Oxygen SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 22 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-1 General Information:
General Information
General Information
General Description
AbbreviationsS7RS0B0101001
A:
ABDC: After Bottom Dead Center
ABS: Anti-lock Brake System
AC: Alternating Current
A/C: Air Conditioning
A-ELR: Automatic-Emergency Locking Retractor
A/F: Air Fuel Mixture Ratio
ALR: Automatic Locking Retractor
API: American Petroleum Institute
APP sensor: Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
A/T: Automatic Transmission , Automatic Transaxle
AT D C : After Top Dead Center
ATF: Automatic Transmission Fluid, Automatic
Transaxle Fluid
B:
B+: Battery Positive Voltage
BBDC: Before Bottom Dead Center
BCM: Body Electrical Control Module
BDC: Bottom Dead Center
BTDC: Before Top Dead Center
C:
CAN: Controller Area Network
CKT: Circuit
CKP Sensor: Crankshaft Position Sensor
CMP Sensor: Camshaft Position Sensor
CO: Carbon Monoxide
CPP Switch: Clutch Pedal Position Switch (Clutch
Switch, Clutch Start Switch)
CPU: Central Processing Unit
CRS: Child Restraint System
D:
DC: Direct Current
DLC: Data Link Connector (Assembly Line Diag. Link,
ALDL, Serial Data Link, SDL)
DOHC: Double Over Head Camshaft
DOJ: Double Offset Joint
DRL: Daytime Running Light
DTC: Diagnostic Trouble Code (Diagnostic Code)
E:
EBCM: Electronic Brake Cont rol Module, ABS Control
Module
EBD: Electronic Brake Force Distribution
ECM: Engine Control Module
ECT Sensor: Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (Water Temp. Sensor, WTS)
EFE Heater: Early Fuel Evaporation Heater (Positive
Temperature Coefficient, PTC Heater)
EGR: Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EGRT Sensor: EGR Temperature Sensor (Recirculated
Exhaust Gas Temp. Sensor, REGTS)
ELR: Emergency Locking Retractor
ESP ®: Electronic Stability Program
EPS: Electronic Power Steering
EVAP: Evaporative Emission EVAP Canister:
Evaporative Emission Canister
(Charcoal Canister)
F:
4WD: 4 Wheel
Drive
G:
GEN: Generator
GND: Ground
GPS: Global Positioning System
H:
HVAC: Heating, Ventilating and Air Conditioning
HC: Hydrocarbons
HO2S: Heated Oxygen Sensor
I:
IAC Valve: Idle Air Control Valve (Idle Speed Control
Solenoid Valve, ISC Solenoid Valve)
IAT Sensor: Intake Air Temperature Sensor (Air
temperature Sensor, ATS)
ICM: Immobilizer Control Module
IG: Ignition
ISC Actuator: Idle Speed Control Actuator
L:
LH: Left Hand
LHD: Left Hand Drive Vehicle
LSPV: Load Sensing Proportioning Valve
M:
MAF Sensor: Mass Air Flow Sensor (Air Flow Sensor, AFS, Air Flow Meter, AFM)
MAP Sensor: Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
(Pressure Sensor, PS)
Max: Maximum
MFI: Multiport Fuel Injection (Mu ltipoint Fuel Injection)
Min: Minimum
MIL: Malfunction Indicator Lamp (“SERVICE ENGINE
SOON” Light)
M/T: Manual Transmission, Manual Transaxle
N:
NOx: Nitrogen Oxides
O:
OBD: On-Board Diagnostic System (Self-Diagnosis
Function)
O/D: Overdrive
OHC: Over Head Camshaft
O2S: Oxygen Sensor
P:
PCM: Powertrain Control Module
PCV: Positive Crankcase Ventilation
PNP: Park / Neutral Position
P/S: Power Steering
PSP Switch: Power Steering Pressure Switch (P/S
Pressure Switch)
R:
RH: Right Hand
RHD: Right Hand Drive Vehicle
S:
SAE: Society of Automotive Engineers
Page 55 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-5
Freeze frame data clearance:
The freeze frame data is cleared at the same time as
clearance of DTC.
Non-Euro-OBD
ECM diagnosis troubles which may occur in the area
including the following parts w hen the ignition switch is
ON and the engine is running, and indicates the result by
turning on or flashing malfunction indicator lamp (1).
• Heated oxygen sensor
• ECT sensor
•TP sensor
• APP sensor
• MAF sensor
• IAT sensor
• MAP sensor
• CMP sensor
• CKP sensor
• Knock sensor
• Wheel speed sensor (VSS)
• CPU (Central Processing Unit) of ECM
• Oil control valve
• EGR valve
• EVAP canister purge valve
• Ignition coil
• Starter relay
• Radiator fan relay
• CAN communication
• Barometric pressure sensor
• ECM back up power supply
ECM and malfunction indicator lamp (1) operate as
follows.
• Malfunction indicator lamp (1) lights when the ignition switch is turned ON (but t he engine at stop) with the
diagnosis switch terminal ungrounded regardless of
the condition of Engine and Emission control system.
