Fuel SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.G Service Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 252 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-202 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
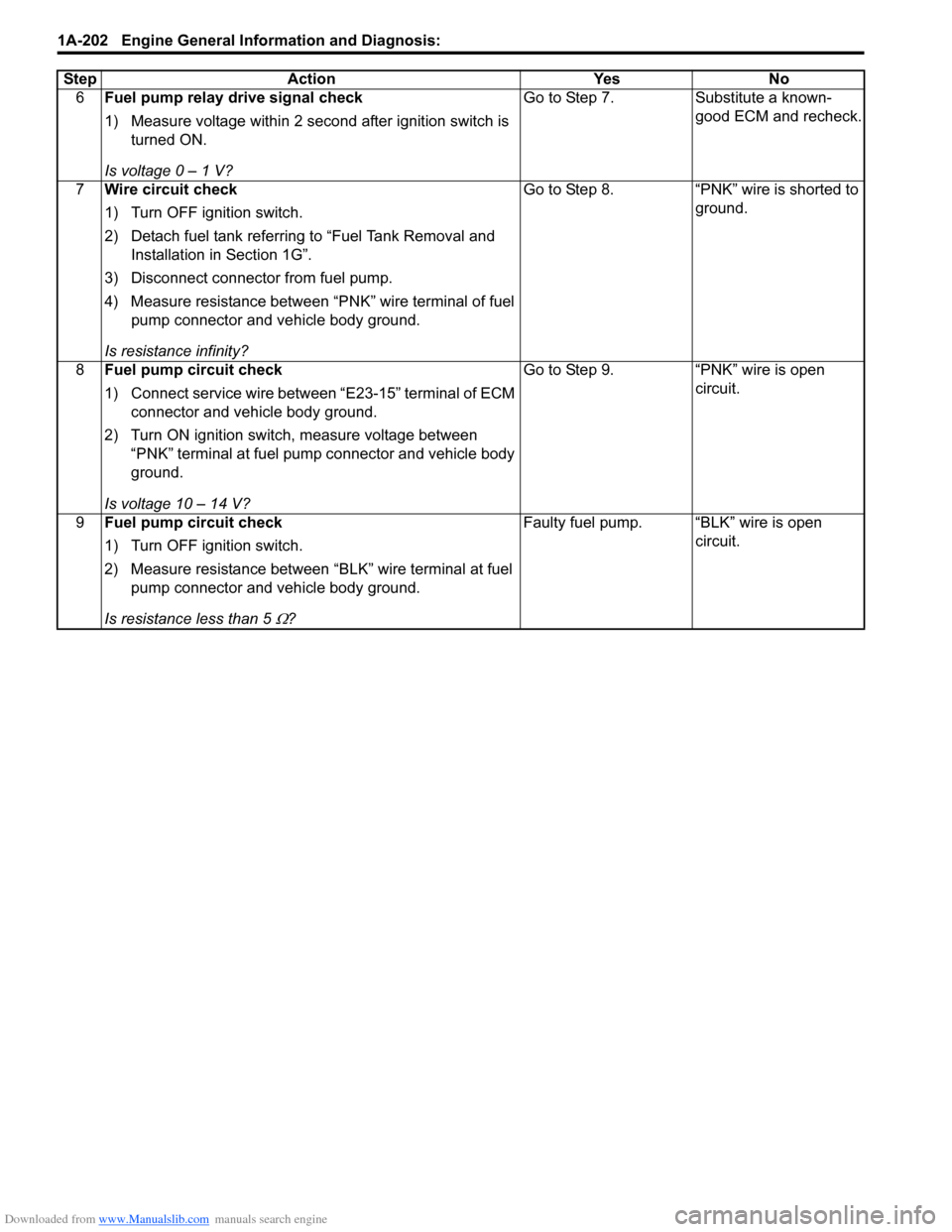
6Fuel pump relay drive signal check
1) Measure voltage within 2 second after ignition switch is
turned ON.
Is voltage 0 – 1 V? Go to Step 7. Substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
7 Wire circuit check
1) Turn OFF ignition switch.
2) Detach fuel tank referring to “Fuel Tank Removal and
Installation in Section 1G”.
3) Disconnect connector from fuel pump.
4) Measure resistance between “PNK” wire terminal of fuel pump connector and vehicle body ground.
Is resistance infinity? Go to Step 8. “PNK” wire is shorted to
ground.
8 Fuel pump circuit check
1) Connect service wire between “E23-15” terminal of ECM
connector and vehicle body ground.
2) Turn ON ignition switch, measure voltage between “PNK” terminal at fuel pump connector and vehicle body
ground.
Is voltage 10 – 14 V? Go to Step 9. “PNK” wire is open
circuit.
9 Fuel pump circuit check
1) Turn OFF ignition switch.
2) Measure resistance between “BLK” wire terminal at fuel
pump connector and vehicle body ground.
Is resistance less than 5
Ω? Faulty fuel pump. “BLK” wire is open
circuit.
