Driver SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.G Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 168 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-118 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
DTC P0403: Exhaust Gas Recirculation Control CircuitS7RS0B1104045
Wiring Diagram
Refer to “DTC P0401 / P0402: Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected / Excessive Detected”.
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
DTC Confirmation Procedure
WARNING!
• When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic accident and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
• Road test should be carried out by 2 persons, a driver and a tester, on a level road.
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect scan tool to DLC.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and clear DTC using scan tool.
3) Start engine and run it for 30 seconds.
4) Check DTC. 3
EGR valve operation check
1) With ignition switch turned OF F, install SUZUKI scan tool
to DTC.
2) Check EGR system referring to “EGR System Inspection
in Section 1B”.
Is it in good condition? Go to Step 4. Go to Step 5.
4 MAP sensor check
1) Check MAP sensor for performance referring to “MAP
Sensor Inspection in Section 1C”.
Is check result satisfactory? Intermittent trouble or
faulty ECM.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection
Inspection in Section
00”.Replace MAP sensor.
5 EGR valve control circuit check
1) Check that EGR valve control circuits are in good
condition referring to Step 2 to 5 of “DTC P0403:
Exhaust Gas Recirculation Control Circuit”
Are circuits in good condition? Go to Step 6. Repair or replace EGR
valve control circuit(s).
6 EGR valve check
1) Check EGR valve referring to “EGR Valve Inspection in
Section 1B”.
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 7. Faulty EGR valve.
7 MAP sensor check
1) Check MAP sensor for performance referring to “MAP
Sensor Inspection in Section 1C”.
Is check result satisfactory? EGR passage clogged.
If OK, substitute a
known-good ECM and
recheck.
Replace MAP sensor.
Step Action Yes No
DTC detecting condition
Trouble area
EGR valve output voltage is differ ent from output command with more
than one pole out of 4 poles.
(1 driving cycle detection logic) • EGR valve circuit open
•EGR valve
•ECM
Page 171 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-121
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
DTC Confirmation Procedure
WARNING!
• When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic accident and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
• Road test should be carried out by 2 persons, a driver and a tester, on a level road.
NOTE
Check to make sure that following conditions ar e satisfied when using this “DTC Confirmation
Procedure”.
• Intake air temperature at engine start: –10 °C (14 ° F) to 80 °C (176 °F)
• Intake air temperature: –10 °C (14 °F) to 70 °C (158 °F)
• Engine coolant temp.: 70 °C, 158 °F to 150 °C (302 °F)
• Altitude (barometric pressure): 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (500 mmHg, 75 kPa or more)
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and clear DTC using scan tool.
3) Increase vehicle speed to 37 – 62 mph, 60 – 100 km/h. (engine speed: 2500 – 3000 r/min.)
4) Keep above vehicle speed for 10 min. or more (Thr ottle valve opening is kept constant in this step).
5) Stop vehicle and check if DTC / pending DTC exists using sc an tool. If not, check if catalyst monitoring test has
been completed using scan tool. If not in both of above checks (i.e., no DTC / pending DTC and catalyst
monitoring test not completed), check vehicle cond ition (environmental) and repeat Step 3) through 5).
DTC Troubleshooting
NOTE
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/ or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors re ferring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm that the trouble has been corrected.
DTC detecting condition Trouble area
Response delay of HO2S-2 signal (shifting delay from rich to lean and
from lean to rich with threshold at 0.45 V) compared to switching cycle
(rich-lean) of A/F feed back is less than specified while vehicle is
running at constant speed and except with high engine load after
warmed up.
(*2 driving cycle detection logic, monitoring once per driving cycle) • Exhaust gas leak
• Warm up three way catalytic converter
malfunction
• HO2S-2 malfunction
• HO2S-1 malfunction
Step Action YesNo
1 Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed? Go to Step 2.
Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check”.
2 Exhaust system visual check
1) Check exhaust system for leaks, damage and loose
connection.
Is it in good condition? Go to Step 3.
Repair or replace
defective part.
Page 173 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-123
DTC Confirmation Procedure
WARNING!
• When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic accident and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
• Road test should be carried out by 2 persons, a driver and a tester, on a level road.
1) With ignition switch OFF, connect scan tool to DLC.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and clear DTC using scan tool.
3) Start engine and warm up normal operating temperature.
4) Drive vehicle at more than 40 km/h, 25 mph for 5 min. or more.
