tail SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 2001 2.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2001, Model line: GRAND VITARA, Model: SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 2001 2.GPages: 656, PDF Size: 14.31 MB
Page 416 of 656
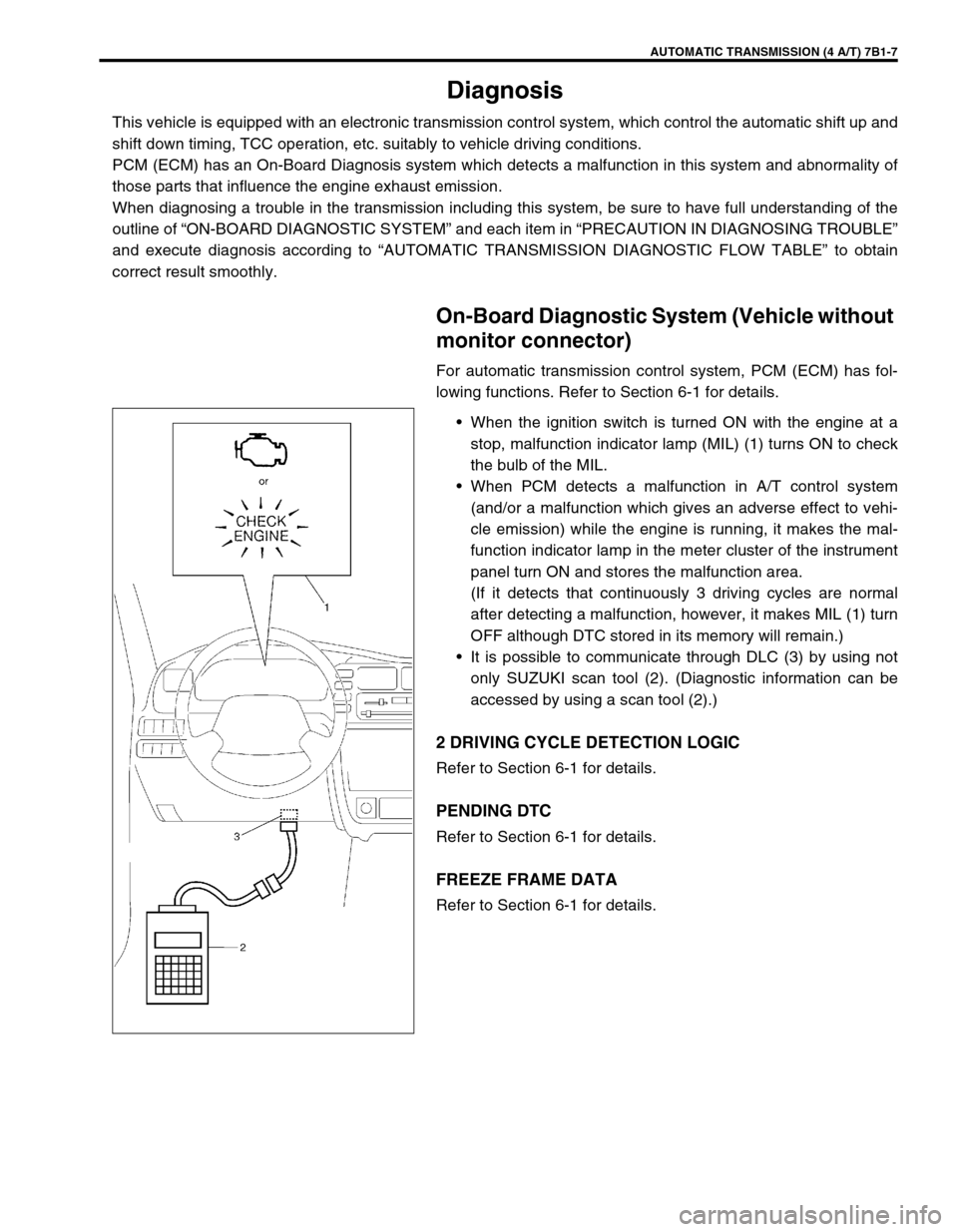
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4 A/T) 7B1-7
Diagnosis
This vehicle is equipped with an electronic transmission control system, which control the automatic shift up and
shift down timing, TCC operation, etc. suitably to vehicle driving conditions.
PCM (ECM) has an On-Board Diagnosis system which detects a malfunction in this system and abnormality of
those parts that influence the engine exhaust emission.
When diagnosing a trouble in the transmission including this system, be sure to have full understanding of the
outline of “ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM” and each item in “PRECAUTION IN DIAGNOSING TROUBLE”
and execute diagnosis according to “AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE” to obtain
correct result smoothly.
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle without
monitor connector)
For automatic transmission control system, PCM (ECM) has fol-
lowing functions. Refer to Section 6-1 for details.
•When the ignition switch is turned ON with the engine at a
stop, malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (1) turns ON to check
the bulb of the MIL.
•When PCM detects a malfunction in A/T control system
(and/or a malfunction which gives an adverse effect to vehi-
cle emission) while the engine is running, it makes the mal-
function indicator lamp in the meter cluster of the instrument
panel turn ON and stores the malfunction area.
(If it detects that continuously 3 driving cycles are normal
after detecting a malfunction, however, it makes MIL (1) turn
OFF although DTC stored in its memory will remain.)
•It is possible to communicate through DLC (3) by using not
only SUZUKI scan tool (2). (Diagnostic information can be
accessed by using a scan tool (2).)
