Wheel pressure SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 22 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-1 General Information:
General Information
General Information
General Description
AbbreviationsS7RS0B0101001
A:
ABDC: After Bottom Dead Center
ABS: Anti-lock Brake System
AC: Alternating Current
A/C: Air Conditioning
A-ELR: Automatic-Emergency Locking Retractor
A/F: Air Fuel Mixture Ratio
ALR: Automatic Locking Retractor
API: American Petroleum Institute
APP sensor: Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
A/T: Automatic Transmission , Automatic Transaxle
AT D C : After Top Dead Center
ATF: Automatic Transmission Fluid, Automatic
Transaxle Fluid
B:
B+: Battery Positive Voltage
BBDC: Before Bottom Dead Center
BCM: Body Electrical Control Module
BDC: Bottom Dead Center
BTDC: Before Top Dead Center
C:
CAN: Controller Area Network
CKT: Circuit
CKP Sensor: Crankshaft Position Sensor
CMP Sensor: Camshaft Position Sensor
CO: Carbon Monoxide
CPP Switch: Clutch Pedal Position Switch (Clutch
Switch, Clutch Start Switch)
CPU: Central Processing Unit
CRS: Child Restraint System
D:
DC: Direct Current
DLC: Data Link Connector (Assembly Line Diag. Link,
ALDL, Serial Data Link, SDL)
DOHC: Double Over Head Camshaft
DOJ: Double Offset Joint
DRL: Daytime Running Light
DTC: Diagnostic Trouble Code (Diagnostic Code)
E:
EBCM: Electronic Brake Cont rol Module, ABS Control
Module
EBD: Electronic Brake Force Distribution
ECM: Engine Control Module
ECT Sensor: Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (Water Temp. Sensor, WTS)
EFE Heater: Early Fuel Evaporation Heater (Positive
Temperature Coefficient, PTC Heater)
EGR: Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EGRT Sensor: EGR Temperature Sensor (Recirculated
Exhaust Gas Temp. Sensor, REGTS)
ELR: Emergency Locking Retractor
ESP ®: Electronic Stability Program
EPS: Electronic Power Steering
EVAP: Evaporative Emission EVAP Canister:
Evaporative Emission Canister
(Charcoal Canister)
F:
4WD: 4 Wheel
Drive
G:
GEN: Generator
GND: Ground
GPS: Global Positioning System
H:
HVAC: Heating, Ventilating and Air Conditioning
HC: Hydrocarbons
HO2S: Heated Oxygen Sensor
I:
IAC Valve: Idle Air Control Valve (Idle Speed Control
Solenoid Valve, ISC Solenoid Valve)
IAT Sensor: Intake Air Temperature Sensor (Air
temperature Sensor, ATS)
ICM: Immobilizer Control Module
IG: Ignition
ISC Actuator: Idle Speed Control Actuator
L:
LH: Left Hand
LHD: Left Hand Drive Vehicle
LSPV: Load Sensing Proportioning Valve
M:
MAF Sensor: Mass Air Flow Sensor (Air Flow Sensor, AFS, Air Flow Meter, AFM)
MAP Sensor: Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
(Pressure Sensor, PS)
Max: Maximum
MFI: Multiport Fuel Injection (Mu ltipoint Fuel Injection)
Min: Minimum
MIL: Malfunction Indicator Lamp (“SERVICE ENGINE
SOON” Light)
M/T: Manual Transmission, Manual Transaxle
N:
NOx: Nitrogen Oxides
O:
OBD: On-Board Diagnostic System (Self-Diagnosis
Function)
O/D: Overdrive
OHC: Over Head Camshaft
O2S: Oxygen Sensor
P:
PCM: Powertrain Control Module
PCV: Positive Crankcase Ventilation
PNP: Park / Neutral Position
P/S: Power Steering
PSP Switch: Power Steering Pressure Switch (P/S
Pressure Switch)
R:
RH: Right Hand
RHD: Right Hand Drive Vehicle
S:
SAE: Society of Automotive Engineers
Page 39 of 1496
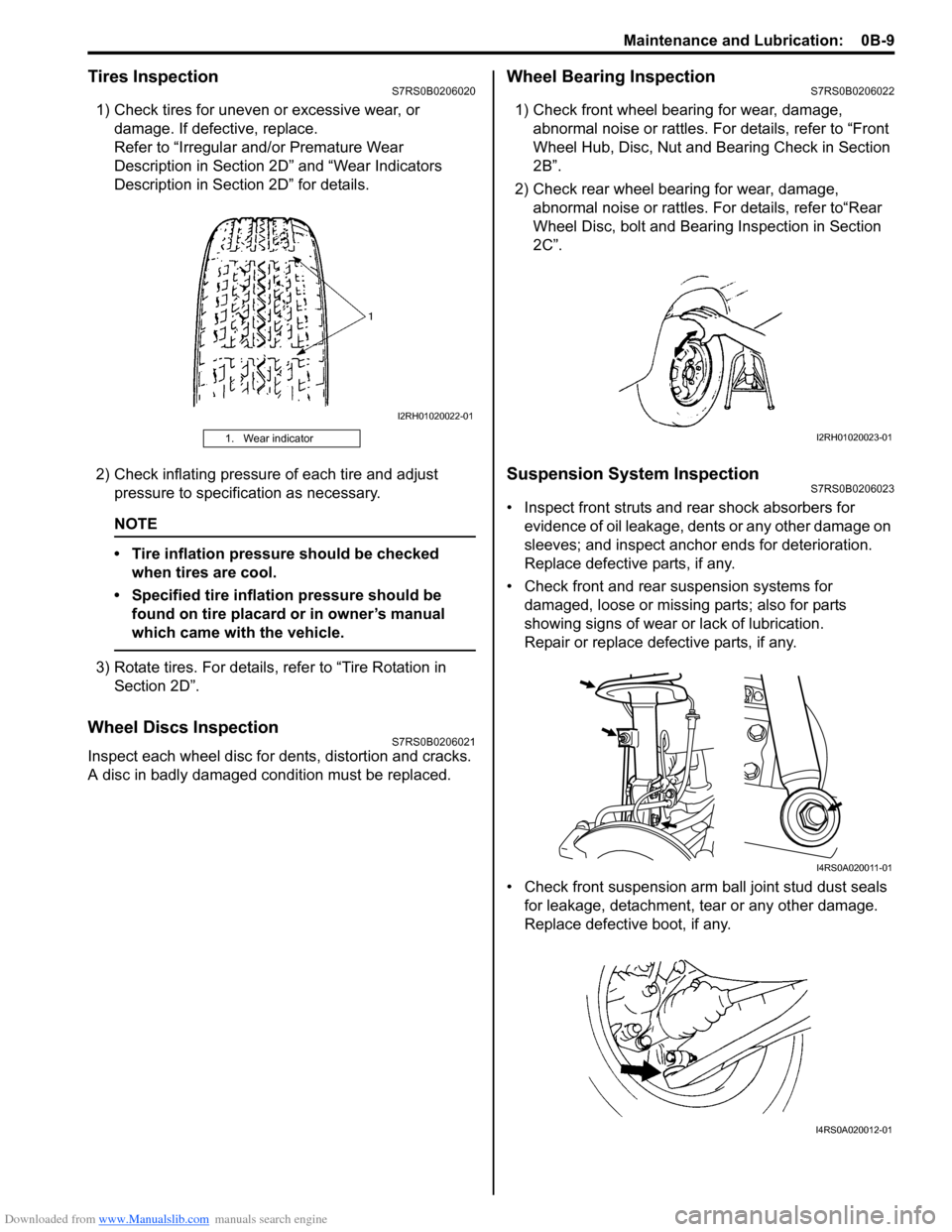
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Maintenance and Lubrication: 0B-9
Tires InspectionS7RS0B0206020
1) Check tires for uneven or excessive wear, or damage. If defective, replace.
