check engine SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 2001 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2001, Model line: GRAND VITARA, Model: SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 2001 2.GPages: 656, PDF Size: 14.31 MB
Page 75 of 656
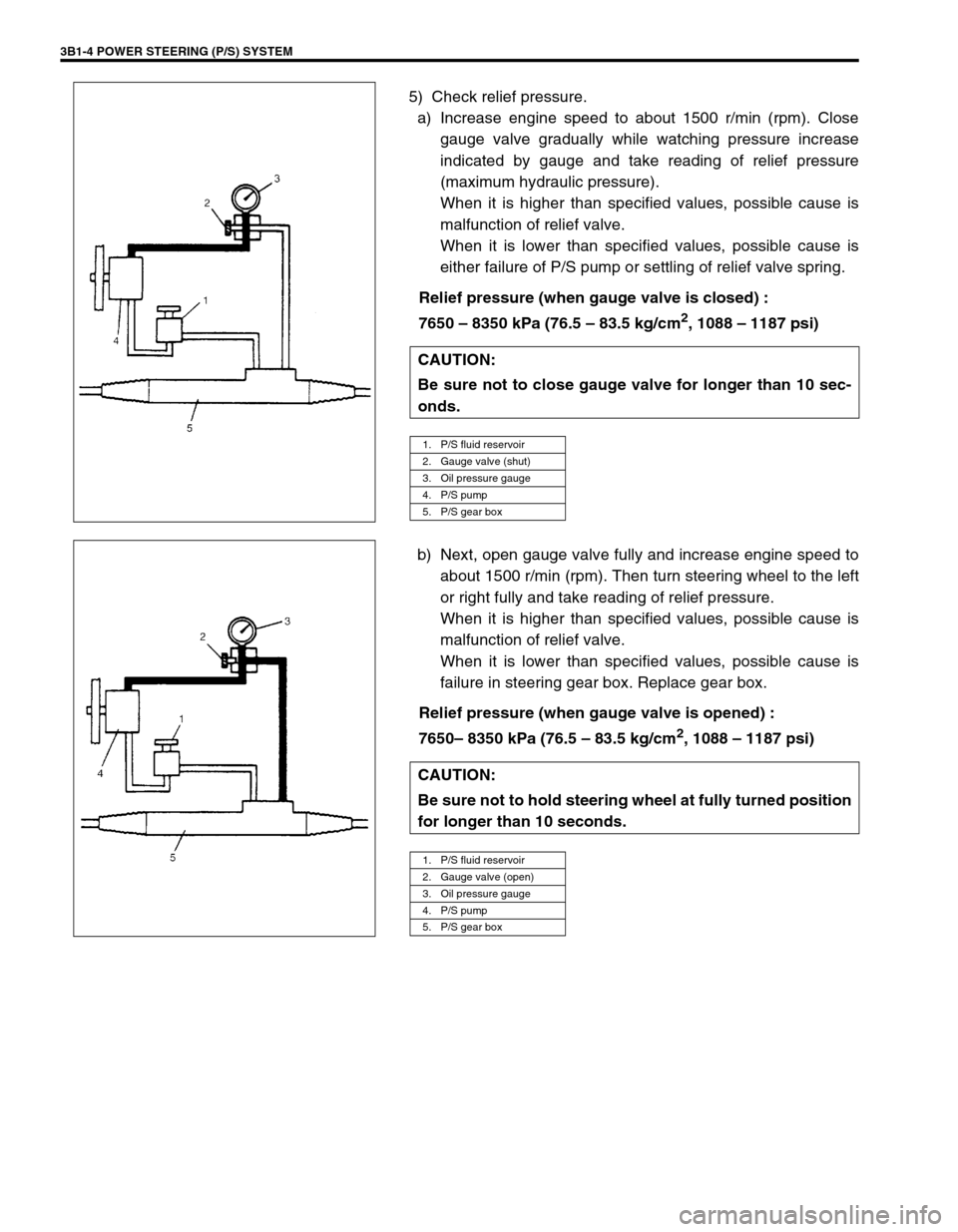
3B1-4 POWER STEERING (P/S) SYSTEM
5) Check relief pressure.
a) Increase engine speed to about 1500 r/min (rpm). Close
gauge valve gradually while watching pressure increase
indicated by gauge and take reading of relief pressure
(maximum hydraulic pressure).
When it is higher than specified values, possible cause is
malfunction of relief valve.
When it is lower than specified values, possible cause is
either failure of P/S pump or settling of relief valve spring.
Relief pressure (when gauge valve is closed) :
7650 – 8350 kPa (76.5 – 83.5 kg/cm
2, 1088 – 1187 psi)
b) Next, open gauge valve fully and increase engine speed to
about 1500 r/min (rpm). Then turn steering wheel to the left
or right fully and take reading of relief pressure.
When it is higher than specified values, possible cause is
malfunction of relief valve.
When it is lower than specified values, possible cause is
failure in steering gear box. Replace gear box.
