tail lamp SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 37 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Maintenance and Lubrication: 0B-7
Fuel Filter ReplacementS7RS0B0206011
Fuel filter is installed in fuel pump assembly in fuel tank.
Replace fuel filter or fuel pump assembly with new one,
referring to “Fuel Pump Assembly Removal and
Installation in Section 1G” for proper procedure.
Fuel Tank InspectionS7RS0B0206012
Check fuel tank damage, cracks, fuel leakage, corrosion
and tank bolts looseness.
If a problem is found, repair or replace.
PCV Valve InspectionS7RS0B0206013
Check crankcase ventilation hose and PCV hose for
leaks, cracks or clog, and PCV valve for stick or clog.
Refer to “PCV Valve Inspection in Section 1B” for PCV
valve checking procedure.
Fuel Evaporative Emission Control System
Inspection
S7RS0B0206014
1) Visually inspect hoses for cracks, damage, or excessive bends. Inspect a ll clamps for damage and
proper position.
2) Check EVAP canister for operation and clog, referring to “EVAP Canister Inspection in Section
1B”.
If a malfunction is found, repair or replace.
Brake Discs and Pads InspectionS7RS0B0206015
1) Remove wheel and caliper but don’t disconnect brake hose from caliper. 2) Check disc brake pads and discs for excessive wear,
damage and deflection. Replace parts as necessary.
For details, refer to “Front Disc Brake Pad Inspection
in Section 4B”, “Front Brake Disc Inspection in
Section 4B”, “Rear Disc Brake Pad Inspection in
Section 4C” and/or “Rear Brake Disc Inspection in
Section 4C”.
Be sure to torque caliper pin bolts to specification.
Brake Hoses and Pipes InspectionS7RS0B0206016
Perform this inspection where these is enough light and
use a mirror as necessary.
• Check brake hoses and pipes for proper hookup, leaks, cracks, chafing and other damage.
• Check that hoses and pipes are clear of sharp edges and moving parts.
Repair or replace any of these parts as necessary.
CAUTION!
After replacing any brake pipe or hose, be
sure to carry out air purge operation.
I4RS0B020002-02
I4RS0A020006-01
I3RM0A020006-01
I4RS0A020008-01
Page 53 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-3
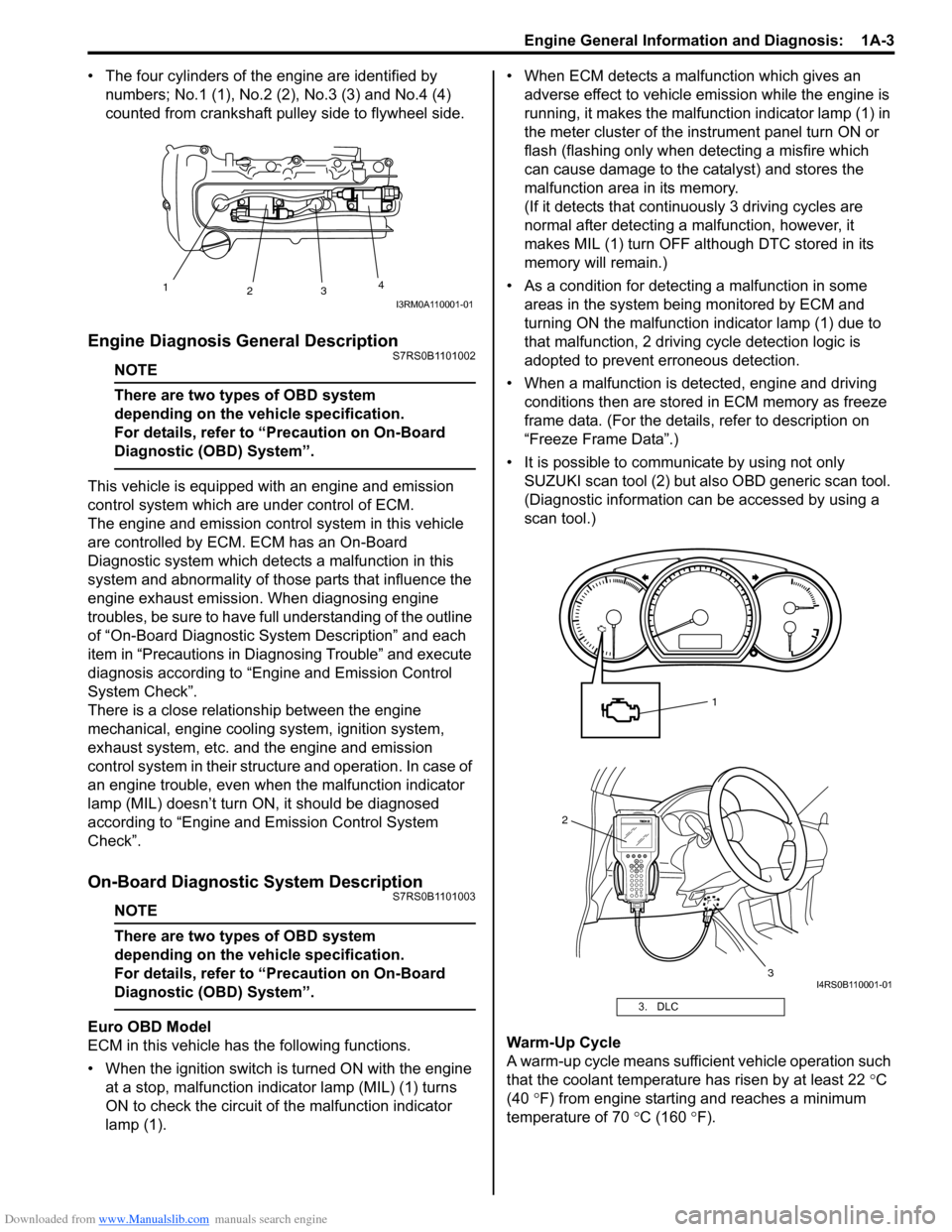
• The four cylinders of the engine are identified by numbers; No.1 (1), No.2 (2 ), No.3 (3) and No.4 (4)
counted from crankshaft pulley side to flywheel side.
Engine Diagnosis General DescriptionS7RS0B1101002
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
This vehicle is equipped with an engine and emission
control system which are under control of ECM.
The engine and emission control system in this vehicle
are controlled by ECM. ECM has an On-Board
Diagnostic system which detects a malfunction in this
system and abnormality of those parts that influence the
