Pressure SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.G Service Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 255 of 1496
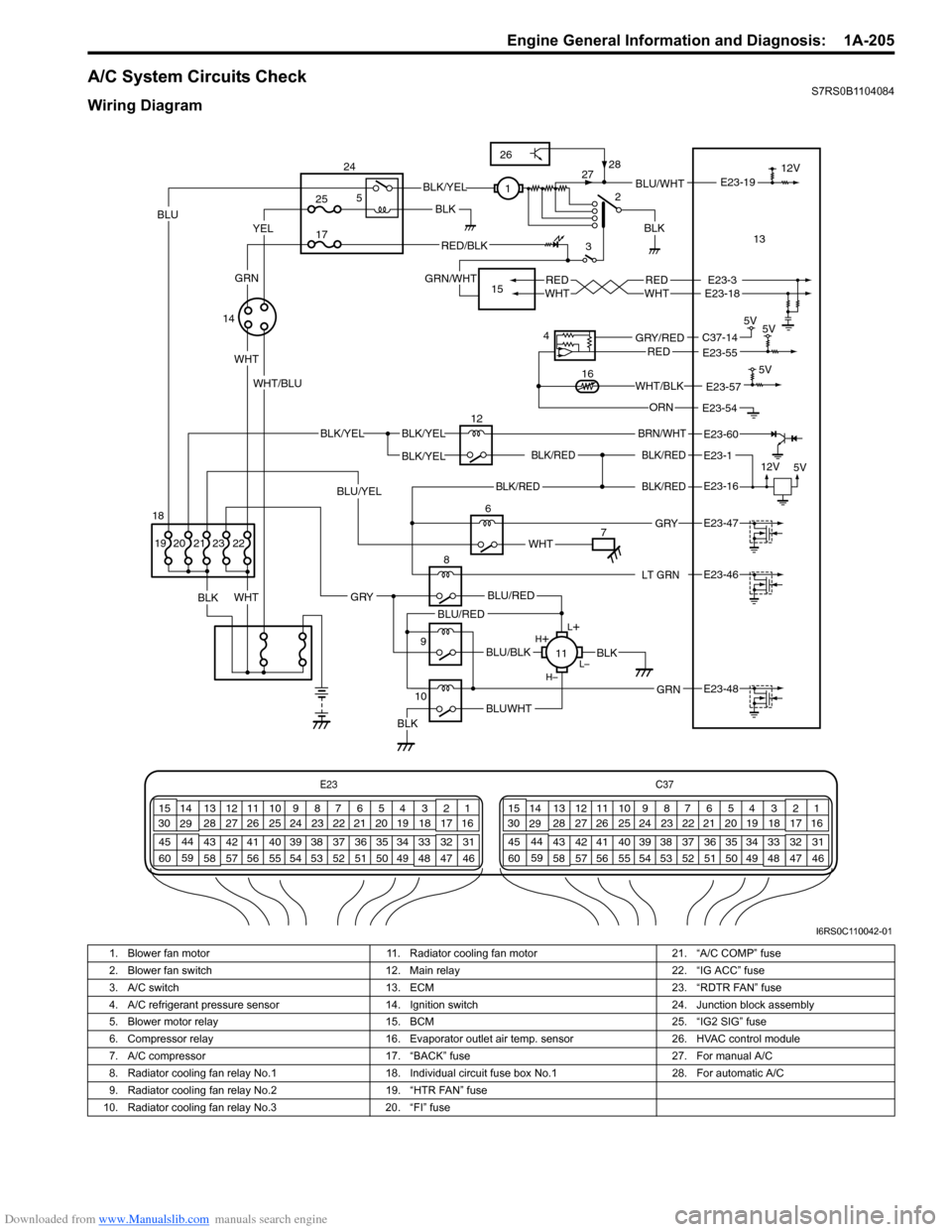
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-205
A/C System Circuits CheckS7RS0B1104084
Wiring Diagram
E23C37
34
1819
567
1011
17
20
47 46
495051
2122
52 16
25 9
24
14
29
55
57 54 53
59
60 58 2
262728
15
30
56 4832 31
34353637
40
42 39 38
44
45 43 41 331
1213
238
34
1819
567
1011
17
20
47 46
495051
2122
52 16
25 9
24
14
29
55
57 54 53
59
60 58 2
262728
15
30
56 4832 31
34353637
40
42 39 38
44
45 43 41 331
1213
238
BLK/REDBLK/RED
BLK/YELBLK/YEL
BLK/YEL
BRN/WHT
12V
5V
12
E23-1
E23-60
BLK/RED
LT GRN
BLK/REDE23-16
E23-46
L+
L–
H–
H
+
BLU/RED
BLK
BLUWHTBLK
BLU/BLK
BLU/RED
GRN
GRY
E23-48
8
11
2
3BLU/WHT
REDWHTREDWHTE23-3E23-18
E23-19
6
BLK
WHT
BLK 12V
E23-47 GRY
WHT
YELBLU
WHT
BLK/YEL
RED/BLK
GRN/WHT
WHT/BLU1
713
14
5V
5V
4
E23-55C37-14GRY/REDRED
E23-54ORN 5V
E23-57WHT/BLK16
9
10
25
17
5
24
15
22
BLU/YEL
23212019
GRN
BLK
18
26
28
27
I6RS0C110042-01
1. Blower fan motor 11. Radiator cooling fan motor 21. “A/C COMP” fuse
2. Blower fan switch 12. Main relay 22. “IG ACC” fuse
3. A/C switch 13. ECM 23. “RDTR FAN” fuse
4. A/C refrigerant pressure sensor 14. Ignition switch 24. Junction block assembly
5. Blower motor relay 15. BCM 25. “IG2 SIG” fuse
6. Compressor relay 16. Evaporator outlet air temp. sensor 26. HVAC control module
7. A/C compressor 17. “BACK” fuse 27. For manual A/C
8. Radiator cooling fan relay No.1 18. Individual circuit fuse box No.1 28. For automatic A/C
9. Radiator cooling fan relay No.2 19. “HTR FAN” fuse
10. Radiator cooling fan relay No.3 20. “FI” fuse
Page 257 of 1496