Relief pressure (when gauge valve is opened) :
7650– 8350 kPa (76.5 – 83.5 kg/cm
2, 1088 – 1187 psi) CAUTION:
Be sure not to close gauge valve for longer than 10 sec-
onds.
1. P/S fluid reservoir
2. Gauge valve (shut)
3. Oil pressure gauge
4. P/S pump
5. P/S gear box
CAUTION:
Be sure not to hold steering wheel at fully turned position
for longer than 10 seconds.
1. P/S fluid reservoir
2. Gauge valve (open)
3. Oil pressure gauge
4. P/S pump
5. P/S gear box
Page 107 of 656
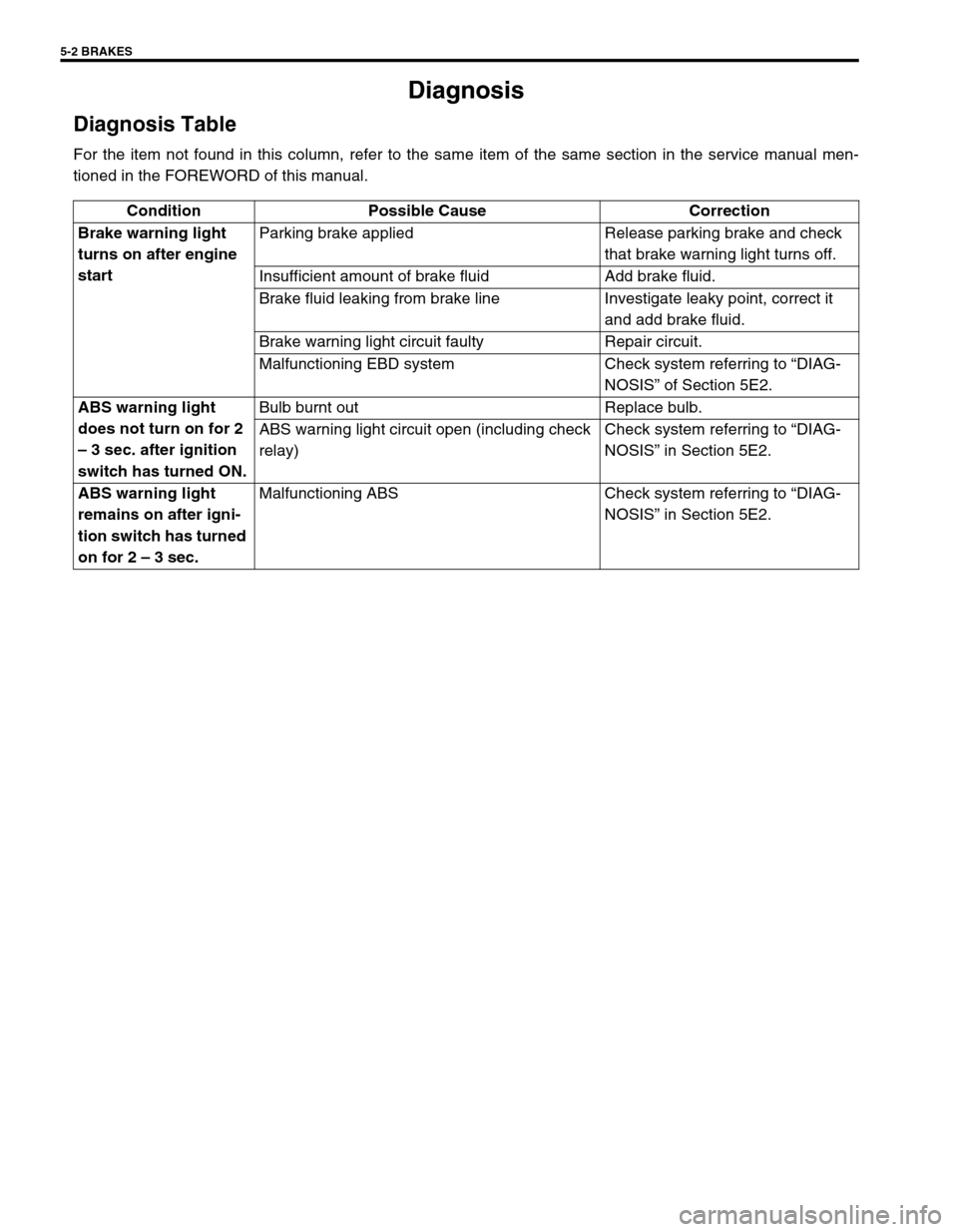
5-2 BRAKES
Diagnosis
Diagnosis Table
For the item not found in this column, refer to the same item of the same section in the service manual men-
tioned in the FOREWORD of this manual.
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Brake warning light
turns on after engine
startParking brake applied Release parking brake and check
that brake warning light turns off.
Insufficient amount of brake fluid Add brake fluid.
Brake fluid leaking from brake line Investigate leaky point, correct it
and add brake fluid.
Brake warning light circuit faulty Repair circuit.
Malfunctioning EBD system Check system referring to “DIAG-
NOSIS” of Section 5E2.
