Back up SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.G Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 315 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-30
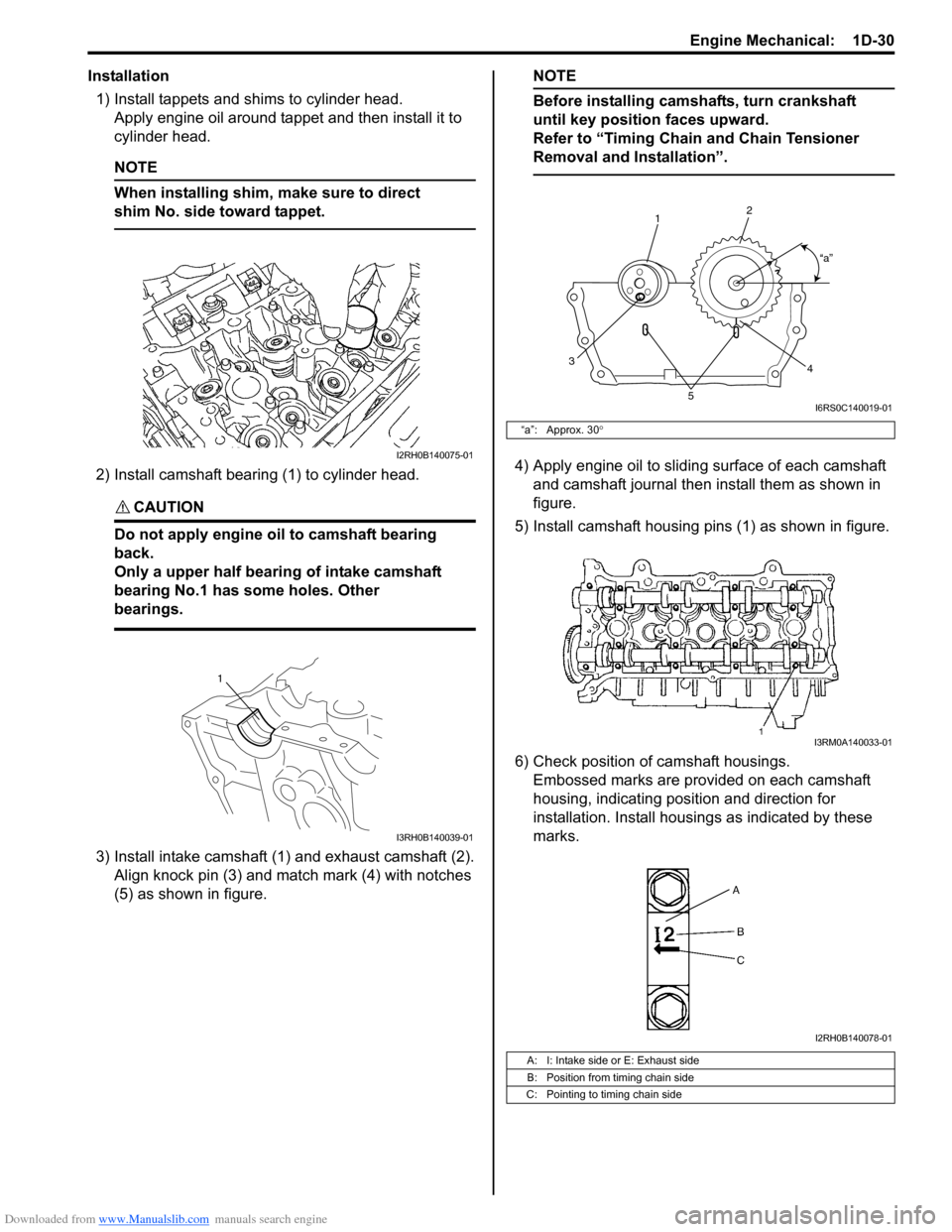
Installation1) Install tappets and shims to cylinder head. Apply engine oil around tappet and then install it to
cylinder head.
NOTE
When installing shim, make sure to direct
shim No. side toward tappet.
2) Install camshaft bearing (1) to cylinder head.
CAUTION!
Do not apply engine oil to camshaft bearing
back.
Only a upper half bearing of intake camshaft
bearing No.1 has some holes. Other
bearings.
3) Install intake camshaft (1) and exhaust camshaft (2). Align knock pin (3) and match mark (4) with notches
(5) as shown in figure.
NOTE
Before installing camshafts, turn crankshaft
until key position faces upward.
Refer to “Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner
Removal and Installation”.
4) Apply engine oil to sliding surface of each camshaft and camshaft journal then install them as shown in
figure.
5) Install camshaft housing pins (1) as shown in figure.