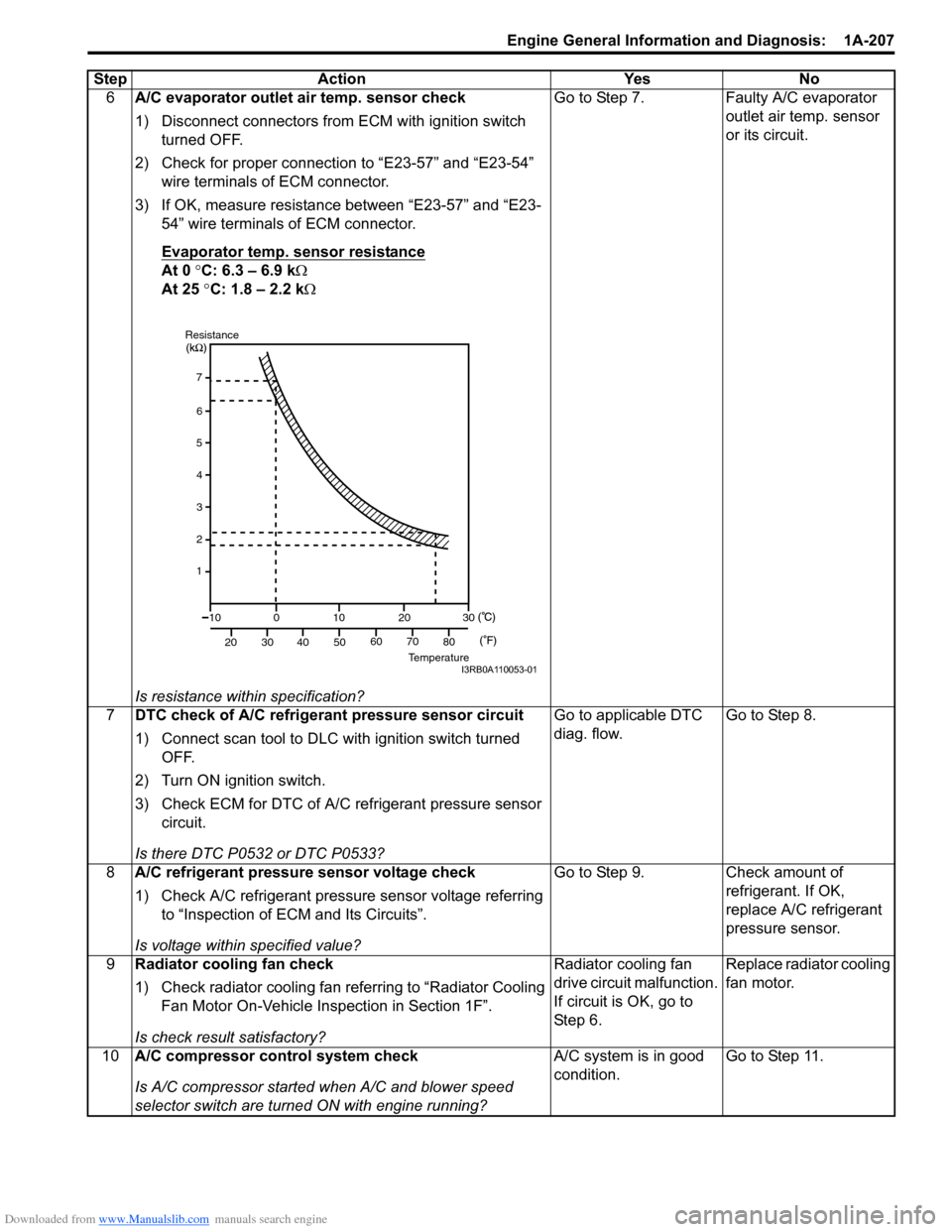
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-207
6A/C evaporator outlet air temp. sensor check
1) Disconnect connectors from ECM with ignition switch
turned OFF.
2) Check for proper connection to “E23-57” and “E23-54” wire terminals of ECM connector.
3) If OK, measure resistance between “E23-57” and “E23- 54” wire terminals of ECM connector.
Evaporator temp. sensor resistance
At 0 °C: 6.3 – 6.9 k Ω
At 25 °C: 1.8 – 2.2 k Ω
Is resistance within specification? Go to Step 7. Faulty A/C evaporator
outlet air temp. sensor
or its circuit.
7 DTC check of A/C refrigerant pressure sensor circuit
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned
OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch.
3) Check ECM for DTC of A/C refrigerant pressure sensor circuit.
Is there DTC P0532 or DTC P0533? Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.
Go to Step 8.
8 A/C refrigerant pressure sensor voltage check
1) Check A/C refrigerant pressure sensor voltage referring
to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
Is voltage within specified value? Go to Step 9. Check amount of
refrigerant. If OK,
replace A/C refrigerant
pressure sensor.
9 Radiator cooling fan check
1) Check radiator cooling fan referring to “Radiator Cooling
Fan Motor On-Vehicle Inspection in Section 1F”.
Is check result satisfactory? Radiator cooling fan
drive circuit malfunction.
If circuit is OK, go to
St ep 6 .
Replace radiator cooling
fan motor.
10 A/C compressor control system check
Is A/C compressor started when A/C and blower speed
selector switch are turned ON with engine running? A/C system is in good
condition.
Go to Step 11.