engine exhaust emission. When diagnosing engine
troubles, be sure to have full understanding of the outline
of “On-Board Diagnostic System Description” and each
item in “Precautions in Diagnosing Trouble” and execute
diagnosis according to “Engine and Emission Control
System Check”.
There is a close relationship between the engine
mechanical, engine cooling system, ignition system,
exhaust system, etc. and the engine and emission
control system in their structure and operation. In case of
an engine trouble, even when the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL) doesn’t turn ON, it should be diagnosed
according to “Engine and Emission Control System
Check”.
On-Board Diagnostic System DescriptionS7RS0B1101003
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
Euro OBD Model
ECM in this vehicle has the following functions.
• When the ignition switch is turned ON with the engine at a stop, malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (1) turns
ON to check the circuit of the malfunction indicator
lamp (1). • When ECM detects a malfunction which gives an
adverse effect to vehicle emission while the engine is
running, it makes the malfunction indicator lamp (1) in
the meter cluster of the inst rument panel turn ON or
flash (flashing only when detecting a misfire which
can cause damage to the catalyst) and stores the
malfunction area in its memory.
(If it detects that contin uously 3 driving cycles are
normal after detecting a malfunction, however, it
makes MIL (1) turn OFF although DTC stored in its
memory will remain.)
• As a condition for detecting a malfunction in some areas in the system being monitored by ECM and
turning ON the malfunction indicator lamp (1) due to
that malfunction, 2 driving cycle detection logic is
adopted to prevent erroneous detection.
• When a malfunction is detected, engine and driving conditions then are stored in ECM memory as freeze
frame data. (For the details, refer to description on
“Freeze Frame Data”.)
• It is possible to communicate by using not only SUZUKI scan tool (2) but also OBD generic scan tool.
(Diagnostic information can be accessed by using a
scan tool.)
Warm-Up Cycle
A warm-up cycle means sufficie nt vehicle operation such
that the coolant temperature has risen by at least 22 °C
(40 °F) from engine starting and reaches a minimum
temperature of 70 °C (160 ° F).
1
23 4
I3RM0A110001-01
3. DLC
2
3
1
I4RS0B110001-01
Page 55 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-5
Freeze frame data clearance:
The freeze frame data is cleared at the same time as
clearance of DTC.
Non-Euro-OBD
ECM diagnosis troubles which may occur in the area
including the following parts w hen the ignition switch is
ON and the engine is running, and indicates the result by
turning on or flashing malfunction indicator lamp (1).
