Ignition system SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2000, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.GPages: 698, PDF Size: 16.01 MB
Page 673 of 698

CRANKING SYSTEM 6G-1
6F1
6F2
6H
6K
6G
7A1
7B1
7C1
7D
7E
7F
8A
8B
8C
8D
8E
9
10
10A
10B
SECTION 6G
CRANKING SYSTEM
CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION .............................. 6G-2
CRANKING CIRCUIT ................................... 6G-2
DIAGNOSIS ..................................................... 6G-2
DIAGNOSIS TABLE ..................................... 6G-2
PERFORMANCE TEST ............................... 6G-4
PULL-IN TEST ......................................... 6G-4
HOLD-IN TEST ........................................ 6G-4
PLUNGER AND PINION RETURN TEST 6G-4
NO-LOAD PERFORMANCE TEST .......... 6G-5ON-VEHICLE SERVICE ...................................6G-5
STARTING MOTOR .....................................6G-5
DISMOUNTING.........................................6G-5
REMOUNTING..........................................6G-5
DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY .......6G-6
SPECIFICATION ..............................................6G-8
1.0 kW TYPE.............................................6G-8
1.2 kW TYPE.............................................6G-8
REQUIRED SERVICE MATERIAL...................6G-8
WARNING:
For vehicles equipped with Supplement Restraint (Air Bag) System:
Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed only by an
authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer to AIR BAG SYSTEM COMPONENTS and WIRING LOCATION VIEW
under DIAGNOSIS in air bag system section in order to confirm whether you are performing service
on or near the air bag system components or wiring. Please observe all WARNINGS and SERVICE
PRECAUTIONS under PRECAUTIONS in air bag system section before performing service on or