Step Action Yes No
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
10
20 30
40 50
0
10
2030
60 70 80
ResistanceTemperatureI3RB0A110053-01
Page 267 of 1496
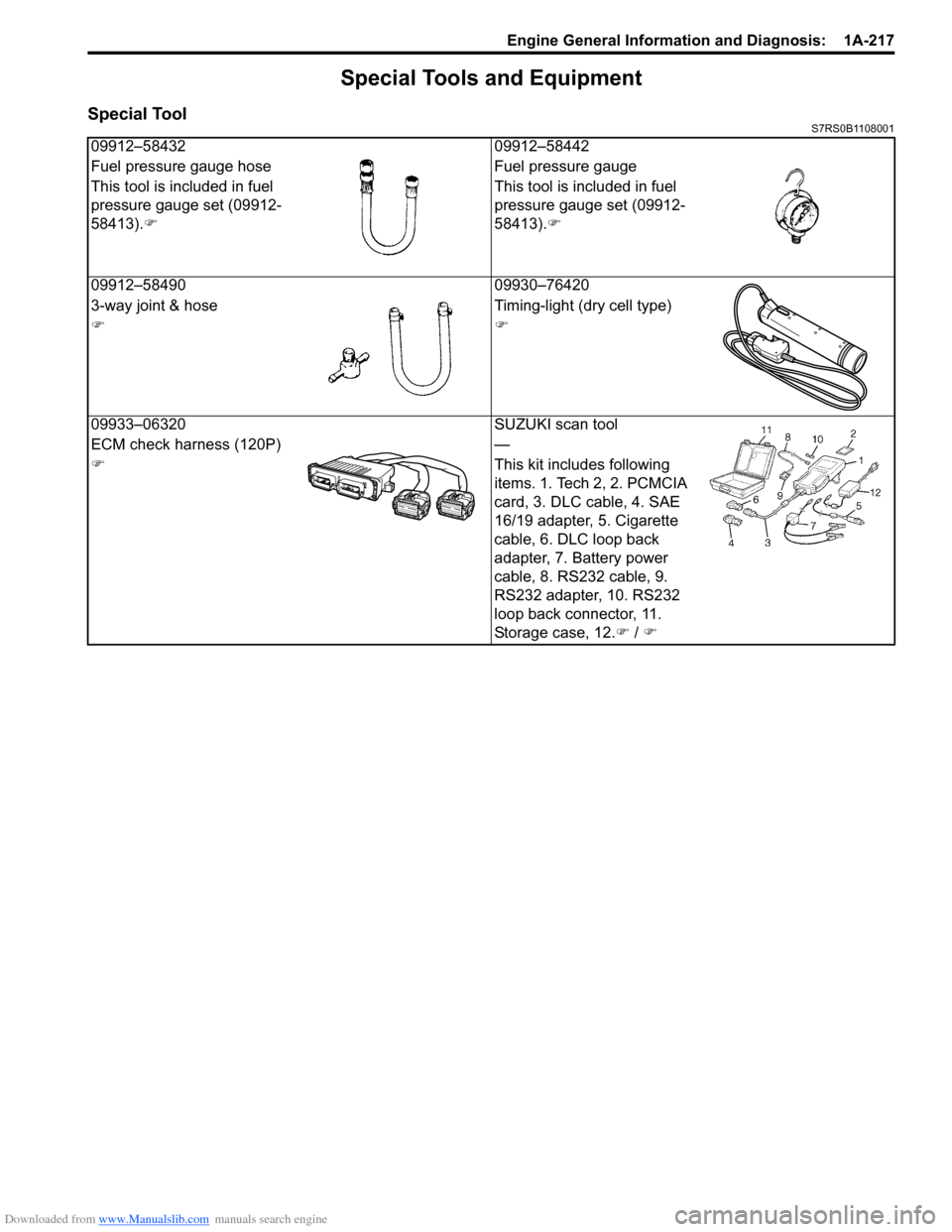
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-217
Special Tools and Equipment
Special ToolS7RS0B1108001
09912–5843209912–58442
Fuel pressure gauge hose Fuel pressure gauge
This tool is included in fuel
pressure gauge set (09912-
58413). �) This tool is included in fuel
pressure gauge set (09912-
58413).
�)
09912–58490 09930–76420
3-way joint & hose Timing-light (dry cell type)
�)�)
09933–06320 SUZUKI scan tool
ECM check harness (120P) —
�) This kit includes following
items. 1. Tech 2, 2. PCMCIA
card, 3. DLC cable, 4. SAE
16/19 adapter, 5. Cigarette
cable, 6. DLC loop back
adapter, 7. Battery power
cable, 8. RS232 cable, 9.
RS232 adapter, 10. RS232
loop back connector, 11.
Storage case, 12.�) / �)
Page 274 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1C-2 Engine Electrical Devices:
MAP Sensor InspectionS7RS0B1306002
1) Remove air cleaner assembly.
2) Disconnect connector from MAP sensor.
3) Remove MAP sensor.
4) Arrange 3 new 1.5 V batteries (2) in series (check that total voltage is 4.5 – 5.0 V) and connect its
positive terminal to “Vin ” terminal of sensor and
negative terminal to “Ground” terminal. Then check
voltage between “Vout” and “Ground”. Also, check if
voltage reduces when vacuum is applied up to 400
mmHg by using vacuum pump (3).
If check result is not satisfactory, replace MAP
sensor (1).
Output voltage (When input voltage is 4.5 – 5.5 V,
ambient temp. 20 – 30 °C, 68 – 86 °F)
5) Install MAP sensor securely.
6) Connect MAP sensor connector securely.
7) Install air cleaner assembly.
Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection
S7RS0B1306003
WARNING!
Never touch throttle valve with finger while
ignition switch is turned ON and accelerator
pedal is depressed. Otherwise, injury may
result by pinching the finger between throttle
valve and throttle body housing.
CAUTION!
• Do not disassemble electric throttle body assembly.
