Pistons SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.G Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 339 of 1496
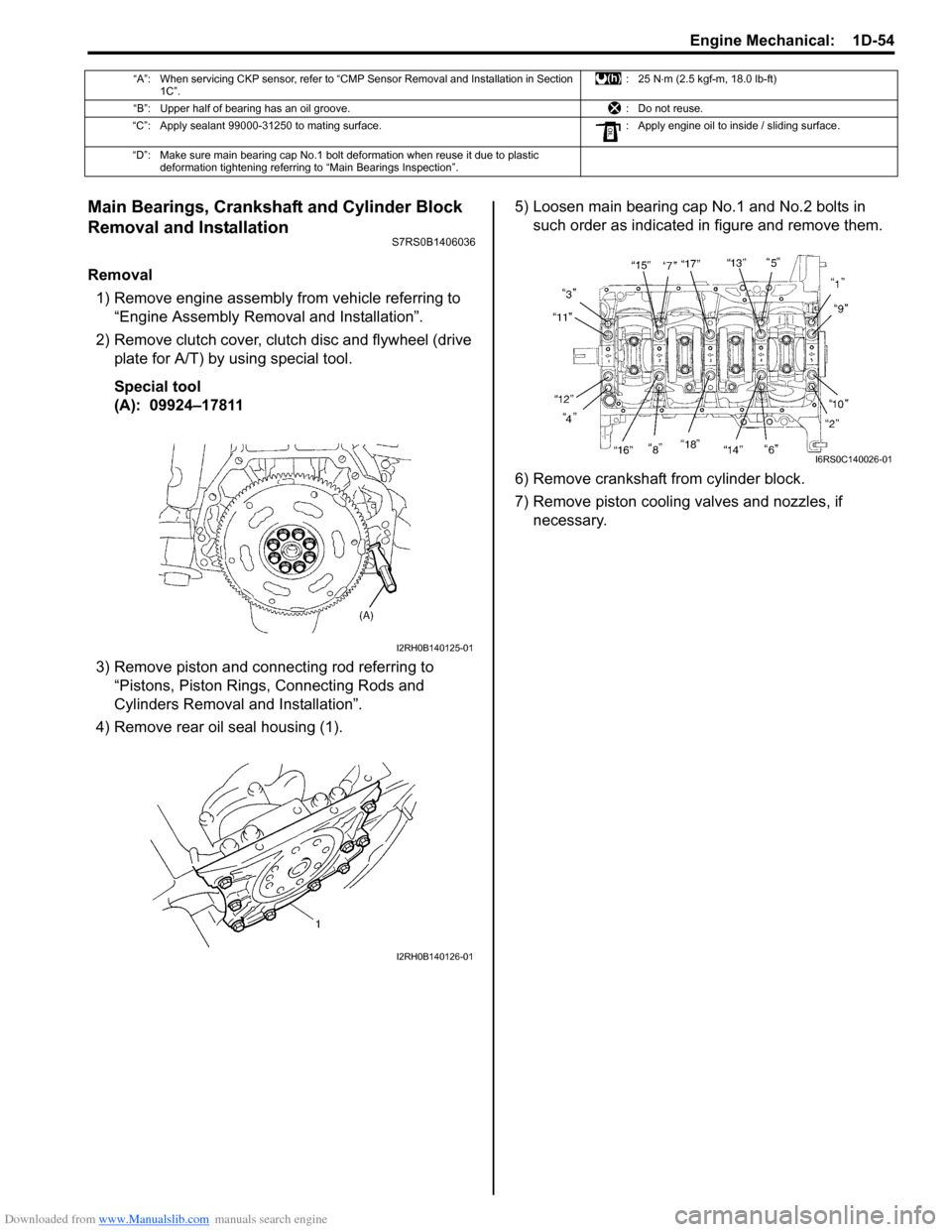
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-54
Main Bearings, Crankshaft and Cylinder Block
Removal and Installation
S7RS0B1406036
Removal1) Remove engine assembly from vehicle referring to “Engine Assembly Removal and Installation”.
2) Remove clutch cover, clut ch disc and flywheel (drive
plate for A/T) by using special tool.
Special tool
(A): 09924–17811
3) Remove piston and connecting rod referring to “Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Removal and Installation”.
4) Remove rear oil seal housing (1). 5) Loosen main bearing cap No.1 and No.2 bolts in
such order as indicated in figure and remove them.
6) Remove crankshaft from cylinder block.
7) Remove piston cooling valves and nozzles, if necessary.
“A”: When servicing CKP sensor, refer to “CMP Sensor Removal and Installation in Section 1C”. :25 N
⋅m (2.5 kgf-m, 18.0 lb-ft)
“B”: Upper half of bearing has an oil groove. : Do not reuse.
“C”: Apply sealant 99000-31250 to mating surface. : Apply engine oil to inside / sliding surface.
“D”: Make sure main bearing cap No.1 bolt deformation when reuse it due to plastic deformation tightening referring to “Main Bearings Inspection”.
I2RH0B140125-01
I2RH0B140126-01
I6RS0C140026-01
Page 340 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-55 Engine Mechanical:
Installation
NOTE
• Use new bearing cap No.1 bolts. They are deformed once they are used because they
are plastic deformation tightening bolts.
• All parts to be insta lled must be perfectly
clean.
• Be sure to oil crankshaft journals, journal bearings, thrust bearings, crankpins,
connecting rod bearings, pistons, piston
rings and cylinder bores.
• Journal bearings, bearing caps, connecting rods, rod bearings, rod bearing
caps, pistons and piston rings are in
combination sets. Do not disturb such
combination and make sure that each part
goes back to where it came from, when
installing.
