light switch SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.G Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 71 of 1496
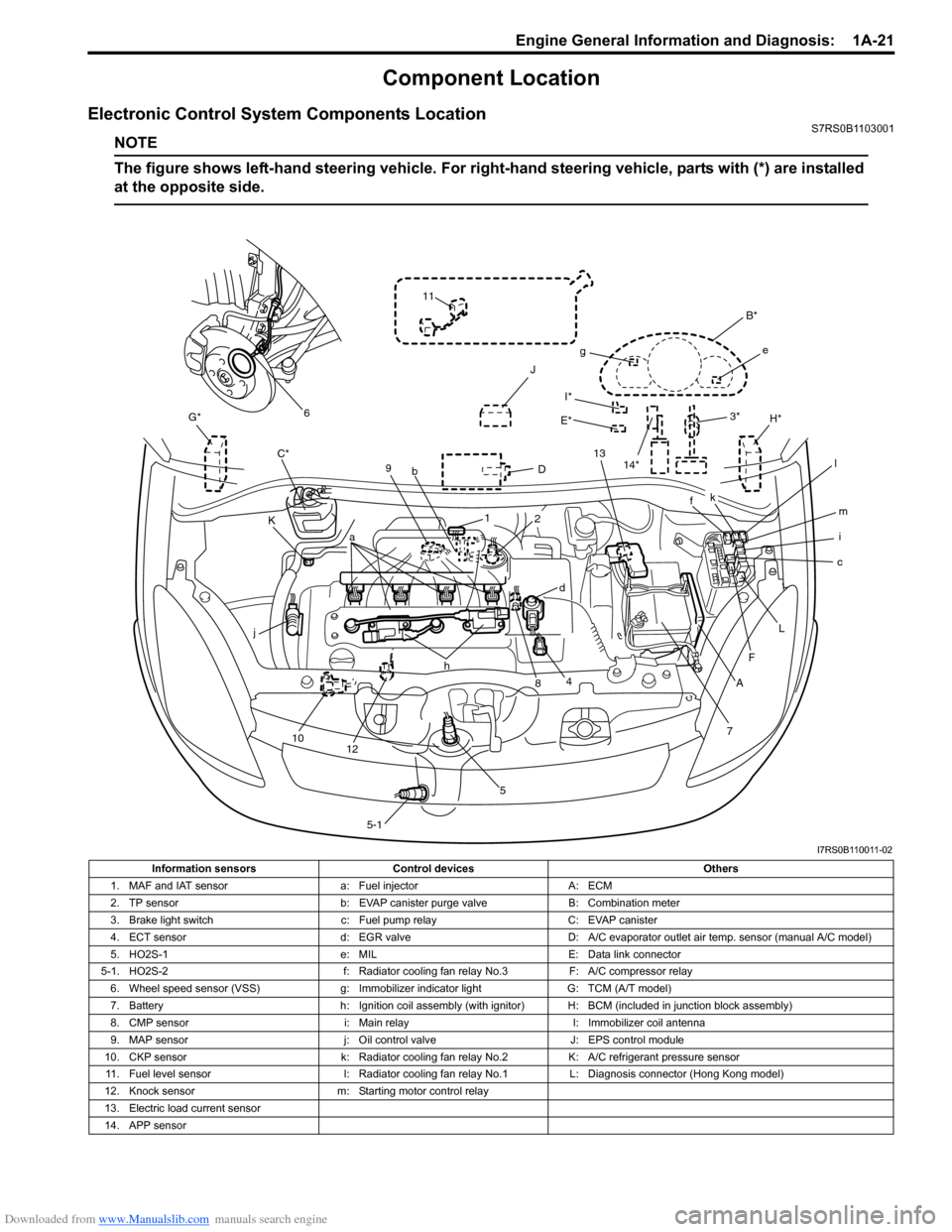
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-21
Component Location
Electronic Control System Components LocationS7RS0B1103001
NOTE
The figure shows left-hand steering vehicle. For right-hand steering vehicle, parts with (*) are installed
at the opposite side.
I*
E*
G*
D
K H*
J
C*
7
A
F
c
L
i m
f
B*
e
g
k
l
13
3*
4
j
10 12 h
58
a
9
b
1
5-1
d
2
11
6
14*
I7RS0B110011-02
Information sensors Control devices Others
1. MAF and IAT sensor a: Fuel injectorA: ECM
2. TP sensor b: EVAP canister purge valve B: Combination meter
3. Brake light switch c: Fuel pump relayC: EVAP canister
4. ECT sensor d: EGR valveD: A/C evaporator outlet air temp. sensor (manual A/C model)
5. HO2S-1 e: MILE: Data link connector
5-1. HO2S-2 f: Radiator cooling fan relay No.3F: A/C compressor relay
6. Wheel speed sensor (VSS) g: Immobilizer indicator lightG: TCM (A/T model)
7. Battery h: Ignition coil assembly (with ignitor) H: BCM (included in junction block assembly)
8. CMP sensor i: Main relayI: Immobilizer coil antenna
9. MAP sensor j: Oil control valveJ: EPS control module
10. CKP sensor k: Radiator cooling fan relay No.2K: A/C refrigerant pressure sensor
11. Fuel level sensor l: Radiator cooling fan relay No.1L: Diagnosis connector (Hong Kong model)
12. Knock sensor m: Starting motor control relay
13. Electric load current sensor
14. APP sensor
Page 75 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-25
Step 2: DTC / Freeze Frame Data Check, Record and
Clearance
First, check DTC (including pending DTC), referring to
“DTC Check”. If DTC is indicated, print it and freeze
frame data or write them down and then clear them by
referring to “DTC Clearance”. DTC indicates malfunction
that occurred in the system but does not indicate
whether it exists now or it occurred in the past and the
normal condition has been restored now. To check which
case applies, check the sy mptom in question according
to Step 5 and recheck DTC according to Step 6 and 7.