• Do not expose electric throttle body assembly to excessive shock like a
dropping it. If electric throttle body
assembly has been exposed to excessive
shock, it should be replaced.
• Be careful not to accurate a foreign material (like dust and/ or metallic particle)
to the throttle body housing and/or throttle
valve.
Otherwise, the throttle body assembly is
breaking down by throttle valve accretion.
• Do not apply excessive moving force to throttle valve for thro ttle valve operation
check and/or TP sensor performance
check.
Otherwise, the throttle body assembly is
breaking down by damaging the internal
resinous gear of throttle valve actuator.
NOTE
After replacing electric throttle body
assembly, perform calibration of electric
throttle body assembly referring to “Electric
Throttle Body System Calibration”.
Throttle Valve Visual Check
1) Remove air cleaner outlet hose.
2) Check that there isn’t any foreign matter caught between throttle valve and throttle body housing. If
there is, take it out after removing throttle body
referring to “Electric Th rottle Body Assembly
Removal and Installation in Section 1D” and clean
inside of throttle body thoroughly.
Altitude (Reference) Barometric pressure
Output
voltage
(ft) (m) (mmHg) (kPa) (V)
0 – 2000 0 – 610 760 – 707 100 – 94 3.3 – 4.3 2001 – 5000 611 –
1524 Under 707
over 634 94 – 85 3.0 – 4.1
5001 – 8000 1525 –
2438 Under 634
over 567 85 – 76 2.7 – 3.7
8001 – 10000 2439 –
3048 Under 567
over 526 76 – 70 2.5 – 3.3
I3RM0A130005-01
Page 278 of 1496
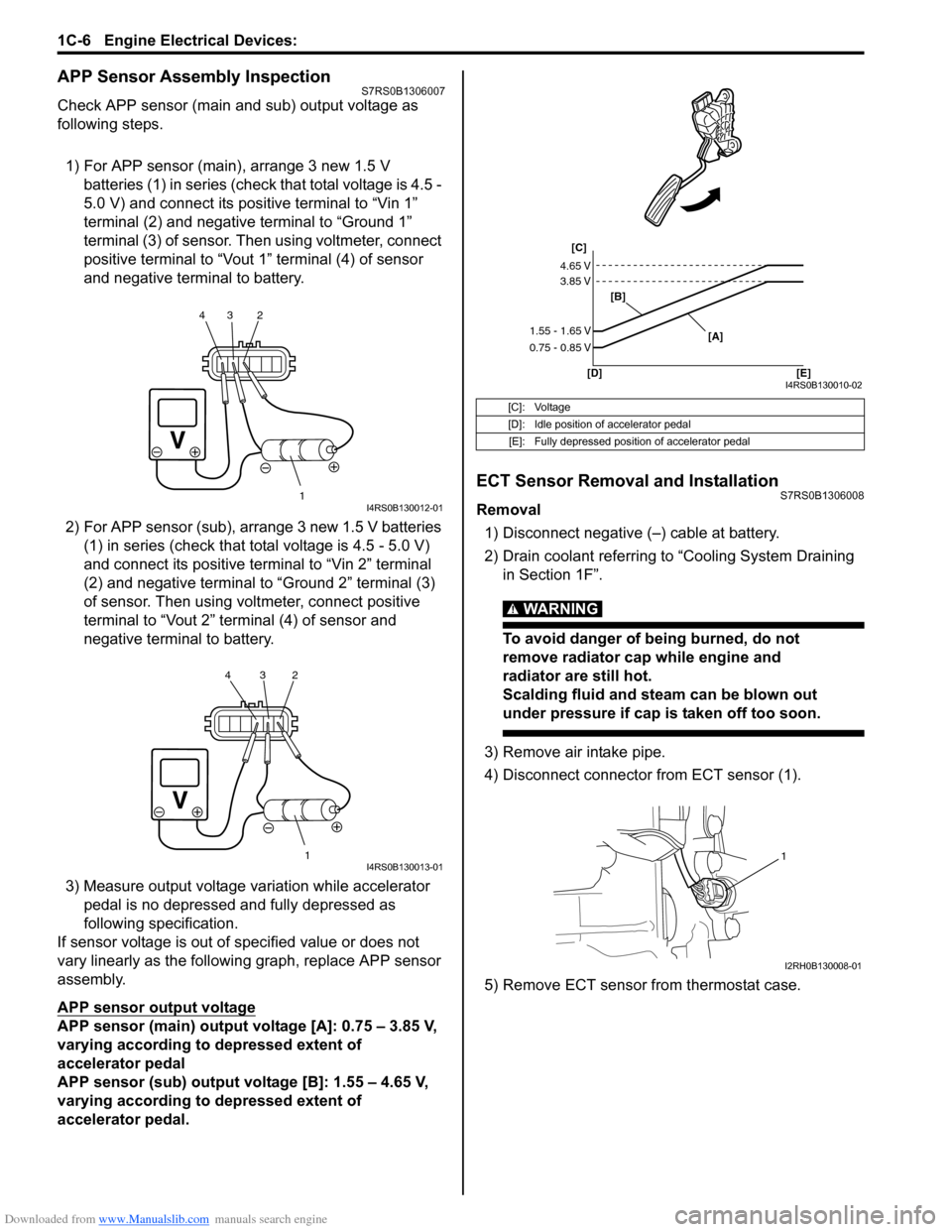
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1C-6 Engine Electrical Devices:
APP Sensor Assembly InspectionS7RS0B1306007
Check APP sensor (main and sub) output voltage as
following steps.
1) For APP sensor (main) , arrange 3 new 1.5 V
batteries (1) in series (check that total voltage is 4.5 -
5.0 V) and connect its positive terminal to “Vin 1”
terminal (2) and negative terminal to “Ground 1”
terminal (3) of sensor. Then using voltmeter, connect
positive terminal to “Vout 1” terminal (4) of sensor
and negative terminal to battery.