ABS warning light
does not turn on for 2
– 3 sec. after ignition
switch has turned ON.Bulb burnt out Replace bulb.
ABS warning light circuit open (including check
relay)Check system referring to “DIAG-
NOSIS” in Section 5E2.
ABS warning light
remains on after igni-
tion switch has turned
on for 2 – 3 sec.Malfunctioning ABS Check system referring to “DIAG-
NOSIS” in Section 5E2.
Page 144 of 656
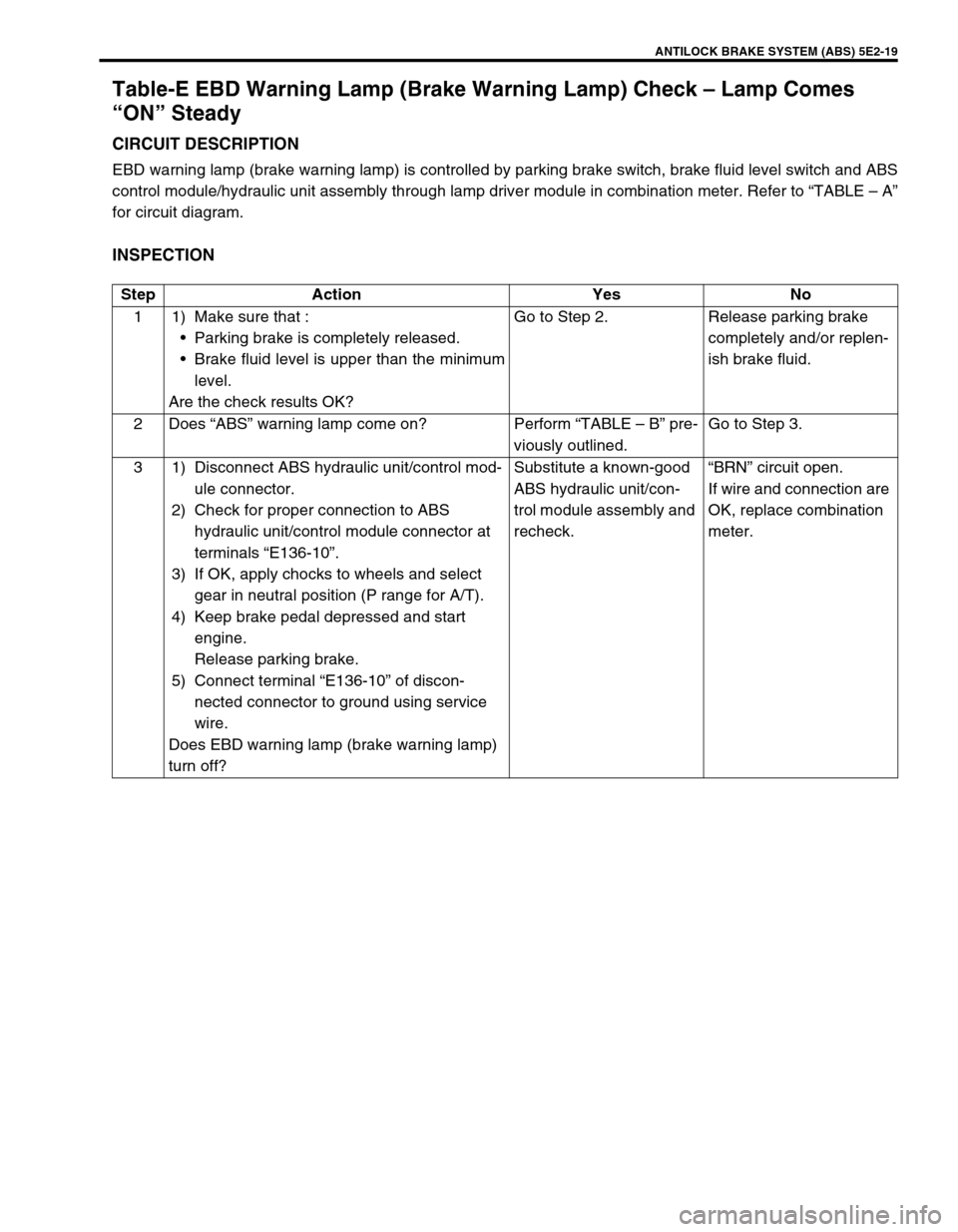
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E2-19
Table-E EBD Warning Lamp (Brake Warning Lamp) Check – Lamp Comes
“ON” Steady
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
EBD warning lamp (brake warning lamp) is controlled by parking brake switch, brake fluid level switch and ABS
control module/hydraulic unit assembly through lamp driver module in combination meter. Refer to “TABLE – A”
for circuit diagram.
INSPECTION
Step Action Yes No
1 1) Make sure that :
Parking brake is completely released.
Brake fluid level is upper than the minimum
level.
Are the check results OK?Go to Step 2. Release parking brake
completely and/or replen-
ish brake fluid.
2Does “ABS” warning lamp come on? Perform “TABLE – B” pre-
viously outlined.Go to Step 3.
