H4 lamp SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.G Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 68 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-18 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
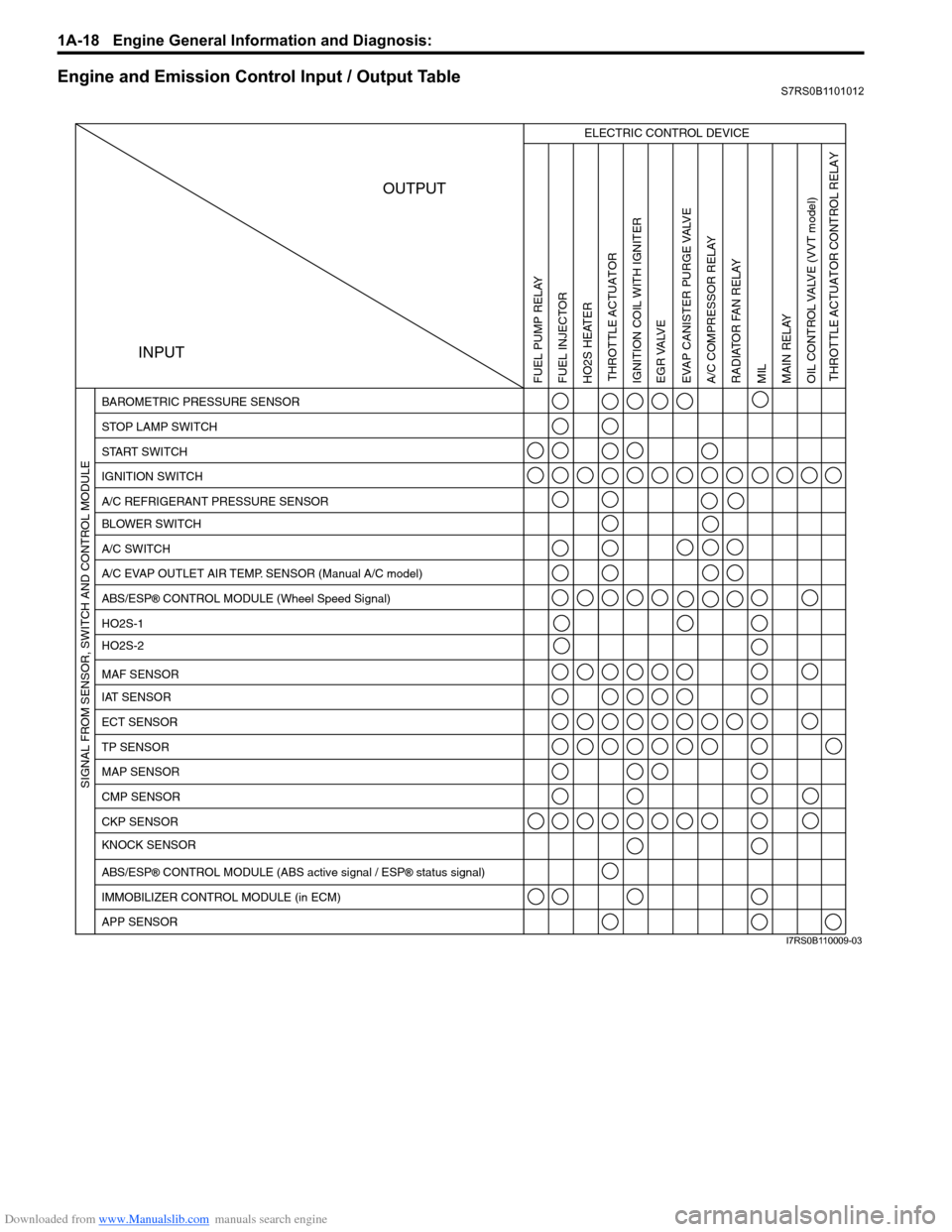
Engine and Emission Control Input / Output TableS7RS0B1101012
INPUTOUTPUT
ELECTRIC CONTROL DEVICE
BAROMETRIC PRESSURE SENSOR
STOP LAMP SWITCH
START SWITCH
IGNITION SWITCH
A/C REFRIGERANT PRESSURE SENSOR
BLOWER SWITCH
A/C SWITCH
A/C EVAP OUTLET AIR TEMP. SENSOR (Manual A/C model)
ABS/ESP
® CONTROL MODULE (Wheel Speed Signal)
HO2S-1
HO2S-2
IAT SENSOR MAF SENSOR
ECT SENSOR
TP SENSOR
MAP SENSOR
CMP SENSOR
CKP SENSOR
KNOCK SENSOR
ABS/ESP
® CONTROL MODULE (ABS active signal / ESP® status signal)
IMMOBILIZER CONTROL MODULE (in ECM)
APP SENSOR
FUEL PUMP RELAY
FUEL INJECTOR
HO2S HEATER THROTTLE ACTUATOR
THROTTLE ACTUATOR CONTROL RELAY
IGNITION COIL WITH IGNITER
EGR VALVE
EVAP CANISTER PURGE VALVEA/C COMPRESSOR RELAY RADIATOR FAN RELAY
MIL
MAIN RELAY
OIL CONTROL VALVE
(VVT model)
SIGNAL FROM SENSOR, SWITCH AND CONTROL MODULE
I7RS0B110009-03
Page 75 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-25
Step 2: DTC / Freeze Frame Data Check, Record and
Clearance
First, check DTC (including pending DTC), referring to
“DTC Check”. If DTC is indicated, print it and freeze
frame data or write them down and then clear them by
referring to “DTC Clearance”. DTC indicates malfunction
that occurred in the system but does not indicate
whether it exists now or it occurred in the past and the
normal condition has been restored now. To check which
case applies, check the sy mptom in question according
to Step 5 and recheck DTC according to Step 6 and 7.
Attempt to diagnose a trouble based on DTC in this step
only or failure to clear the DTC in this step will lead to
incorrect diagnosis, trouble diagnosis of a normal circuit
or difficulty in troubleshooting.