5) Check DTC and pending DTC.
DTC Troubleshooting
WARNING!
In order to reduce risk of fire and personal injury, this work must be performed in a well ventilated area
and away from any open flames such as gas water heater.
NOTE
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/ or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors re ferring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm that the trouble has been corrected.
Step Action YesNo
1 Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed? Go to Step 2.
Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check”.
2 EVAP canister purge power supply circuit check
1) Turn OFF ignition switch and disconnect connector from
EVAP canister purge valve.
2) Measure voltage between engine ground and “BLK/ RED” wire terminal of EVAP canister purge valve
connector with ignition switch turned ON.
Is it voltage 10 – 14 V? Go to Step 3.
“BLK/RED” wire is open
circuit.
3 Wire circuit check
1) Disconnect connectors from ECM with ignition switch
turned OFF.
2) Measure resistance between “C37-29” terminal of ECM connector and vehicle body ground.
Is resistance infinity? Go to Step 4.
“BLU/BLK” wire is
shorted to ground
circuit.
4 Wire circuit check
1) Measure voltage between “C37-29” terminal of ECM
connector and vehicle body ground with ignition switch
turned ON.
Is voltage 0 V? Go to Step 5.
“BLU/BLK” wire is
shorted to other circuit.
Page 179 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-129
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
DTC Confirmation Procedure
WARNING!
• When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic accident and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
• Road test should be carried out by 2 persons, a driver and a tester.
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect scan tool.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and clear DTC using scan tool.
3) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
4) M/T model
a) Drive vehicle at 4000 rpm (e ngine speed) with 3rd gear.
b) Release accelerator pedal and with engine brake applied, keep vehicle coasting for 6 sec. or more (fuel cut condition for 5 sec. or more) and stop vehicle.
A/T model
a) Drive vehicle at more than 3000 rpm for 10 sec.
5) Check pending DTC and DTC.
DTC Troubleshooting
NOTE
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/ or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors re ferring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm that the trouble has been corrected.
DTC detecting condition Trouble area
• Vehicle speed signal is not input while fuel is cut at deceleration for 4 seconds continuously at 3600 rpm or
less.
• Vehicle speed signal is not input even if engine is running with more than 3000 rpm at D-Range for 4 sec. (A/T model).
(2 driving cycle detection logic) • Wheel speed sensor and/or its circuit
• ABS/ESP®
control module
•ECM
Step Action YesNo
1 Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed? Go to Step 2.
Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check”.
2 Vehicle speed signal check
Is vehicle speed displayed on scan tool in Step 4) and 5) of
“DTC Confirmation Procedure”? Intermittent trouble.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection
Inspection in Section
00”.Go to Step 3.
3 DTC check in ABS/ESP ® control module
1) Check ABS/ESP ® control module for DTC.
Is there any DTC of wheel speed sensor or CAN
communication system? Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.
Substitute a know-good
ECM and recheck.
Page 224 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-174 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
DTC Confirmation Procedure
DTC P2227:
WARNING!
• When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic accident and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
• Road test should be carried out by 2 persons, a driver and a tester, on a level road.
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and clear DTC, pending DTC and freeze frame data by using scan tool and warm up
engine to normal operating temperature.
3) Check DTC and pending DTC by using scan tool.
DTC P2228 / P2229: 1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch, clear DTC by using scan tool and run engine for 1 min.
3) Check DTC.
DTC Troubleshooting
NOTE
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/ or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors re ferring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm that the trouble has been corrected.
Step Action YesNo
1 Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed? Go to Step 2.
Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check”.
2 Is DTC P2227 set? Go to Step 3.Substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
3 MAP sensor check
1) Check MAP sensor and its circuit referring to “DTC
P0107: Manifold Absolute Pressure / Barometric
Pressure Circuit Low Input” and/or “DTC P0108:
Manifold Absolute Pressure / Barometric Pressure
Circuit High Input”.
Is check result satisfactory? Substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
MAP sensor or its circuit
malfunction.
