Combination pin SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2008, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 340 of 1496
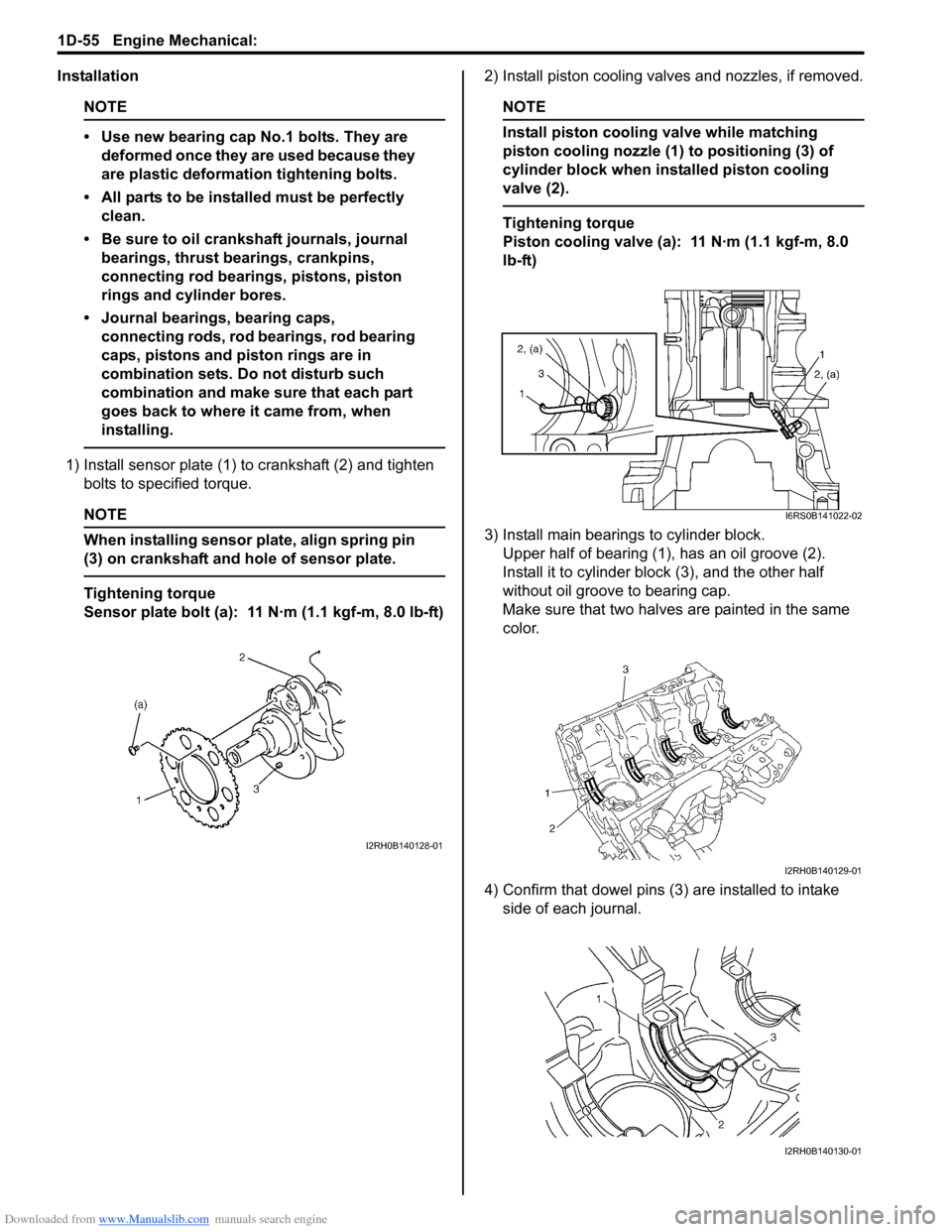
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-55 Engine Mechanical:
Installation
NOTE
• Use new bearing cap No.1 bolts. They are deformed once they are used because they
are plastic deformation tightening bolts.
• All parts to be insta lled must be perfectly
clean.
• Be sure to oil crankshaft journals, journal bearings, thrust bearings, crankpins,
connecting rod bearings, pistons, piston
rings and cylinder bores.
• Journal bearings, bearing caps, connecting rods, rod bearings, rod bearing
caps, pistons and piston rings are in
combination sets. Do not disturb such
combination and make sure that each part
goes back to where it came from, when
installing.
1) Install sensor plate (1) to crankshaft (2) and tighten bolts to spec ified torque.
NOTE
When installing sensor plate, align spring pin
(3) on crankshaft and hole of sensor plate.
