tail SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 2001 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2001, Model line: GRAND VITARA, Model: SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 2001 2.GPages: 656, PDF Size: 14.31 MB
Page 136 of 656

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E2-11
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Check (Using
SUZUKI Scan Tool)
1) After setting cartridge for ABS to SUZUKI scan tool, connect
SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector.
Special tool
(A) : SUZUKI scan tool
2) Turn ignition switch ON.
3) Read DTC according to instructions displayed on SUZUKI
scan tool and print it or write it down. Refer to SUZUKI scan
tool operator’s manual for further details.
4) After completing the check, turn ignition switch off and dis-
connect SUZUKI scan tool from DLC.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Clearance
After repair or replace malfunction part(s), clear all DTCs by per-
forming the following procedure.
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Using service wire (4), connect diagnosis switch terminal (2)
of diagnosis monitor coupler (1) to ground terminal (3).
3) With connection described in above Step 2) maintained, turn
ignition switch ON.
WARNING:
When performing a driving test, select a safe place where
there is neither any traffic nor any traffic accident possi-
bility and be very careful during testing to avoid occur-
rence of an accident.
Page 167 of 656
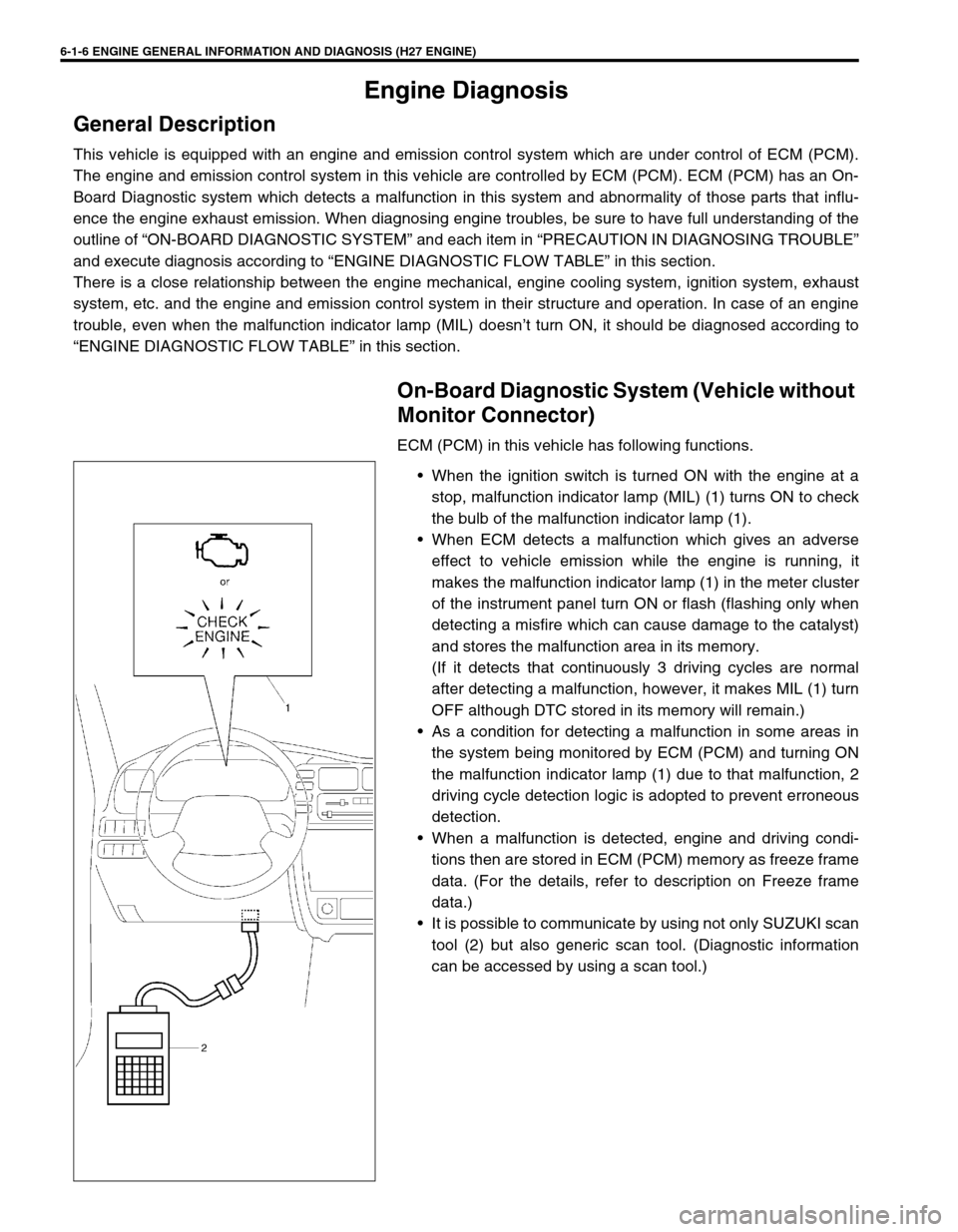
6-1-6 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
Engine Diagnosis
General Description
This vehicle is equipped with an engine and emission control system which are under control of ECM (PCM).
The engine and emission control system in this vehicle are controlled by ECM (PCM). ECM (PCM) has an On-
Board Diagnostic system which detects a malfunction in this system and abnormality of those parts that influ-
ence the engine exhaust emission. When diagnosing engine troubles, be sure to have full understanding of the
outline of “ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM” and each item in “PRECAUTION IN DIAGNOSING TROUBLE”
and execute diagnosis according to “ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE” in this section.