6) Check position of camshaft housings. Embossed marks are provided on each camshaft
housing, indicating position and direction for
installation. Install housings as indicated by these
marks.I2RH0B140075-01
1
I3RH0B140039-01
“a”: Approx. 30 °
A: I: Intake side or E: Exhaust side
B: Position from timing chain side
C: Pointing to timing chain side
1 2
3 4
5
“a”
I6RS0C140019-01
I3RM0A140033-01
I2RH0B140078-01
Page 340 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-55 Engine Mechanical:
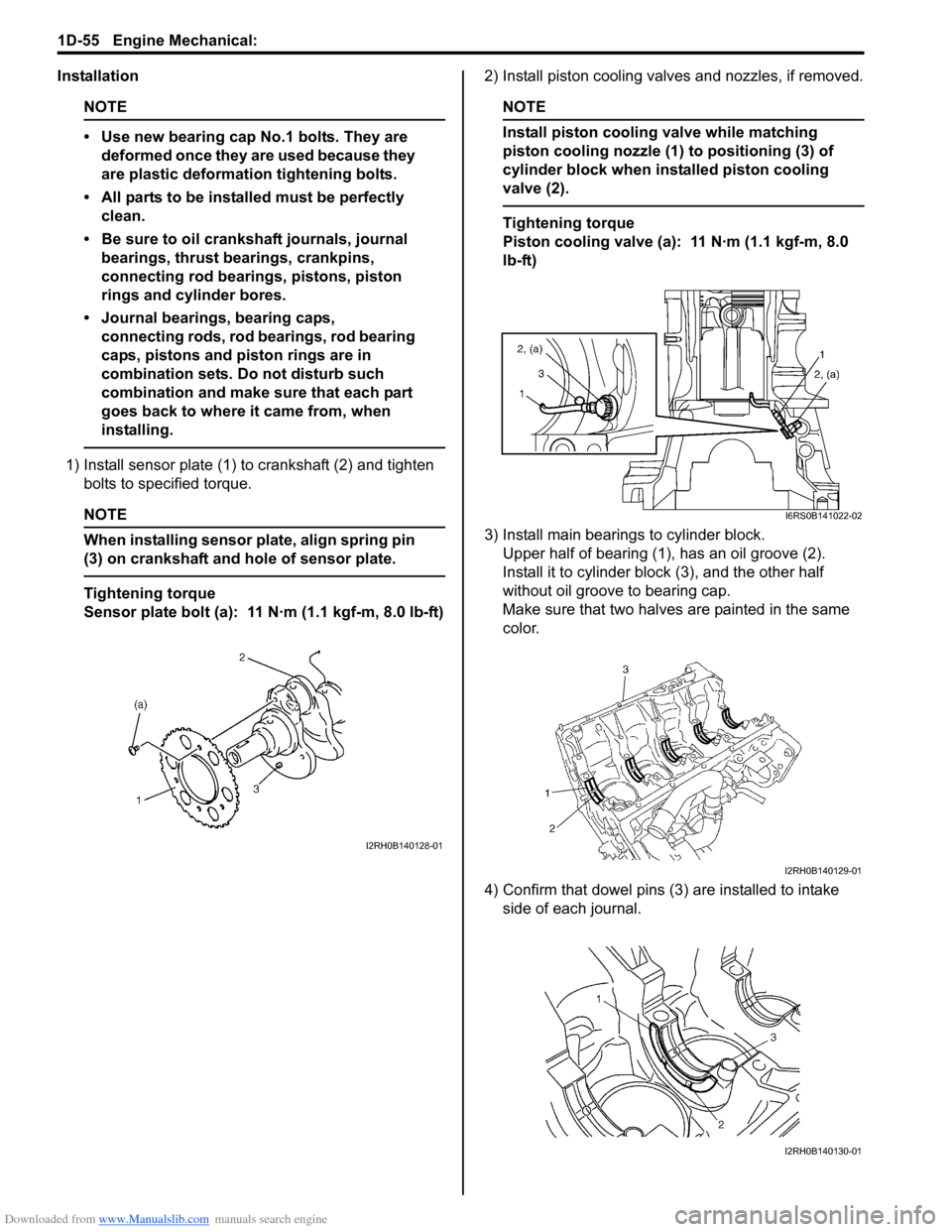
Installation
NOTE
• Use new bearing cap No.1 bolts. They are deformed once they are used because they
are plastic deformation tightening bolts.
• All parts to be insta lled must be perfectly
clean.
• Be sure to oil crankshaft journals, journal bearings, thrust bearings, crankpins,
connecting rod bearings, pistons, piston
rings and cylinder bores.
• Journal bearings, bearing caps, connecting rods, rod bearings, rod bearing
caps, pistons and piston rings are in
combination sets. Do not disturb such
combination and make sure that each part
goes back to where it came from, when
installing.
1) Install sensor plate (1) to crankshaft (2) and tighten bolts to spec ified torque.
NOTE
When installing sensor plate, align spring pin
(3) on crankshaft and hole of sensor plate.
Tightening torque
Sensor plate bolt (a): 11 N·m (1.1 kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft) 2) Install piston cooling valves and nozzles, if removed.
NOTE
Install piston cooling valve while matching
piston cooling nozzle (1) to positioning (3) of
cylinder block when installed piston cooling
valve (2).
Tightening torque
Piston cooling valve (a): 11 N·m (1.1 kgf-m, 8.0
lb-ft)
3) Install main bearings to cylinder block. Upper half of bearing (1), has an oil groove (2).
Install it to cylinder block (3), and the other half
without oil groove to bearing cap.
Make sure that two halves are painted in the same
color.
4) Confirm that dowel pins (3 ) are installed to intake
side of each journal.
I2RH0B140128-01
I6RS0B141022-02
I2RH0B140129-01
I2RH0B140130-01
Page 364 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1F-1 Engine Cooling System:
Engine
Engine Cooling System
General Description
Cooling System DescriptionS7RS0B1601001
The cooling system consists of the radiator cap, radiator, coolant reservoir, hoses, water pump, cooling fan and
thermostat. The radiator is of tube-and-fin type.
Coolant DescriptionS7RS0B1601002
WARNING!
• Do not remove radiator cap to check engine coolant level; check coolant visually at the see-through coolant reservoir. Coolant should be added only to reservoir as necessary.
• As long as there is pressure in the cooling system, the temperature can be considerably higher than the boiling temperature of the solution in the radiator without causing the solution to boil. Removal
of the radiator cap while engine is hot and pressure is high will cause the solution to boil
instantaneously and possibly with explosive force, spewing the solution over engine, fenders and
person removing cap. If the solution contains flammable anti-freeze such as alcohol (not
recommended for use at any time), there is also the possibility of causing a serious fire.
• Check to make sure that engine coolant temperature is cold before removing any part of cooling system.
• Also be sure to disconnect negative cable from battery terminal before removing any part.
The coolant recovery system is standard. The coolant in the radiator expands with heat, and the coolant is overflowed
to the reservoir.
When the system cools down, the coolant is drawn back into the radiator.
The cooling system has be en filled with a quality coolant that is a 50/50 mixture of water and ethylene glycol
antifreeze.
This 50/50 mixture coolant solution provides freezing protection to –36 °C (–33 °F).
• Maintain cooling system freeze protection at –36 °C (–33 °F) to ensure protection against corrosion and loss of
coolant from boiling. This should be done even if freezing temperatures are not expected.
