Pistons SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 47 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Table of Contents 1-iii
EVAP Canister Purge Valve and Its Circuit
Inspection.......................................................... 1B-2
Vacuum Passage Inspection .............................. 1B-3
Vacuum Hose and Purge Valve Chamber Inspection.......................................................... 1B-3
EVAP Canister Purge Valve Inspection .............. 1B-3
EVAP Canister Inspection ... ................................ 1B-4
EGR Valve Removal and Installation .................. 1B-4
EGR Valve Inspection ......................................... 1B-4
PCV Hose Inspection .......................................... 1B-4
PCV Valve Inspection ......................................... 1B-5
Special Tools and Equipmen t ............................. 1B-5
Special Tool ........................................................ 1B-5
Engine Electrical Devices .. ..................... 1C-1
Repair Instructions .............................................. 1C-1
ECM Removal and Installation ............................ 1C-1
MAP Sensor Inspection ...................................... 1C-2
Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection.......................................................... 1C-2
Electric Throttle Body System Calibration ........... 1C-5
APP Sensor Assembly On-V ehicle Inspection .... 1C-5
APP Sensor Assembly Removal and Installation ......................................................... 1C-5
APP Sensor Assembly Inspection ...................... 1C-6
ECT Sensor Removal and In stallation ................ 1C-6
ECT Sensor Inspection ....................................... 1C-7
HO2S-1 and HO2S-2 Heater On-Vehicle Inspection.......................................................... 1C-7
HO2S-1 and HO2S-2 Removal and Installation ......................................................... 1C-7
CMP Sensor Removal and In stallation ............... 1C-8
Camshaft Position (CMP) Se nsor Inspection ...... 1C-8
CKP Sensor Removal and Installation ................ 1C-9
CKP Sensor Inspection ....................................... 1C-9
Knock Sensor Removal and Installation ........... 1C-10
Main Relay, Fuel Pump Relay and Starting
Motor Control Relay Inspection....................... 1C-10
MAF and IAT Sensor On-Vehicle Inspection .... 1C-11
MAF and IAT Sensor Removal and Installation ....................................................... 1C-11
MAF and IAT Sensor Inspection ....................... 1C-12
Electric Load Current Sensor On-Vehicle Inspection........................................................ 1C-12
Specifications ..................................................... 1C-13
Tightening Torque Specifications ...................... 1C-13
Engine Mechanical ......... ......................... 1D-1
General Description ............................................. 1D-1
Engine Construction Description ......................... 1D-1
Camshaft Position Control (VVT Variable Valve Timing) System Description .................... 1D-2
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............ 1D-4 Compression Check ............................................ 1D-4
Engine Vacuum Check ....................................... 1D-5
Valve Lash (Clearance) Inspection ..................... 1D-6
Repair Instructions .............................................. 1D-9 Air Cleaner Components ..................................... 1D-9
Air Cleaner Element Removal and Installation .... 1D-9 Air Cleaner Element Ins
pection and Cleaning ..1D-10
Cylinder Head Co ver Removal and
Installation .......................................................1D-10
Throttle Body and Intake Manifold
Components ....................................................1D-12
Throttle Body On-Vehicle Inspection.................1D-13
Electric Throttle Body Assembly Removal and Installation .......................................................1D-13
Throttle Body Cleaning......................................1D-14
Intake Manifold Removal and Installation .........1D-14
Engine Mountings Components ........................1D-16
Engine Assembly Removal and Installation ......1D-17
Timing Chain Cover Components .....................1D-20
Timing Chain Cover Removal and Installation ..1D-21
Timing Chain Cover Inspection .........................1D-23
Oil Control Valve Removal and Installation .......1D-23
Oil Control Valve Inspection ..............................1D-24
Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner Components ....................................................1D-24
Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner Removal and Installation ................................................1D-25
Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner Inspection ..1D-27
Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Components ........1D-28
Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Removal and Installation .......................................................1D-29
Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Inspection ............1D-31
Valves and Cylinder Head Components ...........1D-34
Valves and Cylinder Head Removal and
Installation .......................................................1D-35
Valves and Cylinder Head Disassembly and Assembly.........................................................1D-37
Valves and Valve Guides Inspection.................1D-40
Cylinder Head Inspection . .................................1D-42
Valve Spring Inspection ....................................1D-43
Pistons, Piston Rings , Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Components ....................................1D-44
Pistons, Piston Rings , Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Removal and Installation .................1D-45
Pistons, Piston Rings , Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Disassembly and Assembly ............1D-46
Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings Inspection ........................................................1D-47
Piston Pins and Connecting Rods Inspection ...1D-49
Crank Pin and Connecting Rod Bearings Inspection ........................................................1D-50
Main Bearings, Cran kshaft and Cylinder
Block Components ..........................................1D-53
Main Bearings, Cran kshaft and Cylinder
Block Removal and Installa tion .......................1D-54
Crankshaft Inspection .......................................1D-57
Main Bearings Inspection . .................................1D-59
Sensor Plate Inspection ....................................1D-63
Rear Oil Seal Inspection ...................................1D-63
Flywheel Inspection...........................................1D-63
Cylinder Block Inspection ..................................1D-63
Specifications .................... .................................1D-64
Tightening Torque Specifications ......................1D-64
Special Tools and Equipmen t ...........................1D-66
Recommended Service Material .......................1D-66
Special Tool ......................................................1D-66
Page 52 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-2 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
• Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit Service in Section 00” befo re inspection and observe
what is written there.
• ECM replacement: When substituting a known-good ECM, check for the
following conditions. Neglec ting this check may cause
damage to a known-good ECM.
– Resistance value of all relays, actuators is as specified respectively.
– MAP sensor, A/C refrigerant pressure sensor and TP sensor are in good condition and none of power
circuits of these sensors is shorted to ground.
• Communication of ECM, BCM, ABS/ESP ® control
module, combination meter, keyless start control
module, steering angle sensor (ESP ® model) and
TCM (A/T model), is esta blished by CAN (Controller
Area Network). (For more detail of CAN
communication for ECM, refer to “CAN
Communication System Description”). Therefore,
handle CAN communication line with care referring to
“Precaution for CAN Communication System in
Section 00”.