2) For APP sensor (s ub), arrange 3 new 1.5 V batteries
(1) in series (check that total voltage is 4.5 - 5.0 V)
and connect its positive terminal to “Vin 2” terminal
(2) and negative terminal to “Ground 2” terminal (3)
of sensor. Then using volt meter, connect positive
terminal to “Vout 2” terminal (4) of sensor and
negative termin al to battery.
3) Measure output voltage variation while accelerator pedal is no depressed and fully depressed as
following specification.
If sensor voltage is out of specified value or does not
vary linearly as the followin g graph, replace APP sensor
assembly.
APP sensor output voltage
APP sensor (main) output voltage [A]: 0.75 – 3.85 V,
varying according to depressed extent of
accelerator pedal
APP sensor (sub) output voltage [B]: 1.55 – 4.65 V,
varying according to depressed extent of
accelerator pedal.
ECT Sensor Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1306008
Removal
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Drain coolant referring to “Cooling System Draining in Section 1F”.
WARNING!
To avoid danger of being burned, do not
remove radiator cap while engine and
radiator are still hot.
Scalding fluid and steam can be blown out
under pressure if cap is taken off too soon.
3) Remove air intake pipe.
4) Disconnect connector from ECT sensor (1).
5) Remove ECT sensor from thermostat case.
1
234I4RS0B130012-01
1
234I4RS0B130013-01
[C]: Voltage
[D]: Idle position of accelerator pedal
[E]: Fully depressed position of accelerator pedal
[C]
[B]
[D] [E] [A]
4.65 V
3.85 V
1.55 - 1.65 V
0.75 - 0.85 V
I4RS0B130010-02
1
I2RH0B130008-01
Page 287 of 1496
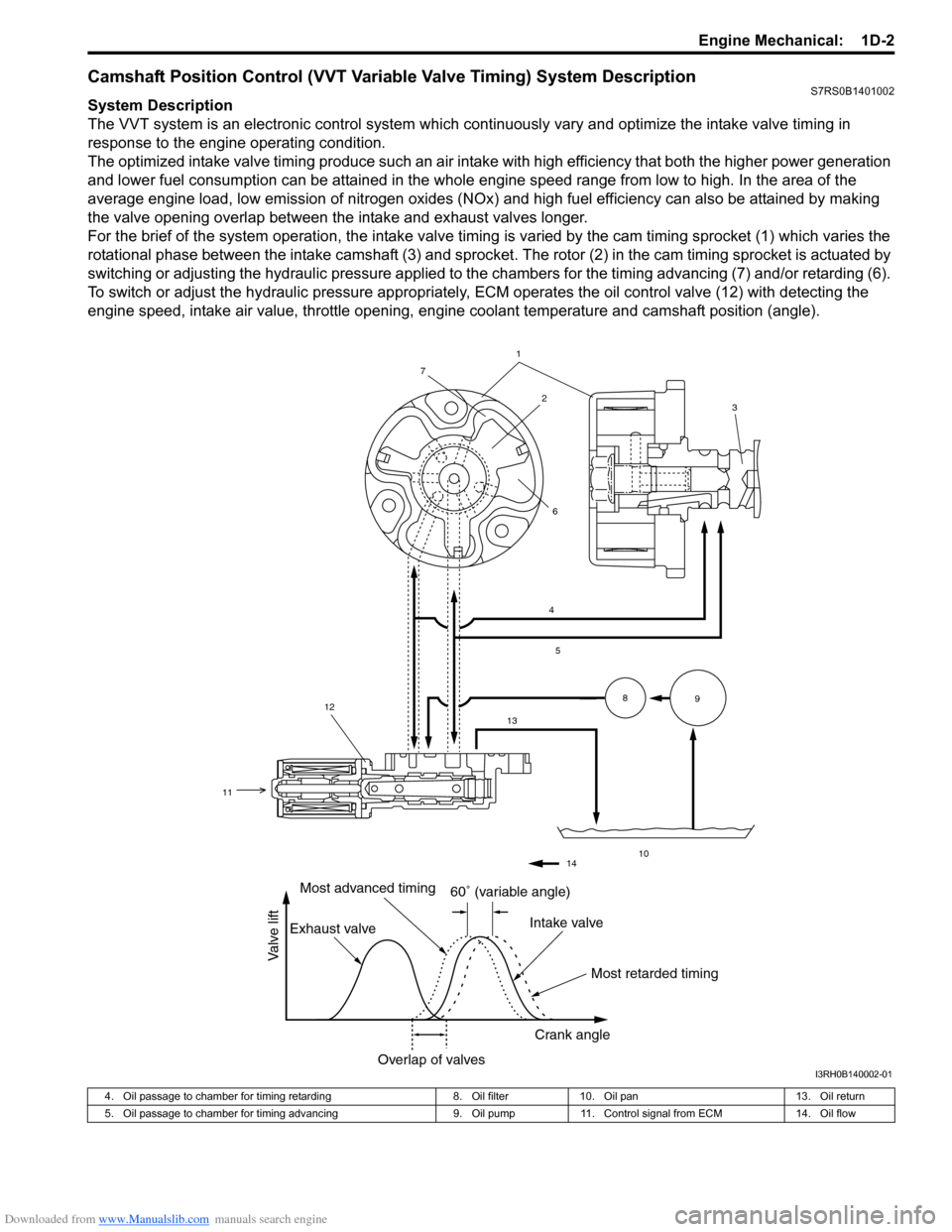
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-2
Camshaft Position Control (VVT Variable Valve Timing) System DescriptionS7RS0B1401002
System Description
The VVT system is an electronic control system which continuously vary and optimize the intake valve timing in
response to the engine operating condition.
