engine check light SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.G Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 290 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-5 Engine Mechanical:
11) Connect negative cable at battery.
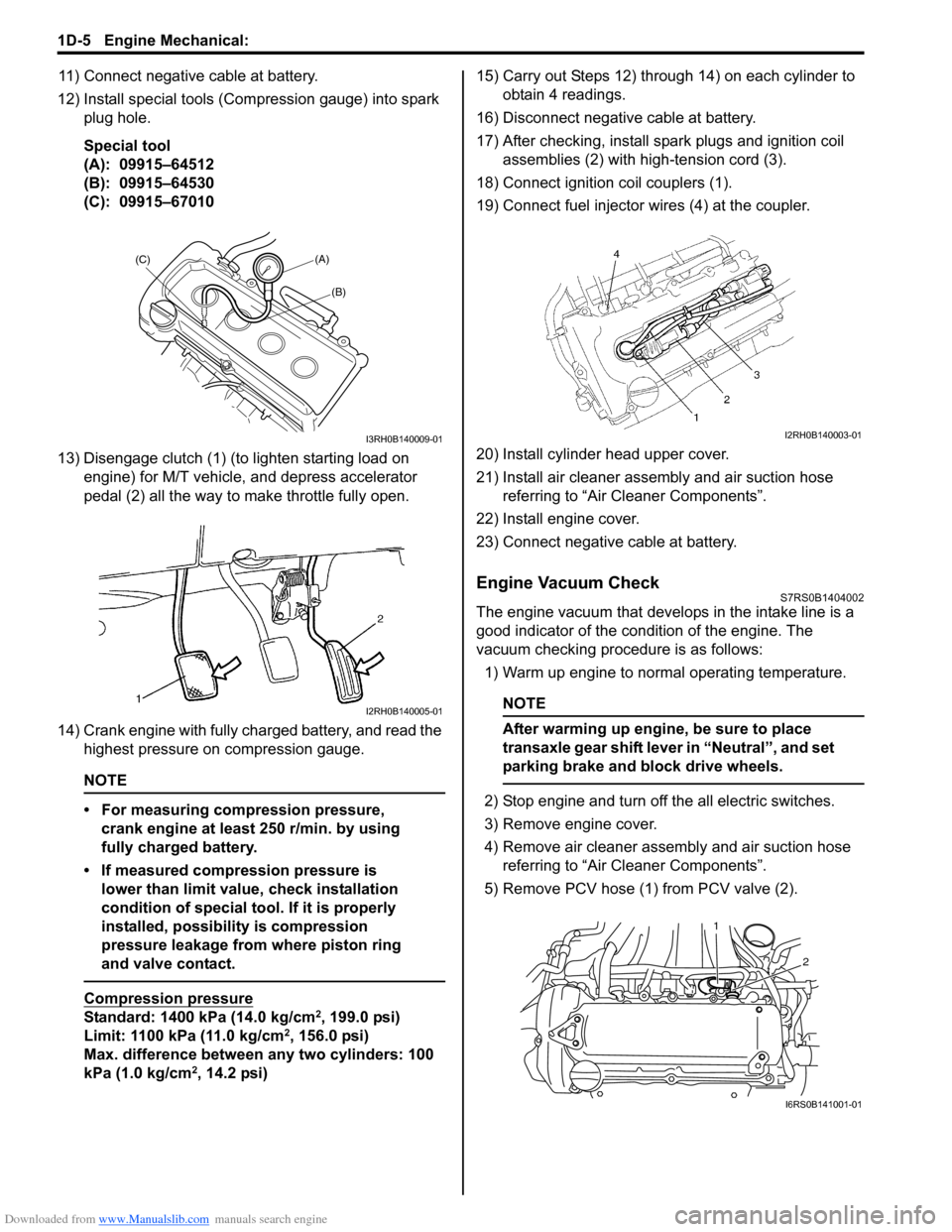
12) Install special tools (Compression gauge) into spark plug hole.
Special tool
(A): 09915–64512
(B): 09915–64530
(C): 09915–67010
13) Disengage clutch (1) (to lighten starting load on engine) for M/T vehicle, and depress accelerator
pedal (2) all the way to make throttle fully open.
14) Crank engine with fully charged battery, and read the highest pressure on compression gauge.
NOTE
• For measuring compression pressure, crank engine at least 250 r/min. by using
fully charged battery.
• If measured compression pressure is lower than limit value, check installation
condition of special tool. If it is properly
installed, possibility is compression
pressure leakage from where piston ring
and valve contact.
Compression pressure
Standard: 1400 kPa (14.0 kg/cm2, 199.0 psi)
Limit: 1100 kPa (11.0 kg/cm2, 156.0 psi)
Max. difference between any two cylinders: 100
kPa (1.0 kg/cm
2, 14.2 psi) 15) Carry out Steps 12) through 14) on each cylinder to
obtain 4 readings.
16) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
17) After checking, install spark plugs and ignition coil assemblies (2) with high-tension cord (3).
18) Connect ignition coil couplers (1).
19) Connect fuel injector wires (4) at the coupler.
20) Install cylinder head upper cover.
21) Install air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
22) Install engine cover.
23) Connect negative cable at battery.
Engine Vacuum CheckS7RS0B1404002
The engine vacuum that develops in the intake line is a
good indicator of the condition of the engine. The
vacuum checking procedure is as follows:
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
NOTE
After warming up engine, be sure to place
transaxle gear shift lever in “Neutral”, and set
parking brake and block drive wheels.
2) Stop engine and turn off the all electric switches.
3) Remove engine cover.
4) Remove air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
5) Remove PCV hose (1) from PCV valve (2).