2 DRIVING CYCLE DETECTION LOGIC
Refer to Section 6-1 for details.
PENDING DTC
Refer to Section 6-1 for details.
FREEZE FRAME DATA
Refer to Section 6-1 for details.
Page 417 of 656
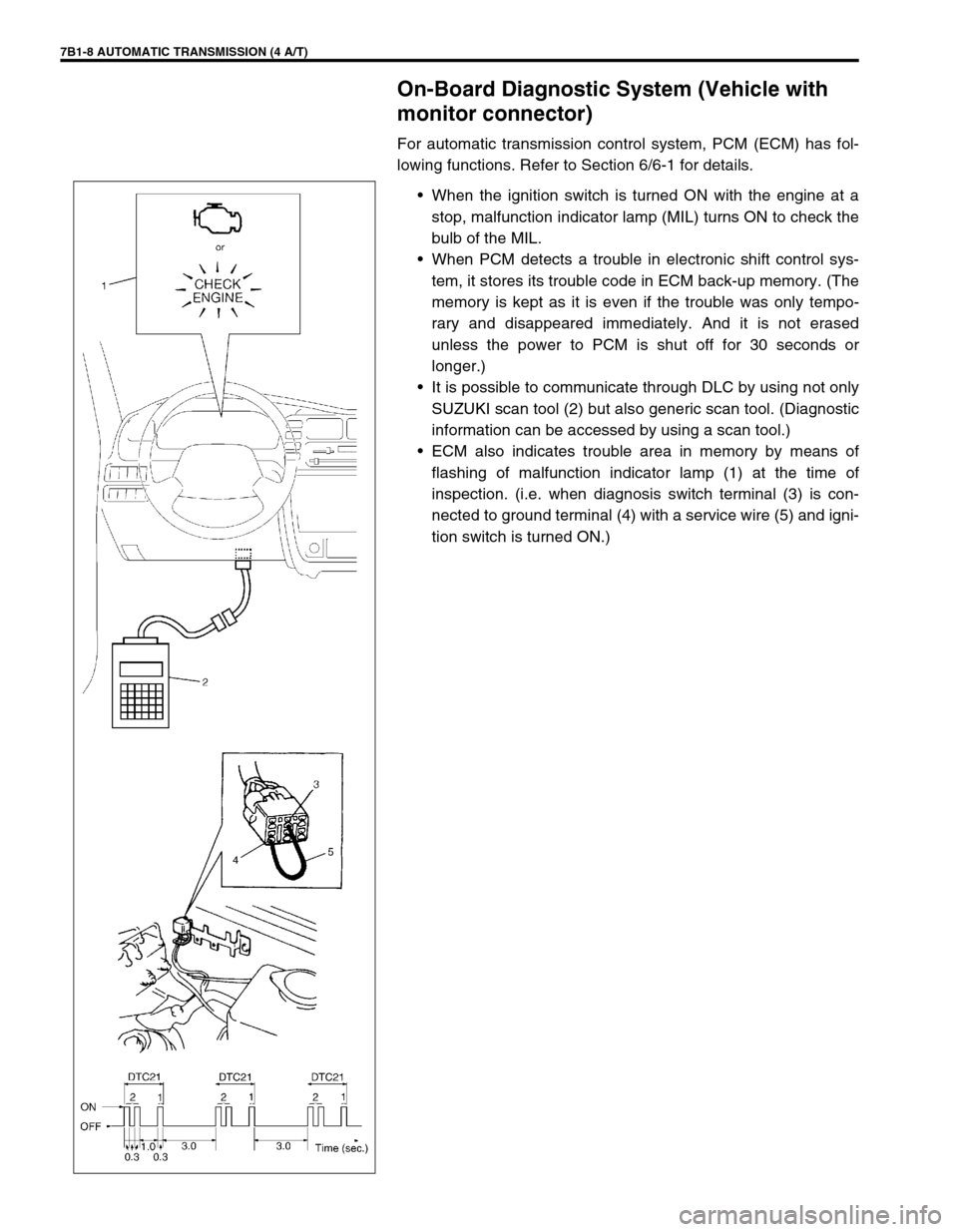
7B1-8 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4 A/T)
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle with
monitor connector)
For automatic transmission control system, PCM (ECM) has fol-
lowing functions. Refer to Section 6/6-1 for details.
•When the ignition switch is turned ON with the engine at a
stop, malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) turns ON to check the
bulb of the MIL.
•When PCM detects a trouble in electronic shift control sys-
tem, it stores its trouble code in ECM back-up memory. (The
memory is kept as it is even if the trouble was only tempo-
rary and disappeared immediately. And it is not erased
unless the power to PCM is shut off for 30 seconds or
longer.)
•It is possible to communicate through DLC by using not only
SUZUKI scan tool (2) but also generic scan tool. (Diagnostic
information can be accessed by using a scan tool.)
•ECM also indicates trouble area in memory by means of
flashing of malfunction indicator lamp (1) at the time of
inspection. (i.e. when diagnosis switch terminal (3) is con-
nected to ground terminal (4) with a service wire (5) and igni-
tion switch is turned ON.)