• Heated oxygen sensor
• ECT sensor
•TP sensor
• APP sensor
• MAF sensor
• IAT sensor
• MAP sensor
• CMP sensor
• CKP sensor
• Knock sensor
• Wheel speed sensor (VSS)
• CPU (Central Processing Unit) of ECM
• Oil control valve
• EGR valve
• EVAP canister purge valve
• Ignition coil
• Starter relay
• Radiator fan relay
• CAN communication
• Barometric pressure sensor
• ECM back up power supply
ECM and malfunction indicator lamp (1) operate as
follows.
• Malfunction indicator lamp (1) lights when the ignition switch is turned ON (but t he engine at stop) with the
diagnosis switch terminal ungrounded regardless of
the condition of Engine and Emission control system.
This is only to check the ma lfunction indicator lamp (1)
in the combination meter and its circuit.
• If the above areas of Engine and Emission control system is free from any trouble after the engine start
(while engine is running), malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turns OFF. • When ECM detects a trouble which has occurred in
the above areas, it makes malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turn ON while the engi ne is running to warn the
driver of such occurrence of trouble and at the same
time it stores the trouble area in ECM back-up
memory. (The memory is kept as it is even if the
trouble was only temporary and disappeared
immediately. And it is not erased unless the power to
ECM is shut off for specified time or it is cleared by
SUZUKI scan tool (2).)
For Hong Kong model, DTC can be read by not only
using SUZUKI scan tool but also displayed on
odometer (5) of the combination meter. (i.e. when
diagnosis switch terminal (3) is grounded with a
service wire (4) and ignition switch is turned ON.) For
further detail of the checking procedure, refer to “DTC
Check”.
6. Diagnosis connector
2
1
6 3
5
4
I5RS0C110021-01
Page 370 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1F-7 Engine Cooling System:
Cooling System Flush and RefillS7RS0B1606005
WARNING!
To help avoid danger of being burned, do not
remove radiator cap while engine and
radiator are still hot. Scalding fluid and steam
can be blown out under pressure if cap is
taken off too soon.
NOTE
For detail of coolant specification, refer to
“Coolant Description”.
1) Remove radiator cap when engine is cool as follows.a) Turn cap counterclockwise slowly until it reaches a “stop” (Do not press down while turning it).
b) Wait until pressure is relieved (indicated by a hissing sound) then press down on cap and
continue to turn it counterclockwise.
2) With radiator cap removed, run engine until upper radiator hose is hot (this shows that thermostat is
open and coolant is flowing through system).
3) Stop engine and drain coolant from radiator drain plug (1).
4) Close radiator drain plug. Add water until system is filled and run engine until up per radiator hose is hot
again.
5) Repeat Steps 3) and 4) several times until drained liquid is nearly colorless.
6) Close radiator drain plug (1) tightly. 7) Remove reservoir (1) and remove cap (2) from
reservoir (1).
8) Pour out any fluid, scrub and clean inside of reservoir with soap and water.
Flush it well with clean water and drain, Reinstall
reservoir.
9) Fill reservoir with coolant up to “Full” level mark (3).
10) Install reservoir cap (2) on reservoir. 11) Fill radiator with coolant up to bottom of radiator filler neck and install radiator cap, making sure that the
ear of cap lines is parallel to radiator.
12) Run engine at idle speed.
13) Run engine until radiator fan motor is operated.
14) Stop engine and wait until engine comes cooled down to help avoid danger of being burned.
15) Add coolant to radiator up to bottom of radiator filler
neck, and install radiator ca p, making sure that the
ear of cap lines is parallel to radiator.
16) Repeat Step 12) through 15).
17) Confirm that reservoir cool ant level is “Full” level
mark (3). If coolant is insu fficient, repeat Step 9) and
10).
Cooling Water Pipes or Hoses Removal and
Installation
S7RS0B1606006
Removal
1) Drain coolant referring to “Cooling System Draining”.
2) To remove these pipes or hoses, loosen clamp on each hose and pull hose end off.
Installation
Install removed parts in reverse order of removal
procedure, noting the following.
• Tighten each clamp securely referring to “Cooling System Components”.
• Refill cooling system referrin g to Step 7) to 22) of
“Cooling System Flush and Refill”.
1I4RS0A160003-01
1
2
1
3
2
I7RS0B160005-01
Page 376 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1G-1 Fuel System:
Engine
Fuel System
Precautions
Precautions on Fuel System ServiceS7RS0B1700001
WARNING!
Before attempting service of any type on fuel system, the following should be always observed in
order to reduce the risk of fire and personal injury.
• Disconnect negative cable at battery.
• Do not smoke, and place no smoking signs near work area.
• Be sure to have CO
2 fire extinguisher handy.
• Be sure to perform work in a well-ventilated area and away from any open flames (such as gas hot heater).
• Wear safety glasses.