Attempt to diagnose a trouble based on DTC in this step
only or failure to clear the DTC in this step will lead to
incorrect diagnosis, trouble diagnosis of a normal circuit
or difficulty in troubleshooting.
Step 3 and 4: Visual Inspection
As a preliminary step, be sure to perform visual check of
the items that support proper function of the engine
referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Step 5: Trouble Symptom Confirmation
Based on information obtained in “Step 1: Customer
Complaint Analysis: ” and “Step 2: DTC / Freeze Frame
Data Check, Record and Clearance: ”, confirm trouble
symptoms. Also, reconfirm DTC according to “DTC
Confirmation Procedure” described in each DTC diag.
flow.
Step 6 and 7: Rechecking and Record of DTC /
Freeze Frame Data
Refer to “DTC Check” for checking procedure.
Step 8: Engine Basic Inspection and Engine
Symptom Diagnosis
Perform basic engine check according to “Engine Basic
Inspection” first. When the end of the flow has been
reached, check the parts of the system suspected as a
possible cause referring to “Engine Symptom Diagnosis”
and based on symptoms appearing on the vehicle
(symptoms obtained through steps of customer
complaint analysis, trouble symptom confirmation and/or
basic engine check) and repair or replace faulty parts, if
any.
Step 9: Troubleshooting for DTC (See each DTC
Diag. Flow)
Based on the DTC indicated in Step 6 or 7 and referring
to the applicable DTC diag. flow, locate the cause of the
trouble, namely in a sensor, switch, wire harness,
connector, actuator, ECM or other part and repair or
replace faulty parts. Step 10: Intermittent Problems Check
Check parts where an intermit
tent trouble is easy to
occur (e.g., wire harness, connector, etc.), referring to
“Intermittent and Poor Connec tion Inspection in Section
00” and related circuit of DTC recorded in Step 2.
Step 11: Final Confirmation Test
Confirm that the problem symptom has gone and the
engine is free from any abnormal conditions. If what has
been repaired is re lated to the DTC, clear the DTC once,
perform DTC confirmation procedure and confirm that no
DTC is indicated.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) CheckS7RS0B1104002
1) Turn ON ignition switch (with engine at stop) and check that MIL (1) lights.
If MIL does not light up (or MIL dims) but engine can
be starting, go to “MIL Does Not Come ON with
Ignition Switch ON and Engine Stop (but Engine Can
Be Started)” for troubleshooting.
If MIL does not light with ignition switch ON and
engine does not start though it is cranked up, go to
“ECM Power and Ground Circuit Check”.
2) Start engine and check that MIL turns OFF. If MIL remains ON and no DTC is stored in ECM, go
to “Malfunction Indicator Lamp Remains ON after
Engine Starts” for troubleshooting.
1
I4RS0A110012-01
Page 76 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-26 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
DTC CheckS7RS0B1104003
NOTE
• There are two types of OBD system depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-
Board Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
• The MIL is turned on when the ECM and/or TCM detect malfunction(s). Each ECM and
TCM stores diagnostic information as the
diagnostic trouble code (DTC) in its
memory and outputs th e DTC to the scan
tool.
Therefore, check both of the ECM and TCM
for any DTC with the SUZUKI scan tool
because the DTC stored in ECM and TCM
is not read and displayed at a time.
However, each of the ECM and TCM needs
not to be checked with the generic scan
tool because the DTC stored in ECM and
TCM is read and displayed at a time.
Using Scan Tool
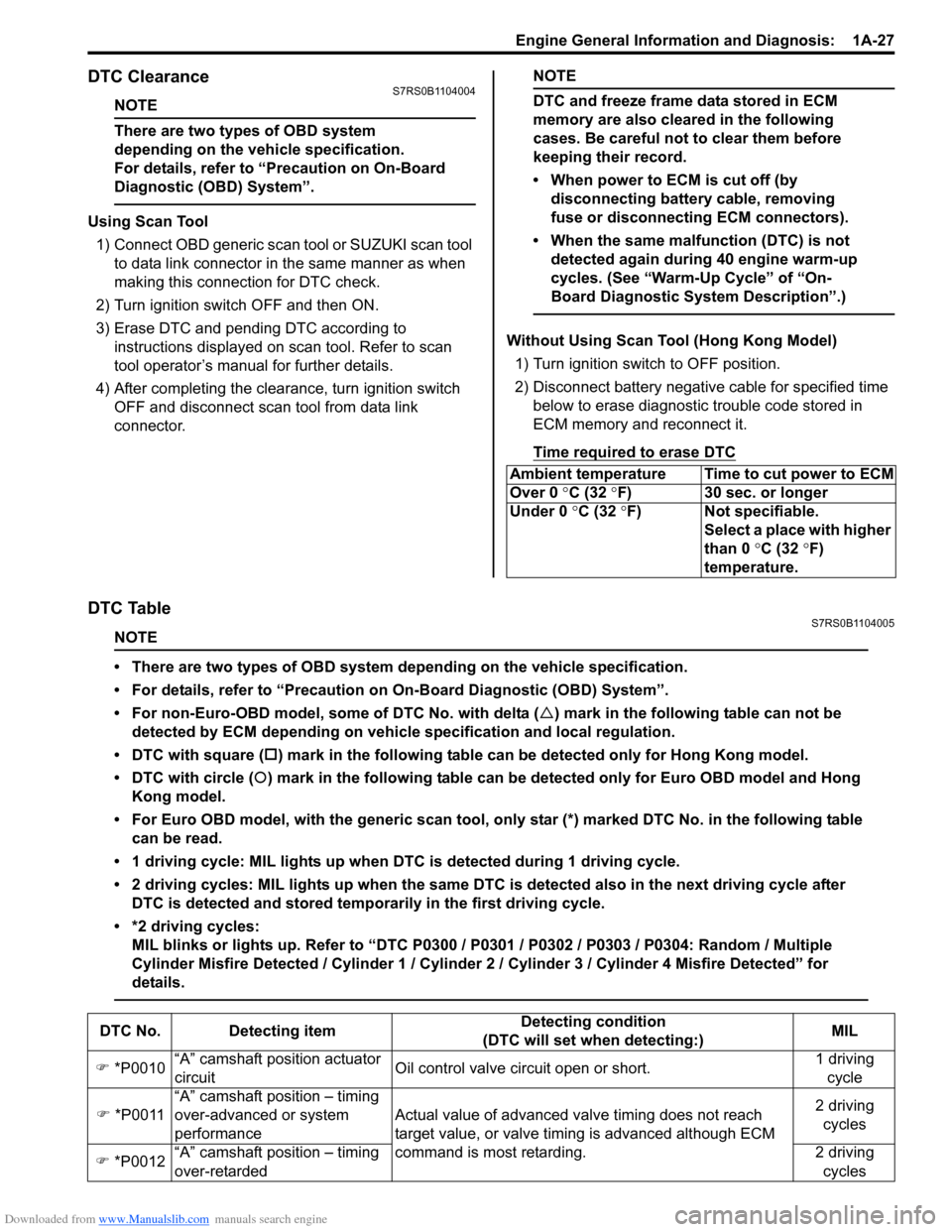
1) Prepare OBD generic scan tool or SUZUKI scan tool.
2) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect it to DLC (1) located on underside of instrument panel at
driver’s seat side.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
3) Turn ignition switch ON and confirm that MIL lights.
4) Read DTC, pending DTC and freeze frame data according to instructions displayed on scan tool and
print them or write them down. Refer to scan tool
operator’s manual for further details.
If communication between scan tool and ECM is not
possible, check if scan tool is communicable by
connecting it to ECM in another vehicle. If
communication is possible in this case, scan tool is
in good condition. Then check data link connector
and serial data line (circuit) in the vehicle with which
communication was not possible. If connector and
circuit are OK, check that power supply and ground
circuits of ECM and DLC are in good condition
referring to “ECM Power and Ground Circuit Check”. 5) After completing the check,
turn ignition switch OFF
and disconnect scan tool from data link connector.
Without Using Scan Tool (Hong Kong Model) 1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Using service wire, ground diagnosis switch terminal (1) of diagnosis connector (2).
3) Turn ON ignition switch and check DTC displayed on
odometer (3) of combination meter.
When more than 2 DTCs are stored in memory,
blinking for each DTC star ts with the smallest DTC
number in increasing order. Also, DTC is indicated
repeatedly until the ignition switch is turned OFF or
disconnect service wire.
NOTE
When no DTC is detected, display on
odometer of combinatio n meter is “0000”.
4) After completing the check, turn ignition switch to
OFF position and disconnect service wire from
diagnosis connector.
(A)
1
I4RS0B110026-01
21
3
I5RS0C110009-01
Page 77 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-27
DTC ClearanceS7RS0B1104004
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
Using Scan Tool1) Connect OBD generic scan to ol or SUZUKI scan tool
to data link connector in the same manner as when
making this connection for DTC check.
2) Turn ignition switch OFF and then ON.
3) Erase DTC and pending DTC according to instructions displayed on scan tool. Refer to scan
tool operator’s manual for further details.
4) After completing the clear ance, turn ignition switch
OFF and disconnect scan tool from data link
connector.
NOTE
DTC and freeze frame data stored in ECM
memory are also cleared in the following
cases. Be careful not to clear them before
keeping their record.
• When power to ECM is cut off (by disconnecting battery cable, removing
fuse or disconnecting ECM connectors).
• When the same malfunction (DTC) is not detected again during 40 engine warm-up
cycles. (See “Warm-Up Cycle” of “On-
Board Diagnostic System Description”.)
Without Using Scan Tool (Hong Kong Model)
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Disconnect battery negative cable for specified time below to erase diagnostic trouble code stored in
ECM memory and reconnect it.
Time required to erase DTC
DTC TableS7RS0B1104005
NOTE
• There are two types of OBD system depending on the vehicle specification.
• For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
• For non-Euro-OBD model, some of DTC No. with delta ( �U) mark in the following table can not be
detected by ECM depending on vehicl e specification and local regulation.
• DTC with square ( �†) mark in the following table can be detected only for Hong Kong model.
• DTC with circle ( �{) mark in the following table can be detected only for Euro OBD model and Hong
Kong model.
• For Euro OBD model, with the generic scan tool, onl y star (*) marked DTC No. in the following table
can be read.
• 1 driving cycle: MIL lights up when DTC is detected during 1 driving cycle.
• 2 driving cycles: MIL lights up when the same DTC is detected also in the next driving cycle after DTC is detected and stored temporarily in the first driving cycle.
• *2 driving cycles: MIL blinks or lights up. Refer to “DTC P0300 / P0301 / P0302 / P0303 / P0304: Random / Multiple
Cylinder Misfire Detected / Cylinder 1 / Cylinder 2 / Cylinder 3 / Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected” for
details.
Ambient temperature Time to cut power to ECM
Over 0 °C (32 ° F) 30 sec. or longer
Under 0 °C (32 °F) Not specifiable.
Select a place with higher
than 0 °C (32 °F)
temperature.