Page 419 of 656
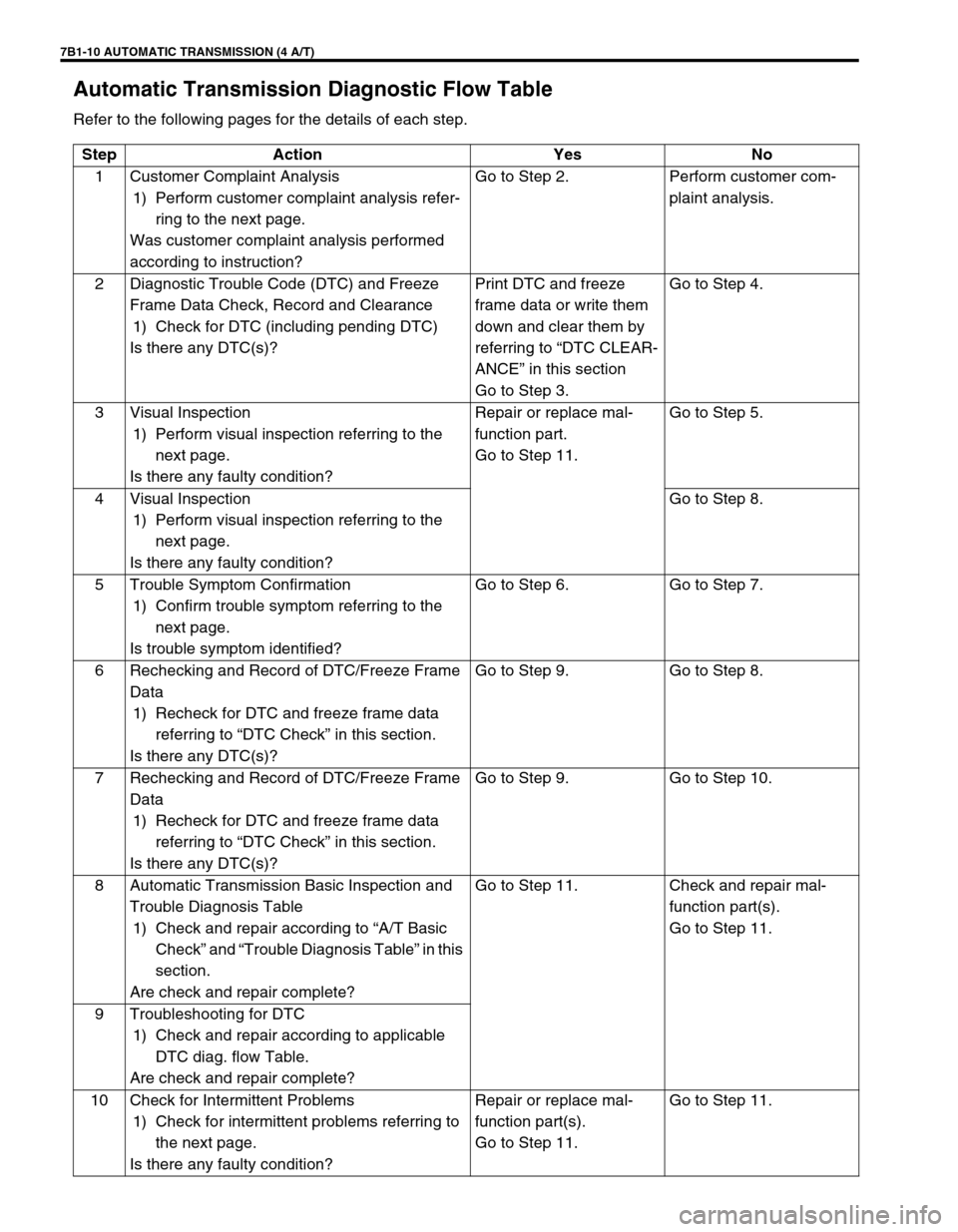
7B1-10 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4 A/T)
Automatic Transmission Diagnostic Flow Table
Refer to the following pages for the details of each step.
Step Action Yes No
1 Customer Complaint Analysis
1) Perform customer complaint analysis refer-
ring to the next page.
Was customer complaint analysis performed
according to instruction?Go to Step 2. Perform customer com-
plaint analysis.
2 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and Freeze
Frame Data Check, Record and Clearance
1) Check for DTC (including pending DTC)
Is there any DTC(s)?Print DTC and freeze
frame data or write them
down and clear them by
referring to “DTC CLEAR-
ANCE” in this section
Go to Step 3.Go to Step 4.
3 Visual Inspection
1) Perform visual inspection referring to the
next page.
Is there any faulty condition?Repair or replace mal-
function part.
Go to Step 11.Go to Step 5.
4 Visual Inspection
1) Perform visual inspection referring to the
next page.
Is there any faulty condition?Go to Step 8.
5 Trouble Symptom Confirmation
1) Confirm trouble symptom referring to the
next page.
Is trouble symptom identified?Go to Step 6. Go to Step 7.
6 Rechecking and Record of DTC/Freeze Frame
Data
1) Recheck for DTC and freeze frame data
referring to “DTC Check” in this section.
Is there any DTC(s)?Go to Step 9. Go to Step 8.
7 Rechecking and Record of DTC/Freeze Frame
Data
1) Recheck for DTC and freeze frame data
referring to “DTC Check” in this section.
Is there any DTC(s)?Go to Step 9. Go to Step 10.
8 Automatic Transmission Basic Inspection and
Trouble Diagnosis Table
1) Check and repair according to “A/T Basic
Check” and “Trouble Diagnosis Table” in this
section.
Are check and repair complete?Go to Step 11. Check and repair mal-
function part(s).
Go to Step 11.
9 Troubleshooting for DTC
1) Check and repair according to applicable
DTC diag. flow Table.