Page 471 of 1496
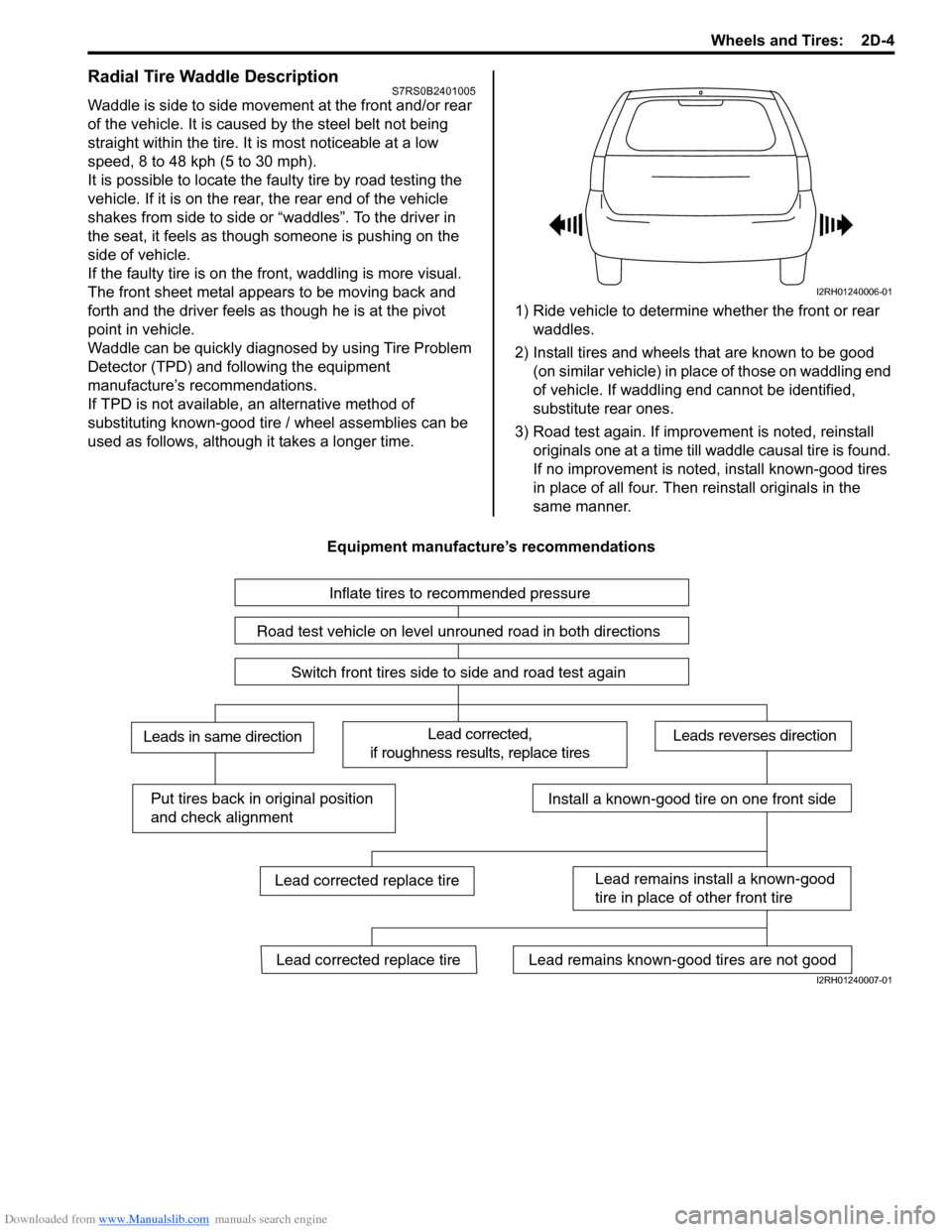
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Wheels and Tires: 2D-4
Radial Tire Waddle DescriptionS7RS0B2401005
Waddle is side to side movement at the front and/or rear
of the vehicle. It is caused by the steel belt not being
straight within the tire. It is most noticeable at a low
speed, 8 to 48 kph (5 to 30 mph).
It is possible to locate the f aulty tire by road testing the
vehicle. If it is on the rear , the rear end of the vehicle
shakes from side to side or “waddles”. To the driver in
the seat, it feels as though someone is pushing on the
side of vehicle.
If the faulty tire is on the front, waddling is more visual.
The front sheet metal appears to be moving back and
forth and the driver feels as though he is at the pivot
point in vehicle.
Waddle can be quickly diagnosed by using Tire Problem
Detector (TPD) and following the equipment
manufacture’s recommendations.
If TPD is not available, an alternative method of
substituting known-good tire / wheel assemblies can be
used as follows, although it takes a longer time. 1) Ride vehicle to determine whether the front or rear
waddles.