Step Action Yes No
Page 253 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-203
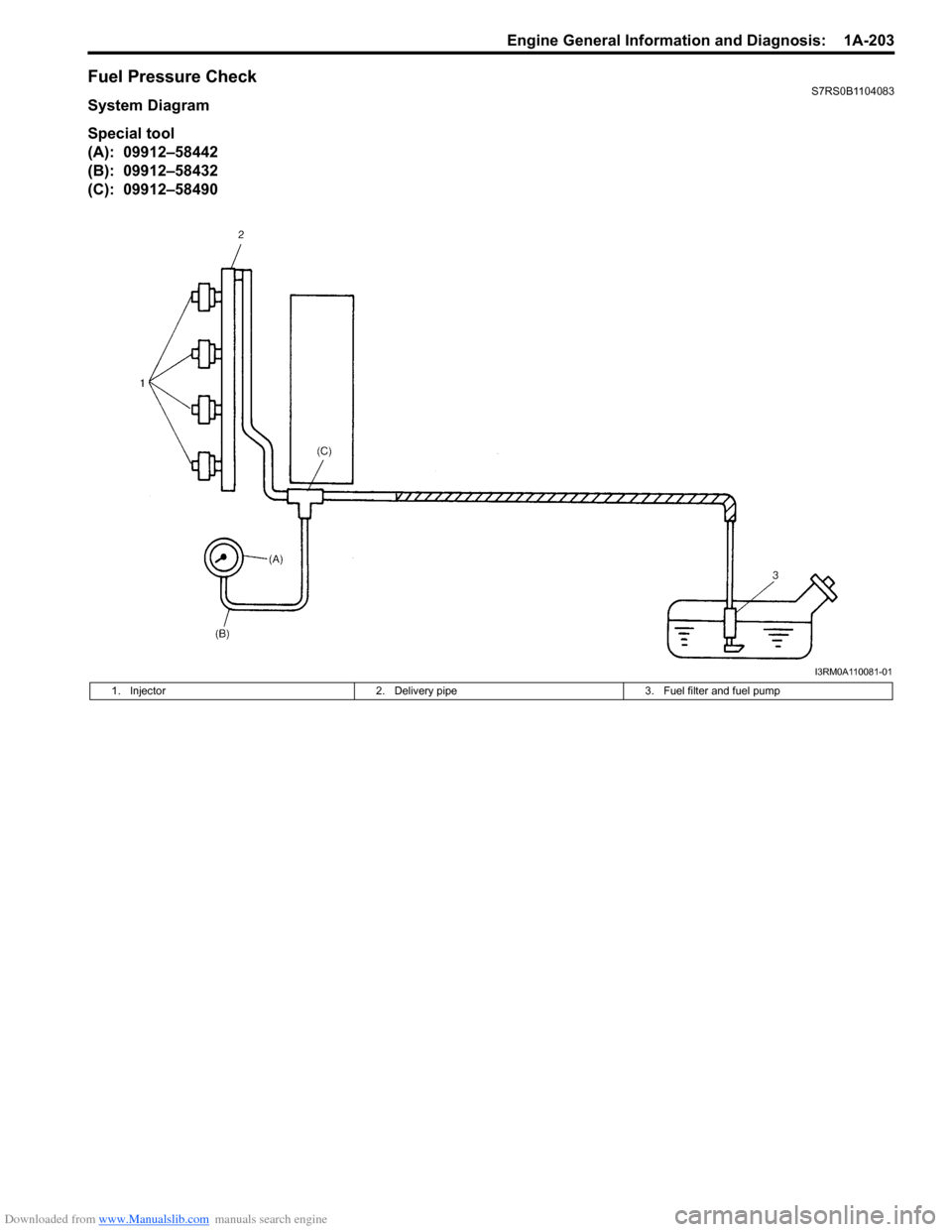
Fuel Pressure CheckS7RS0B1104083
System Diagram
Special tool
(A): 09912–58442
(B): 09912–58432
(C): 09912–58490
I3RM0A110081-01
1. Injector2. Delivery pipe 3. Fuel filter and fuel pump
Page 254 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-204 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
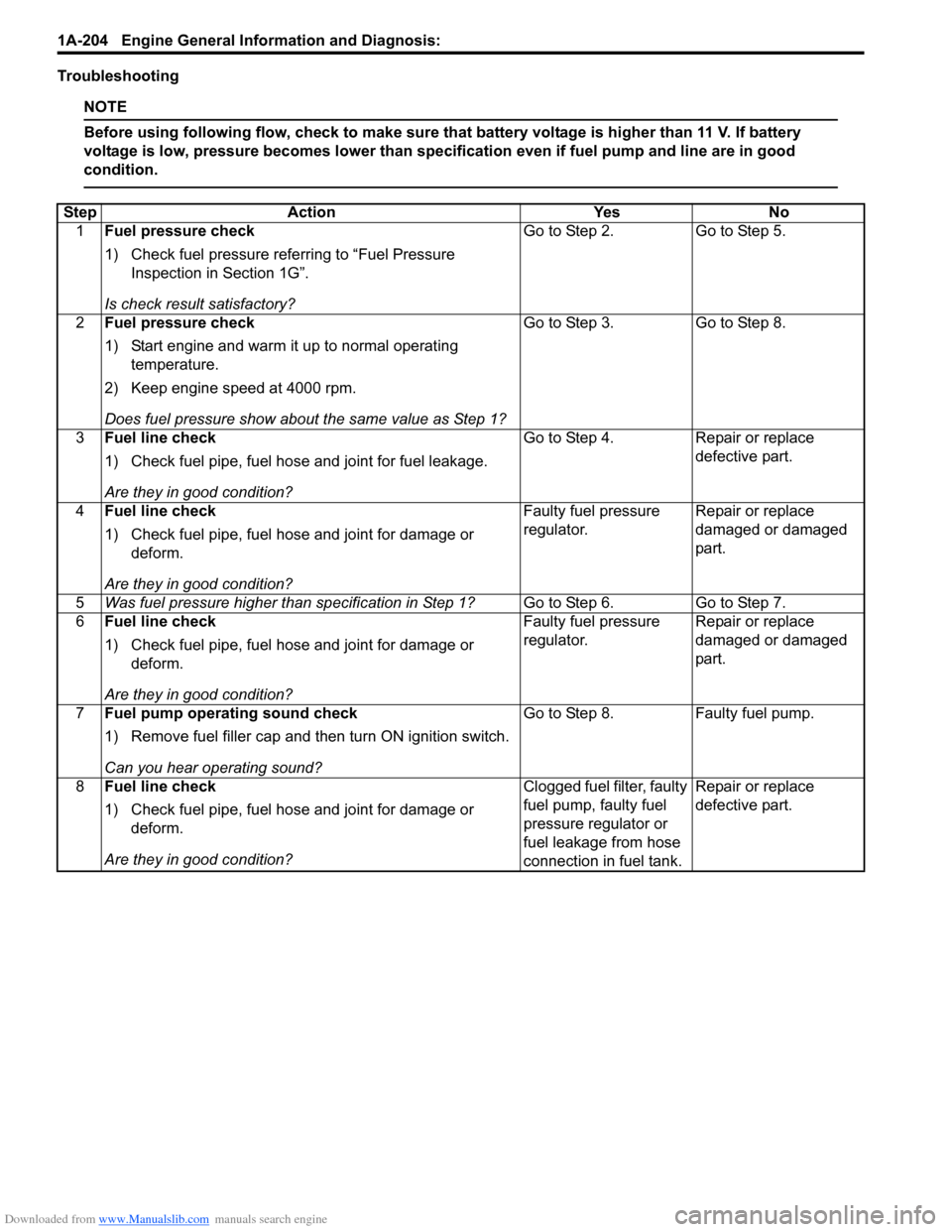
Troubleshooting
NOTE
Before using following flow, check to make sure that battery voltage is higher than 11 V. If battery
voltage is low, pressure becomes lower than specification even if fuel pump and line are in good
condition.