(A)
(C)
(B)
I3RH0B140009-01
I2RH0B140005-01
I2RH0B140003-01
2
1
I6RS0B141001-01
Page 401 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Ignition System: 1H-9
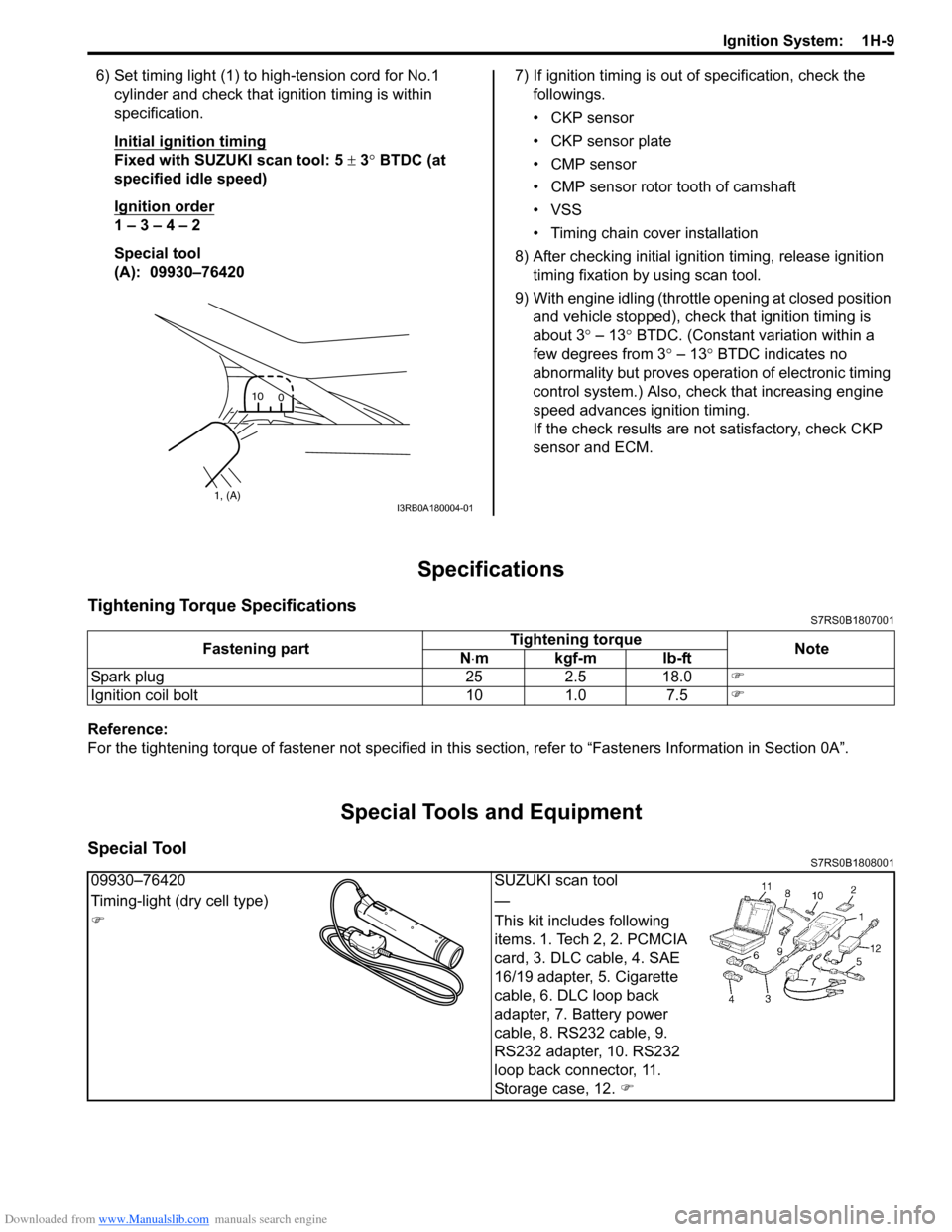
6) Set timing light (1) to high-tension cord for No.1 cylinder and check that ignition timing is within
specification.
Initial ignition timing
Fixed with SUZUKI scan tool: 5 ± 3° BTDC (at
specified idle speed)
Ignition order
1 – 3 – 4 – 2
Special tool
(A): 09930–76420 7) If ignition timing is out
of specification, check the
followings.
• CKP sensor
• CKP sensor plate
• CMP sensor
• CMP sensor rotor tooth of camshaft
• VSS
• Timing chain cover installation
8) After checking initial igniti on timing, release ignition
timing fixation by using scan tool.
9) With engine idling (throttl e opening at closed position
and vehicle stopped), check that ignition timing is
about 3 ° – 13° BTDC. (Constant variation within a
few degrees from 3 ° – 13° BTDC indicates no
abnormality but proves operation of electronic timing
control system.) Also, check that increasing engine
speed advances ignition timing.
If the check results are not satisfactory, check CKP
sensor and ECM.
Specifications
Tightening Torque SpecificationsS7RS0B1807001
Reference:
For the tightening torque of fastener not specified in this section, refer to “Fasteners Information in Section 0A”.
Special Tools and Equipment
Special ToolS7RS0B1808001
1, (A)10
0I3RB0A180004-01
Fastening part Tightening torque
Note
N ⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
Spark plug 25 2.5 18.0 �)
Ignition coil bolt 10 1.0 7.5 �)
09930–76420SUZUKI scan tool
Timing-light (dry cell type) —
�) This kit includes following
items. 1. Tech 2, 2. PCMCIA
card, 3. DLC cable, 4. SAE
16/19 adapter, 5. Cigarette
cable, 6. DLC loop back
adapter, 7. Battery power
cable, 8. RS232 cable, 9.