Step 3 and 4: Visual Inspection
As a preliminary step, be sure to perform visual check of
the items that support proper function of the engine
referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Step 5: Trouble Symptom Confirmation
Based on information obtained in “Step 1: Customer
Complaint Analysis: ” and “Step 2: DTC / Freeze Frame
Data Check, Record and Clearance: ”, confirm trouble
symptoms. Also, reconfirm DTC according to “DTC
Confirmation Procedure” described in each DTC diag.
flow.
Step 6 and 7: Rechecking and Record of DTC /
Freeze Frame Data
Refer to “DTC Check” for checking procedure.
Step 8: Engine Basic Inspection and Engine
Symptom Diagnosis
Perform basic engine check according to “Engine Basic
Inspection” first. When the end of the flow has been
reached, check the parts of the system suspected as a
possible cause referring to “Engine Symptom Diagnosis”
and based on symptoms appearing on the vehicle
(symptoms obtained through steps of customer
complaint analysis, trouble symptom confirmation and/or
basic engine check) and repair or replace faulty parts, if
any.
Step 9: Troubleshooting for DTC (See each DTC
Diag. Flow)
Based on the DTC indicated in Step 6 or 7 and referring
to the applicable DTC diag. flow, locate the cause of the
trouble, namely in a sensor, switch, wire harness,
connector, actuator, ECM or other part and repair or
replace faulty parts. Step 10: Intermittent Problems Check
Check parts where an intermit
tent trouble is easy to
occur (e.g., wire harness, connector, etc.), referring to
“Intermittent and Poor Connec tion Inspection in Section
00” and related circuit of DTC recorded in Step 2.
Step 11: Final Confirmation Test
Confirm that the problem symptom has gone and the
engine is free from any abnormal conditions. If what has
been repaired is re lated to the DTC, clear the DTC once,
perform DTC confirmation procedure and confirm that no
DTC is indicated.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) CheckS7RS0B1104002
1) Turn ON ignition switch (with engine at stop) and check that MIL (1) lights.
If MIL does not light up (or MIL dims) but engine can
be starting, go to “MIL Does Not Come ON with
Ignition Switch ON and Engine Stop (but Engine Can
Be Started)” for troubleshooting.
If MIL does not light with ignition switch ON and
engine does not start though it is cranked up, go to
“ECM Power and Ground Circuit Check”.
2) Start engine and check that MIL turns OFF. If MIL remains ON and no DTC is stored in ECM, go
to “Malfunction Indicator Lamp Remains ON after
Engine Starts” for troubleshooting.
1
I4RS0A110012-01
Page 87 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-37
TP SENSOR 2 VOLT (THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
(SUB) OUTPUT VOLTAGE, V)
The TP sensor (sub) reading provides throttle valve
opening information in the form of voltage.
APP SENSOR 1 VOLT (ACCELERATOR PEDAL
POSITION (APP) SENSOR (MAIN) OUTPUT
VOLTAGE, V)
The APP sensor (main) read ing provides accelerator
pedal opening information in the form of voltage.
APP SENSOR 2 VOLT (ACCELERATOR PEDAL
POSITION (APP) SENSOR (S UB) OUTPUT VOLTAGE,
V)
The APP sensor (sub) reading provides accelerator
pedal opening information in the form of voltage.
ACCEL POSITION (ABSOLUTE ACCELERATOR
PEDAL POSITION, %)
When accelerator pedal is at fully released position,
accelerator pedal is indicated as 0 – 5% and 90 – 100%
fully depressed position. THROTTLE TARGET POSI (TARGET THROTTLE
VALVE POSITION, %)
Target throttle valve position is ECM internal parameter
which indicates the ECM requested throttle valve
position.
BATTERY CURRENT (A)
This parameter indicates elec
tric load value (current
consumption) that detected by electric load current
sensor.
GENERATOR CONT DUTY (GENERATOR CONTROL
DUTY, %)
This parameter indicates generator control duty ratio that
controls production electricity of generator by ECM.