StepAction YesNo
1 Fuel pressure check
1) Check fuel pressure referring to “Fuel Pressure
Inspection in Section 1G”.
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 2.
Go to Step 5.
2 Fuel pressure check
1) Start engine and warm it up to normal operating
temperature.
2) Keep engine speed at 4000 rpm.
Does fuel pressure show about the same value as Step 1? Go to Step 3.
Go to Step 8.
3 Fuel line check
1) Check fuel pipe, fuel hose and joint for fuel leakage.
Are they in good condition? Go to Step 4.
Repair or replace
defective part.
4 Fuel line check
1) Check fuel pipe, fuel hose and joint for damage or
deform.
Are they in good condition? Faulty fuel pressure
regulator.
Repair or replace
damaged or damaged
part.
5 Was fuel pressure higher than specification in Step 1? Go to Step 6.Go to Step 7.
6 Fuel line check
1) Check fuel pipe, fuel hose and joint for damage or
deform.
Are they in good condition? Faulty fuel pressure
regulator.
Repair or replace
damaged or damaged
part.
7 Fuel pump operating sound check
1) Remove fuel filler cap and th en turn ON ignition switch.
Can you hear operating sound? Go to Step 8.
Faulty fuel pump.
8 Fuel line check
1) Check fuel pipe, fuel hose and joint for damage or
deform.
Are they in good condition? Clogged fuel filter, faulty
fuel pump, faulty fuel
pressure regulator or
fuel leakage from hose
connection in fuel tank.Repair or replace
defective part.
Page 266 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-216 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Repair Instructions
Idle Speed and IAC Throttle Valve Opening
Inspection
S7RS0B1106001
Before idle speed check, make sure of the following.
• Lead wires and hoses of electronic fuel injection and engine and emission control systems are connected
securely.
• Valve lash is checked according to maintenance schedule.
• Ignition timing is within specification.
• All accessories (wipers, heater, lights, A/C, etc.) are out of service.
• Air cleaner has been properly installed and is in good condition.
• No abnormal air drawn in from air intake system.
After all items are confirmed, check idle speed and IAC
duty as follows.
NOTE