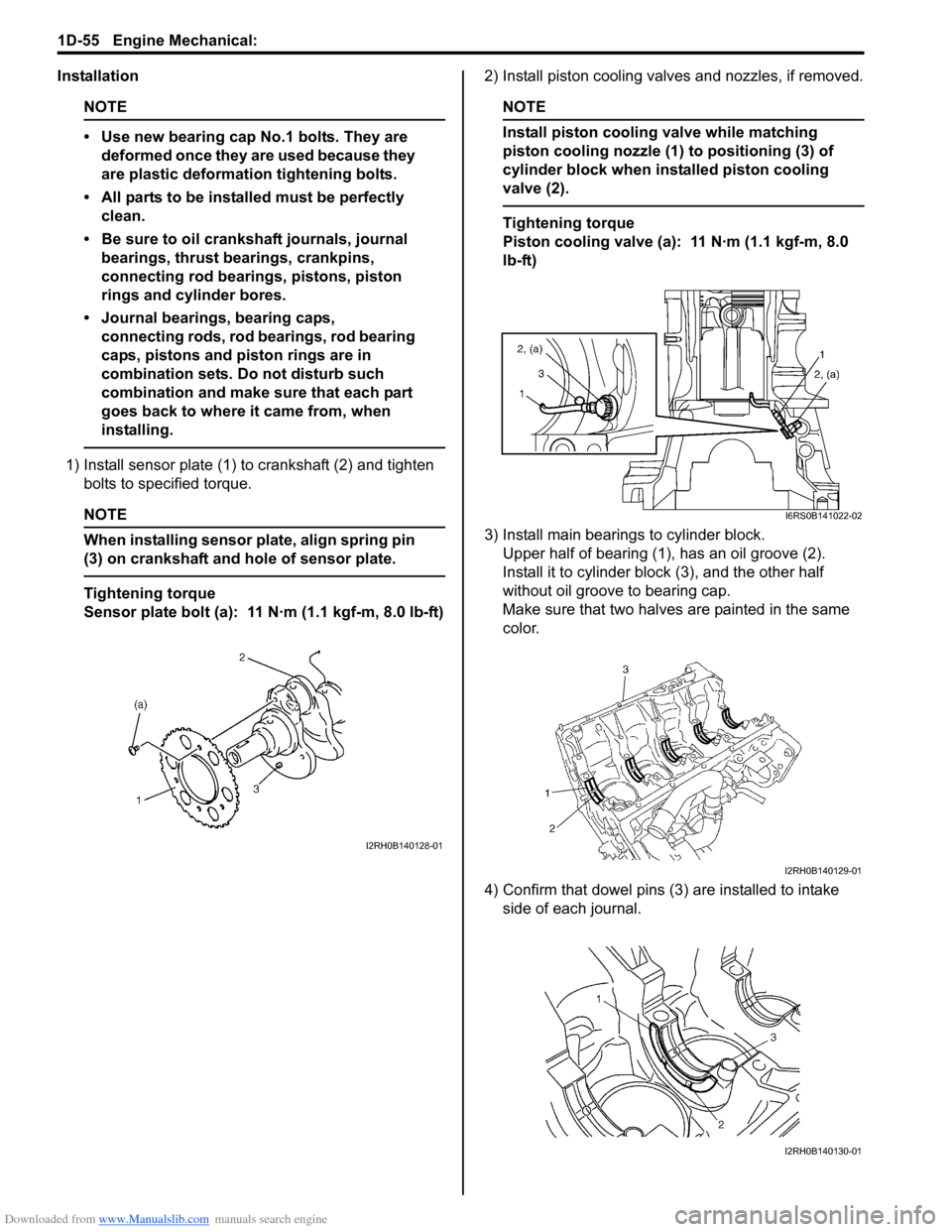
1) Install sensor plate (1) to crankshaft (2) and tighten bolts to spec ified torque.
NOTE
When installing sensor plate, align spring pin
(3) on crankshaft and hole of sensor plate.
Tightening torque
Sensor plate bolt (a): 11 N·m (1.1 kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft) 2) Install piston cooling valves and nozzles, if removed.
NOTE
Install piston cooling valve while matching
piston cooling nozzle (1) to positioning (3) of
cylinder block when installed piston cooling
valve (2).
Tightening torque
Piston cooling valve (a): 11 N·m (1.1 kgf-m, 8.0
lb-ft)
3) Install main bearings to cylinder block. Upper half of bearing (1), has an oil groove (2).
Install it to cylinder block (3), and the other half
without oil groove to bearing cap.
Make sure that two halves are painted in the same
color.
4) Confirm that dowel pins (3 ) are installed to intake
side of each journal.
I2RH0B140128-01
I6RS0B141022-02
I2RH0B140129-01
I2RH0B140130-01
Page 342 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-57 Engine Mechanical:
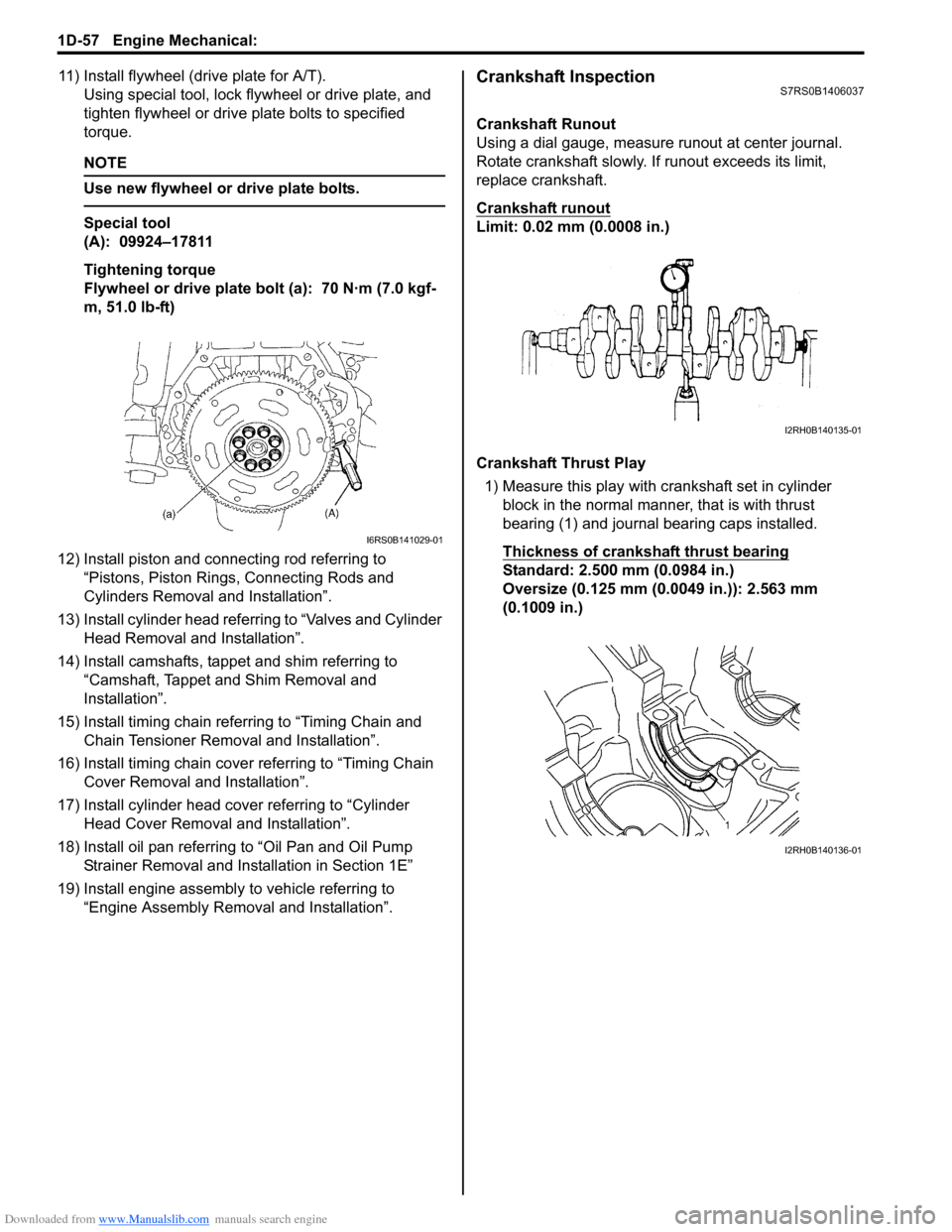
11) Install flywheel (drive plate for A/T).Using special tool, lock flyw heel or drive plate, and
tighten flywheel or drive plate bolts to specified
torque.