There is a close relationship between the engine mechanical, engine cooling system, ignition system, exhaust
system, etc. and the engine and emission control system in their structure and operation. In case of an engine
trouble, even when the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) doesn’t turn ON, it should be diagnosed according to
“ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE” in this section.
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle without
Monitor Connector)
ECM (PCM) in this vehicle has following functions.
When the ignition switch is turned ON with the engine at a
stop, malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (1) turns ON to check
the bulb of the malfunction indicator lamp (1).
When ECM detects a malfunction which gives an adverse
effect to vehicle emission while the engine is running, it
makes the malfunction indicator lamp (1) in the meter cluster
of the instrument panel turn ON or flash (flashing only when
detecting a misfire which can cause damage to the catalyst)
and stores the malfunction area in its memory.
(If it detects that continuously 3 driving cycles are normal
after detecting a malfunction, however, it makes MIL (1) turn
OFF although DTC stored in its memory will remain.)
As a condition for detecting a malfunction in some areas in
the system being monitored by ECM (PCM) and turning ON
the malfunction indicator lamp (1) due to that malfunction, 2
driving cycle detection logic is adopted to prevent erroneous
detection.
When a malfunction is detected, engine and driving condi-
tions then are stored in ECM (PCM) memory as freeze frame
data. (For the details, refer to description on Freeze frame
data.)
It is possible to communicate by using not only SUZUKI scan
tool (2) but also generic scan tool. (Diagnostic information
can be accessed by using a scan tool.)
Page 172 of 656
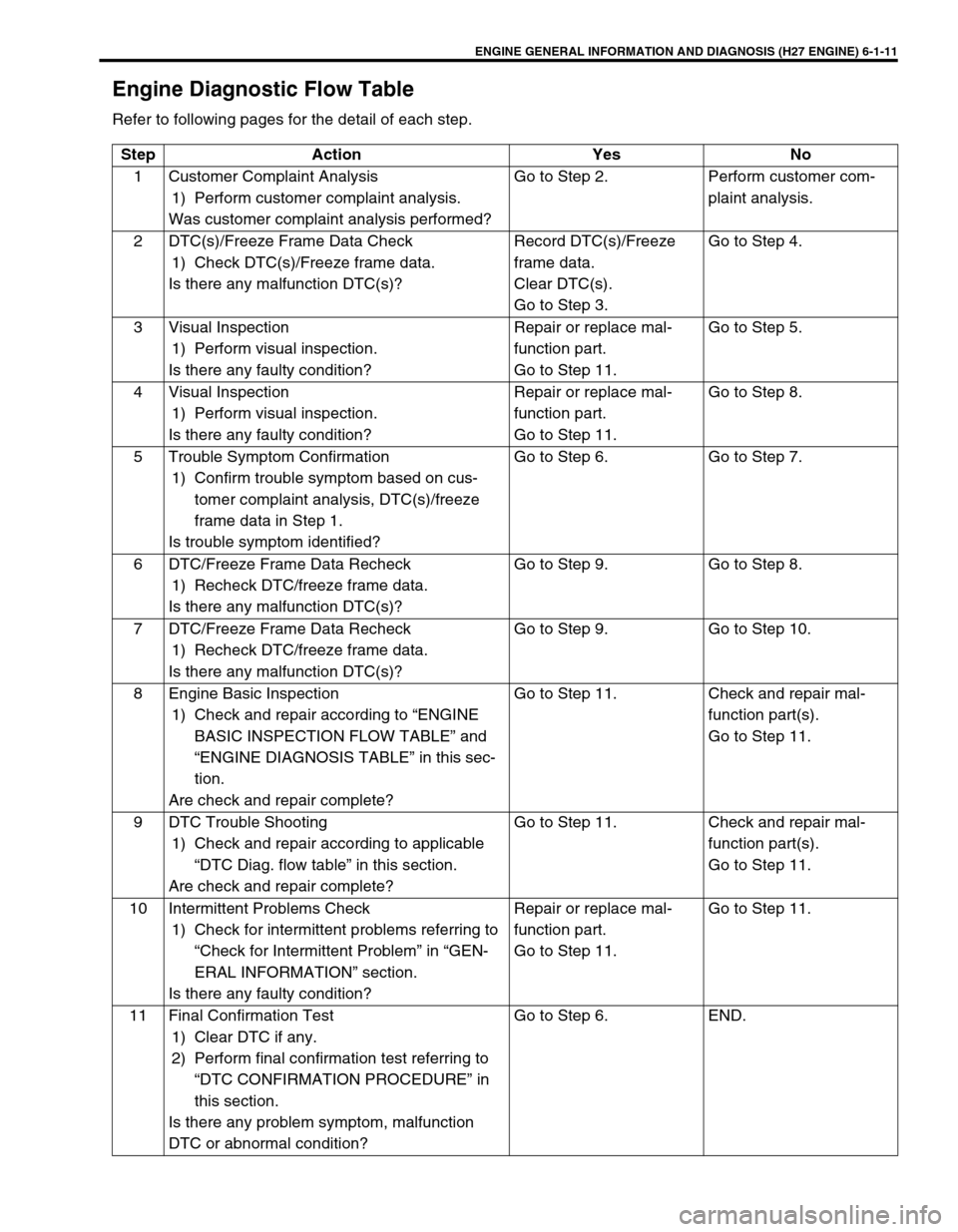
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-11
Engine Diagnostic Flow Table
Refer to following pages for the detail of each step.
Step Action Yes No
1 Customer Complaint Analysis
1) Perform customer complaint analysis.
Was customer complaint analysis performed?Go to Step 2. Perform customer com-
plaint analysis.
2 DTC(s)/Freeze Frame Data Check
1) Check DTC(s)/Freeze frame data.