Tightening torque
Sensor plate bolt (a): 11 N·m (1.1 kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft) 2) Install piston cooling valves and nozzles, if removed.
NOTE
Install piston cooling valve while matching
piston cooling nozzle (1) to positioning (3) of
cylinder block when installed piston cooling
valve (2).
Tightening torque
Piston cooling valve (a): 11 N·m (1.1 kgf-m, 8.0
lb-ft)
3) Install main bearings to cylinder block. Upper half of bearing (1), has an oil groove (2).
Install it to cylinder block (3), and the other half
without oil groove to bearing cap.
Make sure that two halves are painted in the same
color.
4) Confirm that dowel pins (3 ) are installed to intake
side of each journal.
I2RH0B140128-01
I6RS0B141022-02
I2RH0B140129-01
I2RH0B140130-01
Page 414 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1J-4 Charging System:
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Battery InspectionS7RS0B1A04001
Common Causes of Failure
A battery is not designed to last indefinitely; however, with proper care, it will provide many years of service. If the
battery performs satisfactorily during te st but fails to operate properly for no apparent reason, the following are some
factors that may point to the cause of trouble:
• Accessories left on overnight or for an extended period without the generator operating.
• Slow average driving speeds for short periods.
• Electrical load exceeding generator output partic ularly with addition of aftermarket equipment.
• Defects in charging system such as high resistance, s lipping drive belt, loose generator output terminal, faulty
generator or voltage regulator, Refer to “Generator Symptom Diagnosis”.
• Battery abuse, including failure to keep battery cable terminals clean and tight or loose battery hold down.
• Mechanical problems in electrical sys tem such as shorted or pinched wires.
Visual Inspection
Check for obvious damage, such as cracked or broken case or cover, that could permit loss of electrolyte. If obvious
damage is noted, replace battery. Determine cause of damage and correct as needed.
Generator Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B1A04002
CAUTION!
• Do not mistake polarities of “IG” terminal and “L” terminal.
• Do not create short circuit between “IG” and “L” terminals. Always connect these terminals through a lamp.
• Do not connect any load between “L” and “E” terminals.
• When connecting charger or booster battery to vehicle battery, refer to “Jump Starting in Case of Emergency”.
Trouble in charging system will show up as one or more of the following conditions:
1) Faulty indicator lamp operation.
2) An undercharged battery as evidenced by slow cranking or indicator dark.
3) An overcharged battery as evidenced by ex cessive spewing of electrolyte from vents.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Noisy generator Loose drive belt Adjust or replace drive belt.
Loose drive belt pulley Tighten by specified torque.
Loose mounting bolts Tighten by specified torque.
Worn or dirty bearings Replace.
Defective diode or stator Replace.
Charge light does not
light with ignition ON and
engine off Fuse blown
Replace fuse and check for shorted circuit.
Indicator lamp (LED) faulty Replace combination meter.
Wiring connection loose Tighten loose connection.
IC regulator or field coil faulty Replace.
Poor contact between brush and slip
ring Repair or replace.
Charge light does not go
out with engine running
(battery requires frequent
recharging) Drive belt loose or worn
Adjust or replace drive belt.
IC regulator or generator faulty Replace.
Wiring faulty Repair wiring.
Page 540 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4E-1 ABS:
Brakes
ABS
Precautions
Precautions in Diagnosing TroublesS7RS0B4500001
To ensure that the trouble diagnosis is done accurately
and smoothly, observe the following and follow “ABS
Check”.
• Diagnostic information stored in ABS cont rol module
memory can be cleared as well as checked by using
SUZUKI scan tool. Before us ing scan tool, read its
Operator’s (Instruction) Manual carefully to have good
understanding as to what functions are available and
how to use it.
• If the vehicles was operated in any of the following ways, ABS warning light may light momentarily but
this does not indicate anything abnormal in ABS.
– The vehicle was driven with parking brake pulled.
– The vehicle was driven with brake dragging.
– The vehicle was stuck in mud, sand, etc.
– Wheel spin occurred while driving.
– Wheel(s) was rotated while the vehicle was jacked up.
• Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit Service in Section 00” befo re inspection and observe
what is written there.
• Be sure to use the trouble diagnosis procedure as described in “ABS Check”. Failure to follow it may
result in incorrect diagnosis. (Some other diagnosis
trouble code may be stored by mistake in the memory
of ABS control module during inspection.)
• When disconnecting ABS co ntrol module connector
(1), pull down lock lever (2) of connector.