Are check and repair complete?
10 Check for Intermittent Problems
1) Check for intermittent problems referring to
the next page.
Is there any faulty condition?Repair or replace mal-
function part(s).
Go to Step 11.Go to Step 11.
Page 420 of 656

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4 A/T) 7B1-11
STEP 1. CUSTOMER COMPLAINT ANALYSIS
Record details of the problem (failure, complaint) and how it occurred as described by the customer.
For this purpose, use of such a inspection form will facilitate collecting information to the point required for
proper analysis and diagnosis.
STEP 2. DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC)/FREEZE FRAME DATA CHECK, RECORD AND
CLEARANCE
First, referring to DTC check section, check DTC (including pending DTC). If DTC exists, print or write down
DTC and freeze frame data and then clear them by referring to DTC clearance section. DTC indicates malfunc-
tion in the system but it is not possible to know from it whether the malfunction is occurring now or it occurred in
the past and normal condition has been restored. In order to know that, check symptom in question according to
Step 5 and then recheck DTC according to Step 6.
Diagnosing a trouble based on the DTC in this step only or failure to clear the DTC in this step may result in an
faulty diagnosis, trouble diagnosis of a normal circuit or difficulty in troubleshooting which is otherwise unneces-
sary.
STEP 3 and STEP 4. VISUAL INSPECTION
As a preliminary step, be sure to perform visual check of the items that support proper function of the A/T and
engine referring to Visual Inspection section.
STEP 5. TROUBLE SYMPTOM CONFIRMATION
Check trouble symptoms based on information obtained in Step 1 “CUSTOMER COMPLAINT ANALYSIS” and
Step 2 “DTC/FREEZE FRAME DATA CHECK”.
Also, recheck DTC according to “DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE” described in each “DTC FLOW
TABLE”.
STEP 6 and STEP 7. RECHECKING AND RECORD OF DTC/FREEZE FRAME DATA
Refer to “DTC CHECK” in this section for checking procedure.
STEP 8. A/T BASIC CHECK AND TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS TABLE
Perform A/T basic check according to the “A/T Basic Check Flow Table” first. When the end of the flow table has