3 1) Disconnect ABS hydraulic unit/control mod-
ule connector.
2) Check for proper connection to ABS
hydraulic unit/control module connector at
terminals “E136-10”.
3) If OK, apply chocks to wheels and select
gear in neutral position (P range for A/T).
4) Keep brake pedal depressed and start
engine.
Release parking brake.
5) Connect terminal “E136-10” of discon-
nected connector to ground using service
wire.
Does EBD warning lamp (brake warning lamp)
turn off?Substitute a known-good
ABS hydraulic unit/con-
trol module assembly and
recheck.“BRN” circuit open.
If wire and connection are
OK, replace combination
meter.
Page 150 of 656
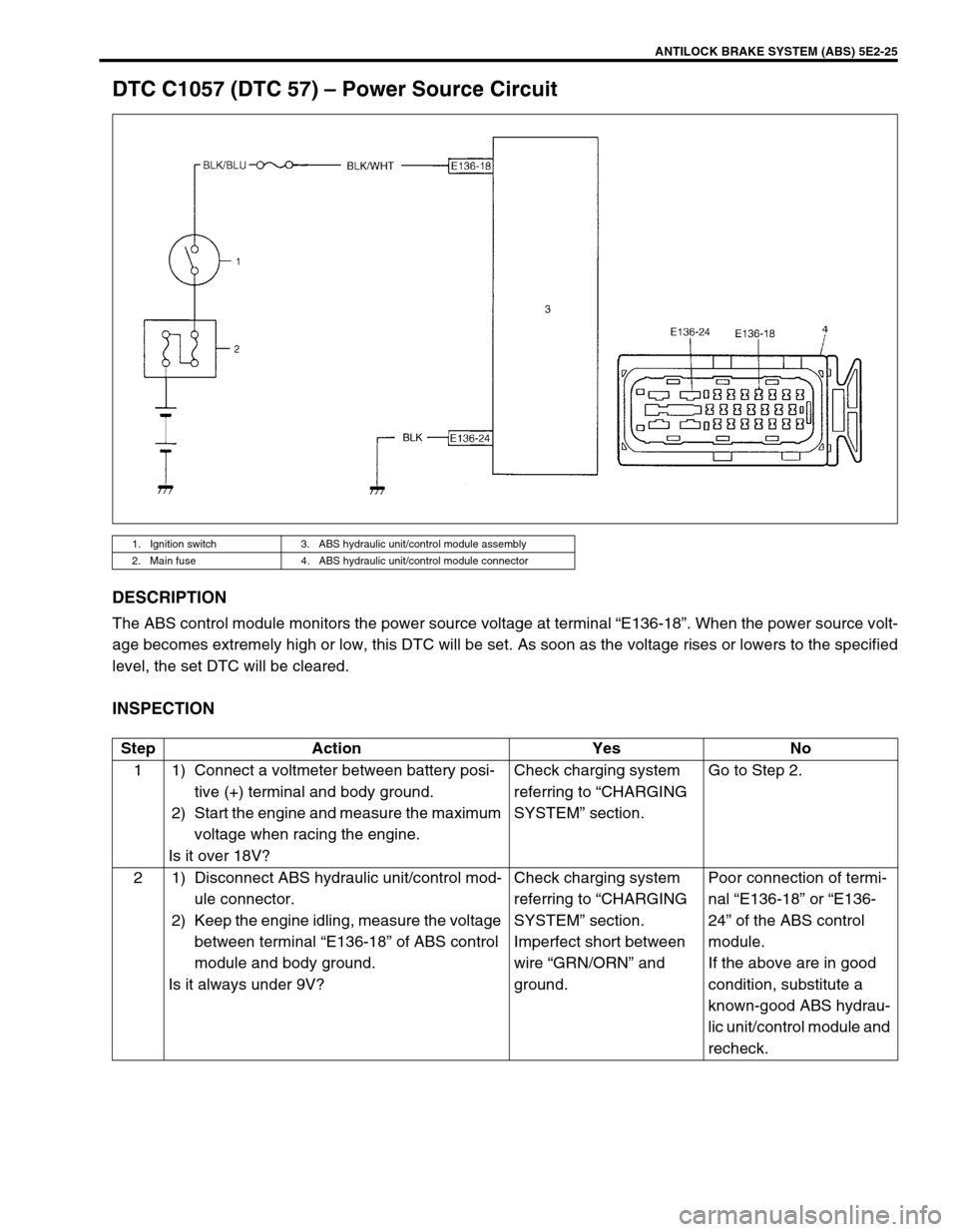
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E2-25
DTC C1057 (DTC 57) – Power Source Circuit
DESCRIPTION
The ABS control module monitors the power source voltage at terminal “E136-18”. When the power source volt-
age becomes extremely high or low, this DTC will be set. As soon as the voltage rises or lowers to the specified
level, the set DTC will be cleared.
INSPECTION
1. Ignition switch 3. ABS hydraulic unit/control module assembly
2. Main fuse 4. ABS hydraulic unit/control module connector
Step Action Yes No
1 1) Connect a voltmeter between battery posi-
tive (+) terminal and body ground.