Is there any malfunction DTC(s)?Record DTC(s)/Freeze
frame data.
Clear DTC(s).
Go to Step 3.Go to Step 4.
3 Visual Inspection
1) Perform visual inspection.
Is there any faulty condition?Repair or replace mal-
function part.
Go to Step 11.Go to Step 5.
4 Visual Inspection
1) Perform visual inspection.
Is there any faulty condition?Repair or replace mal-
function part.
Go to Step 11.Go to Step 8.
5 Trouble Symptom Confirmation
1) Confirm trouble symptom based on cus-
tomer complaint analysis, DTC(s)/freeze
frame data in Step 1.
Is trouble symptom identified?Go to Step 6. Go to Step 7.
6 DTC/Freeze Frame Data Recheck
1) Recheck DTC/freeze frame data.
Is there any malfunction DTC(s)?Go to Step 9. Go to Step 8.
7 DTC/Freeze Frame Data Recheck
1) Recheck DTC/freeze frame data.
Is there any malfunction DTC(s)?Go to Step 9. Go to Step 10.
8 Engine Basic Inspection
1) Check and repair according to “ENGINE
BASIC INSPECTION FLOW TABLE” and
“ENGINE DIAGNOSIS TABLE” in this sec-
tion.
Are check and repair complete?Go to Step 11. Check and repair mal-
function part(s).
Go to Step 11.
9 DTC Trouble Shooting
1) Check and repair according to applicable
“DTC Diag. flow table” in this section.
Are check and repair complete?Go to Step 11. Check and repair mal-
function part(s).
Go to Step 11.
10 Intermittent Problems Check
1) Check for intermittent problems referring to
“Check for Intermittent Problem” in “GEN-
ERAL INFORMATION” section.
Is there any faulty condition?Repair or replace mal-
function part.
Go to Step 11.Go to Step 11.
11 Final Confirmation Test
1) Clear DTC if any.
2) Perform final confirmation test referring to
“DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE” in
this section.
Is there any problem symptom, malfunction
DTC or abnormal condition?Go to Step 6. END.
Page 173 of 656
6-1-12 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
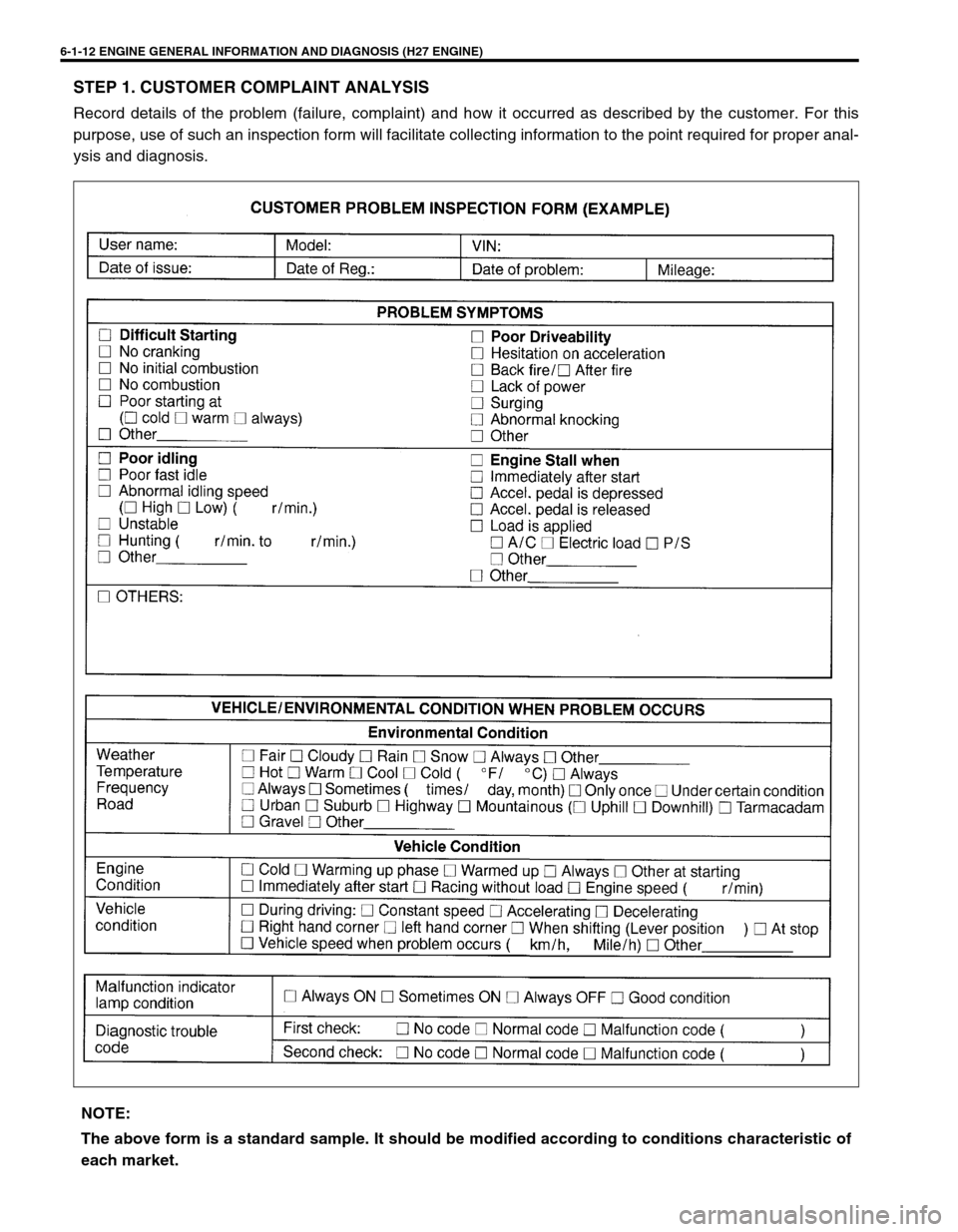
STEP 1. CUSTOMER COMPLAINT ANALYSIS
Record details of the problem (failure, complaint) and how it occurred as described by the customer. For this
purpose, use of such an inspection form will facilitate collecting information to the point required for proper anal-
ysis and diagnosis.