This is only to check the ma lfunction indicator lamp (1)
in the combination meter and its circuit.
• If the above areas of Engine and Emission control system is free from any trouble after the engine start
(while engine is running), malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turns OFF. • When ECM detects a trouble which has occurred in
the above areas, it makes malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turn ON while the engi ne is running to warn the
driver of such occurrence of trouble and at the same
time it stores the trouble area in ECM back-up
memory. (The memory is kept as it is even if the
trouble was only temporary and disappeared
immediately. And it is not erased unless the power to
ECM is shut off for specified time or it is cleared by
SUZUKI scan tool (2).)
For Hong Kong model, DTC can be read by not only
using SUZUKI scan tool but also displayed on
odometer (5) of the combination meter. (i.e. when
diagnosis switch terminal (3) is grounded with a
service wire (4) and ignition switch is turned ON.) For
further detail of the checking procedure, refer to “DTC
Check”.
6. Diagnosis connector
2
1
6 3
5
4
I5RS0C110021-01
Page 62 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-12 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Electronic Control System DescriptionS7RS0B1101011
The electronic control system consists of 1) various sensors which detect the state of engine and driving conditions, 2)
ECM which controls various devices ac cording to the signals from the sensors and 3) various controlled devices.
Functionally, it is divided into the following sub systems:
• Fuel injection control system
• Ignition control system
• Electric throttle body control system
• Fuel pump control system
• Radiator cooling fan control system
• Evaporative emission control system
• EGR system
• Oxygen sensor heater control system
• A/C control system (A/C model)
• Camshaft position control system
• Immobilizer control system
• Generator control system
• Controller (computer) communication system
Especially, ECM, BCM, combination meter, TCM (A/T model), ABS/ESP ® control module, steering angle sensor
(ESP® model) and keyless start control module (if equipped) intercommunicate by means of CAN communication.
Page 66 of 1496
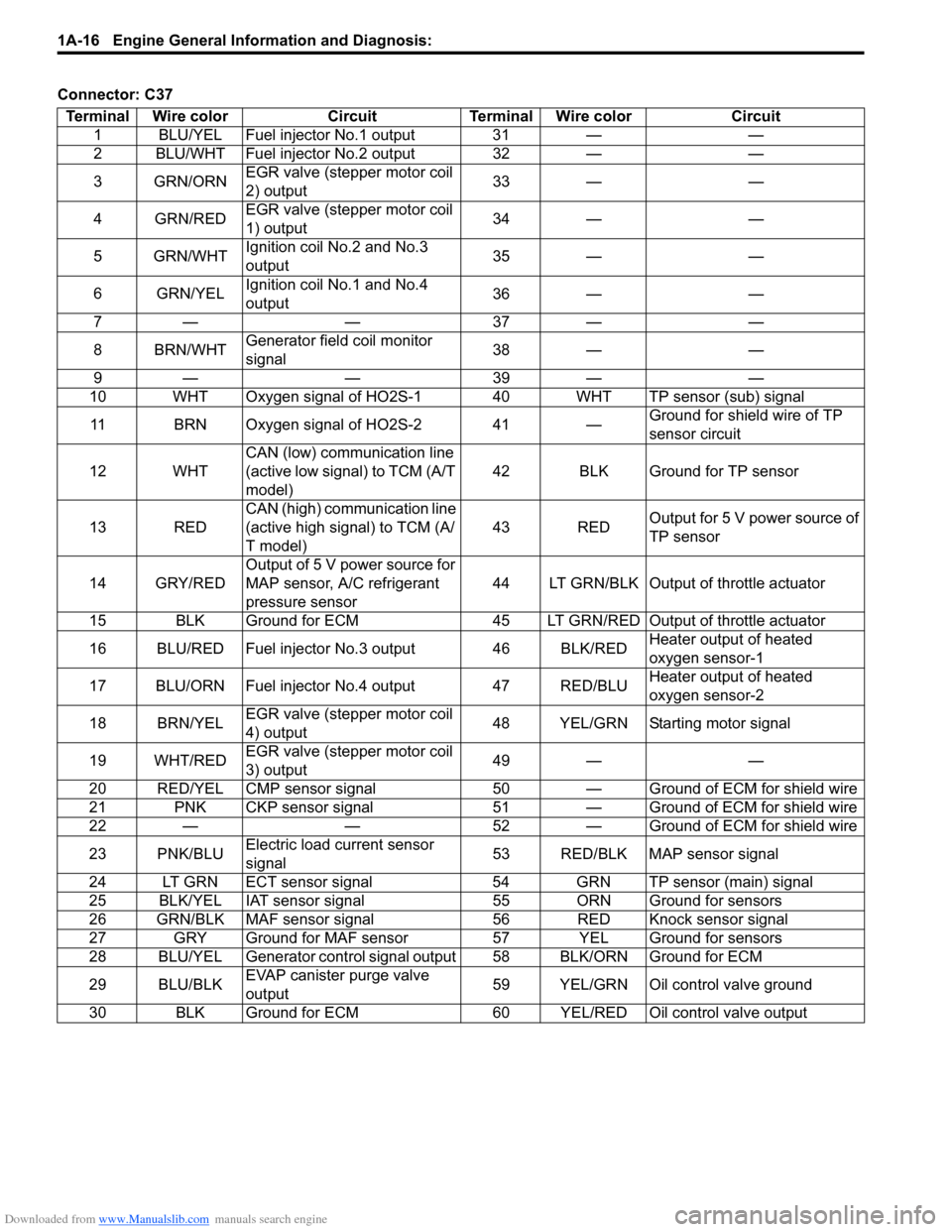
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-16 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Connector: C37Terminal Wire color Circuit Terminal Wire color Circuit 1 BLU/YEL Fuel injector No.1 output 31 — —
2 BLU/WHT Fuel injector No.2 output 32 — —
3GRN/ORN EGR valve (stepper motor coil
2) output 33 — —
4 GRN/RED EGR valve (stepper motor coil
1) output 34 — —
5 GRN/WHT Ignition coil No.2 and No.3
output 35 — —
6 GRN/YEL Ignition coil No.1 and No.4
output 36 — —
7— — 37— —
8 BRN/WHT Generator field coil monitor
signal 38 — —
9— — 39— —
10 WHT Oxygen signal of HO2S-1 40 WHT TP sensor (sub) signal
11 BRN Oxygen signal of HO2S-2 41 — Ground for shield wire of TP
sensor circuit
12 WHT CAN (low) communication line
(active low signal) to TCM (A/T
