Rear wheel SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.G Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2008, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 467 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Rear Suspension: 2C-13
Spindle InspectionS7RS0B2306015
• Inspect for cracks, deformation or damage.Replace any defective part.
Rear Suspension Fasteners InspectionS7RS0B2306016
Check each bolt and nut fastening suspension parts for
tightness. Tighten loose one, if any, to specified torque
referring to the figure in “Rear Suspension Construction”.
Specifications
Tightening Torque SpecificationsS7RS0B2307001
NOTE
The specified tightening torque is also described in the following.
“Rear Suspension Construction”
“Rear Wheel Hub Components”
Reference:
For the tightening torque of fastener not specified in this section, refer to “Fasteners Information in Section 0A”.
Special Tools and Equipment
Special ToolS7RS0B2308001
I6RS0B230017-01
Fastening part Tightening torque
Note
N ⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
Wheel nut 85 8.5 61.5 �) / �) / �) / �) / �)
Rear shock absorber upper nut 28 2.8 20.0 �)
Rear shock absorber lower nut 90 9.0 65.0 �) / �) / �)
Wheel speed sensor bolt 11 1.1 8.0 �) / �)
Brake pipe flare nut 16 1.6 11.5 �) / �)
Parking brake cable clamp bolt 11 1.1 8.0 �)
Trailing arm bolt 73 7.3 53.0 �)
Rear axle nut 175 17.5 126.5 �)
Rear spindle bolt 88 8.8 64.0 �)
09942–1551109943–17912
Sliding hammer Wheel hub remover
�)�)
Page 470 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2D-3 Wheels and Tires:
Metric Lug Nuts and Wheel Studs
All models use metric lug nuts and wheel studs.
Metric lug nuts and wheel studs size
M12 x 1.25
If broken stud or nut are found, be sure to replace both
stud and nut with new one.
Irregular and/or Premature Wear DescriptionS7RS0B2401003
Irregular and premature wear has many causes. Some
of them are as follows: incorrect inflation pressures, lack
of tire rotation, driving habits, improper alignment.
If the following conditions are noted, tire rotation is
necessary:
• Front tire wear is different from rear’s.
• Uneven wear exists across tread of any tires.
• Both sides of front tire wears are not even.
• Both sides of rear tire wears are not even.
• There is cupping, flat spotting, etc.
A wheel alignment check is necessary if following
conditions are noted:
• Both sides of front tire wears are not even.
• Wear is uneven across the tread of any front tire.
• Front tire treads have scuffed appearance with “feather” edges on one side of tread ribs or blocks.
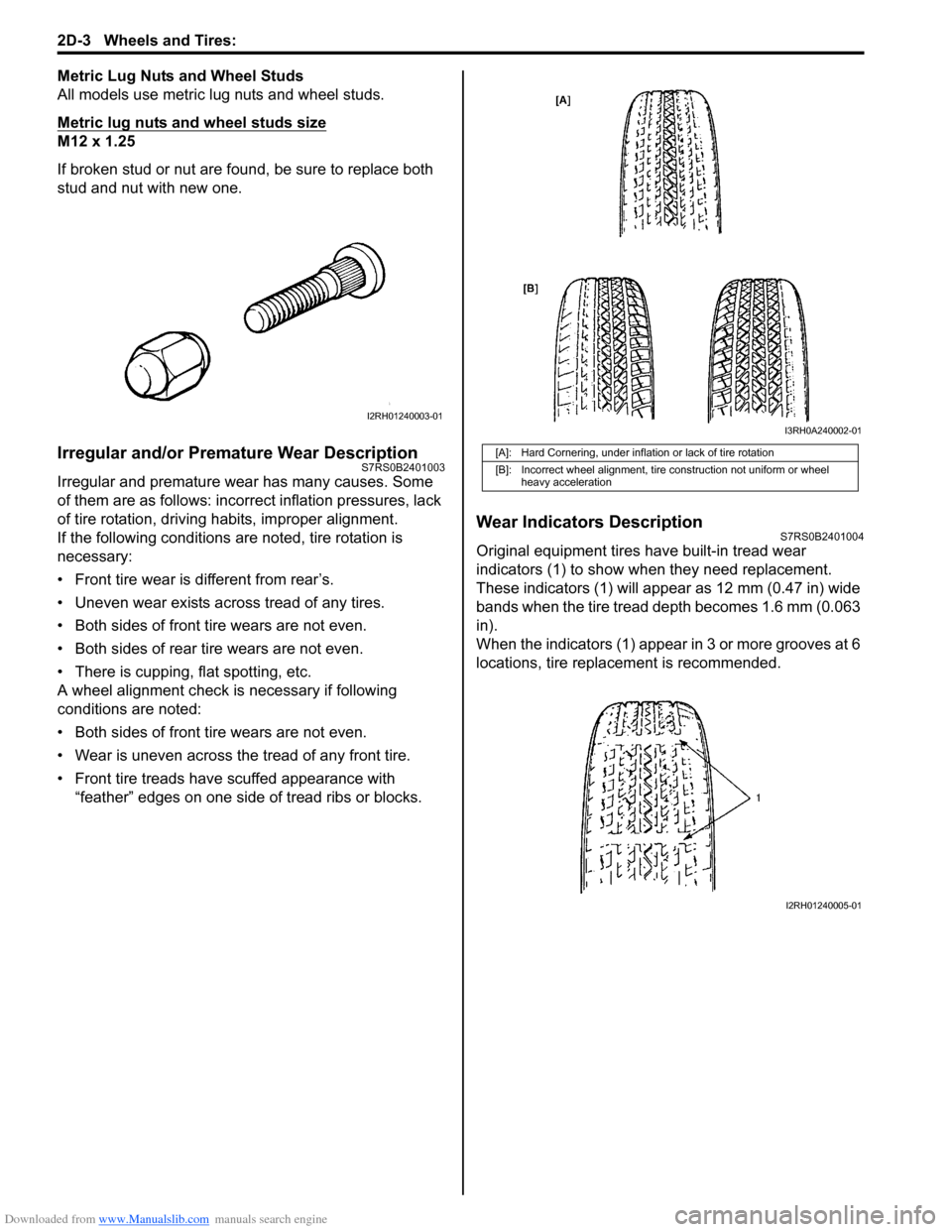
Wear Indicators DescriptionS7RS0B2401004
Original equipment tires have built-in tread wear
indicators (1) to show when they need replacement.