When connecting, set the connector on ABS control
module assembly and pull up the lock lever (2) until it
locks. • Communication of ECM,
BCM, ABS control module,
keyless start control module (if equipped), and
combination meter is established by CAN (Controller
Area Network).
Therefore, be sure to read “Precautions for Installing
Mobile Communication Equipment in Section 00”
before inspection and handle CAN communication
line.
Precautions in On-Vehicle ServiceS7RS0B4500002
When connector is connected to ABS control module
assembly, do not disconnect connectors of sensors with
ignition switch ON. Otherwise, DTC will be set in ABS
control module.
Precautions in Hydraulic Unit Operation CheckS7RS0B4500003
ABS hydraulic unit / control module assembly function is
checked by correct wheel lock / release condition when
brake pressure is pressurized / depressurized using
SUZUKI scan tool. The hydraulic unit operation check
referring to “ABS Hydraulic Unit Operation Check”
should be performed to confirm the correct brake pipe
connection in the following cases.
• ABS hydraulic unit / cont rol module assembly was
replaced.
• Brake pipe and/or hose ware replaced.
[A]: Disconnect C: Pull down to disconnect
[B]: Connect D: Pull up to connect
21
C D
[A]
[B]
I4RH01450001-01
Page 575 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-1
Brakes
Electronic Stability Program
Precautions
Precautions in Diagnosing TroublesS7RS0B4600001
To ensure that the trouble diagnosis is done accurately
and smoothly, observe the following and follow
“Electronic Stability Program System Check”.
• Diagnostic information stored in ESP® control module
memory can be cleared as well as checked by using
SUZUKI scan tool. Before us ing scan tool, read its
Operator’s (Instruction) Manual carefully to have good
understanding as to what functions are available and
how to use it.
• If the vehicles was operated in any of the following ways, ESP ® warning lamp may light momentarily but
this does not indicate anything abnormal in ESP ®.
– The vehicle was driven with parking brake pulled.
– The vehicle was driven with brake dragging.
– The vehicle was stuck in mud, sand, etc.
– Wheel spin occurred while driving.
– Wheel(s) was rotated while the vehicle was jacked up.
• Be sure to use the trouble diagnosis procedure as described in “Electronic Stability Program System
Check”. Failure to follow it may resu lt in incorrect
diagnosis. (Some other diagnosis trouble code may
be stored by mistake in the memory of ESP ® control
module during inspection.)
• When disconnecting ESP ® control module connector
(1), pull down the lock lever (2) of connector.
When connecting, set the connector on ESP ®
hydraulic unit / control module assembly and pull up
the lock lever (2) until it locks. • Communication of ECM, BCM, ESP
® control module,
keyless start control module (if equipped), steering
angle sensor and combination meter is established by
CAN (Controller Area Network).
Therefore, be sure to read “Precautions for Installing
Mobile Communication Equipment in Section 00”
before inspection and handling CAN communication
line.
Precautions in On-Vehicle ServiceS7RS0B4600002
When connector is connected to ESP ® hydraulic unit /
control module assembly, do not disconnect connectors
of sensors with ignition switch ON. Otherwise, DTC will
be set in ESP ® control module.
Precautions in Hydraulic Unit Operation CheckS7RS0B4600003
ESP® hydraulic unit / control module assembly function
is checked by correct wheel lock / release condition
when brake pressure is pressurized / depressurized
using SUZUKI scan tool. The hydraulic unit operation
check referring to “ESP ® Hydraulic Unit Operation
Check” should be performed to confirm the correct brake
pipe connection in the following cases.
• ESP® hydraulic unit / contro l module assembly was
replaced.
• Brake pipe and/or hose were replaced.
Precautions in Sensor CalibrationS7RS0B4600004
ESP ® control module stores calibration points data of yaw rate / G sensor assembly and master cylinder pressure
sensor. Steering angle sensor stores calibration point data of itself.
TCS and stability control system use these sets of data.
When the following operation is done, sensor calibration should be performed since the original calibration points are
deleted.