• To relieve fuel vapor pressure in fuel tank, remove fuel filler cap from fuel filler neck and then
reinstall it.
• As fuel feed line is still under high fuel pr essure even after stopping engine, loosening or
disconnecting fuel feed line directly may cause dangerous spout of fuel. Before loosening or
disconnecting fuel feed line, make sure to relieve fuel pressure referring to “Fuel Pressure Relief
Procedure”.
• A small amount of fuel may be released when the fuel line is disconnected. In order to reduce the risk of personal injury, cover a shop cloth to the fitting to be disconnected. Be sure to put that cloth
in an approved container after disconnecting.
• Never run engine with fuel pump relay disconnected when engine and exhaust system are hot.
• Note that fuel hose connection varies with each type of pipe. Be sure to connect and clamp each hose correctly referring to “Fuel Hose Disconnecting and Reconnecting”.
After connecting, make sure that it has no twist or kink.
• When installing inje ctor or fuel feed pipe, lubr icate its O-ring with gasoline.
General Description
Fuel System DescriptionS7RS0B1701001
CAUTION!
This engine requires the unleaded fuel only.
The leaded and/or low lead fuel can result in
engine damage and reduce the effectiveness
of the emission control system.
The main components of the fuel system are fuel tank,
fuel pump assembly (with fuel filter, fuel level gauge, fuel
pressure regulator, fuel feed line and fuel vapor line.
For the details of fuel flow, refer to “Fuel Delivery System
Diagram”.
Fuel Delivery System DescriptionS7RS0B1701002
The fuel delivery system consists of the fuel tank, fuel
pump assembly (with built-in f uel filter and fuel pressure
regulator), delivery pipe, injectors and fuel feed line.
The fuel in the fuel tank is pumped up by the fuel pump,
sent into delivery pipe and injected by the injectors.
As the fuel pump assembly is equipped with built-in fuel
filter and fuel pressure regulator, the fuel is filtered and
its pressure is regulated before being sent to the feed
pipe.
The excess fuel at fuel pressure regulation process is
returned back into the fuel tank.