These indicators (1) will app ear as 12 mm (0.47 in) wide
bands when the tire tread depth becomes 1.6 mm (0.063
in).
When the indicators (1) appear in 3 or more grooves at 6
locations, tire replacement is recommended.
I2RH01240003-01
[A]: Hard Cornering, under inflation or lack of tire rotation
[B]: Incorrect wheel alignment, tire construction not uniform or wheel heavy acceleration
I3RH0A240002-01
I2RH01240005-01
Page 471 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Wheels and Tires: 2D-4
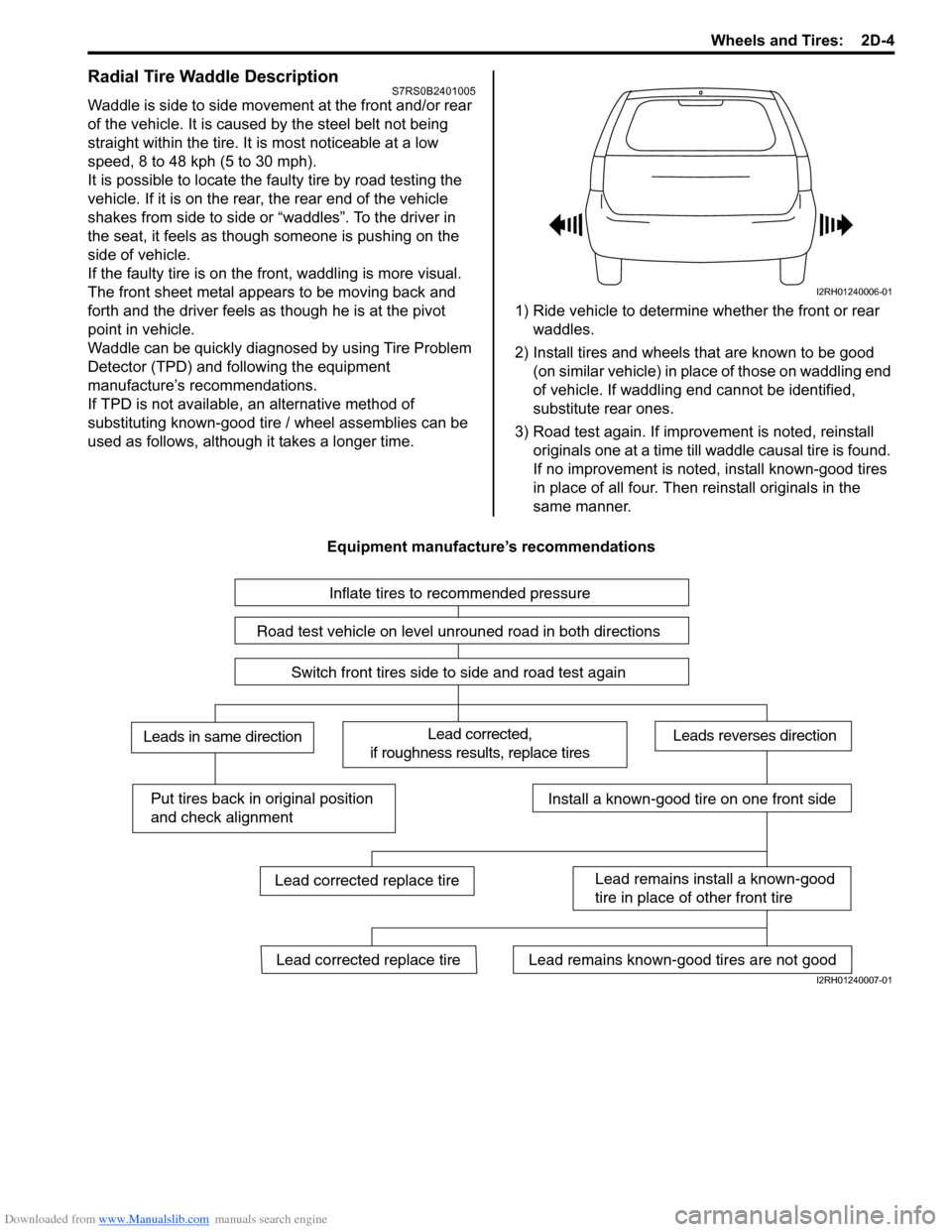
Radial Tire Waddle DescriptionS7RS0B2401005
Waddle is side to side movement at the front and/or rear
of the vehicle. It is caused by the steel belt not being
straight within the tire. It is most noticeable at a low
speed, 8 to 48 kph (5 to 30 mph).
It is possible to locate the f aulty tire by road testing the
vehicle. If it is on the rear , the rear end of the vehicle
shakes from side to side or “waddles”. To the driver in
the seat, it feels as though someone is pushing on the
side of vehicle.