NOTE:
The above form is a standard sample. It should be modified according to conditions characteristic of
each market.
Page 177 of 656
6-1-16 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
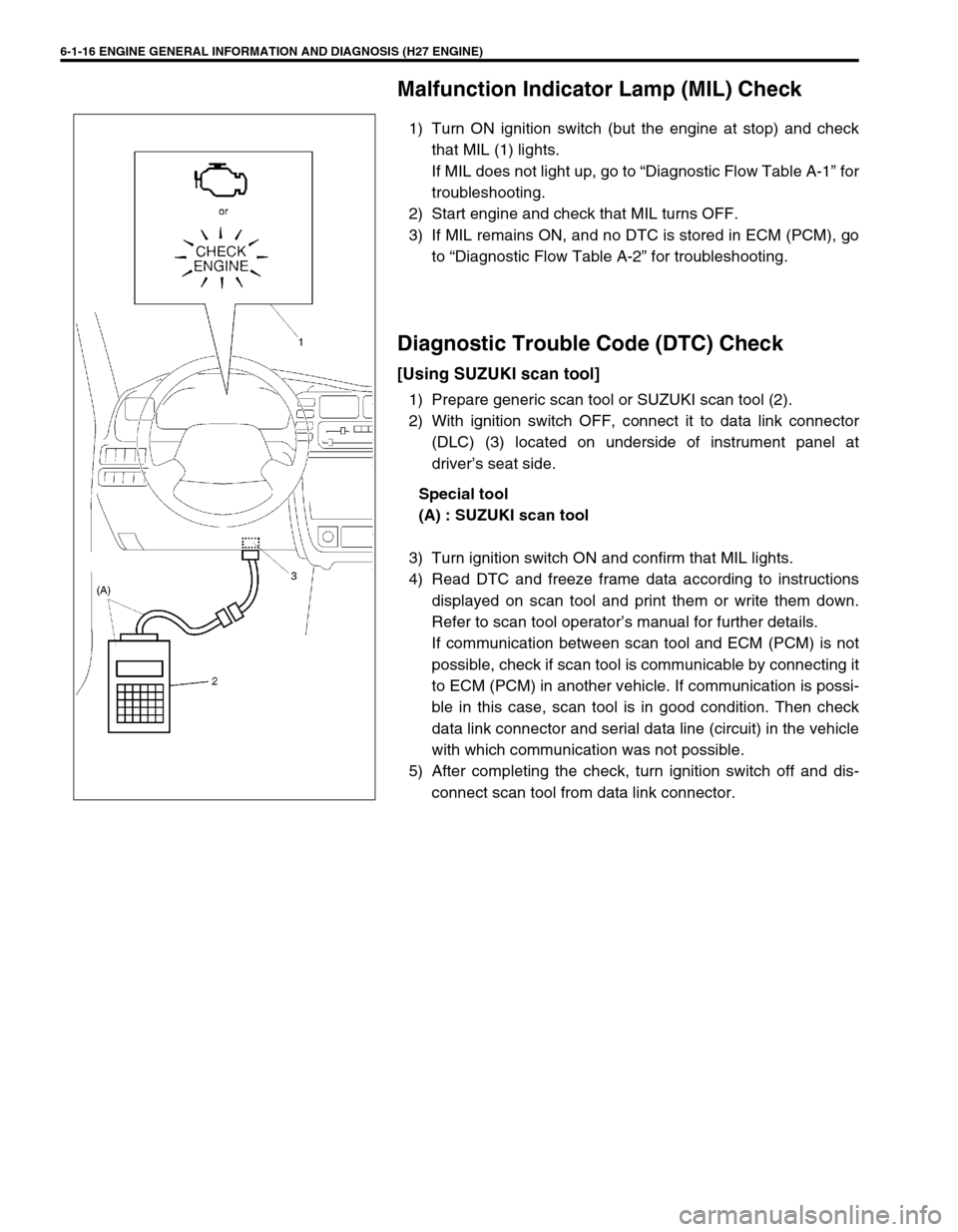
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Check
1) Turn ON ignition switch (but the engine at stop) and check
that MIL (1) lights.
If MIL does not light up, go to “Diagnostic Flow Table A-1” for
troubleshooting.
2) Start engine and check that MIL turns OFF.
3) If MIL remains ON, and no DTC is stored in ECM (PCM), go
to “Diagnostic Flow Table A-2” for troubleshooting.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Check
[Using SUZUKI scan tool]
1) Prepare generic scan tool or SUZUKI scan tool (2).
2) With ignition switch OFF, connect it to data link connector
(DLC) (3) located on underside of instrument panel at
driver’s seat side.
Special tool
(A) : SUZUKI scan tool
3) Turn ignition switch ON and confirm that MIL lights.
4) Read DTC and freeze frame data according to instructions
displayed on scan tool and print them or write them down.
Refer to scan tool operator’s manual for further details.
If communication between scan tool and ECM (PCM) is not
possible, check if scan tool is communicable by connecting it
to ECM (PCM) in another vehicle. If communication is possi-
ble in this case, scan tool is in good condition. Then check
data link connector and serial data line (circuit) in the vehicle
with which communication was not possible.