model) 42 BLK Ground for TP sensor
13 RED CAN (high) communication line
(active high signal) to TCM (A/
T model) 43 RED
Output for 5 V power source of
TP sensor
14 GRY/RED Output of 5 V power source for
MAP sensor, A/C refrigerant
pressure sensor 44 LT GRN/BLK Output of throttle actuator
15 BLK Ground for ECM 45 LT GRN/RE D Output of throttle actuator
16 BLU/RED Fuel injector No.3 output 46 BLK/RED Heater output of heated
oxygen sensor-1
17 BLU/ORN Fuel injector No.4 output 47 RED/BLU Heater output of heated
oxygen sensor-2
18 BRN/YEL EGR valve (stepper motor coil
4) output 48 YEL/GRN Starting motor signal
19 WHT/RED EGR valve (stepper motor coil
3) output 49 — —
20 RED/YEL CMP sensor signal 50 — G round of ECM for shield wire
21 PNK CKP sensor signal 51 — Ground of ECM for shield wire
22 — — 52 — Ground of ECM for shield wire
23 PNK/BLU Electric load current sensor
signal 53 RED/BLK MAP sensor signal
24 LT GRN ECT sensor signal 54 GRN TP sensor (main) signal
25 BLK/YEL IAT sensor signal 55 ORN Ground for sensors
26 GRN/BLK MAF sensor signal 56 RED Knock sensor signal
27 GRY Ground for MAF sensor 57 YEL Ground for sensors
28 BLU/YEL Generator control signal output 58 BLK/ORN Ground for ECM
29 BLU/BLK EVAP canister purge valve
output 59 YEL/GRN Oil control valve ground
30 BLK Ground for ECM 60 YEL/RED Oil control valve output
Page 85 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-35
Scan Tool Data Definitions
COOLANT TEMP (ENGINE COOLANT
TEMPERATURE, °C, °F)
It is detected by engine coolant temp. sensor.
INTAKE AIR TEMP. ( °C, °F)
It is detected by intake air temp. sensor.
ENGINE SPEED (rpm)
It is computed by reference pulses from the camshaft
position sensor.
INJ PULSE WIDTH (FUEL INJECTION PULSE WIDTH,
msec.)
This parameter indicates time of the injector drive (valve
opening) pulse which is output from ECM (but injector
drive time of NO.1 cylinder fo r multiport fuel injection).
DESIRED IDLE (DESIRED IDLE SPEED, rpm)
The Desired Idle Speed is an ECM internal parameter
which indicates the ECM requested idle. If the engine is
not running, this number is not valid.
SHORT FT B1 (SHORT TERM FUEL TRIM, %)
Short term fuel trim valu e represents short term
corrections to the air/fuel mixture computation. A value
of 0 indicates no correction, a value greater than 0
means an enrichment correction, and a value less than 0
implies an enleanment correction. LONG FT B1 (LONG TERM FUEL TRIM, %)
Long term fuel trim value represents long term
corrections to the air/fuel mixture computation. A value
of 0 indicates no correction, a value greater than 0
means an enrichment correction, and a value less than 0
implies an enleanment correction.
TOTAL FUEL TRIM B1 (%)
The value of Total Fuel Trim is obtained by calculating
based on values of Short Term Fuel Trim and Long Term
Fuel Trim. This value indica
tes how much correction is
necessary to keep the air/fuel mixture stoichiometrical.
MAF (MASS AIR FLOW RATE, g/s, lb/min.)
It represents total mass of air entering intake manifold
which is measured by mass air flow sensor.