around the air bag system components or wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could result in unin-
tentional activation of the system or could render the system inoperative. Either of these two condi-
tions may result in severe injury.
Technical service work must be started at least 90 seconds after the ignition switch is turned to the
“LOCK” position and the negative cable is disconnected from the battery. Otherwise, the system
may be activated by reserve energy in the Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM).
NOTE:
Starting motor varies depending on specifications, etc. Therefore, be sure to check model and speci-
fication of the vehicle being serviced before replacing parts.
Page 674 of 698
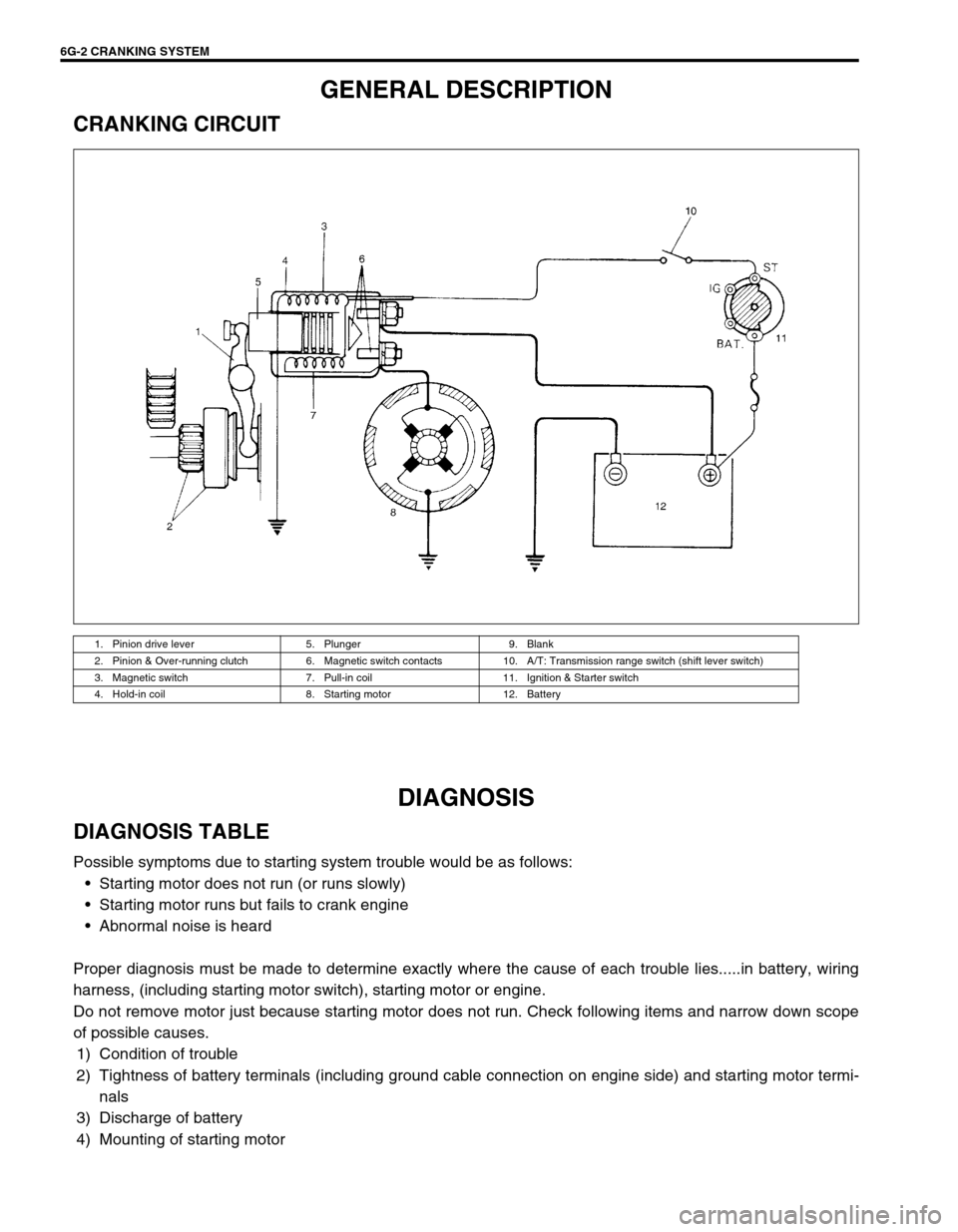
6G-2 CRANKING SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
CRANKING CIRCUIT
DIAGNOSIS
DIAGNOSIS TABLE
Possible symptoms due to starting system trouble would be as follows:
Starting motor does not run (or runs slowly)
Starting motor runs but fails to crank engine
Abnormal noise is heard
Proper diagnosis must be made to determine exactly where the cause of each trouble lies.....in battery, wiring
harness, (including starting motor switch), starting motor or engine.
Do not remove motor just because starting motor does not run. Check following items and narrow down scope
of possible causes.
1) Condition of trouble
2) Tightness of battery terminals (including ground cable connection on engine side) and starting motor termi-
nals
3) Discharge of battery
4) Mounting of starting motor
1. Pinion drive lever 5. Plunger 9. Blank
2. Pinion & Over-running clutch 6. Magnetic switch contacts 10. A/T: Transmission range switch (shift lever switch)
3. Magnetic switch 7. Pull-in coil 11. Ignition & Starter switch
4. Hold-in coil 8. Starting motor 12. Battery
Page 675 of 698
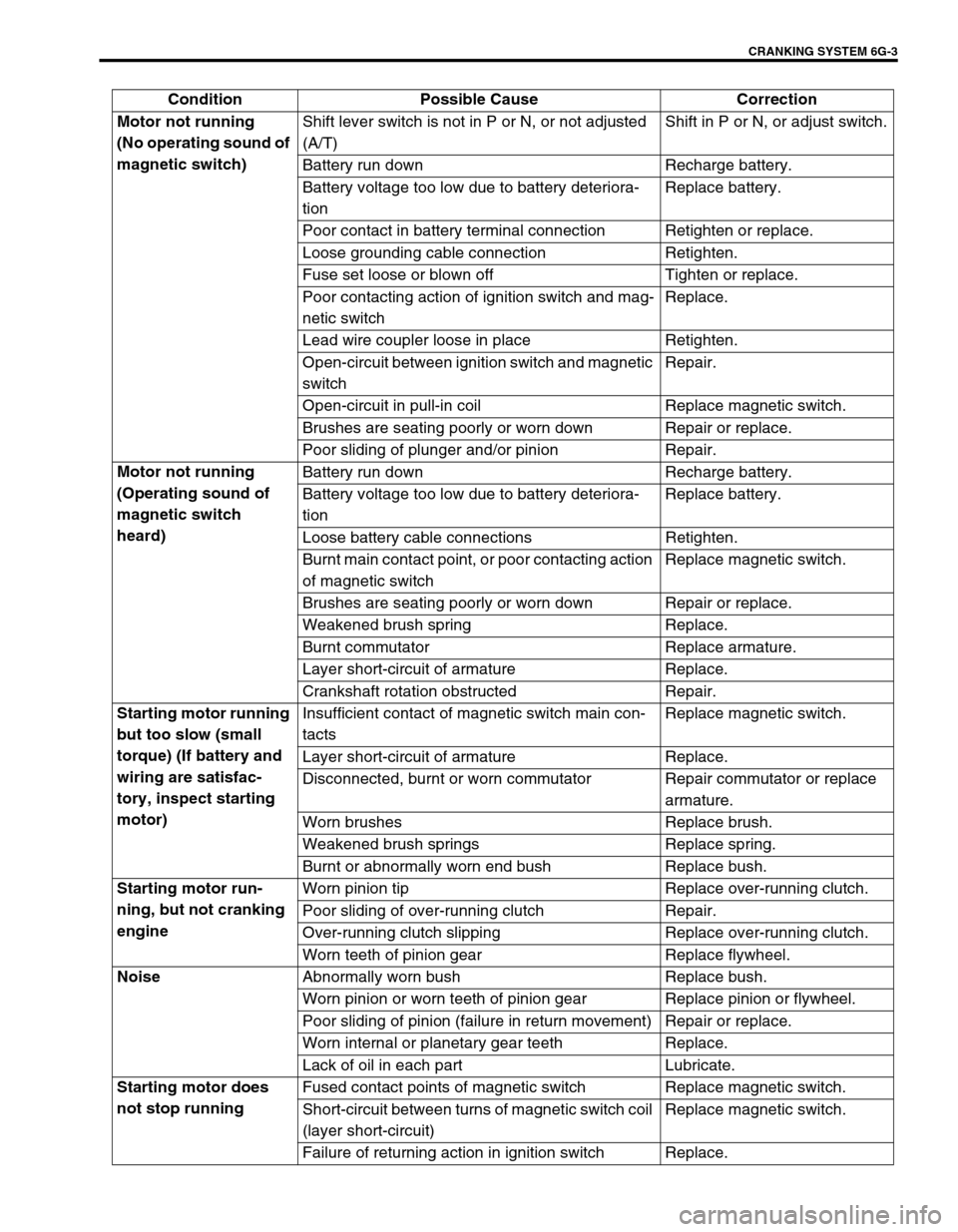
CRANKING SYSTEM 6G-3
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Motor not running