• Add ethylene glycol base coolant when coolant has to be added because of coolant loss or to provide added protection against freezing at temperature lower than –36 °C (–33 °F).
NOTE
• Alcohol or methanol base coolant or plain water alone should not be used in cooling system at any
time as damage to cooling system could occur.
• Coolant must be mixed with deminerated water or distilled water.
Anti-freeze proportioning table
For M/T model For A/T model
Freezing temperature °
C –36 –36
° F –33 –33
Anti-freeze / Anti-corrosion coolant concentration % 50 50
Ratio of compound to cooling water ltr. 3.10/3.10 3.05/3.05
US pt. 6.55/6.55 6.44/6.44
Imp pt. 5.46/5.46 5.37/5.37
Page 376 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1G-1 Fuel System:
Engine
Fuel System
Precautions
Precautions on Fuel System ServiceS7RS0B1700001
WARNING!
Before attempting service of any type on fuel system, the following should be always observed in
order to reduce the risk of fire and personal injury.
• Disconnect negative cable at battery.
• Do not smoke, and place no smoking signs near work area.
• Be sure to have CO
2 fire extinguisher handy.
• Be sure to perform work in a well-ventilated area and away from any open flames (such as gas hot heater).
• Wear safety glasses.
• To relieve fuel vapor pressure in fuel tank, remove fuel filler cap from fuel filler neck and then
reinstall it.
• As fuel feed line is still under high fuel pr essure even after stopping engine, loosening or
disconnecting fuel feed line directly may cause dangerous spout of fuel. Before loosening or
disconnecting fuel feed line, make sure to relieve fuel pressure referring to “Fuel Pressure Relief
Procedure”.
• A small amount of fuel may be released when the fuel line is disconnected. In order to reduce the risk of personal injury, cover a shop cloth to the fitting to be disconnected. Be sure to put that cloth
in an approved container after disconnecting.
• Never run engine with fuel pump relay disconnected when engine and exhaust system are hot.
• Note that fuel hose connection varies with each type of pipe. Be sure to connect and clamp each hose correctly referring to “Fuel Hose Disconnecting and Reconnecting”.
After connecting, make sure that it has no twist or kink.
• When installing inje ctor or fuel feed pipe, lubr icate its O-ring with gasoline.
General Description
Fuel System DescriptionS7RS0B1701001
CAUTION!
This engine requires the unleaded fuel only.
The leaded and/or low lead fuel can result in
engine damage and reduce the effectiveness
of the emission control system.
The main components of the fuel system are fuel tank,
fuel pump assembly (with fuel filter, fuel level gauge, fuel
pressure regulator, fuel feed line and fuel vapor line.
For the details of fuel flow, refer to “Fuel Delivery System
Diagram”.
Fuel Delivery System DescriptionS7RS0B1701002
The fuel delivery system consists of the fuel tank, fuel
pump assembly (with built-in f uel filter and fuel pressure
regulator), delivery pipe, injectors and fuel feed line.
The fuel in the fuel tank is pumped up by the fuel pump,
sent into delivery pipe and injected by the injectors.
As the fuel pump assembly is equipped with built-in fuel
filter and fuel pressure regulator, the fuel is filtered and
its pressure is regulated before being sent to the feed
pipe.
The excess fuel at fuel pressure regulation process is
returned back into the fuel tank.
Also, fuel vapor generated in fuel tank is led through the
fuel vapor line into the EVAP canister.
For system diagram, refer to “Fuel Delivery System
Diagram”.
Page 392 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1G-17 Fuel System:
Special Tools and Equipment
Special ToolS7RS0B1708001
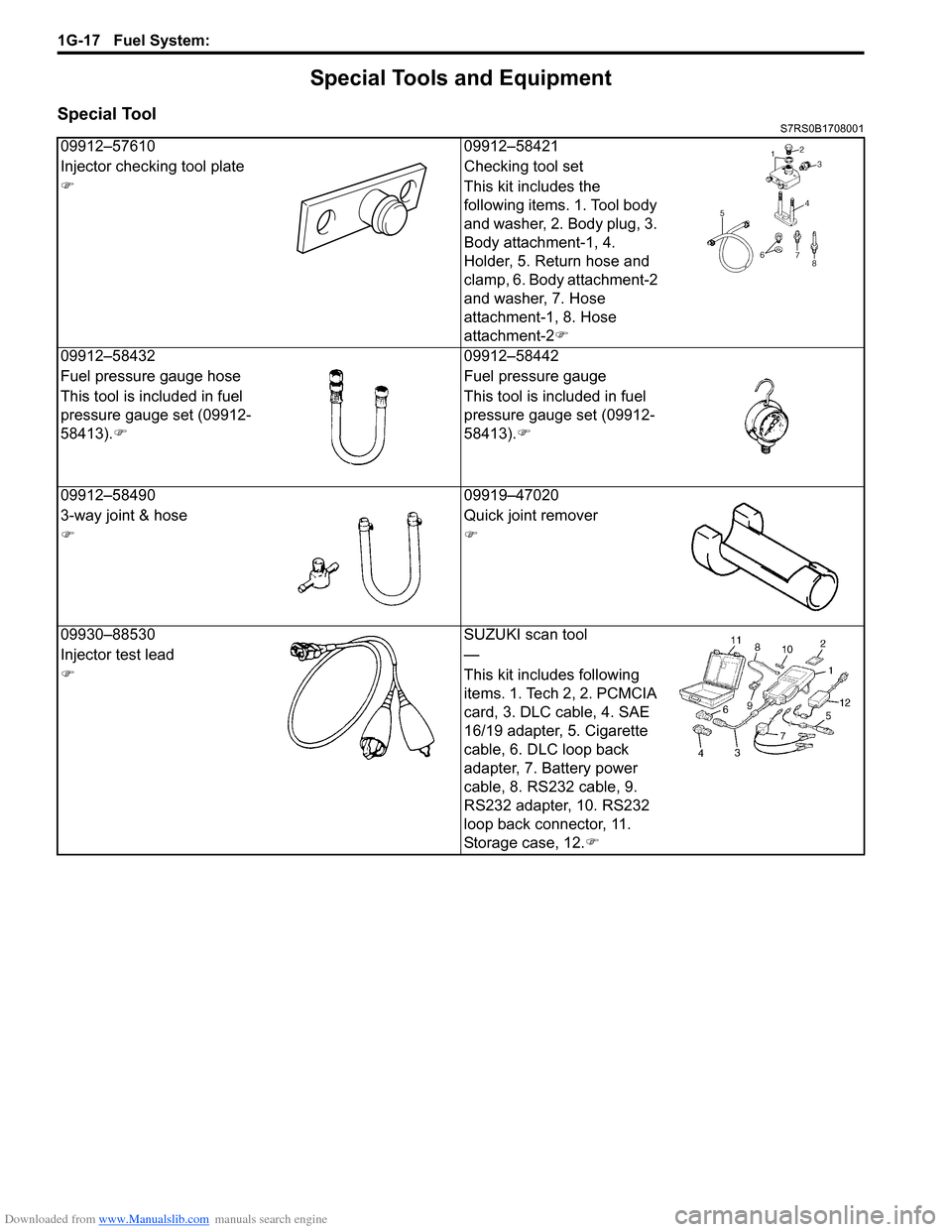
09912–5761009912–58421
Injector checking tool plate Checking tool set
�) This kit includes the
following items. 1. Tool body
and washer, 2. Body plug, 3.