NOTE
Use new flywheel or drive plate bolts.
Special tool
(A): 09924–17811
Tightening torque
Flywheel or drive plate bolt (a): 70 N·m (7.0 kgf-
m, 51.0 lb-ft)
12) Install piston and connecting rod referring to “Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Removal and Installation”.
13) Install cylinder head referring to “Valves and Cylinder Head Removal and Installation”.
14) Install camshafts, tappet and shim referring to “Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Removal and
Installation”.
15) Install timing chain referring to “Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner Removal and Installation”.
16) Install timing chain cover referring to “Timing Chain Cover Removal and Installation”.
17) Install cylinder head cover referring to “Cylinder Head Cover Removal and Installation”.
18) Install oil pan referring to “Oil Pan and Oil Pump
Strainer Removal and Installation in Section 1E”
19) Install engine assembly to vehicle referring to “Engine Assembly Removal and Installation”.
Crankshaft InspectionS7RS0B1406037
Crankshaft Runout
Using a dial gauge, measure runout at center journal.
Rotate crankshaft slowly. If runout exceeds its limit,
replace crankshaft.
Crankshaft runout
Limit: 0.02 mm (0.0008 in.)
Crankshaft Thrust Play
1) Measure this play with crankshaft set in cylinder block in the normal manner, that is with thrust
bearing (1) and journal bearing caps installed.
Thickness of crankshaft thrust bearing
Standard: 2.500 mm (0.0984 in.)
Oversize (0.125 mm (0.0049 in.)): 2.563 mm
(0.1009 in.)
I6RS0B141029-01
I2RH0B140135-01
I2RH0B140136-01
Page 350 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-65 Engine Mechanical:
NOTE
The specified tightening torque is also described in the following.
“Air Cleaner Components”
“Throttle Body and Intake Manifold Components”
“Engine Mountings Components”
“Timing Chain Cover Components”
“Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner Components”
“Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Components”
“Valves and Cylinder Head Components”
“Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and Cylinders Components”
“Main Bearings, Crankshaft and Cylinder Block Components”
Reference:
For the tightening torque of fastener not specified in this section, refer to “Fasteners Information in Section 0A”.
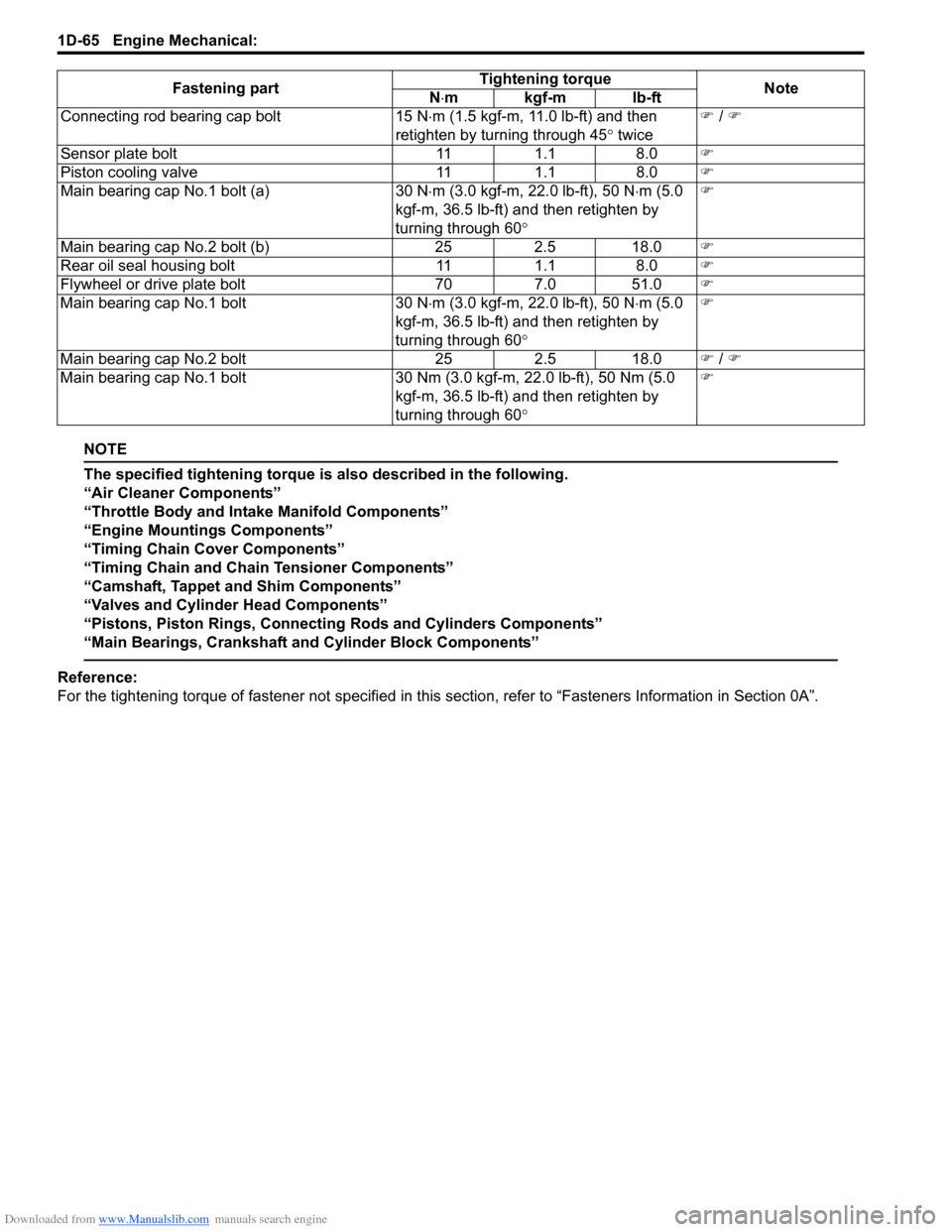
Connecting rod bearing cap bolt
15 N⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft) and then
retighten by turning through 45 ° twice �)
/ �)
Sensor plate bolt 111.1 8.0 �)
Piston cooling valve 111.1 8.0 �)
Main bearing cap No.1 bolt (a) 30 N⋅m (3.0 kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft), 50 N ⋅m (5.0
kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft) and then retighten by
turning through 60 ° �)
Main bearing cap No.2 bolt (b) 252.5 18.0 �)
Rear oil seal housing bolt 111.1 8.0 �)
Flywheel or drive plate bolt 707.0 51.0 �)
Main bearing cap No.1 bolt 30 N⋅m (3.0 kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft), 50 N ⋅m (5.0
kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft) and then retighten by
turning through 60 ° �)
Main bearing cap No.2 bolt 252.5 18.0 �) / �)
Main bearing cap No.1 bolt 30 Nm (3.0 kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft), 50 Nm (5.0
kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft) and then retighten by
turning through 60 ° �)
Fastening part
Tightening torque
Note
N ⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
Page 351 of 1496
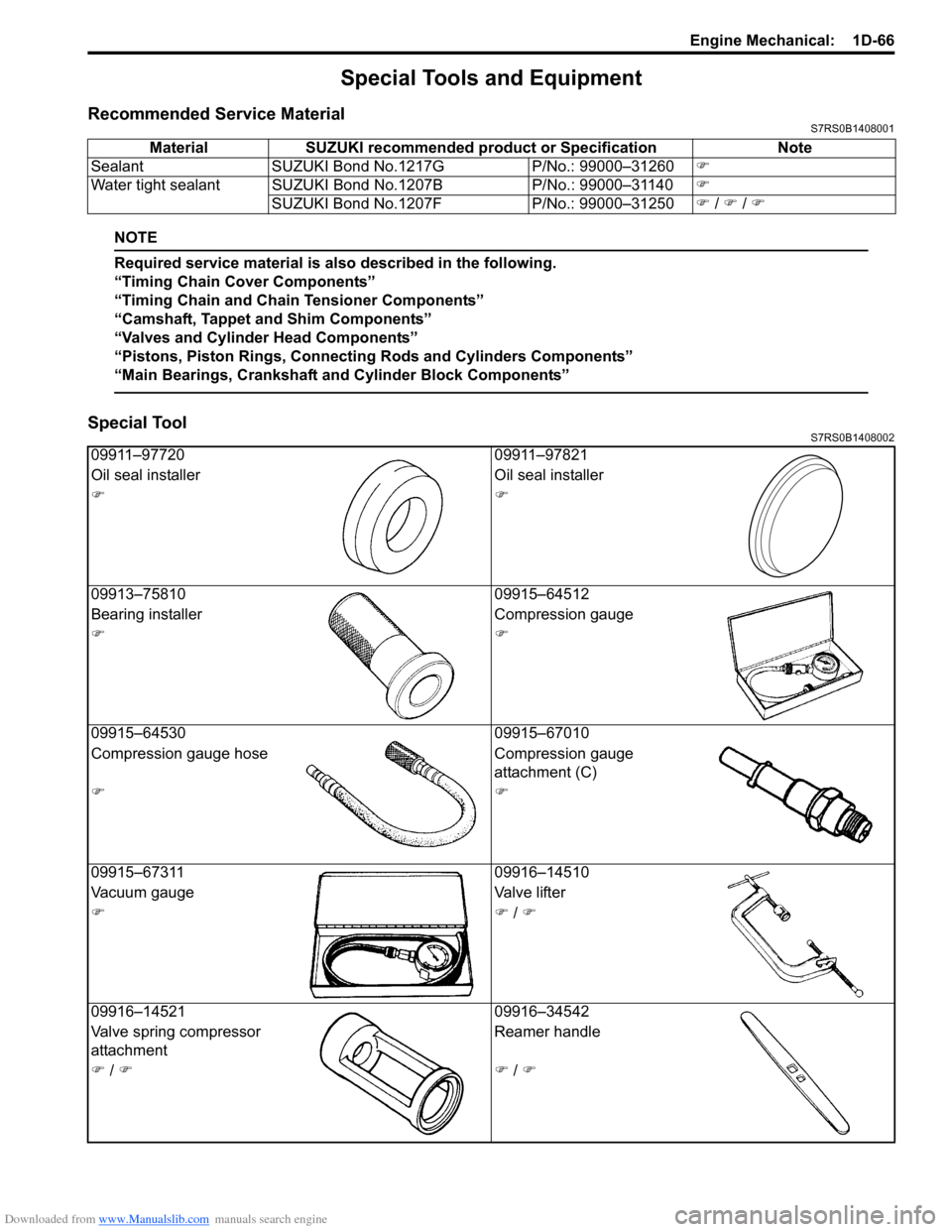
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-66
Special Tools and Equipment
Recommended Service MaterialS7RS0B1408001
NOTE
Required service material is also described in the following.