(No operating sound of
magnetic switch)Shift lever switch is not in P or N, or not adjusted
(A/T)Shift in P or N, or adjust switch.
Battery run down Recharge battery.
Battery voltage too low due to battery deteriora-
tionReplace battery.
Poor contact in battery terminal connection Retighten or replace.
Loose grounding cable connection Retighten.
Fuse set loose or blown off Tighten or replace.
Poor contacting action of ignition switch and mag-
netic switchReplace.
Lead wire coupler loose in place Retighten.
Open-circuit between ignition switch and magnetic
switchRepair.
Open-circuit in pull-in coil Replace magnetic switch.
Brushes are seating poorly or worn down Repair or replace.
Poor sliding of plunger and/or pinion Repair.
Motor not running
(Operating sound of
magnetic switch
heard)Battery run down Recharge battery.
Battery voltage too low due to battery deteriora-
tionReplace battery.
Loose battery cable connections Retighten.
Burnt main contact point, or poor contacting action
of magnetic switchReplace magnetic switch.
Brushes are seating poorly or worn down Repair or replace.
Weakened brush spring Replace.
Burnt commutator Replace armature.
Layer short-circuit of armature Replace.
Crankshaft rotation obstructed Repair.
Starting motor running
but too slow (small
torque) (If battery and
wiring are satisfac-
tory, inspect starting
motor)Insufficient contact of magnetic switch main con-
tactsReplace magnetic switch.
Layer short-circuit of armature Replace.
Disconnected, burnt or worn commutator Repair commutator or replace
armature.
Worn brushes Replace brush.
Weakened brush springs Replace spring.
Burnt or abnormally worn end bush Replace bush.
Starting motor run-
ning, but not cranking
engineWorn pinion tip Replace over-running clutch.
Poor sliding of over-running clutch Repair.
Over-running clutch slipping Replace over-running clutch.
Worn teeth of pinion gear Replace flywheel.