• Immobilizer transponder code registration after
replacing ECM
When ECM is replaced with new one or with another
one, make sure to register immobilizer transponder
code to ECM correctly according to “Procedure after
ECM Replacement in Section 10C”.Precautions of ECM Circuit InspectionS7RS0B1100003
• ECM connectors are waterproofed. Each terminal of the ECM connectors is sealed up with the grommet.
Therefore, when measuring ci rcuit voltage, resistance
and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, do not insert
the tester’s probe into th e sealed terminal at the
harness side. When measuring circuit voltage,
resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector,
connect the special tool to the ECM connectors. And,
insert the tester’s probe into the special tool’s
connectors at the harness side, and then measure
voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal. Or, ECM and
its circuits may be damaged by water.
• Wire colors of the special tool’s connectors are different from the ones of the ECM connectors.
However, the circuit arrangement of the special tool’s
connectors is same as the one of the ECM
connectors. Therefore, measure circuit voltage and
resistance by identifying the terminal location subject
to the measurement.
Precautions of Electric Throttle Body System
Calibration
S7RS0B1100004
After performing one of works described below, it is
necessary to re-register the completely closed throttle
valve reference position stored in memory of ECM. (For
detailed information, refer to “Description of Electric
Throttle Body System Calibration”.) For the procedure to
register such data in ECM, refer to “Electric Throttle
Body System Calibration in Section 1C”.
• To shut off backup power of ECM for such purposes of battery replacement or “DOME” fuse removal
• To erase DTCs P0122, P01 23, P0222, P0223, P2101,
P2102, P2103, P2111, P2112, P2113, P2119, P2123,
P2127, P2128, P2135 and/or P2138
• To replace ECM
• To replace throttle body and/or accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor assembly
General Description
Statement on Cleanliness and CareS7RS0B1101001
An automobile engine is a combination of many
machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with
tolerances that are measured in the thousands of an
millimeter (ten thous ands of an inch).
Accordingly, when any internal engine parts are
serviced, care and cleanliness are important.
It should be understood that proper cleaning and
protection of machined surfaces and friction areas is part
of the repair procedure. This is considered standard
shop practice even if not specifically stated.
• A liberal coating of engine oil should be applied to friction areas during assembly to protect and lubricate
the surfaces on initial operation. • Whenever valve train components, pistons, piston
rings, connecting rods, rod bearings, and crankshaft
journal bearings are removed for service, they should
be retained in order.
At the time of installation, they should be installed in
the same locations and with the same mating
surfaces as when removed.
• Battery cables should be disconnected before any major work is performed on the engine.
Failure to disconnect cables may result in damage to
wire harness or other electrical parts.