Refer to “Irregular and/or Premature Wear
Description in Section 2D” and “Wear Indicators
Description in Section 2D” for details.
2) Check inflating pressure of each tire and adjust pressure to specification as necessary.
NOTE
• Tire inflation pressure should be checked when tires are cool.
• Specified tire inflation pressure should be found on tire placard or in owner’s manual
which came with the vehicle.
3) Rotate tires. For details, refer to “Tire Rotation in Section 2D”.
Wheel Discs InspectionS7RS0B0206021
Inspect each wheel disc for de nts, distortion and cracks.
A disc in badly damaged condition must be replaced.
Wheel Bearing InspectionS7RS0B0206022
1) Check front wheel bearing for wear, damage, abnormal noise or rattles. For details, refer to “Front
Wheel Hub, Disc, Nut and Bearing Check in Section
2B”.
2) Check rear wheel bearing for wear, damage, abnormal noise or rattles. For details, refer to“Rear
Wheel Disc, bolt and Bearing Inspection in Section
2C”.
Suspension System InspectionS7RS0B0206023
• Inspect front struts and rear shock absorbers for evidence of oil leakage, dents or any other damage on
sleeves; and inspect anchor ends for deterioration.
Replace defective parts, if any.
• Check front and rear suspension systems for damaged, loose or missing parts; also for parts
showing signs of wear or lack of lubrication.
Repair or replace defective parts, if any.
• Check front suspension arm ball joint stud dust seals for leakage, detachment, tear or any other damage.
Replace defective boot, if any.
1. Wear indicator
I2RH01020022-01
I2RH01020023-01
I4RS0A020011-01
I4RS0A020012-01
Page 55 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-5
Freeze frame data clearance:
The freeze frame data is cleared at the same time as
clearance of DTC.
Non-Euro-OBD
ECM diagnosis troubles which may occur in the area
including the following parts w hen the ignition switch is
ON and the engine is running, and indicates the result by
turning on or flashing malfunction indicator lamp (1).
• Heated oxygen sensor
• ECT sensor
•TP sensor
• APP sensor
• MAF sensor
• IAT sensor
• MAP sensor
• CMP sensor
• CKP sensor
• Knock sensor
• Wheel speed sensor (VSS)
• CPU (Central Processing Unit) of ECM
• Oil control valve
• EGR valve
• EVAP canister purge valve
• Ignition coil
• Starter relay
• Radiator fan relay
• CAN communication
• Barometric pressure sensor
• ECM back up power supply
ECM and malfunction indicator lamp (1) operate as
follows.
• Malfunction indicator lamp (1) lights when the ignition switch is turned ON (but t he engine at stop) with the
diagnosis switch terminal ungrounded regardless of
the condition of Engine and Emission control system.
This is only to check the ma lfunction indicator lamp (1)
in the combination meter and its circuit.
• If the above areas of Engine and Emission control system is free from any trouble after the engine start
(while engine is running), malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turns OFF. • When ECM detects a trouble which has occurred in
the above areas, it makes malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turn ON while the engi ne is running to warn the
driver of such occurrence of trouble and at the same
time it stores the trouble area in ECM back-up
memory. (The memory is kept as it is even if the
trouble was only temporary and disappeared
immediately. And it is not erased unless the power to
ECM is shut off for specified time or it is cleared by
SUZUKI scan tool (2).)
