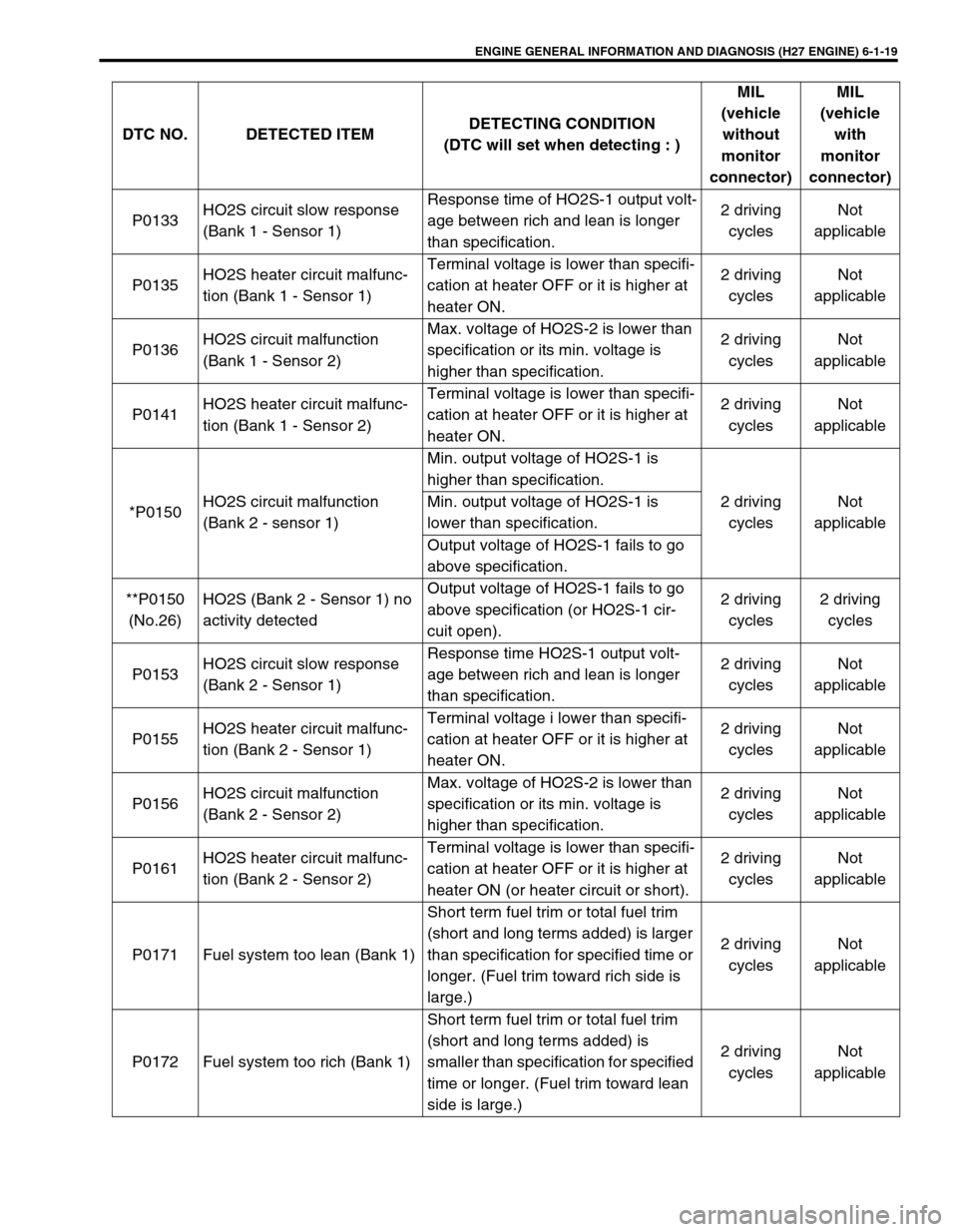
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-19
P0133HO2S circuit slow response
(Bank 1 - Sensor 1)Response time of HO2S-1 output volt-
age between rich and lean is longer
than specification.2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0135HO2S heater circuit malfunc-
tion (Bank 1 - Sensor 1)Terminal voltage is lower than specifi-
cation at heater OFF or it is higher at
heater ON.2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0136HO2S circuit malfunction
(Bank 1 - Sensor 2)Max. voltage of HO2S-2 is lower than
specification or its min. voltage is
higher than specification.2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0141HO2S heater circuit malfunc-
tion (Bank 1 - Sensor 2)Terminal voltage is lower than specifi-
cation at heater OFF or it is higher at
heater ON.2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
*P0150HO2S circuit malfunction
(Bank 2 - sensor 1)Min. output voltage of HO2S-1 is
higher than specification.