Before starting engine, place transmission
gear shift lever in “Neutral” (shift selector
lever to “P” range for A/T vehicle), and set
parking brake and block drive wheels.
1) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to DLC (1) with ignition
switch turned OFF.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool 2) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
3) Check engine idle speed and “IAC throttle opening”
by using “Data List” mode on scan tool to check “IAC
throttle opening”.
4) If check result is out of sp ecification, inspect electric
throttle body assembly referring to “Electric Throttle
Body Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection in Section
1C”.
Engine idle speed
A/C OFF: 700 ± 50 rpm (IAC duty: 5 – 55%)
A/C ON: 850 ± 50 rpm
5) Check that specified engine idle speed is obtained with A/C turned ON if vehi cle is equipped with A/C.
If not, check A/C system.
(A)
1
I4RS0B110093-01
Page 267 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-217
Special Tools and Equipment
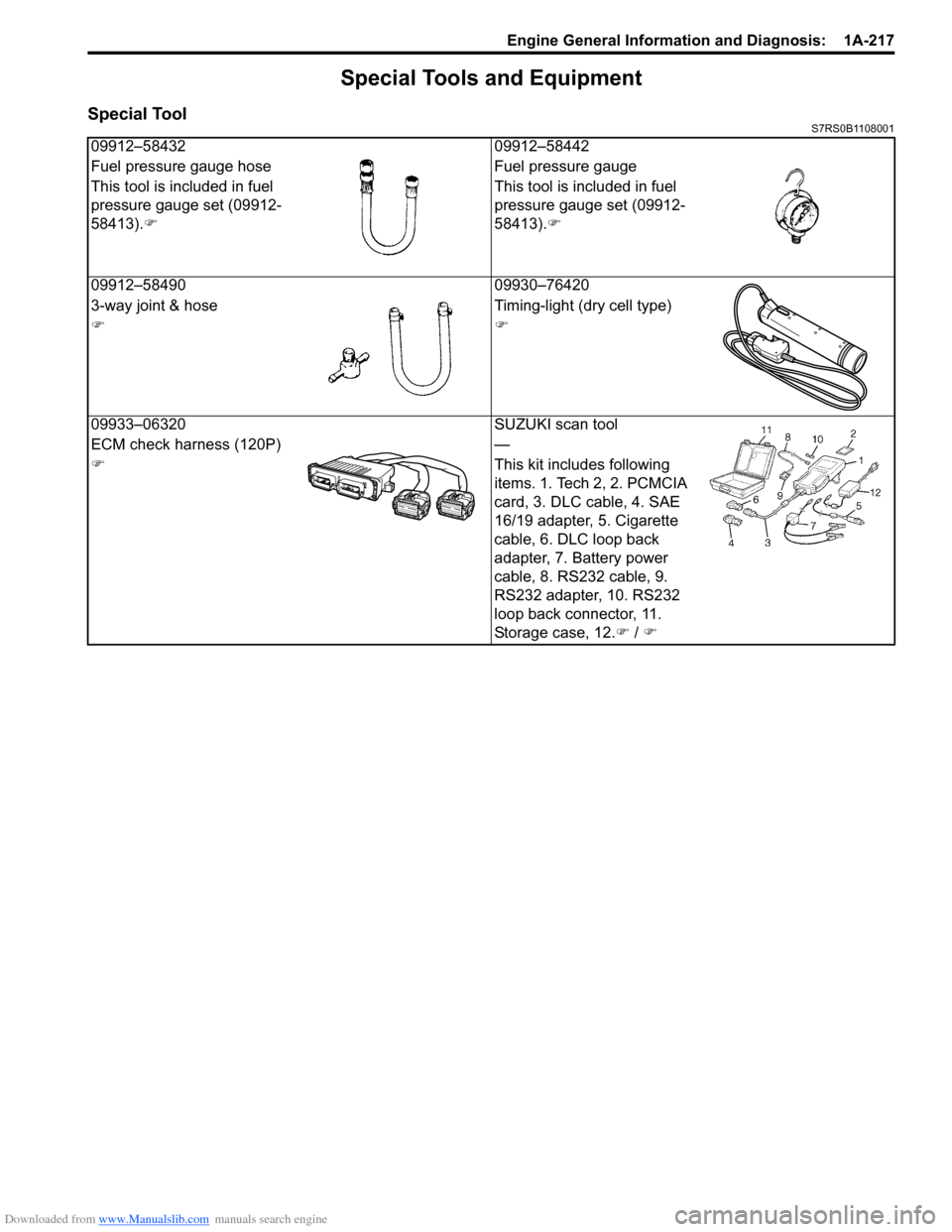
Special ToolS7RS0B1108001
09912–5843209912–58442
Fuel pressure gauge hose Fuel pressure gauge
This tool is included in fuel
pressure gauge set (09912-
58413). �) This tool is included in fuel
pressure gauge set (09912-
58413).
�)
09912–58490 09930–76420
3-way joint & hose Timing-light (dry cell type)
�)�)
09933–06320 SUZUKI scan tool
ECM check harness (120P) —
�) This kit includes following
items. 1. Tech 2, 2. PCMCIA
card, 3. DLC cable, 4. SAE
16/19 adapter, 5. Cigarette
cable, 6. DLC loop back
adapter, 7. Battery power
cable, 8. RS232 cable, 9.
RS232 adapter, 10. RS232
loop back connector, 11.
Storage case, 12.�) / �)
Page 269 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Aux. Emission Control Devices: 1B-2
EVAP Canister Purge Valve and Its Circuit
Inspection
S7RS0B1206002
WARNING!
Do not apply vacuum by mouth; otherwise
harmful fuel vapor can be breathed in.
CAUTION!
Do not apply vacuum more than –86 kPa (–
12.47 psi); otherwise EVAP canister purge
valve could be damaged.
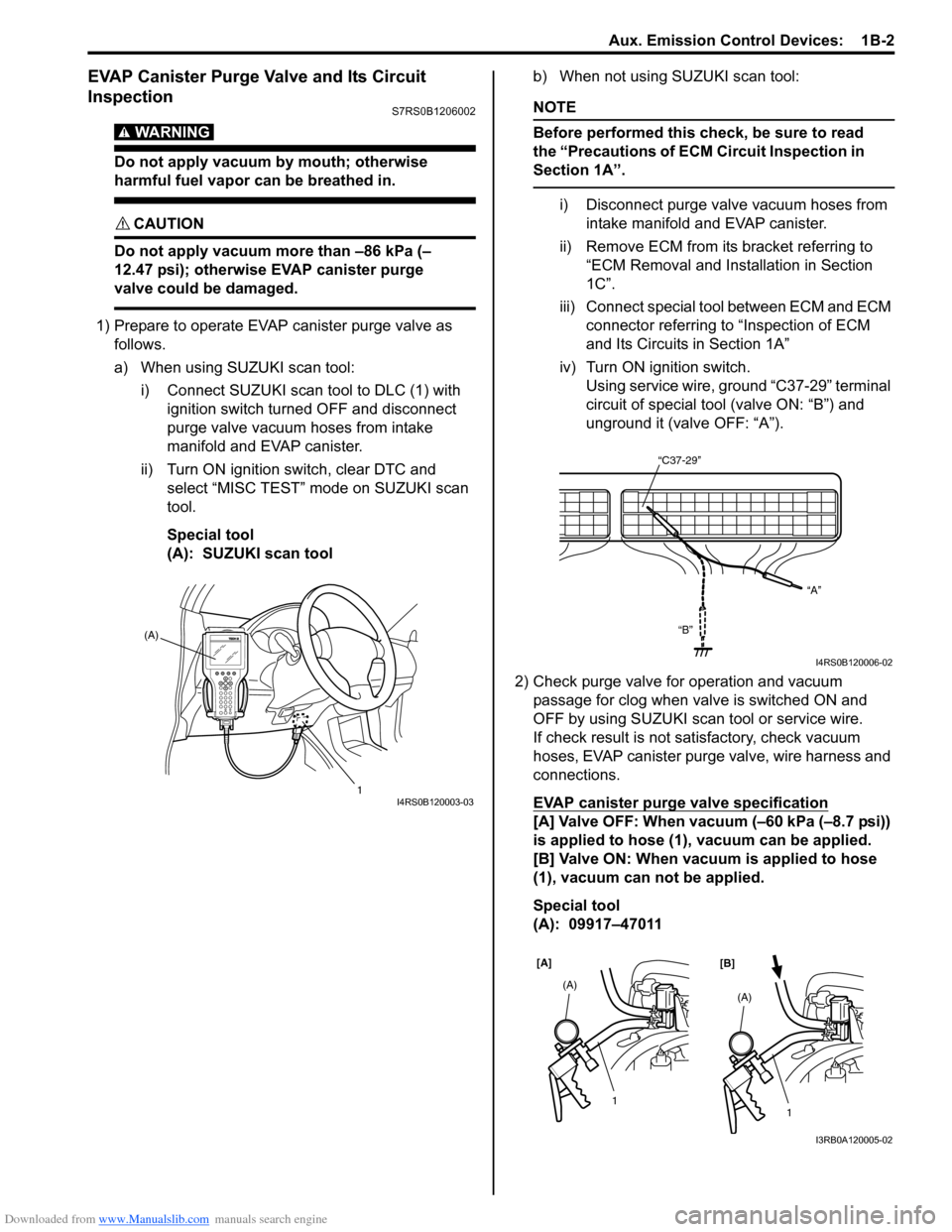
1) Prepare to operate EVAP canister purge valve as follows.