2) Install tires and wheels that are known to be good (on similar vehicle) in place of those on waddling end
of vehicle. If waddling end cannot be identified,
substitute rear ones.
3) Road test again. If improvement is noted, reinstall originals one at a time till w addle causal tire is found.
If no improvement is noted, install known-good tires
in place of all four. Then reinstall originals in the
same manner.
Equipment manufacture’s recommendations
I2RH01240006-01
Inflate tires to recommended pressure
Road test vehicle on level unrouned road in both directions
Switch front tires side to side and road test again
Lead corrected,
if roughness results, replace tiresLeads in same directionLeads reverses direction
Put tires back in original position
and check alignmentInstall a known-good tire on one front side
Lead remains install a known-good
tire in place of other front tire
Lead remains known-good tires are not goodLead corrected replace tire
Lead corrected replace tire
I2RH01240007-01
Page 488 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3A-10 Drive Shaft / Axle:
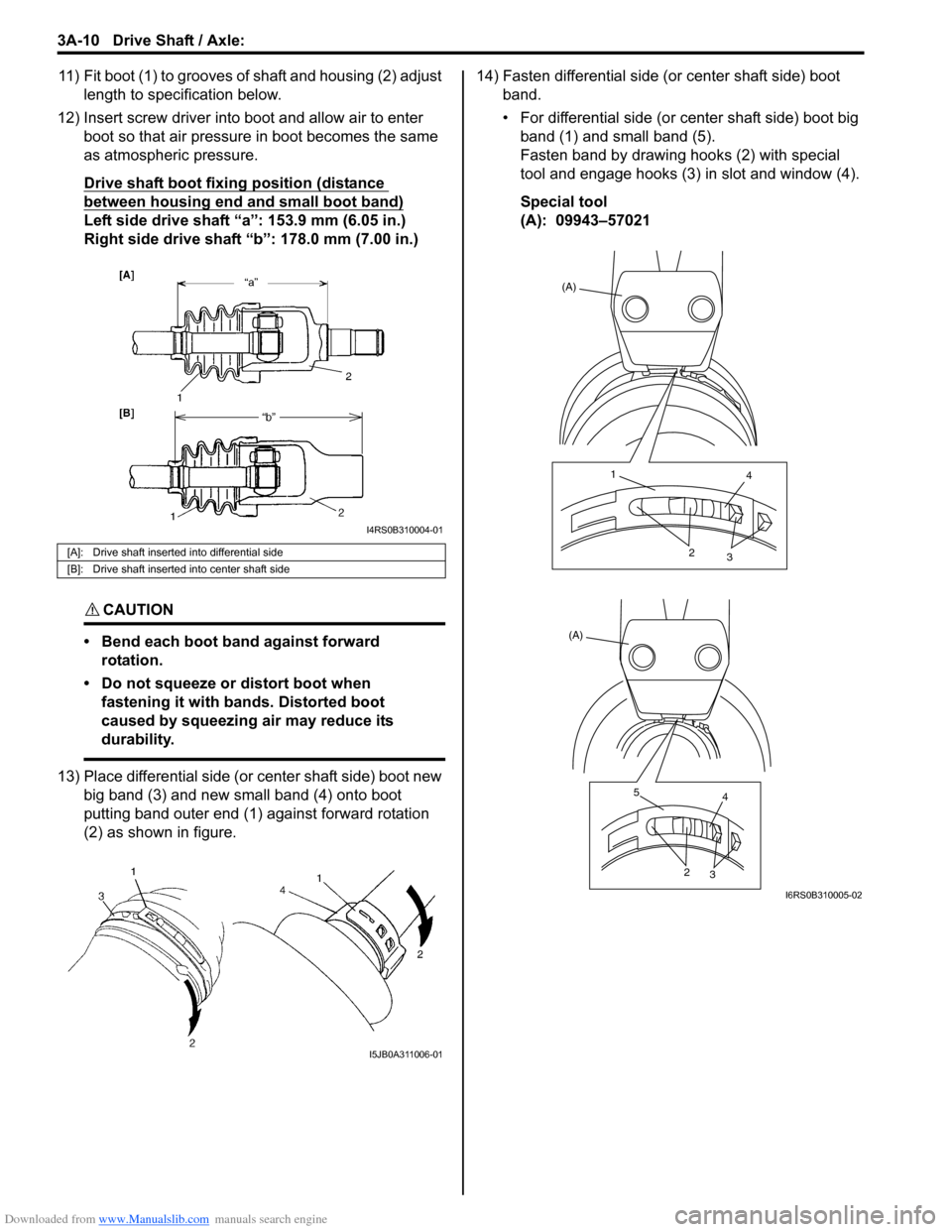
11) Fit boot (1) to grooves of shaft and housing (2) adjust
length to specification below.