The optimized intake valve timing produce such an air intake with high efficiency that both the higher power generation
and lower fuel consumption can be attained in the whole engine speed range from low to high. In the area of the
average engine load, low emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and high fuel efficiency can also be attained by making
the valve opening overlap between the intake and exhaust valves longer.
For the brief of the system operation, the intake valve timing is varied by the cam timing sprocket (1) which varies the
rotational phase between the intake camshaft (3) and sprocket . The rotor (2) in the cam timing sprocket is actuated by
switching or adjusting the hydraulic pressure applied to the chambers for the timing advancing (7) and/or retarding (6).
To switch or adjust the hydraulic pressure appropriately, ECM operates the oil control valve (12) with detecting the
engine speed, intake air value, throttle opening, engine coolant temperature and camshaft position (angle).
1
4
5
13
10
89
2
7
6
12
11
3
14
60� (variable angle)
Most retarded timing
Most advanced timing
Exhaust valve Intake valve
Crank angle
Overlap of valves
Valve lift
I3RH0B140002-01
4. Oil passage to chamber for timing retarding 8. Oil filter10. Oil pan 13. Oil return
5. Oil passage to chamber for timing advancing 9. Oil pump11. Control signal from ECM 14. Oil flow
Page 288 of 1496
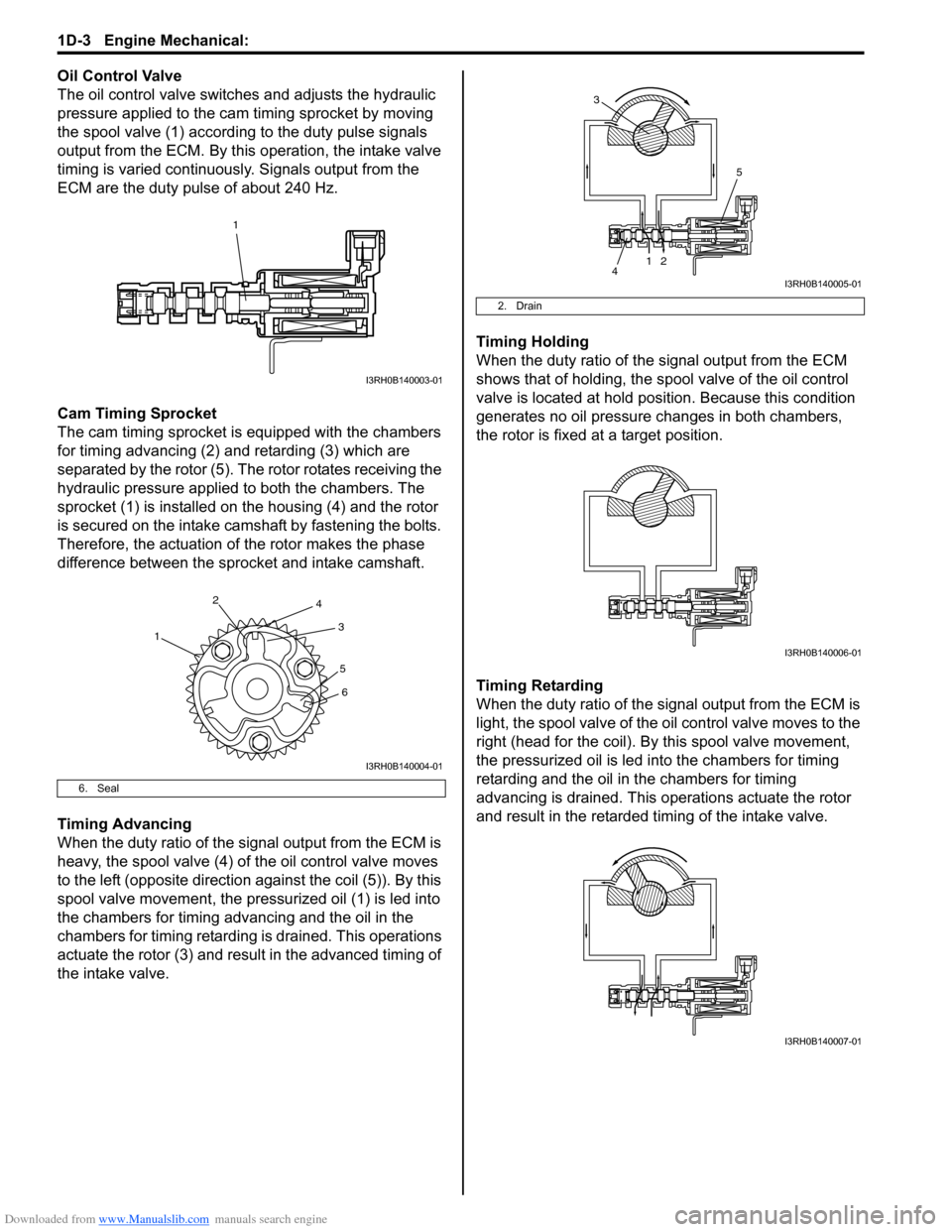
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-3 Engine Mechanical:
Oil Control Valve
The oil control valve switches and adjusts the hydraulic
pressure applied to the cam timing sprocket by moving
the spool valve (1) according to the duty pulse signals
output from the ECM. By this operation, the intake valve
timing is varied continuously. Signals output from the
ECM are the duty pulse of about 240 Hz.
Cam Timing Sprocket
The cam timing sprocket is equipped with the chambers
for timing advancing (2) and retarding (3) which are
separated by the rotor (5). The rotor rotates receiving the
hydraulic pressure applied to both the chambers. The
sprocket (1) is installed on the housing (4) and the rotor
is secured on the intake camshaft by fastening the bolts.
Therefore, the actuation of the rotor makes the phase
difference between the sprocket and intake camshaft.