been reached, check the parts of the system suspected as a possible cause referring to “TROUBLE DIAGNO-
SIS TABLE” and based on symptoms appearing on the vehicle (symptoms obtained through steps of customer
complaint analysis, trouble symptom confirmation and/or A/T basic check) and repair or replace faulty parts, if
any.
STEP 9. DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE FLOW TABLE
Based on the DTC indicated in Step 6 and 7 and referring to “DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE FLOW TABLE” in
this section, locate the cause of the trouble, namely in a sensor, switch, wire harness, connector, actuator, PCM
or other part and repair or replace faulty parts.11 Final Confirmation Test
1) Clear DTC if any.
2) Perform final confirmation test referring to
the next page.
Is there any problem symptom, DTC or abnor-
mal condition?Go to Step 6. End. Step Action Yes No
Page 552 of 656
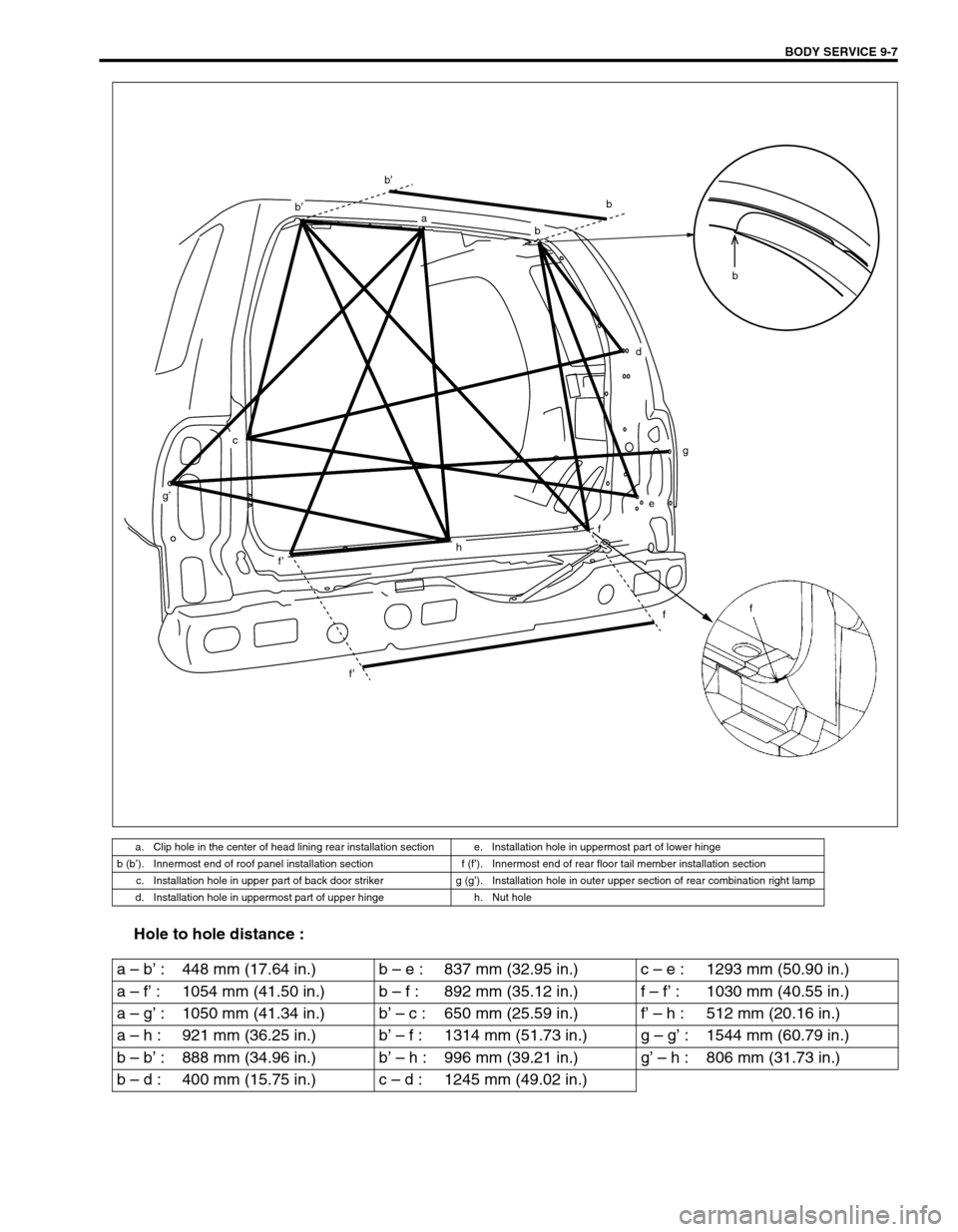
BODY SERVICE 9-7
Hole to hole distance :
a. Clip hole in the center of head lining rear installation section e. Installation hole in uppermost part of lower hinge
b (b’). Innermost end of roof panel installation section f (f’). Innermost end of rear floor tail member installation section
c. Installation hole in upper part of back door striker g (g’). Installation hole in outer upper section of rear combination right lamp
d. Installation hole in uppermost part of upper hinge h. Nut hole
b
ba
b’
b’
c
g’
f’
f’
h
f
f
e
g
d
f
b
a – b’ : 448 mm (17.64 in.) b – e : 837 mm (32.95 in.) c – e : 1293 mm (50.90 in.)
a – f’ : 1054 mm (41.50 in.) b – f : 892 mm (35.12 in.) f – f’ : 1030 mm (40.55 in.)
a – g’ : 1050 mm (41.34 in.) b’ – c : 650 mm (25.59 in.) f’ – h : 512 mm (20.16 in.)
a – h : 921 mm (36.25 in.) b’ – f : 1314 mm (51.73 in.) g – g’ : 1544 mm (60.79 in.)
b – b’ : 888 mm (34.96 in.) b’ – h : 996 mm (39.21 in.) g’ – h : 806 mm (31.73 in.)
b – d : 400 mm (15.75 in.) c – d : 1245 mm (49.02 in.)
Page 555 of 656
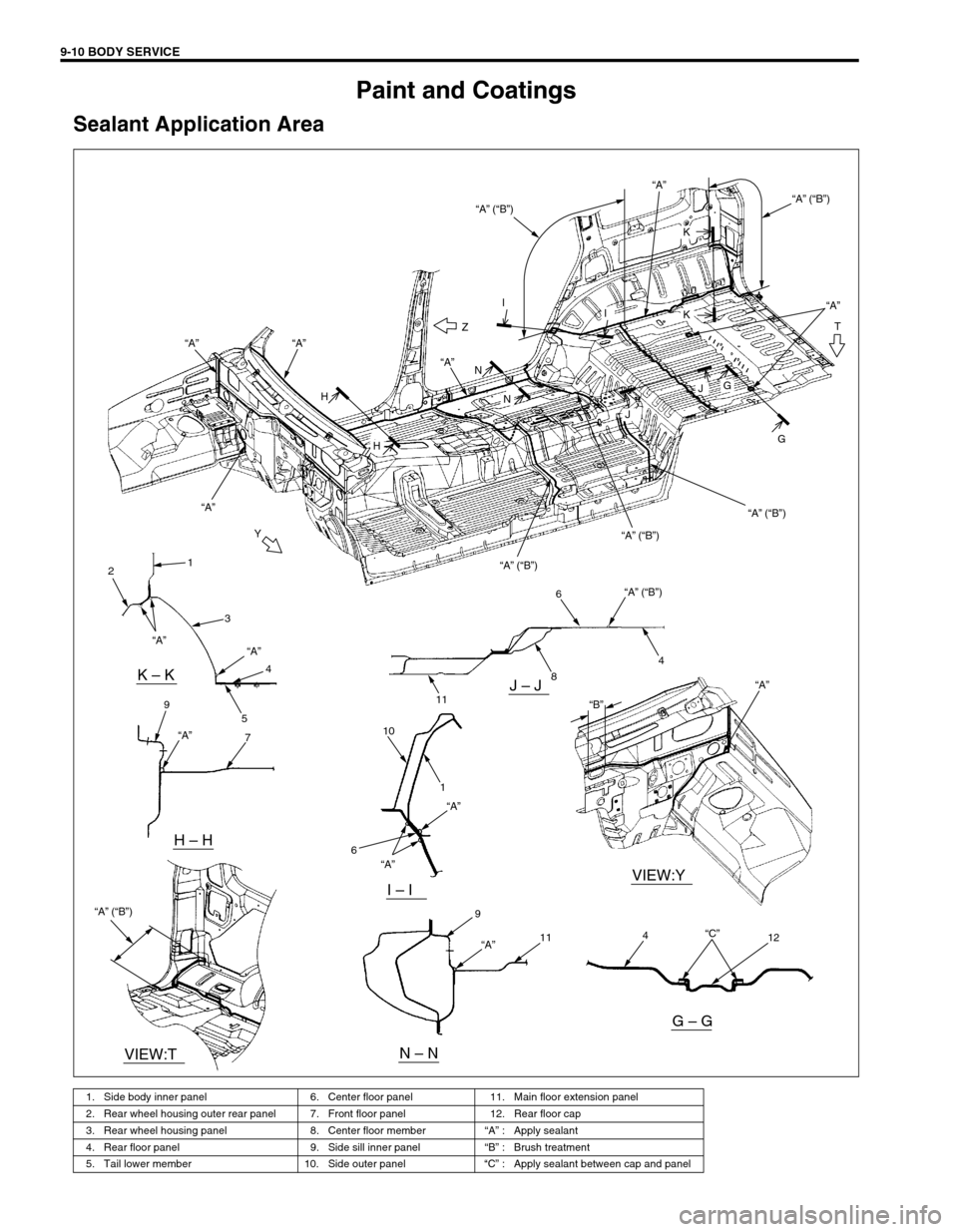
9-10 BODY SERVICE
Paint and Coatings
Sealant Application Area
1. Side body inner panel 6. Center floor panel 11. Main floor extension panel
2. Rear wheel housing outer rear panel 7. Front floor panel 12. Rear floor cap