Noise
Abnormally worn bush Replace bush.
Worn pinion or worn teeth of pinion gear Replace pinion or flywheel.
Poor sliding of pinion (failure in return movement) Repair or replace.
Worn internal or planetary gear teeth Replace.
Lack of oil in each part Lubricate.
Starting motor does
not stop runningFused contact points of magnetic switch Replace magnetic switch.
Short-circuit between turns of magnetic switch coil
(layer short-circuit)Replace magnetic switch.
Failure of returning action in ignition switch Replace.
Page 681 of 698

CHARGING SYSTEM 6H-1
6F1
6F2
6G
6K
7A
6H
7B1
7C1
7D
7E
7F
8A
8B
8C
8D
8E
9
10
10A
10B
SECTION 6H
CHARGING SYSTEM
CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION .............................. 6H-2
BATTERY ..................................................... 6H-2
CARRIER AND HOLD-DOWN ................. 6H-2
ELECTROLYTE FREEZING .................... 6H-2
SULFATION ............................................. 6H-2
BUILT-IN INDICATOR (IF EQUIPPED) ... 6H-2
CARE OF BATTERY ................................ 6H-3
GENERATOR .............................................. 6H-4
DIAGNOSIS ..................................................... 6H-5
BATTERY ..................................................... 6H-5
VISUAL INSPECTION.............................. 6H-5
HYDROMETER TEST.............................. 6H-5
GENERATOR .............................................. 6H-6
CHARGING INDICATOR LAMP
OPERATION ............................................ 6H-6
UNDERCHARGED BATTERY ................. 6H-7
OVERCHARGED BATTERY.................... 6H-8ON-VEHICLE SERVICE .................................. 6H-9
BATTERY .................................................... 6H-9
JUMP STARTING IN CASE OF
EMERGENCY .......................................... 6H-9
DISMOUNTING...................................... 6H-10
HANDLING............................................. 6H-10
REMOUNTING....................................... 6H-10
GENERATOR ............................................ 6H-10
GENERATOR BELT .............................. 6H-10
DISMOUNTING AND REMOUNTING ... 6H-11
DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY .... 6H-11
INSPECTION ......................................... 6H-12
SPECIFICATION ........................................... 6H-14
BATTERY .................................................. 6H-14
GENERATOR ............................................ 6H-14
TIGHTENING TORQUE SPECIFICATION.... 6H-14
WARNING:
For vehicles equipped with Supplemental Restraint (Air Bag) System:
Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed only by an
authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer to “Air Bag System Components and Wiring Location View” under
“General Description” in air bag system section in order to confirm whether you are performing ser-
vice on or near the air bag system components or wiring. Please observe all WARNINGS and “Ser-
vice Precautions” under “On-Vehicle Service” in air bag system section before performing service
on or around the air bag system components or wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could result in
unintentional activation of the system or could render the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
Technical service work must be started at least 90 seconds after the ignition switch is turned to the
“LOCK” position and the negative cable is disconnected from the battery. Otherwise, the system
may be activated by reserve energy in the Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM).