12) Insert screw driver into boot and allow air to enter boot so that air pressure in boot becomes the same
as atmospheric pressure.
Drive shaft boot fixing position (distance
between housing end and small boot band)
Left side drive shaft “a”: 153.9 mm (6.05 in.)
Right side drive shaft “b”: 178.0 mm (7.00 in.)
CAUTION!
• Bend each boot band against forward rotation.
• Do not squeeze or distort boot when fastening it with bands. Distorted boot
caused by squeezing air may reduce its
durability.
13) Place differential side (or center shaft side) boot new big band (3) and new small band (4) onto boot
putting band outer end (1) against forward rotation
(2) as shown in figure. 14) Fasten differential side (or center shaft side) boot
band.
• For differential side (or center shaft side) boot big band (1) and small band (5).
Fasten band by drawing hooks (2) with special
tool and engage hooks (3) in slot and window (4).
Special tool
(A): 09943–57021
[A]: Drive shaft inserted into differential side
[B]: Drive shaft inserted into center shaft side
I4RS0B310004-01
I5JB0A311006-01
(A)
1 4
2 3
(A)
5 4
2 3
I6RS0B310005-02
Page 489 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Drive Shaft / Axle: 3A-11
DOJ
Judging from abnormality noted before disassembly and
what is found through visual check of components parts
after disassembly, prepare replacing parts and proceed
to reassembly.
Make sure that wheel side joint assembly and DOJ