If the faulty tire is on the front, waddling is more visual.
The front sheet metal appears to be moving back and
forth and the driver feels as though he is at the pivot
point in vehicle.
Waddle can be quickly diagnosed by using Tire Problem
Detector (TPD) and following the equipment
manufacture’s recommendations.
If TPD is not available, an alternative method of
substituting known-good tire / wheel assemblies can be
used as follows, although it takes a longer time. 1) Ride vehicle to determine whether the front or rear
waddles.
2) Install tires and wheels that are known to be good (on similar vehicle) in place of those on waddling end
of vehicle. If waddling end cannot be identified,
substitute rear ones.
3) Road test again. If improvement is noted, reinstall originals one at a time till w addle causal tire is found.
If no improvement is noted, install known-good tires
in place of all four. Then reinstall originals in the
same manner.
Equipment manufacture’s recommendations
I2RH01240006-01
Inflate tires to recommended pressure
Road test vehicle on level unrouned road in both directions
Switch front tires side to side and road test again
Lead corrected,
if roughness results, replace tiresLeads in same directionLeads reverses direction
Put tires back in original position
and check alignmentInstall a known-good tire on one front side
Lead remains install a known-good
tire in place of other front tire
Lead remains known-good tires are not goodLead corrected replace tire
Lead corrected replace tire
I2RH01240007-01
Page 472 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2D-5 Wheels and Tires:
Radial Tire Lead / Pull DescriptionS7RS0B2401006
“Lead / Pull” is the deviation of the vehicle from a straight
path on a level road even with no pressure on the
steering wheel.
Lead is usually caused by the following conditions.
• Improper tire and wheel alignment.
• Uneven brake assemblies.
• Tire construction.
The way in which a tire is built can produce lead in a
vehicle. An example of this is placement of the belt. Off
center belts on radial tires can cause the tire to develop
a side force while rolling straight down the road. If one
side of the tire has a little larger diameter than the other,
the tire will tend to roll to one side. This will develop a
side force which can produce vehicle lead.
The procedure in the figure (Lead Diagnosis) should be
used to make sure that wheel alignment is not mistaken
for tire lead.
• Part of the lead diagnosis procedure is different from the proper tire rotation pattern currently in the owner
and service manuals. If a medium to high mileage tire
is moved to the other side of the vehicle, be sure to
check that ride roughness has not developed.
• Rear tires will not cause lead.
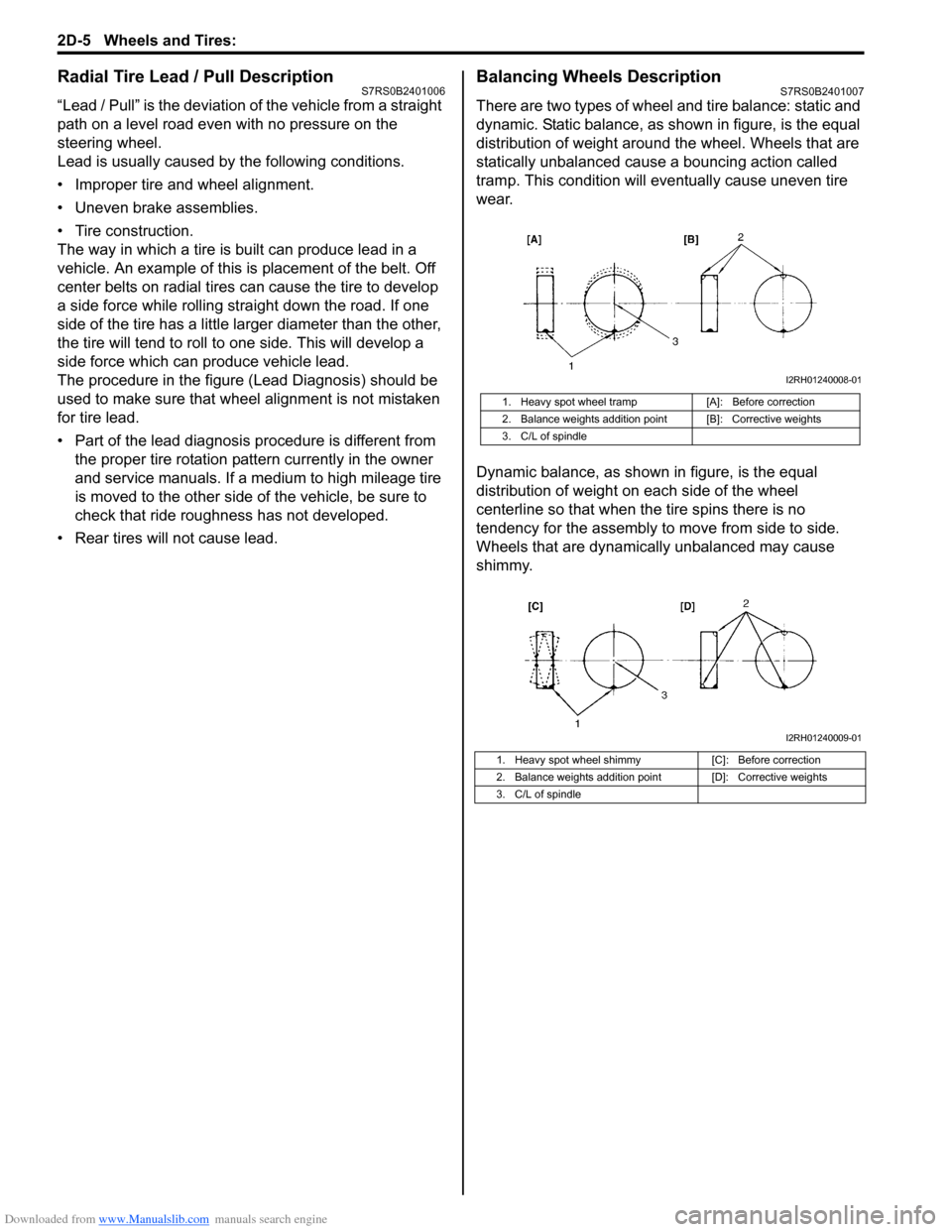
Balancing Wheels DescriptionS7RS0B2401007
There are two types of wheel an d tire balance: static and
dynamic. Static balance, as shown in figure, is the equal
distribution of weight around the wheel. Wheels that are
statically unbalanced cause a bouncing action called
tramp. This condition will eventually cause uneven tire
wear.