Timing Advancing
When the duty ratio of the signal output from the ECM is
heavy, the spool valve (4) of the oil control valve moves
to the left (opposite direction against the coil (5)). By this
spool valve movement, the pressurized oil (1) is led into
the chambers for timing advancing and the oil in the
chambers for timing retarding is drained. This operations
actuate the rotor (3) and result in the advanced timing of
the intake valve. Timing Holding
When the duty ratio of the si
gnal output from the ECM
shows that of holding, the sp ool valve of the oil control
valve is located at hold posi tion. Because this condition
generates no oil pressure changes in both chambers,
the rotor is fixed at a target position.
Timing Retarding
When the duty ratio of the sig nal output from the ECM is
light, the spool valve of the o il control valve moves to the
right (head for the coil). By this spool valve movement,
the pressurized oil is led into the chambers for timing
retarding and the oil in the chambers for timing
advancing is drained. This operations actuate the rotor
and result in the retarded timing of the intake valve.
6. Seal
1
I3RH0B140003-01
1 2
3
4
56
I3RH0B140004-01
2. Drain
12
5
4
3
I3RH0B140005-01
I3RH0B140006-01
I3RH0B140007-01
Page 289 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-4
Targeted Timing Varying Operation
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Compression CheckS7RS0B1404001
Check compression pressure on all 4 cylinders as
follows:
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
2) Stop engine after warming up.
NOTE
After warming up engine, place transaxle
gear shift lever in “Neutral”, and set parking
brake and block drive wheels.
3) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
4) Remove engine cover.
5) Remove air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
6) Remove cylinder head upper cover.
7) Disconnect ignition coil couplers (1).
8) Remove ignition coil assemblies (2) with high- tension cord (3).
9) Remove all spark plugs.
10) Disconnect fuel injector wires (4) at the coupler. Driving condition Valve timing Target of control Effect
Engine running at idle
speed Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Stabilization of the engine
rotation at idle speed.
Average engine load
range To the advanced
sideTo lengthen the valve opening overlap
in order to enhance the internal
exhaust gas recirculation and reduce
the pumping loss. Improvement of the fuel
efficiency.
Lowering of the exhaust
emission.
Light engine load
range To the retarded sideTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Keeping of the engine stability.
Low or average
engine speed range
with heavy engine
load To the advanced
side
To advance the closing timing of the
intake valve in order to improve the
volumetric efficiency. Improvement of generating the
engine torque at low and
average engine speed.
High engine speed
range with heavy
engine load To the retarded sideTo retard the closing timing of the
intake valve in order to improve the
volumetric efficiency. Improvement of generating the
engine power.
Low engine coolant
temperature Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to intake manifold and
reduce the fuel increasing.
To slow the fast idle speed of the
engine as a result of stabilizing the
engine idling. Stabilization of the fast idling of
the engine.
Improvement of the fuel
efficiency.
At engine starting and
stopping Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Improvement of start ability.I2RH0B140003-01
Page 290 of 1496
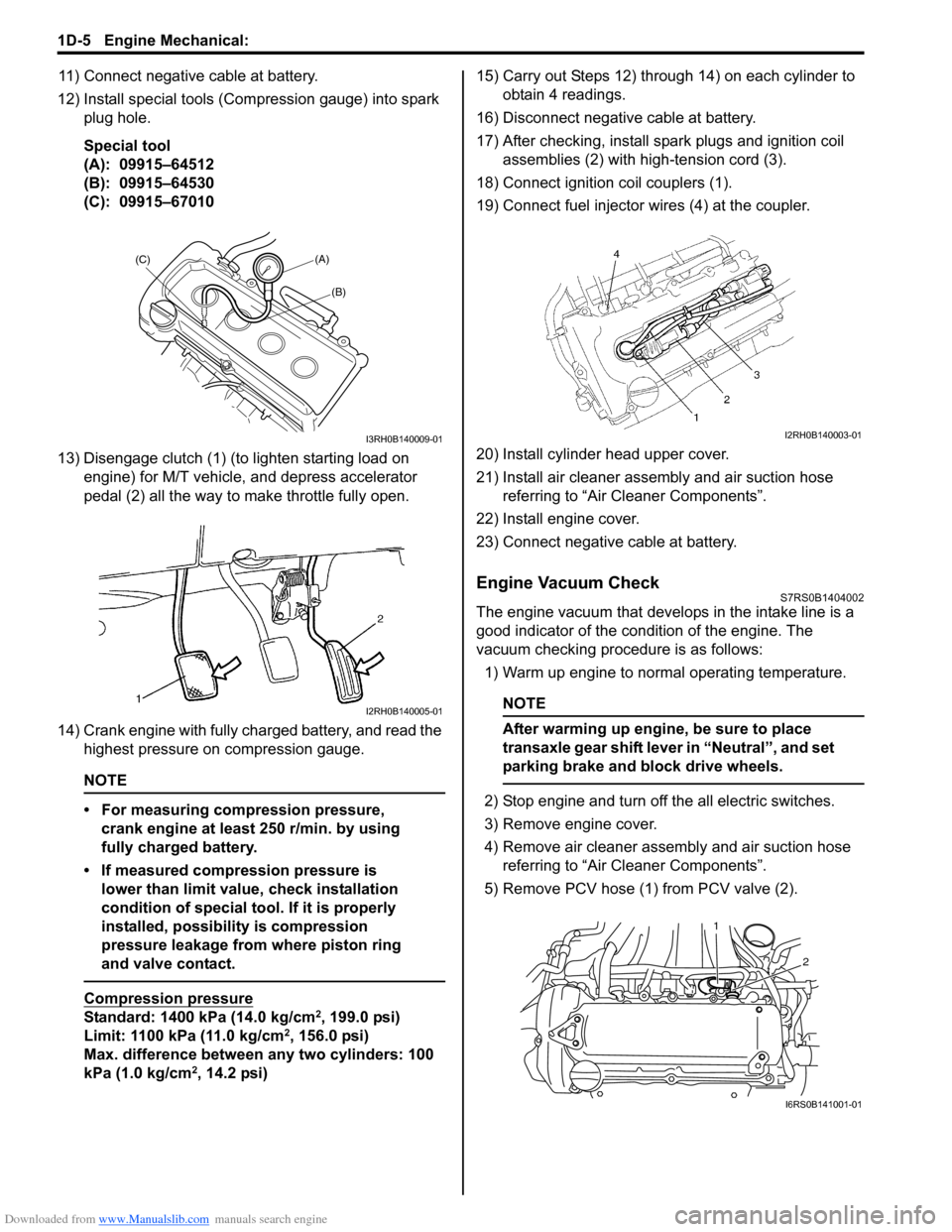
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-5 Engine Mechanical:
11) Connect negative cable at battery.