For Hong Kong model, DTC can be read by not only
using SUZUKI scan tool but also displayed on
odometer (5) of the combination meter. (i.e. when
diagnosis switch terminal (3) is grounded with a
service wire (4) and ignition switch is turned ON.) For
further detail of the checking procedure, refer to “DTC
Check”.
6. Diagnosis connector
2
1
6 3
5
4
I5RS0C110021-01
Page 58 of 1496
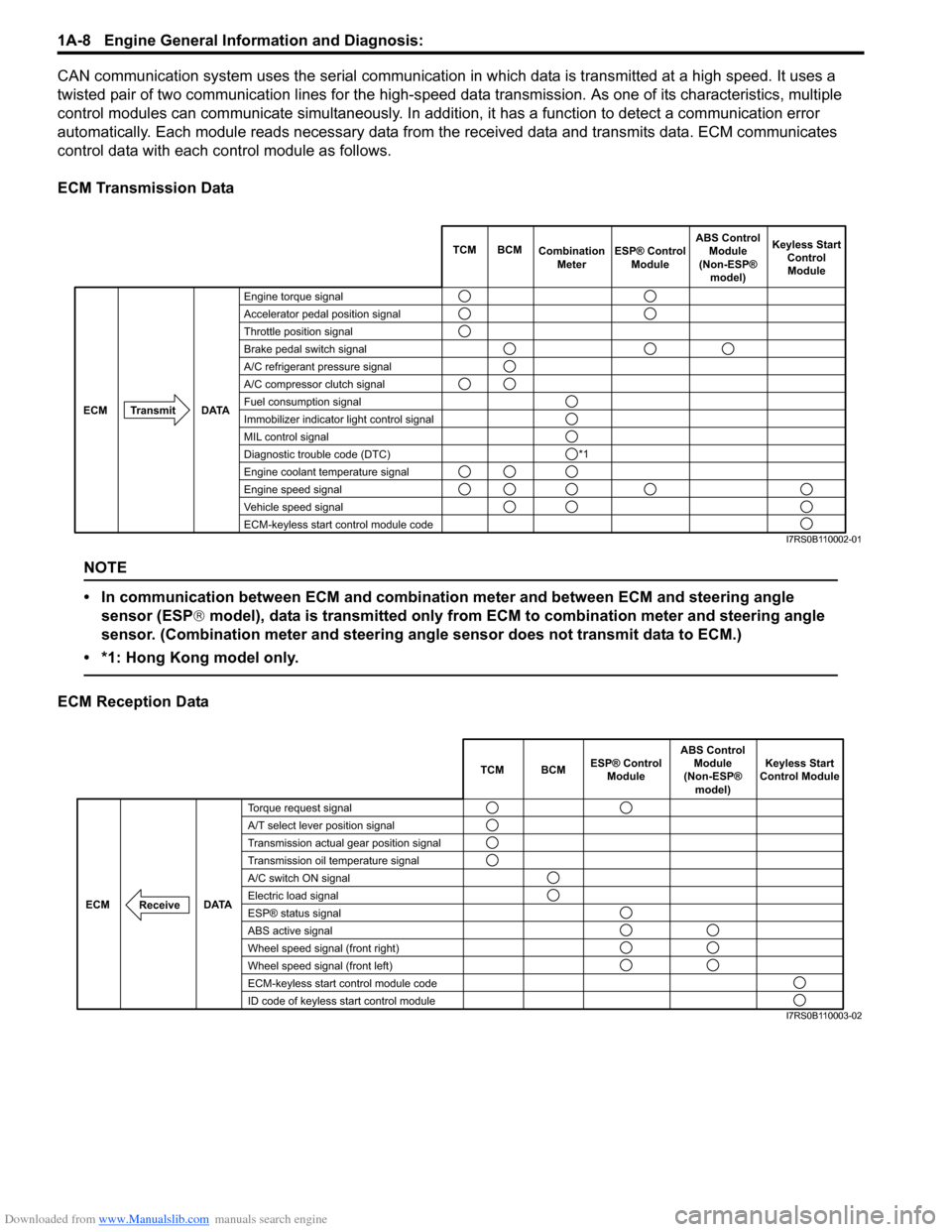
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-8 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
CAN communication system uses the serial communication in which data is transmitted at a high speed. It uses a
twisted pair of two communication lines for the high-speed da ta transmission. As one of its characteristics, multiple
control modules can communicate simultaneously. In addition, it has a function to detect a communication error
automatically. Each module reads necessary data from the received data and transmits data. ECM communicates
control data with each control module as follows.
ECM Transmission Data
NOTE
• In communication between ECM and combination meter and between ECM and steering angle sensor (ESP ® model), data is transmitted only from ECM to combination meter and steering angle
sensor. (Combination meter and steering angle sensor does not transmit data to ECM.)
• *1: Hong Kong model only.