Page 91 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-41
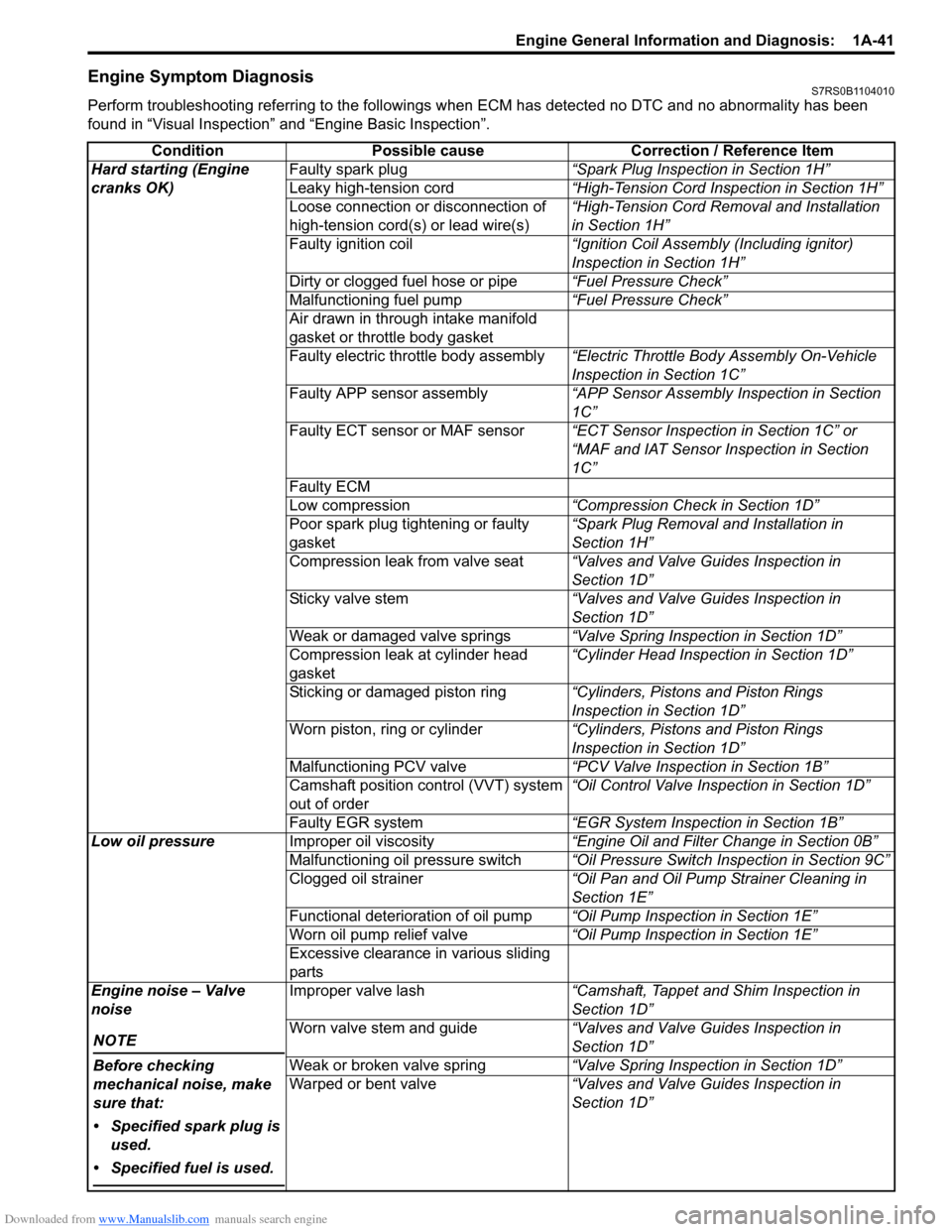
Engine Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B1104010
Perform troubleshooting referring to the followings when ECM has detected no DTC and no abnormality has been
found in “Visual Inspection” and “Engine Basic Inspection”.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Hard starting (Engine
cranks OK) Faulty spark plug
“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Leaky high-tension cord “High-Tension Cord Inspection in Section 1H”
Loose connection or disconnection of
high-tension cord(s) or lead wire(s) “High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty ignition coil “Ignition Coil Assembly (Including ignitor)
Inspection in Section 1H”
Dirty or clogged fuel hose or pipe “Fuel Pressure Check”
Malfunctioning fuel pump “Fuel Pressure Check”
Air drawn in through intake manifold
gasket or throttle body gasket
Faulty electric throttle body assembly “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly “APP Sensor Assembly Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty ECT sensor or MAF sensor “ECT Sensor Inspection in Section 1C” or
“MAF and IAT Sensor Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty ECM
Low compression “Compression Check in Section 1D”
Poor spark plug tightening or faulty
gasket “Spark Plug Removal and Installation in
Section 1H”
Compression leak from valve seat “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Sticky valve stem “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Weak or damaged valve springs “Valve Spring Inspection in Section 1D”
Compression leak at cylinder head
gasket “Cylinder Head Inspection in Section 1D”
Sticking or damaged piston ring “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn piston, ring or cylinder “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Malfunctioning PCV valve “PCV Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order “Oil Control Valve Inspection in Section 1D”
Faulty EGR system “EGR System Inspection in Section 1B”
Low oil pressure Improper oil viscosity “Engine Oil and Filter Change in Section 0B”
Malfunctioning oil pressure switch “Oil Pressure Switch Inspection in Section 9C”
Clogged oil strainer “Oil Pan and Oil Pump Strainer Cleaning in
Section 1E”
Functional deterioration of oil pump “Oil Pump Inspection in Section 1E”
Worn oil pump relief valve “Oil Pump Inspection in Section 1E”
Excessive clearance in various sliding
parts
Engine noise – Valve
noise
NOTE
Before checking
mechanical noise, make
sure that:
• Specified spark plug is used.
• Specified fuel is used.
Improper valve lash “Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Inspection in
Section 1D”
Worn valve stem and guide “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Weak or broken valve spring “Valve Spring Inspection in Section 1D”
Warped or bent valve “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Page 92 of 1496
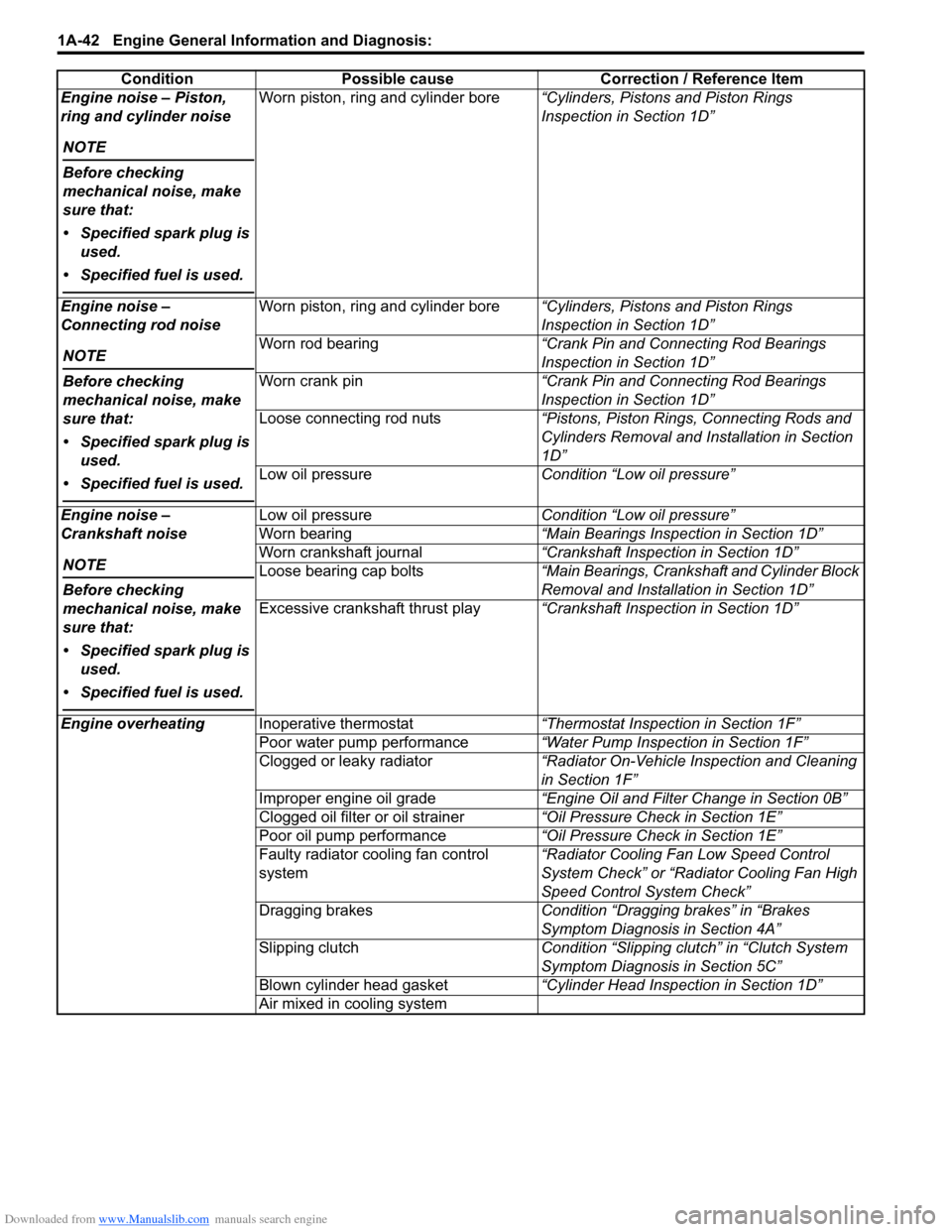
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-42 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Engine noise – Piston,
ring and cylinder noise
NOTE
Before checking
mechanical noise, make
sure that:
• Specified spark plug is used.