12) Install special tools (Compression gauge) into spark plug hole.
Special tool
(A): 09915–64512
(B): 09915–64530
(C): 09915–67010
13) Disengage clutch (1) (to lighten starting load on engine) for M/T vehicle, and depress accelerator
pedal (2) all the way to make throttle fully open.
14) Crank engine with fully charged battery, and read the highest pressure on compression gauge.
NOTE
• For measuring compression pressure, crank engine at least 250 r/min. by using
fully charged battery.
• If measured compression pressure is lower than limit value, check installation
condition of special tool. If it is properly
installed, possibility is compression
pressure leakage from where piston ring
and valve contact.
Compression pressure
Standard: 1400 kPa (14.0 kg/cm2, 199.0 psi)
Limit: 1100 kPa (11.0 kg/cm2, 156.0 psi)
Max. difference between any two cylinders: 100
kPa (1.0 kg/cm
2, 14.2 psi) 15) Carry out Steps 12) through 14) on each cylinder to
obtain 4 readings.
16) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
17) After checking, install spark plugs and ignition coil assemblies (2) with high-tension cord (3).
18) Connect ignition coil couplers (1).
19) Connect fuel injector wires (4) at the coupler.
20) Install cylinder head upper cover.
21) Install air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
22) Install engine cover.
23) Connect negative cable at battery.
Engine Vacuum CheckS7RS0B1404002
The engine vacuum that develops in the intake line is a
good indicator of the condition of the engine. The
vacuum checking procedure is as follows:
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
NOTE
After warming up engine, be sure to place
transaxle gear shift lever in “Neutral”, and set
parking brake and block drive wheels.
2) Stop engine and turn off the all electric switches.
3) Remove engine cover.
4) Remove air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
5) Remove PCV hose (1) from PCV valve (2).
(A)
(C)
(B)
I3RH0B140009-01
I2RH0B140005-01
I2RH0B140003-01
2
1
I6RS0B141001-01
Page 302 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-17 Engine Mechanical:
Engine Assembly Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1406011
NOTE
After replacing electric throttle body
assembly, perform calibration of throttle
valve referring to “Electric Throttle Body
System Calibration in Section 1C”.
Removal1) Relieve fuel pressure according to “Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure in Section 1G”.
2) Disconnect negative and pos itive cable at battery.
3) Remove battery and tray.
4) Remove engine hood after disconnecting windshield washer hose.
5) Remove right and left side engine under covers.
6) Remove A/C compressor belt by referring to “Compressor Drive Belt Remo val and Installation in
Section 7B” or “Compressor Drive Belt Removal and
Installation in Section 7B”.
7) Drain engine oil, transaxle oil and coolant.
8) Remove cowl top plate referring to “Cowl Top Components in Section 9K”.
9) Remove air cleaner assembly referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
10) With hose connected, detach A/C compressor from its bracket (A/C model) referring to “Compressor
Assembly Removal and Installation in Section 7B” or
“Compressor Assembly Removal and Installation in
Section 7B”.
CAUTION!
Suspend removed A/C compressor at a place
where no damage will be caused during
removal and installation of engine assembly.
11) Remove intake manifold rear stiffener (1) from intake manifold and cylinder block. 12) Disconnect the following electric wires:
• MAP sensor (1)
• ECT sensor (2)
•EGR valve (3)
• CMP sensor (4)
• Electric throttle body assembly (5)
• Ignition coil assembly (6)
• Injectors (7)
• Heated oxygen sensor No. 2 (8) and No. 1 (9)
• Oil control valve (10)
• Engine oil pressure switch (11)
• CKP sensor (12)
• Knock sensor (13)
• Back up light switch (14)
• Generator (15)
• Starting motor (16)
• Ground terminal (17) from intake manifold
• Battery ground terminal (18) from exhaust manifold
• Battery ground cable (19) from transaxle
• Magnet clutch switch of A/C compressor (A/C model)
• Each wire harness clamps
• Output shaft speed sensor (VSS) (34) (A/T model)
• Solenoid valve (33) (A/T model)
• Transmission range sensor (32) (A/T model)
• Input shaft speed sensor (31) (A/T model)
13) Remove fuse box from its bracket.
14) Disconnect the following cables: • Gear select control cable (23) (M/T model)
• Gear shift control cable (24) (M/T model)
• A/T select cable (A/T model)
15) Disconnect the following hoses: • Brake booster hose (26) from intake manifold
• Radiator inlet and outlet hoses (20) from each pipe
• Heater inlet and outlet hoses (21) from each pipe
• Fuel feed hoses (22) from fuel feed pipe
• EVAP canister purge valve hose (30) from purge pipe
• A/T fluid cooler hoses (A/T model)
16) With hose connected, detach clutch operating cylinder (25). (M/T model)
CAUTION!
Suspend removed clutch operating cylinder
at a place where no damage will be caused
during removal and installation of engine
assembly.
1
I6RS0B141014-01