100%: No limitation for the generating
0%: Maximum limitation for the generating
GENERATOR FIELD DUTY (GENERATOR FIELD
COIL DUTY, %)
This parameter indicates ope rating rate (status of
production electricity) for gen erator by field coil duty
ratio.
100%: maximum operation.
0%: minimum operation.
Visual InspectionS7RS0B1104008
Visually check the following parts and systems.
Inspection item Reference section
• Engine oil – level, leakage “Engine Oil and Filter Change in Section 0B”
• Engine coolant – level, leakage “Co olant Level Check in Section 1F”
• Fuel – level, leakage “Fuel Lines and Connections Inspection in Section 0B”
• Air cleaner element – dirt, clogging “Air Cleaner Filter Inspection in Section 0B”
• Battery – fluid level, corrosion of terminal “Battery Description in Section 1J”
• Water pump belt – tension damage “Accessory Drive Belt Inspection in Section 0B”
• Throttle valve – operating sound “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection in Section 1C”
• Vacuum hoses of air intake system – disconnection, looseness,
deterioration, bend “Vacuum Hose and Purge Valve Chamber
Inspection in Section 1B”
• Connectors of electric wire harness – disconnection, friction
• Fuses – burning
• Parts – installation, bolt – looseness
• Parts – deformation
• Other parts that can be checked visually
Also check the following items at engine start, if possible
• Malfunction indicator lamp – Operation “Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Check”
• Charge warning lamp – Operation “Genera tor Symptom Diagnosis in Section 1J”
• Engine oil pressure warning lamp – Operation “O il Pressure Switch Inspection in Section 9C”
• Engine coolant temp. meter – Operation “ECT Sensor Inspection in Section 1C”
• Fuel level meter – Operation “Fuel Level Sensor Inspection in Section 9C”
• Tachometer – Operation
• Abnormal air being inhaled from air intake system
• Exhaust system – leakage of exhaust gas, noise
• Other parts that can be checked visually
Page 89 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-39
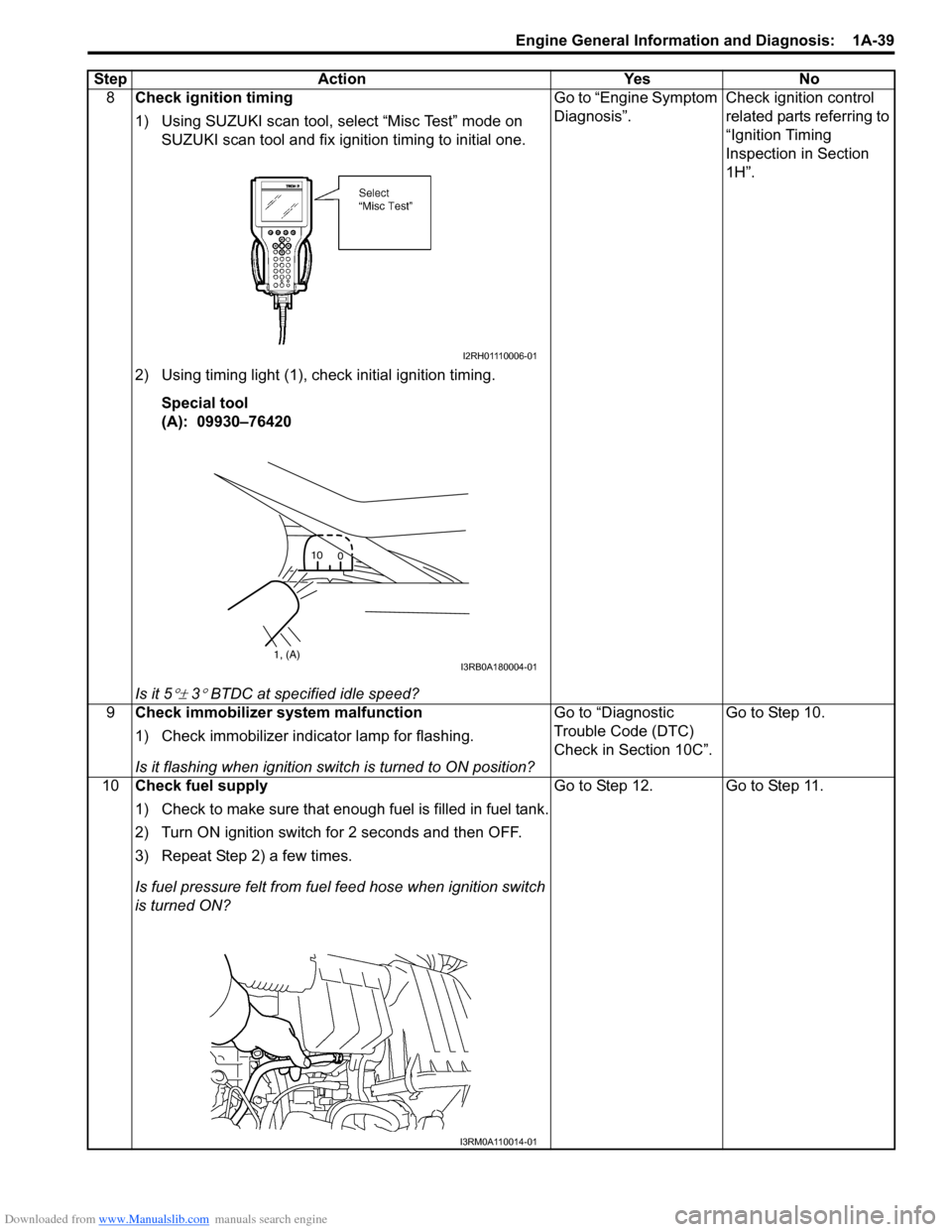
8Check ignition timing
1) Using SUZUKI scan tool, select “Misc Test” mode on
SUZUKI scan tool and fix ignition timing to initial one.
2) Using timing light (1), check initial ignition timing. Special tool
(A): 09930–76420
Is it 5
°± 3° BTDC at specif ied idle speed? Go to “Engine Symptom
Diagnosis”.
Check ignition control
related parts referring to
“Ignition Timing
Inspection in Section
1H”.
9 Check immobilizer system malfunction
1) Check immobilizer indica tor lamp for flashing.
Is it flashing when ignition switch is turned to ON position? Go to “Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC)
Check in Section 10C”.
Go to Step 10.
10 Check fuel supply
1) Check to make sure that enough fuel is filled in fuel tank.
2) Turn ON ignition switch for 2 seconds and then OFF.
3) Repeat Step 2) a few times.
Is fuel pressure felt from fuel feed hose when ignition switch
is turned ON? Go to Step 12. Go to Step 11.
Step Action Yes No
I2RH01110006-01
1, (A)
10
0I3RB0A180004-01
I3RM0A110014-01
Page 97 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-47
MIL Does Not Come ON with Ignition Switch ON and Engine Stop (but Engine Can Be Started)S7RS0B1104011
Wiring Diagram
Circuit Description
When the ignition switch is turned ON, ECM causes the main relay to turn ON (close the contact point). Then, ECM
being supplied with the main power, transmits indication ON si gnal of MIL to combination meter in order to turn MIL
ON. And then, combination meter turns MIL ON. When the engine starts to run and no malfunction is detected in the
system, ECM transmits MIL indication OFF signal to combination meter in order to turn MIL OFF. And then,
combination meter turns MIL OFF, but if a malfunction was or is detected, MIL remains ON even when the engine is
running.