RS232 adapter, 10. RS232
loop back connector, 11.
Storage case, 12. �)
Page 411 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Charging System: 1J-1
Engine
Charging System
General Description
Battery DescriptionS7RS0B1A01001
The battery has three major functions in the electrical
system.
• It is a source of electrical energy for cranking the engine.
• It acts as a voltage stabilizer for the electrical system.
• It can, for a limited time, provide energy when the electrical load exceeds the output of the generator.
Carrier and Hold-Down
The battery carrier should be in good condition so that it
will support the battery securely and keep it level. Before
installing the battery, the ba ttery carrier and hold-down
clamp should be clean and free from corrosion and
make certain there are no parts in carrier.
To prevent the battery from shaking in its carrier, the
hold-down bolts should be tight enough but not over-
tightened.
Electrolyte Freezing
The freezing point of electrolyte depends on its specific
gravity. Since freezing may ruin a battery, it should be
protected against freezing by keeping it in a fully
charged condition. If a battery is frozen accidentally, it
should not be charged until it is warmed.
Sulfation
If the battery is allowed to stand for a long period in
discharged condition, the lead sulfate becomes
converted into a hard, cryst alline substance, which will
not easily turn back to the active material again during
the subsequent recharging. “Sulfation” means the result
as well as the process of that reaction. Such a battery
can be revived by very slow charging and may be
restored to usable condition but its capacity is lower than
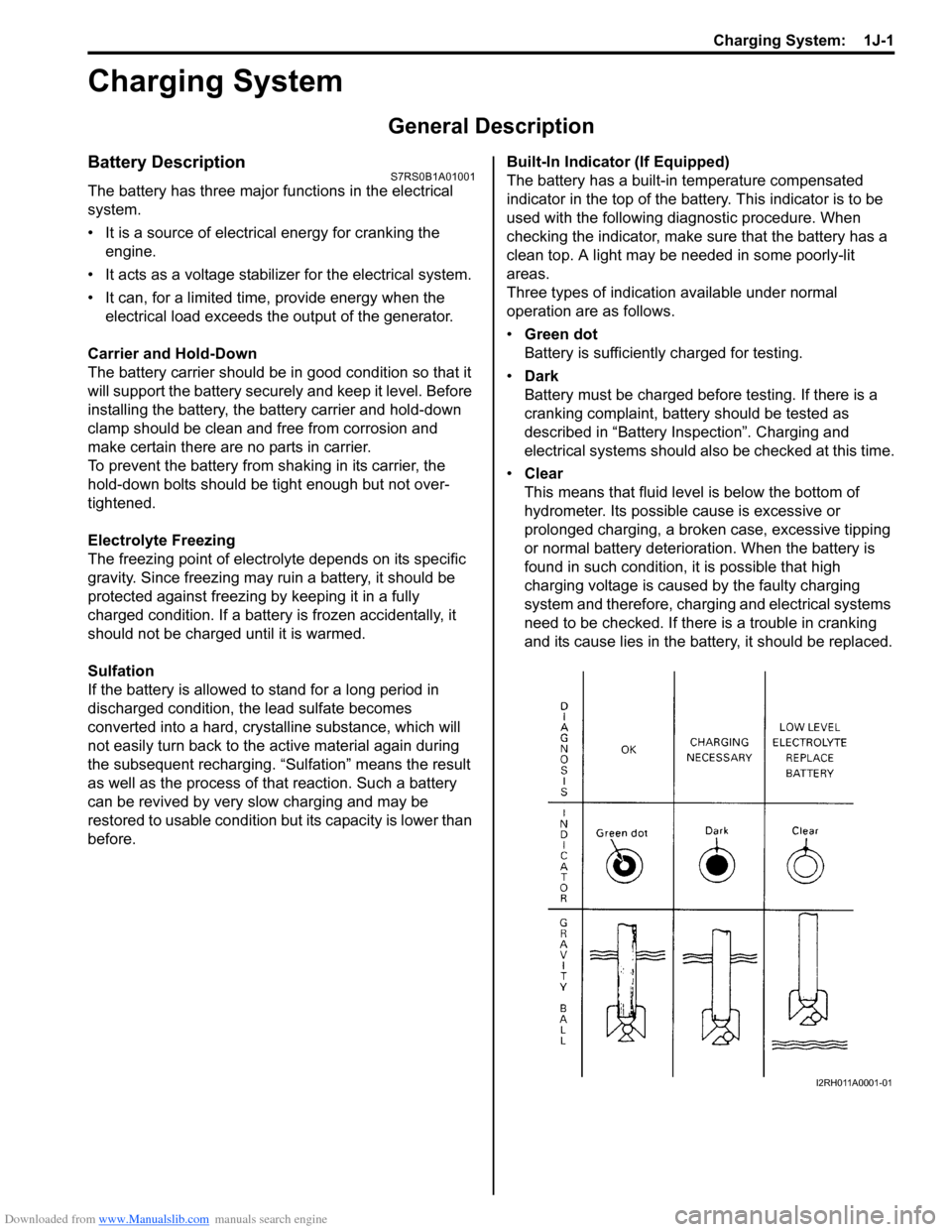
before. Built-In Indicator (If Equipped)
The battery has a built-in temperature compensated
indicator in the top of the battery. This indicator is to be
used with the following diagnostic procedure. When
checking the indicator, make sure that the battery has a
clean top. A light may be needed in some poorly-lit
areas.
Three types of indication available under normal
operation are as follows.