Dynamic balance, as shown in figure, is the equal
distribution of weight on each side of the wheel
centerline so that when the tire spins there is no
tendency for the assembly to move from side to side.
Wheels that are dynamically unbalanced may cause
shimmy.
1. Heavy spot wheel tramp [A]: Before correction
2. Balance weights addition point [B]: Corrective weights
3. C/L of spindle
1. Heavy spot wheel shimmy [C]: Before correction
2. Balance weights addition point [D]: Corrective weights
3. C/L of spindle
I2RH01240008-01
I2RH01240009-01
Page 496 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4-ii Table of Contents
Repair Instructions ..............................................4D-2Parking Brake Inspection and Adjustment ..........4D-2
Parking Brake Cable Removal and Installation ......................................................... 4D-3
Parking Brake Lever Removal and Installation ....4D-3
Specifications .... ...................................................4D-4
Tightening Torque Specifications ........................4D-4
ABS ........................................... .................4E-1
Precautions........................................................... 4E-1
Precautions in Diagnosing Troubles ................... 4E-1
Precautions in On-Vehicle Service...................... 4E-1
Precautions in Hydraulic Unit Operation Check ................................................................ 4E-1
General Description ............................................. 4E-2 ABS Description .................................................. 4E-2
ABS Hydraulic Unit / Control Module Assembly Description ....................................... 4E-2
CAN Communication System Description........... 4E-3
Schematic and Routing Diagram ........................ 4E-4 ABS Schematic ................................................... 4E-4
ABS Wiring Circuit Diagram ................................ 4E-5
Component Location ........... ................................ 4E-7
ABS Components Location ................................. 4E-7
Front Wheel Speed Sensor Components Location ............................................................ 4E-7
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Components Location ............................................................ 4E-8
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............ 4E-8 ABS Check .......................................................... 4E-8
ABS Warning Light Check................................. 4E-10
EBD Warning Light (Brake Warning Light) Check .............................................................. 4E-10
DTC Check........................................................ 4E-11
DTC Table ......................................................... 4E-11
DTC Clearance ................................................. 4E-12
Scan Tool Data ................................................. 4E-12
ABS Warning Light Does Not Come ON at Ignition Switch ON .......................................... 4E-13
ABS Warning Light Comes ON Steady ............. 4E-14
EBD Warning Light (Brake Warning Light) Comes ON Steady .......................................... 4E-15
Serial Data Link Circuit Check .......................... 4E-16
DTC C1021, C1022 / C1025, C1026 / C1031, C1032 / C1035, C1036: Right-Front / Left-
Front / Right-Rear / Left-Rear Wheel Speed
Sensor Circuit or Sensor Ring ........................ 4E-18
DTC C1041 / C1045 / C1051 / C1055, DTC C1042 / C1046 / C1052 / C1056: Right-Front
/ Left-Front / Right-Rear / Left-Rear Inlet
Solenoid Circuit, Right-Front / Left-Front /
Right-Rear / Left-Rear Outlet Solenoid
Circuit .............................................................. 4E-20
DTC C1057: Power Source Circuit ................... 4E-21
DTC C1061: ABS Pump Motor and/or Motor Driver Circuit ................................................... 4E-22
DTC C1063: Solenoid Valve Power Supply Driver Circuit ................................................... 4E-23
DTC C1071: ABS Control Module..................... 4E-24 DTC U1073: Control Module Communication
Bus Off ............................................................ 4E-25
DTC U1100: Lost Communication with ECM (Reception Error)............................................. 4E-27
Repair Instructions ............ ................................ 4E-28
ABS Hydraulic Unit Operati on Check................ 4E-28
ABS Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly Components ...... ............................. 4E-29
ABS Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection .................... 4E-29
ABS Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly Removal and Inst allation ................ 4E-29
Front / Rear Wheel Speed Sensor On-Vehicle Inspection ........................................................ 4E-31
Front Wheel Speed Sensor Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4E-32
Front Wheel Speed Sensor Inspection ............. 4E-32
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4E-33
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Inspection .............. 4E-34
Front Wheel Encoder On-Veh icle Inspection .... 4E-34
Front wheel Enco der Removal and
Installation ....................................................... 4E-34
Rear Wheel Encoder On-Veh icle Inspection..... 4E-34
Rear Wheel Encoder Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4E-34
Specifications ..................... ................................ 4E-35
Tightening Torque Specifications ...................... 4E-35
Special Tools and Equipmen t ........................... 4E-35
Special Tool ...................................................... 4E-35
Electronic Stability Prog ram ...................4F-1
Precautions ........................................................... 4F-1
Precautions in Diagnosing Troubles ................... 4F-1
Precautions in On-Vehicle Service...................... 4F-1
Precautions in Hydraulic Unit Operation Check ................................................................ 4F-1
Precautions in Sensor Calibration ....................... 4F-1
Precautions in Speedometer Test or Other Tests ................................................................. 4F-2
General Description ............................................. 4F-2 Electronic Stability Program Description ............. 4F-2
Electronic Stability Program Construction ........... 4F-3
ESP® Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly Description........................................ 4F-5
Warning Lamp, Indicator Lamp Description ........ 4F-6
CAN Communication System Description........... 4F-6
CAN Communication System For Electronic Stability Program Description ............................ 4F-7
Schematic and Routing Diagram ........................ 4F-8 Electronic Stability Program Schematic .............. 4F-8