2) Start the engine and measure the maximum
voltage when racing the engine.
Is it over 18V?Check charging system
referring to “CHARGING
SYSTEM” section.Go to Step 2.
2 1) Disconnect ABS hydraulic unit/control mod-
ule connector.
2) Keep the engine idling, measure the voltage
between terminal “E136-18” of ABS control
module and body ground.
Is it always under 9V?Check charging system
referring to “CHARGING
SYSTEM” section.
Imperfect short between
wire “GRN/ORN” and
ground.Poor connection of termi-
nal “E136-18” or “E136-
24” of the ABS control
module.
If the above are in good
condition, substitute a
known-good ABS hydrau-
lic unit/control module and
recheck.
Page 162 of 656

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-1
6-1
SECTION 6-1
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND
DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
CONTENTS
General Information ...................................... 6-1-3
Statement of Cleanliness and Care ............ 6-1-3
General Information on Engine Service ...... 6-1-3
Precaution on Fuel System Service ............ 6-1-4
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure .................. 6-1-5
Fuel Leakage Check Procedure .................. 6-1-5
Engine Diagnosis .......................................... 6-1-6
General Description .................................... 6-1-6
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle
without Monitor Connector) ......................... 6-1-6
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle with
Monitor Connector) ..................................... 6-1-9
Precaution in Diagnosing Trouble ............. 6-1-10
Engine Diagnostic Flow Table ................... 6-1-11
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Check... 6-1-16
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Check ..... 6-1-16
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Clearance 6-1-17
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Table ...... 6-1-18For A/T system (Refer to Section 7B1
for diagnosis)......................................... 6-1-21
For immobilizer control system (Refer to
Section 8G for diagnosis) ...................... 6-1-22
Fail-Safe Table.......................................... 6-1-23
Scan Tool Data ......................................... 6-1-24
Scan tool data definitions ...................... 6-1-27
Engine Diagnosis Table ............................ 6-1-31
Inspection of PCM (ECM) and its Circuits. 6-1-36
Table A-1 Malfunction Indicator Lamp
Circuit Check – Lamp Does Not Come
“ON” or Dims at Ignition Switch ON
(But Engine at Stop).................................. 6-1-43
Table A-2 Malfunction Indicator Lamp
Circuit Check – Lamp Remains “ON” after
Engine Starts ............................................ 6-1-44
Table A-3 Malfunction Indicator Lamp
Check – MIL Flashes at Ignition Switch
ON (Vehicle with Monitor Connector) ....... 6-1-45 WARNING:
For vehicles equipped with Supplemental Restraint (Air Bag) System:
Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed only by an
authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer to “Air Bag System Components and Wiring Location View” under
“General Description” in air bag system section in order to confirm whether you are performing ser-
vice on or near the air bag system components or wiring. Please observe all WARNINGS and “Ser-
vice Precautions” under “On-Vehicle Service” in air bag system section before performing service
on or around the air bag system components or wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could result in
unintentional activation of the system or could render the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
Technical service work must be started at least 90 seconds after the ignition switch is turned to the
“LOCK” position and the negative cable is disconnected from the battery. Otherwise, the system
may be activated by reserve energy in the Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM).
NOTE:
Whether following systems (parts) are used in the particular vehicle or not depends on specifications.