2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable Min. output voltage of HO2S-1 is
lower than specification.
Output voltage of HO2S-1 fails to go
above specification.
**P0150
(No.26)HO2S (Bank 2 - Sensor 1) no
activity detectedOutput voltage of HO2S-1 fails to go
above specification (or HO2S-1 cir-
cuit open).2 driving
cycles2 driving
cycles
P0153HO2S circuit slow response
(Bank 2 - Sensor 1)Response time HO2S-1 output volt-
age between rich and lean is longer
than specification.2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0155HO2S heater circuit malfunc-
tion (Bank 2 - Sensor 1)Terminal voltage i lower than specifi-
cation at heater OFF or it is higher at
heater ON.2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0156HO2S circuit malfunction
(Bank 2 - Sensor 2)Max. voltage of HO2S-2 is lower than
specification or its min. voltage is
higher than specification.2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0161HO2S heater circuit malfunc-
tion (Bank 2 - Sensor 2)Terminal voltage is lower than specifi-
cation at heater OFF or it is higher at
heater ON (or heater circuit or short).2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0171 Fuel system too lean (Bank 1)Short term fuel trim or total fuel trim
(short and long terms added) is larger
than specification for specified time or
longer. (Fuel trim toward rich side is
large.)2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0172 Fuel system too rich (Bank 1)Short term fuel trim or total fuel trim
(short and long terms added) is
smaller than specification for specified
time or longer. (Fuel trim toward lean
side is large.)2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable DTC NO. DETECTED ITEMDETECTING CONDITION
(DTC will set when detecting : )MIL
(vehicle
without
monitor
connector)MIL
(vehicle
with
monitor
connector)
Page 192 of 656
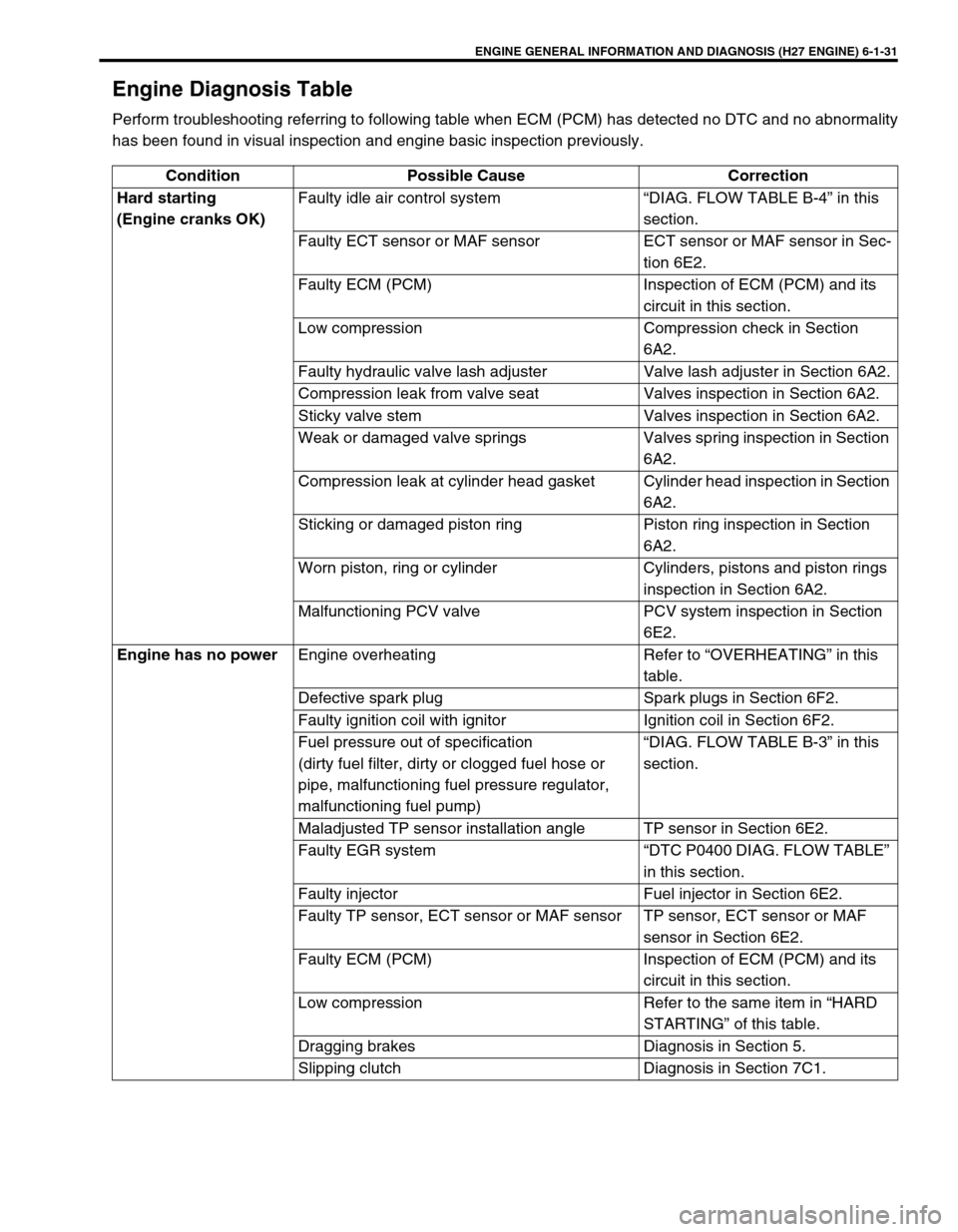
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-31
Engine Diagnosis Table