• Specified fuel is used.
Worn piston, ring and cylinder bore “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Engine noise –
Connecting rod noise
NOTE
Before checking
mechanical noise, make
sure that:
• Specified spark plug is used.
• Specified fuel is used.
Worn piston, ring and cylinder bore “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn rod bearing “Crank Pin and Connecting Rod Bearings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn crank pin “Crank Pin and Connecting Rod Bearings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Loose connecting rod nuts “Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Removal and Installation in Section
1D”
Low oil pressure Condition “Low oil pressure”
Engine noise –
Crankshaft noise
NOTE
Before checking
mechanical noise, make
sure that:
• Specified spark plug is used.
• Specified fuel is used.
Low oil pressure Condition “Low oil pressure”
Worn bearing “Main Bearings Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn crankshaft journal “Crankshaft Inspection in Section 1D”
Loose bearing cap bolts “Main Bearings, Crankshaft and Cylinder Block
Removal and Installation in Section 1D”
Excessive crankshaft thrust play “Crankshaft Inspection in Section 1D”
Engine overheating Inoperative thermostat “Thermostat Inspection in Section 1F”
Poor water pump performance “Water Pump Inspection in Section 1F”
Clogged or leaky radiator “Radiator On-Vehicle Inspection and Cleaning
in Section 1F”
Improper engine oil grade “Engine Oil and Filter Change in Section 0B”
Clogged oil filter or oil strainer “Oil Pressure Check in Section 1E”
Poor oil pump performance “Oil Pressure Check in Section 1E”
Faulty radiator cooling fan control
system “Radiator Cooling Fan Low Speed Control
System Check” or “Rad
iator Cooling Fan High
Speed Control System Check”
Dragging brakes Condition “Dragging brakes” in “Brakes
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 4A”
Slipping clutch Condition “Slipping clutch” in “Clutch System
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 5C”
Blown cylinder head gasket “Cylinder Head Inspection in Section 1D”
Air mixed in cooling system
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Page 93 of 1496
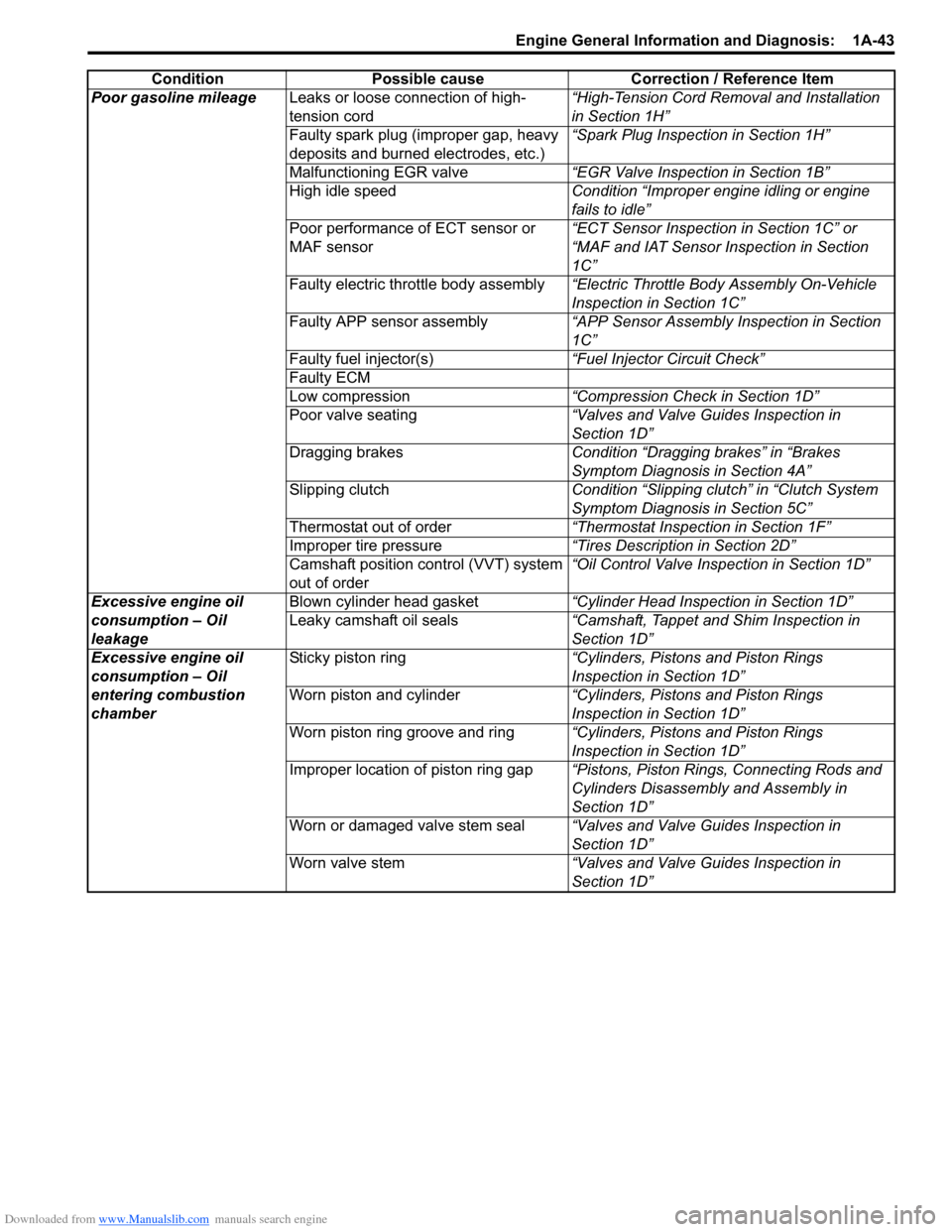
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-43
Poor gasoline mileageLeaks or loose connection of high-
tension cord “High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty spark plug (improper gap, heavy
deposits and burned electrodes, etc.) “Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Malfunctioning EGR valve “EGR Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
High idle speed Condition “Improper engine idling or engine
fails to idle”
Poor performance of ECT sensor or
MAF sensor “ECT Sensor Inspection in Section 1C” or
“MAF and IAT Sensor Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty electric throttle body assembly “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly “APP Sensor Assembly Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty fuel injector(s) “Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty ECM
Low compression “Compression Check in Section 1D”
Poor valve seating “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Dragging brakes Condition “Dragging brakes” in “Brakes
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 4A”
Slipping clutch Condition “Slipping clutch” in “Clutch System
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 5C”
Thermostat out of order “Thermostat Inspection in Section 1F”
Improper tire pressure “Tires Description in Section 2D”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order “Oil Control Valve Inspection in Section 1D”
Excessive engine oil
consumption – Oil
leakage Blown cylinder head gasket
“Cylinder Head Inspection in Section 1D”
Leaky camshaft oil seals “Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Inspection in
Section 1D”
Excessive engine oil
consumption – Oil
entering combustion
chamber Sticky piston ring
“Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn piston and cylinder “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn piston ring groove and ring “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Improper location of piston ring gap “Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Disassembly and Assembly in
Section 1D”
Worn or damaged valve stem seal “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Worn valve stem “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Page 94 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-44 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Engine hesitates –
Momentary lack of
response as accelerator
is depressed. Can occur
at all vehicle speeds.