G281234567
8
910
11
1213141516
1718
19
20
212223242526272829303132
[B]
[A]
E23 C37
34
1819
567
10
11
17
20
47 46
495051
2122
52 16
25 9
24
14
29
5557 54 53
59
60 58 2
262728
15
30
56 4832 31
34353637
4042 39 38
44
45 43 41 331
1213
238
34
1819
567
10
11
17
20
47 46
495051
2122
52 16
25 9
24
14
29
5557 54 53
59
60 58 2
262728
15
30
56 4832 31
34353637
4042 39 38
44
45 43 41 331
12
13
238
BLK/WHT
BLK/RED
BLK/RED
BRN/WHT
BLK/REDWHTBLK/YEL
GRN
12V 5V
2
3
8
6 7
E23-29
E23-3
E23-1
E23-60
E23-18
E23-16
1014
14
12
11
RED/BLK
C37-58
C37-15
C37-30
BLK
E23-31
BLK
BLK/ORNBLK/ORN
4
WHTREDWHTRED
BLK/ORN
G28-16
15
13
14
1414
G28-31
BLK/YEL
BLK/YEL
WHTRED
WHTRED
WHTREDC37-13 C37-12
WHTRED
9
17
5 1 16
I7RS0B110012-02
[A]: ECM connector (viewed from harness side)
6. “METER” fuse13. TCM (A/T model)
[B]: Combination meter connector (viewed from harness side) 7. ECM14. CAN communication line
1. Main fuse box 8. Junction block assembly15. ABS/ESP® control module
2. Ignition switch 9. BCM16. CAN junction connector (ESP® model)
3. Main relay 10. “FI” fuse17. Combination meter
4. Malfunction indicator lamp in combination meter 11. Individual circuit fuse box No.1
5. “IG COIL” fuse 12. “IG ACC” fuse
Page 98 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-48 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
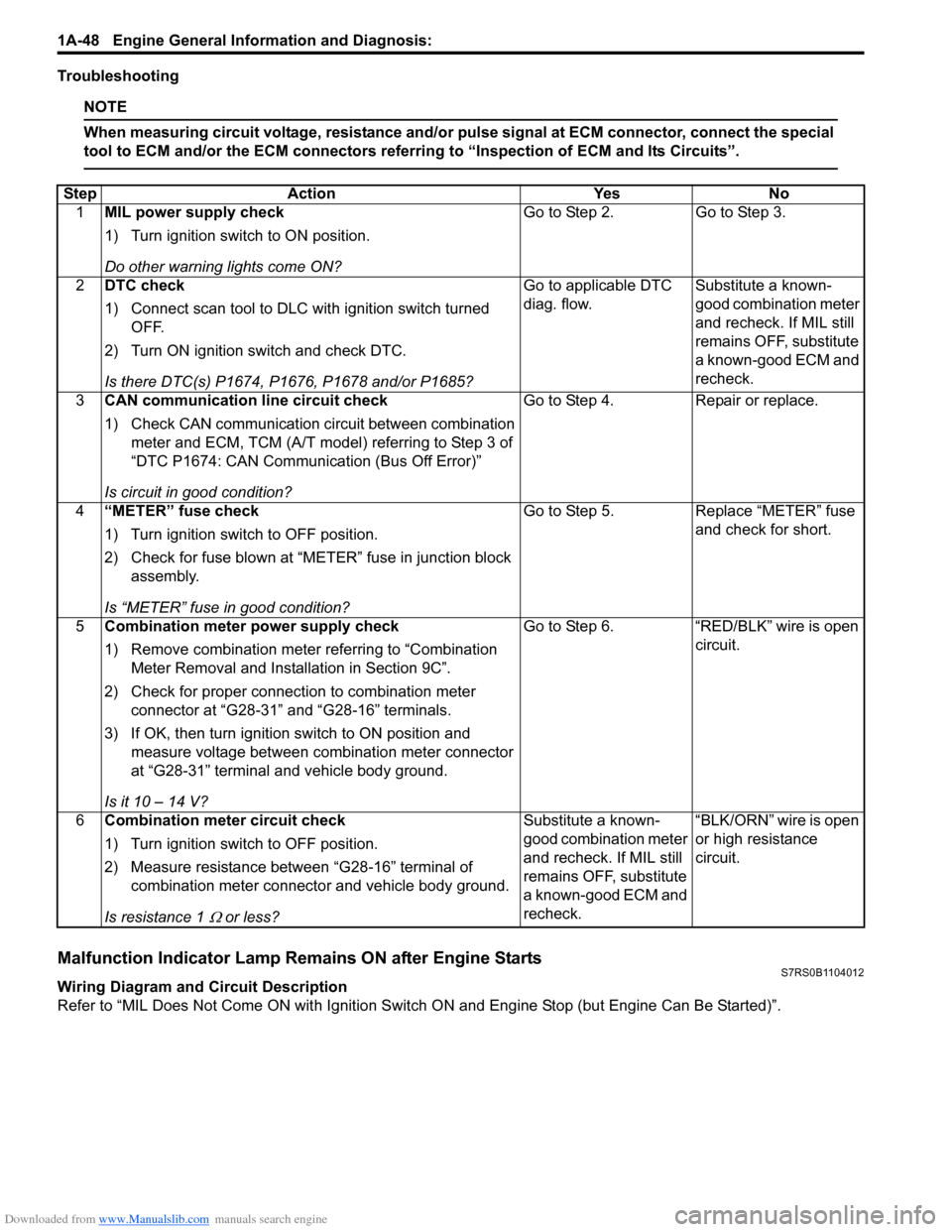
Troubleshooting
NOTE
When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the special
tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors referri ng to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp Remains ON after Engine StartsS7RS0B1104012
Wiring Diagram and Circuit Description
Refer to “MIL Does Not Come ON wit h Ignition Switch ON and Engine Stop (but Engine Can Be Started)”.
Step
Action YesNo
1 MIL power supply check
1) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
Do other warning lights come ON? Go to Step 2.
Go to Step 3.
2 DTC check
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned
OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and check DTC.
Is there DTC(s) P1674, P1676, P1678 and/or P1685? Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.
Substitute a known-
good combination meter
and recheck. If MIL still
remains OFF, substitute
a known-good ECM and
recheck.
3 CAN communication line circuit check
1) Check CAN communication circuit between combination
meter and ECM, TCM (A/T model) referring to Step 3 of
“DTC P1674: CAN Communication (Bus Off Error)”
Is circuit in good condition? Go to Step 4.
Repair or replace.
4 “METER” fuse check
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Check for fuse blown at “M ETER” fuse in junction block
assembly.
Is “METER” fuse in good condition? Go to Step 5.
Replace “METER” fuse
and check for short.
5 Combination meter power supply check
1) Remove combination meter referring to “Combination
Meter Removal and Installation in Section 9C”.
2) Check for proper connection to combination meter connector at “G28-31” and “G28-16” terminals.
3) If OK, then turn ignition switch to ON position and measure voltage between combination meter connector
at “G28-31” terminal and vehicle body ground.