“Timing Chain Cover Components”
“Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner Components”
“Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Components”
“Valves and Cylinder Head Components”
“Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and Cylinders Components”
“Main Bearings, Crankshaft and Cylinder Block Components”
Special ToolS7RS0B1408002
Material SUZUKI recommended product or Specification Note
Sealant SUZUKI Bond No.1217G P/No.: 99000–31260�)
Water tight sealant SUZUKI Bond No.1207B P/No.: 99000–31140�)
SUZUKI Bond No.1207F P/No.: 99000–31250�) / �) / �)
09911–97720 09911–97821
Oil seal installer Oil seal installer
�)�)
09913–75810 09915–64512
Bearing installer Compression gauge
�)�)
09915–64530 09915–67010
Compression gauge hose Compression gauge
attachment (C)
�)�)
09915–67311 09916–14510
Vacuum gauge Valve lifter
�)�) / �)
09916–14521 09916–34542
Valve spring compressor
attachment Reamer handle
�) / �)�) / �)
Page 499 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Brake Control System and Diagnosis: 4A-1
Brakes
Brake Control System and Diagnosis
Precautions
Precautions on BrakeS7RS0B4100001
Air Bag Warning
Refer to “Air Bag System Service Warning in Section 00”.
Brakes Diagnosis Note
Refer to “Brakes Diagnosis Note”.
General Description
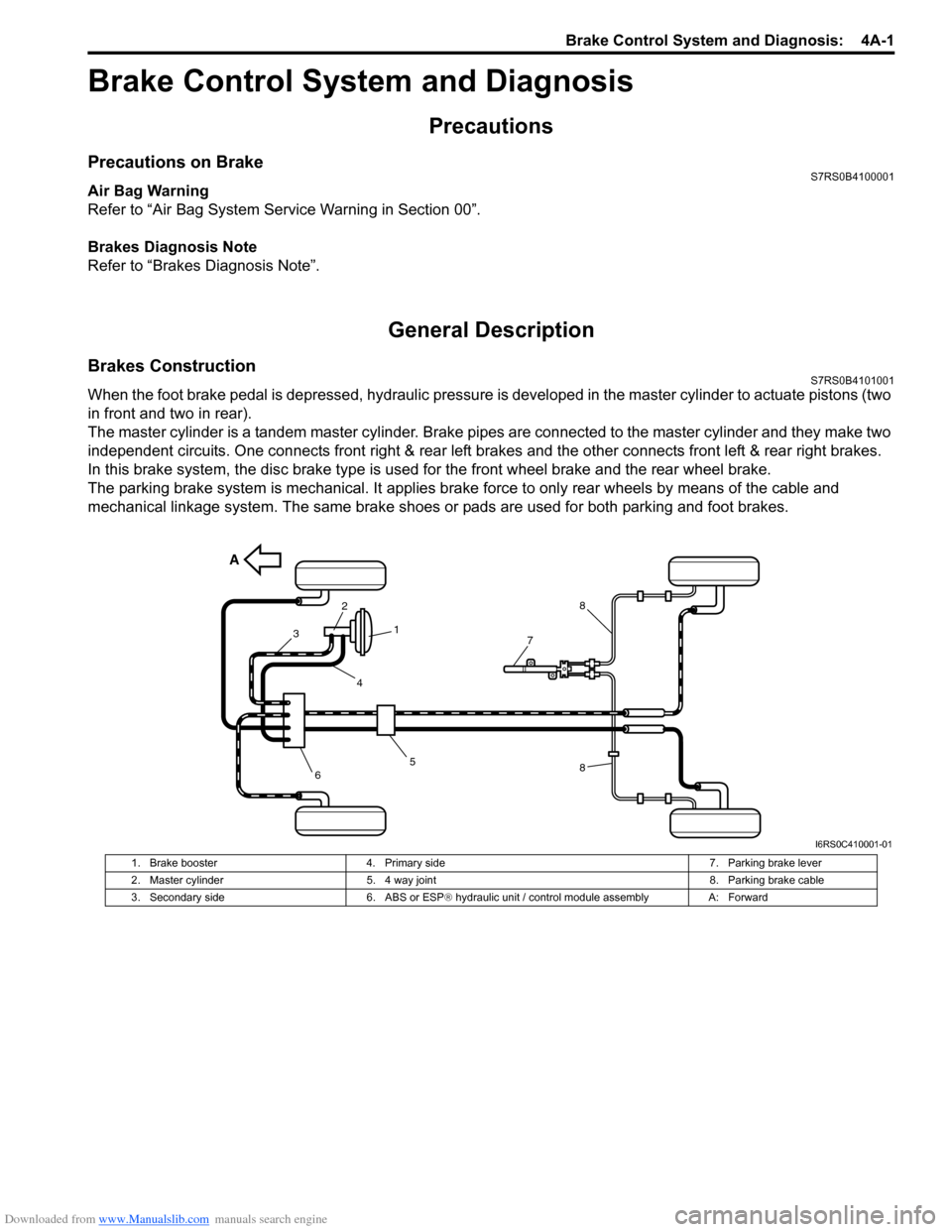
Brakes ConstructionS7RS0B4101001
When the foot brake pedal is depressed, hydraulic pressure is developed in the master cylinder to actuate pistons (two
in front and two in rear).
The master cylinder is a tandem master cylinder. Brake pipes are connected to the master cylinder and they make two
independent circuits. One connects front right & rear left brakes and the other connects front left & rear right brakes.
In this brake system, the disc brake type is used for the front wheel brake and the rear wheel brake.
The parking brake system is mechanical. It applies brake force to only rear wheels by means of the cable and
mechanical linkage system. The same brake shoes or pads are used for both parking and foot brakes.
A
5
3
2
1
4
8
8
6
7
I6RS0C410001-01
1. Brake booster 4. Primary side 7. Parking brake lever
2. Master cylinder 5. 4 way joint 8. Parking brake cable
3. Secondary side 6. ABS or ESP® hydraulic unit / control module assembly A: Forward
Page 503 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Brake Control System and Diagnosis: 4A-5
If deterioration of rubber is evident, disassemble all
hydraulic parts and wash with alcohol. Dry these parts
with compressed air before assembly to keep alcohol out
of the system. Replace all rubber parts in the system,
including hoses. Also, when working on the brake
mechanisms, check for fluid on the linings.