Body attachment-1, 4.
Holder, 5. Return hose and
clamp, 6. Body attachment-2
and washer, 7. Hose
attachment-1, 8. Hose
attachment-2�)
09912–58432 09912–58442
Fuel pressure gauge hose Fuel pressure gauge
This tool is included in fuel
pressure gauge set (09912-
58413). �) This tool is included in fuel
pressure gauge set (09912-
58413).
�)
09912–58490 09919–47020
3-way joint & hose Quick joint remover
�)�)
09930–88530 SUZUKI scan tool
Injector test lead —
�) This kit includes following
items. 1. Tech 2, 2. PCMCIA
card, 3. DLC cable, 4. SAE
16/19 adapter, 5. Cigarette
cable, 6. DLC loop back
adapter, 7. Battery power
cable, 8. RS232 cable, 9.
RS232 adapter, 10. RS232
loop back connector, 11.
Storage case, 12.�)
Page 401 of 1496
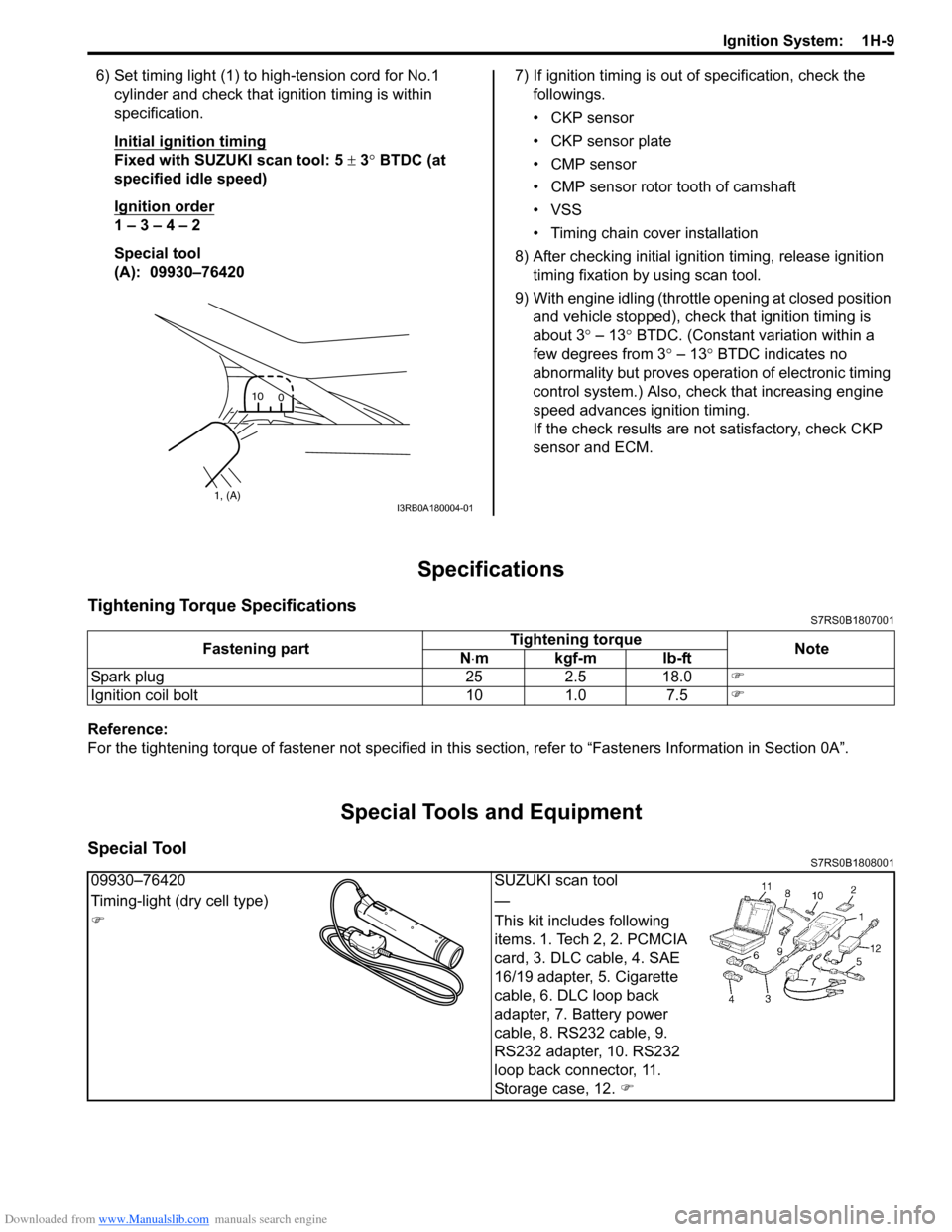
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Ignition System: 1H-9
6) Set timing light (1) to high-tension cord for No.1 cylinder and check that ignition timing is within
specification.