DTC No. Detecting item Detecting condition
(DTC will set when detecting:) MIL
�) *P0010 “A” camshaft position actuator
circuit Oil control valve circuit open or short. 1 driving
cycle
�) *P0011 “A” camshaft position – timing
over-advanced or system
performance Actual value of advanced va
lve timing does not reach
target value, or valve timi ng is advanced although ECM
command is most retarding. 2 driving
cycles
�) *P0012 “A” camshaft position – timing
over-retarded 2 driving
cycles
Page 83 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-33
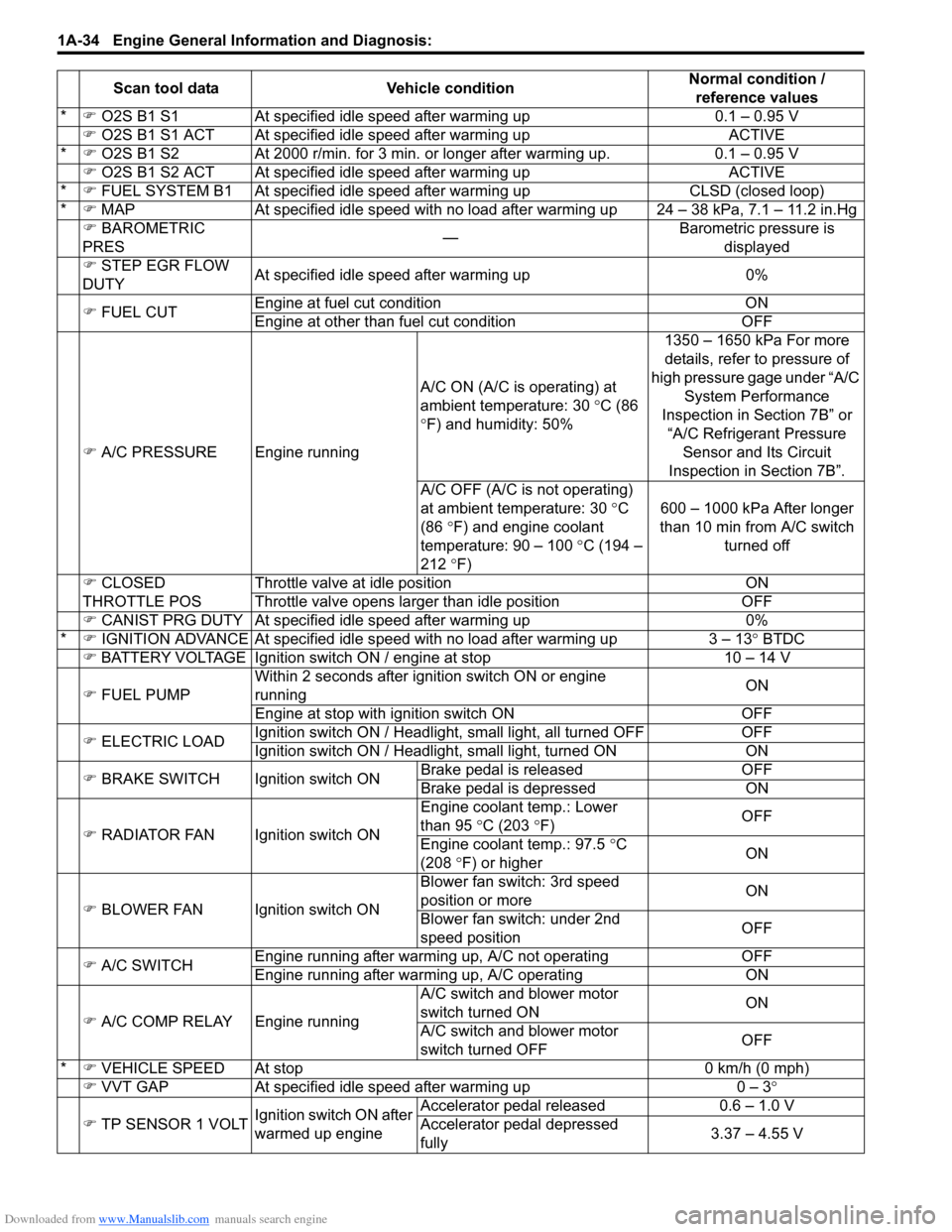
Scan Tool DataS7RS0B1104007
As the data values are standard values estimated on the basis of values obtained from the normally operating vehicles
by using a scan tool, use them as re ference values. Even when the vehicle is in good condition, there may be cases
where the checked value does not fall within each specified data range. Therefore, judgment as abnormal should not
be made by checking with these data alone.
Also, conditions that can be checked by the scan tool are those detected by ECM and output from ECM as commands
and there may be cases where the engine or actuator is not operating (in the condition) as indicated by the scan tool.
Be sure to use the timing light to check the ignition timing.
NOTE
• There are two types of OBD system depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
• With the generic scan tool, only star (*) marked data in the following table can be read.
• When checking the data with the engine running at idle or racing, be sure to shift M/T gear to the neutral position and A/T gear to the “Park” position and pull the parking brake fully. Also, if nothing
or “no load” is indicated, turn O FF A/C (if equipped with A/C), all electric loads, P/S and all the other
necessary switches.
�) P2122 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“D” (main)
circuit low input
• ECM turns off throttle actuator control relay and throttle valve is fixed at the specified opening from
its completely closed position (default opening).
For details, refer to “Description of Electric
Throttle Body System”.
• ECM controls fuel cut at specified engine speed.
• ECM stops air/fuel ratio control.
�)
P2123 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“D” (main)
circuit high input
�) P2127 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“E” (sub)
circuit low input
�) P2128 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“E” (sub)
circuit high input
�) P2135 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“A”/“B”
(main) / (sub) voltage correction
�) P2138 Throttle pedal position sensor/switch “D”/“E”
(main) / (sub) voltage correlation
�) P2227 Barometric pressure sensor performance problem ECM controls actuators assuming that barometric
pressure is 101.33 kPa (762 mmHg).
DTC No. Detected item Fail-safe operation
Scan tool data
Vehicle condition Normal condition /
reference values
* �) COOLANT TEMP At specified idle speed after warming up 80 – 100 °C, 176 – 212 °F
* �) INTAKE AIR TEMP. At specifie d idle speed after warming up –5
°C (23 °F) + environmental
temp. to 40 °C (104 °F) +
environmental temp.
* �) ENGINE SPEED It idling with no load after warming upDesired idle speed ± 50 rpm
�) INJ PULSE WIDTH At specified idle speed with no load after warming up
2.0 – 4.0 msec.
At 2500 r/min. with no load after warming up 2.0 – 3.6 msec.