housing are washed thoroughly and air dried.
Replace boot(s) with new one(s).
CAUTION!
• Do not wash boots in degreaser such as gasoline or kerosene. etc. Washing in
degreaser causes deterioration of boot.
• To ensure full performance of joint as designed, be sure to distinguish between
two types of grease in repair set and apply
specified volume to respective joint
referring to the followings for identification
of the grease.
1) Wash disassembled parts (except boots). After washing, dry parts completely by blowing air.
2) Clean boots with cloth.
3) Apply grease to wheel side joint. Use specified
grease in tube in wheel side boot set as a spare
parts.
Grease color
: Black
Amount
: 55 – 75 g (1.9 – 2.6 oz)
4) Install wheel side boot on shaft.
5) Fill up boot inside wi th specified grease.
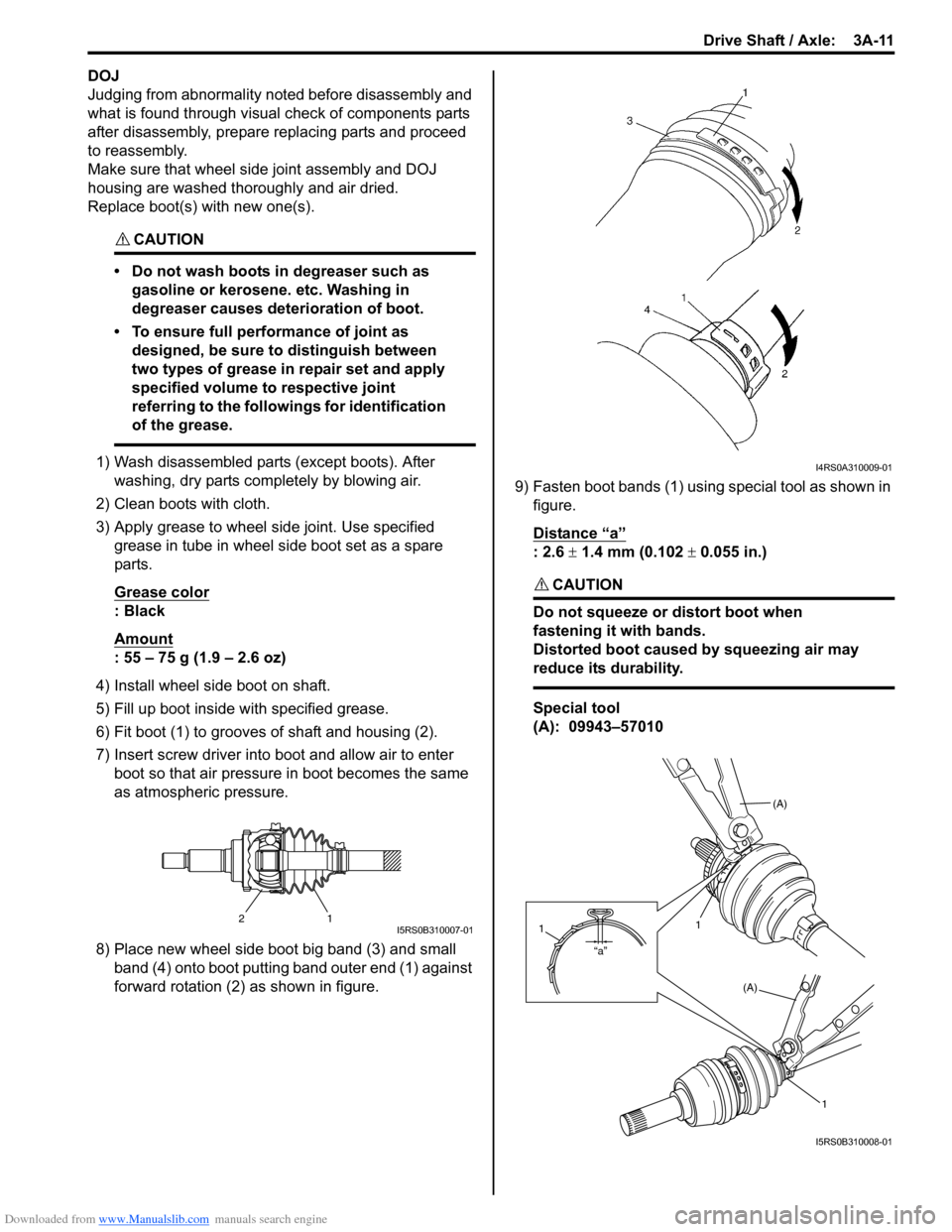
6) Fit boot (1) to grooves of shaft and housing (2).
7) Insert screw driver into boot and allow air to enter boot so that air pressure in boot becomes the same
as atmospheric pressure.
8) Place new wheel side boot big band (3) and small band (4) onto boot putting band outer end (1) against
forward rotation (2) as shown in figure. 9) Fasten boot bands (1) using special tool as shown in
figure.
Distance “a”
: 2.6 ± 1.4 mm (0.102 ± 0.055 in.)
CAUTION!
Do not squeeze or distort boot when
fastening it with bands.
Distorted boot caused by squeezing air may
reduce its durability.
Special tool
(A): 09943–57010
21I5RS0B310007-01