Initial ignition timing
Fixed with SUZUKI scan tool: 5 ± 3° BTDC (at
specified idle speed)
Ignition order
1 – 3 – 4 – 2
Special tool
(A): 09930–76420 7) If ignition timing is out
of specification, check the
followings.
• CKP sensor
• CKP sensor plate
• CMP sensor
• CMP sensor rotor tooth of camshaft
• VSS
• Timing chain cover installation
8) After checking initial igniti on timing, release ignition
timing fixation by using scan tool.
9) With engine idling (throttl e opening at closed position
and vehicle stopped), check that ignition timing is
about 3 ° – 13° BTDC. (Constant variation within a
few degrees from 3 ° – 13° BTDC indicates no
abnormality but proves operation of electronic timing
control system.) Also, check that increasing engine
speed advances ignition timing.
If the check results are not satisfactory, check CKP
sensor and ECM.
Specifications
Tightening Torque SpecificationsS7RS0B1807001
Reference:
For the tightening torque of fastener not specified in this section, refer to “Fasteners Information in Section 0A”.
Special Tools and Equipment
Special ToolS7RS0B1808001
1, (A)10
0I3RB0A180004-01
Fastening part Tightening torque
Note
N ⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
Spark plug 25 2.5 18.0 �)
Ignition coil bolt 10 1.0 7.5 �)
09930–76420SUZUKI scan tool
Timing-light (dry cell type) —
�) This kit includes following
items. 1. Tech 2, 2. PCMCIA
card, 3. DLC cable, 4. SAE
16/19 adapter, 5. Cigarette
cable, 6. DLC loop back
adapter, 7. Battery power
cable, 8. RS232 cable, 9.
RS232 adapter, 10. RS232
loop back connector, 11.
Storage case, 12. �)
Page 411 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Charging System: 1J-1
Engine
Charging System
General Description
Battery DescriptionS7RS0B1A01001
The battery has three major functions in the electrical
system.
• It is a source of electrical energy for cranking the engine.
• It acts as a voltage stabilizer for the electrical system.
• It can, for a limited time, provide energy when the electrical load exceeds the output of the generator.
Carrier and Hold-Down
The battery carrier should be in good condition so that it
will support the battery securely and keep it level. Before
installing the battery, the ba ttery carrier and hold-down
clamp should be clean and free from corrosion and
make certain there are no parts in carrier.
To prevent the battery from shaking in its carrier, the
hold-down bolts should be tight enough but not over-
tightened.
Electrolyte Freezing
The freezing point of electrolyte depends on its specific
gravity. Since freezing may ruin a battery, it should be
protected against freezing by keeping it in a fully
charged condition. If a battery is frozen accidentally, it
should not be charged until it is warmed.
Sulfation
If the battery is allowed to stand for a long period in
discharged condition, the lead sulfate becomes
converted into a hard, cryst alline substance, which will
not easily turn back to the active material again during
the subsequent recharging. “Sulfation” means the result
as well as the process of that reaction. Such a battery
can be revived by very slow charging and may be
restored to usable condition but its capacity is lower than
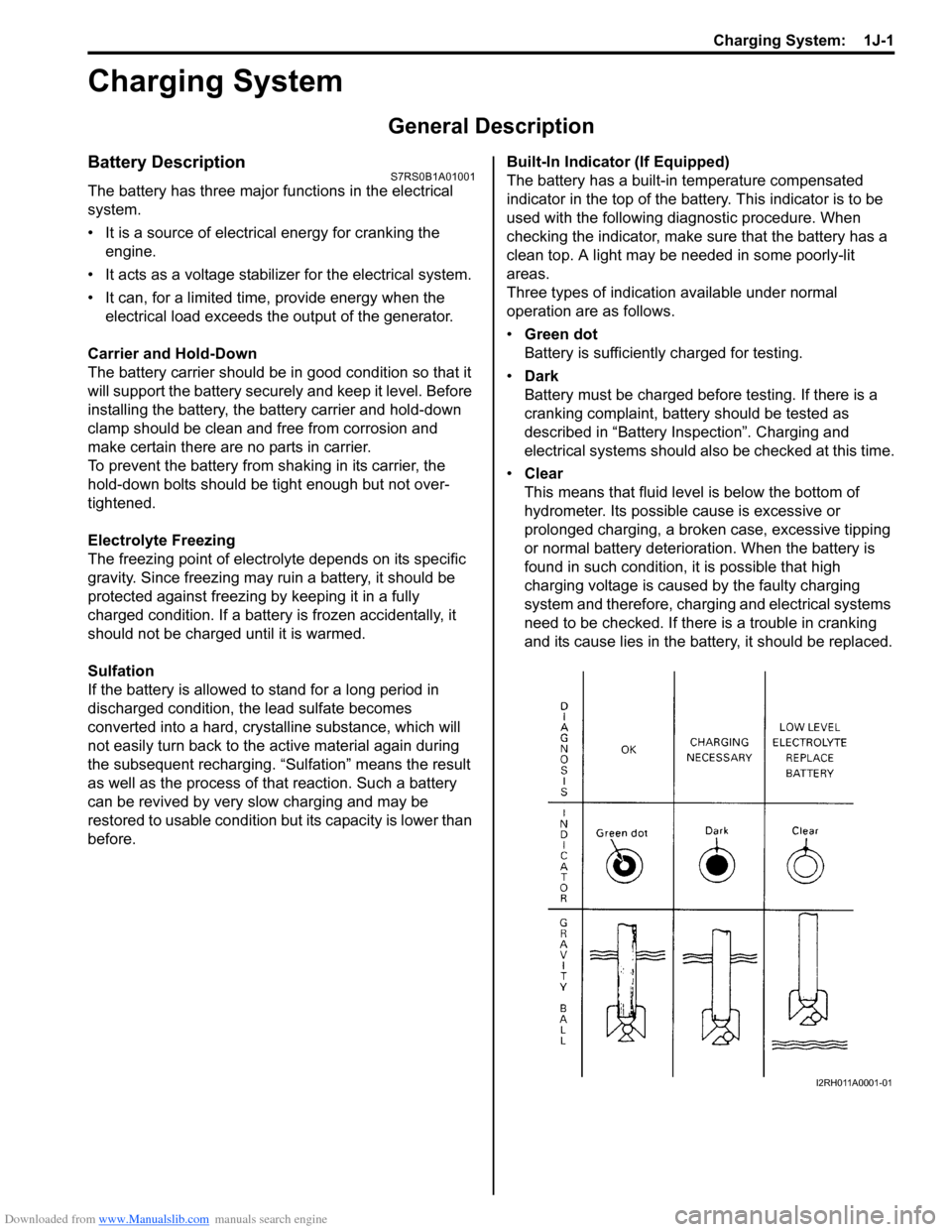
before. Built-In Indicator (If Equipped)
The battery has a built-in temperature compensated
indicator in the top of the battery. This indicator is to be
used with the following diagnostic procedure. When
checking the indicator, make sure that the battery has a
clean top. A light may be needed in some poorly-lit
areas.
