checking engine SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.G Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2008, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 890 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6C-8 Power Assisted Steering System:
Step 2: DTC Check, Record and Clearance
First, check DTC, referring to “DTC Check”. If DTC is
indicated, print it or write them down and then clear them
by referring to “DTC Clearance”. DTC indicates
malfunction that occurred in the system but does not
indicate whether it exists now or it occurred in the past
and the normal condition has been restored now. To
check which case applies, check the symptom in
question according to Step 5 and recheck DTC
according to Step 6 and 7.
Attempt to diagnose a trouble based on DTC in this step
only or failure to clear the DTC in this step will lead to
incorrect diagnosis, trouble diagnosis of a normal circuit
or difficulty in troubleshooting.
Step 3 and 4: Visual Inspection
As a preliminary step, be sure to perform visual check of
the items that support proper function of the P/S system
referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Step 5: Trouble Symptom Confirmation
Based on information obtained in “Step 1: Customer
Complaint Analysis: ” and “S tep 2: DTC Check, Record
and Clearance: ”, confirm trouble symptoms. Also,
reconfirm trouble symptom by performing test drive and
turning steering wheel fully to right and left at stopped
vehicle.
Step 6 and 7: Rechecking and Record of DTC
Refer to “DTC Check” for checking procedure.
Step 8: Steering Symptom Diagnosis and P/S
System Symptom Diagnosis
Perform basic steering system check according to
“Steering Symptom Diagnosis in Section 6A” first. When
the end of the flow has been reached, check the parts of
the system suspected as a possible cause referring to
“P/S System Symptom Diagnosis” and based on
symptoms appearing on the vehicle (symptoms obtained
through steps of customer complaint analysis, trouble
symptom confirmation and/or basic P/S system check)
and repair or replace faulty parts, if any.
Step 9: Troubleshooting for DTC (See each DTC
Diag. Flow)
Based on the DTC indicated in Step 6 or 7 and referring
to the applicable DTC diag. flow, locate the cause of the
trouble, namely in a sensor, switch, wire harness,
connector, actuator, P/S control module or other part and
repair or replace faulty parts.
Step 10: Intermittent Problems Check
Check parts where an intermittent trouble is easy to
occur (e.g., wire harness, connector, etc.), referring to
“Intermittent and Poor Connection Inspection in Section
00” and related circuit of DTC recorded in Step 2. Step 11: Final Confirmation Test
Confirm that the problem symptom has gone and the P/
S system is free from any abnormal conditions. If what
has been repaired is related to the DTC, clear the DTC
once, perform DTC confirmation procedure and confirm
that no DTC is indicated.
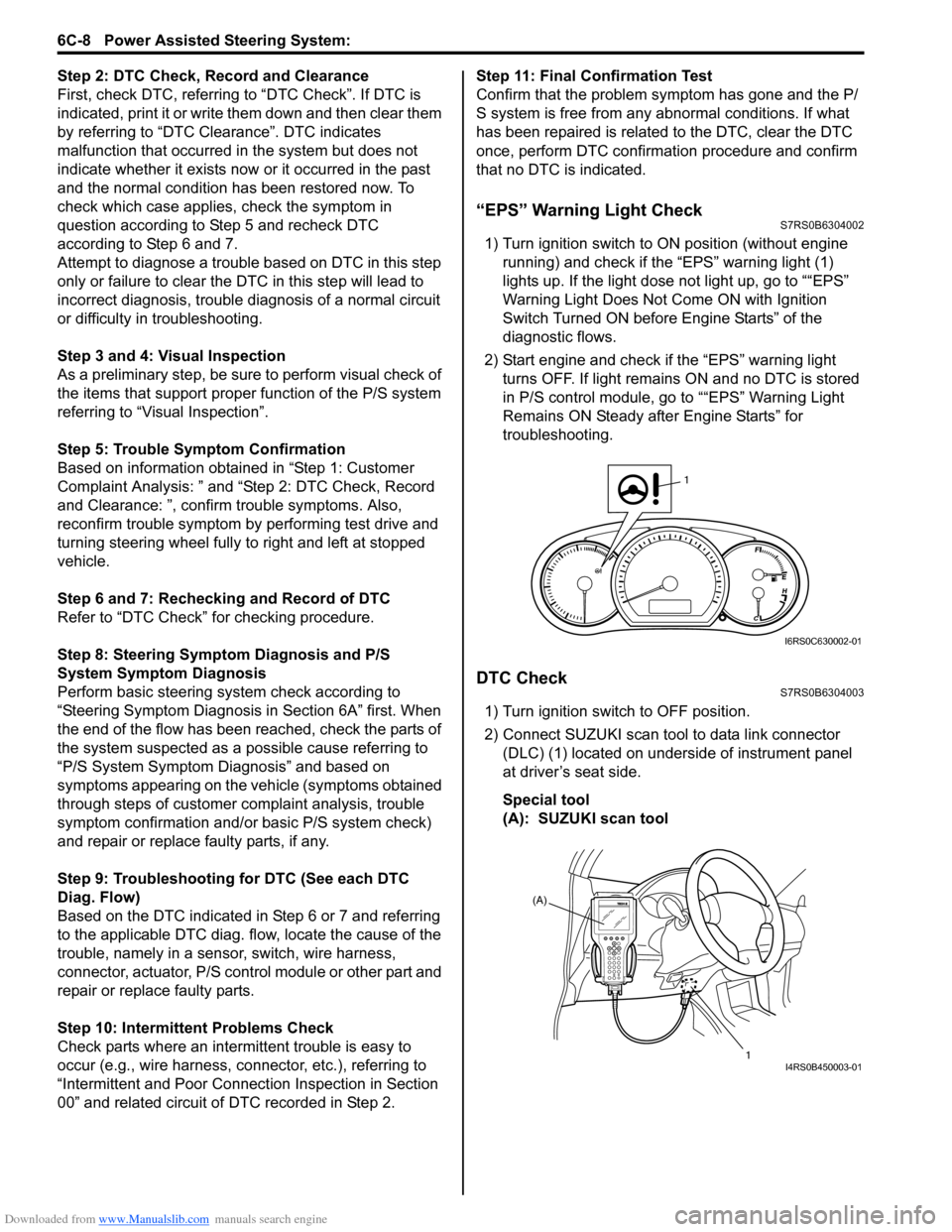
“EPS” Warning Light CheckS7RS0B6304002
1) Turn ignition switch to ON position (without engine
running) and chec k if the “EPS” warning light (1)
lights up. If the light dose not light up, go to ““EPS”
Warning Light Does Not Come ON with Ignition
Switch Turned ON before Engine Starts” of the
diagnostic flows.