Electronic Stability Program Wiring Circuit Diagram............................................................. 4F-9
Component Location ............ ............................. 4F-11
Electronic Stability Program Component
Location........................................................... 4F-11
Diagnostic Information and Procedures .......... 4F-12 Electronic Stability Program System Check ...... 4F-12
ESP® Warning lamp Check .............................. 4F-14
Page 497 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Table of Contents 4-iii
ABS Warning Lamp Check ............................... 4F-14
EBD Warning Lamp (Brake Warning Lamp) Check .............................................................. 4F-15
DTC Check ....................................................... 4F-15
DTC Table ......................................................... 4F-15
DTC Clearance ................................................. 4F-18
Fail-Safe Table ................ .................................. 4F-19
Scan Tool Data ................................................. 4F-20
Visual Inspection ............................................... 4F-21
ESP ® Warning Lamp Does Not Come ON at
Ignition Switch ON .......................................... 4F-21
ESP ® Warning Lamp Comes ON Steady......... 4F-22
ABS Warning Lamp Does Not Come ON at Ignition Switch ON .......................................... 4F-23
ABS Warning Lamp Comes ON Steady............ 4F-24
EBD Warning Lamp (Brake Warning Lamp) Comes ON Steady .......................................... 4F-24
Serial Data Link Circuit Check .......................... 4F-26
DTC C1016: Stop Lamp Swit ch Circuit Failure .. 4F-28
DTC C1017 / C1023: Yaw Rate / G Sensor Assembly Failure ............................................ 4F-29
DTC C1018: Brake Fluid Le vel Switch Failure .. 4F-30
DTC 1020: Master Cylinder Pressure Sensor Power Supply Failure ...................................... 4F-31
DTC C1021, C1022 / C1025, C1026 / C1031, C1032 / C1035, C1036: Wheel Speed
Sensor Circuit or Encode r Failure ................... 4F-32
DTC C1024: Steering Angle Sensor Circuit
Failure ............................................................. 4F-34
DTC C1027: ESP ® OFF Switch Circuit
Failure ............................................................. 4F-34
DTC C1028: Master Cylinder Pressure Sensor Circuit Failure ....... .............................. 4F-35
DTC C1034: Yaw Rate / G Sensor Assembly Power Supply Failure ...................................... 4F-36
DTC C1037: Steering Angle Sensor Power Supply Failure ................................................. 4F-37
DTC C1038: Steering Angle Sensor Detect Rolling Counter Fa ilure from ESP® Control
Module ............................................................ 4F-38
DTC C1039: Yaw Rate / G Sensor Assembly Internal Failure .............. .................................. 4F-39
DTC C1040: Stability Control System Function Failure .............................................. 4F-39
DTC C1041 / C1042 / C1043 / C1044 / C1045 / C1046 / C1051 / C1052 / C1053 / C1054 /
C1055 / C1056: Solenoid Circuit Failure ......... 4F-40
DTC C1057: ESP ® Control Module Power
Supply Circuit Failure .... .................................. 4F-41
DTC C1061: Pump Motor and/or Motor Driver Circuit Failure .................................................. 4F-42
DTC C1063: Solenoid Valve Power Supply Driver Circuit Failure ....................................... 4F-43
DTC 1071: ESP ® Control Module Internal
Defect.............................................................. 4F-44 DTC C1073: Lost Communication With Yaw
Rate / G Sensor Assembly .............................. 4F-45
DTC C1075 / 1076 / 1078: Sensor Calibration Incomplete.......................... ............................. 4F-46
DTC C1090: Invalid Communication with
ECM ................................................................ 4F-47
DTC C1091 / C1094: ECM Data in CAN Line Failure / Invalid Torque Control
Communication with ECM .. ............................. 4F-48
DTC U1073: Control Module Communication Bus Off ............................................................ 4F-49
DTC U1100: Lost Communication with ECM (Reception Error)............................................. 4F-50
DTC U1126: Lost Communication with Steering Angle Sensor (Reception Error)........ 4F-51
DTC U1140: Lost Communication with BCM (Reception Error)............................................. 4F-52
Repair Instructions ........... ................................. 4F-54
ESP® Hydraulic Unit Operation Check ............. 4F-54
Sensor Calibration............................................. 4F-54
ESP® Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection .................... 4F-55
ESP ® Hydraulic
Unit / Control Module
Assembly Removal and Inst allation ................ 4F-56
Front / Rear Wheel Speed Sensor On-Vehicle Inspection ........................................................ 4F-57
Front Wheel Speed Sensor Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4F-58
Front Wheel Speed Sensor Inspection ............. 4F-59
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4F-59
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Inspection .............. 4F-60
Front Wheel Encode r On-Vehicle Inspection .... 4F-61
Front Wheel Encoder Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4F-61
Rear Wheel Encoder On-Veh icle Inspection..... 4F-61
Rear Wheel Encoder Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4F-61
Master Cylinder Pressure Sensor On-Vehicle
Inspection ........................................................ 4F-61
Yaw Rate / G Sensor Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection ........................................................ 4F-62
Yaw Rate / G Sensor Assembly Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4F-63
Yaw Rate / G Sensor Inspection ....................... 4F-64
Steering Angle Sensor On-Vehicle Inspection .. 4F-64
Steering Angle Sensor Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4F-65
Steering Angle Sensor Inspection ..................... 4F-65
ESP® OFF Switch Removal an d Installation .... 4F-65
ESP® OFF Switch Inspection ........................... 4F-65
Specifications .................... ................................. 4F-66
Tightening Torque Specifications ...................... 4F-66
Special Tools and Equipmen t ........................... 4F-66
Special Tool ...................................................... 4F-66
Page 499 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Brake Control System and Diagnosis: 4A-1
Brakes
Brake Control System and Diagnosis
Precautions
Precautions on BrakeS7RS0B4100001
Air Bag Warning
Refer to “Air Bag System Service Warning in Section 00”.