5) After completing the check, turn ignition switch off and dis-
connect scan tool from data link connector.
Page 178 of 656
![SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 2001 2.G User Guide ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-17
[Without Using SUZUKI Scan Tool] (Vehicle with Monitor
Connector)
1) Check malfunction indicator lamp referring to “Malfunction
Indicato SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 2001 2.G User Guide ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-17
[Without Using SUZUKI Scan Tool] (Vehicle with Monitor
Connector)
1) Check malfunction indicator lamp referring to “Malfunction
Indicato](/img/20/7584/w960_7584-177.png)
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-17
[Without Using SUZUKI Scan Tool] (Vehicle with Monitor
Connector)
1) Check malfunction indicator lamp referring to “Malfunction
Indicator Lamp Check” in this section.
2) With the ignition switch OFF position, disconnect SUZUKI
scan tool if connected and using service wire (4), connect
diagnosis switch terminal (1) to ground terminal (2) in moni-
tor connector (3).
3) With the ignition switch ON position and leaving engine OFF,
read DTC from flashing pattern of malfunction indicator
lamp. Refer to “Diagnostic Trouble Code Table”.
If lamp remains ON, go to “Diagnostic Flow Table A-4”.
4) After completing the check, turn the ignition switch OFF posi-
tion and disconnect service wire from monitor coupler.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Clearance
[Using scan tool]
1) With ignition switch OFF, connect generic scan tool or
SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector (DLC).
2) Turn ignition switch ON.
3) Erase DTC according to instructions displayed on scan tool.
Freeze frame data is cleared with the DTC. Refer to scan tool
operator’s manual for further details.
4) After completing the clearance, turn ignition switch off and
disconnect scan tool from data link connector. NOTE:
If abnormality or malfunction lies in two or more areas,
malfunction indicator lamp indicates applicable codes
three times each.
And flashing of these codes is repeated as long as
diagnosis terminal is grounded and ignition switch is
held at ON position.
Take a note of diagnostic trouble code indicated first.
NOTE:
DTC and freeze frame data stored in ECM (PCM) memory
are also cleared in following cases. Be careful not to
clear them before keeping their record.
When power to ECM (PCM) is cut off (by disconnecting
battery cable, removing fuse or disconnecting ECM
(PCM) connectors)
When the same malfunction (DTC) is not detected
again during 40 engine warm-up cycles (refer to
“WARM-UP CYCLE” of “ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYS-
TEM” in this section) (Vehicle without monitor connec-
tor)
Page 328 of 656
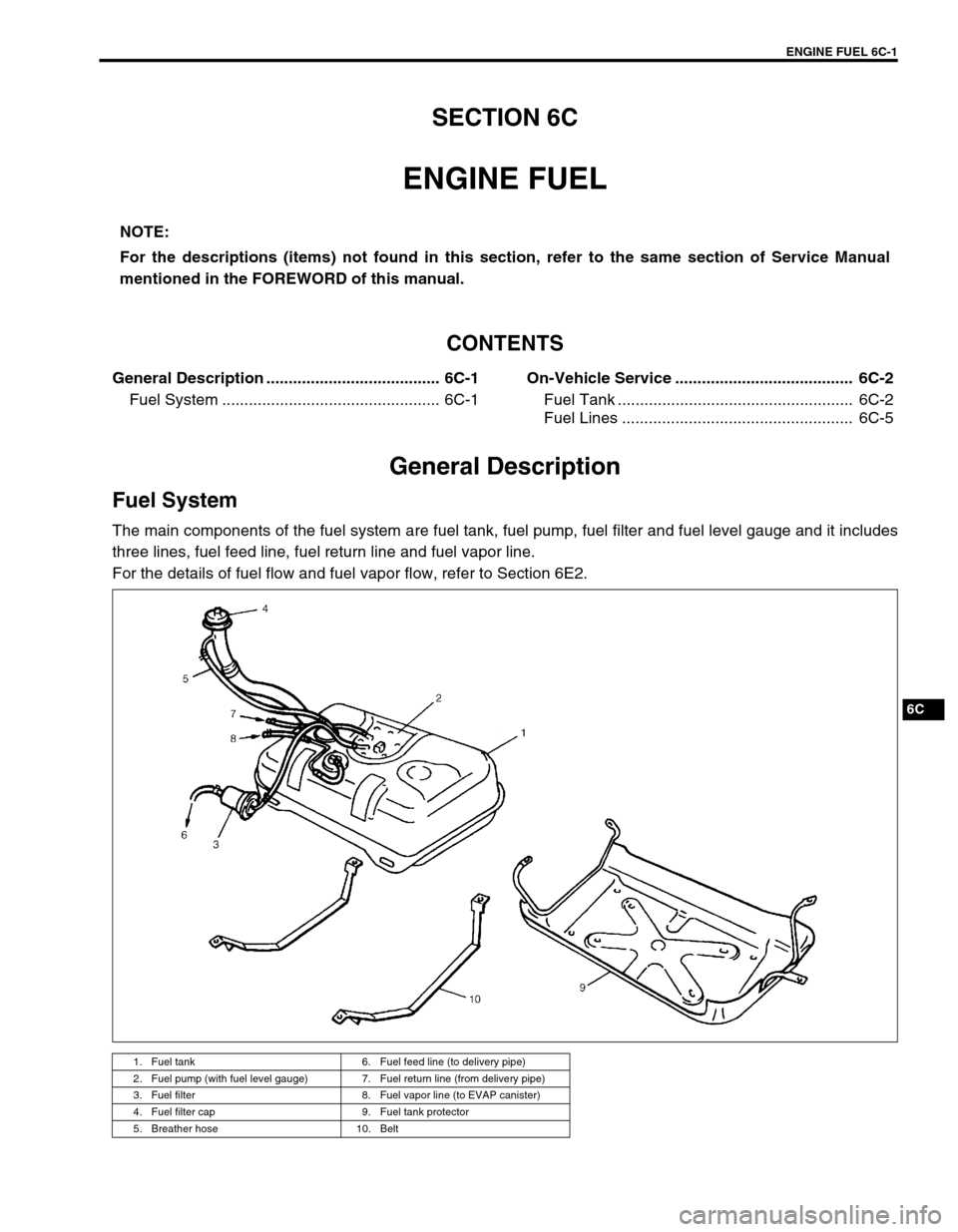
ENGINE FUEL 6C-1
6C
SECTION 6C
ENGINE FUEL
CONTENTS
General Description ....................................... 6C-1
Fuel System ................................................. 6C-1On-Vehicle Service ........................................ 6C-2
Fuel Tank ..................................................... 6C-2
Fuel Lines .................................................... 6C-5
General Description
Fuel System
The main components of the fuel system are fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel filter and fuel level gauge and it includes
three lines, fuel feed line, fuel return line and fuel vapor line.