ECM Reception Data
Engine torque signal
Accelerator pedal position signal
Throttle position signal
Brake pedal switch signal
A/C refrigerant pressure signal
A/C compressor clutch signal
Fuel consumption signal
Immobilizer indicator light control signal
MIL control signal
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC)
Engine coolant temperature signal
Engine speed signal
Vehicle speed signal
ECM-keyless start control module code TCM BCM
Combination
Meter Keyless Start
ControlModule
Transmit DATA
ECM
ESP® Control
Module ABS Control
Module
(Non-ESP® model)
*1
I7RS0B110002-01
TCM BCM Keyless Start
Control Module
DATA
ECM
Torque request signal
A/T select lever position signal
Transmission actual gear position signal
Transmission oil temperature signal
A/C switch ON signal
Electric load signal
ESP® status signal
ABS active signal
Wheel speed signal (front right)
Wheel speed signal (front left)
ECM-keyless start control module code
ID code of keyless start control module
Receive
ABS Control
Module
(Non-ESP® model)
ESP® Control
Module
I7RS0B110003-02
Page 63 of 1496
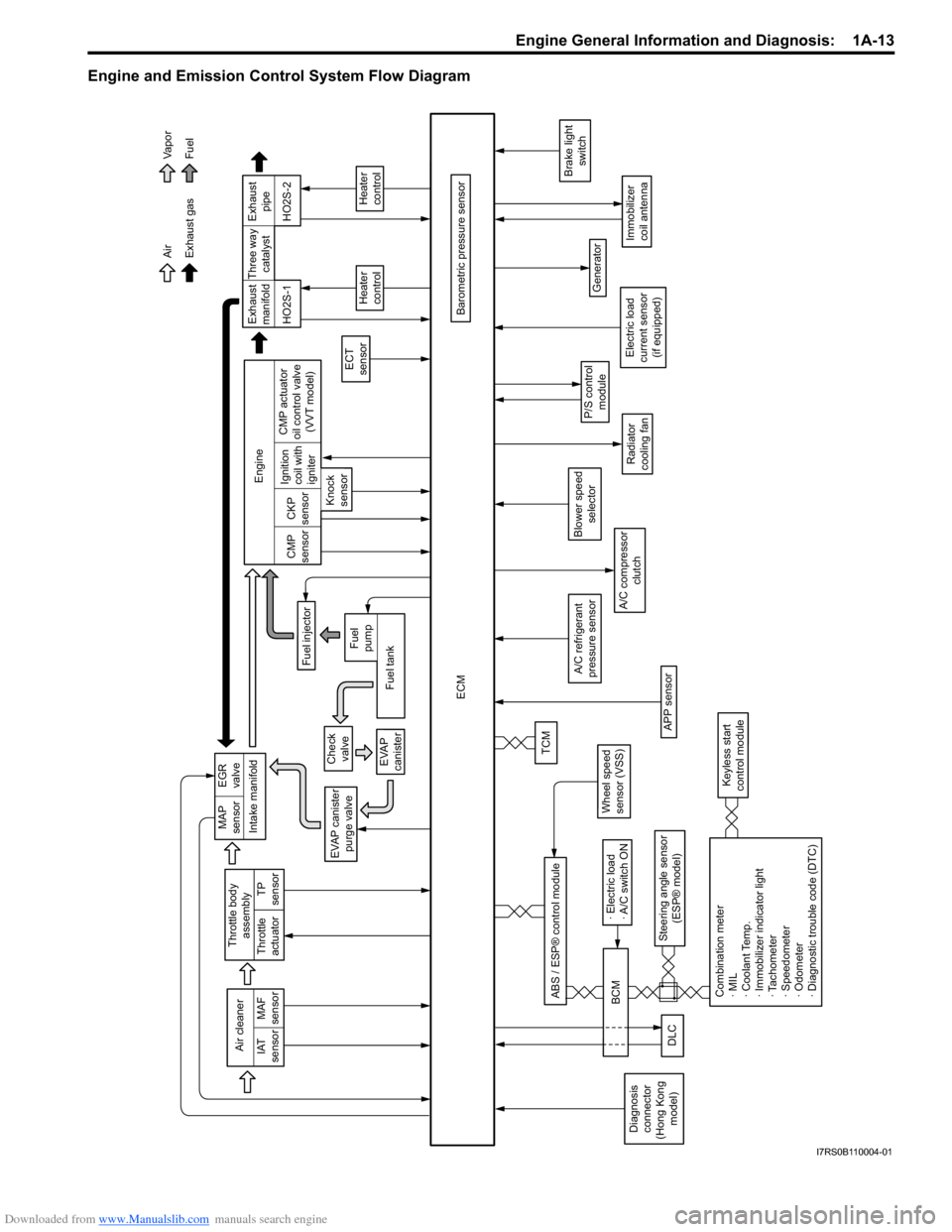
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-13
Engine and Emission Control System Flow Diagram
Intake manifold
Exhaust gas AirFuel
Va p o r
EVAP canister purge valve
ECM
Barometric pressure sensor
A/C compressor clutch
Generator
Immobilizer
coil antenna
P/S controlmodule
Brake light switch
Air cleaner
IAT
sensor MAF
sensor
A/C refrigerant
pressure sensor
TP
sensor
Throttle body
assembly
Throttle
actuator
Wheel speed
sensor (VSS)
Steering angle sensor (ESP® model)
ABS / ESP® control module
Blower speed
selector
MAP
sensor EGR
valve
Check valve
EVAP
canisterTCM
Exhaust
manifold Exhaust
pipe
Fuel injector
ECT
sensor
Heater
control
HO2S-1 HO2S-2
Engine
CMP
sensor CKP
sensor
Knock
sensor Ignition
coil with
igniter
Fuel tank
Fuel
pump CMP actuator
oil control valve (VVT model) Three way
catalyst
Heater
control
Radiator
cooling fan
Combination meter
· MIL
· Coolant Temp.