�) DESIRED IDLE It idling with radiator cooling fan stopped and all electrical
parts turned OFF after warming up, M/T at neutral 700 rpm
* �) SHORT FT B1 At specified idle speed after warming up –20 – +20%
* �) LONG FT B1 At specified idle speed after warming up –20 – +20%
�) TOTAL FUEL TRIM
B1 At specified idle speed after warming up
–35 – +35%
* �) MAF At specified idle speed wit
h no load after warming up 1.0 – 4.0 g/s 0.14 – 0.52 lb/
min.
At 2500 r/min. with no load after warming up 4.0 – 12.0 g/s 0.53 – 1.58 lb/
min.
* �) CALC LOAD At specified idle speed with no load after warming up
18 – 28%
At 2500 r/min. with no load after warming up 13 – 23%
* �)
THROTTLE
POSITION Ignition switch ON /
warmed up engine
stoppedAccelerator pedal released
0 – 5%
Accelerator pedal depressed
fully 90 – 100%
Page 84 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-34 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
*�) O2S B1 S1 At specified idle speed after warming up 0.1 – 0.95 V
�) O2S B1 S1 ACT At specified id le speed after warming up ACTIVE
* �) O2S B1 S2 At 2000 r/min. for 3 min. or longer after warming up. 0.1 – 0.95 V
�) O2S B1 S2 ACT At specified id le speed after warming up ACTIVE
* �) FUEL SYSTEM B1 At specif ied idle speed after warming up CLSD (closed loop)
* �) MAP At specified idle speed with no load after warming up 24 – 38 kPa, 7.1 – 11.2 in.Hg
�) BAROMETRIC
PRES —Barometric pressure is
displayed
�) STEP EGR FLOW
DUTY At specified idle speed after warming up 0%
�) FUEL CUT Engine at fuel cut condition ON
Engine at other than fuel cut condition OFF
�) A/C PRESSURE Engine running A/C ON (A/C is operating) at
ambient temperature: 30
°C (86
° F) and humidity: 50% 1350 – 1650 kPa For more
details, refer to pressure of
high pressure gage under “A/C System Performance
Inspection in Section 7B” or “A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor and Its Circuit
Inspection in Section 7B”.
A/C OFF (A/C is not operating)
at ambient temperature: 30 ° C
(86 °F) and engine coolant
temperature: 90 – 100 °C (194 –
212 °F) 600 – 1000 kPa After longer
than 10 min from A/C switch turned off
�) CLOSED
THROTTLE POS Throttle valve at idle position ON
Throttle valve opens larger than idle position OFF
�) CANIST PRG DUTY At specified idle speed after warming up 0%
* �) IGNITION ADVANCE At specified idle s peed with no load after warming up 3 – 13 ° BTDC
�) BATTERY VOLTAGE Ignition switch ON / engine at stop 10 – 14 V
�) FUEL PUMP Within 2 seconds after ignition switch ON or engine
running
ON
Engine at stop with ignition switch ON OFF
�) ELECTRIC LOAD Ignition switch ON / Headligh
t, small light, all turned OFF OFF
Ignition switch ON / Headli ght, small light, turned ON ON
�) BRAKE SWITCH Igni tion switch ONBrake pedal is released OFF
Brake pedal is depressed ON
�) RADIATOR FAN Ignition switch ON Engin
e coolant temp.: Lower
than 95 °C (203 °F) OFF
Engine coolant temp.: 97.5 °C
(208 °F) or higher ON
�) BLOWER FAN Ignition switch ON Blower fan switch: 3rd speed
position or more
ON
Blower fan switch: under 2nd
speed position OFF
�) A/C SWITCH Engine running after warming up, A/C not operating
OFF
Engine running after warming up, A/C operating ON
�) A/C COMP RELAY Engine running A/C switch and blower motor
switch turned ON
ON
A/C switch and blower motor
switch turned OFF OFF
* �) VEHICLE SPEED At stop 0 km/h (0 mph)
�) VVT GAP At specified idle speed after warming up 0 – 3°
�) TP SENSOR 1 VOLT Ignition switch ON after
warmed up engine Accelerator pedal released
0.6 – 1.0 V
Accelerator pedal depressed
fully 3.37 – 4.55 V
Scan tool data
Vehicle condition Normal condition /
reference values
Page 86 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-36 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
O2S B1 S1 ACT (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR-1,
ACTIVE / INACTIVE)
This parameter indicates activation condition of HO2S-1.
ACTIVE: Activating
INACTIVE: warming up or at stop
O2S SENSOR B1 S2 (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR-2,
V)
It indicates output voltage of HO2S-2 installed on
exhaust pipe (post-catalyst). It is used to detect catalyst
deterioration.
O2S B1 S2 ACT (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR-2,
ACTIVE / INACTIVE)
This parameter indicates acti vation condition of HO2S-2.
ACTIVE: Activating
INACTIVE: warming up or at stop
FUEL SYSTEM (FUEL SYSTEM STATUS)
Air/fuel ratio feedback loop status displayed as one of
the followings.
OPEN: Open-loop has not yet satisfied conditions to go
closed loop.
CLOSED: Closed-loop using oxygen sensor(s) as
feedback for fuel control.
OPEN-DRIVE COND: Open-loop due to driving
conditions (Power enrichment, etc.).
OPEN SYS FAULT: Open-loop due to detected system
fault.
MAP (MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE, in.Hg,
kPa)
This value indicates how much correction is necessary
to keep the air/fuel mixture stoichiometrical.
It is detected by manifold absolute pressure sensor.
BAROMETRIC PRESS (kPa, in.Hg)
This parameter represents a measurement of barometric
air pressure and is used for al titude correction of the fuel
injection quantity and IAC valve control.
STEP EGR FLOW DUTY (%)
This parameter indicates opening rate of EGR valve
which controls the amount of EGR flow.
FUEL CUT (ON/OFF)
ON: Fuel being cut (output signal to injector is stopped)
OFF: Fuel not being cut
A/C PRESSURE (A/C REFRIGERANT ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE, kPa)
This parameter indicates A/C refrigerant absolute
pressure calculated by ECM.