Page 684 of 698
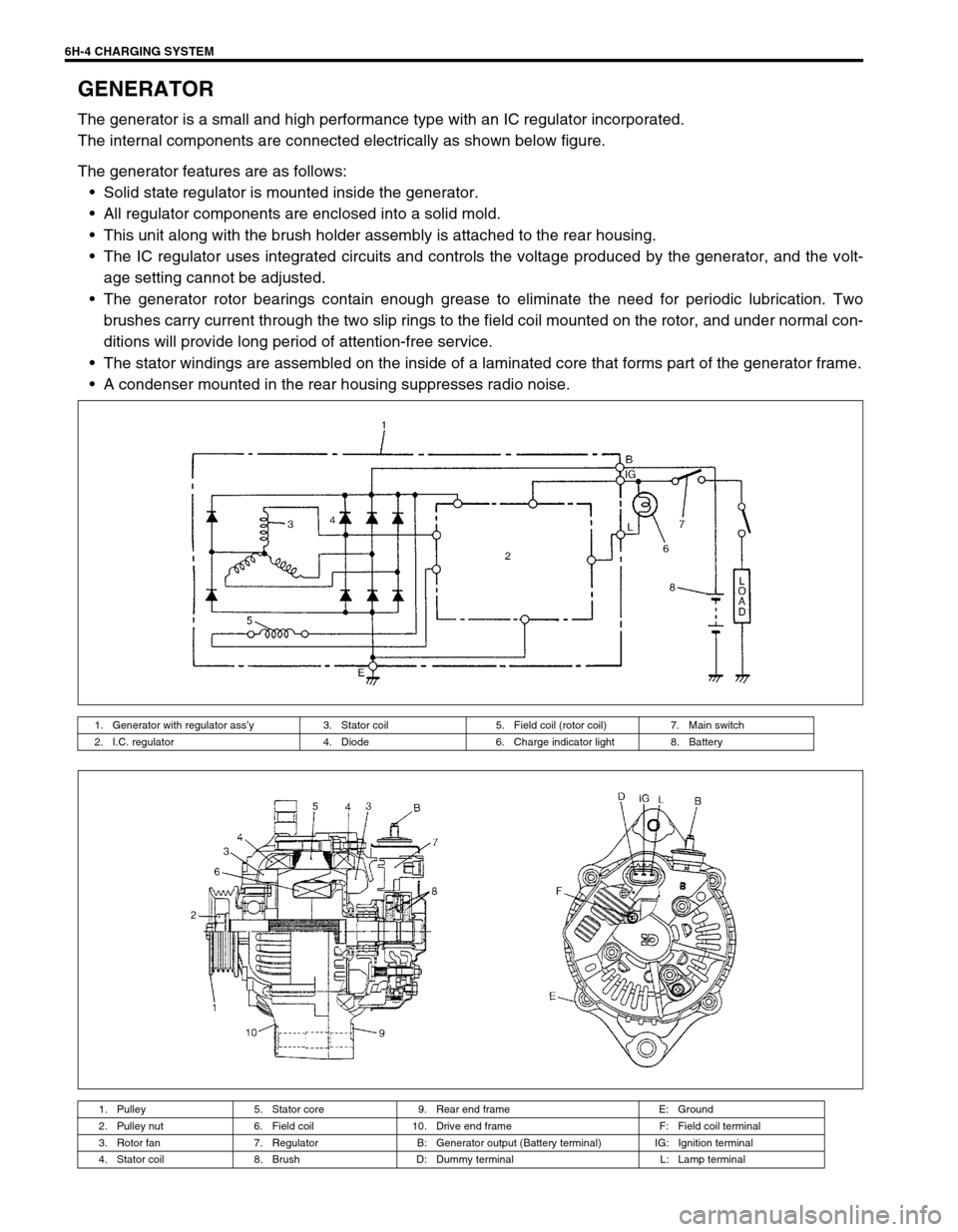
6H-4 CHARGING SYSTEM
GENERATOR
The generator is a small and high performance type with an IC regulator incorporated.
The internal components are connected electrically as shown below figure.
The generator features are as follows:
Solid state regulator is mounted inside the generator.
All regulator components are enclosed into a solid mold.
This unit along with the brush holder assembly is attached to the rear housing.
The IC regulator uses integrated circuits and controls the voltage produced by the generator, and the volt-
age setting cannot be adjusted.
The generator rotor bearings contain enough grease to eliminate the need for periodic lubrication. Two
brushes carry current through the two slip rings to the field coil mounted on the rotor, and under normal con-
ditions will provide long period of attention-free service.
The stator windings are assembled on the inside of a laminated core that forms part of the generator frame.
A condenser mounted in the rear housing suppresses radio noise.
1. Generator with regulator ass’y 3. Stator coil 5. Field coil (rotor coil) 7. Main switch
2. I.C. regulator 4. Diode 6. Charge indicator light 8. Battery
1. Pulley 5. Stator core 9. Rear end frame E: Ground
2. Pulley nut 6. Field coil 10. Drive end frame F: Field coil terminal
3. Rotor fan 7. Regulator B: Generator output (Battery terminal) IG: Ignition terminal
4. Stator coil 8. Brush D: Dummy terminal L: Lamp terminal
Page 686 of 698

6H-6 CHARGING SYSTEM
GENERATOR
Trouble in charging system will show up as one or more of the fol-
lowing conditions:
1) Faulty indicator lamp operation.
2) An undercharged battery as evidenced by slow cranking or
indicator dark.
3) An overcharged battery as evidenced by excessive spewing
of electrolyte from vents.