For the details of fuel flow and fuel vapor flow, refer to Section 6E2.NOTE:
For the descriptions (items) not found in this section, refer to the same section of Service Manual
mentioned in the FOREWORD of this manual.
1. Fuel tank 6. Fuel feed line (to delivery pipe)
2. Fuel pump (with fuel level gauge) 7. Fuel return line (from delivery pipe)
3. Fuel filter 8. Fuel vapor line (to EVAP canister)
4. Fuel filter cap 9. Fuel tank protector
5. Breather hose 10. Belt
Page 385 of 656
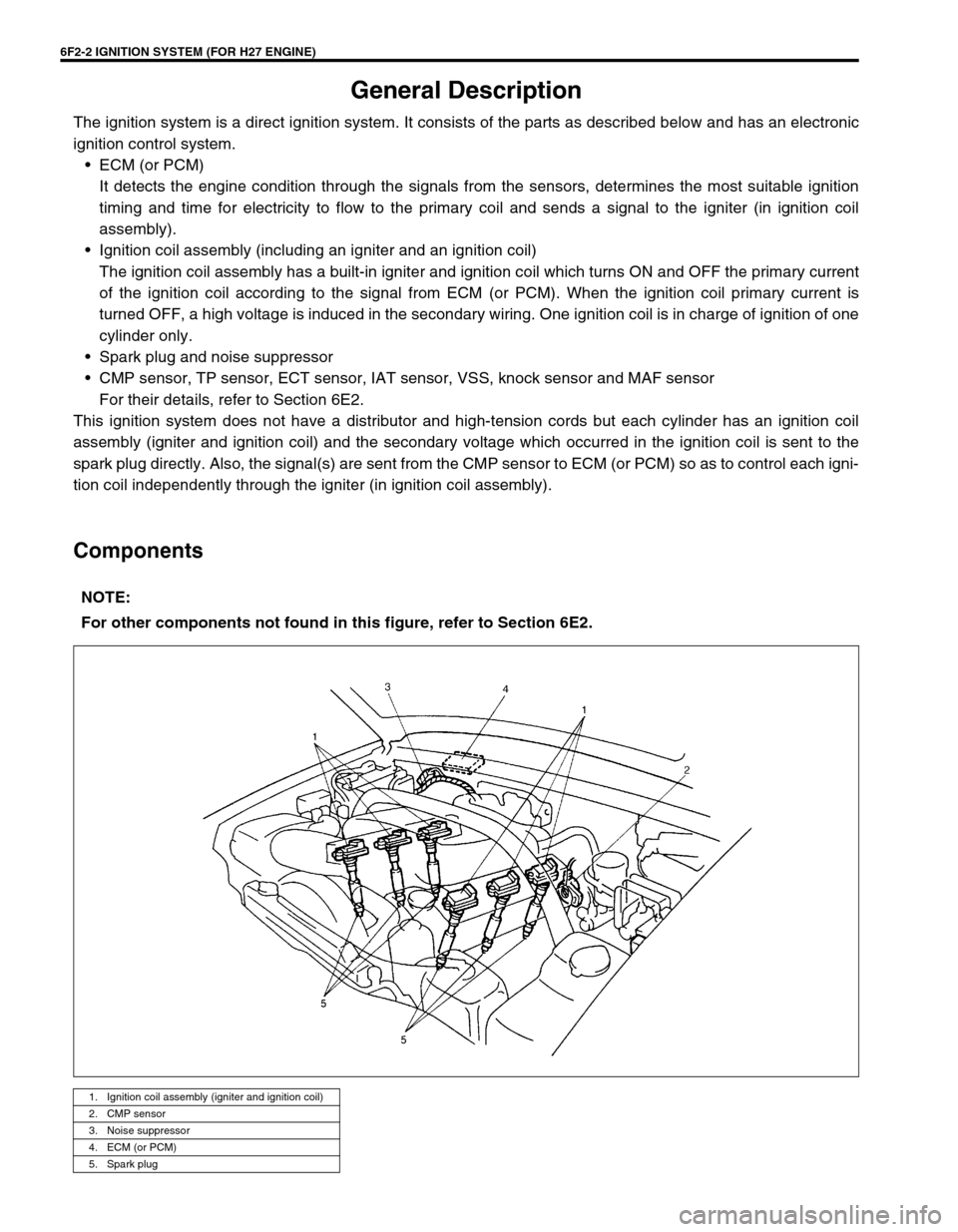
6F2-2 IGNITION SYSTEM (FOR H27 ENGINE)
General Description
The ignition system is a direct ignition system. It consists of the parts as described below and has an electronic
ignition control system.