CLOSED THROTTLE PO S (CLOSED THROTTLE
POSITION, ON/OFF)
This parameter reads ON wh en throttle valve is fully
closed, or OFF when it is not fully closed. CANIST PRG DUTY (EVAP CANISTER PURGE FLOW
DUTY, %)
This parameter indicates valve ON (valve open) time
rate within a certain set cycle of EVAP canister purge
valve which controls the amount of EVAP purge.
IGNITION ADVANCE (IGNITION TIMING ADVANCE
FOR NO.1 CYLINDER,
°)
Ignition timing of No.1 cylinder is commanded by ECM.
The actual ignition timing should be checked by using
the timing light.
BATTERY VOLTAGE (V)
This parameter indicates battery positive voltage
inputted from main relay to ECM.
FUEL PUMP (ON/OFF)
ON is displayed when ECM activates the fuel pump via
the fuel pump relay switch.
ELECTRIC LOAD (ON/OFF)
ON: Headlight or small light ON signal inputted.
OFF: Above electric loads all turned OFF.
BRAKE SW (ON/OFF)
This parameter indicates the state of the brake switch.
RADIATOR COOLING FAN (RADIATOR COOLING
FAN CONTROL RELAY, ON/OFF)
ON: Command for radiator cooling fan control relay
operation being output.
OFF: Command for relay operation not being output.
BLOWER FAN (ON/OFF)
This parameter indicates the state of the blower fan
motor switch.
A/C SWITCH (ON/OFF)
ON: Command for A/C operatio n being output from ECM
to HVAC.
OFF: Command for A/C oper ation not being output.
A/C COMP RELAY (A/C COMPRESSOR RELAY, ON/
OFF)
This parameter indicates the state of the A/C switch.
VEHICLE SPEED (km/h, mph)
It is computed based on pulse signals from vehicle
speed sensor.
VVT GAP (TARGET-ACTUAL POSITION, °)
It is calculated using the formula: target valve timing
advance – actual valve timing advance.
TP SENSOR 1 VOLT (THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
(MAIN) OUTPUT VOLTAGE, V)
The TP sensor (main) reading provides throttle valve
opening information in the form of voltage.
Page 89 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-39
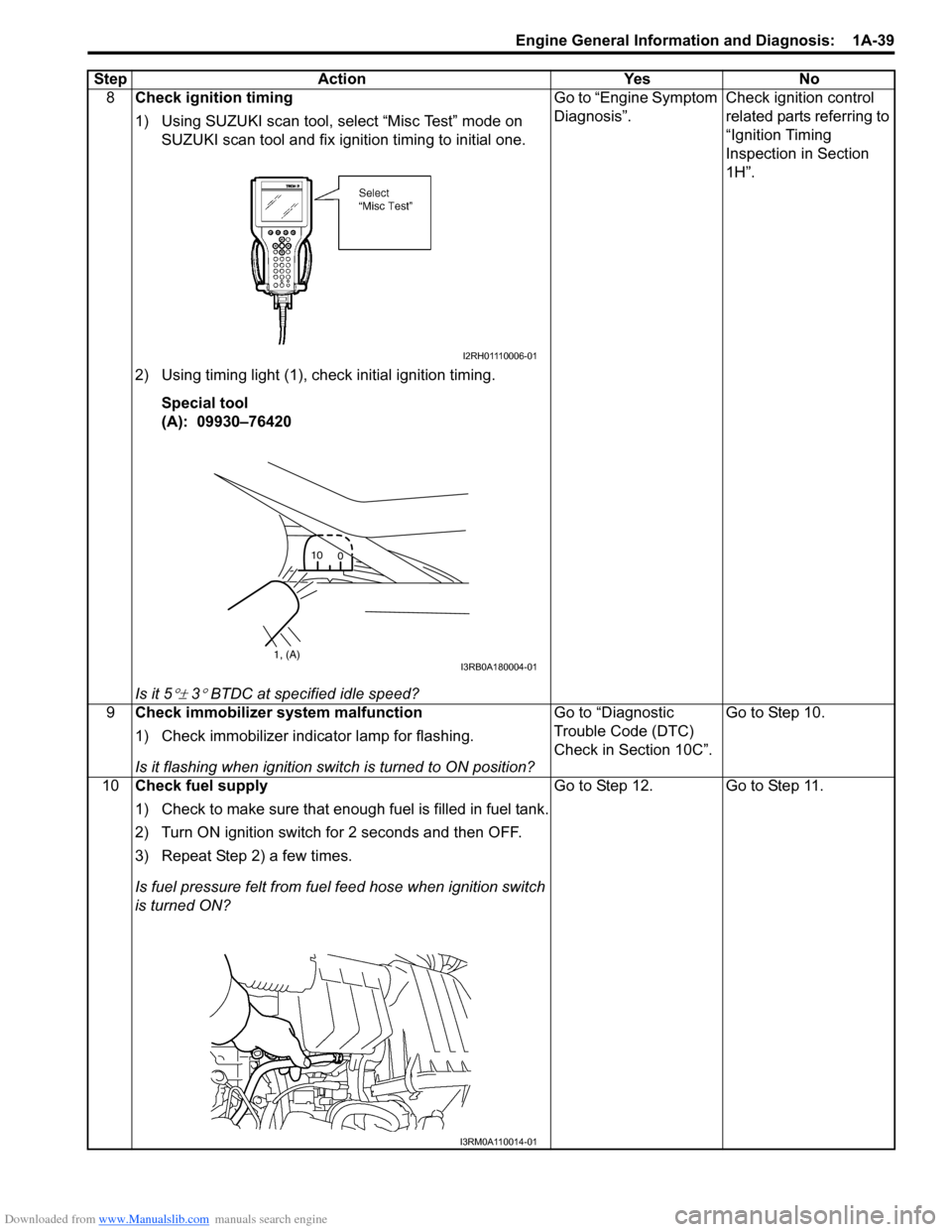
8Check ignition timing
1) Using SUZUKI scan tool, select “Misc Test” mode on
SUZUKI scan tool and fix ignition timing to initial one.