Brakes Diagnosis Note
Refer to “Brakes Diagnosis Note”.
General Description
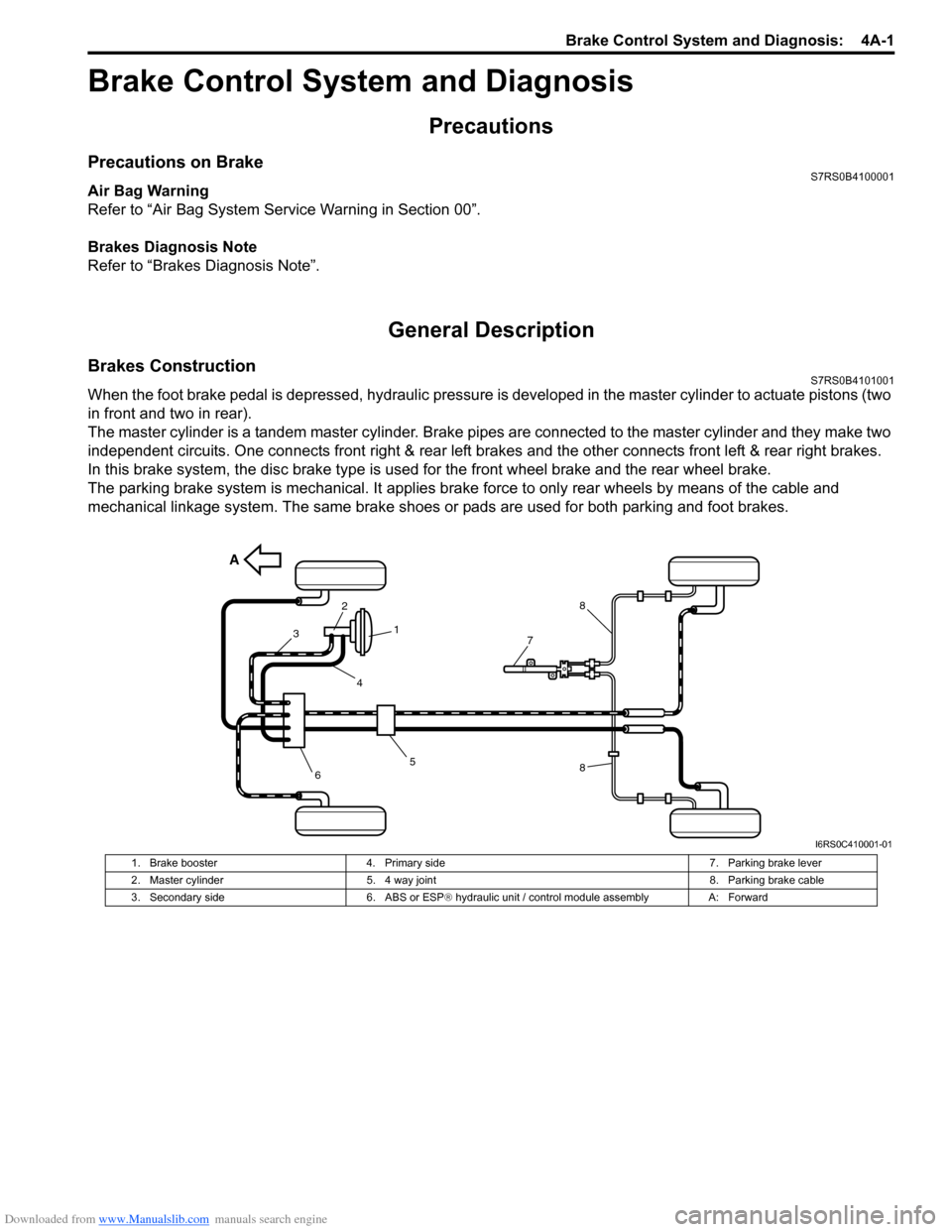
Brakes ConstructionS7RS0B4101001
When the foot brake pedal is depressed, hydraulic pressure is developed in the master cylinder to actuate pistons (two
in front and two in rear).
The master cylinder is a tandem master cylinder. Brake pipes are connected to the master cylinder and they make two
independent circuits. One connects front right & rear left brakes and the other connects front left & rear right brakes.
In this brake system, the disc brake type is used for the front wheel brake and the rear wheel brake.
The parking brake system is mechanical. It applies brake force to only rear wheels by means of the cable and
mechanical linkage system. The same brake shoes or pads are used for both parking and foot brakes.