2) Start engine and check if the “EPS” warning light turns OFF. If light remains ON and no DTC is stored
in P/S control module, go to ““EPS” Warning Light
Remains ON Steady after Engine Starts” for
troubleshooting.
DTC CheckS7RS0B6304003
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector (DLC) (1) located on underside of instrument panel
at driver’s seat side.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
1
I6RS0C630002-01
(A)
1
I4RS0B450003-01
Page 928 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6C-46 Power Assisted Steering System:
P/S Control Module Removal and InstallationS7RS0B6306011
Removal1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Remove console box.
3) Disconnect connectors (1) from P/S control module (2).
4) Disconnect connector from yaw rate / G sensor
(ESP ® model).
5) Remove P/S control module (2) with bracket (3) from floor panel.
6) Separate P/S control module and bracket.
Installation
Reverse removal procedure for installation noting the
following.
• Tighten each screw to the specified torque. Tightening torque
P/S control module bracket screw (ABS model)
(a): 9 N·m (0.9 kgf-m, 6.5 lb-ft)
P/S control module bracket screw (ESP ® model)
(a): 7 N·m (0.7 kgf-m, 5.0 lb-ft)
P/S control module mounting screw (b): 5 N·m (
0.5 kgf-m, 3.7 lb-ft)
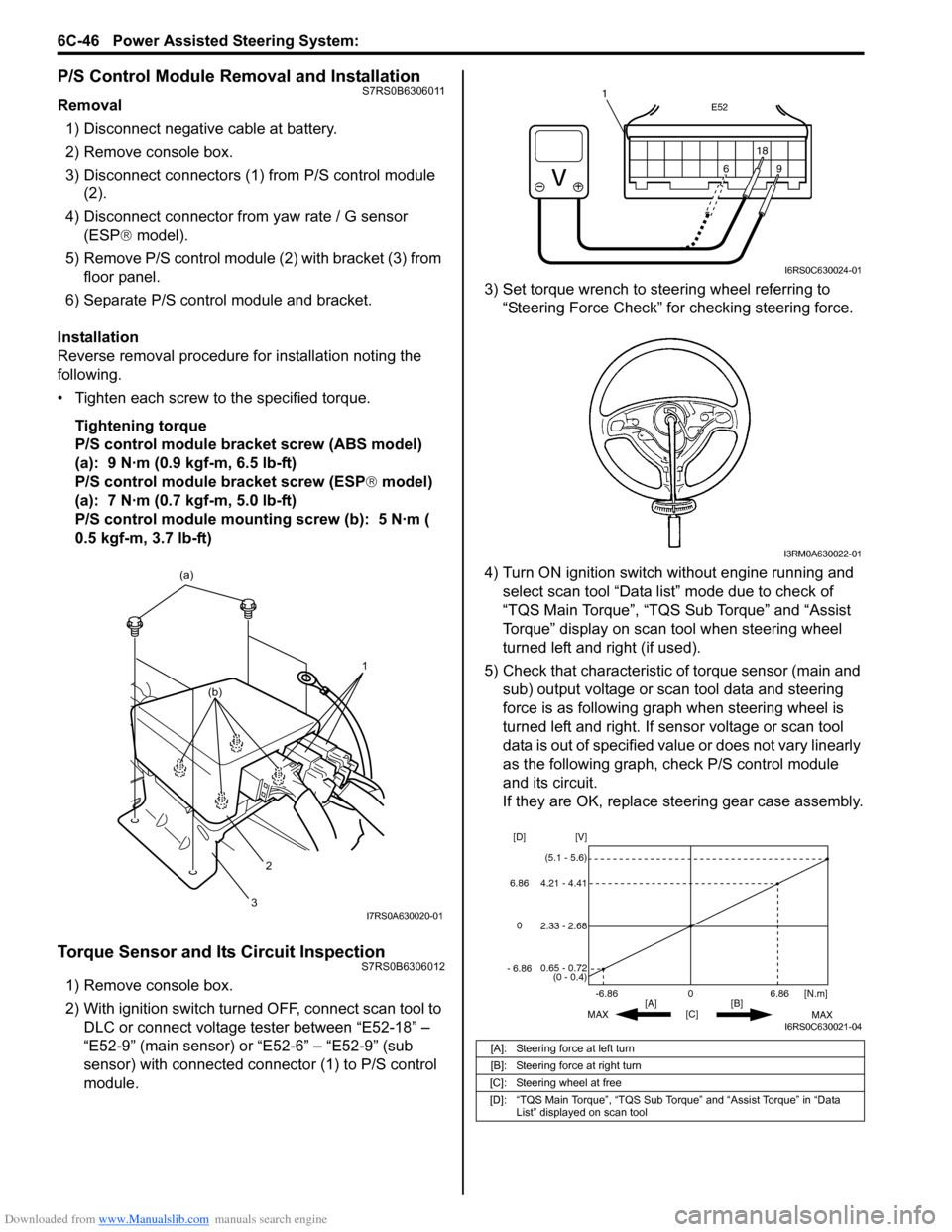
Torque Sensor and Its Circuit InspectionS7RS0B6306012
1) Remove console box.
2) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect scan tool to DLC or connect voltage tester between “E52-18” –
“E52-9” (main sensor) or “E52-6” – “E52-9” (sub
sensor) with connected connector (1) to P/S control
module. 3) Set torque wrench to stee
ring wheel referring to
“Steering Force Check” for checking steering force.
4) Turn ON ignition switch without engine running and select scan tool “Data list” mode due to check of
“TQS Main Torque”, “TQS Sub Torque” and “Assist
Torque” display on scan tool when steering wheel
turned left and right (if used).
5) Check that characteristic of torque sensor (main and sub) output voltage or scan tool data and steering
force is as following graph when steering wheel is
turned left and right. If sensor voltage or scan tool
data is out of specified value or does not vary linearly
as the following graph, check P/S control module
and its circuit.
If they are OK, replace steering gear case assembly.
1
(a)
2
3
(b)
I7RS0A630020-01
[A]: Steering force at left turn
[B]: Steering force at right turn
[C]: Steering wheel at free
[D]: “TQS Main Torque”, “TQS Sub Torque” and “Assist Torque” in “Data List” displayed on scan tool
E52
18
9
6
9
6 18
1
I6RS0C630024-01
I3RM0A630022-01
0
[C] [N.m]
MAX MAX
[B]
[A]
2.33 - 2.68 [V]
[D]
0.65 - 0.72
(0 - 0.4)
4.21 - 4.41
(5.1 - 5.6)
6.86
-6.86
0
6.86
- 6.86
I6RS0C630021-04
Page 931 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Power Assisted Steering System: 6C-49
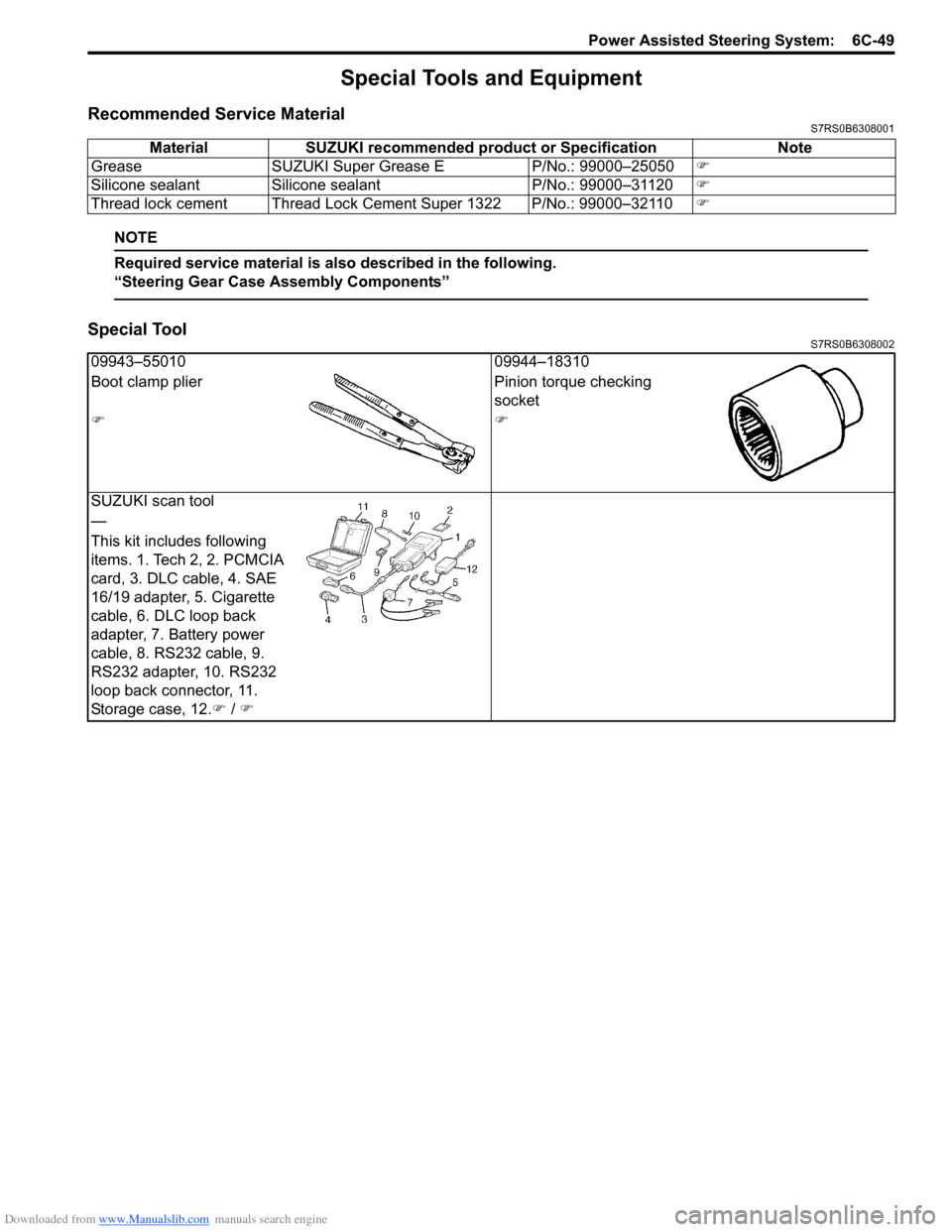
Special Tools and Equipment
Recommended Service MaterialS7RS0B6308001
NOTE
Required service material is also described in the following.