•ECM (or PCM)
It detects the engine condition through the signals from the sensors, determines the most suitable ignition
timing and time for electricity to flow to the primary coil and sends a signal to the igniter (in ignition coil
assembly).
•Ignition coil assembly (including an igniter and an ignition coil)
The ignition coil assembly has a built-in igniter and ignition coil which turns ON and OFF the primary current
of the ignition coil according to the signal from ECM (or PCM). When the ignition coil primary current is
turned OFF, a high voltage is induced in the secondary wiring. One ignition coil is in charge of ignition of one
cylinder only.
•Spark plug and noise suppressor
•CMP sensor, TP sensor, ECT sensor, IAT sensor, VSS, knock sensor and MAF sensor
For their details, refer to Section 6E2.
This ignition system does not have a distributor and high-tension cords but each cylinder has an ignition coil
assembly (igniter and ignition coil) and the secondary voltage which occurred in the ignition coil is sent to the
spark plug directly. Also, the signal(s) are sent from the CMP sensor to ECM (or PCM) so as to control each igni-
tion coil independently through the igniter (in ignition coil assembly).
Components
NOTE:
For other components not found in this figure, refer to Section 6E2.
1. Ignition coil assembly (igniter and ignition coil)
2. CMP sensor
3. Noise suppressor
4. ECM (or PCM)
5. Spark plug
Page 405 of 656
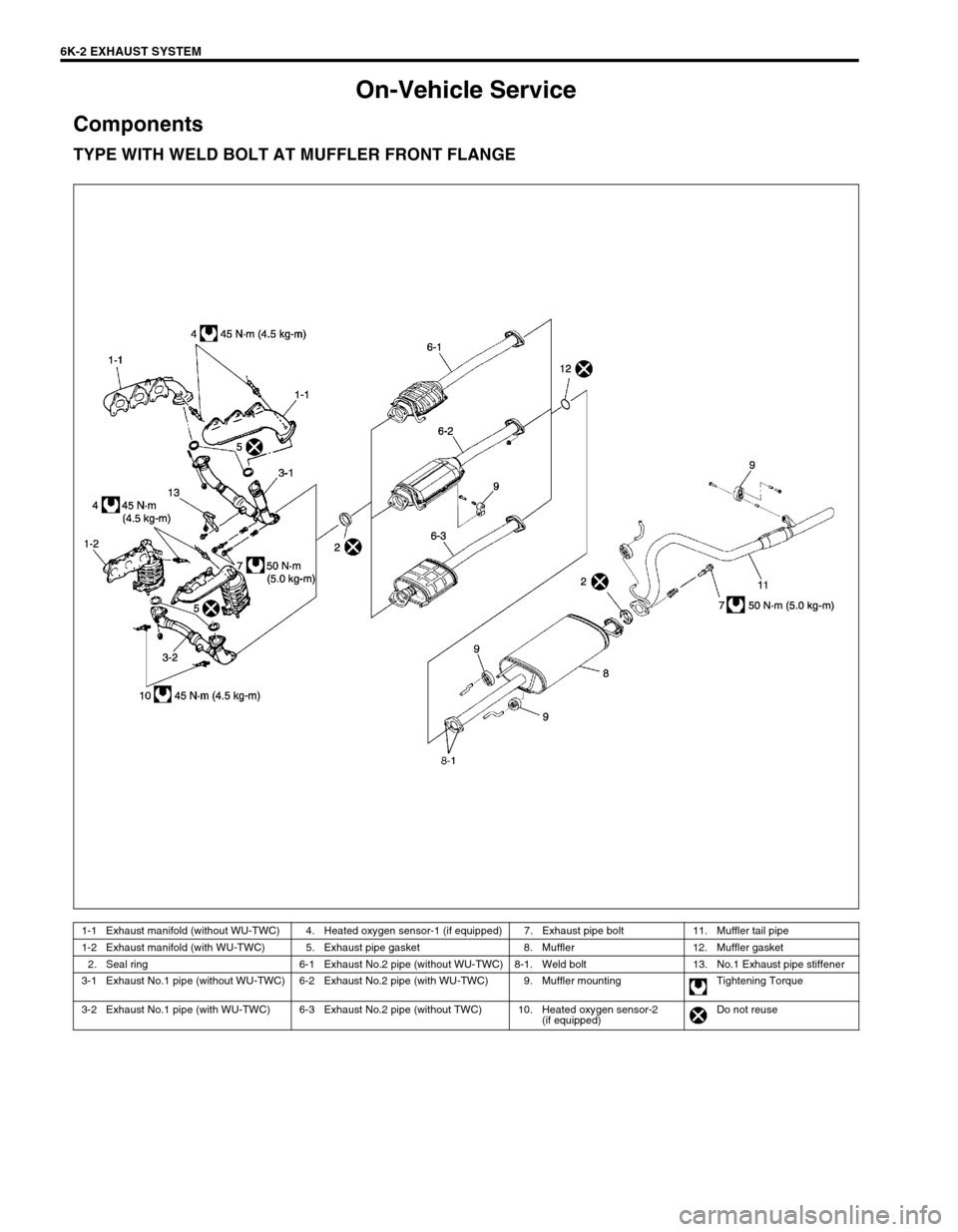
6K-2 EXHAUST SYSTEM
On-Vehicle Service
Components
TYPE WITH WELD BOLT AT MUFFLER FRONT FLANGE
1-1 Exhaust manifold (without WU-TWC) 4. Heated oxygen sensor-1 (if equipped) 7. Exhaust pipe bolt 11. Muffler tail pipe
1-2 Exhaust manifold (with WU-TWC) 5. Exhaust pipe gasket 8. Muffler 12. Muffler gasket
2. Seal ring 6-1 Exhaust No.2 pipe (without WU-TWC) 8-1. Weld bolt 13. No.1 Exhaust pipe stiffener
3-1 Exhaust No.1 pipe (without WU-TWC) 6-2 Exhaust No.2 pipe (with WU-TWC) 9. Muffler mounting Tightening Torque
3-2 Exhaust No.1 pipe (with WU-TWC) 6-3 Exhaust No.2 pipe (without TWC) 10. Heated oxygen sensor-2
(if equipped)Do not reuse
Page 406 of 656
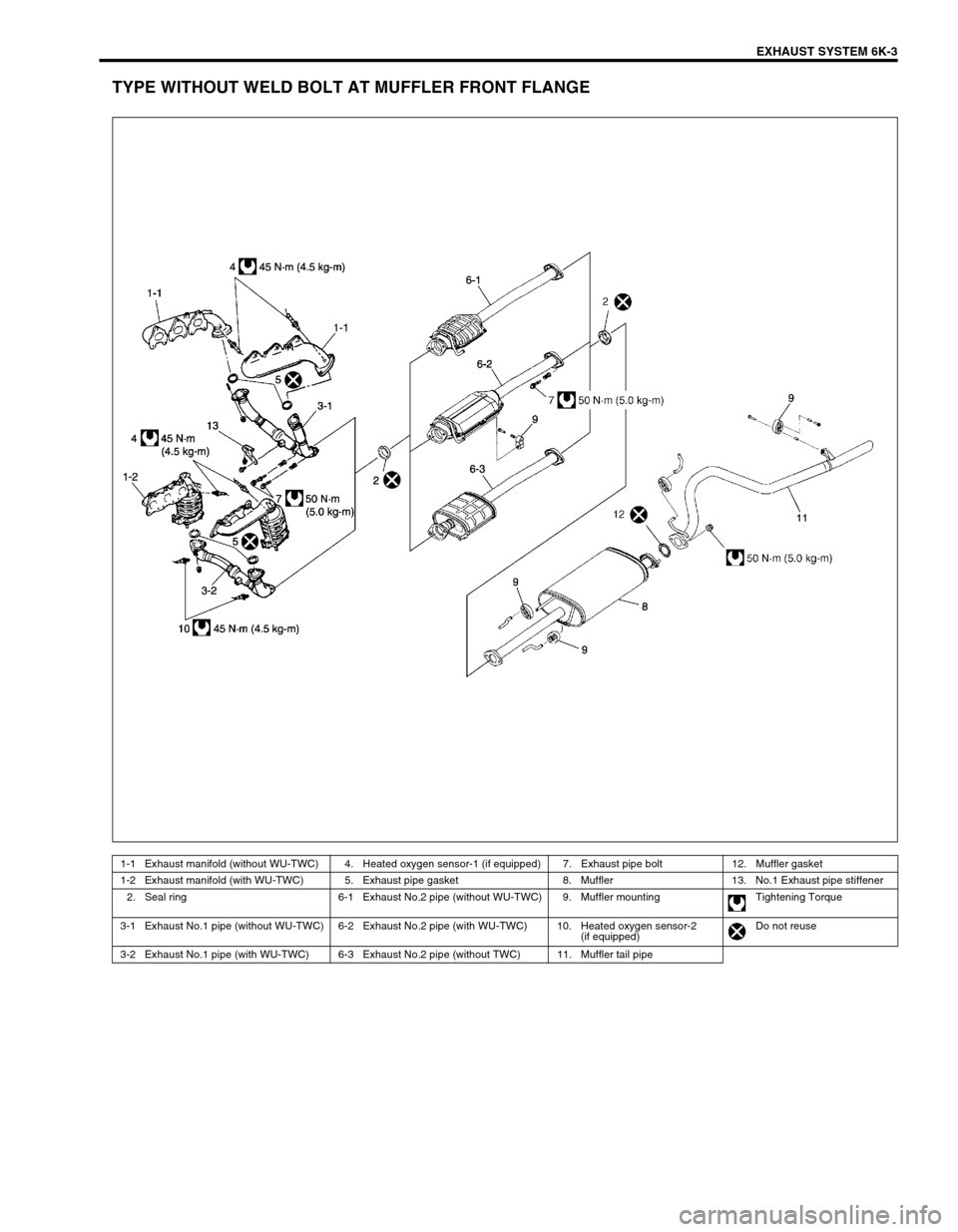
EXHAUST SYSTEM 6K-3
TYPE WITHOUT WELD BOLT AT MUFFLER FRONT FLANGE
1-1 Exhaust manifold (without WU-TWC) 4. Heated oxygen sensor-1 (if equipped) 7. Exhaust pipe bolt 12. Muffler gasket
1-2 Exhaust manifold (with WU-TWC) 5. Exhaust pipe gasket 8. Muffler 13. No.1 Exhaust pipe stiffener
2. Seal ring 6-1 Exhaust No.2 pipe (without WU-TWC) 9. Muffler mounting Tightening Torque
3-1 Exhaust No.1 pipe (without WU-TWC) 6-2 Exhaust No.2 pipe (with WU-TWC) 10. Heated oxygen sensor-2
(if equipped)Do not reuse
3-2 Exhaust No.1 pipe (with WU-TWC) 6-3 Exhaust No.2 pipe (without TWC) 11. Muffler tail pipe