2) Using timing light (1), check initial ignition timing. Special tool
(A): 09930–76420
Is it 5
°± 3° BTDC at specif ied idle speed? Go to “Engine Symptom
Diagnosis”.
Check ignition control
related parts referring to
“Ignition Timing
Inspection in Section
1H”.
9 Check immobilizer system malfunction
1) Check immobilizer indica tor lamp for flashing.
Is it flashing when ignition switch is turned to ON position? Go to “Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC)
Check in Section 10C”.
Go to Step 10.
10 Check fuel supply
1) Check to make sure that enough fuel is filled in fuel tank.
2) Turn ON ignition switch for 2 seconds and then OFF.
3) Repeat Step 2) a few times.
Is fuel pressure felt from fuel feed hose when ignition switch
is turned ON? Go to Step 12. Go to Step 11.
Step Action Yes No
I2RH01110006-01
1, (A)
10
0I3RB0A180004-01
I3RM0A110014-01
Page 98 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-48 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
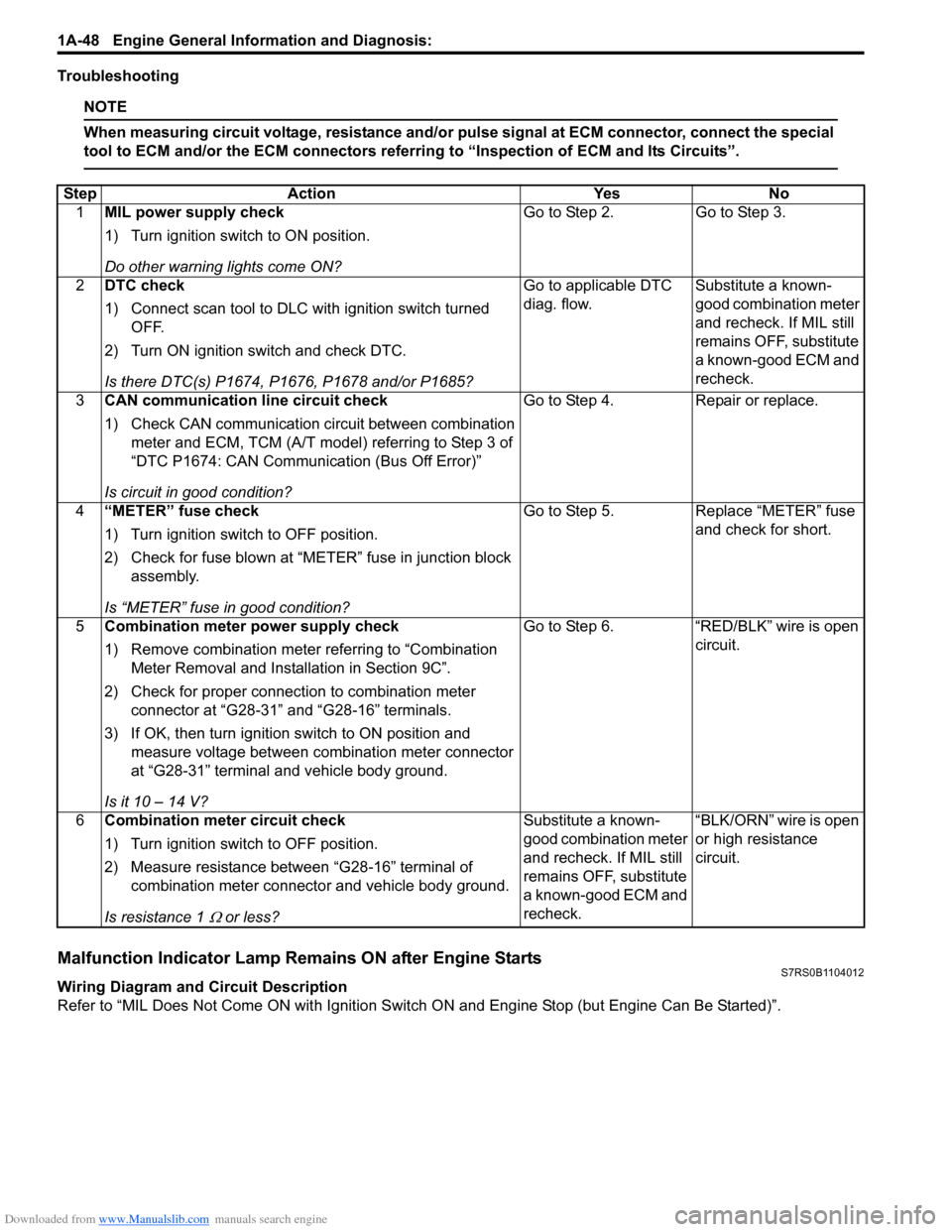
Troubleshooting
NOTE
When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the special
tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors referri ng to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp Remains ON after Engine StartsS7RS0B1104012
Wiring Diagram and Circuit Description
Refer to “MIL Does Not Come ON wit h Ignition Switch ON and Engine Stop (but Engine Can Be Started)”.
Step
Action YesNo
1 MIL power supply check
1) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
Do other warning lights come ON? Go to Step 2.
Go to Step 3.
2 DTC check
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned
OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and check DTC.
Is there DTC(s) P1674, P1676, P1678 and/or P1685? Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.
Substitute a known-
good combination meter
and recheck. If MIL still
remains OFF, substitute
a known-good ECM and
recheck.
3 CAN communication line circuit check
1) Check CAN communication circuit between combination
meter and ECM, TCM (A/T model) referring to Step 3 of
“DTC P1674: CAN Communication (Bus Off Error)”
Is circuit in good condition? Go to Step 4.
Repair or replace.
4 “METER” fuse check
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Check for fuse blown at “M ETER” fuse in junction block
assembly.
Is “METER” fuse in good condition? Go to Step 5.