Noise from generator may be caused by loose drive pulley, loose
mounting bolts, worn or dirty bearings, defective diode, or defec-
tive stator.
CHARGING INDICATOR LAMP OPERATION
CAUTION:
Do not mistake polarities of IG terminal and L terminal.
Do not create short circuit between IG and L terminals.
Always connect these terminals through a lamp.
Do not connect any load between L and E.
When connecting charger or booster battery to vehicle
battery, refer to this section describing battery charg-
ing.
B: Generator output (Battery terminal)
D: Dummy terminal
E: Ground
F: Field coil terminal
IG: Ignition terminal
L: Lamp terminal
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Charge light does not
light with ignition ON
and engine offFuse blown Check fuse.
Light burned out Replace light.
Wiring connection loose Tighten loose connection.
IC regulator or field coil faulty Check generator.
Poor contact between brush and slip ring Repair or replace.
Charge light does not go
out with engine running
(battery requires fre-
quent recharging)Drive belt loose or worn Adjust or replace drive belt.
IC regulator or generator faulty Check charging system.
Wiring faulty Repair wiring.
Page 687 of 698
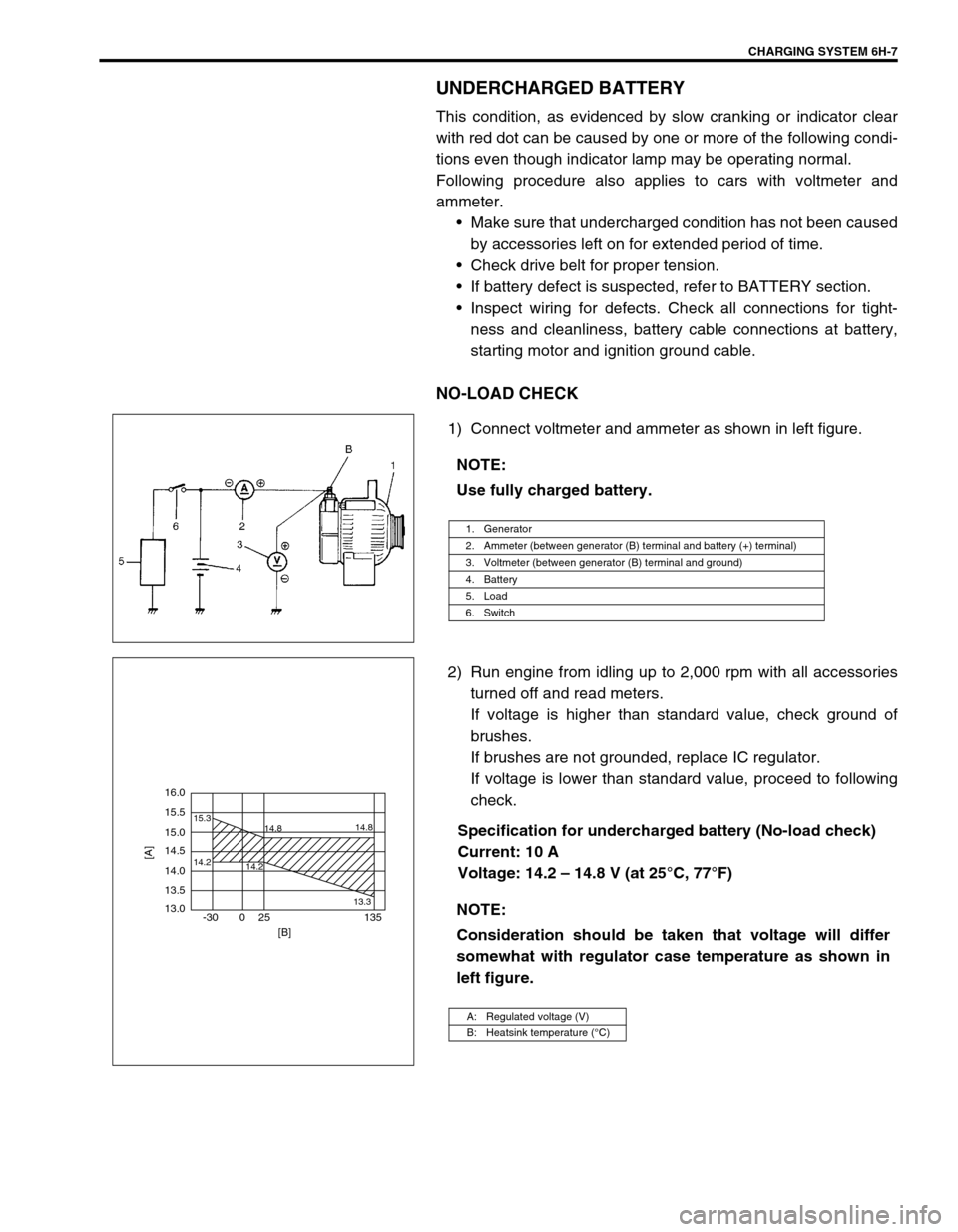
CHARGING SYSTEM 6H-7
UNDERCHARGED BATTERY
This condition, as evidenced by slow cranking or indicator clear
with red dot can be caused by one or more of the following condi-
tions even though indicator lamp may be operating normal.