CALC LOAD (CALCULATED LOAD VALUE, %)
Engine load displayed as a percentage of maximum
possible load. Value is calculated mathematically using
the formula: actual (current) intake air volume ÷
maximum possible intake air volume × 100%
THROTTLE POS (ABSOLUTE THROTTLE POSITION,
%)
When throttle position sensor is at fully closed position,
throttle opening is indicated as 0 – 5% and 90 – 100%
full open position.
O2S SENSOR B1 S1 (HEA TED OXYGEN SENSOR-1,
V)
It indicates output voltage of HO2S-1 installed on
exhaust manifold (pre-catalyst).
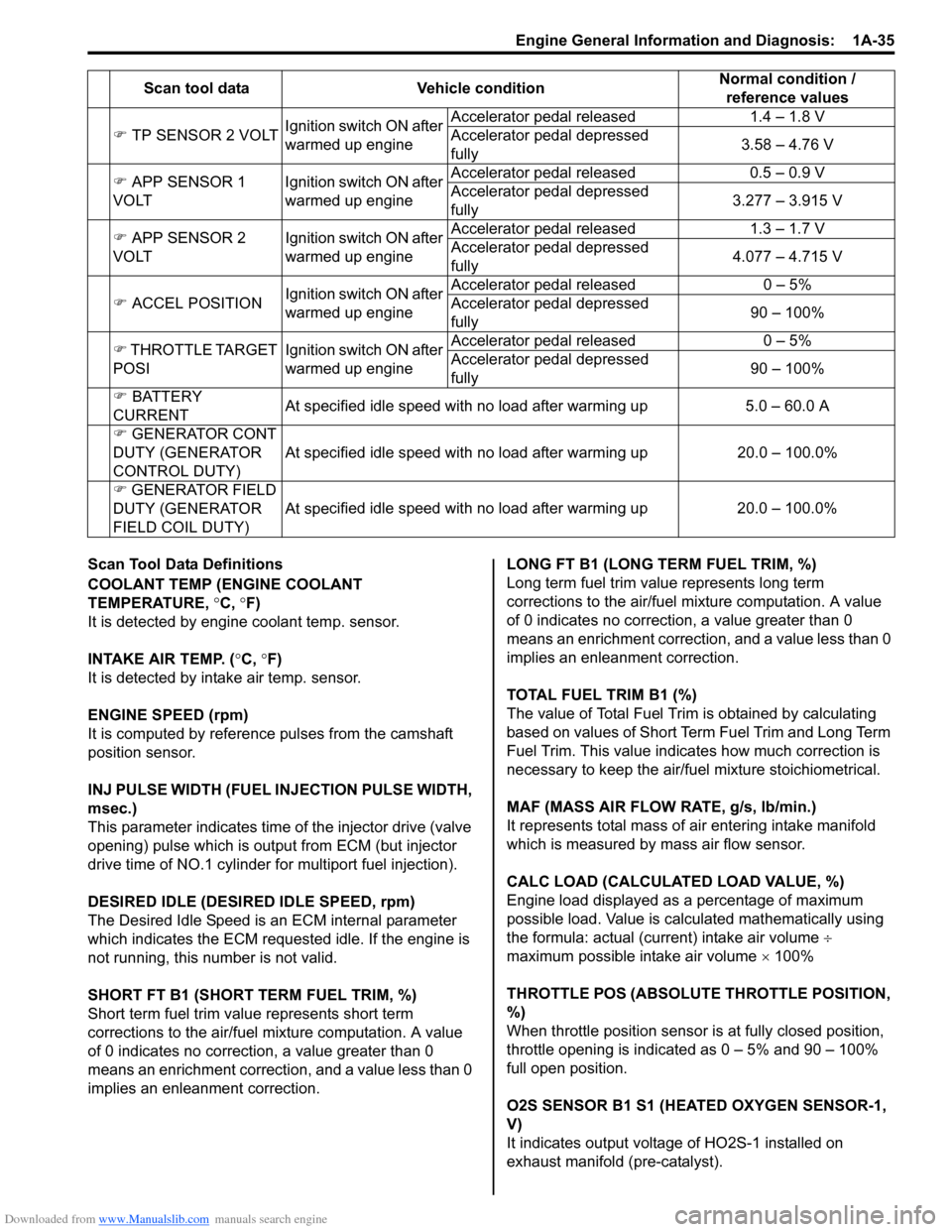
�)
TP SENSOR 2 VOLT Ignition switch ON after
warmed up engine Accelerator pedal released
1.4 – 1.8 V
Accelerator pedal depressed
fully 3.58 – 4.76 V
�) APP SENSOR 1
VOLT Ignition switch ON after
warmed up engineAccelerator pedal released
0.5 – 0.9 V
Accelerator pedal depressed
fully 3.277 – 3.915 V
�) APP SENSOR 2
VOLT Ignition switch ON after
warmed up engineAccelerator pedal released
1.3 – 1.7 V
Accelerator pedal depressed
fully 4.077 – 4.715 V
�) ACCEL POSITION Ignition switch ON after
warmed up engine Accelerator pedal released
0 – 5%
Accelerator pedal depressed
fully 90 – 100%
�) THROTTLE TARGET
POSI Ignition switch ON after
warmed up engineAccelerator pedal released
0 – 5%
Accelerator pedal depressed
fully 90 – 100%
�) BATTERY
CURRENT At specified idle speed with no load after warming up
5.0 – 60.0 A
�) GENERATOR CONT
DUTY (GENERATOR
CONTROL DUTY) At specified idle speed with no load after warming up
20.0 – 100.0%
�) GENERATOR FIELD
DUTY (GENERATOR
FIELD COIL DUTY) At spe
cified idle speed with no load after warming up
20.0 – 100.0%
Scan tool data
Vehicle condition Normal condition /
reference values
Page 86 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-36 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
O2S B1 S1 ACT (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR-1,
ACTIVE / INACTIVE)
This parameter indicates activation condition of HO2S-1.