Also, fuel vapor generated in fuel tank is led through the
fuel vapor line into the EVAP canister.
For system diagram, refer to “Fuel Delivery System
Diagram”.
Page 461 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Rear Suspension: 2C-7
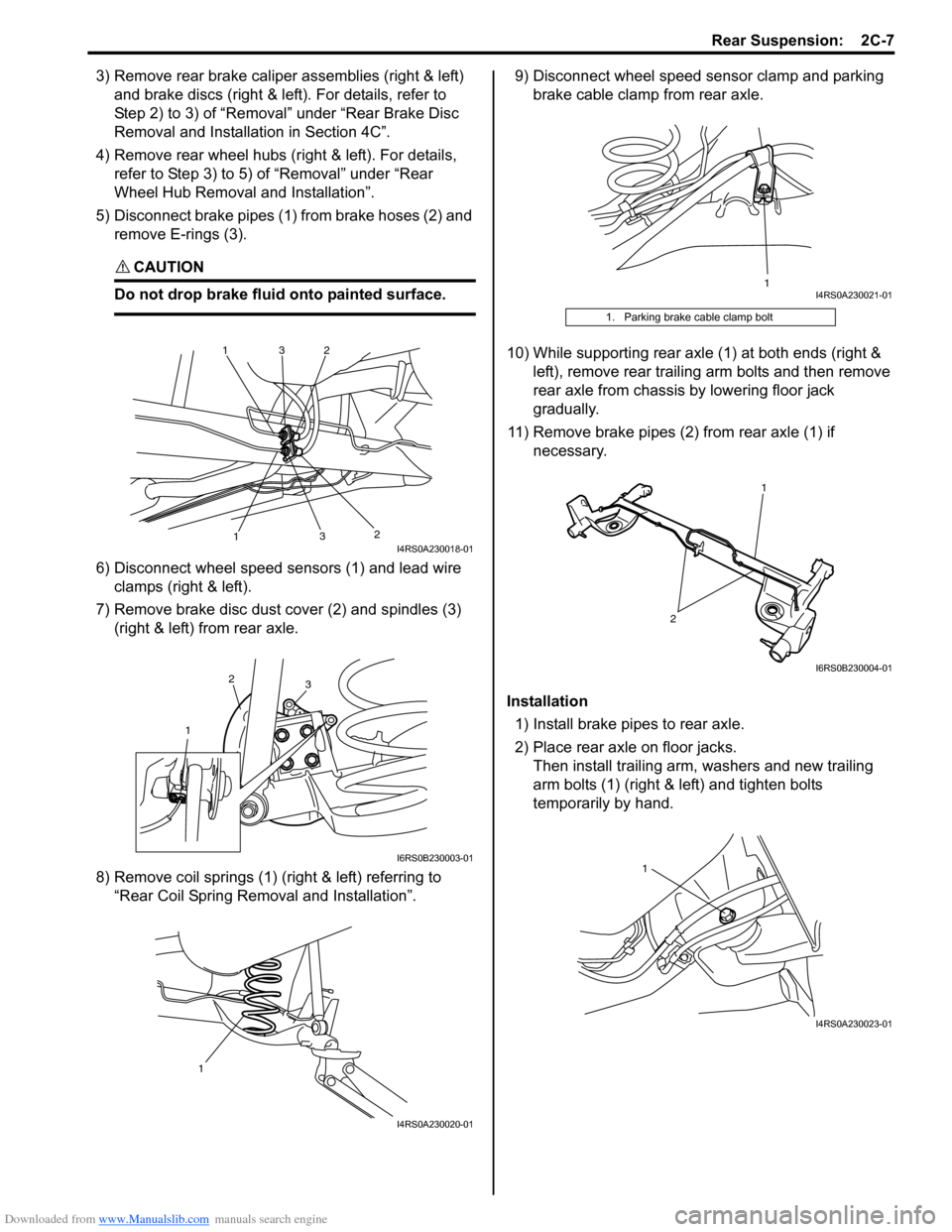
3) Remove rear brake caliper assemblies (right & left)
and brake discs (right & left ). For details, refer to
Step 2) to 3) of “Removal” under “Rear Brake Disc
Removal and Installa tion in Section 4C”.
4) Remove rear wheel hubs (r ight & left). For details,
refer to Step 3) to 5) of “Removal” under “Rear
Wheel Hub Removal and Installation”.
5) Disconnect brake pipes (1) from brake hoses (2) and remove E-rings (3).
CAUTION!
Do not drop brake fluid onto painted surface.
6) Disconnect wheel speed sensors (1) and lead wire clamps (right & left).
7) Remove brake disc dust cover (2) and spindles (3) (right & left) from rear axle.
8) Remove coil springs (1) (right & left) referring to “Rear Coil Spring Removal and Installation”. 9) Disconnect wheel speed sensor clamp and parking
brake cable clamp from rear axle.
10) While supporting rear axle (1) at both ends (right & left), remove rear trailing arm bolts and then remove
rear axle from chassis by lowering floor jack
gradually.
11) Remove brake pipes (2) from rear axle (1) if necessary.
Installation 1) Install brake pipes to rear axle.
2) Place rear axle on floor jacks. Then install trailing arm, washers and new trailing
arm bolts (1) (right & left) and tighten bolts
temporarily by hand.
1
1
2
2
3
3I4RS0A230018-01
1
2
3
I6RS0B230003-01
1
I4RS0A230020-01
1. Parking brake cable clamp bolt
1I4RS0A230021-01
2
1
I6RS0B230004-01
1
I4RS0A230023-01
Page 579 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-5
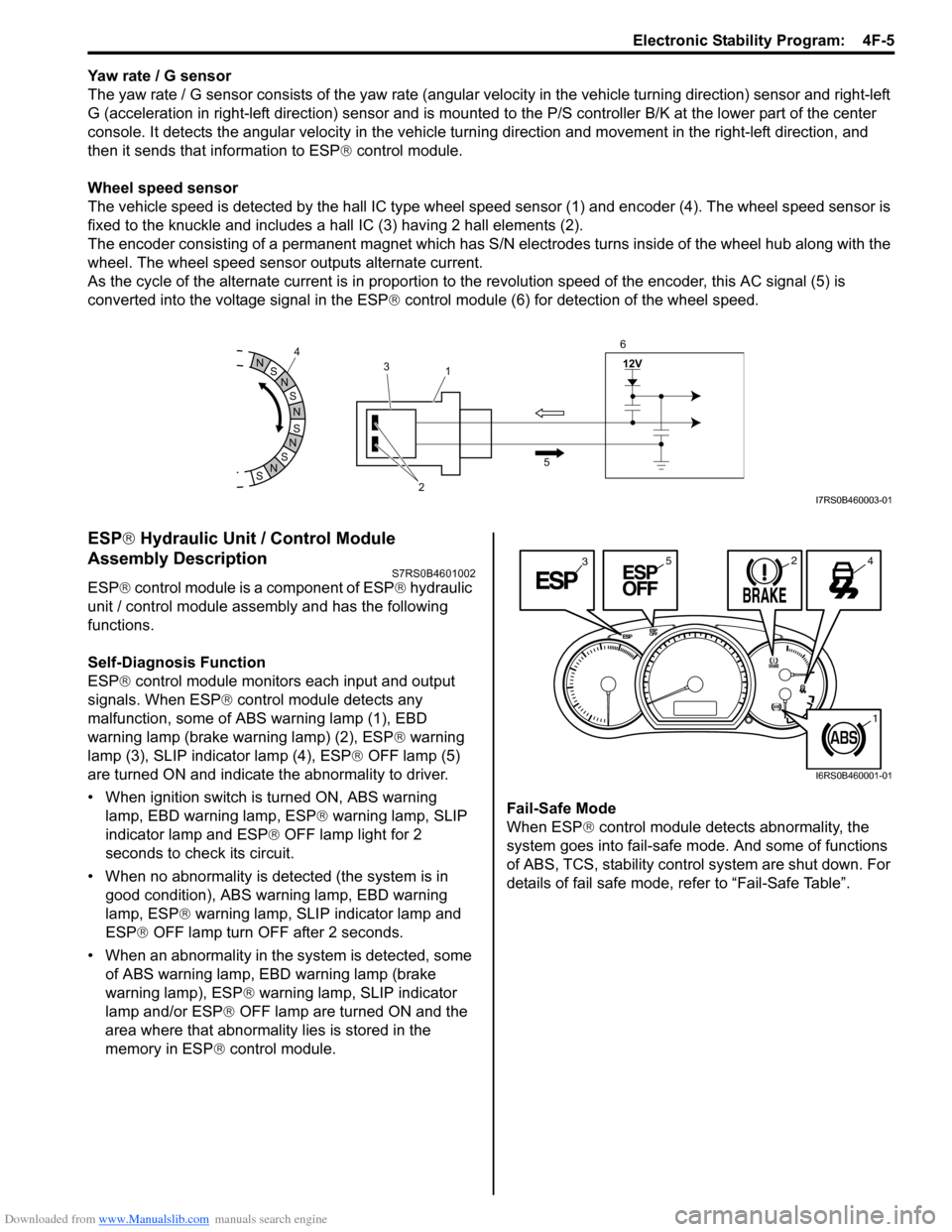
Yaw rate / G sensor
The yaw rate / G sensor consists of the yaw rate (angular velocity in the vehicle turning direction) sensor and right-left
G (acceleration in right-left direction) sensor and is mounted to the P/S controller B/K at the lower part of the center