3. Rear wheel housing panel 8. Center floor member“A” : Apply sealant
4. Rear floor panel 9. Side sill inner panel“B” : Brush treatment
5. Tail lower member 10. Side outer panel“C” : Apply sealant between cap and panel
Y
T
H
N “A”
“A” (“B”)“A”“A”
“A” (“B”)
“A” (“B”)
“A” (“B”)
“A” (“B”) “A”Z
“A”
“A” “A”
II
H
N
J
GJ
G
K
K
1
2
3
4
7 5 9
11
8
1
4 6
10“A” (“B”) “A” (“B”)
“A”“A”
“A”
“A” “A”
“A”
6
9
114
12
“B”
“C”
VIEW:Y
VIEW:T
K – KJ – J
I – I
H – H
N – N
G – G
Page 588 of 656

AIR BAG SYSTEM 10B-11
DTC Check
Using SUZUKI scan tool
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) After setting cartridge to SUZUKI scan tool, connect it to
data link connector (DLC) located on underside of instru-
ment panel at driver’s seat side.
Special tool
(A) : SUZUKI scan tool
3) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
4) Read DTC according to instructions displayed on SUZUKI
scan tool and print it or write it down. Refer to SUZUKI scan
tool operator’s manual for further details.
If communication between scan tool and SDM is not possi-
ble, proceed to Diagnostic Flow Table E (Serial data check
circuit).
5) After completing the check, turn ignition switch to OFF posi-
tion and disconnect SUZUKI scan tool from data link connec-
tor (DLC).
Not using SUZUKI scan tool
1) Check that malfunction indicator lamp (“AIR BAG” warning
lamp) comes ON when ignition switch is turned to ON posi-
tion.
If it does not come “ON”, proceed to Diagnostic Flow Table B
(“AIR BAG” warning lamp circuit).
2) Using service wire, ground diagnosis switch terminal in mon-
itor coupler.
3) Read DTC from flashing pattern of malfunction indicator
lamp (“AIR BAG” warning lamp). (Refer to DTC TABLE.)
If lamp does not indicate DTC, proceed to Diagnostic Flow
Table D (Diagnosis switch terminal circuit check).
4) After completing the check, turn ignition switch to OFF posi-
tion and disconnect service wire from “AIR BAG” monitor
coupler.
1. Data link connector (DLC)
1.“AIR BAG” monitor coupler
2. Body ground
3. Diagnosis switch terminal
4. Service wire
Page 589 of 656
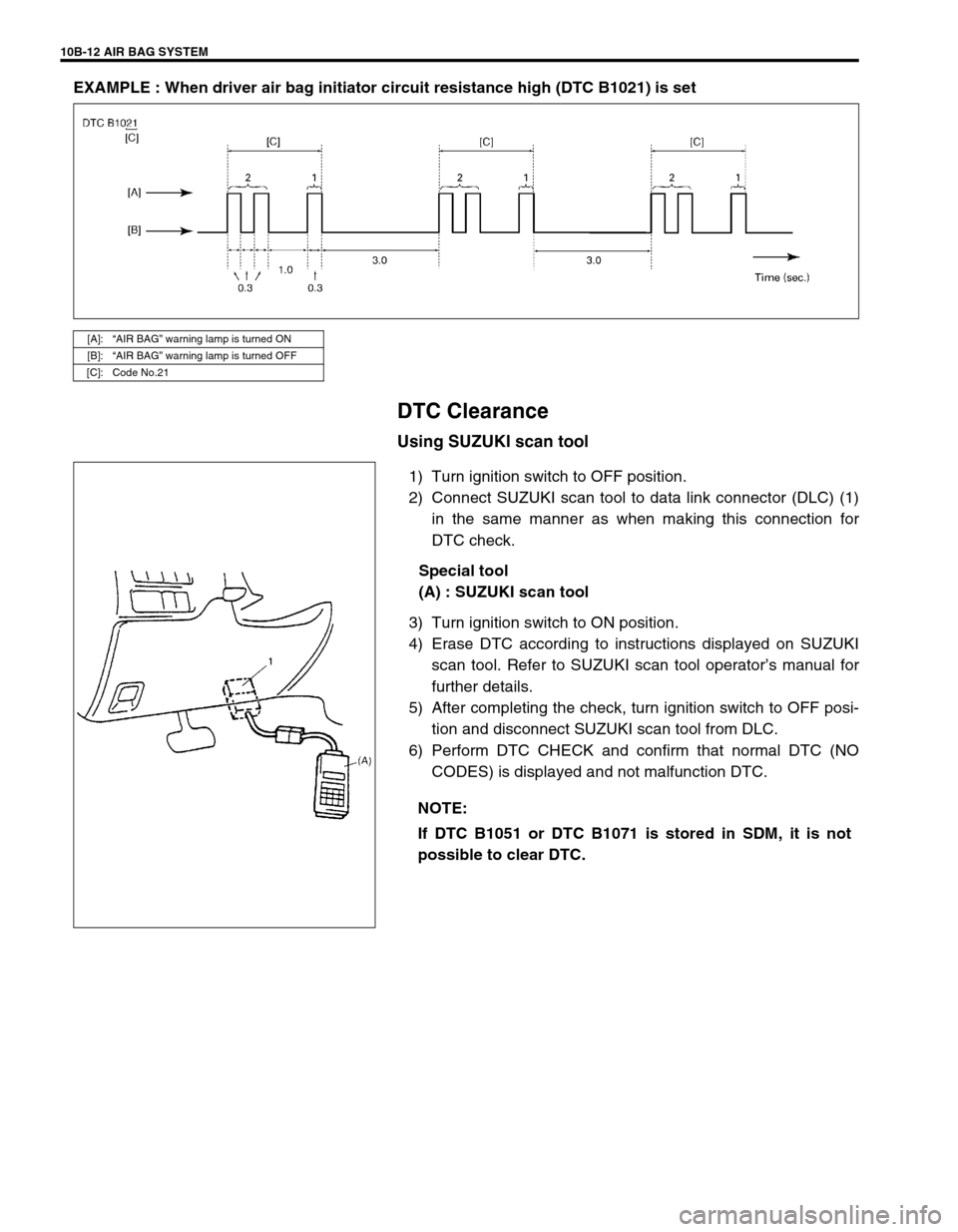
10B-12 AIR BAG SYSTEM
EXAMPLE : When driver air bag initiator circuit resistance high (DTC B1021) is set
DTC Clearance
Using SUZUKI scan tool