“Steering Gear Case Assembly Components”
Special ToolS7RS0B6308002
Material SUZUKI recommended product or Specification Note
Grease SUZUKI Super Grease E P/No.: 99000–25050�)
Silicone sealant Silicone sealant P/No.: 99000–31120�)
Thread lock cement Thread Lock Cement Super 1322 P/No.: 99000–32110 �)
09943–5501009944–18310
Boot clamp plier Pinion torque checking
socket
�)�)
SUZUKI scan tool
—
This kit includes following
items. 1. Tech 2, 2. PCMCIA
card, 3. DLC cable, 4. SAE
16/19 adapter, 5. Cigarette
cable, 6. DLC loop back
adapter, 7. Battery power
cable, 8. RS232 cable, 9.
RS232 adapter, 10. RS232
loop back connector, 11.
Storage case, 12. �) / �)
Page 963 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Air Conditioning System: Manual Type 7B-15
A/C System Inspection at ECMS7RS0B7214004
Voltage Check
When checking voltage at ECM connector terminals related to A/C system, refer to “DTC P2101: Throttle Actuator
Control Motor Circuit Range / Performance in Section 1A”.
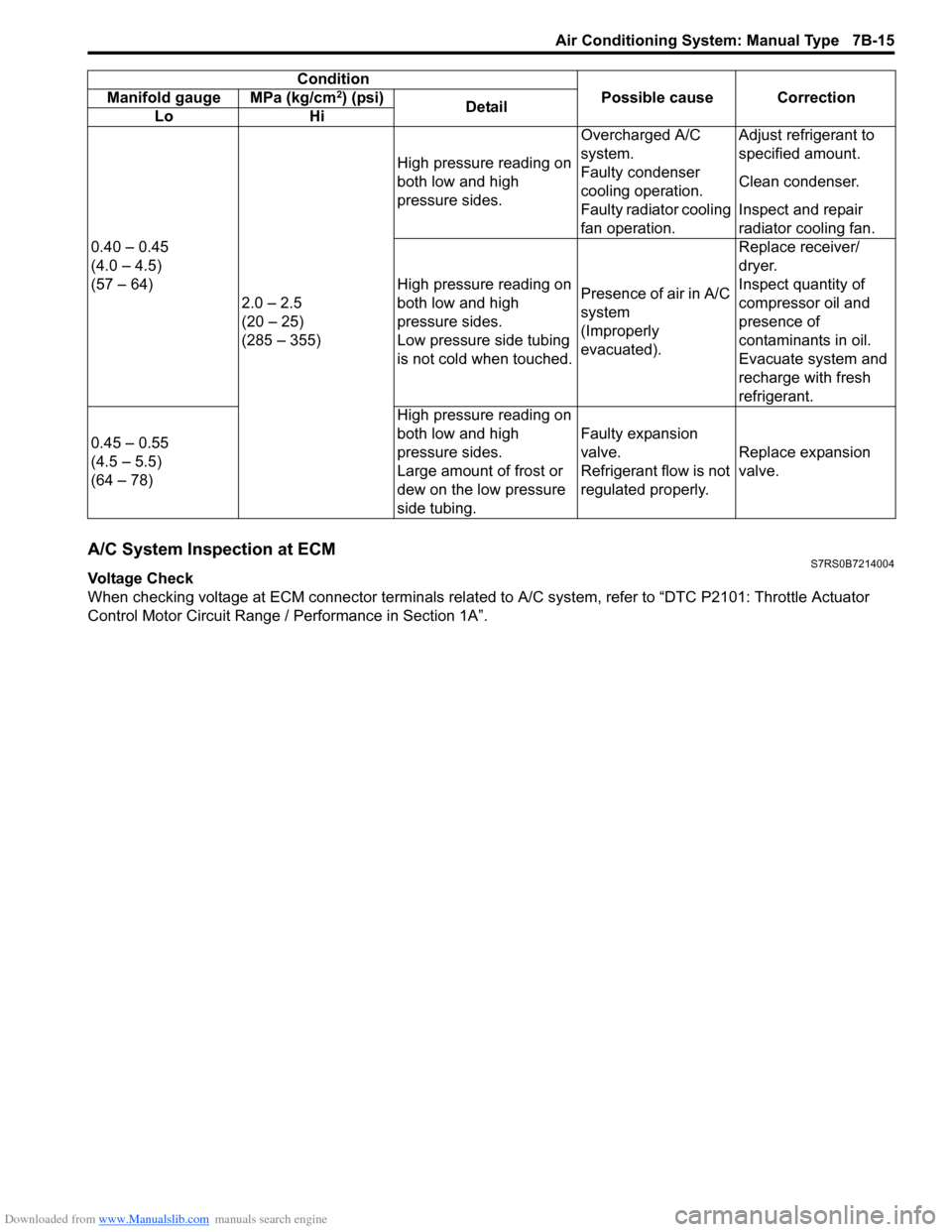
0.40 – 0.45
(4.0 – 4.5)
(57 – 64)
2.0 – 2.5
(20 – 25)
(285 – 355) High pressure reading on
both low and high
pressure sides.