Replace “METER” fuse
and check for short.
5 Combination meter power supply check
1) Remove combination meter referring to “Combination
Meter Removal and Installation in Section 9C”.
2) Check for proper connection to combination meter connector at “G28-31” and “G28-16” terminals.
3) If OK, then turn ignition switch to ON position and measure voltage between combination meter connector
at “G28-31” terminal and vehicle body ground.
Is it 10 – 14 V? Go to Step 6.
“RED/BLK” wire is open
circuit.
6 Combination meter circuit check
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Measure resistance between “G28-16” terminal of
combination meter connector and vehicle body ground.
Is resistance 1
Ω or less? Substitute a known-
good combination meter
and recheck. If MIL still
remains OFF, substitute
a known-good ECM and
recheck.
“BLK/ORN” wire is open
or high resistance
circuit.
Page 180 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-130 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
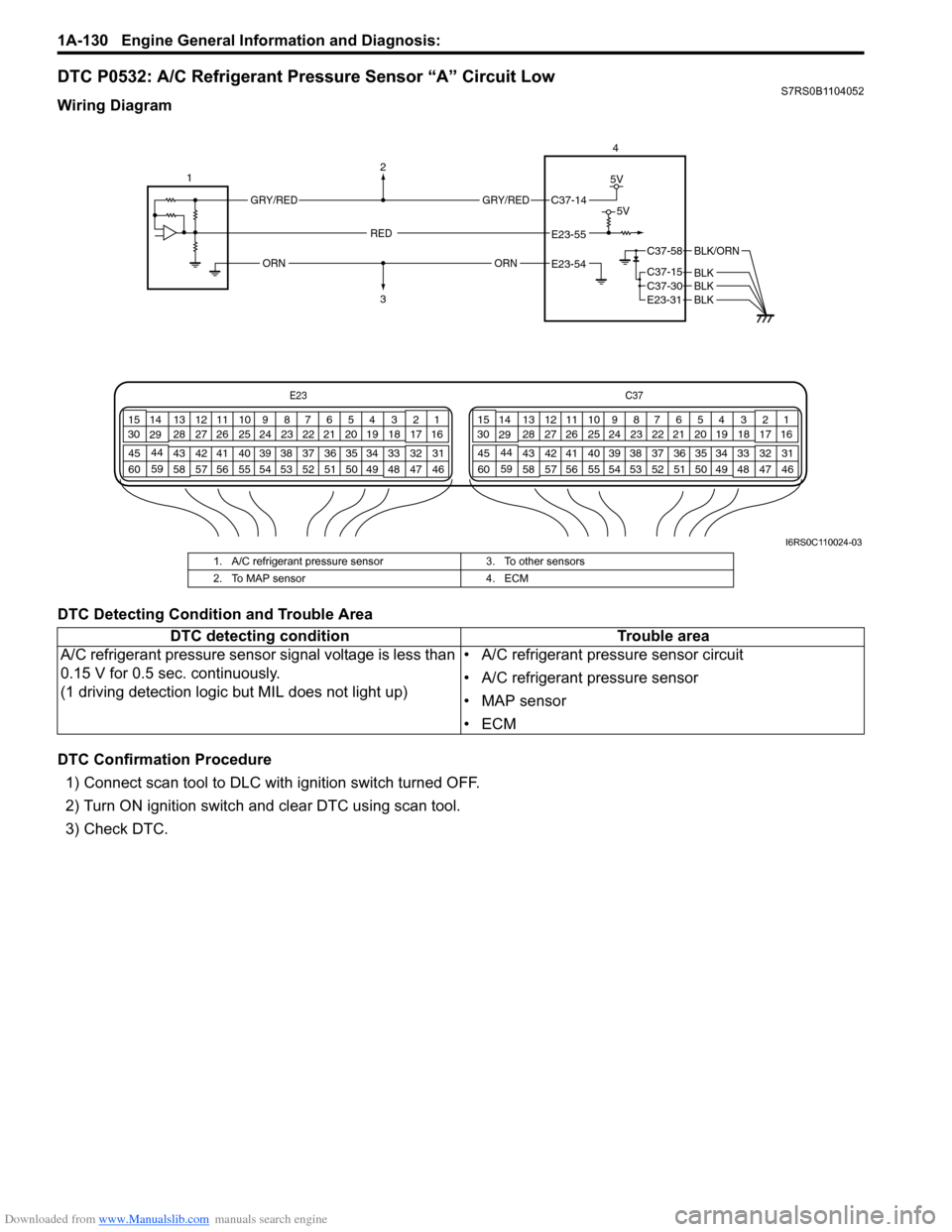
DTC P0532: A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor “A” Circuit LowS7RS0B1104052
Wiring Diagram
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
DTC Confirmation Procedure1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and clear DTC using scan tool.
3) Check DTC.
E23 C37
34
1819
567
1011
17
20
47 46
495051
2122
52 16
25 9
24
14
29
55
57 54 53
59
60 58 2
262728
15
30
56 4832 31
34353637
40
42 39 38
44
45 43 41 331
1213
238
34
1819
567
1011
17
20
47 46
495051
2122
52 16
25 9
24
14
29
55
57 54 53
59
60 58 2
262728
15
30
56 4832 31
34353637
40
42 39 38
44
45 43 41 331
1213
238
4
C37-58
C37-15 C37-30
BLK/ORN
BLKBLKE23-31 BLK
1
2
3
GRY/REDGRY/RED
ORNORN
5V
5VC37-14
E23-55
E23-54
RED
I6RS0C110024-03
1. A/C refrigerant pressure sensor
3. To other sensors
2. To MAP sensor 4. ECM
DTC detecting condition Trouble area
A/C refrigerant pressure sensor signal voltage is less than
0.15 V for 0.5 sec. continuously.
(1 driving detection logic but MIL does not light up) • A/C refrigerant pressure sensor circuit
• A/C refrigerant pressure sensor
• MAP sensor
•ECM