Is it 10 – 14 V? Go to Step 6.
“RED/BLK” wire is open
circuit.
6 Combination meter circuit check
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Measure resistance between “G28-16” terminal of
combination meter connector and vehicle body ground.
Is resistance 1
Ω or less? Substitute a known-
good combination meter
and recheck. If MIL still
remains OFF, substitute
a known-good ECM and
recheck.
“BLK/ORN” wire is open
or high resistance
circuit.
Page 187 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-137
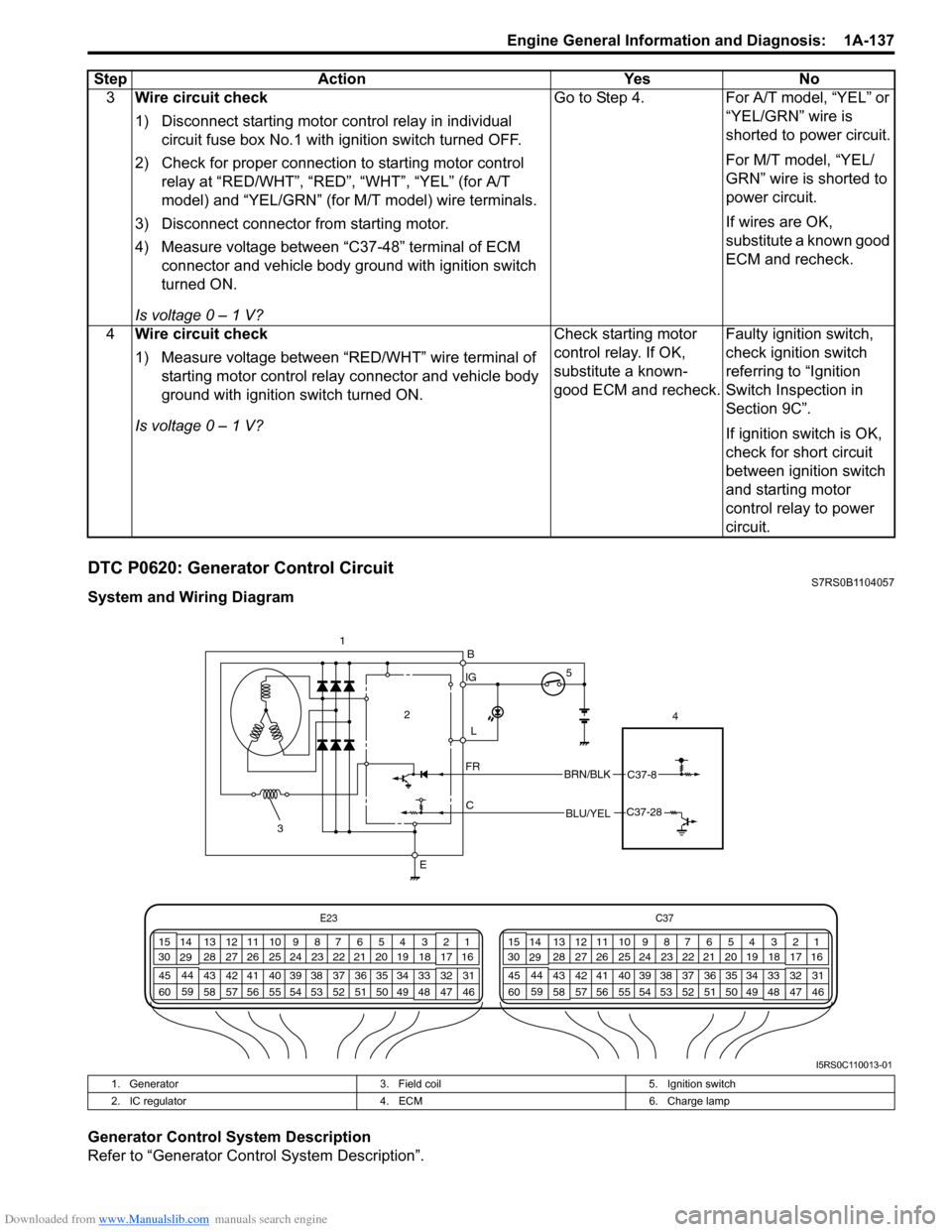
DTC P0620: Generator Control CircuitS7RS0B1104057
System and Wiring Diagram
Generator Control System Description
Refer to “Generator Control System Description”.3
Wire circuit check
1) Disconnect starting motor control relay in individual
circuit fuse box No.1 with ignition switch turned OFF.
2) Check for proper connection to starting motor control relay at “RED/WHT”, “RED”, “WHT”, “YEL” (for A/T
model) and “YEL/GRN” (for M/T model) wire terminals.
3) Disconnect connector from starting motor.
4) Measure voltage between “C37-48” terminal of ECM connector and vehicle body ground with ignition switch
turned ON.
Is voltage 0 – 1 V? Go to Step 4. For A/T model, “YEL” or
“YEL/GRN” wire is
shorted to power circuit.
For M/T model, “YEL/
GRN” wire is shorted to
power circuit.
If wires are OK,
substitute a known good
ECM and recheck.
4 Wire circuit check
1) Measure voltage between “RED/WHT” wire terminal of
starting motor control relay connector and vehicle body
ground with ignition switch turned ON.
Is voltage 0 – 1 V? Check starting motor
control relay. If OK,
substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
Faulty ignition switch,
check ignition switch
referring to “Ignition
Switch Inspection in
Section 9C”.
If ignition switch is OK,
check for short circuit
between ignition switch
and starting motor
control relay to power
circuit.