a) When using SUZUKI scan tool:
i) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to DLC (1) with ignition switch turned OFF and disconnect
purge valve vacuum hoses from intake
manifold and EVAP canister.
ii) Turn ON ignition switch, clear DTC and select “MISC TEST” mode on SUZUKI scan
tool.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool b) When not using SUZUKI scan tool:
NOTE
Before performed this check, be sure to read
the “Precautions of ECM Circuit Inspection in
Section 1A”.
i) Disconnect purge valve vacuum hoses from
intake manifold and EVAP canister.
ii) Remove ECM from it s bracket referring to
“ECM Removal and Inst allation in Section
1C”.
iii) Connect special tool between ECM and ECM connector referring to “Inspection of ECM
and Its Circuits in Section 1A”
iv) Turn ON ignition switch. Using service wire, ground “C37-29” terminal
circuit of special tool (valve ON: “B”) and
unground it (valve OFF: “A”).
2) Check purge valve for operation and vacuum passage for clog when valve is switched ON and
OFF by using SUZUKI scan tool or service wire.
If check result is not satisfactory, check vacuum
hoses, EVAP canister purge valve, wire harness and
connections.
EVAP canister purge valve specification
[A] Valve OFF: When vacuum (–60 kPa (–8.7 psi))
is applied to hose (1), vacuum can be applied.
[B] Valve ON: When vacuum is applied to hose
(1), vacuum can not be applied.
Special tool
(A): 09917–47011
(A)
1
I4RS0B120003-03
“C37-29”“A”
“B”
I4RS0B120006-02
[A] [B]
1
(A)1
(A)
I3RB0A120005-02
Page 270 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1B-3 Aux. Emission Control Devices:
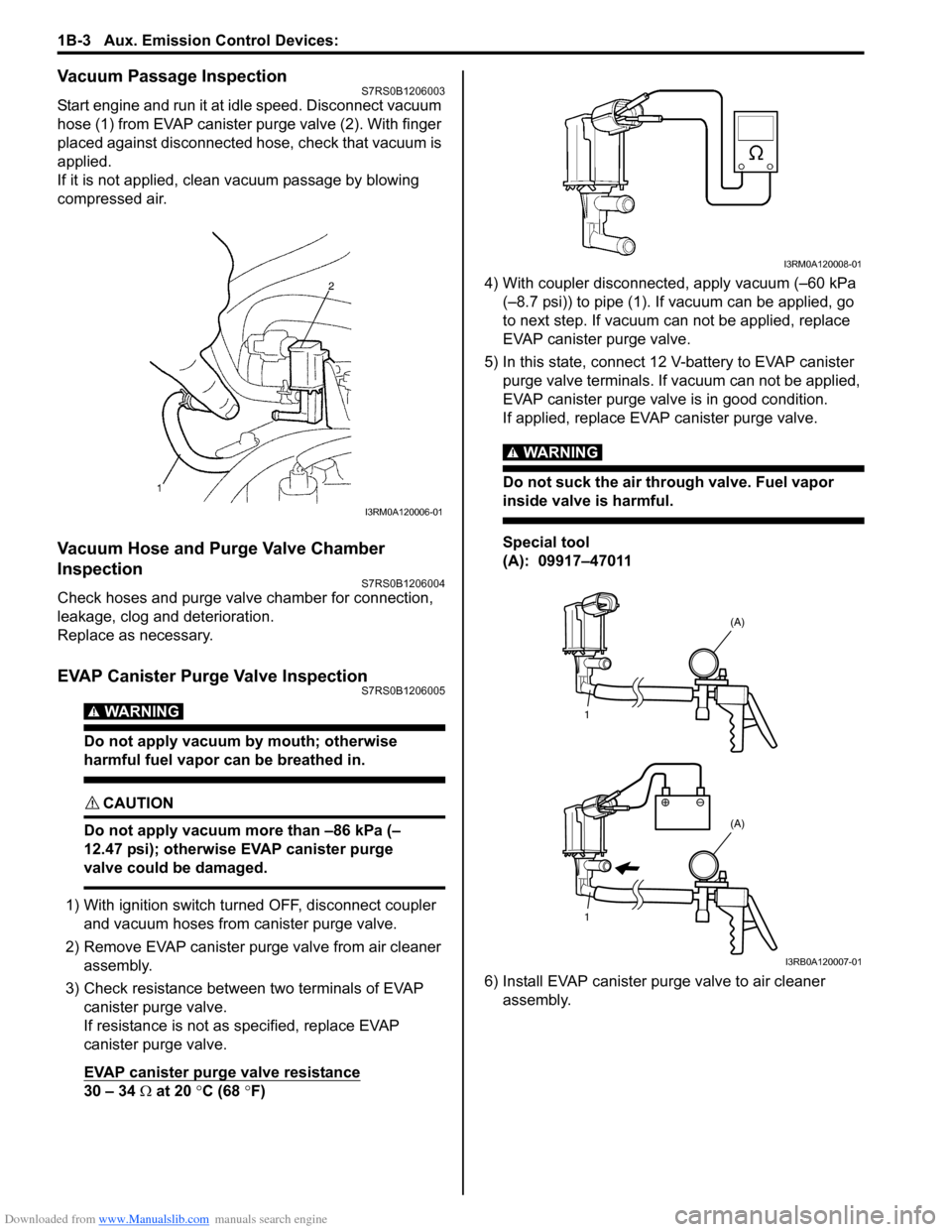
Vacuum Passage InspectionS7RS0B1206003
Start engine and run it at idle speed. Disconnect vacuum
hose (1) from EVAP canister purge valve (2). With finger
placed against disconnected hose, check that vacuum is
applied.