I4RS0A310009-01
(A)
1
(A)
1
“a”
1
I5RS0B310008-01
Page 490 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3A-12 Drive Shaft / Axle:
10) Set new differential side (or center shaft side) small band and new differential side (or center shaft side)
boot on shaft temporarily.
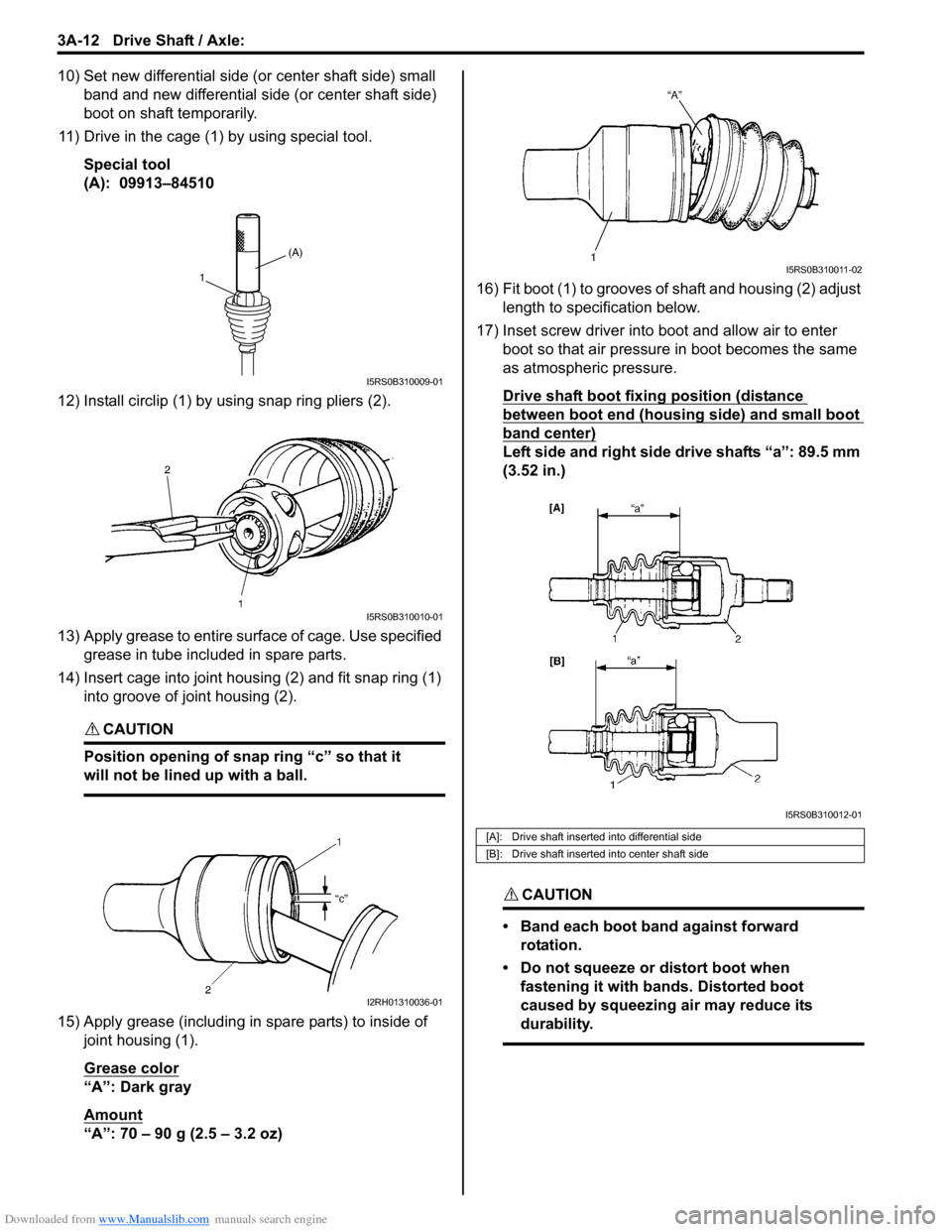
11) Drive in the cage (1) by using special tool.
Special tool
(A): 09913–84510
12) Install circlip (1) by using snap ring pliers (2).
13) Apply grease to entire su rface of cage. Use specified
grease in tube included in spare parts.
14) Insert cage into joint housing (2) and fit snap ring (1) into groove of joint housing (2).
CAUTION!
Position opening of snap ring “c” so that it
will not be lined up with a ball.
15) Apply grease (including in spare parts) to inside of joint housing (1).
Grease color
“A”: Dark gray
Amount
“A”: 70 – 90 g (2.5 – 3.2 oz) 16) Fit boot (1) to grooves of shaft and housing (2) adjust
length to specification below.
17) Inset screw driver into boot and allow air to enter boot so that air pressure in boot becomes the same
as atmospheric pressure.
Drive shaft boot fixing position (distance
between boot end (housing side) and small boot
band center)
Left side and right side drive shafts “a”: 89.5 mm
(3.52 in.)
CAUTION!
• Band each boot band against forward rotation.
• Do not squeeze or distort boot when fastening it with bands. Distorted boot
caused by squeezing air may reduce its
durability.