· Immobilizer indicator light
· Tachometer
· Speedometer
· Odometer
· Diagnostic trouble code (DTC)
Keyless start
control module
DLC
· Electric load
· A/C switch ON
BCM
Diagnosis
connector
(Hong Kong model) Electric load
current sensor (if equipped)
APP sensor
I7RS0B110004-01
Page 68 of 1496
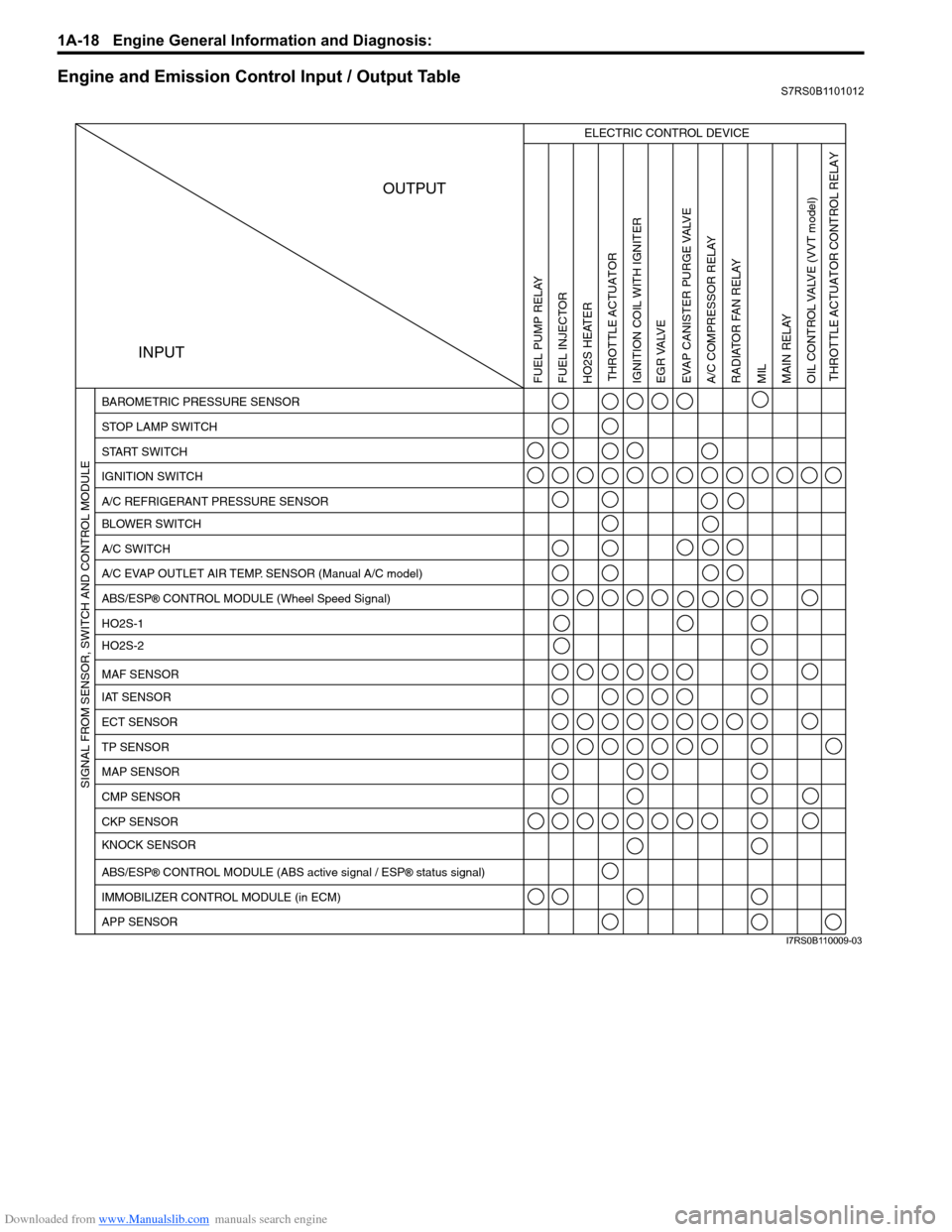
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-18 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Engine and Emission Control Input / Output TableS7RS0B1101012
INPUTOUTPUT
ELECTRIC CONTROL DEVICE
BAROMETRIC PRESSURE SENSOR
STOP LAMP SWITCH
START SWITCH
IGNITION SWITCH
A/C REFRIGERANT PRESSURE SENSOR
BLOWER SWITCH
A/C SWITCH
A/C EVAP OUTLET AIR TEMP. SENSOR (Manual A/C model)
ABS/ESP
® CONTROL MODULE (Wheel Speed Signal)
HO2S-1
HO2S-2
IAT SENSOR MAF SENSOR
ECT SENSOR
TP SENSOR
MAP SENSOR
CMP SENSOR
CKP SENSOR
KNOCK SENSOR
ABS/ESP
® CONTROL MODULE (ABS active signal / ESP® status signal)
IMMOBILIZER CONTROL MODULE (in ECM)
APP SENSOR
FUEL PUMP RELAY
FUEL INJECTOR
HO2S HEATER THROTTLE ACTUATOR
THROTTLE ACTUATOR CONTROL RELAY
IGNITION COIL WITH IGNITER
EGR VALVE
EVAP CANISTER PURGE VALVEA/C COMPRESSOR RELAY RADIATOR FAN RELAY
MIL
MAIN RELAY
OIL CONTROL VALVE
(VVT model)
SIGNAL FROM SENSOR, SWITCH AND CONTROL MODULE
I7RS0B110009-03
Page 70 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-20 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