Overcharged A/C
system.
Adjust refrigerant to
specified amount.
Faulty condenser
cooling operation. Clean condenser.
Faulty radiator cooling
fan operation. Inspect and repair
radiator cooling fan.
High pressure reading on
both low and high
pressure sides.
Low pressure side tubing
is not cold when touched. Presence of air in A/C
system
(Improperly
evacuated).Replace receiver/
dryer.
Inspect quantity of
compressor oil and
presence of
contaminants in oil.
Evacuate system and
recharge with fresh
refrigerant.
0.45 – 0.55
(4.5 – 5.5)
(64 – 78) High pressure reading on
both low and high
pressure sides.
Large amount of frost or
dew on the low pressure
side tubing.Faulty expansion
valve.
Refrigerant flow is not
regulated properly.
Replace expansion
valve.
Condition
Possible cause Correction
Manifold gauge MPa (kg/cm
2) (psi)
Detail
Lo Hi
Page 966 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 7B-18 Air Conditioning System: Manual Type
When replacing other parts
Replenish the following amount of oil to compressor.
Amount of compressor oil to be replenished
Evaporator: 25 cm3 (25 ml, 0.85 US. oz, 0.88 Imp. oz)
Condenser: 15 cm3 (15 ml, 0.51 US. oz, 0.53 Imp. oz)
Receiver/dryer: 10 cm3 (10 ml, 0.34 US. oz, 0.35 lmp.
oz)
Hoses: 10 cm
3 (10 ml, 0.34 US. oz, 0.35 Imp. oz) each
Pipes: 10 cm3 (10 ml, 0.34 US. oz, 0.35 Imp. oz) each
Evacuation
CAUTION!
Do not evacuate before recovering
refrigerant in A/C system.
NOTE
Once air conditioning system circuit is
opened (exposed) to atmospheric air, system
must be evacuated by using a vacuum pump.
The A/C system should be attached with a
manifold gauge set, and should be evacuated
for approximately 15 minutes.
1) Connect high charging hose (1) and low charging hose (2) of manifold gauge set (3) respectively as
follows:
High charging hose → High pressure charging valve
(4) on condenser outlet pipe
Low charging hose → Low pressure charging valve
(5) on suction pipe
2) Attach center charging hose (6) of manifold gauge set to vacuum pump (7).
3) Operate vacuum pump, and then open discharge
side valve (Hi) (8) of manifold gauge set.
If there is no blockage in the system, there will be an
indication on high pressure gauge (9).
In this case, open the other side valve (Lo) (10) of
the set and repair the system.
4) Approximately 10 minutes later, low pressure gauge (11) should show a vacuum lower than –100 kPa (–
1.0 kg/cm
2, –760 mmHg, –14.7 psi) providing no
leakage exists.
NOTE
• If the system does not show a vacuum below –100 kPa (–1.0 kg/cm
2, –760 mmHg,
–14.7 psi), close both valves, stop vacuum
pump and watch movement of low
pressure gauge.
• Increase in the gauge reading suggests existence of leakage. In this case, repair
the system before continuing its
evacuation.
• If the gauge shows a stable reading (suggesting no leakage), continue
evacuation.
5) Evacuation should be carried out for a total of at least 15 minutes.
6) Continue evacuation until low pressure gauge indicates a vacuum less than –100 kPa (–1.0 kg/cm
2,
–760 mmHg, –14.7 psi), and then close both valves.
7) Stop vacuum pump. Disconnect center charging hose from pump inlet. No w, the system is ready for
charging refrigerant.
Checking A/C System for Pressure Leaks
After completing the evacuation, close manifold gauge
high pressure valve and low pressure valve and wait 10
minutes. Verify that low pressure gauge reading has not
changed.
CAUTION!
If the gauge reading moves closer to “0”,
there is a leak somewhere. Inspect the tubing
connections and make necessary
corrections. And then, evacuate system once
again and make sure that there are no leaks.
7 5
2
4
1
10
11
3
9 8
6
I4RS0A720014-01
Page 982 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 7B-34 Air Conditioning System: Automatic Type
Automatic Type
Precautions
A/C System CautionS7RS0B7220001
Refer to “A/C System Caution”.