Step Action Yes No
IG
L
C
FR
E 4
2
BRN/BLKC37-8
BLU/YELC37-28
B
E23
C37
34
1819
567
1011
17
20
47 46
495051
2122
52 16
25 9
24
14
29
55
57 54 53
59
60 58 2
262728
15
30
56 4832 31
34353637
40
42 39 38
44
45 43 41 331
1213
238
34
1819
567
1011
17
20
47 46
495051
2122
52 16
25 9
24
14
29
55
57 54 53
59
60 58 2
262728
15
30
56 4832 31
34353637
40
42 39 38
44
45 43 41 331
1213
238 1
3 5
I5RS0C110013-01
1. Generator
3. Field coil 5. Ignition switch
2. IC regulator 4. ECM 6. Charge lamp
Page 231 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-181
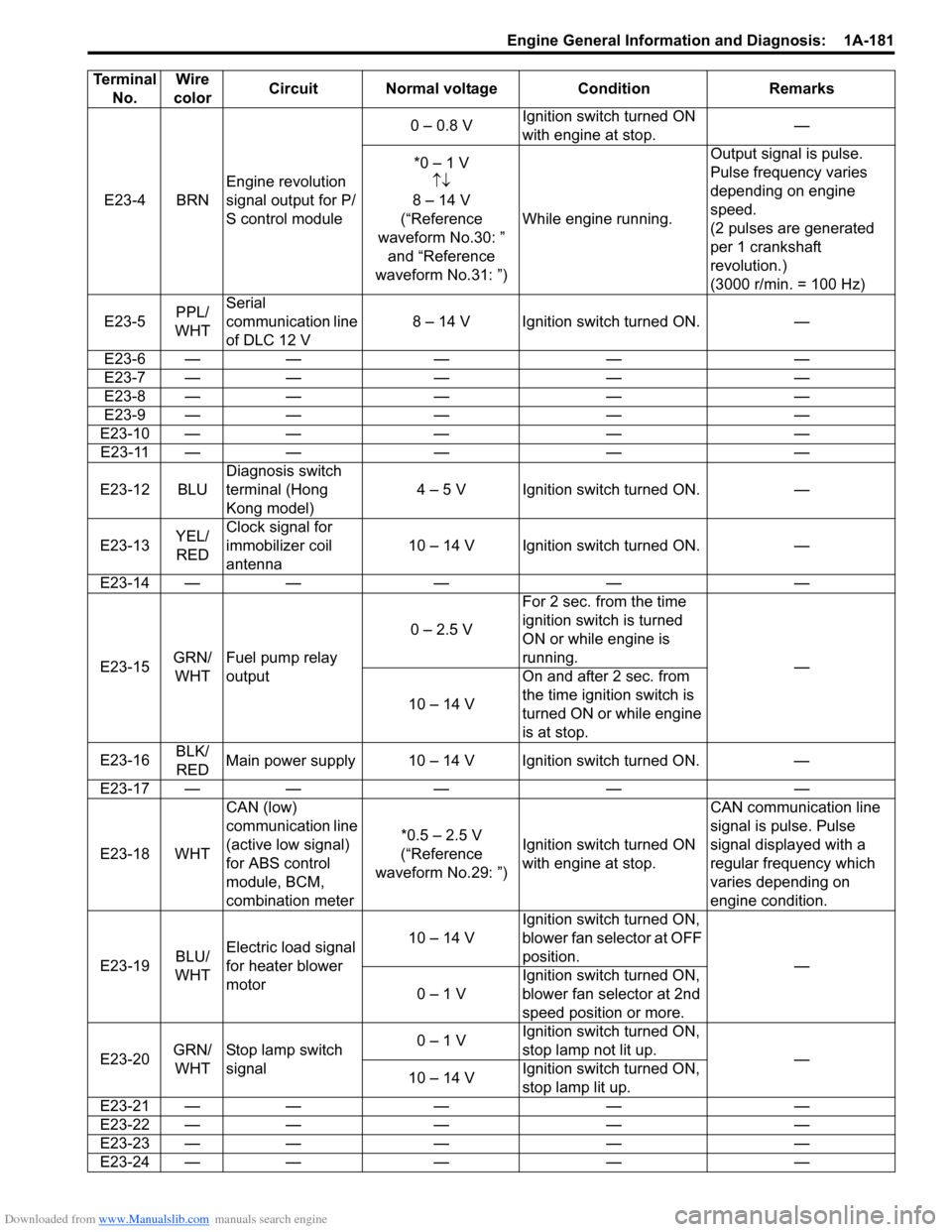
E23-4 BRNEngine revolution
signal output for P/
S control module 0 – 0.8 V
Ignition switch turned ON
with engine at stop. —
*0 – 1 V ↑↓
8 – 14 V
(“Reference
waveform No.30: ” and “Reference
waveform No.31: ”) While engine running. Output signal is pulse.
Pulse frequency varies
depending on engine
speed.
(2 pulses are generated
per 1 crankshaft
revolution.)
(3000 r/min. = 100 Hz)
E23-5 PPL/
WHT Serial
communication line
of DLC 12 V
8 – 14 V Ignition switch turned ON. —
E23-6 — — — — —
E23-7 — — — — —
E23-8 — — — — —
E23-9 — — — — —
E23-10 — — — — — E23-11 — — — — —
E23-12 BLU Diagnosis switch
terminal (Hong
Kong model) 4 – 5 V Ignition switch turned ON. —
E23-13 YEL/
RED Clock signal for
immobilizer coil
antenna
10 – 14 V Ignition switch turned ON. —
E23-14 — — — — —
E23-15 GRN/
WHT Fuel pump relay
output 0 – 2.5 V
For 2 sec. from the time
ignition switch is turned
ON or while engine is
running.
—
10 – 14 V On and after 2 sec. from
the time ignition switch is
turned ON or while engine
is at stop.
E23-16 BLK/
RED Main power supply 10 – 14 V Ignition switch turned ON. —
E23-17 — — — — —
E23-18 WHT CAN (low)
communication line
(active low signal)
for ABS control
module, BCM,
combination meter *0.5 – 2.5 V
(“Reference
waveform No.29: ”) Ignition switch turned ON
with engine at stop. CAN communication line
signal is pulse. Pulse
signal displayed with a
regular frequency which
varies depending on
engine condition.
E23-19 BLU/
WHT Electric load signal
for heater blower
motor 10 – 14 V
Ignition switch turned ON,
blower fan selector at OFF
position.
—
0 – 1 V Ignition switch turned ON,
blower fan selector at 2nd
speed position or more.