Three types of indication available under normal
operation are as follows.
•
Green dot
Battery is sufficiently charged for testing.
• Dark
Battery must be charged before testing. If there is a
cranking complaint, battery should be tested as
described in “Battery Inspection”. Charging and
electrical systems should also be checked at this time.
• Clear
This means that fluid level is below the bottom of
hydrometer. Its possible cause is excessive or
prolonged charging, a broken case, excessive tipping
or normal battery deteriorat ion. When the battery is
found in such condition, it is possible that high
charging voltage is caused by the faulty charging
system and therefore, charging and electrical systems
need to be checked. If there is a trouble in cranking
and its cause lies in the battery, it should be replaced.
I2RH011A0001-01
Page 455 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Rear Suspension: 2C-1
Suspension
Rear Suspension
General Description
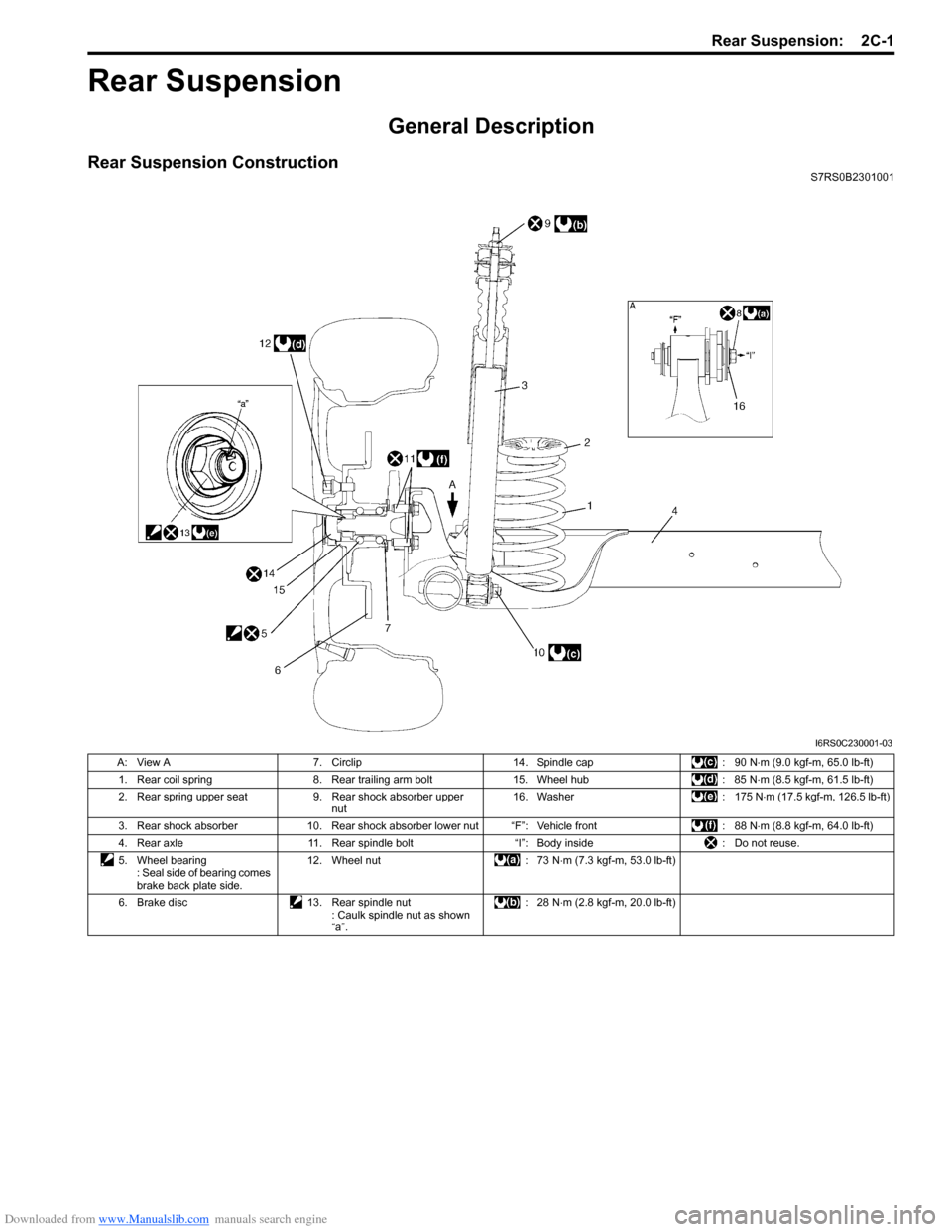
Rear Suspension ConstructionS7RS0B2301001
I6RS0C230001-03
A: View A7. Circlip 14. Spindle cap : 90 N⋅m (9.0 kgf-m, 65.0 lb-ft)
1. Rear coil spring 8. Rear trailing arm bolt 15. Wheel hub : 85 N⋅m (8.5 kgf-m, 61.5 lb-ft)
2. Rear spring upper seat 9. Rear shock absorber upper
nut 16. Washer
: 175 N⋅m (17.5 kgf-m, 126.5 lb-ft)