Perform troubleshooting referring to following table when ECM (PCM) has detected no DTC and no abnormality
has been found in visual inspection and engine basic inspection previously.
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Hard starting
(Engine cranks OK)Faulty idle air control system “DIAG. FLOW TABLE B-4” in this
section.
Faulty ECT sensor or MAF sensor ECT sensor or MAF sensor in Sec-
tion 6E2.
Faulty ECM (PCM) Inspection of ECM (PCM) and its
circuit in this section.
Low compression Compression check in Section
6A2.
Faulty hydraulic valve lash adjuster Valve lash adjuster in Section 6A2.
Compression leak from valve seat Valves inspection in Section 6A2.
Sticky valve stem Valves inspection in Section 6A2.
Weak or damaged valve springs Valves spring inspection in Section
6A2.
Compression leak at cylinder head gasket Cylinder head inspection in Section
6A2.
Sticking or damaged piston ring Piston ring inspection in Section
6A2.
Worn piston, ring or cylinder Cylinders, pistons and piston rings
inspection in Section 6A2.
Malfunctioning PCV valve PCV system inspection in Section
6E2.
Engine has no power
Engine overheating Refer to “OVERHEATING” in this
table.
Defective spark plug Spark plugs in Section 6F2.
Faulty ignition coil with ignitor Ignition coil in Section 6F2.
Fuel pressure out of specification
(dirty fuel filter, dirty or clogged fuel hose or
pipe, malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator,
malfunctioning fuel pump)“DIAG. FLOW TABLE B-3” in this
section.
Maladjusted TP sensor installation angle TP sensor in Section 6E2.
Faulty EGR system “DTC P0400 DIAG. FLOW TABLE”
in this section.
Faulty injector Fuel injector in Section 6E2.
Faulty TP sensor, ECT sensor or MAF sensor TP sensor, ECT sensor or MAF
sensor in Section 6E2.
Faulty ECM (PCM) Inspection of ECM (PCM) and its
circuit in this section.
Low compression Refer to the same item in “HARD
STARTING” of this table.
Dragging brakes Diagnosis in Section 5.
Slipping clutch Diagnosis in Section 7C1.