•
Green dot
Battery is sufficiently charged for testing.
• Dark
Battery must be charged before testing. If there is a
cranking complaint, battery should be tested as
described in “Battery Inspection”. Charging and
electrical systems should also be checked at this time.
• Clear
This means that fluid level is below the bottom of
hydrometer. Its possible cause is excessive or
prolonged charging, a broken case, excessive tipping
or normal battery deteriorat ion. When the battery is
found in such condition, it is possible that high
charging voltage is caused by the faulty charging
system and therefore, charging and electrical systems
need to be checked. If there is a trouble in cranking
and its cause lies in the battery, it should be replaced.
I2RH011A0001-01
Page 414 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1J-4 Charging System:
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Battery InspectionS7RS0B1A04001
Common Causes of Failure
A battery is not designed to last indefinitely; however, with proper care, it will provide many years of service. If the
battery performs satisfactorily during te st but fails to operate properly for no apparent reason, the following are some
factors that may point to the cause of trouble:
• Accessories left on overnight or for an extended period without the generator operating.
• Slow average driving speeds for short periods.
• Electrical load exceeding generator output partic ularly with addition of aftermarket equipment.
• Defects in charging system such as high resistance, s lipping drive belt, loose generator output terminal, faulty
generator or voltage regulator, Refer to “Generator Symptom Diagnosis”.
• Battery abuse, including failure to keep battery cable terminals clean and tight or loose battery hold down.
• Mechanical problems in electrical sys tem such as shorted or pinched wires.
Visual Inspection
Check for obvious damage, such as cracked or broken case or cover, that could permit loss of electrolyte. If obvious
damage is noted, replace battery. Determine cause of damage and correct as needed.
Generator Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B1A04002
CAUTION!
• Do not mistake polarities of “IG” terminal and “L” terminal.
• Do not create short circuit between “IG” and “L” terminals. Always connect these terminals through a lamp.
• Do not connect any load between “L” and “E” terminals.
• When connecting charger or booster battery to vehicle battery, refer to “Jump Starting in Case of Emergency”.
Trouble in charging system will show up as one or more of the following conditions:
1) Faulty indicator lamp operation.
2) An undercharged battery as evidenced by slow cranking or indicator dark.
3) An overcharged battery as evidenced by ex cessive spewing of electrolyte from vents.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Noisy generator Loose drive belt Adjust or replace drive belt.
Loose drive belt pulley Tighten by specified torque.
Loose mounting bolts Tighten by specified torque.
Worn or dirty bearings Replace.
Defective diode or stator Replace.
Charge light does not
light with ignition ON and
engine off Fuse blown
Replace fuse and check for shorted circuit.
Indicator lamp (LED) faulty Replace combination meter.
Wiring connection loose Tighten loose connection.
IC regulator or field coil faulty Replace.
Poor contact between brush and slip
ring Repair or replace.
Charge light does not go
out with engine running
(battery requires frequent
recharging) Drive belt loose or worn
Adjust or replace drive belt.
IC regulator or generator faulty Replace.
Wiring faulty Repair wiring.
Page 415 of 1496
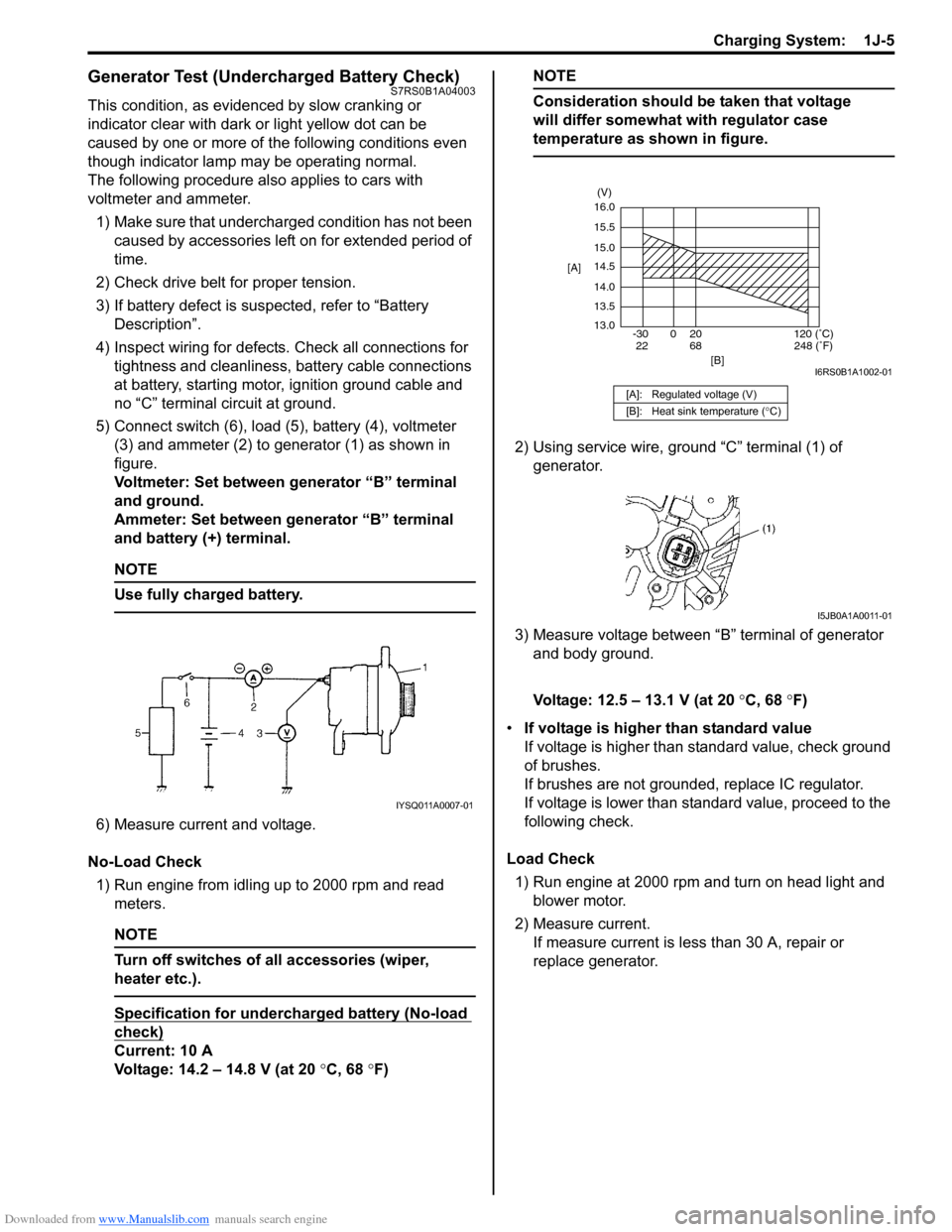
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Charging System: 1J-5
Generator Test (Undercharged Battery Check)S7RS0B1A04003
This condition, as evidenced by slow cranking or
indicator clear with dark or light yellow dot can be
caused by one or more of the following conditions even
though indicator lamp may be operating normal.