Be sure to bear this in mind when performing service work.
Monitor connector
CKP sensor
MAP sensor
EGR valve
Heated oxygen sensor or CO adjusting resistor
Three way catalytic converter, Warm-up three way catalytic converter
Page 163 of 656

6-1-2 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
Table A-4 Malfunction Indicator Lamp
Check – MIL Does Not Flash or Just
Remains ON Even with Grounding
Diagnosis Switch Terminal (Vehicle with
Monitor Connector) ................................... 6-1-45
Table A-5 ECM (PCM) Power and Ground
Circuit Check – MIL Doesn’t Light at
Ignition Switch ON and Engine Doesn’t
Start Though It Is Cranked Up .................. 6-1-46
DTC P0100 (DTC No.33, 34) Mass Air
Flow Circuit Malfunction ............................ 6-1-48
DTC P0110 (DTC No.23, 25) Intake Air
Temp. (IAT) Circuit Malfunction ................ 6-1-50
DTC P0115 (DTC No.14, 15) Engine
Coolant Temp. Circuit Malfunction ............ 6-1-52
DTC P0120 (DTC No.21, 22) Throttle
Position Circuit Malfunction....................... 6-1-54
DTC P0121 Throttle Position Circuit
Range/Performance Problem ................... 6-1-56
DTC P0130 (DTC No.13) HO2S-1 (Bank 1)
Circuit Malfunction or No Activity
Detected.................................................... 6-1-58
DTC P0133 HO2S-1 (Bank 1) Circuit Slow
Response .................................................. 6-1-60
DTC P0135 HO2S-1 (Bank 1) Heater
Circuit Malfunction .................................... 6-1-61
DTC P0136 HO2S-2 (Bank 1) Circuit
Malfunction................................................ 6-1-63
DTC P0141 HO2S-2 (Bank 1) Heater
Circuit Malfunction .................................... 6-1-65
DTC P0150 (DTC No.26) HO2S-1 (Bank 2)
Circuit Malfunction or No Activity
Detected.................................................... 6-1-67
DTC P0153 HO2S-1 (Bank 2) Circuit Slow
Response .................................................. 6-1-69
DTC P0155 HO2S-1 (Bank 2) Heater
Circuit Malfunction .................................... 6-1-70
DTC P0156 HO2S-2 (Bank 2) Circuit
Malfunction................................................ 6-1-72
DTC P0161 HO2S-2 (Bank 2) Heater
Circuit Malfunction .................................... 6-1-74
DTC P0171/P0172 Fuel System Too
Lean/Rich (Bank 1) ................................... 6-1-76
DTC P0174/P0175 Fuel System Too
Lean/Rich (Bank 2) ................................... 6-1-78
DTC P0300/P0301/P0302/P0303/P0304/
P0305/P0306 Random Misfire/Cylinder 1
Misfire/Cylinder 2 Misfire/Cylinder 3 Misfire/
Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected/Cylinder 5
Misfire Detected/Cylinder 6 Misfire
Detected.................................................... 6-1-80
DTC P0325 (DTC No.43) Knock Sensor Circuit Malfunction ..................................... 6-1-82
DTC P0335 Crankshaft Position Sensor
Circuit Malfunction ..................................... 6-1-84
DTC P0340 (DTC No.42) Camshaft
Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction ........... 6-1-86
DTC P0400 Exhaust Gas Recirculation
Flow Malfunction ........................................ 6-1-89
DTC P0403 (DTC No.51) Exhaust Gas
Recirculation Circuit Malfunction ............... 6-1-92
DTC P0420 Catalyst System Efficiency
Below Threshold (Bank 1) ......................... 6-1-94
DTC P0430 Catalyst System Efficiency
Below Threshold (Bank 2) ......................... 6-1-96
DTC P0443 Evap Control System Purge
Control Valve Circuit Malfunction............... 6-1-98
Evap canister purge system
inspection ............................................. 6-1-100
Vacuum passage inspection ................ 6-1-100
Vacuum hose inspection ...................... 6-1-101
Evap canister purge valve and its
circuit inspection .................................. 6-1-101
Evap canister purge valve inspection .. 6-1-101
DTC P0460 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit
High Input ................................................ 6-1-103
DTC P0500 (DTC No.24) Vehicle Speed
Sensor Malfunction .................................. 6-1-105
DTC P0505 Idle Air Control System
Malfunction .............................................. 6-1-108