console. It detects the angular velocity in the vehicle turn ing direction and movement in the right-left direction, and
then it sends that information to ESP ® control module.
Wheel speed sensor
The vehicle speed is detected by the hall IC type wheel speed sensor (1) and encoder (4). The wheel speed sensor is
fixed to the knuckle and includes a hall IC (3) having 2 hall elements (2).
The encoder consisting of a permanent ma gnet which has S/N electrodes turns inside of the wheel hub along with the
wheel. The wheel speed sensor outputs alternate current.
As the cycle of the alternate current is in proportion to the revolution speed of the encoder, this AC signal (5) is
converted into the voltage signal in the ESP ® control module (6) for detection of the wheel speed.
ESP ® Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly Description
S7RS0B4601002
ESP ® control module is a component of ESP ® hydraulic
unit / control module assembly and has the following
functions.
Self-Diagnosis Function
ESP ® control module monitors each input and output
signals. When ESP ® control module detects any
malfunction, some of ABS warning lamp (1), EBD
warning lamp (brake warning lamp) (2), ESP ® warning
lamp (3), SLIP indicator lamp (4), ESP ® OFF lamp (5)
are turned ON and indicate the abnormality to driver.
• When ignition switch is turned ON, ABS warning lamp, EBD warning lamp, ESP ® warning lamp, SLIP
indicator lamp and ESP ® OFF lamp light for 2
seconds to check its circuit.
• When no abnormality is detected (the system is in good condition), ABS warning lamp, EBD warning
lamp, ESP ® warning lamp, SLIP indicator lamp and
ESP ® OFF lamp turn OFF after 2 seconds.
• When an abnormality in the system is detected, some of ABS warning lamp, EBD warning lamp (brake
warning lamp), ESP ® warning lamp, SLIP indicator
lamp and/or ESP ® OFF lamp are turned ON and the
area where that abnormality lies is stored in the
memory in ESP ® control module. Fail-Safe Mode
When ESP
® control module detects abnormality, the
system goes into fail-safe mode. And some of functions
of ABS, TCS, stability control system are shut down. For
details of fail safe mode, re fer to “Fail-Safe Table”.