Precautions in Diagnosing TroubleS7RS0B7220002
• Do not disconnect couplers from HVAC control module, battery cable from battery, HVAC control module ground
wire harness from body or main fuse before confirming diagnostic information (diagnostic trouble code) stored in
HVAC control module memory.
• Diagnostic information (diagnostic trouble code) stored in HVAC control module can be checked by display of HVAC
control module. Also, it can be checked by using SU ZUKI scan tool. Before checking diagnostic information
(diagnostic trouble code), read this manual and operator's manual for SUZUKI scan tool to know how to read
diagnostic information (diagnostic trouble code).
• When trouble is diagnosed using diagnostic information (diagnostic trouble code) on display of HVAC control
module, keep in your mind that each diagnostic inform ation (diagnostic trouble code) has priority, and only
diagnostic information (diagnostic troub le code) which has the highest priority is indicated. Therefore, after
troubleshooting the malfunction, make sure if there exists any other diagnostic information (diagnostic trouble
code).
• Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit Service in Section 00” before inspection.
Precautions on Servicing A/C SystemS7RS0B7220003
Refer to “Precautions on Servicing A/C System”.
General Description
Auto A/C System DescriptionS7RS0B7221001
The automatic type air conditioning system (auto A/C) is pr ovided with the function to automatically control the inside
air temperature, fan speed, air flow outl et direction and air intake position by HVAC control module in addition to
functions of the manual type air conditioning system (manua l A/C). Once the inside air temperature is set using the
temperature selector, HVAC control module automatically controls the inside air temperature at the constant level at all
times based on the inside air temperature, outside ai r temperature, amount of sunlight and engine coolant
temperature detected respectively by the inside air te mperature sensor, outside air temperature sensor, sunload
sensor and ECT sensor. At this time, “FULL AUTO A/ C” appears on the display of HVAC control module.
With the air intake selector pushed in the above state, it is possible to select any position of the air intake actuator.
Then, “FULL AUTO A/C” on the display changes to “AUTO A/C”.
Page 994 of 1496
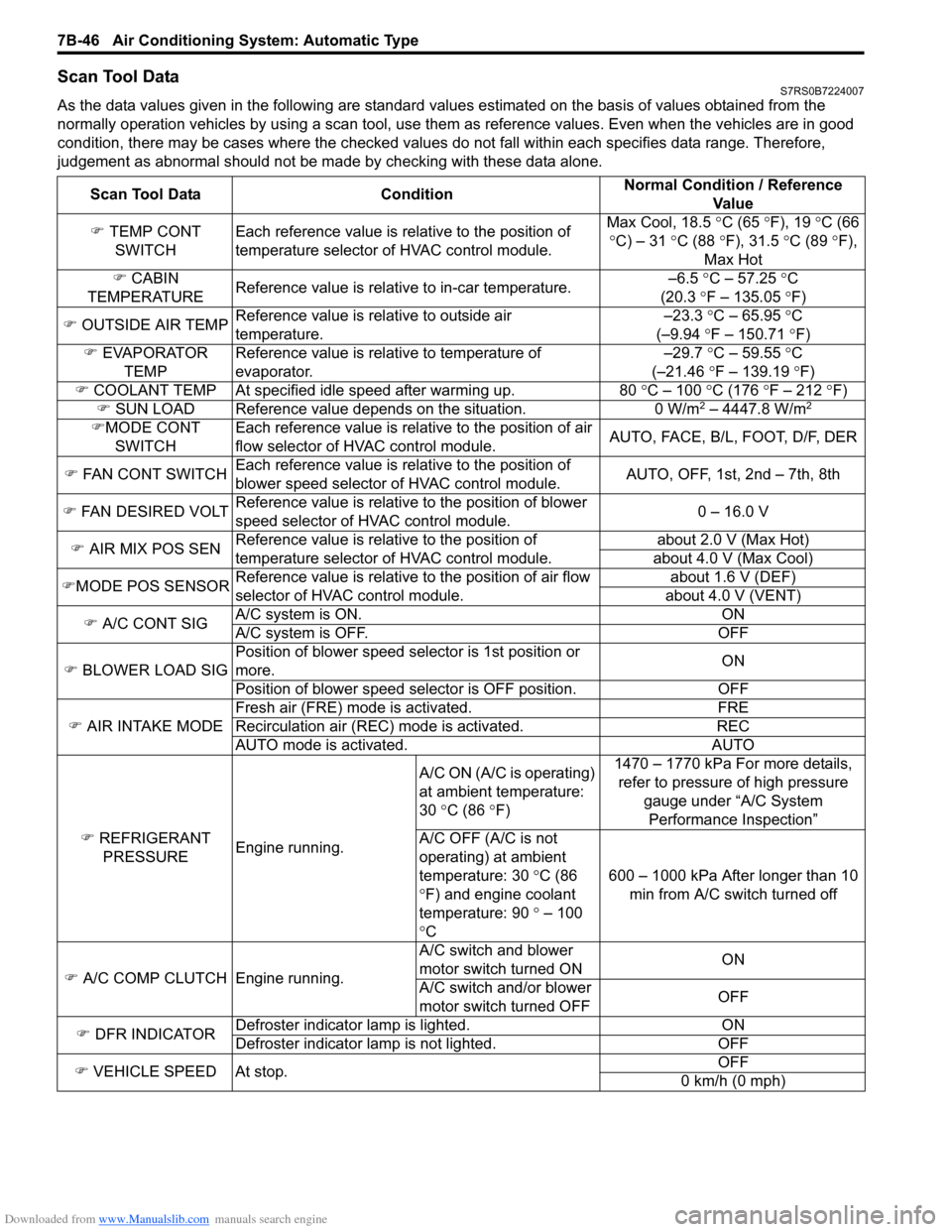
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 7B-46 Air Conditioning System: Automatic Type
Scan Tool DataS7RS0B7224007
As the data values given in the following are standard values estimated on the basis of values obtained from the
normally operation vehicles by using a scan tool, use them as reference values. Even when the vehicles are in good
condition, there may be cases where the checked values do not fall within each specifies data range. Therefore,
judgement as abnormal should not be ma de by checking with these data alone.