DTC P0601 (DTC No.71) Internal Control
Module Memory Check Sum Error .......... 6-1-110
DTC P1408 Manifold Absolute Pressure
Sensor Circuit Malfunction ....................... 6-1-111
DTC P1450/P1451 Barometric Pressure
Sensor Circuit Malfunction/Performance
Problem ................................................... 6-1-113
DTC P1500 Engine Starter Signal Circuit
Malfunction .............................................. 6-1-114
DTC P1510 Ecm Back-Up Power Supply
Malfunction .............................................. 6-1-115
Table B-1 Fuel Pump Circuit Inspection .. 6-1-116
Table B-2 Fuel Injectors and Circuit
Inspection ................................................ 6-1-117
Table B-3 Fuel Pressure Inspection ........ 6-1-119
Table B-4 Idle Air Control System
Inspection ................................................ 6-1-121
Table B-5 A/C Signal Circuits Inspection
(If Equipped) ............................................ 6-1-123
Table B-6 A/C Condenser Fan Motor
Relay Control System Inspection
(If Equipped) ............................................ 6-1-124
Special Tool ............................................... 6-1-125
Page 166 of 656
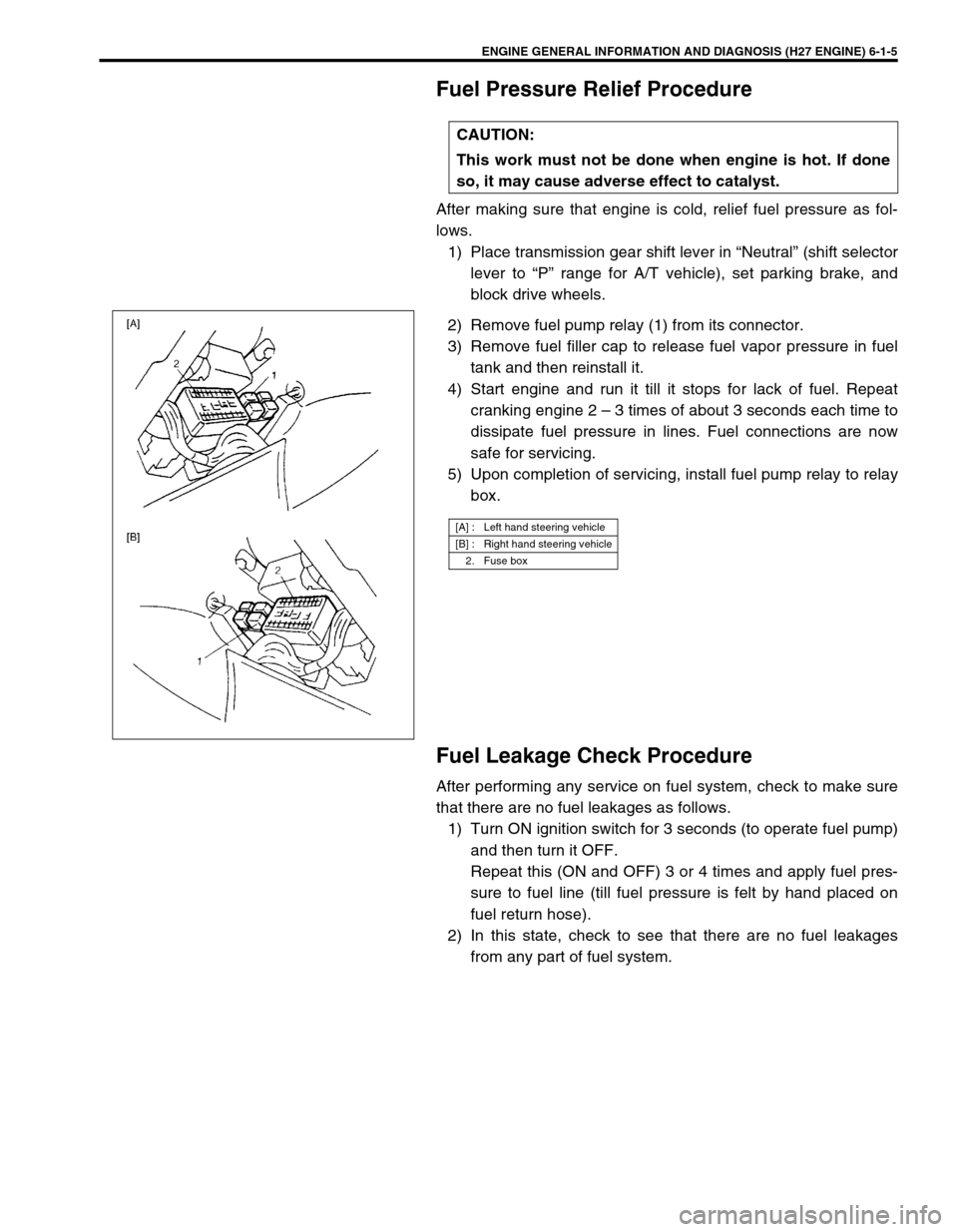
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-5
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure
After making sure that engine is cold, relief fuel pressure as fol-
lows.
1) Place transmission gear shift lever in “Neutral” (shift selector
lever to “P” range for A/T vehicle), set parking brake, and
block drive wheels.
2) Remove fuel pump relay (1) from its connector.
3) Remove fuel filler cap to release fuel vapor pressure in fuel
tank and then reinstall it.
4) Start engine and run it till it stops for lack of fuel. Repeat
cranking engine 2 – 3 times of about 3 seconds each time to
dissipate fuel pressure in lines. Fuel connections are now
safe for servicing.
5) Upon completion of servicing, install fuel pump relay to relay
box.
Fuel Leakage Check Procedure
After performing any service on fuel system, check to make sure
that there are no fuel leakages as follows.
1) Turn ON ignition switch for 3 seconds (to operate fuel pump)
and then turn it OFF.
Repeat this (ON and OFF) 3 or 4 times and apply fuel pres-
sure to fuel line (till fuel pressure is felt by hand placed on
fuel return hose).
2) In this state, check to see that there are no fuel leakages
from any part of fuel system. CAUTION:
This work must not be done when engine is hot. If done
so, it may cause adverse effect to catalyst.
[A] : Left hand steering vehicle
[B] : Right hand steering vehicle
2. Fuse box
Page 167 of 656
6-1-6 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
Engine Diagnosis
General Description
This vehicle is equipped with an engine and emission control system which are under control of ECM (PCM).
The engine and emission control system in this vehicle are controlled by ECM (PCM). ECM (PCM) has an On-
Board Diagnostic system which detects a malfunction in this system and abnormality of those parts that influ-
ence the engine exhaust emission. When diagnosing engine troubles, be sure to have full understanding of the
outline of “ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM” and each item in “PRECAUTION IN DIAGNOSING TROUBLE”
and execute diagnosis according to “ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE” in this section.
There is a close relationship between the engine mechanical, engine cooling system, ignition system, exhaust
system, etc. and the engine and emission control system in their structure and operation. In case of an engine
trouble, even when the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) doesn’t turn ON, it should be diagnosed according to
“ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE” in this section.
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle without
Monitor Connector)
ECM (PCM) in this vehicle has following functions.
When the ignition switch is turned ON with the engine at a
stop, malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (1) turns ON to check
the bulb of the malfunction indicator lamp (1).