S
N
S
N
S
N
N
S
N
S
12V
2
3
1
5
4
6I7RS0B460003-01
3245
1
I6RS0B460001-01
Page 589 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-15
EBD Warning Lamp (Brake Warning Lamp)
Check
S7RS0B4604047
NOTE
Perform this check on a level place.
1) Turn ignition switch ON with parking brake applied.
2) Check that EBD warning lamp (brake warning lamp)
(1) is turned ON.
3) Release parking brake with ignition switch ON and check that EBD warning lamp (brake warning lamp)
goes off.
If it doesn't go off, go to “EBD Warning Lamp (Brake
Warning Lamp) Comes ON Steady”.
DTC CheckS7RS0B4604004
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector (1).
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
3) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
4) Read DTC according to instructions displayed on
SUZUKI scan tool and print it or write it down. Refer
to SUZUKI scan tool operator’s manual for further
details.
NOTE
If SUZUKI scan tool can not communicate
ESP® control module, perform “Serial Data
Link Circuit Check”.
5) After completing the check, turn ignition switch off and disconnect SUZUKI scan tool from DLC.
DTC TableS7RS0B4604005
CAUTION!
Be sure to perform “Electronic Stability Program System Check” before starting diagnosis.
BRAKE
1
I4RS0A450008-01
(A)
1
I4RS0B450003-01
DTC (displayed
on SUZUKI scan tool) Diagnostic Items
Detecting condition (DTC will
beset when detecting) ABS
warning lamp EBD
warning lamp ESP
®
warning lamp
NO DTC Normal — — — —
�) C1016 Stop lamp switch failure Vehicle behavior and stop lamp
switch signal is disagreed for
specified time.———
�) C1017 Lateral G sensor range /
performance Lateral G sensor signal is out of
specified range.
——
�{
�) C1018 Brake fluid level switch
failure • Brake fluid level is too low.
• Input signal of brake fluid level
switch to BCM is low level. ——
�{
�) C1020 Master cylinder pressure
sensor power supply failure Power supply volt
age to master
cylinder pressure sensor in ESP ®
hydraulic unit / control module
assembly is out of specification. ——
�{
�) C1021 Right-front wheel speed
sensor circuit failure Wheel sensor signal is out of
specified range.
�{
*1 �{
Page 745 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-101
Pressure Control Solenoid Valves (Pressure
Control Solenoid and TCC Pressure Control
Solenoid) Removal and Installation
S7RS0B5106024
Removal1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Lift up vehicle.
3) Remove drain plug and drain A/T fluid.
4) Install drain plug.
Tightening torque
A/T fluid drain plug: 17 N·m (1.7 kgf-m, 12.5 lb-ft)
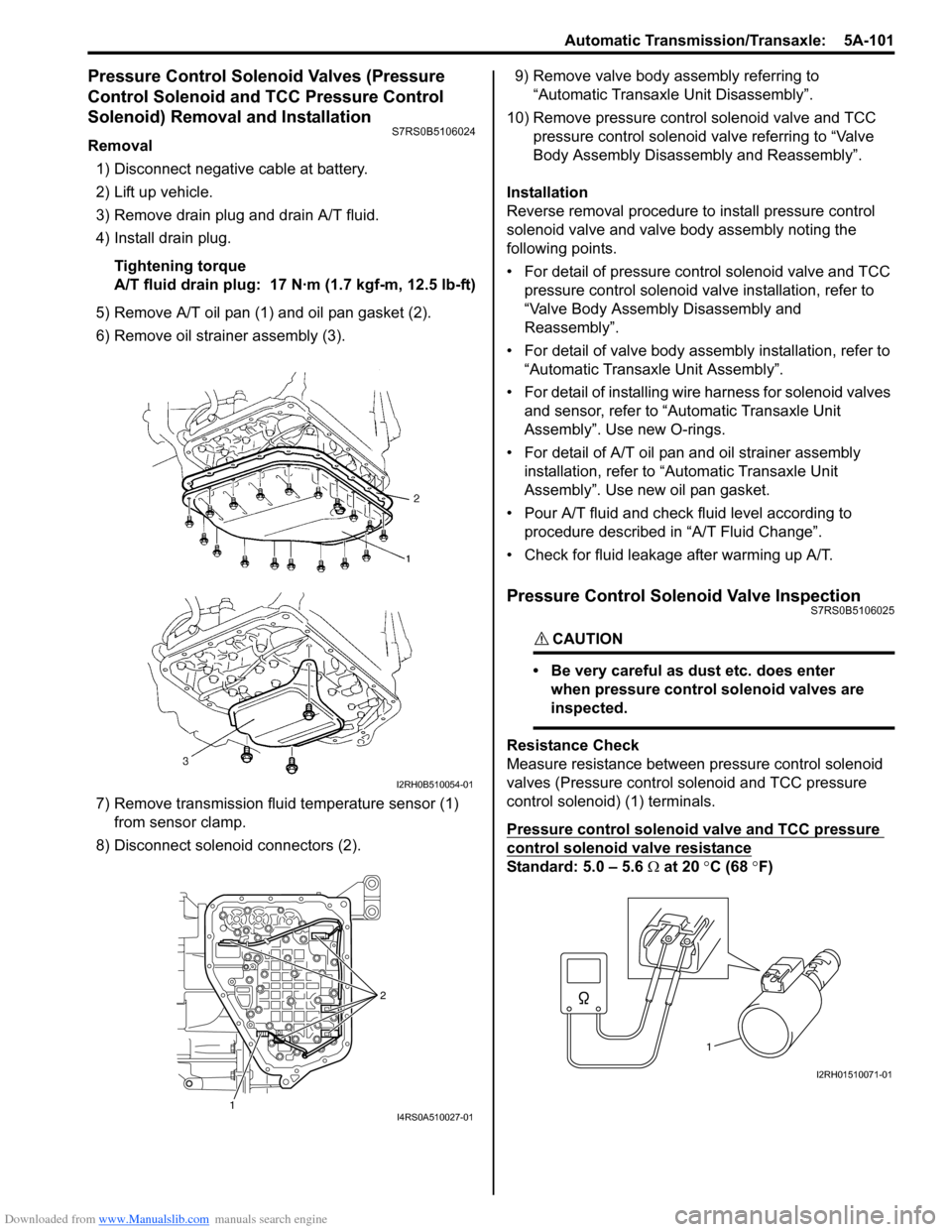
5) Remove A/T oil pan (1) and oil pan gasket (2).
6) Remove oil strain er assembly (3).