1. Air cleaner16. CMP sensor31. Battery
2. EVAP canister purge valve 17. CKP sensor32. A/C compressor relay
3. MAF and IAT sensor 18. Radiator cooling fan33. A/C switch
4. TP sensor 19. Combination meter34. A/C evaporator outlet air temp. sensor (manual A/C model)
5. Throttle actuator 20. BCM35.Immobilizer coil antenna
6. MAP sensor 21. Ignition switch36. Main relay
7. EGR valve 22. Starter magnetic switch37. APP sensor
8. EVAP canister 23. HO2S-238. Oil control valve (VVT model)
9. Tank pressure control valve (built-in fuel pump) 24. DLC 39. TCM (A/T model)
10. Fuel pump (with pressure regulator) 25. Electric load40. Starting motor control relay
11. Ignition coil assembly 26. Fuel level sensor41. A/C refrigerant pressure sensor
12. Fuel injector 27. Brake light42. Throttle actuator control relay
13. HO2S-1 28. Brake light switch43. ABS/ESP® control module
14. Knock sensor 29. ECM44. Wheel speed sensor (VSS)
15. ECT sensor 30. Barometric pressure sensor
Page 71 of 1496
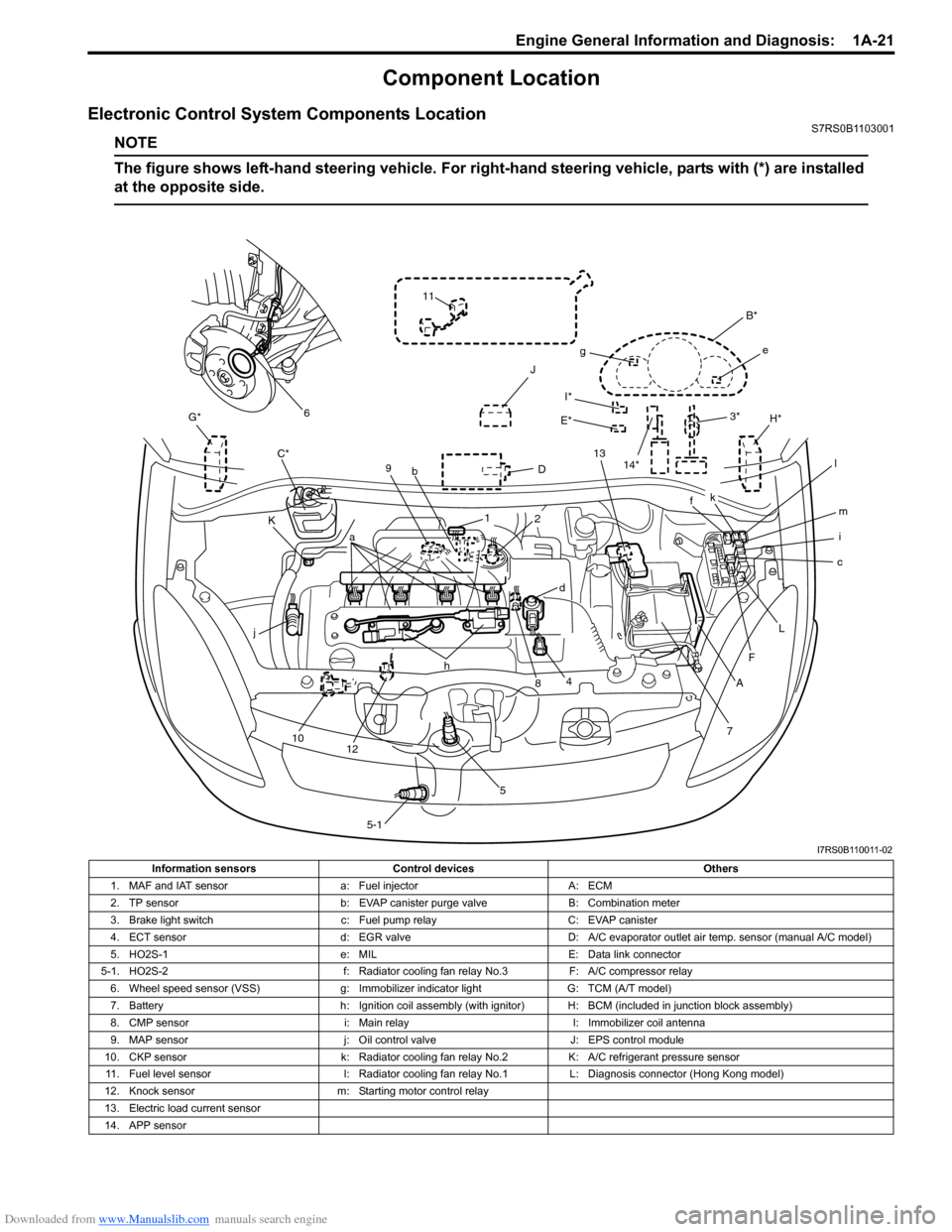
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-21
Component Location
Electronic Control System Components LocationS7RS0B1103001
NOTE
The figure shows left-hand steering vehicle. For right-hand steering vehicle, parts with (*) are installed
at the opposite side.