Usually most severe when
first trying to make
vehicle move, as from a
stop sign.Spark plug faulty
“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Leaky high-tension cord “High-Tension Cord Inspection in Section 1H”
Fuel pressure out of specification “Fuel Pressure Check”
Malfunctioning EGR valve “EGR Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Poor performance of ECT sensor or
MAF sensor “ECT Sensor Inspection in Section 1C” or
“MAF and IAT Sensor Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty electric throttle body assembly “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly “APP Sensor Assembly Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty fuel injector “Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty ECM
Engine overheating Condition “Engine overheating”
Low compression “Compression Check in Section 1D”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order “Oil Control Valve Inspection in Section 1D”
Surge – Engine power
variation under steady
throttle or cruise. Feels
like vehicle speeds up
and down with no change
in accelerator pedal. Leaky or loosely connected high-tension
cord
“High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty spark plug (excess carbon
deposits, improper gap, burned
electrodes, etc.) “Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Variable fuel pressure “Fuel Pressure Check”
Kinky or damaged fuel hose and lines
Faulty fuel pump (clogged fuel filter)
Malfunctioning EGR valve “EGR Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Poor performance of MAF sensor “MAF and IAT Sensor Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty fuel injector “Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty electric throttle body assembly “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly “APP Sensor Assembly Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty ECM
Excessive detonation –
Engine makes
continuously sharp
metallic knocks that
change with throttle
opening. Sounds like pop
corn popping. Faulty spark plug
“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Loose connection of high-tension cord “High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Engine overheating Condition “Engine overheating”
Clogged fuel filter (faulty fuel pump) or
fuel lines “Fuel Pressure Check” or “Fuel Pump and Its
Circuit Check”
Air drawn in through intake manifold or
throttle body gasket
Malfunctioning EGR valve “EGR Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Poor performance of knock sensor, ECT
sensor or MAF sensor “DTC P0327 / P0328: Knock Sensor 1 Circuit
Low / High”, “ECT Sensor Inspection in
Section 1C” or “MAF and IAT Sensor
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty fuel injector(s) “Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty ECM
Excessive combustion chamber
deposits “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D” and/or “Piston Pins
and Connecting Rods In
spection in Section
1D”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order “Oil Control Valve Inspection in Section 1D”
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Page 329 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-44
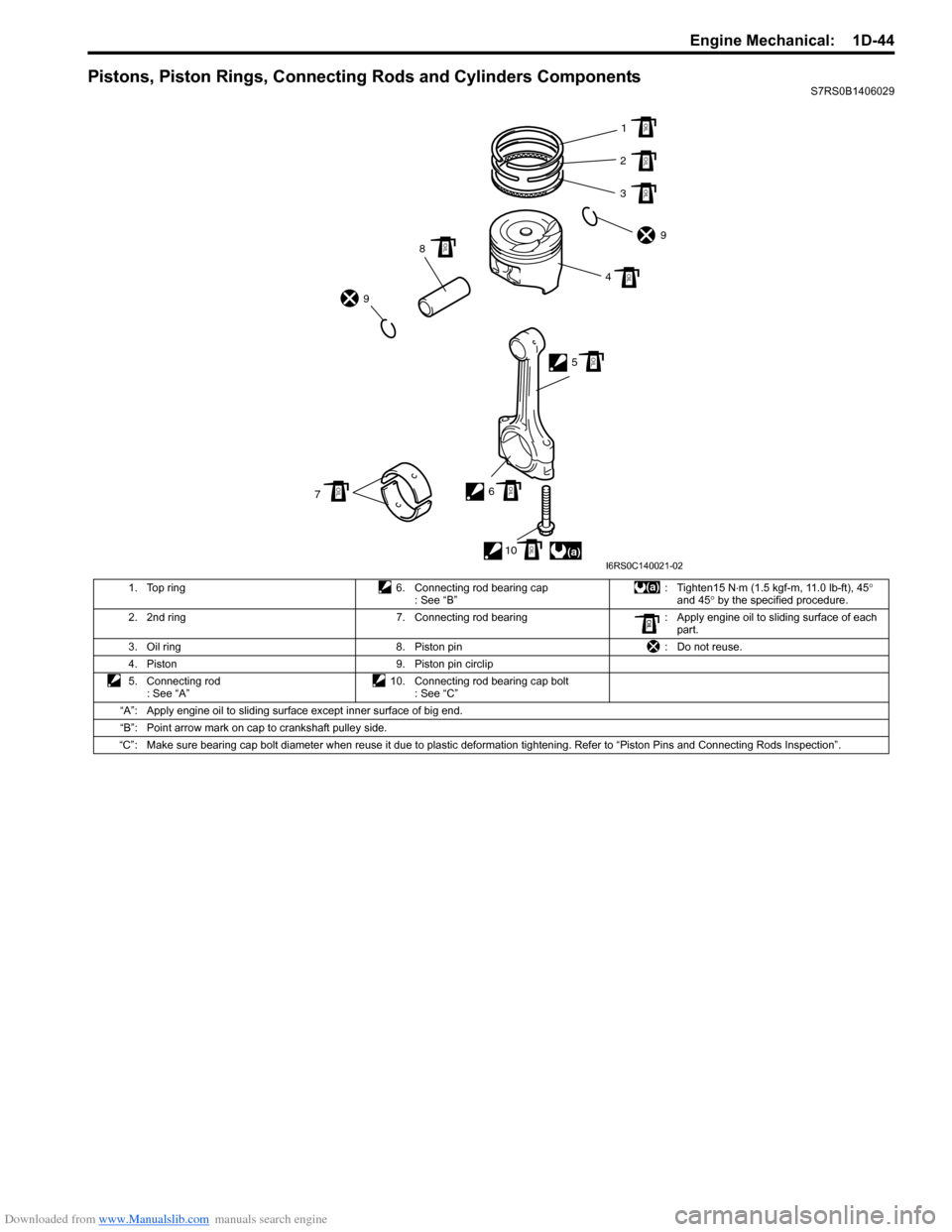
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and Cylinders ComponentsS7RS0B1406029
1. Top ring 6. Connecting rod bearing cap : See “B”: Tighten15 N
⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft), 45 °
and 45 ° by the specified procedure.