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector (DLC) (1)
in the same manner as when making this connection for
DTC check.
Special tool
(A) : SUZUKI scan tool
3) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
4) Erase DTC according to instructions displayed on SUZUKI
scan tool. Refer to SUZUKI scan tool operator’s manual for
further details.
5) After completing the check, turn ignition switch to OFF posi-
tion and disconnect SUZUKI scan tool from DLC.
6) Perform DTC CHECK and confirm that normal DTC (NO
CODES) is displayed and not malfunction DTC.
[A]:“AIR BAG” warning lamp is turned ON
[B]:“AIR BAG” warning lamp is turned OFF
[C]: Code No.21
NOTE:
If DTC B1051 or DTC B1071 is stored in SDM, it is not
possible to clear DTC.
Page 648 of 656

AIR BAG SYSTEM 10B-71
18) Dispose of the deployed air bag (inflator) module and the
activated seat belt pretensioner through normal refuse chan-
nels after it has cooled for at least 10 minutes and tightly seal
the air bag (inflator) module and the seat belt pretensioner in
a strong vinyl bag. (Refer to “DEPLOYED AIR BAG (INFLA-
TOR) MODULE AND ACTIVATED SEAT BELT PRETEN-
SIONER DISPOSAL” in detail.)
19) Wash your hands with mild soap and water afterward.
20) Ensure that the deployment harness has been disconnected
from the power source and that its two banana plugs have
been shorted together by fully seating one banana plug into
the other.
21) Disconnect the deployment harness from the air bag (infla-
tor) module and the seat belt pretensioner.
22) Temporarily store air bag (inflator) module or seat belt pre-
tensioner.
[For driver air bag (inflator) module]
Temporarily store the air bag (inflator) module with its vinyl
trim cover facing up, away from the surface upon which it
rests. Refer to “SERVICE PRECAUTIONS” for details.
[For seat belt pretensioner]
When temporarily strong the seat belt pretensioner, be sure
NOT to face its exhaust hole provided side down. It must
face up. Refer to “SERVICE PRECAUTIONS” for details.
23) Contact your local distributor for further assistance.
NOTE:
The remaining steps are to be followed in the unlikely
event that the air bag (inflator) module did not deploy or
the seat belt pretensioner did not activate after following
these procedures.