A
5
3
2
1
4
8
8
6
7
I6RS0C410001-01
1. Brake booster 4. Primary side 7. Parking brake lever
2. Master cylinder 5. 4 way joint 8. Parking brake cable
3. Secondary side 6. ABS or ESP® hydraulic unit / control module assembly A: Forward
Page 502 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4A-4 Brake Control System and Diagnosis:
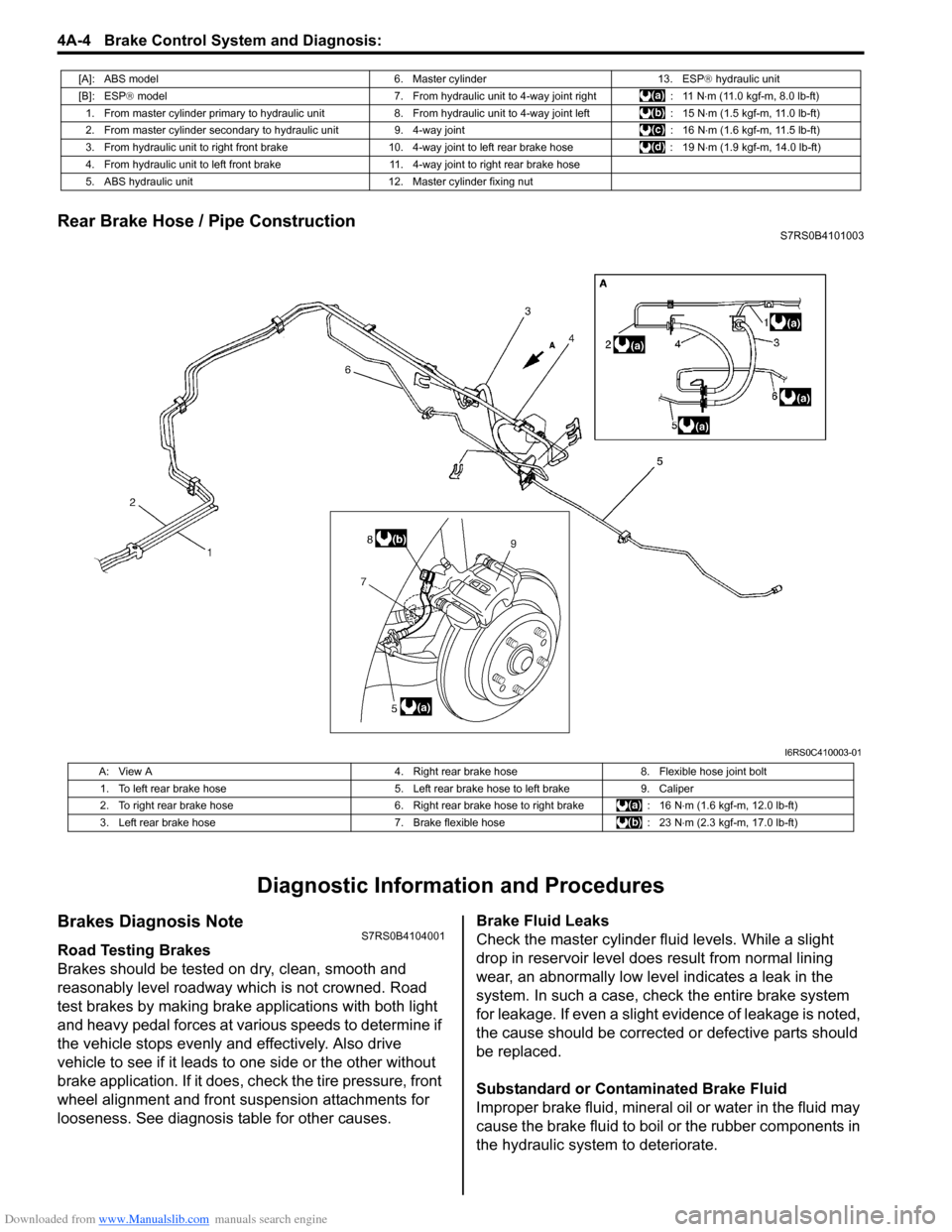
Rear Brake Hose / Pipe ConstructionS7RS0B4101003
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Brakes Diagnosis NoteS7RS0B4104001
Road Testing Brakes
Brakes should be tested on dry, clean, smooth and
reasonably level roadway which is not crowned. Road
test brakes by making brake applications with both light
and heavy pedal forces at vari ous speeds to determine if
the vehicle stops evenly and effectively. Also drive
vehicle to see if it leads to one side or the other without
brake application. If it does, check the tire pressure, front
wheel alignment and front suspension attachments for
looseness. See diagnosis table for other causes. Brake Fluid Leaks
Check the master cylinder fl
uid levels. While a slight
drop in reservoir level does result from normal lining
wear, an abnormally low leve l indicates a leak in the
system. In such a case, chec k the entire brake system
for leakage. If even a slight ev idence of leakage is noted,
the cause should be corrected or defective parts should
be replaced.
Substandard or Contaminated Brake Fluid
Improper brake fluid, mineral oil or water in the fluid may
cause the brake fluid to boil or the rubber components in
the hydraulic system to deteriorate.