If excessive fluid is found, replace the pads. If master cylinder piston seals
are satisfactory, check for
leakage or excessive heat co nditions. If leakage is not
found, drain fluid, flush with brake fluid, refill and bleed
system.
The system must be flushed if there is any doubt as to
the grade of fluid in the system or if fluid has been used
which contained parts that have been subjected to
contaminated fluid.
Brakes Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B4104002
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Not enough braking force Brake oil leakage from brake lines Locate leaking point and repair.
Brake disc or brake pad stained with oil Clean or replace.
Overheated brakes Determine cause and repair.
Badly worn brake pad Replace.
Malfunctioning caliper assembly Repair or replace.
Malfunctioning brake booster Check system and replace assembly.
Malfunctioning brake master cylinder Check system and replace as necessary.
Air in system Bleed system.
Malfunctioning ABS (ESP ®). Check system and replace as necessary.
Brake pull (Brakes not
working in unison) Brake pad and disc are wet with water or
stained with oil in some brakes Clean or replace.
Disc is out of round in some brakes Replace.
Tires are inflated unequally Inflate equally.
Disturbed front wheel alignment Adjust as prescribed.
Unmatched tires on same axle Tires with approximately the same amount of
tread should be used on the same axle.
Restricted brake pipes or hoses Check for soft hoses and damaged lines.
Replace with new hoses and new double-
walled steel brake tubing.
Malfunctioning caliper assembly Caliper should slide.
Check for stuck or sluggish pistons and proper
lubrication of caliper slide pin.
Loose suspension parts Check all suspension mountings.
Loose calipers Check and torque bolts to specifications.
Noise (High pitched
squeak without brake
applied) Contact wear indicator to brake disc
Replace brake pads.
Worn brake pad Replace brake pads.
Excessive pedal travel
(Pedal stroke too large) Partial brake system failure
Check brake systems and repair as necessary.
Brake fluid leaking Repair the leaking point and bleed air.
Air in system (soft / spongy pedal) Bleed system.
Brake locked Malfunctioning ABS (ESP®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
Dragging brakes (A very
light drag is present in all
brakes immediately after
pedal is released.) Master cylinder pistons not returning
correctly
Replace master cylinder.
Restricted brake pipes or hoses Check for soft hoses or damaged pipes and
replace with new hoses and/or new brake
piping.
Incorrect parking brake adjustment on
rear brakes Check and adjust to correct specifications.
Weakened or broken return springs in
rear brakes. Replace.
Sluggish parking brake cables or linkage Repair or replace.
Brake caliper piston sticking Repair as necessary.
Badly worn piston seal in caliper Replace piston seal.
Improper brake pedal free height Check brake pedal free height.
Page 512 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4A-14 Brake Control System and Diagnosis:
6) Fill reservoir with specified fluid.
7) After completing the work, bleed air from brake and clutch system referring to “Air Bleeding of Brake
System” and “Air Bleeding of Clutch System in
Section 5C” (M/T model).
8) Install cowl top panel referring to “Cowl Top Components in Section 9K”.
9) Install windshield wiper referring to “Windshield
Wiper Removal and Insta llation in Section 9D”.
10) Perform brake test and check each installed part for fluid leakage.
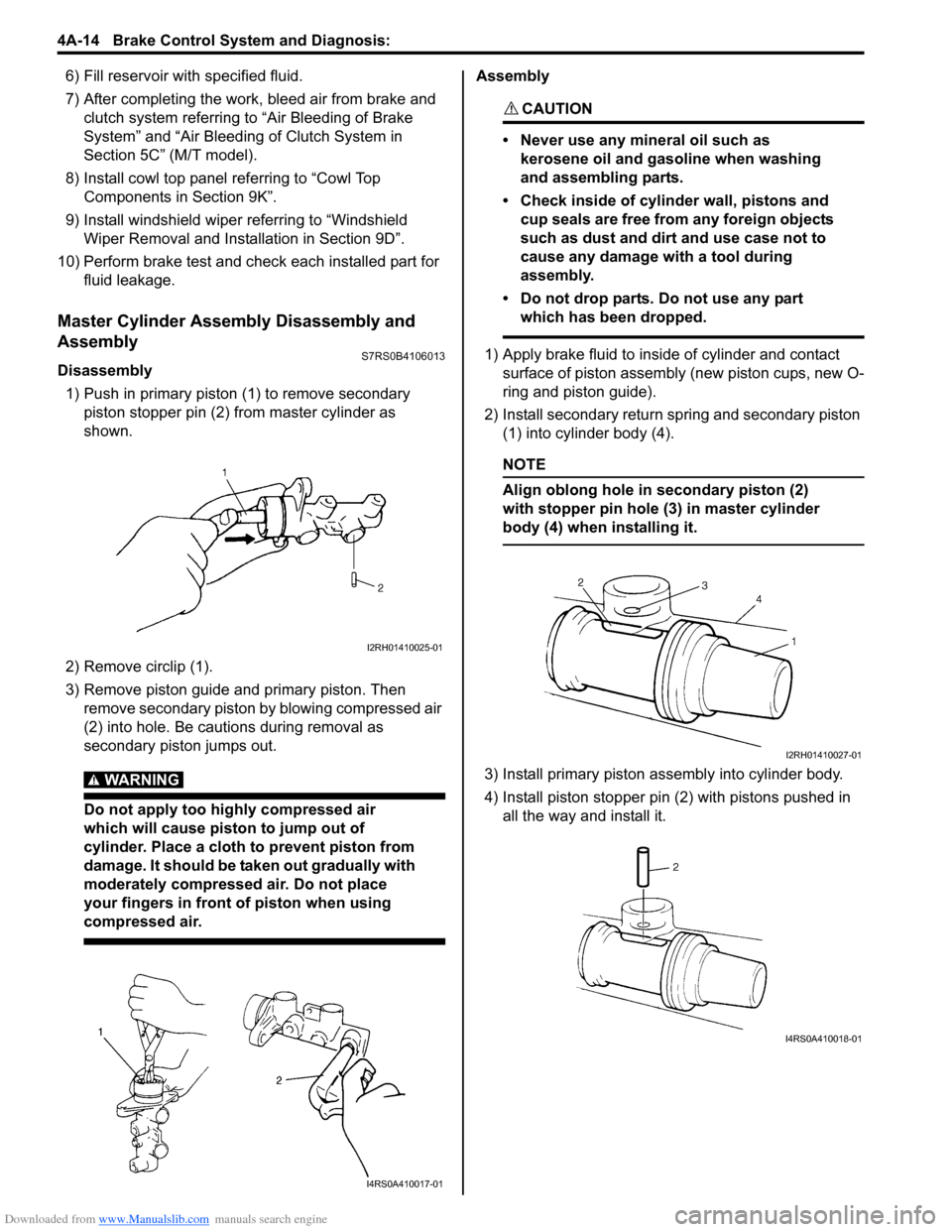
Master Cylinder Assembly Disassembly and
Assembly
S7RS0B4106013
Disassembly
1) Push in primary piston (1) to remove secondary
piston stopper pin (2) from master cylinder as
shown.