ACTIVE: Activating
INACTIVE: warming up or at stop
O2S SENSOR B1 S2 (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR-2,
V)
It indicates output voltage of HO2S-2 installed on
exhaust pipe (post-catalyst). It is used to detect catalyst
deterioration.
O2S B1 S2 ACT (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR-2,
ACTIVE / INACTIVE)
This parameter indicates acti vation condition of HO2S-2.
ACTIVE: Activating
INACTIVE: warming up or at stop
FUEL SYSTEM (FUEL SYSTEM STATUS)
Air/fuel ratio feedback loop status displayed as one of
the followings.
OPEN: Open-loop has not yet satisfied conditions to go
closed loop.
CLOSED: Closed-loop using oxygen sensor(s) as
feedback for fuel control.
OPEN-DRIVE COND: Open-loop due to driving
conditions (Power enrichment, etc.).
OPEN SYS FAULT: Open-loop due to detected system
fault.
MAP (MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE, in.Hg,
kPa)
This value indicates how much correction is necessary
to keep the air/fuel mixture stoichiometrical.
It is detected by manifold absolute pressure sensor.
BAROMETRIC PRESS (kPa, in.Hg)
This parameter represents a measurement of barometric
air pressure and is used for al titude correction of the fuel
injection quantity and IAC valve control.
STEP EGR FLOW DUTY (%)
This parameter indicates opening rate of EGR valve
which controls the amount of EGR flow.
FUEL CUT (ON/OFF)
ON: Fuel being cut (output signal to injector is stopped)
OFF: Fuel not being cut
A/C PRESSURE (A/C REFRIGERANT ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE, kPa)
This parameter indicates A/C refrigerant absolute
pressure calculated by ECM.
CLOSED THROTTLE PO S (CLOSED THROTTLE
POSITION, ON/OFF)
This parameter reads ON wh en throttle valve is fully
closed, or OFF when it is not fully closed. CANIST PRG DUTY (EVAP CANISTER PURGE FLOW
DUTY, %)
This parameter indicates valve ON (valve open) time
rate within a certain set cycle of EVAP canister purge
valve which controls the amount of EVAP purge.
IGNITION ADVANCE (IGNITION TIMING ADVANCE
FOR NO.1 CYLINDER,
°)
Ignition timing of No.1 cylinder is commanded by ECM.
The actual ignition timing should be checked by using
the timing light.
BATTERY VOLTAGE (V)
This parameter indicates battery positive voltage
inputted from main relay to ECM.
FUEL PUMP (ON/OFF)
ON is displayed when ECM activates the fuel pump via
the fuel pump relay switch.
ELECTRIC LOAD (ON/OFF)
ON: Headlight or small light ON signal inputted.
OFF: Above electric loads all turned OFF.
BRAKE SW (ON/OFF)
This parameter indicates the state of the brake switch.
RADIATOR COOLING FAN (RADIATOR COOLING
FAN CONTROL RELAY, ON/OFF)
ON: Command for radiator cooling fan control relay
operation being output.
OFF: Command for relay operation not being output.
BLOWER FAN (ON/OFF)
This parameter indicates the state of the blower fan
motor switch.
A/C SWITCH (ON/OFF)
ON: Command for A/C operatio n being output from ECM
to HVAC.
OFF: Command for A/C oper ation not being output.
A/C COMP RELAY (A/C COMPRESSOR RELAY, ON/
OFF)
This parameter indicates the state of the A/C switch.
VEHICLE SPEED (km/h, mph)
It is computed based on pulse signals from vehicle
speed sensor.
VVT GAP (TARGET-ACTUAL POSITION, °)
It is calculated using the formula: target valve timing
advance – actual valve timing advance.
TP SENSOR 1 VOLT (THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
(MAIN) OUTPUT VOLTAGE, V)
The TP sensor (main) reading provides throttle valve
opening information in the form of voltage.
Page 141 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-91
DTC P0133: O2 Sensor (HO2S) Circuit Slow Response (Sensor-1)S7RS0B1104032
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
DTC Confirmation Procedure
WARNING!