I*
E*
G*
D
K H*
J
C*
7
A
F
c
L
i m
f
B*
e
g
k
l
13
3*
4
j
10 12 h
58
a
9
b
1
5-1
d
2
11
6
14*
I7RS0B110011-02
Information sensors Control devices Others
1. MAF and IAT sensor a: Fuel injectorA: ECM
2. TP sensor b: EVAP canister purge valve B: Combination meter
3. Brake light switch c: Fuel pump relayC: EVAP canister
4. ECT sensor d: EGR valveD: A/C evaporator outlet air temp. sensor (manual A/C model)
5. HO2S-1 e: MILE: Data link connector
5-1. HO2S-2 f: Radiator cooling fan relay No.3F: A/C compressor relay
6. Wheel speed sensor (VSS) g: Immobilizer indicator lightG: TCM (A/T model)
7. Battery h: Ignition coil assembly (with ignitor) H: BCM (included in junction block assembly)
8. CMP sensor i: Main relayI: Immobilizer coil antenna
9. MAP sensor j: Oil control valveJ: EPS control module
10. CKP sensor k: Radiator cooling fan relay No.2K: A/C refrigerant pressure sensor
11. Fuel level sensor l: Radiator cooling fan relay No.1L: Diagnosis connector (Hong Kong model)
12. Knock sensor m: Starting motor control relay
13. Electric load current sensor
14. APP sensor
Page 289 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-4
Targeted Timing Varying Operation
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
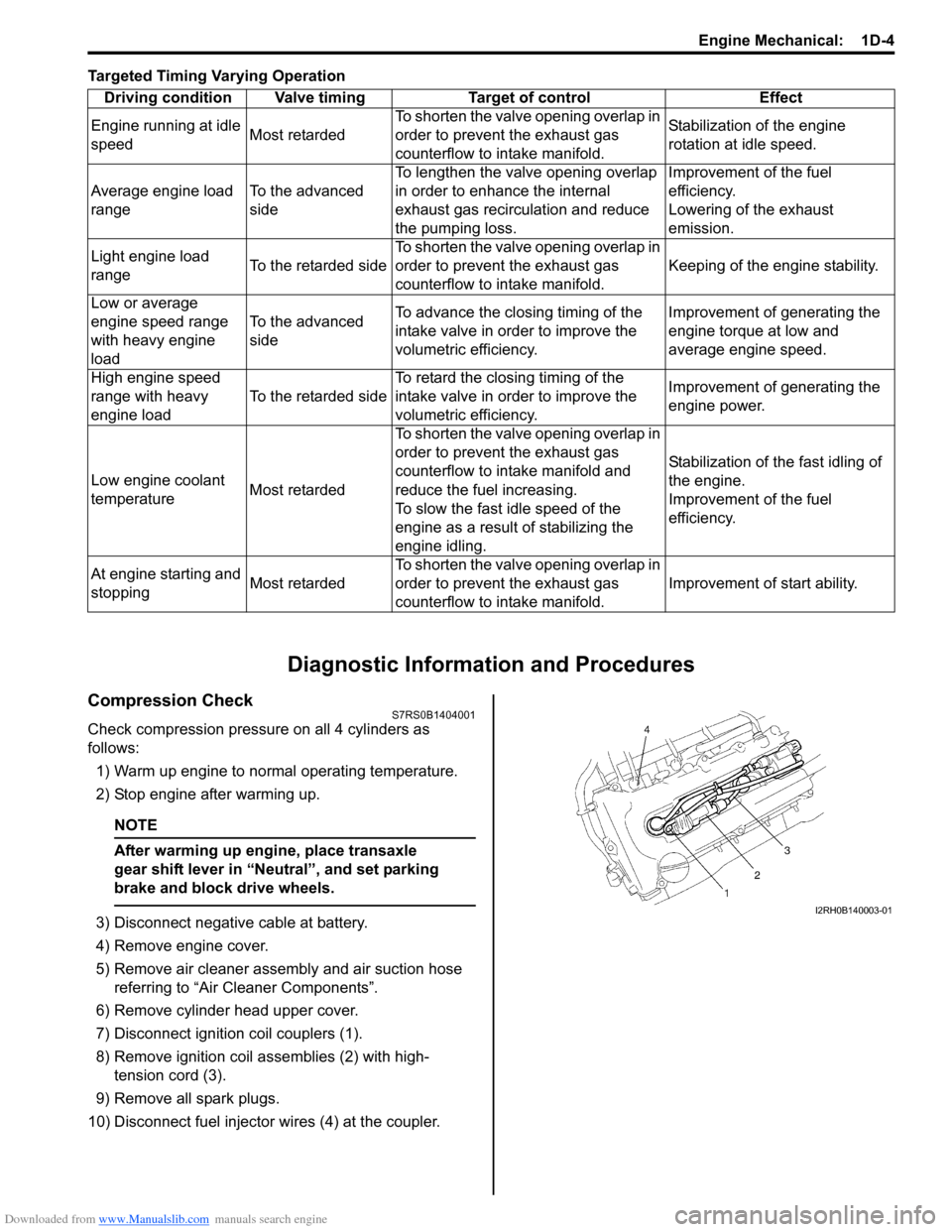
Compression CheckS7RS0B1404001
Check compression pressure on all 4 cylinders as
follows:
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
2) Stop engine after warming up.
NOTE
After warming up engine, place transaxle
gear shift lever in “Neutral”, and set parking
brake and block drive wheels.
3) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
4) Remove engine cover.
5) Remove air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
6) Remove cylinder head upper cover.
7) Disconnect ignition coil couplers (1).
8) Remove ignition coil assemblies (2) with high- tension cord (3).
9) Remove all spark plugs.
10) Disconnect fuel injector wires (4) at the coupler. Driving condition Valve timing Target of control Effect
Engine running at idle
speed Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Stabilization of the engine
rotation at idle speed.
Average engine load
range To the advanced
sideTo lengthen the valve opening overlap
in order to enhance the internal
exhaust gas recirculation and reduce
the pumping loss. Improvement of the fuel
efficiency.
Lowering of the exhaust
emission.
Light engine load
range To the retarded sideTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Keeping of the engine stability.
Low or average
engine speed range
with heavy engine
load To the advanced
side
To advance the closing timing of the
intake valve in order to improve the
volumetric efficiency. Improvement of generating the
engine torque at low and
average engine speed.
High engine speed
range with heavy
engine load To the retarded sideTo retard the closing timing of the
intake valve in order to improve the
volumetric efficiency. Improvement of generating the
engine power.
Low engine coolant
temperature Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to intake manifold and
reduce the fuel increasing.
To slow the fast idle speed of the
engine as a result of stabilizing the
engine idling. Stabilization of the fast idling of
the engine.
Improvement of the fuel
efficiency.