The following procedure also applies to cars with
voltmeter and ammeter.1) Make sure that undercharged condition has not been caused by accessories left on for extended period of
time.
2) Check drive belt for proper tension.
3) If battery defect is suspected, refer to “Battery Description”.
4) Inspect wiring for defects. Check all connections for tightness and cleanliness, battery cable connections
at battery, starting motor, ignition ground cable and
no “C” terminal circuit at ground.
5) Connect switch (6), load (5), battery (4), voltmeter (3) and ammeter (2) to generator (1) as shown in
figure.
Voltmeter: Set between generator “B” terminal
and ground.
Ammeter: Set between generator “B” terminal
and battery (+) terminal.
NOTE
Use fully charged battery.
6) Measure current and voltage.
No-Load Check 1) Run engine from idling up to 2000 rpm and read meters.
NOTE
Turn off switches of all accessories (wiper,
heater etc.).
Specification for undercharged battery (No-load
check)
Current: 10 A
Voltage: 14.2 – 14.8 V (at 20 °C, 68 °F)
NOTE
Consideration should be taken that voltage
will differ somewhat with regulator case
temperature as shown in figure.
2) Using service wire, ground “C” terminal (1) of
generator.
3) Measure voltage between “B” terminal of generator and body ground.
Voltage: 12.5 – 13.1 V (at 20 °C, 68 °F)
• If voltage is higher than standard value
If voltage is higher than standard value, check ground
of brushes.
If brushes are not grounded, replace IC regulator.
If voltage is lower than standard value, proceed to the
following check.
Load Check 1) Run engine at 2000 rpm and turn on head light and blower motor.
2) Measure current. If measure current is less than 30 A, repair or
replace generator.
IYSQ011A0007-01
[A]: Regulated voltage (V)
[B]: Heat sink temperature ( °C)
16.0
15.5
15.0
14.5
14.0
13.5
13.0
-30 0 20
[A]
[B]
68
22120 (˚C)
248 (˚F)
(V)
I6RS0B1A1002-01
I5JB0A1A0011-01
Page 416 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1J-6 Charging System:
Generator Test (Overcharged Battery Check)S7RS0B1A04004
1) To determine battery condition, refer to “Battery Description”.
2) If obvious overcharge condition exists as evidenced by excessive spewing of electrolyte, measure
generator “B” terminal voltage at engine 2000 rpm. 3) If measured voltage is higher than upper limit value,
proceed to disassemble generator.
4) Check ground of brushes. If brushes are not grounded, replace IC regulator. Then check field coil
for grounds and shorts, referring to “Generator
Inspection”.
Repair Instructions
Jump Starting in Case of EmergencyS7RS0B1A06001
CAUTION!
If vehicle is manual transaxle model and has
a catalytic converter, do not push or tow it to
start. Damage to its emission system and/or
to other parts may result.
Both booster and discharged battery should be treated
carefully when using ju mper cables. Follow the
procedure outlined as follows, being careful not to cause
sparks.
WARNING!
• Departure from these conditions or procedure described as follows could
result in:
– Serious personal injury (particularly to eyes) or property damage from such
causes as battery explosion, battery
acid, or electrical burns.
– Damage to electronic components of either vehicle.
• Remove rings, watches, and other jewelry. Wear approved eye protection.
• Be careful so that metal tools or jumper cables do not contact positive battery
terminal (or metal in contact with it) and
any other metal on vehicle, because a
short circuit could occur. • Never expose battery to open flame or
electric spark. Batteries generate gas
which is flammable and explosive.
• Do not allow battery fluid to contact eyes, skin, fabrics, or painted surface as fluid is
a corrosive acid. Flush any contacted area
with water immediately and thoroughly.
• Batteries should always be kept out of reach of children.
• Do not connect negative cable directly to negative terminal of dead battery.
1) Set parking brake and place automatic transaxle in PARK (NEUTRAL on manual transaxle). Turn off
ignition, turn off lights and all other electrical loads.
2) Check electrolyte level. If it is below low level line, add distilled water.
3) Attach end of one jumper cable to positive terminal of booster battery and the other end of the same
cable to positive terminal of discharged battery. (Use
12-volt battery only to jump start engine).