• When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic accident and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
• Road test should be carried out by 2 persons, a driver and a tester, on a level road.
NOTE
Check to make sure that following conditions ar e satisfied when using this “DTC Confirmation
Procedure”.
• Intake air temperature at engine start: –10 °C (14 ° F) to 80 °C (176 °F)
• Intake air temperature: –10 °C (14 °F) to 70 °C (158 °F)
• Engine coolant temperature: 70 °C (158 °F) to 150 °C (302 °F)
• Altitude (barometric pressure): 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg, 75 kPa or more)
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect scan tool.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and clear DTC using scan tool.
3) Start engine and warm up to normal operating temperature.
4) Drive vehicle at 40 mph (60 km/h) or higher. (engine speed: 2500 – 3000 r/min.)
5) Keep above vehicle speed for 6 min. or more. (Throt tle valve opening is kept constant in this step.)
6) Release accelerator pedal and with engine brake applied, keep vehicle coasting (with fuel cut for 3 sec. or more)
and then stop vehicle.
7) Check if DTC and pending DTC exist by using scan tool. If not, check if oxygen sensor monitoring test has been
completed by using scan tool. If not in both of above c hecks (i.e., no DTC and pending DTC and oxygen sensor
monitoring test not completed), check vehicle cond ition (environmental) and repeat Step 3) through 6).
DTC Troubleshooting
NOTE
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/ or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors re ferring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm that the trouble has been corrected.
DTC detecting condition Trouble area
Response time (time to change from lean to rich or from rich to lean) of HO2S-1 output
voltage is about 1 sec. at minimum or aver age time of 1 cycle is 5 sec. at minimum.
(*2 driving cycle detection logic, monitoring once per driving cycle) Heated oxygen sensor-1
Step
Action YesNo
1 Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed? Go to Step 2.
Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check”.
2 Is there DTC(s) other than HO2S-1 (DTC P0133)? Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.Replace HO2S-1.
Page 142 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-92 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
DTC P0134: O2 Sensor (HO2S) Circuit No Activity Detected (Sensor-1)S7RS0B1104033
Wiring Diagram
Refer to “DTC P0131 / P0132: O2 Sensor (HO2S) Circuit Low Voltage / High Voltage (Sensor-1)”
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
DTC Confirmation Procedure
WARNING!
• When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic accident and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
• Road test should be carried out by 2 persons, a driver and a tester, on a level road.
NOTE
Check to make sure that following conditions ar e satisfied when using this “DTC Confirmation
Procedure”.
• Intake air temperature at engine start: –10 °C (14 ° F) to 80 °C (176 °F)
• Intake air temperature: –10 °C (14 °F) to 70 °C (158 °F)
• Engine Coolant temperature: 70 °C (158 °F) to 150 °C (302 ° F)
• Altitude (barometric pressure): 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg, 75 kPa or more)
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect scan tool.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and clear DTC using scan tool.
3) Start engine and warm up to normal operating temperature.
4) Drive vehicle at 40 mph (60 km/h) or higher. (engine speed: 2500 – 3000 r/min.)
5) Keep above vehicle speed for 6 min. or more. (Throt tle valve opening is kept constant in this step.)
6) Release accelerator pedal and with engine brake applied, keep vehicle coasting (with fuel cut for 3 sec. or more)
and then stop vehicle.
7) Check if DTC and pending DTC exist by using scan tool. If not, check if oxygen sensor monitoring test has been
completed by using scan tool. If not in both of above c hecks (i.e., no DTC and pending DTC and oxygen sensor
monitoring test not completed), check vehicle cond ition (environmental) and repeat Step 3) through 6).
DTC Troubleshooting
NOTE
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/ or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors re ferring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm that the trouble has been corrected.
DTC detecting condition Trouble area
HO2S voltage is higher than 0.6 V for more than 1 min
continuously after warming up engine or HO2S voltage is lower
than 0.3 V for more than 1 min continuously after warming up
engine.
(2 driving cycle detection logic) •HO2S-1
• HO2S-1 circuit
• Exhaust gas leakage
•ECM
• Air intake system
Step
Action YesNo
1 Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed? Go to Step 2.
Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check”.
Page 148 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-98 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
DTC P0171 / P0172: Fuel System Too Lean / RichS7RS0B1104036
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
DTC Confirmation Procedure
WARNING!
• When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic accident and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
• Road test should be carried out by 2 persons, a driver and a tester, on a level road.
NOTE
Check to make sure that following conditions ar e satisfied when using this “DTC Confirmation
Procedure”.