Scan Tool Data Condition Normal Condition / Reference
Va l u e
�) TEMP CONT
SWITCH Each reference value is relative to the position of
temperature selector of HVAC control module. Max Cool, 18.5
°C (65 ° F), 19 °C (66
° C) – 31 °C (88 °F), 31.5 °C (89 °F),
Max Hot
�) CABIN
TEMPERATURE Reference value is relative to in-car temperature. –6.5
°C – 57.25 ° C
(20.3 °F – 135.05 °F)
�) OUTSIDE AIR TEMP Reference value is relative to outside air
temperature. –23.3
°C – 65.95 °C
(–9.94 °F – 150.71 °F)
�) EVAPORATOR
TEMP Reference value is relative to temperature of
evaporator. –29.7
°C – 59.55 °C
(–21.46 °F – 139.19 °F)
�) COOLANT TEMP At specified id le speed after warming up. 80 °C – 100 °C (176 ° F – 212 ° F)
�) SUN LOAD Reference value depends on the situation. 0 W/m
2 – 4447.8 W/m2
�)MODE CONT
SWITCH Each reference value is relative to the position of air
flow selector of HVAC control module.
AUTO, FACE, B/L, FOOT, D/F, DER
�) FAN CONT SWITCH Each reference value is relative to the position of
blower speed selector of HVAC control module. AUTO, OFF, 1st, 2nd – 7th, 8th
�) FAN DESIRED VOLT Reference value is relative to the position of blower
speed selector of HVAC control module. 0 – 16.0 V
�) AIR MIX POS SEN Reference value is relative to the position of
temperature selector of HVAC control module. about 2.0 V (Max Hot)
about 4.0 V (Max Cool)
�) MODE POS SENSOR Reference value is relative to the position of air flow
selector of HVAC control module. about 1.6 V (DEF)
about 4.0 V (VENT)
�) A/C CONT SIG A/C system is ON. ON
A/C system is OFF. OFF
�) BLOWER LOAD SIG Position of blower speed selector is 1st position or
more.
ON
Position of blower speed selector is OFF position. OFF
�) AIR INTAKE MODE Fresh air (FRE) mode is activated. FRE
Recirculation air (REC) mode is activated. REC
AUTO mode is activated. AUTO
�) REFRIGERANT
PRESSURE Engine running. A/C ON (A/C is operating)
at ambient temperature:
30
°C (86 °F) 1470 – 1770 kPa For more details,
refer to pressure of high pressure
gauge under “A/C System Performance Inspection”
A/C OFF (A/C is not
operating) at ambient
temperature: 30 °C (86
° F) and engine coolant
temperature: 90 ° – 100
° C 600 – 1000 kPa After longer than 10
min from A/C switch turned off
�) A/C COMP CLUTCH Engine running. A/C switch and blower
motor switch turned ON
ON
A/C switch and/or blower
motor switch turned OFF OFF
�) DFR INDICATOR Defroster indicator
lamp is lighted. ON
Defroster indicator la mp is not lighted. OFF
�) VEHICLE SPEED At stop. OFF
0 km/h (0 mph)
Page 1033 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Seat Belts: 8A-2
Seat Belt with ELR
The seat belt with emergency locking retractor (ELR) is
designed so that it locks immediately (to prevent the
webbing from being pulled out of the retractor any
further) when any of the following items is detected as
exceeding each set value;
• Speed at which the webbing is pulled out of the retractor.
• Acceleration or deceleration of the vehicle speed.
• Inclination.
Seat Belt with A-ELR
The automatic and emergency locking retractor (A-ELR)
works as an Emergency Locking Retractor (ELR) till its
webbing is pulled all the way out and then on as an
Automatic Locking Retractor (ALR ) till it is retracted fully.
ALR: Automatically locks when the webbing is pulled out
from the retractor and allowed to retract even a little.
Then the webbing can not be pulled out any further,
unless it is wound all the way back into the retractor,
which releases the lock and allows the webbing to be
pulled out.
Seat Belt with ELR and Pretensioner
The seat belt with ELR and a pretensioner has a
pretensioner mechanism whic h operates in linkage with
the air bag in addition to the described ELR.
The pretensioner is incorporated in retractor assembly
and controlled by SDM as one of air bag system
components. It will be activated at the same time as the
driver and passenger air bag module when an impact at
the front of vehicle exceeds the specified value.