4) Attach one end of the remaining negative cable to negative terminal of booster battery, and the other
end to a solid engine ground (such as exhaust
manifold) at least 45 cm (18 in.) away from battery of
vehicle being started.
5) Start engine of vehicle with booster battery and turn off electrical accessories. Then start engine of the
vehicle with discharged battery.
16.0
15.5
15.0
14.5
14.0
13.5
13.0 -30 0 20
[C]
[D]
68
22120 (˚C)
248 (˚F)
(V)
I6RS0C1A0001-02
Page 496 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4-ii Table of Contents
Repair Instructions ..............................................4D-2Parking Brake Inspection and Adjustment ..........4D-2
Parking Brake Cable Removal and Installation ......................................................... 4D-3
Parking Brake Lever Removal and Installation ....4D-3
Specifications .... ...................................................4D-4
Tightening Torque Specifications ........................4D-4
ABS ........................................... .................4E-1
Precautions........................................................... 4E-1
Precautions in Diagnosing Troubles ................... 4E-1
Precautions in On-Vehicle Service...................... 4E-1
Precautions in Hydraulic Unit Operation Check ................................................................ 4E-1
General Description ............................................. 4E-2 ABS Description .................................................. 4E-2
ABS Hydraulic Unit / Control Module Assembly Description ....................................... 4E-2
CAN Communication System Description........... 4E-3
Schematic and Routing Diagram ........................ 4E-4 ABS Schematic ................................................... 4E-4
ABS Wiring Circuit Diagram ................................ 4E-5
Component Location ........... ................................ 4E-7
ABS Components Location ................................. 4E-7
Front Wheel Speed Sensor Components Location ............................................................ 4E-7
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Components Location ............................................................ 4E-8
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............ 4E-8 ABS Check .......................................................... 4E-8
ABS Warning Light Check................................. 4E-10
EBD Warning Light (Brake Warning Light) Check .............................................................. 4E-10
DTC Check........................................................ 4E-11
DTC Table ......................................................... 4E-11
DTC Clearance ................................................. 4E-12
Scan Tool Data ................................................. 4E-12
ABS Warning Light Does Not Come ON at Ignition Switch ON .......................................... 4E-13
ABS Warning Light Comes ON Steady ............. 4E-14
EBD Warning Light (Brake Warning Light) Comes ON Steady .......................................... 4E-15
Serial Data Link Circuit Check .......................... 4E-16
DTC C1021, C1022 / C1025, C1026 / C1031, C1032 / C1035, C1036: Right-Front / Left-
Front / Right-Rear / Left-Rear Wheel Speed
Sensor Circuit or Sensor Ring ........................ 4E-18
DTC C1041 / C1045 / C1051 / C1055, DTC C1042 / C1046 / C1052 / C1056: Right-Front
/ Left-Front / Right-Rear / Left-Rear Inlet
Solenoid Circuit, Right-Front / Left-Front /
Right-Rear / Left-Rear Outlet Solenoid
Circuit .............................................................. 4E-20
DTC C1057: Power Source Circuit ................... 4E-21
DTC C1061: ABS Pump Motor and/or Motor Driver Circuit ................................................... 4E-22
DTC C1063: Solenoid Valve Power Supply Driver Circuit ................................................... 4E-23
DTC C1071: ABS Control Module..................... 4E-24 DTC U1073: Control Module Communication
Bus Off ............................................................ 4E-25
DTC U1100: Lost Communication with ECM (Reception Error)............................................. 4E-27
Repair Instructions ............ ................................ 4E-28
ABS Hydraulic Unit Operati on Check................ 4E-28