3. Rear shock absorber 10. Rear shock absorber lower nut “F”: Vehicle front : 88 N⋅m (8.8 kgf-m, 64.0 lb-ft)
4. Rear axle 11. Rear spindle bolt “I”: Body inside : Do not reuse.
5. Wheel bearing : Seal side of bearing comes
brake back plate side. 12. Wheel nut
: 73 N⋅m (7.3 kgf-m, 53.0 lb-ft)
6. Brake disc 13. Rear spindle nut
: Caulk spindle nut as shown
“a”. :28 N
⋅m (2.8 kgf-m, 20.0 lb-ft)
Page 471 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Wheels and Tires: 2D-4
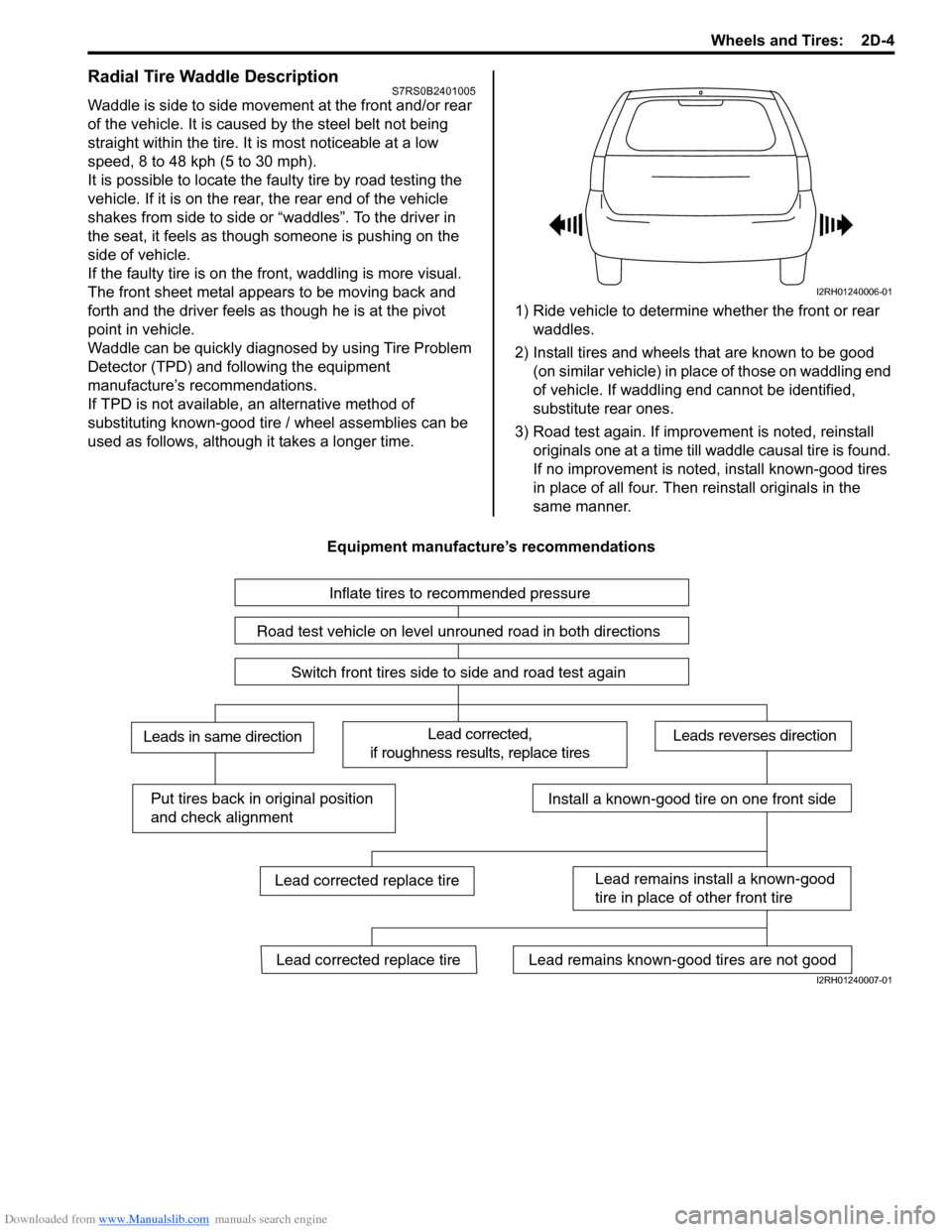
Radial Tire Waddle DescriptionS7RS0B2401005
Waddle is side to side movement at the front and/or rear
of the vehicle. It is caused by the steel belt not being
straight within the tire. It is most noticeable at a low
speed, 8 to 48 kph (5 to 30 mph).
It is possible to locate the f aulty tire by road testing the
vehicle. If it is on the rear , the rear end of the vehicle
shakes from side to side or “waddles”. To the driver in
the seat, it feels as though someone is pushing on the
side of vehicle.
If the faulty tire is on the front, waddling is more visual.
The front sheet metal appears to be moving back and
forth and the driver feels as though he is at the pivot
point in vehicle.
Waddle can be quickly diagnosed by using Tire Problem
Detector (TPD) and following the equipment
manufacture’s recommendations.
If TPD is not available, an alternative method of
substituting known-good tire / wheel assemblies can be
used as follows, although it takes a longer time. 1) Ride vehicle to determine whether the front or rear
waddles.
2) Install tires and wheels that are known to be good (on similar vehicle) in place of those on waddling end
of vehicle. If waddling end cannot be identified,
substitute rear ones.
3) Road test again. If improvement is noted, reinstall originals one at a time till w addle causal tire is found.
If no improvement is noted, install known-good tires
in place of all four. Then reinstall originals in the
same manner.