If it is not applied, clean vacuum passage by blowing
compressed air.
Vacuum Hose and Purge Valve Chamber
Inspection
S7RS0B1206004
Check hoses and purge valv e chamber for connection,
leakage, clog and deterioration.
Replace as necessary.
EVAP Canister Purge Valve InspectionS7RS0B1206005
WARNING!
Do not apply vacuum by mouth; otherwise
harmful fuel vapor can be breathed in.
CAUTION!
Do not apply vacuum more than –86 kPa (–
12.47 psi); otherwise EVAP canister purge
valve could be damaged.
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, disconnect coupler and vacuum hoses from canister purge valve.
2) Remove EVAP canister purge valve from air cleaner assembly.
3) Check resistance between two terminals of EVAP canister purge valve.
If resistance is not as specified, replace EVAP
canister purge valve.
EVAP canister purge valve resistance
30 – 34 Ω at 20 °C (68 °F) 4) With coupler disconnected, apply vacuum (–60 kPa
(–8.7 psi)) to pipe (1). If vacuum can be applied, go
to next step. If vacuum can not be applied, replace
EVAP canister purge valve.
5) In this state, connect 12 V-battery to EVAP canister purge valve terminals. If vacuum can not be applied,
EVAP canister purge valve is in good condition.
If applied, replace EVAP canister purge valve.
WARNING!
Do not suck the air through valve. Fuel vapor
inside valve is harmful.
Special tool
(A): 09917–47011
6) Install EVAP canister purge valve to air cleaner assembly.
I3RM0A120006-01
I3RM0A120008-01
1
1 (A)
(A)
I3RB0A120007-01
Page 271 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Aux. Emission Control Devices: 1B-4
EVAP Canister InspectionS7RS0B1206006
WARNING!
DO NOT SUCK nozzles on EVAP canister.
Fuel vapor inside EVAP canister is harmful.
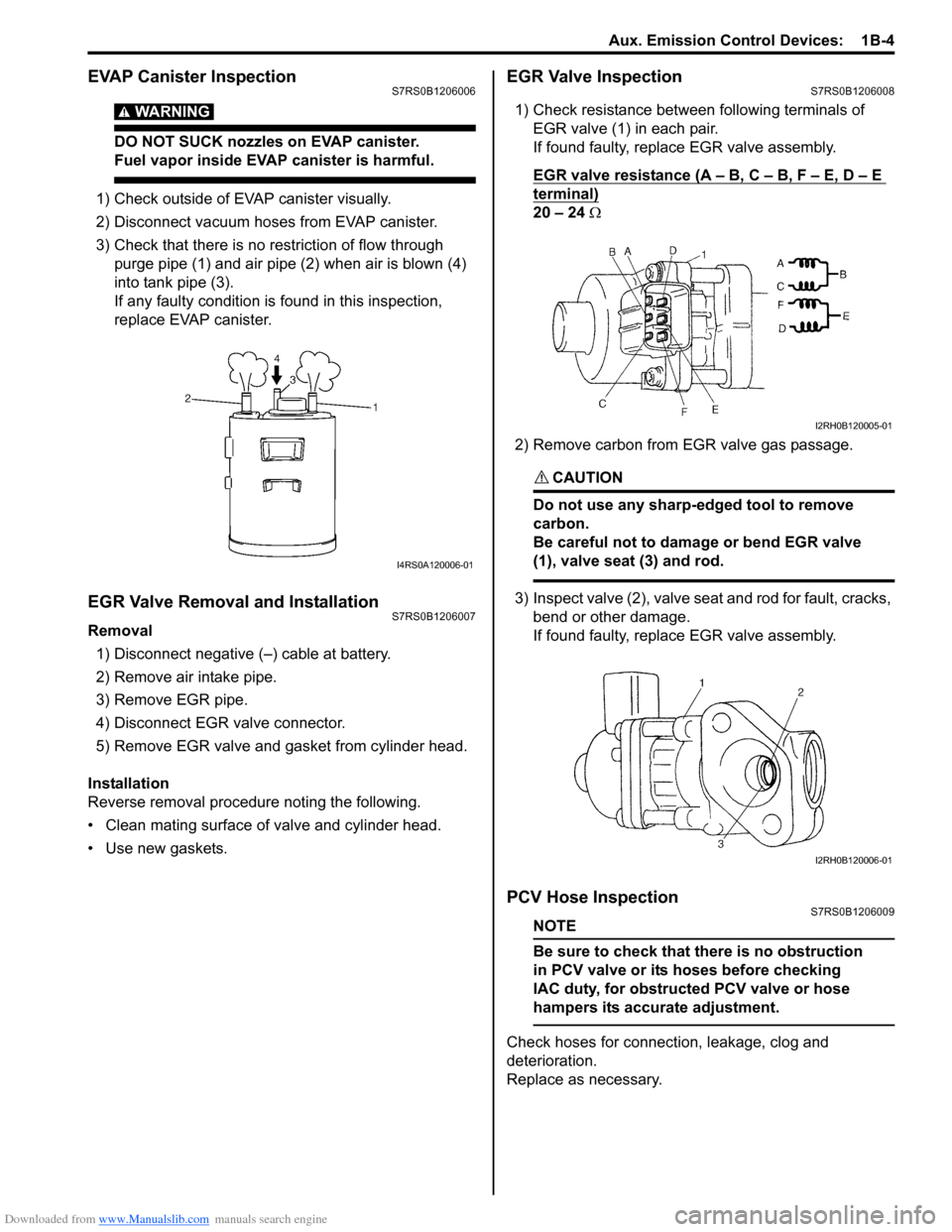
1) Check outside of EVAP canister visually.