• Intake air temperature at engine start: –10 °C (14 ° F) to 80 °C (176 °F)
• Intake air temperature: –10 °C (14 °F) to 70 °C (158 °F)
• Engine coolant temperature: 40 °C (104 °F) to 120 °C (248 °F)
• Altitude (barometric pressure): 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg, 75 kPa or more)
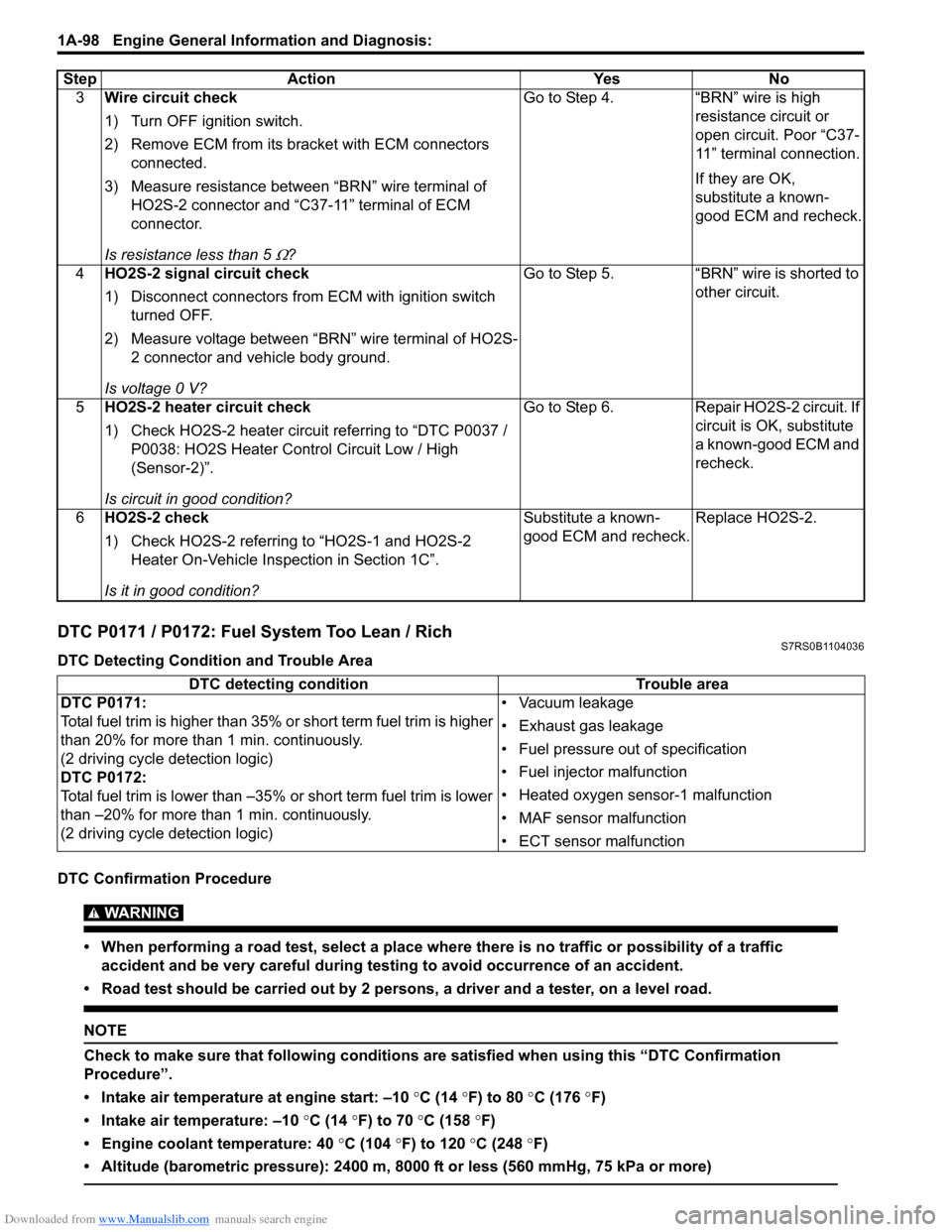
3 Wire circuit check
1) Turn OFF ignition switch.
2) Remove ECM from its br acket with ECM connectors
connected.
3) Measure resistance between “BRN” wire terminal of HO2S-2 connector and “C37-11” terminal of ECM
connector.
Is resistance less than 5
Ω? Go to Step 4. “BRN” wire is high
resistance circuit or
open circuit. Poor “C37-
11” terminal connection.
If they are OK,
substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
4 HO2S-2 signal circuit check
1) Disconnect connectors from ECM with ignition switch
turned OFF.
2) Measure voltage between “BRN” wire terminal of HO2S- 2 connector and vehicle body ground.
Is voltage 0 V? Go to Step 5. “BRN” wire is shorted to
other circuit.
5 HO2S-2 heater circuit check
1) Check HO2S-2 heater circuit referring to “DTC P0037 /
P0038: HO2S Heater Control Circuit Low / High
(Sensor-2)”.
Is circuit in good condition? Go to Step 6. Repair HO2S-2 circuit. If
circuit is OK, substitute
a known-good ECM and
recheck.
6 HO2S-2 check
1) Check HO2S-2 referring to “HO2S-1 and HO2S-2
Heater On-Vehicle Inspection in Section 1C”.
Is it in good condition? Substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
Replace HO2S-2.
Step Action Yes No
DTC detecting condition
Trouble area
DTC P0171:
Total fuel trim is higher than 35% or short term fuel trim is higher
than 20% for more than 1 min. continuously.