When ECM detects a malfunction which gives an adverse
effect to vehicle emission while the engine is running, it
makes the malfunction indicator lamp (1) in the meter cluster
of the instrument panel turn ON or flash (flashing only when
detecting a misfire which can cause damage to the catalyst)
and stores the malfunction area in its memory.
(If it detects that continuously 3 driving cycles are normal
after detecting a malfunction, however, it makes MIL (1) turn
OFF although DTC stored in its memory will remain.)
As a condition for detecting a malfunction in some areas in
the system being monitored by ECM (PCM) and turning ON
the malfunction indicator lamp (1) due to that malfunction, 2
driving cycle detection logic is adopted to prevent erroneous
detection.
When a malfunction is detected, engine and driving condi-
tions then are stored in ECM (PCM) memory as freeze frame
data. (For the details, refer to description on Freeze frame
data.)
It is possible to communicate by using not only SUZUKI scan
tool (2) but also generic scan tool. (Diagnostic information
can be accessed by using a scan tool.)
Page 168 of 656

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-7
WARM-UP CYCLE
A warm-up cycle means sufficient vehicle operation such that the
coolant temperature has risen by at least 22°C (40°F) from
engine starting and reaches a minimum temperature of 70 °C
(160 °F).
DRIVING CYCLE
A “Driving Cycle” consists of engine startup, driving mode where
a malfunction would be detected if present and engine shutoff.
2 DRIVING CYCLE DETECTION LOGIC
The malfunction detected in the first driving cycle is stored in
ECM (PCM) memory (in the form of pending DTC) but the mal-
function indicator lamp does not light at this time. It lights up at the
second detection of same malfunction also in the next driving
cycle.
PENDING DTC
Pending DTC means a DTC detected and stored temporarily at 1
driving cycle of the DTC which is detected in the 2 driving cycle
detection logic.
FREEZE FRAME DATA
ECM (PCM) stores the engine and driving conditions (in the form
of data as shown in the figure) at the moment of the detection of a
malfunction in its memory. This data is called “Freeze frame data”.
Therefore, it is possible to know engine and driving conditions
(e.g., whether the engine was warm or not, where the vehicle was
running or stopped, where air/fuel mixture was lean or rich) when
a malfunction was detected by checking the freeze frame data.
Also, ECM (PCM) has a function to store each freeze frame data
for three different malfunctions in the order as the malfunction is
detected. Utilizing this function, it is possible to know the order of
malfunctions that have been detected. Its use is helpful when
rechecking or diagnosing a trouble.
1. 1st, 2nd or 3rd in parentheses here represents which position in the
order the malfunction is detected.
1. TROUBLE CODE
2. COOLANT TEMP.
3. ENGINE SPEED
4. SHORT FT B1
5. SHORT FT B2
6. LONG FT B1
7. LONG FT B2
8. CALC LOAD
9. FUEL SYSTEM B1
10. FUEL SYSTEM B2
11. MAP
12. VEHICLE SPEEDP0100
80 C
750 RPM
– 0.8
– 0.1
– 1.3
– 1.5
20.5
CLOSED
CLOSED
30.6 kPa
0 km/h(1st)
1
Page 170 of 656

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-9
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle with
Monitor Connector)
ECM diagnosis troubles which may occur in the area including the
following parts when the ignition switch is ON and the engine is
running, and indicates the result by turning on of flashing mal-
function indicator lamp (1).
• Heated oxygen sensor (if equipped)
•ECT sensor
•TP sensor
• IAT sensor
• CMP sensor
•MAF sensor
• Knock sensor
• EGR (if equipped)
•VSS
• CPU (Central Processing Unit) of ECM
ECM and malfunction indicator lamp (1) operate as follows.
• Malfunction indicator lamp (1) light when the ignition switch
is turned ON (but the engine at stop) with the diagnosis
switch terminal ungrounded regardless of the condition of
Engine and Emission control system. This is only to check
the malfunction indicator lamp (1) bulb and its circuit.
• If the above areas of Engine and Emission control system is
free from any trouble after the engine start (while engine is
running), malfunction indicator lamp (1) turns OFF.
• When ECM detects a trouble which has occurred in the
above areas, it makes malfunction indicator lamp (1) turn ON
while the engine is running to warn the driver of such occur-
rence of trouble and at the same time it stores the trouble
area in ECM back-up memory. (The memory is kept as it is
even if the trouble was only temporary and disappeared
immediately. And it is not erased unless the power to ECM is
shut off for specified time.)
ECM also indicates trouble area in memory by means of
flashing of malfunction indicator lamp (1) at the time of
inspection. (i.e. when diagnosis switch terminal (2) is con-
nected to ground terminal (3) with a service wire and ignition
switch is turned ON.)
NOTE:
When a trouble occurs in the above areas and disappears
soon while the diagnosis switch terminal is ungrounded
and the engine is running, malfunction indicator lamp (1)
lights and remains ON as the trouble exists but it turns
OFF when the normal condition is restored.