[A]: ABS model 6. Master cylinder13. ESP® hydraulic unit
[B]: ESP ® model 7. From hydraulic unit to 4-way joint right : 11 N⋅m (11.0 kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft)
1. From master cylinder primary to hydraulic unit 8. From hydraulic unit to 4-way joint left: 15 N⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft)
2. From master cylinder secondary to hydraulic unit 9. 4-way joint: 16 N⋅m (1.6 kgf-m, 11.5 lb-ft)
3. From hydraulic unit to right front brake 10.4-way joint to left rear brake hose : 19 N⋅m (1.9 kgf-m, 14.0 lb-ft)
4. From hydraulic unit to left front brake 11. 4-way joint to right rear brake hose
5. ABS hydraulic unit 12. Master cylinder fixing nut
I6RS0C410003-01
A: View A4. Right rear brake hose8. Flexible hose joint bolt
1. To left rear brake hose 5. Left rear brake hose to left brake9. Caliper
2. To right rear brake hose 6. Right rear brake hose to right brake: 16 N⋅m (1.6 kgf-m, 12.0 lb-ft)
3. Left rear brake hose 7. Brake flexible hose: 23 N⋅m (2.3 kgf-m, 17.0 lb-ft)
Page 503 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Brake Control System and Diagnosis: 4A-5
If deterioration of rubber is evident, disassemble all
hydraulic parts and wash with alcohol. Dry these parts
with compressed air before assembly to keep alcohol out
of the system. Replace all rubber parts in the system,
including hoses. Also, when working on the brake
mechanisms, check for fluid on the linings.
If excessive fluid is found, replace the pads. If master cylinder piston seals
are satisfactory, check for
leakage or excessive heat co nditions. If leakage is not
found, drain fluid, flush with brake fluid, refill and bleed
system.
The system must be flushed if there is any doubt as to
the grade of fluid in the system or if fluid has been used
which contained parts that have been subjected to
contaminated fluid.
Brakes Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B4104002
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Not enough braking force Brake oil leakage from brake lines Locate leaking point and repair.
Brake disc or brake pad stained with oil Clean or replace.
Overheated brakes Determine cause and repair.
Badly worn brake pad Replace.
Malfunctioning caliper assembly Repair or replace.
Malfunctioning brake booster Check system and replace assembly.
Malfunctioning brake master cylinder Check system and replace as necessary.
Air in system Bleed system.
Malfunctioning ABS (ESP ®). Check system and replace as necessary.
Brake pull (Brakes not
working in unison) Brake pad and disc are wet with water or
stained with oil in some brakes Clean or replace.
Disc is out of round in some brakes Replace.
Tires are inflated unequally Inflate equally.
Disturbed front wheel alignment Adjust as prescribed.
Unmatched tires on same axle Tires with approximately the same amount of
tread should be used on the same axle.
Restricted brake pipes or hoses Check for soft hoses and damaged lines.
Replace with new hoses and new double-
walled steel brake tubing.
Malfunctioning caliper assembly Caliper should slide.
Check for stuck or sluggish pistons and proper
lubrication of caliper slide pin.
Loose suspension parts Check all suspension mountings.
Loose calipers Check and torque bolts to specifications.
Noise (High pitched
squeak without brake
applied) Contact wear indicator to brake disc
Replace brake pads.
Worn brake pad Replace brake pads.
Excessive pedal travel
(Pedal stroke too large) Partial brake system failure
Check brake systems and repair as necessary.
Brake fluid leaking Repair the leaking point and bleed air.
Air in system (soft / spongy pedal) Bleed system.
Brake locked Malfunctioning ABS (ESP®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
Dragging brakes (A very
light drag is present in all
brakes immediately after
pedal is released.) Master cylinder pistons not returning
correctly
Replace master cylinder.
Restricted brake pipes or hoses Check for soft hoses or damaged pipes and
replace with new hoses and/or new brake
piping.
Incorrect parking brake adjustment on
rear brakes Check and adjust to correct specifications.
Weakened or broken return springs in
rear brakes. Replace.
Sluggish parking brake cables or linkage Repair or replace.
Brake caliper piston sticking Repair as necessary.
Badly worn piston seal in caliper Replace piston seal.
Improper brake pedal free height Check brake pedal free height.
Page 504 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4A-6 Brake Control System and Diagnosis:
Pedal pulsation (Pedal
pulsates when depressed
for braking)Damaged or loose wheel bearings
Replace wheel bearings.
Distorted steering knuckle or rear wheel
spindle Replace knuckle or rear wheel spindle.
Excessive disc lateral runout Check per instructions. If not within
specifications, replace or machine disc.
Parallelism between brake pad and disc
not within specifications Check per instructions. If not within
specifications, replace or machine disc.
Brake caliper piston sticking Repair as necessary.
Braking noise Worn or distorted brake pad Replace pads.
Loose front wheel bearings Replace wheel bearings.
Distorted backing plates or loose
mounting bolts Replace or retighten securing bolts.
Contact wear indicator to brake disc Replace brake pad.
Brake warning light lights
after engine start Parking brake applied
Release parking brake and check that brake
warning light turns off.
Insufficient amount of brake fluid Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Brake fluid leaking Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Brake warning light circuit faulty Repair circuit.
Malfunctioning EBD system Check system referring to “EBD Warning Light
(Brake Warning Light) Comes ON Steady in
Section 4E”.
Brake warning light turns
on when brake is applied Brake fluid leaking
Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Insufficient amount of brake fluid Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Brake warning light fails
to turn on even when
parking brake is applied Brake warning light circuit faulty
Replace bulb or repair circuit.
ABS warning light or
ESP
® warning light turns
on after engine start Malfunctioning ABS (ESP
®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
ABS warning light or
ESP
® warning light turns
on when brake is applied Malfunctioning ABS (ESP
®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
ABS warning light or
ESP
® warning light does
not turn on for 2 sec. after
ignition switch has turned
ON Bulb burnt out
Replace bulb.
Malfunctioning ABS (ESP ®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
ABS warning light flashes New ABS hydraulic unit / control module
assembly installed. Perform “ABS Hydraulic
Unit Operation Check
in Section 4E”.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item