Page 652 of 656
AIR BAG SYSTEM 10B-75
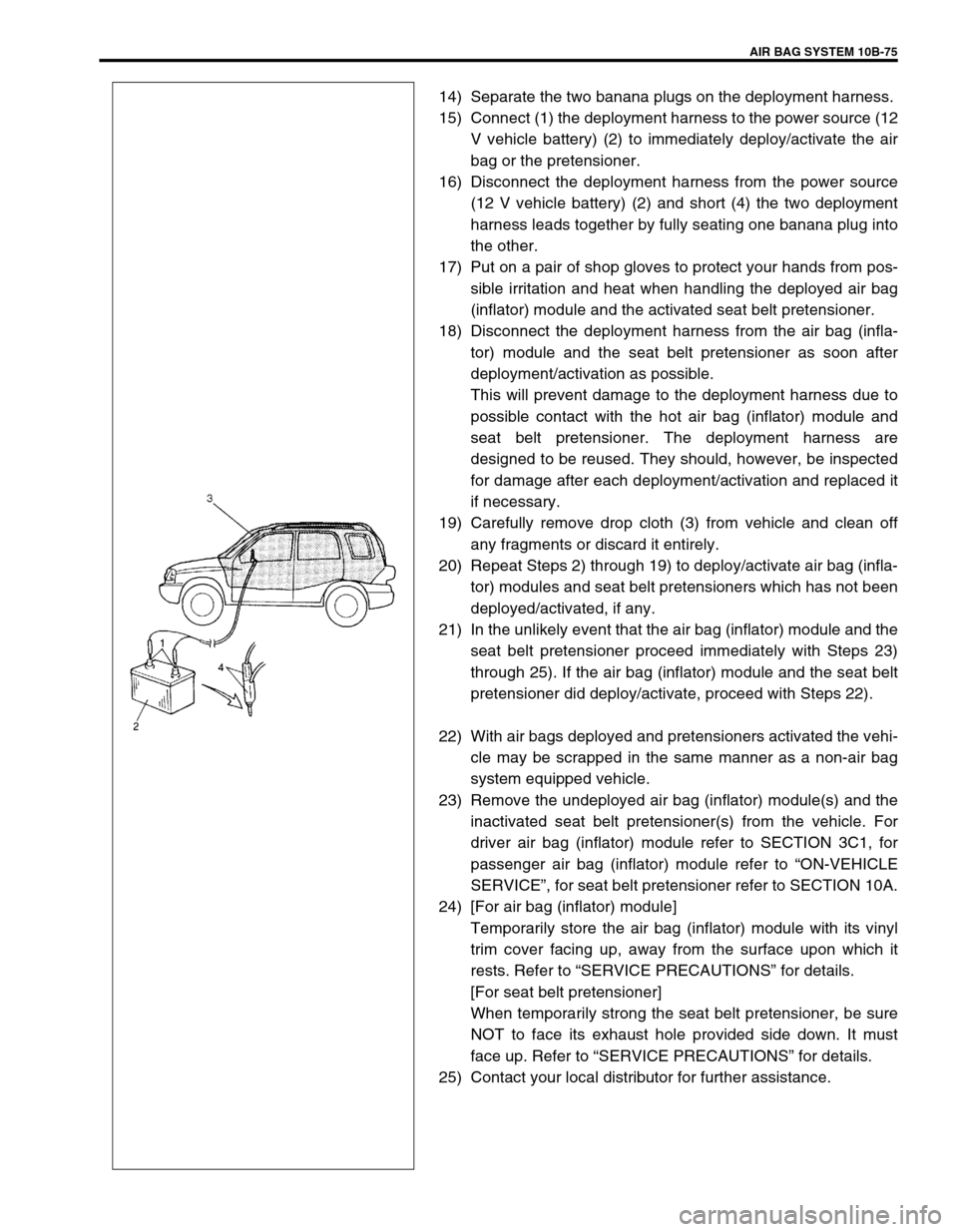
14) Separate the two banana plugs on the deployment harness.
15) Connect (1) the deployment harness to the power source (12
V vehicle battery) (2) to immediately deploy/activate the air
bag or the pretensioner.
16) Disconnect the deployment harness from the power source
(12 V vehicle battery) (2) and short (4) the two deployment
harness leads together by fully seating one banana plug into
the other.
17) Put on a pair of shop gloves to protect your hands from pos-
sible irritation and heat when handling the deployed air bag
(inflator) module and the activated seat belt pretensioner.
18) Disconnect the deployment harness from the air bag (infla-
tor) module and the seat belt pretensioner as soon after
deployment/activation as possible.
This will prevent damage to the deployment harness due to
possible contact with the hot air bag (inflator) module and
seat belt pretensioner. The deployment harness are
designed to be reused. They should, however, be inspected
for damage after each deployment/activation and replaced it
if necessary.
19) Carefully remove drop cloth (3) from vehicle and clean off
any fragments or discard it entirely.
20) Repeat Steps 2) through 19) to deploy/activate air bag (infla-
tor) modules and seat belt pretensioners which has not been
deployed/activated, if any.
21) In the unlikely event that the air bag (inflator) module and the
seat belt pretensioner proceed immediately with Steps 23)
through 25). If the air bag (inflator) module and the seat belt
pretensioner did deploy/activate, proceed with Steps 22).
22) With air bags deployed and pretensioners activated the vehi-
cle may be scrapped in the same manner as a non-air bag
system equipped vehicle.
23) Remove the undeployed air bag (inflator) module(s) and the
inactivated seat belt pretensioner(s) from the vehicle. For
driver air bag (inflator) module refer to SECTION 3C1, for
passenger air bag (inflator) module refer to “ON-VEHICLE
SERVICE”, for seat belt pretensioner refer to SECTION 10A.
24) [For air bag (inflator) module]
Temporarily store the air bag (inflator) module with its vinyl
trim cover facing up, away from the surface upon which it
rests. Refer to “SERVICE PRECAUTIONS” for details.
[For seat belt pretensioner]
When temporarily strong the seat belt pretensioner, be sure
NOT to face its exhaust hole provided side down. It must
face up. Refer to “SERVICE PRECAUTIONS” for details.
25) Contact your local distributor for further assistance.