2) Disconnect vacuum hoses from EVAP canister.
3) Check that there is no restriction of flow through purge pipe (1) and air pipe (2) when air is blown (4)
into tank pipe (3).
If any faulty condition is found in this inspection,
replace EVAP canister.
EGR Valve Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1206007
Removal
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Remove air intake pipe.
3) Remove EGR pipe.
4) Disconnect EGR valve connector.
5) Remove EGR valve and gasket from cylinder head.
Installation
Reverse removal procedure noting the following.
• Clean mating surface of valve and cylinder head.
• Use new gaskets.
EGR Valve InspectionS7RS0B1206008
1) Check resistance between following terminals of EGR valve (1) in each pair.
If found faulty, replace EGR valve assembly.
EGR valve resistance (A – B, C – B, F – E, D – E
terminal)
20 – 24 Ω
2) Remove carbon from EGR valve gas passage.
CAUTION!
Do not use any sharp-edged tool to remove
carbon.
Be careful not to damage or bend EGR valve
(1), valve seat (3) and rod.
3) Inspect valve (2), valve seat and rod for fault, cracks, bend or other damage.
If found faulty, replace EGR valve assembly.
PCV Hose InspectionS7RS0B1206009
NOTE
Be sure to check that there is no obstruction
in PCV valve or its hoses before checking
IAC duty, for obstructed PCV valve or hose
hampers its accurate adjustment.
Check hoses for connection, leakage, clog and
deterioration.
Replace as necessary.
I4RS0A120006-01
I2RH0B120005-01
I2RH0B120006-01
Page 282 of 1496
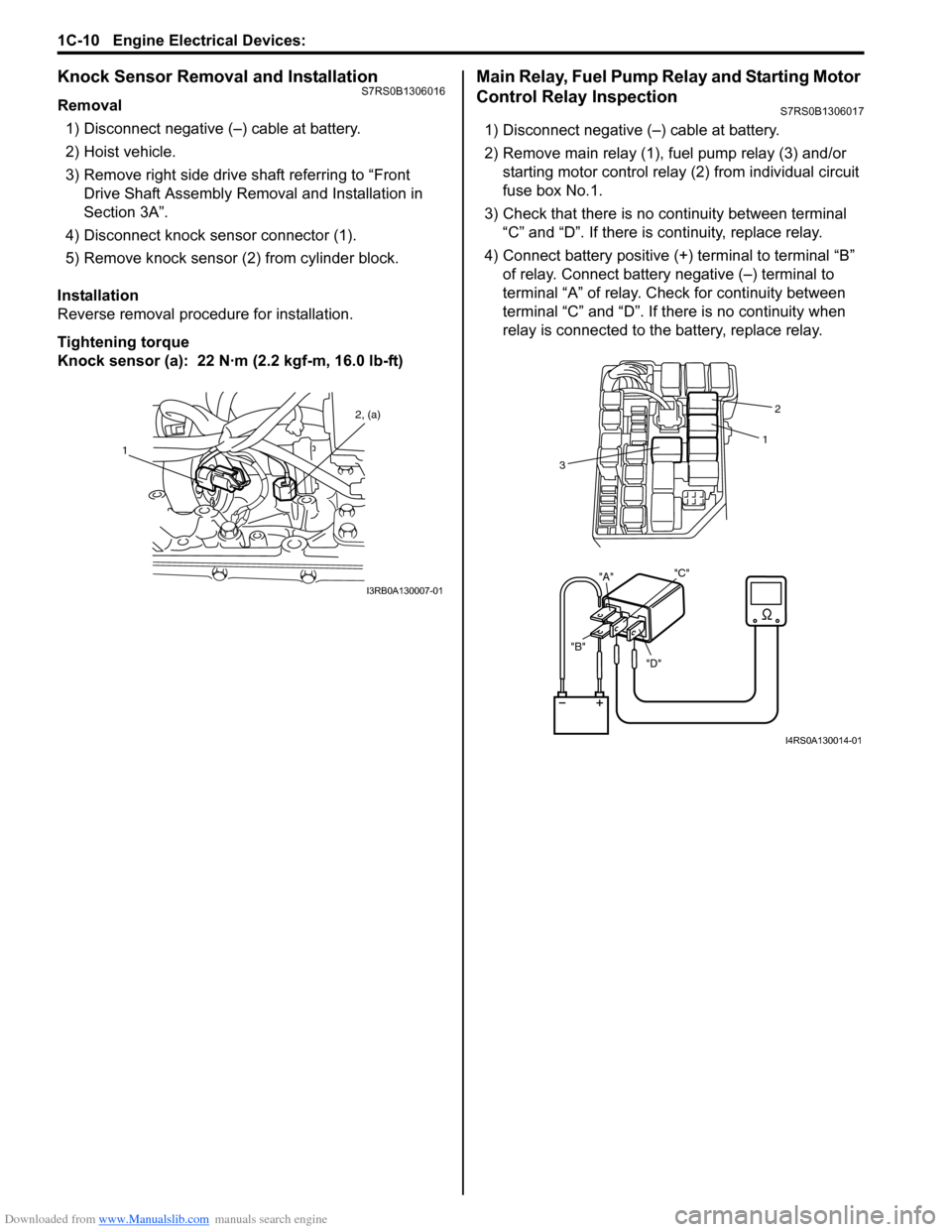
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1C-10 Engine Electrical Devices:
Knock Sensor Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1306016
Removal1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Hoist vehicle.
3) Remove right side drive shaft referring to “Front Drive Shaft Assembly Removal and Installation in
Section 3A”.
4) Disconnect knock sensor connector (1).
5) Remove knock sensor (2) from cylinder block.
Installation
Reverse removal procedure for installation.