2) Remove circlip (1).
3) Remove piston guide and primary piston. Then remove secondary piston by blowing compressed air
(2) into hole. Be cautions during removal as
secondary piston jumps out.
WARNING!
Do not apply too highly compressed air
which will cause piston to jump out of
cylinder. Place a cloth to prevent piston from
damage. It should be taken out gradually with
moderately compressed air. Do not place
your fingers in front of piston when using
compressed air.
Assembly
CAUTION!
• Never use any mineral oil such as kerosene oil and gasoline when washing
and assembling parts.
• Check inside of cylinder wall, pistons and cup seals are free from any foreign objects
such as dust and dirt and use case not to
cause any damage with a tool during
assembly.
• Do not drop parts. Do not use any part which has been dropped.
1) Apply brake fluid to inside of cylinder and contact surface of piston assembly (new piston cups, new O-
ring and piston guide).
2) Install secondary return spring and secondary piston (1) into cylinder body (4).
NOTE
Align oblong hole in secondary piston (2)
with stopper pin hole (3) in master cylinder
body (4) when installing it.
3) Install primary piston assembly into cylinder body.
4) Install piston stopper pin (2) with pistons pushed in all the way and install it.
I2RH01410025-01
I4RS0A410017-01
I2RH01410027-01
I4RS0A410018-01
Page 756 of 1496
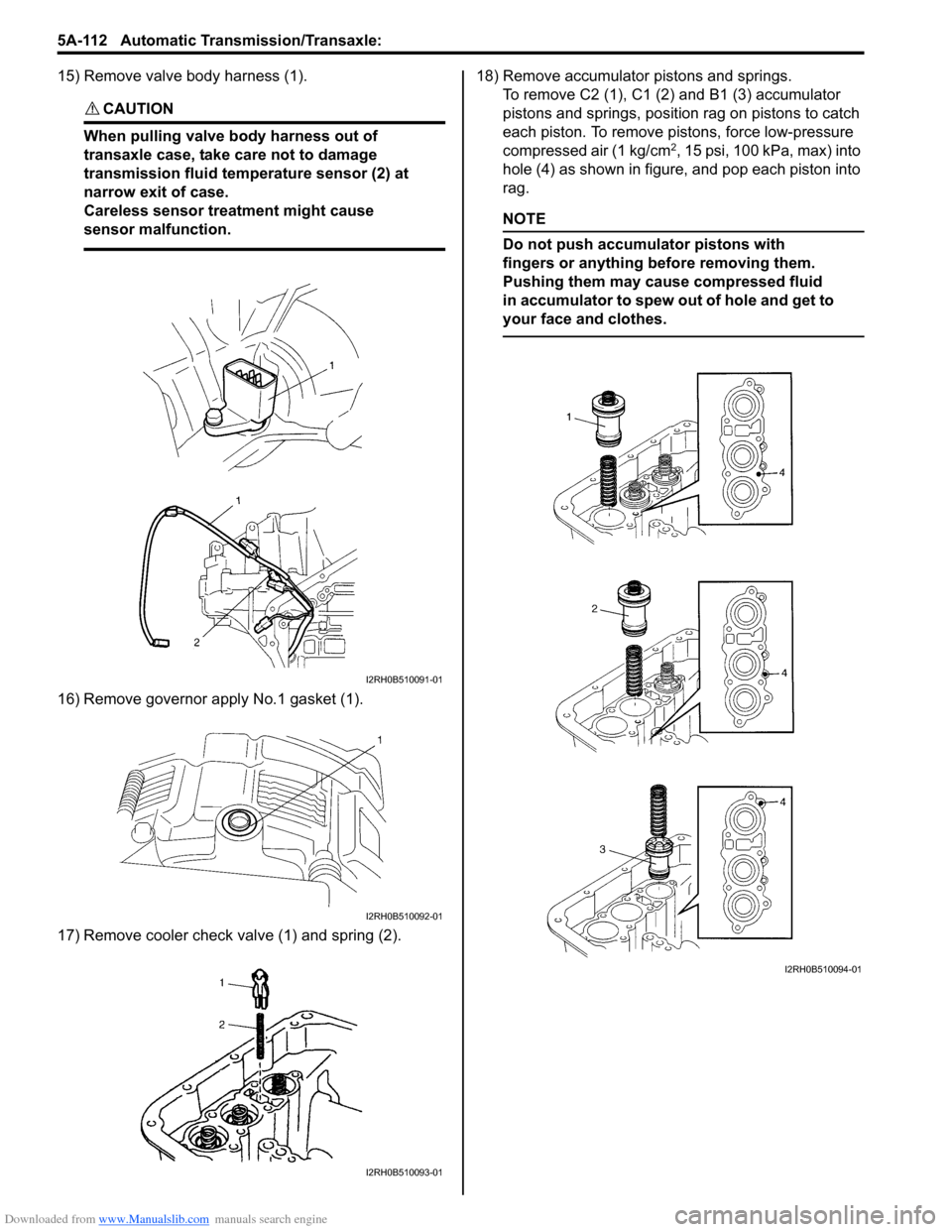
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5A-112 Automatic Transmission/Transaxle:
15) Remove valve body harness (1).
CAUTION!
When pulling valve body harness out of
transaxle case, take care not to damage
transmission fluid temperature sensor (2) at
narrow exit of case.
Careless sensor treatment might cause
sensor malfunction.