(2 driving cycle detection logic)
DTC P0172:
Total fuel trim is lower than –35% or short term fuel trim is lower
than –20% for more than 1 min. continuously.
(2 driving cycle detection logic) • Vacuum leakage
• Exhaust gas leakage
• Fuel pressure out of specification
• Fuel injector malfunction
• Heated oxygen sensor-1 malfunction
• MAF sensor malfunction
• ECT sensor malfunction
Page 170 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-120 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
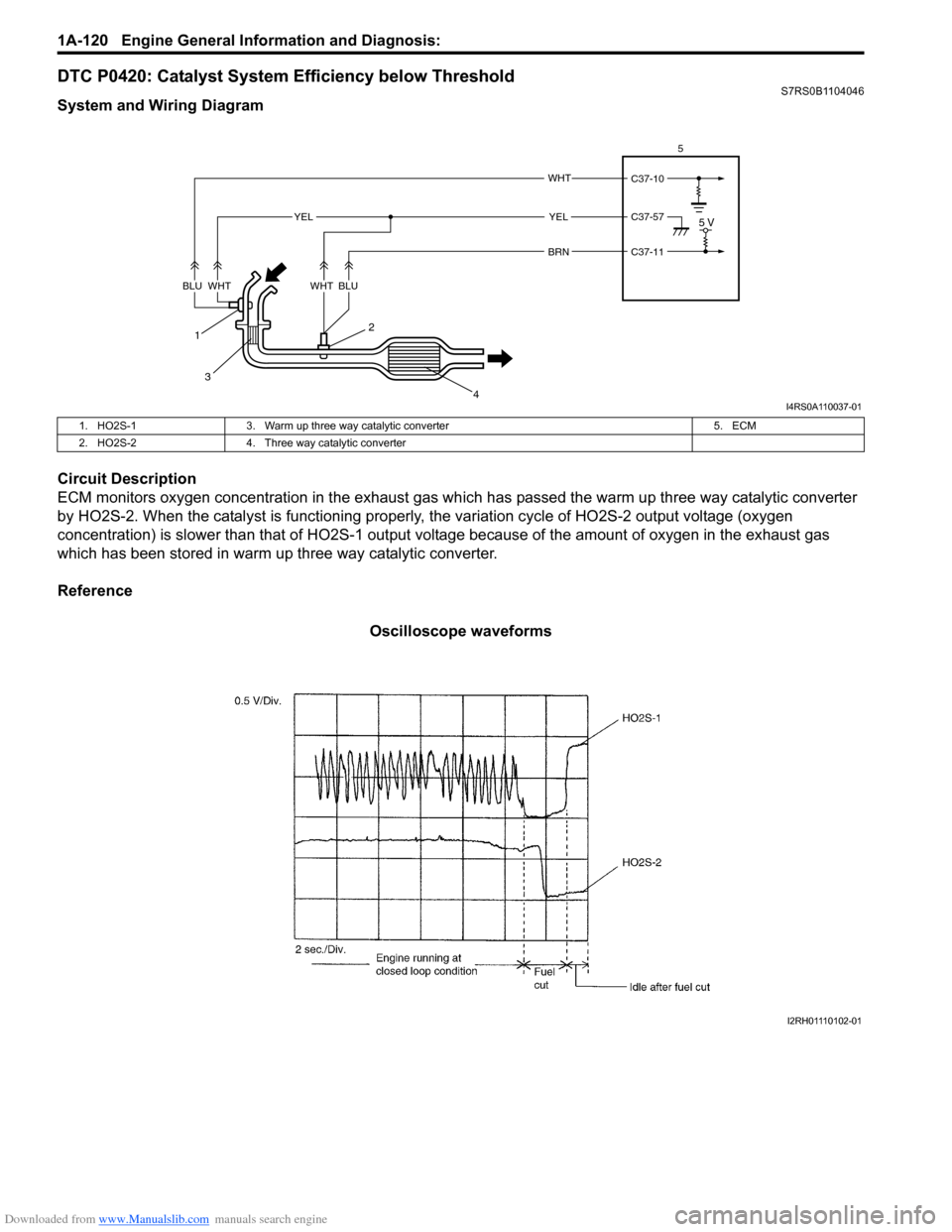
DTC P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency below ThresholdS7RS0B1104046
System and Wiring Diagram
Circuit Description
ECM monitors oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas which has passed the warm up three way catalytic converter
by HO2S-2. When the catalyst is functioning properly, the variation cycle of HO2S-2 output voltage (oxygen
concentration) is slower than that of HO2S-1 output voltage because of the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas
which has been stored in warm up three way catalytic converter.
Reference
Oscilloscope waveforms
C37-11
C37-10
C37-57
WHT
BRN
1
3 2
4
5 VYELYEL
BLUWHTBLUWHT 5
I4RS0A110037-01
1. HO2S-1
3. Warm up three way catalytic converter 5. ECM
2. HO2S-2 4. Three way catalytic converter
I2RH01110102-01