Tightening torque
Knock sensor (a): 22 N· m (2.2 kgf-m, 16.0 lb-ft)
Main Relay, Fuel Pump Relay and Starting Motor
Control Relay Inspection
S7RS0B1306017
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Remove main relay (1), fuel pump relay (3) and/or
starting motor control relay (2) from individual circuit
fuse box No.1.
3) Check that there is no continuity between terminal “C” and “D”. If there is continuity, replace relay.
4) Connect battery positive (+ ) terminal to terminal “B”
of relay. Connect battery negative (–) terminal to
terminal “A” of relay. Ch eck for continuity between
terminal “C” and “D”. If t here is no continuity when
relay is connected to the battery, replace relay.
1 2, (a)
I3RB0A130007-01
"D"
"B" "A"
"C"
2
1
3
I4RS0A130014-01
Page 287 of 1496
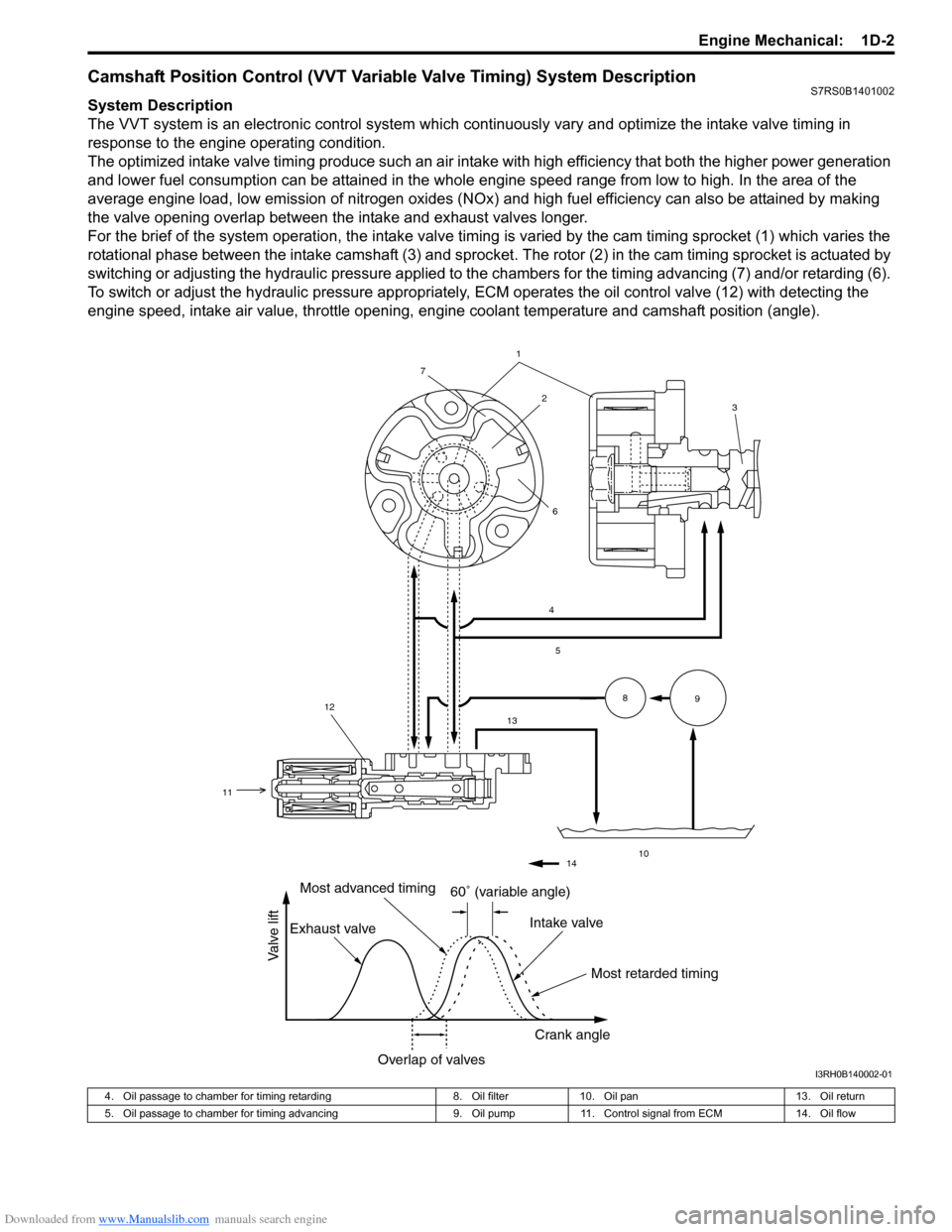
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-2
Camshaft Position Control (VVT Variable Valve Timing) System DescriptionS7RS0B1401002
System Description
The VVT system is an electronic control system which continuously vary and optimize the intake valve timing in
response to the engine operating condition.
The optimized intake valve timing produce such an air intake with high efficiency that both the higher power generation
and lower fuel consumption can be attained in the whole engine speed range from low to high. In the area of the
average engine load, low emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and high fuel efficiency can also be attained by making
the valve opening overlap between the intake and exhaust valves longer.
For the brief of the system operation, the intake valve timing is varied by the cam timing sprocket (1) which varies the
rotational phase between the intake camshaft (3) and sprocket . The rotor (2) in the cam timing sprocket is actuated by
switching or adjusting the hydraulic pressure applied to the chambers for the timing advancing (7) and/or retarding (6).
To switch or adjust the hydraulic pressure appropriately, ECM operates the oil control valve (12) with detecting the
engine speed, intake air value, throttle opening, engine coolant temperature and camshaft position (angle).
1
4
5
13
10
89
2
7
6
12
11
3
14
60� (variable angle)
Most retarded timing
Most advanced timing
Exhaust valve Intake valve
Crank angle
Overlap of valves
Valve lift
I3RH0B140002-01
4. Oil passage to chamber for timing retarding 8. Oil filter10. Oil pan 13. Oil return
5. Oil passage to chamber for timing advancing 9. Oil pump11. Control signal from ECM 14. Oil flow