(A)
1
I5RS0B310009-01
I5RS0B310010-01
I2RH01310036-01
[A]: Drive shaft inserted into differential side
[B]: Drive shaft inserted into center shaft side
I5RS0B310011-02
I5RS0B310012-01
Page 496 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4-ii Table of Contents
Repair Instructions ..............................................4D-2Parking Brake Inspection and Adjustment ..........4D-2
Parking Brake Cable Removal and Installation ......................................................... 4D-3
Parking Brake Lever Removal and Installation ....4D-3
Specifications .... ...................................................4D-4
Tightening Torque Specifications ........................4D-4
ABS ........................................... .................4E-1
Precautions........................................................... 4E-1
Precautions in Diagnosing Troubles ................... 4E-1
Precautions in On-Vehicle Service...................... 4E-1
Precautions in Hydraulic Unit Operation Check ................................................................ 4E-1
General Description ............................................. 4E-2 ABS Description .................................................. 4E-2
ABS Hydraulic Unit / Control Module Assembly Description ....................................... 4E-2
CAN Communication System Description........... 4E-3
Schematic and Routing Diagram ........................ 4E-4 ABS Schematic ................................................... 4E-4
ABS Wiring Circuit Diagram ................................ 4E-5
Component Location ........... ................................ 4E-7
ABS Components Location ................................. 4E-7
Front Wheel Speed Sensor Components Location ............................................................ 4E-7
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Components Location ............................................................ 4E-8
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............ 4E-8 ABS Check .......................................................... 4E-8
ABS Warning Light Check................................. 4E-10
EBD Warning Light (Brake Warning Light) Check .............................................................. 4E-10
DTC Check........................................................ 4E-11
DTC Table ......................................................... 4E-11
DTC Clearance ................................................. 4E-12
Scan Tool Data ................................................. 4E-12
ABS Warning Light Does Not Come ON at Ignition Switch ON .......................................... 4E-13
ABS Warning Light Comes ON Steady ............. 4E-14
EBD Warning Light (Brake Warning Light) Comes ON Steady .......................................... 4E-15
Serial Data Link Circuit Check .......................... 4E-16
DTC C1021, C1022 / C1025, C1026 / C1031, C1032 / C1035, C1036: Right-Front / Left-
Front / Right-Rear / Left-Rear Wheel Speed
Sensor Circuit or Sensor Ring ........................ 4E-18
DTC C1041 / C1045 / C1051 / C1055, DTC C1042 / C1046 / C1052 / C1056: Right-Front
/ Left-Front / Right-Rear / Left-Rear Inlet
Solenoid Circuit, Right-Front / Left-Front /
Right-Rear / Left-Rear Outlet Solenoid
Circuit .............................................................. 4E-20
DTC C1057: Power Source Circuit ................... 4E-21
DTC C1061: ABS Pump Motor and/or Motor Driver Circuit ................................................... 4E-22
DTC C1063: Solenoid Valve Power Supply Driver Circuit ................................................... 4E-23
DTC C1071: ABS Control Module..................... 4E-24 DTC U1073: Control Module Communication
Bus Off ............................................................ 4E-25
DTC U1100: Lost Communication with ECM (Reception Error)............................................. 4E-27
Repair Instructions ............ ................................ 4E-28
ABS Hydraulic Unit Operati on Check................ 4E-28
ABS Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly Components ...... ............................. 4E-29
ABS Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection .................... 4E-29
ABS Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly Removal and Inst allation ................ 4E-29
Front / Rear Wheel Speed Sensor On-Vehicle Inspection ........................................................ 4E-31
Front Wheel Speed Sensor Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4E-32
Front Wheel Speed Sensor Inspection ............. 4E-32
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4E-33
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Inspection .............. 4E-34
Front Wheel Encoder On-Veh icle Inspection .... 4E-34
Front wheel Enco der Removal and
Installation ....................................................... 4E-34
Rear Wheel Encoder On-Veh icle Inspection..... 4E-34
Rear Wheel Encoder Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4E-34
Specifications ..................... ................................ 4E-35
Tightening Torque Specifications ...................... 4E-35
Special Tools and Equipmen t ........................... 4E-35
Special Tool ...................................................... 4E-35
Electronic Stability Prog ram ...................4F-1
Precautions ........................................................... 4F-1
Precautions in Diagnosing Troubles ................... 4F-1
Precautions in On-Vehicle Service...................... 4F-1
Precautions in Hydraulic Unit Operation Check ................................................................ 4F-1
Precautions in Sensor Calibration ....................... 4F-1
Precautions in Speedometer Test or Other Tests ................................................................. 4F-2
General Description ............................................. 4F-2 Electronic Stability Program Description ............. 4F-2
Electronic Stability Program Construction ........... 4F-3
ESP® Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly Description........................................ 4F-5
Warning Lamp, Indicator Lamp Description ........ 4F-6
CAN Communication System Description........... 4F-6
CAN Communication System For Electronic Stability Program Description ............................ 4F-7
Schematic and Routing Diagram ........................ 4F-8 Electronic Stability Program Schematic .............. 4F-8
Electronic Stability Program Wiring Circuit Diagram............................................................. 4F-9
Component Location ............ ............................. 4F-11
Electronic Stability Program Component
Location........................................................... 4F-11
Diagnostic Information and Procedures .......... 4F-12 Electronic Stability Program System Check ...... 4F-12
ESP® Warning lamp Check .............................. 4F-14