2. 2nd ring 7. Connecting rod bearing : Apply engine oil to sliding surface of each
part.
3. Oil ring 8. Piston pin : Do not reuse.
4. Piston 9. Piston pin circlip
5. Connecting rod : See “A” 10. Connecting rod bearing cap bolt
: See “C”
“A”: Apply engine oil to sliding surface except inner surface of big end.
“B”: Point arrow mark on cap to crankshaft pulley side.
“C”: Make sure bearing cap bolt diameter when reuse it due to plastic deformation tightening. Refer to “Piston Pins and Connecti ng Rods Inspection”.
(a)1
2
3
9
4
5
6 10
7 8
9
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
I6RS0C140021-02
Page 330 of 1496
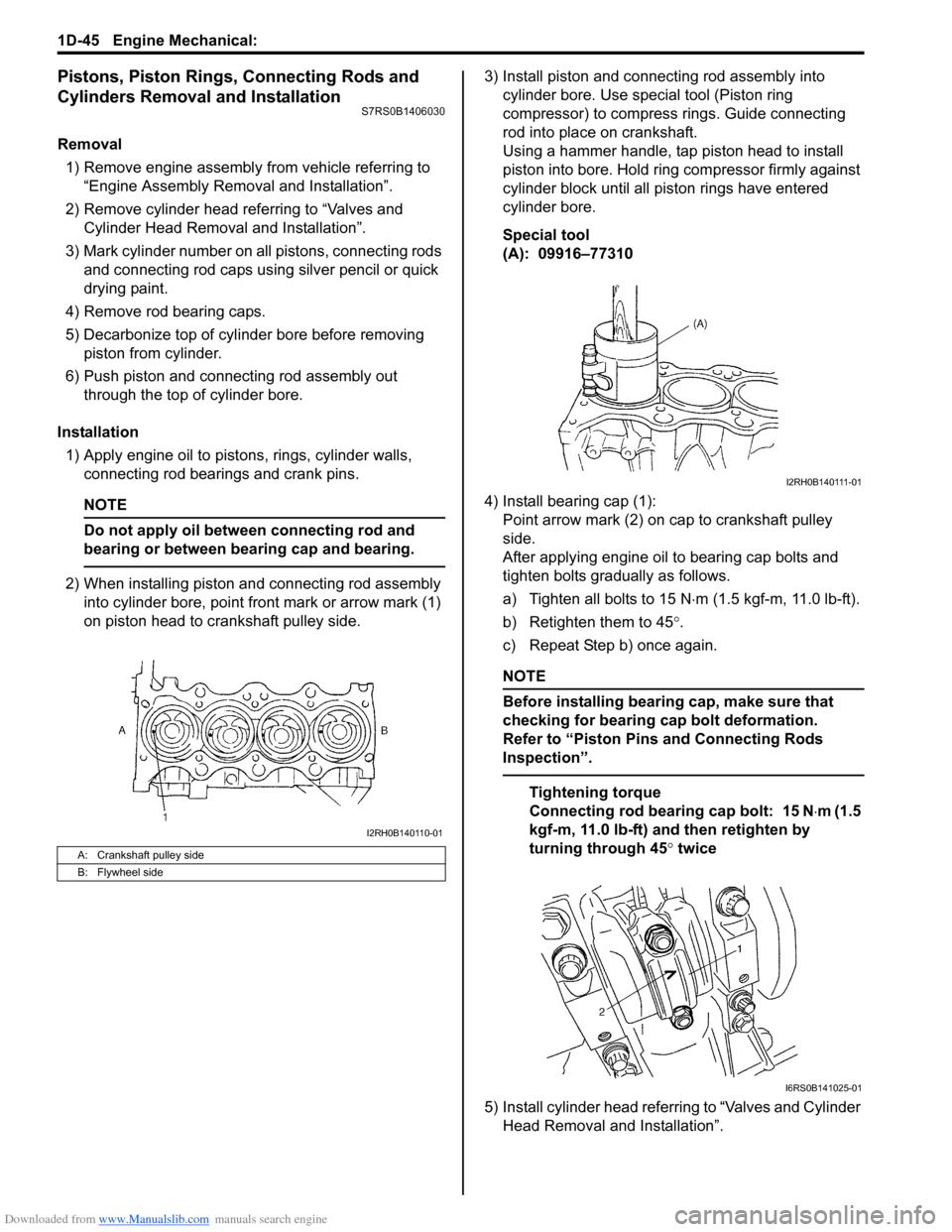
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-45 Engine Mechanical:
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Removal and Installation
S7RS0B1406030
Removal1) Remove engine assembly from vehicle referring to “Engine Assembly Removal and Installation”.
2) Remove cylinder head referring to “Valves and Cylinder Head Removal and Installation”.
3) Mark cylinder number on all pistons, connecting rods
and connecting rod caps using silver pencil or quick
drying paint.
4) Remove rod bearing caps.
5) Decarbonize top of cylinder bore before removing piston from cylinder.
6) Push piston and connecting rod assembly out through the top of cylinder bore.
Installation 1) Apply engine oil to pistons, rings, cylinder walls, connecting rod bearings and crank pins.
NOTE
Do not apply oil between connecting rod and
bearing or between bearing cap and bearing.