16) Remove governor apply No.1 gasket (1).
17) Remove cooler check valve (1) and spring (2).18) Remove accumulator pistons and springs.
To remove C2 (1), C1 (2) and B1 (3) accumulator
pistons and springs, position rag on pistons to catch
each piston. To remove pistons, force low-pressure
compressed air (1 kg/cm
2, 15 psi, 100 kPa, max) into
hole (4) as shown in figure, and pop each piston into
rag.
NOTE
Do not push accumulator pistons with
fingers or anything before removing them.
Pushing them may cause compressed fluid
in accumulator to spew out of hole and get to
your face and clothes.
I2RH0B510091-01
I2RH0B510092-01
I2RH0B510093-01
I2RH0B510094-01
Page 806 of 1496
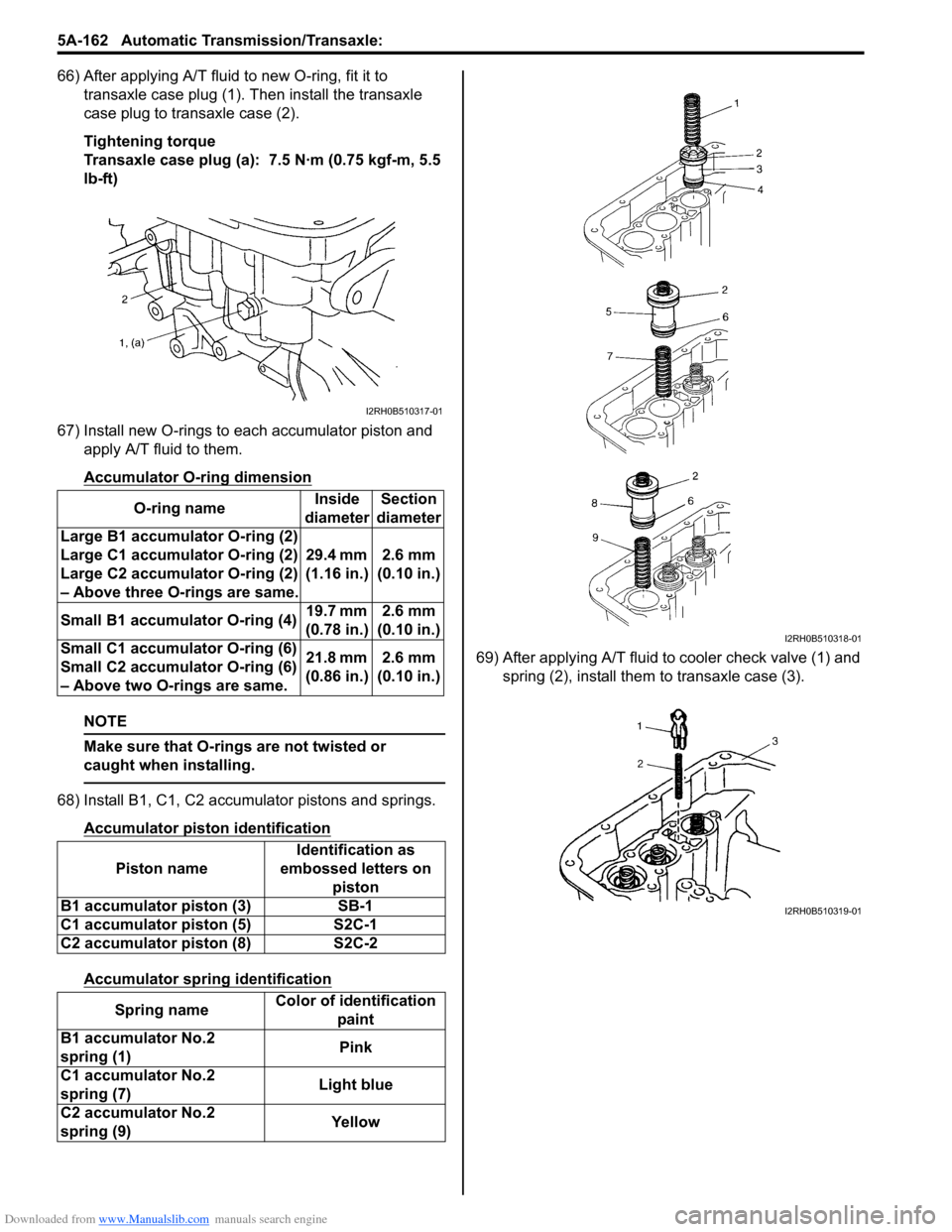
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5A-162 Automatic Transmission/Transaxle:
66) After applying A/T fluid to new O-ring, fit it to transaxle case plug (1). Then install the transaxle
case plug to transaxle case (2).
Tightening torque
Transaxle case plug (a): 7.5 N·m (0.75 kgf-m, 5.5
lb-ft)
67) Install new O-rings to each accumulator piston and apply A/T fluid to them.
Accumulator O-ri ng dimension
NOTE
Make sure that O-rings are not twisted or
caught when installing.
68) Install B1, C1, C2 accumulator pistons and springs.
Accumulator piston identification
Accumulator spring identification
69) After applying A/T fluid to cooler check valve (1) and
spring (2), install them to transaxle case (3).
O-ring name
Inside
diameter Section
diameter
Large B1 accumula tor O-ring (2)
Large C1 accumula tor O-ring (2)
Large C2 accumula tor O-ring (2)
– Above three O-rings are same. 29.4 mm
(1.16 in.) 2.6 mm
(0.10 in.)
Small B1 accumulator O-ring (4) 19.7 mm
(0.78 in.) 2.6 mm
(0.10 in.)
Small C1 accumulator O-ring (6)
Small C2 accumulator O-ring (6)
– Above two O-rings are same. 21.8 mm
(0.86 in.) 2.6 mm
(0.10 in.)
Piston name Identification as
embossed letters on piston
B1 accumulator piston (3) SB-1
C1 accumulator piston (5) S2C-1
C2 accumulator piston (8) S2C-2
Spring name Color of identification
paint
B1 accumulator No.2
spring (1) Pink
C1 accumulator No.2
spring (7) Light blue
C2 accumulator No.2
spring (9) Yellow
I2RH0B510317-01
I2RH0B510318-01
I2RH0B510319-01