Following procedure also applies to cars with voltmeter and
ammeter.
Make sure that undercharged condition has not been caused
by accessories left on for extended period of time.
Check drive belt for proper tension.
If battery defect is suspected, refer to BATTERY section.
Inspect wiring for defects. Check all connections for tight-
ness and cleanliness, battery cable connections at battery,
starting motor and ignition ground cable.
NO-LOAD CHECK
1) Connect voltmeter and ammeter as shown in left figure.
2) Run engine from idling up to 2,000 rpm with all accessories
turned off and read meters.
If voltage is higher than standard value, check ground of
brushes.
If brushes are not grounded, replace IC regulator.
If voltage is lower than standard value, proceed to following
check.
Specification for undercharged battery (No-load check)
Current: 10 A
Voltage: 14.2 – 14.8 V (at 25°C, 77°F) NOTE:
Use fully charged battery.
1. Generator
2. Ammeter (between generator (B) terminal and battery (+) terminal)
3. Voltmeter (between generator (B) terminal and ground)
4. Battery
5. Load
6. Switch
NOTE:
Consideration should be taken that voltage will differ
somewhat with regulator case temperature as shown in
left figure.
A: Regulated voltage (V)
B: Heatsink temperature (°C)
16.0
15.5
14.2 15.3
14.8
14.2
13.314.8
15.0
14.5
14.0
13.5
13.0
-30 0 25 135
[A]
[B]
Page 689 of 698
CHARGING SYSTEM 6H-9
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
BATTERY
JUMP STARTING IN CASE OF EMERGENCY
WITH AUXILIARY (BOOSTER) BATTERY
Both booster and discharged battery should be treated carefully when using jumper cables. Follow procedure
outlined below, being careful not to cause sparks.
1) Set parking brake and place automatic transmission in PARK (NEUTRAL on manual transmission). Turn off
ignition, turn off lights and all other electrical loads.
2) Check electrolyte level. If it is below low level line, add distilled water.
3) Attach end of one jumper cable to positive terminal of booster battery and the other end of the same cable to
positive terminal of discharged battery. (Use 12-volt battery only to jump start engine).
4) Attach one end of the remaining negative cable to negative terminal of booster battery, and the other end to
a solid engine ground (such as exhaust manifold) at least 45 cm (18 in.) away from battery of vehicle being
started.
5) Start engine of vehicle with booster battery and turn off electrical accessories. Then Start engine of the vehi-
cle with discharged battery.
6) Disconnect jumper cables in the exact reverse order.
WITH CHARGING EQUIPMENT
CAUTION:
If vehicle is manual transmission model and has a catalytic converter, do not push or tow it to start.
Damage to its emission system and/or to other parts may result.
WARNING:
Departure from these conditions or procedure described below could result in:
–Serious personal injury (particularly to eyes) or property damage from such causes as battery
explosion, battery acid, or electrical burns.
–Damage to electronic components of either vehicle.
Remove rings, watches, and other jewelry. Wear approved eye protection.
Be careful so that metal tools or jumper cables do not contact positive battery terminal (or metal in
contact with it) and any other metal on vehicle, because a short circuit could occur.
WARNING:
Do not connect negative cable directly to negative terminal of dead battery.
CAUTION:
When jump starting engine with charging equipment, be sure equipment used is 12-volt and negative
ground. Do not use 24-volt charging equipment. Using such equipment can cause serious damage to
electrical system or electronic parts.