2) When installing piston and connecting rod assembly into cylinder bore, point front mark or arrow mark (1)
on piston head to crankshaft pulley side. 3) Install piston and connecting rod assembly into
cylinder bore. Use special tool (Piston ring
compressor) to compress rings. Guide connecting
rod into place on crankshaft.
Using a hammer handle, tap piston head to install
piston into bore. Hold ring compressor firmly against
cylinder block until all piston rings have entered
cylinder bore.
Special tool
(A): 09916–77310
4) Install bearing cap (1): Point arrow mark (2) on cap to crankshaft pulley
side.
After applying engine oil to bearing cap bolts and
tighten bolts gradually as follows.
a) Tighten all bolts to 15 N ⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft).
b) Retighten them to 45 °.
c) Repeat Step b) once again.
NOTE
Before installing bearing cap, make sure that
checking for bearing cap bolt deformation.
Refer to “Piston Pins and Connecting Rods
Inspection”.
Tightening torque
Connecting rod bearing cap bolt: 15 N ⋅m (1.5
kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft) and then retighten by
turning through 45 ° twice
5) Install cylinder head referring to “Valves and Cylinder Head Removal and Installation”.
A: Crankshaft pulley side
B: Flywheel side
I2RH0B140110-01
I2RH0B140111-01
I6RS0B141025-01
Page 331 of 1496
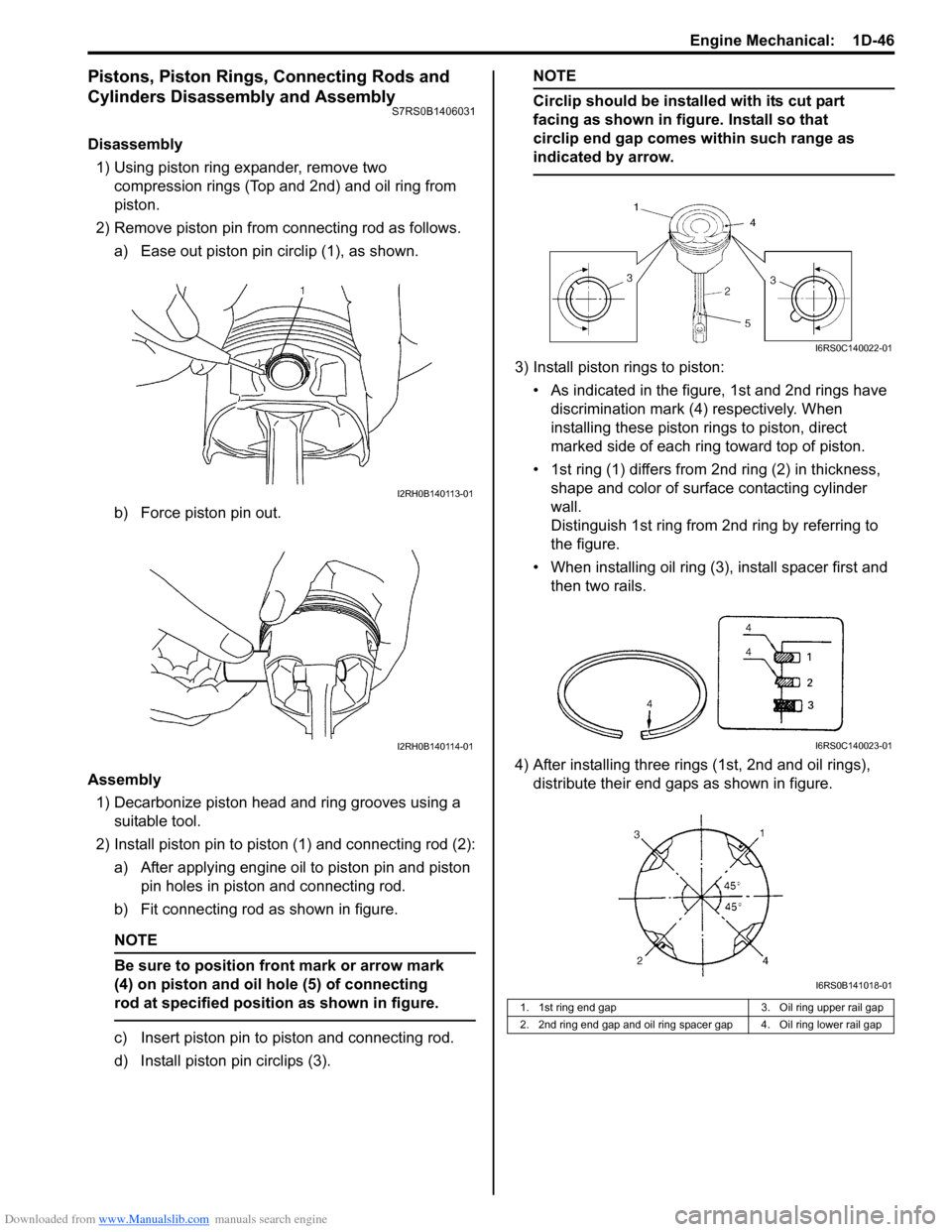
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-46
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Disassembly and Assembly
S7RS0B1406031
Disassembly1) Using piston ring expander, remove two compression rings (Top and 2nd) and oil ring from
piston.
2) Remove piston pin from connecting rod as follows. a) Ease out piston pin circlip (1), as shown.
b) Force piston pin out.
Assembly 1) Decarbonize piston head and ring grooves using a suitable tool.
2) Install piston pin to piston (1) and connecting rod (2): a) After applying engine oil to piston pin and piston pin holes in piston and connecting rod.
b) Fit connecting rod as shown in figure.
NOTE
Be sure to position front mark or arrow mark
(4) on piston and oil hole (5) of connecting
rod at specified position as shown in figure.
c) Insert piston pin to piston and connecting rod.
d) Install piston pin circlips (3).
NOTE
Circlip should be installed with its cut part
facing as shown in figure. Install so that
circlip end gap comes within such range as
indicated by arrow.
3) Install piston rings to piston:
• As indicated in the figure, 1st and 2nd rings have discrimination mark (4) respectively. When
installing these piston rings to piston, direct
marked side of each ring toward top of piston.