When servicing seat belt (retractor assembly) with
pretensioner, be sure to observe all WARNINGS and
CAUTIONS and “Precautions on Service and Diagnosis
of Air Bag System in Section 8B”. CAUTION!
Do not reuse the seat belt pretensioner
(retractor assembly) that has activated.
Replace it with a new seat belt assembly and
buckle together as a set. For checking
procedure of its activation, refer to “Repair
and Inspection Required after Accident in
Section 8B”.
Seat Belt Remainder
When driver’s seat belt is unfastened (under the
following conditions), seat belt reminder light and
warning buzzer inform that driver’s seat belt is
unfastened. Seat belt reminder light located in
combination meter and warning buzzer located inside
BCM operate as follows:
• Seat belt reminder light comes on when driver’s seat belt is unfastened while igni tion key switch is at ON
position.
• If vehicle speed exceeds 15 km/h with seat belt unfastened, warning buzzer operates for
approximately 95 seconds and seat belt reminder light
flashes synchronously with buzzer. When warning
buzzer stops operating, seat belt reminder light is
turned on.
• If driver’s seat belt state is changed from “fastened” to “unfastened” while vehicle speed is above 15 km/h,
warning buzzer operates for approximately 95
seconds and seat belt reminder light flashes
synchronously with buzzer. When warning buzzer
stops operating, seat belt reminder light is turned on.
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Repair and Inspection Required after AccidentS7RS0B8104001
After an accident, whether the seat belt pretensioner has been activated or not, be sure to perform checks and repairs
described on “Repair and Inspection Required after Accident in Section 8B”.
Page 1040 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 8B-2 Air Bag System:
Precautions on Handling and Storage of Air Bag
System Components
S7RS0B8200002
SDM
WARNING!
Never power up air bag system when SDM is
not rigidly attached to the vehicle. Otherwise,
personal injury may result.
CAUTION!
After detecting one time of such collision as
to meet deployment conditions, SDM must
not be used. Refer to “Air Bag Diagnostic
System Check” when checking SDM.
• Never attempt disassembly of SDM.
• When storing SDM, select a place where neither high temperature nor high humidity is anticipated and oil,
water and dust are kept off.
• If SDM has been dropped, replace it with a new one.
• If SDM installation part of floor was damaged, repair that part completely before reinstallation.
• All SDM and mounting bracket fasteners must be carefully torqued and the arrow must be pointed
toward the front of the vehicle to ensure proper
operation of the air bag system. Live (Undeployed) Air Bag (Inflator) Modules
Special care is necessary when handling and storing a
live (undeployed) air bag (inflator) modules.
The rapid gas generation produced during deployment
of the air bag could cause the air bag (inflator) module,
or an object in front of the air bag (inflator) module, to be
thrown through the air in the unlikely event of an
accidental deployment.
WARNING!
Never attempt to measure the resistance of
the air bag (inflator) modules (driver,
passenger and side of both sides and curtain
of both sides). It is
very dangerous as the
electric current from the tester may deploy
the air bag.
I5RH01820001-01
I4RS0A820001-03
Page 1134 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 8B-96 Air Bag System:
Repair and Inspection Required after AccidentS7RS0B8204049
CAUTION!
• All air bag system components, including the electrical harness (component
mounting points), must be inspected after
an accident. If any components are
damaged or bent, they must be replaced
even if air bag system activation did not
occur.
• Never use air bag system parts from another vehicle.
• Do not attempt to service the parts below. Service of these parts is by replacement
only.
– Driver / Passenger air bag (inflator) modules
– Driver / Passenger side-air bag (inflator) modules
– Driver / Passenger side curtain-air bag (inflator) modules
– Driver / Passenger seat belt pretensioners
–Forward-sensor
– Driver / Passenger side-sensors
–SDM
– Contact coil and combination switch assembly
– Air bag wire harness in main harness, instrument panel harness and floor
harness.
• Proper operation of the sensors and air bag system requires that any repairs to the
vehicle structure return it to its original
production configuration.
CAUTION!
After detecting one time of such collision as
to meet deployment conditions, the SDM
must not be used.
Refer to “Air Bag Diagnostic System Check”
when checking the SDM.
Accident with Deployment / Activation – Component
Replacement
When driver and passenger air bags are deployed, the
following components must be replaced.
• Driver and passenger air bag (inflator) modules
• Driver and passenger seat belt pretensioners
• SDM after detecting such collision as to meet
deployment conditions
• Forward-sensor
• Instrument panel When side-air bag and side curtain-air bag are deployed,
the following components must be replaced.
• Deployed side-air bag (inflator) module
• Deployed side curtain-air bag (inflator) module
• Side-sensor
•SDM
Accident with or without Deployment / Activation –
Component Inspections
Certain air bag and restraint system components must
be inspected after any crash, whether the air bag system
activated or not. If any faul
ty condition is found in the
following checks, replace faulty part.
Those components are:
• Steering column (1) and shaft joints
– Check for length, damage and bend according to “Checking Steering Column for Accident Damage in
Section 6B”.
• Steering column bracket (2) and capsules – Check for damage and bent.
• Steering wheel and driver air bag (inflator) module – Check for damage or air bag (inflator) module fitness.
– Check trim cover (pad surface) for cracks.
– Check wire harness and connector for damage or tightness.
2
1
I4RS0A820046-01
I4RS0A820047-01