Equipment manufacture’s recommendations
I2RH01240006-01
Inflate tires to recommended pressure
Road test vehicle on level unrouned road in both directions
Switch front tires side to side and road test again
Lead corrected,
if roughness results, replace tiresLeads in same directionLeads reverses direction
Put tires back in original position
and check alignmentInstall a known-good tire on one front side
Lead remains install a known-good
tire in place of other front tire
Lead remains known-good tires are not goodLead corrected replace tire
Lead corrected replace tire
I2RH01240007-01
Page 504 of 1496
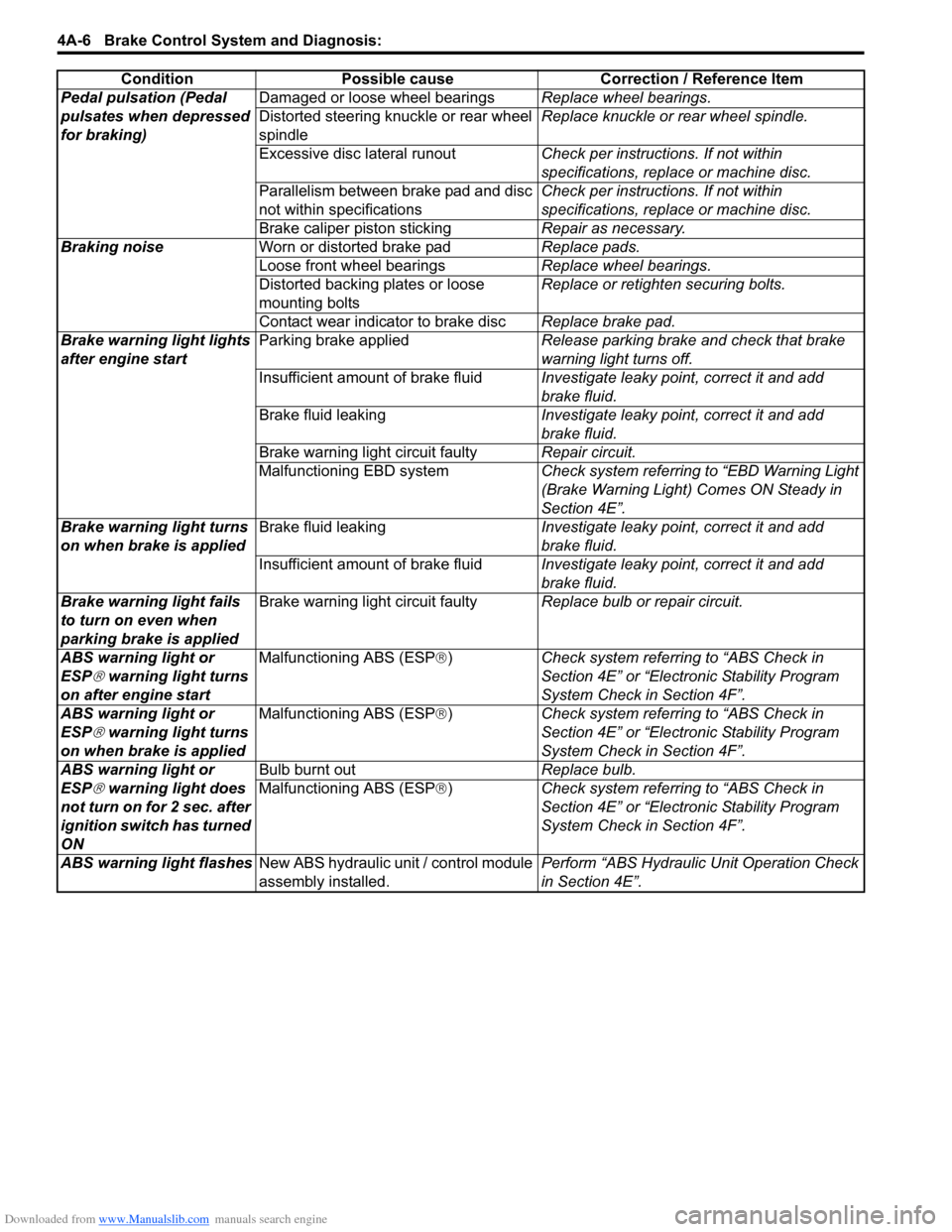
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4A-6 Brake Control System and Diagnosis:
Pedal pulsation (Pedal
pulsates when depressed
for braking)Damaged or loose wheel bearings
Replace wheel bearings.
Distorted steering knuckle or rear wheel
spindle Replace knuckle or rear wheel spindle.
Excessive disc lateral runout Check per instructions. If not within
specifications, replace or machine disc.
Parallelism between brake pad and disc
not within specifications Check per instructions. If not within
specifications, replace or machine disc.
Brake caliper piston sticking Repair as necessary.
Braking noise Worn or distorted brake pad Replace pads.
Loose front wheel bearings Replace wheel bearings.
Distorted backing plates or loose
mounting bolts Replace or retighten securing bolts.
Contact wear indicator to brake disc Replace brake pad.
Brake warning light lights
after engine start Parking brake applied
Release parking brake and check that brake
warning light turns off.
Insufficient amount of brake fluid Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Brake fluid leaking Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Brake warning light circuit faulty Repair circuit.
Malfunctioning EBD system Check system referring to “EBD Warning Light
(Brake Warning Light) Comes ON Steady in
Section 4E”.
Brake warning light turns
on when brake is applied Brake fluid leaking
Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Insufficient amount of brake fluid Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Brake warning light fails
to turn on even when
parking brake is applied Brake warning light circuit faulty
Replace bulb or repair circuit.
ABS warning light or
ESP
® warning light turns
on after engine start Malfunctioning ABS (ESP
®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
ABS warning light or
ESP
® warning light turns
on when brake is applied Malfunctioning ABS (ESP
®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
ABS warning light or
ESP
® warning light does
not turn on for 2 sec. after
ignition switch has turned
ON Bulb burnt out
Replace bulb.
Malfunctioning ABS (ESP ®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
ABS warning light flashes New ABS hydraulic unit / control module
assembly installed. Perform “ABS Hydraulic
Unit Operation Check
in Section 4E”.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item