• 1st ring (1) differs from 2nd ring (2) in thickness, shape and color of surface contacting cylinder
wall.
Distinguish 1st ring from 2nd ring by referring to
the figure.
• When installing oil ring (3), install spacer first and then two rails.
4) After installing three rings (1st, 2nd and oil rings), distribute their end gaps as shown in figure.
I2RH0B140113-01
I2RH0B140114-01
1. 1st ring end gap 3. Oil ring upper rail gap
2. 2nd ring end gap and oil ring spacer gap 4. Oil ring lower rail gap
I6RS0C140022-01
I6RS0C140023-01
I6RS0B141018-01
Page 332 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-47 Engine Mechanical:
Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings InspectionS7RS0B1406032
Cylinder
Visual inspection
Inspect cylinder walls for scratches, roughness or ridges
which indicate excessive wear. If cylinder bore is very
rough or deeply scratched, or ridged, rebore cylinder and
use over size piston.
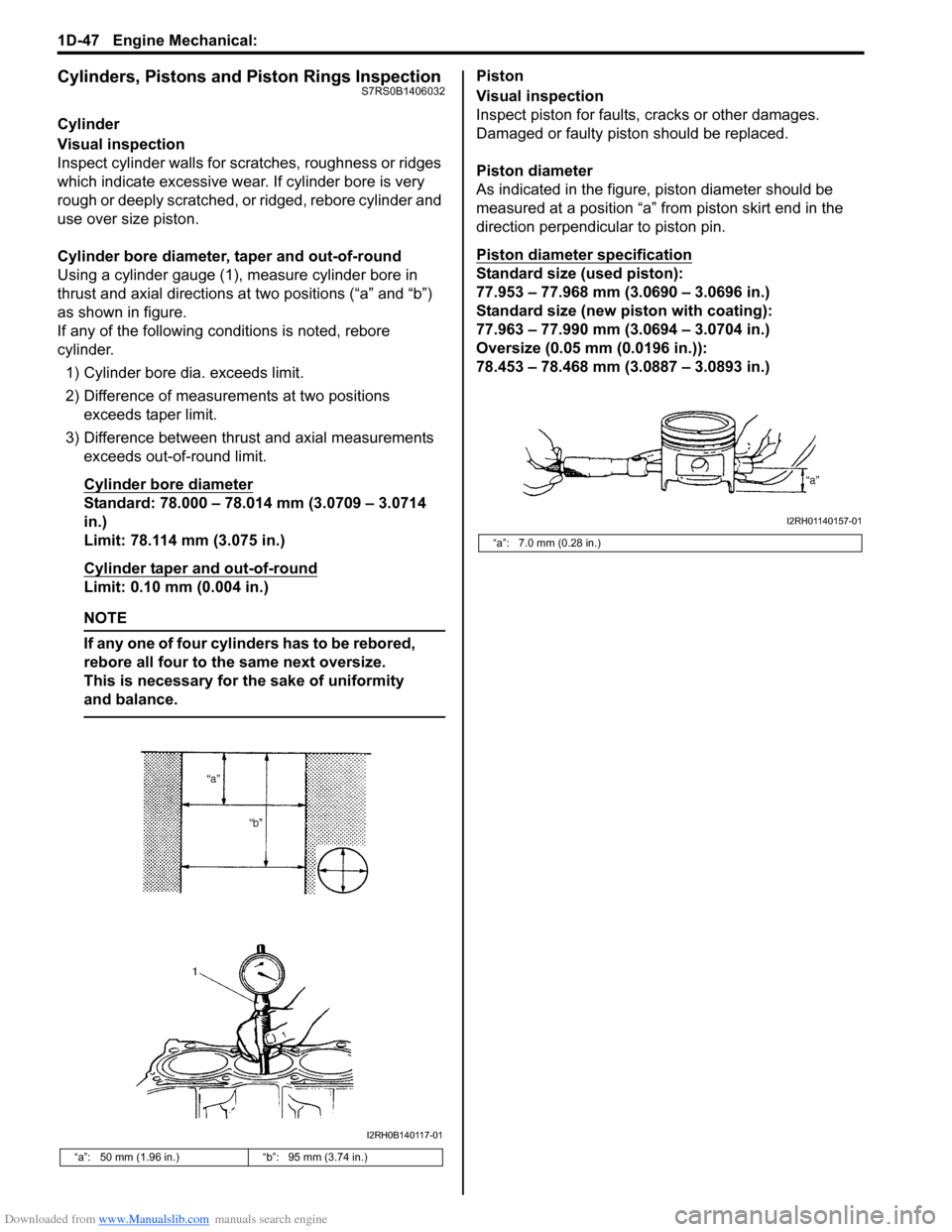
Cylinder bore diameter, taper and out-of-round
Using a cylinder gauge (1), measure cylinder bore in
thrust and axial directions at two positions (“a” and “b”)
as shown in figure.
If any of the following conditions is noted, rebore
cylinder.1) Cylinder bore dia. exceeds limit.
2) Difference of measurements at two positions exceeds taper limit.
3) Difference between thrust and axial measurements exceeds out-of-round limit.
Cylinder bore diameter
Standard: 78.000 – 78.014 mm (3.0709 – 3.0714
in.)
Limit: 78.114 mm (3.075 in.)
Cylinder taper and out-of-round
Limit: 0.10 mm (0.004 in.)
NOTE
If any one of four cylinders has to be rebored,
rebore all four to the same next oversize.
This is necessary for the sake of uniformity
and balance.
Piston
Visual inspection
Inspect piston for faults, cracks or other damages.
Damaged or faulty piston should be replaced.
Piston diameter
As indicated in the figure, piston diameter should be
measured at a position “a” from piston skirt end in the
direction perpendicular to piston pin.
Piston diameter specification
Standard size (used piston):
77.953 – 77.968 mm (3.0690 – 3.0696 in.)
Standard size (new piston with coating):
77.963 – 77.990 mm (3.0694 – 3.0704 in.)
Oversize (0.05 mm (0.0196 in.)):
78.453 – 78.468 mm (3.0887 – 3.0893 in.)
“a”: 50 mm (1.96 in.) “b”: 95 mm (3.74 in.)
I2RH0B140117-01
“a”: 7.0 mm (0.28 in.)
I2RH01140157-01