E23-20 GRN/
WHT Stop lamp switch
signal 0 – 1 V
Ignition switch turned ON,
stop lamp not lit up.
—
10 – 14 V Ignition switch turned ON,
stop lamp lit up.
E23-21 — — — — —
E23-22 — — — — —
E23-23 — — — — —
E23-24 — — — — —
Terminal
No. Wire
color Circuit Normal voltage Condition Remarks
Page 279 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Electrical Devices: 1C-7
Installation
Reverse removal procedure noting the following.
• Clean mating surfaces of ECT sensor and thermostat case.
• Check O-ring for damage and replace, if necessary.
• Tighten ECT sensor (1) to specified torque.
Tightening torque
ECT sensor (a): 15 N·m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft)
• Connect connector to ECT sensor securely.
• Refill coolant referring to “Cooling System Flush and
Refill in Section 1F”.
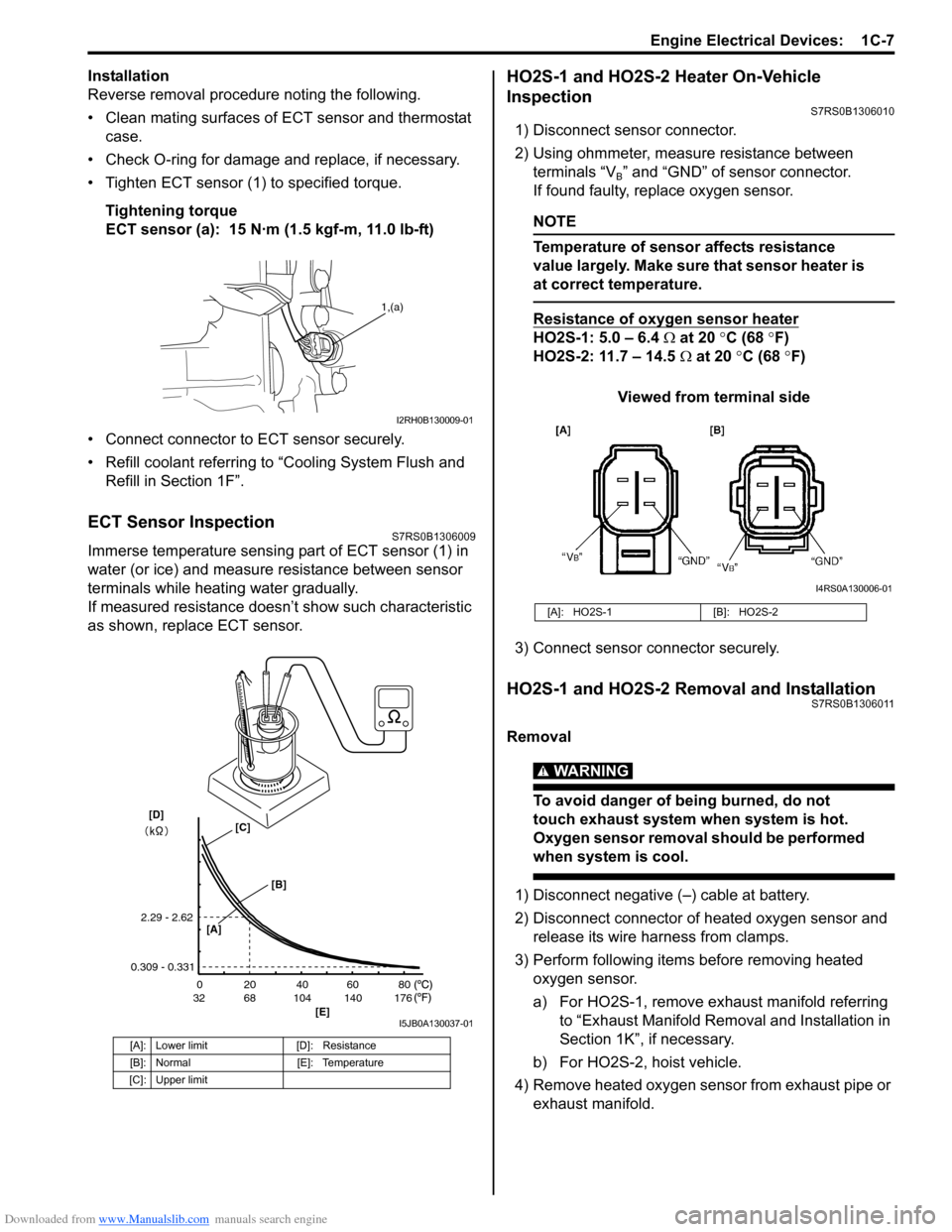
ECT Sensor InspectionS7RS0B1306009
Immerse temperature sensing part of ECT sensor (1) in
water (or ice) and measure resistance between sensor
terminals while heating water gradually.
If measured resistance doesn’t show such characteristic
as shown, replace ECT sensor.
HO2S-1 and HO2S-2 Heater On-Vehicle
Inspection
S7RS0B1306010
1) Disconnect sensor connector.
2) Using ohmmeter, measure resistance between terminals “V
B” and “GND” of sensor connector.
If found faulty, replace oxygen sensor.
NOTE
Temperature of sensor affects resistance
value largely. Make sure that sensor heater is
at correct temperature.
Resistance of oxygen sensor heater
HO2S-1: 5.0 – 6.4 Ω at 20 °C (68 °F)
HO2S-2: 11.7 – 14.5 Ω at 20 °C (68 °F)
Viewed from terminal side
3) Connect sensor co nnector securely.
HO2S-1 and HO2S-2 Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1306011
Removal
WARNING!
To avoid danger of being burned, do not
touch exhaust system when system is hot.
Oxygen sensor removal should be performed
when system is cool.
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Disconnect connector of heated oxygen sensor and
release its wire harness from clamps.
3) Perform following items before removing heated oxygen sensor.
a) For HO2S-1, remove exhaust manifold referring to “Exhaust Manifold Remo val and Installation in
Section 1K”, if necessary.
b) For HO2S-2, hoist vehicle.
4) Remove heated oxygen sensor from exhaust pipe or exhaust manifold.