At engine starting and
stopping Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Improvement of start ability.I2RH0B140003-01
Page 290 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-5 Engine Mechanical:
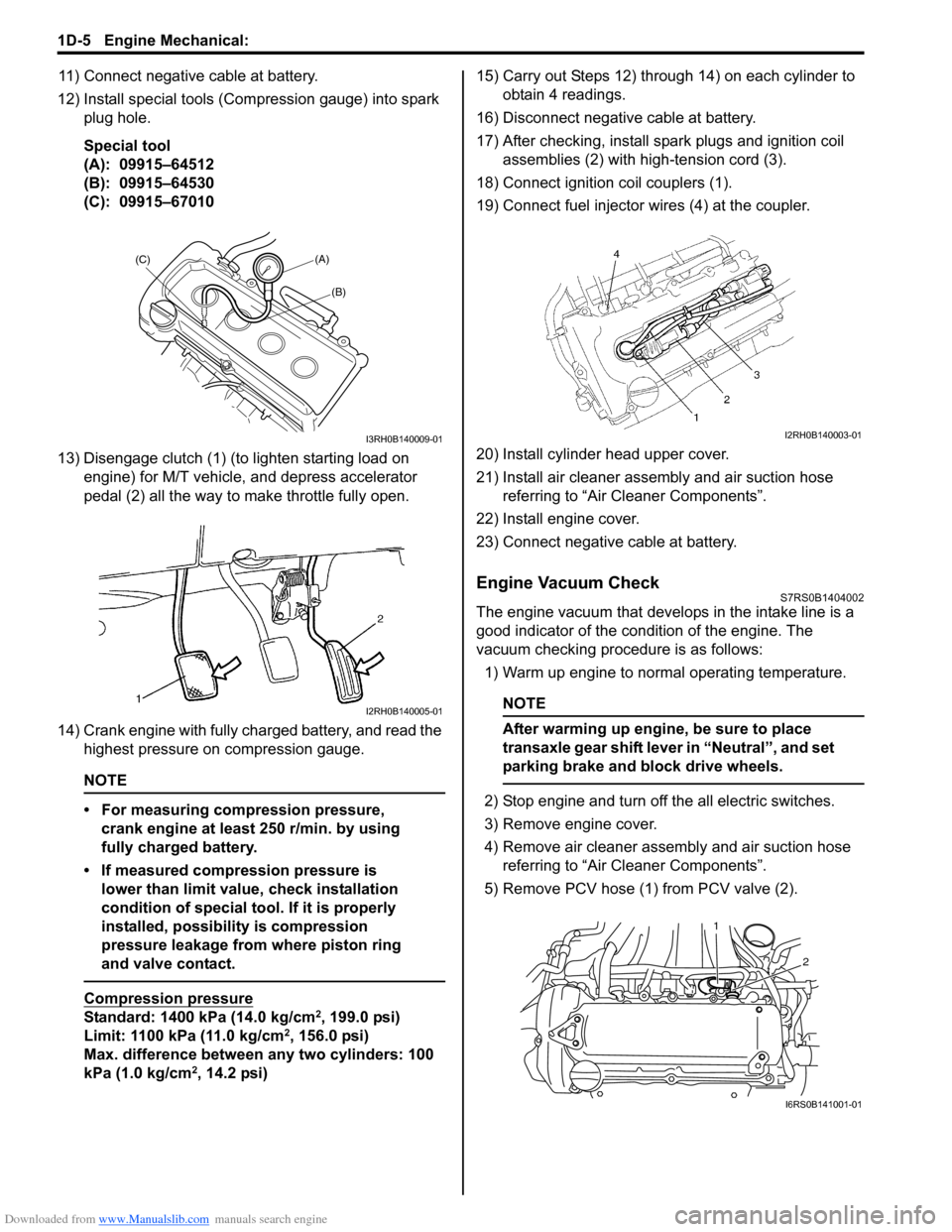
11) Connect negative cable at battery.
12) Install special tools (Compression gauge) into spark plug hole.
Special tool
(A): 09915–64512
(B): 09915–64530
(C): 09915–67010
13) Disengage clutch (1) (to lighten starting load on engine) for M/T vehicle, and depress accelerator
pedal (2) all the way to make throttle fully open.
14) Crank engine with fully charged battery, and read the highest pressure on compression gauge.
NOTE
• For measuring compression pressure, crank engine at least 250 r/min. by using
fully charged battery.
• If measured compression pressure is lower than limit value, check installation
condition of special tool. If it is properly
installed, possibility is compression
pressure leakage from where piston ring
and valve contact.
Compression pressure
Standard: 1400 kPa (14.0 kg/cm2, 199.0 psi)
Limit: 1100 kPa (11.0 kg/cm2, 156.0 psi)
Max. difference between any two cylinders: 100
kPa (1.0 kg/cm
2, 14.2 psi) 15) Carry out Steps 12) through 14) on each cylinder to
obtain 4 readings.
16) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
17) After checking, install spark plugs and ignition coil assemblies (2) with high-tension cord (3).
18) Connect ignition coil couplers (1).
19) Connect fuel injector wires (4) at the coupler.
20) Install cylinder head upper cover.
21) Install air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
22) Install engine cover.
23) Connect negative cable at battery.
Engine Vacuum CheckS7RS0B1404002
The engine vacuum that develops in the intake line is a
good indicator of the condition of the engine. The
vacuum checking procedure is as follows:
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
NOTE
After warming up engine, be sure to place
transaxle gear shift lever in “Neutral”, and set
parking brake and block drive wheels.
2) Stop engine and turn off the all electric switches.
3) Remove engine cover.
4) Remove air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
5) Remove PCV hose (1) from PCV valve (2).
(A)
(C)
(B)
I3RH0B140009-01
I2RH0B140005-01
I2RH0B140003-01
2
1
I6RS0B141001-01