7) Remove transmission fluid temperature sensor (1) from sensor clamp.
8) Disconnect solenoid connectors (2). 9) Remove valve body assembly referring to
“Automatic Transaxl e Unit Disassembly”.
10) Remove pressure control solenoid valve and TCC pressure control solenoid valve referring to “Valve
Body Assembly Disassembly and Reassembly”.
Installation
Reverse removal procedure to install pressure control
solenoid valve and valve body assembly noting the
following points.
• For detail of pressure control solenoid valve and TCC pressure control solenoid va lve installation, refer to
“Valve Body Assembly Disassembly and
Reassembly”.
• For detail of valve body asse mbly installation, refer to
“Automatic Transaxle Unit Assembly”.
• For detail of installing wire harness for solenoid valves and sensor, refer to “Automatic Transaxle Unit
Assembly”. Use new O-rings.
• For detail of A/T oil pan and oil strainer assembly
installation, refer to “A utomatic Transaxle Unit
Assembly”. Use new oil pan gasket.
• Pour A/T fluid and check fluid level according to procedure described in “A/T Fluid Change”.
• Check for fluid leakage after warming up A/T.
Pressure Control Solenoid Valve InspectionS7RS0B5106025
CAUTION!
• Be very careful as dust etc. does enter when pressure control solenoid valves are
inspected.
Resistance Check
Measure resistance between pressure control solenoid
valves (Pressure control solenoid and TCC pressure
control solenoid) (1) terminals.
Pressure control solenoid valve and TCC pressure
control solenoid valve resistance
Standard: 5.0 – 5.6 Ω at 20 °C (68 °F)
I2RH0B510054-01
1 2I4RS0A510027-01
1
I2RH01510071-01
Page 985 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Air Conditioning System: Automatic Type 7B-37
On-Board Diagnostic System DescriptionS7RS0B7221007
NOTE
The diagnostic information as diagnostic
trouble code (DTC) can be known by using
SUZUKI scan tool. For further details, refer to
“DTC Check”.
HVAC control module detect s malfunctions, which may
occur in the following area.
• Outside air temperature sensor
• Inside air temperature sensor
• Evaporator temperature sensor
• Sunload sensor
• ECT sensor
• Temperature control actuator of HVAC unit
• Air flow control actuator of HVAC unit
• A/C refrigerant pressure sensor • HVAC control module
• VSS
• Serial Communication line
• CAN communication line
When HVAC control module detects malfunction, the
“AUTO” indicator lamp (1) flashes to warn and the
diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is stored in the memory of
the module. When diagnosing trouble, the DTC can be
checked according to “DTC Check”.
Schematic and Routing Diagram
Major Components of A/C SystemS7RS0B7222001
Refer to “Major Components of A/C System”.
1
I5RS0A722003-01