ABS Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly Components ...... ............................. 4E-29
ABS Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection .................... 4E-29
ABS Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly Removal and Inst allation ................ 4E-29
Front / Rear Wheel Speed Sensor On-Vehicle Inspection ........................................................ 4E-31
Front Wheel Speed Sensor Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4E-32
Front Wheel Speed Sensor Inspection ............. 4E-32
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4E-33
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Inspection .............. 4E-34
Front Wheel Encoder On-Veh icle Inspection .... 4E-34
Front wheel Enco der Removal and
Installation ....................................................... 4E-34
Rear Wheel Encoder On-Veh icle Inspection..... 4E-34
Rear Wheel Encoder Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4E-34
Specifications ..................... ................................ 4E-35
Tightening Torque Specifications ...................... 4E-35
Special Tools and Equipmen t ........................... 4E-35
Special Tool ...................................................... 4E-35
Electronic Stability Prog ram ...................4F-1
Precautions ........................................................... 4F-1
Precautions in Diagnosing Troubles ................... 4F-1
Precautions in On-Vehicle Service...................... 4F-1
Precautions in Hydraulic Unit Operation Check ................................................................ 4F-1
Precautions in Sensor Calibration ....................... 4F-1
Precautions in Speedometer Test or Other Tests ................................................................. 4F-2
General Description ............................................. 4F-2 Electronic Stability Program Description ............. 4F-2
Electronic Stability Program Construction ........... 4F-3
ESP® Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly Description........................................ 4F-5
Warning Lamp, Indicator Lamp Description ........ 4F-6
CAN Communication System Description........... 4F-6
CAN Communication System For Electronic Stability Program Description ............................ 4F-7
Schematic and Routing Diagram ........................ 4F-8 Electronic Stability Program Schematic .............. 4F-8
Electronic Stability Program Wiring Circuit Diagram............................................................. 4F-9
Component Location ............ ............................. 4F-11
Electronic Stability Program Component
Location........................................................... 4F-11
Diagnostic Information and Procedures .......... 4F-12 Electronic Stability Program System Check ...... 4F-12
ESP® Warning lamp Check .............................. 4F-14
Page 502 of 1496
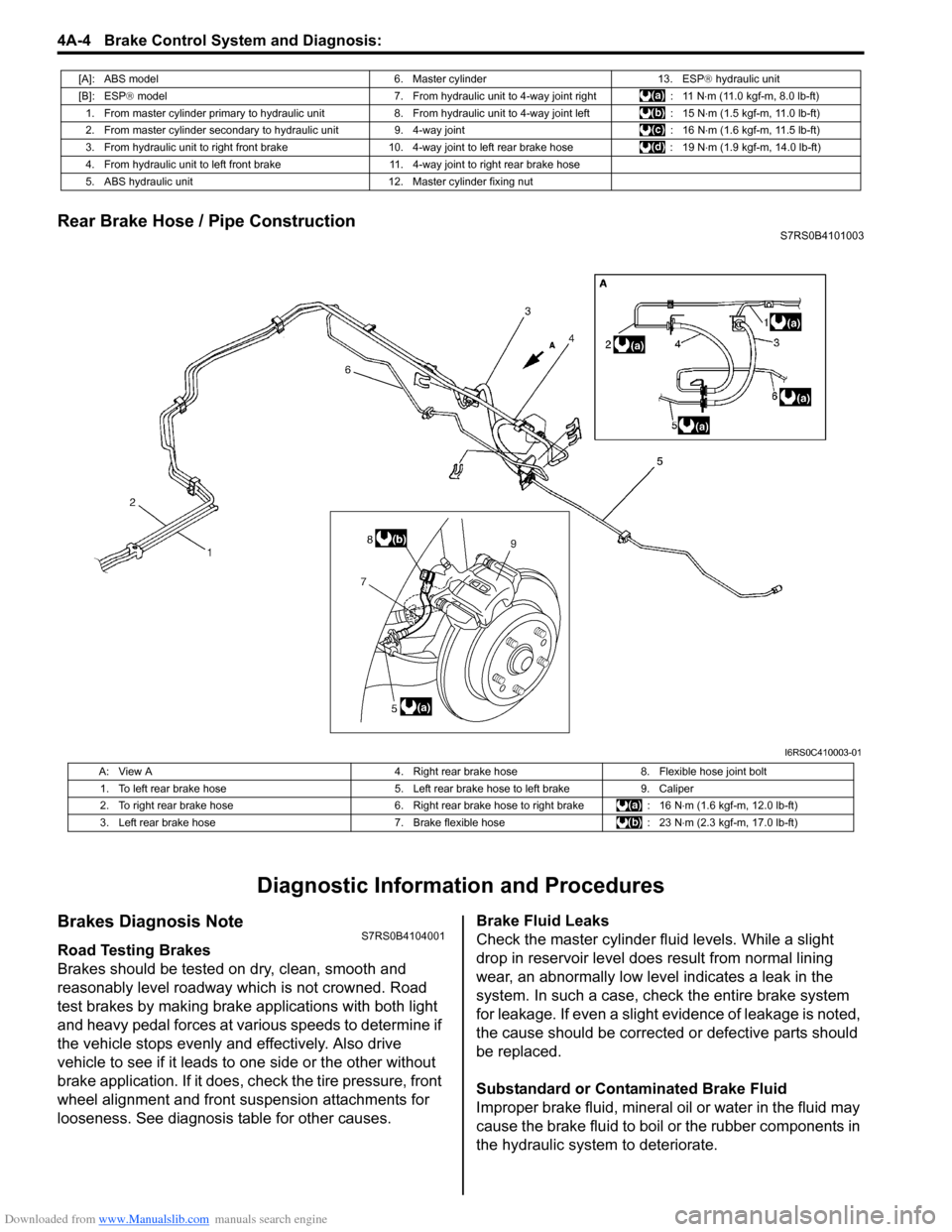
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4A-4 Brake Control System and Diagnosis:
Rear Brake Hose / Pipe ConstructionS7RS0B4101003
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Brakes Diagnosis NoteS7RS0B4104001
Road Testing Brakes
Brakes should be tested on dry, clean, smooth and
reasonably level roadway which is not crowned. Road
test brakes by making brake applications with both light
and heavy pedal forces at vari ous speeds to determine if
the vehicle stops evenly and effectively. Also drive
vehicle to see if it leads to one side or the other without
brake application. If it does, check the tire pressure, front
wheel alignment and front suspension attachments for
looseness. See diagnosis table for other causes. Brake Fluid Leaks
Check the master cylinder fl
uid levels. While a slight
drop in reservoir level does result from normal lining
wear, an abnormally low leve l indicates a leak in the
system. In such a case, chec k the entire brake system
for leakage. If even a slight ev idence of leakage is noted,
the cause should be corrected or defective parts should
be replaced.
Substandard or Contaminated Brake Fluid
Improper brake fluid, mineral oil or water in the fluid may
cause the brake fluid to boil or the rubber components in
the hydraulic system to deteriorate.