[A]: Lower limit [D]: Resistance
[B]: Normal [E]: Temperature
[C]: Upper limit
1,(a)
I2RH0B130009-01
20
0
68
32 104 140 176 40 60 80
[E]
2.29 - 2.62
0.309 - 0.331
[A]
[B]
[C][D]
I5JB0A130037-01
[A]: HO2S-1 [B]: HO2S-2
I4RS0A130006-01
Page 280 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1C-8 Engine Electrical Devices:
Installation
Reverse removal procedure noting the following.
• Tighten heated oxygen sensor to specified torque.Tightening torque
Heated oxygen sensor (a): 45 N·m (4.5 kgf-m,
32.5 lb-ft)
• Install exhaust manifold referring to “Exhaust Manifold Removal and Installation in Section 1K”, if removed.
• Connect connector of heated oxygen sensor and clamp wire harness securely.
• After installing heated oxygen sensor, start engine and check that no exhaust gas leakage exists.
CMP Sensor Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1306012
Removal
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Disconnect connector from CMP sensor.
3) Remove CMP sensor from cylinder head.
Installation 1) Install CMP sensor to cylinder head.
Tightening torque
CMP sensor bolt (a): 10 N·m (1.0 kgf-m, 7.5 lb-ft)
2) Connect connector to CMP sensor securely.
3) Connect negative (–) cable to battery.
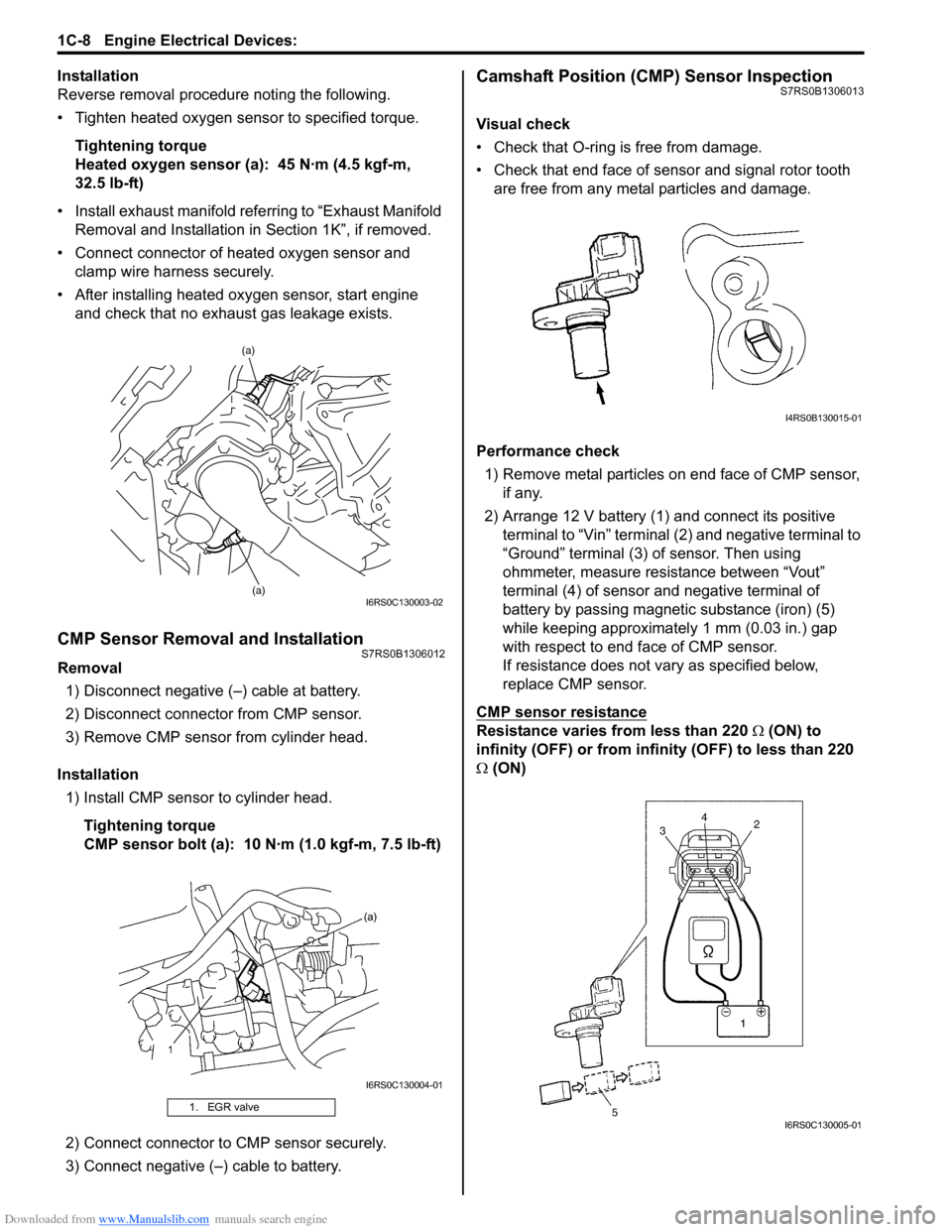
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor InspectionS7RS0B1306013
Visual check
• Check that O-ring is free from damage.
• Check that end face of sensor and signal rotor tooth are free from any metal particles and damage.
Performance check 1) Remove metal particles on end face of CMP sensor, if any.
2) Arrange 12 V battery (1) and connect its positive terminal to “Vin” terminal (2) and negative terminal to
“Ground” terminal (3) of sensor. Then using
ohmmeter, measure resistance between “Vout”
terminal (4) of sensor and negative terminal of
battery by passing magnetic substance (iron) (5)
while keeping approximately 1 mm (0.03 in.) gap
with respect to end face of CMP sensor.
If resistance does not vary as specified below,
replace CMP sensor.
CMP sensor resistance
Resistance varies from less than 220 Ω (ON) to
infinity (OFF) or from infinity (OFF) to less than 220
Ω (ON)
1. EGR valve
(a)
(a)
I6RS0C130003-02
I6RS0C130004-01
I4RS0B130015-01
I6RS0C130005-01