[A]: ABS model 6. Master cylinder13. ESP® hydraulic unit
[B]: ESP ® model 7. From hydraulic unit to 4-way joint right : 11 N⋅m (11.0 kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft)
1. From master cylinder primary to hydraulic unit 8. From hydraulic unit to 4-way joint left: 15 N⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft)
2. From master cylinder secondary to hydraulic unit 9. 4-way joint: 16 N⋅m (1.6 kgf-m, 11.5 lb-ft)
3. From hydraulic unit to right front brake 10.4-way joint to left rear brake hose : 19 N⋅m (1.9 kgf-m, 14.0 lb-ft)
4. From hydraulic unit to left front brake 11. 4-way joint to right rear brake hose
5. ABS hydraulic unit 12. Master cylinder fixing nut
I6RS0C410003-01
A: View A4. Right rear brake hose8. Flexible hose joint bolt
1. To left rear brake hose 5. Left rear brake hose to left brake9. Caliper
2. To right rear brake hose 6. Right rear brake hose to right brake: 16 N⋅m (1.6 kgf-m, 12.0 lb-ft)
3. Left rear brake hose 7. Brake flexible hose: 23 N⋅m (2.3 kgf-m, 17.0 lb-ft)
Page 503 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Brake Control System and Diagnosis: 4A-5
If deterioration of rubber is evident, disassemble all
hydraulic parts and wash with alcohol. Dry these parts
with compressed air before assembly to keep alcohol out
of the system. Replace all rubber parts in the system,
including hoses. Also, when working on the brake
mechanisms, check for fluid on the linings.
If excessive fluid is found, replace the pads. If master cylinder piston seals
are satisfactory, check for
leakage or excessive heat co nditions. If leakage is not
found, drain fluid, flush with brake fluid, refill and bleed
system.
The system must be flushed if there is any doubt as to
the grade of fluid in the system or if fluid has been used
which contained parts that have been subjected to
contaminated fluid.
Brakes Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B4104002
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Not enough braking force Brake oil leakage from brake lines Locate leaking point and repair.
Brake disc or brake pad stained with oil Clean or replace.
Overheated brakes Determine cause and repair.
Badly worn brake pad Replace.
Malfunctioning caliper assembly Repair or replace.
Malfunctioning brake booster Check system and replace assembly.
Malfunctioning brake master cylinder Check system and replace as necessary.
Air in system Bleed system.
Malfunctioning ABS (ESP ®). Check system and replace as necessary.
Brake pull (Brakes not
working in unison) Brake pad and disc are wet with water or
stained with oil in some brakes Clean or replace.
Disc is out of round in some brakes Replace.
Tires are inflated unequally Inflate equally.
Disturbed front wheel alignment Adjust as prescribed.
Unmatched tires on same axle Tires with approximately the same amount of
tread should be used on the same axle.
Restricted brake pipes or hoses Check for soft hoses and damaged lines.
Replace with new hoses and new double-
walled steel brake tubing.
Malfunctioning caliper assembly Caliper should slide.
Check for stuck or sluggish pistons and proper
lubrication of caliper slide pin.
Loose suspension parts Check all suspension mountings.
Loose calipers Check and torque bolts to specifications.
Noise (High pitched
squeak without brake
applied) Contact wear indicator to brake disc
Replace brake pads.
Worn brake pad Replace brake pads.
Excessive pedal travel
(Pedal stroke too large) Partial brake system failure
Check brake systems and repair as necessary.
Brake fluid leaking Repair the leaking point and bleed air.
Air in system (soft / spongy pedal) Bleed system.
Brake locked Malfunctioning ABS (ESP®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
Dragging brakes (A very
light drag is present in all
brakes immediately after
pedal is released.) Master cylinder pistons not returning
correctly
Replace master cylinder.
Restricted brake pipes or hoses Check for soft hoses or damaged pipes and
replace with new hoses and/or new brake
piping.
Incorrect parking brake adjustment on
rear brakes Check and adjust to correct specifications.
Weakened or broken return springs in
rear brakes. Replace.
Sluggish parking brake cables or linkage Repair or replace.
Brake caliper piston sticking Repair as necessary.
Badly worn piston seal in caliper Replace piston seal.
Improper brake pedal free height Check brake pedal free height.
Page 504 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4A-6 Brake Control System and Diagnosis:
Pedal pulsation (Pedal
pulsates when depressed
for braking)Damaged or loose wheel bearings
Replace wheel bearings.
Distorted steering knuckle or rear wheel
spindle Replace knuckle or rear wheel spindle.
Excessive disc lateral runout Check per instructions. If not within
specifications, replace or machine disc.
Parallelism between brake pad and disc
not within specifications Check per instructions. If not within
specifications, replace or machine disc.
Brake caliper piston sticking Repair as necessary.
Braking noise Worn or distorted brake pad Replace pads.
Loose front wheel bearings Replace wheel bearings.
Distorted backing plates or loose
mounting bolts Replace or retighten securing bolts.
Contact wear indicator to brake disc Replace brake pad.
Brake warning light lights
after engine start Parking brake applied
Release parking brake and check that brake
warning light turns off.
Insufficient amount of brake fluid Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Brake fluid leaking Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Brake warning light circuit faulty Repair circuit.
Malfunctioning EBD system Check system referring to “EBD Warning Light
(Brake Warning Light) Comes ON Steady in
Section 4E”.
Brake warning light turns
on when brake is applied Brake fluid leaking
Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Insufficient amount of brake fluid Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Brake warning light fails
to turn on even when
parking brake is applied Brake warning light circuit faulty
Replace bulb or repair circuit.
ABS warning light or
ESP
® warning light turns
on after engine start Malfunctioning ABS (ESP
®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
ABS warning light or
ESP
® warning light turns
on when brake is applied Malfunctioning ABS (ESP
®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
ABS warning light or
ESP
® warning light does
not turn on for 2 sec. after
ignition switch has turned
ON Bulb burnt out
Replace bulb.
Malfunctioning ABS (ESP ®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
ABS warning light flashes New ABS hydraulic unit / control module
assembly installed. Perform “ABS Hydraulic
Unit Operation Check
in Section 4E”.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item