[A]: Disconnect [C]: Pull down to disconnect
[B]: Connect [D]: Pull up to connect
21
C D
[A]
[B]
I4RH01450001-01
Page 577 of 1496
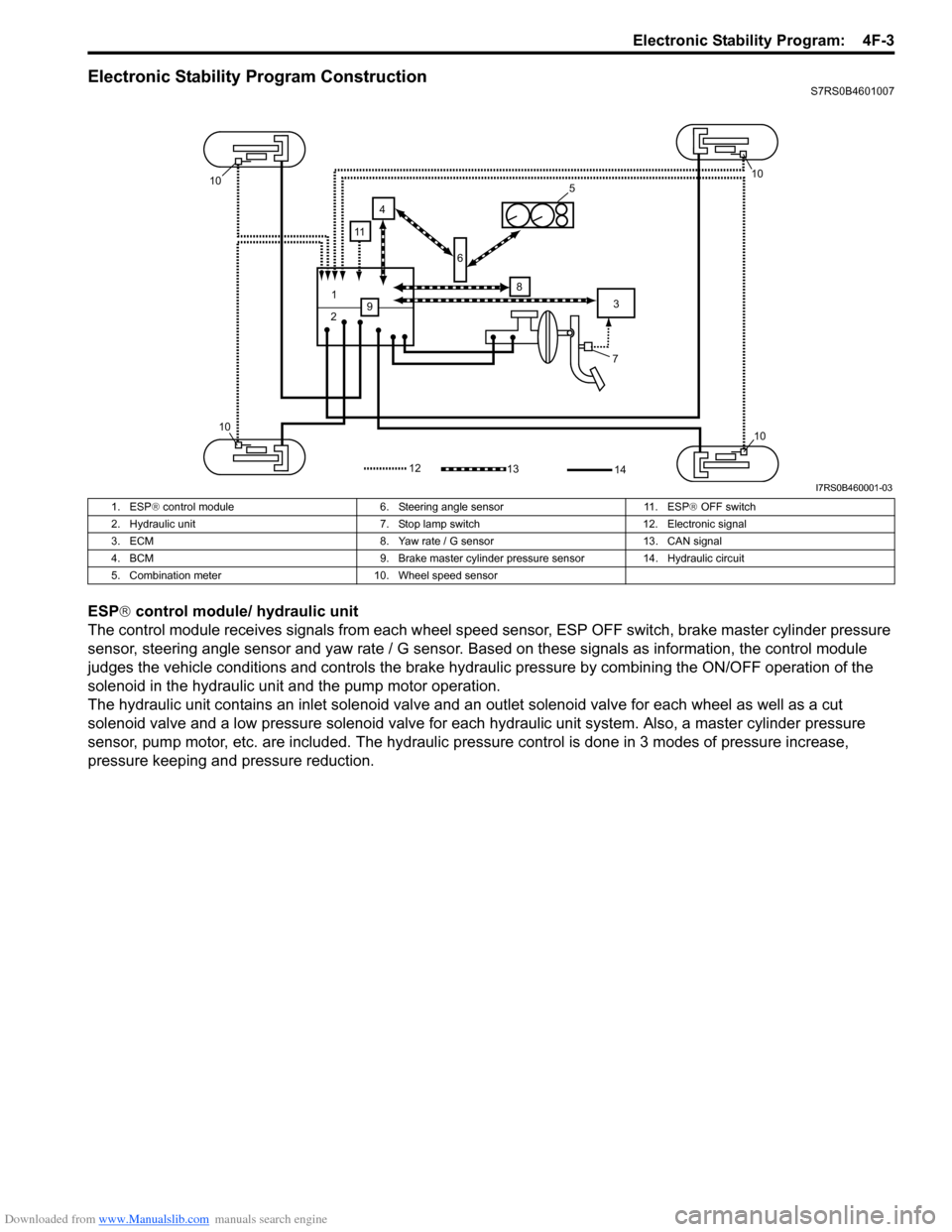
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-3
Electronic Stability Program ConstructionS7RS0B4601007
ESP® control module/ hydraulic unit
The control module receives signals from each wheel speed sensor, ESP O FF switch, brake master cylinder pressure
sensor, steering angle sensor and yaw rate / G sensor. Ba sed on these signals as information, the control module
judges the vehicle conditions and controls the brake hydraulic pressure by combining the ON/OFF operation of the
solenoid in the hydraulic unit and the pump motor operation.
The hydraulic unit contains an inlet so lenoid valve and an outlet solenoid valve for each wheel as well as a cut
solenoid valve and a low pressure solenoid valve for each hydraulic unit system. Also, a master cylinder pressure
sensor, pump motor, etc. are included. The hydraulic pre ssure control is done in 3 modes of pressure increase,
pressure keeping and pressure reduction.
7
1
2 3
4
5
6
8
9
10
1010
10
1312
11
14
I7RS0B460001-03
1. ESP ® control module 6. Steering angle sensor 11. ESP ® OFF switch
2. Hydraulic unit 7. Stop lamp switch 12. Electronic signal
3. ECM 8. Yaw rate / G sensor 13. CAN signal
4. BCM 9. Brake master cylinder pre ssure sensor 14. Hydraulic circuit
5. Combination meter 10. Wheel speed sensor
Page 580 of 1496
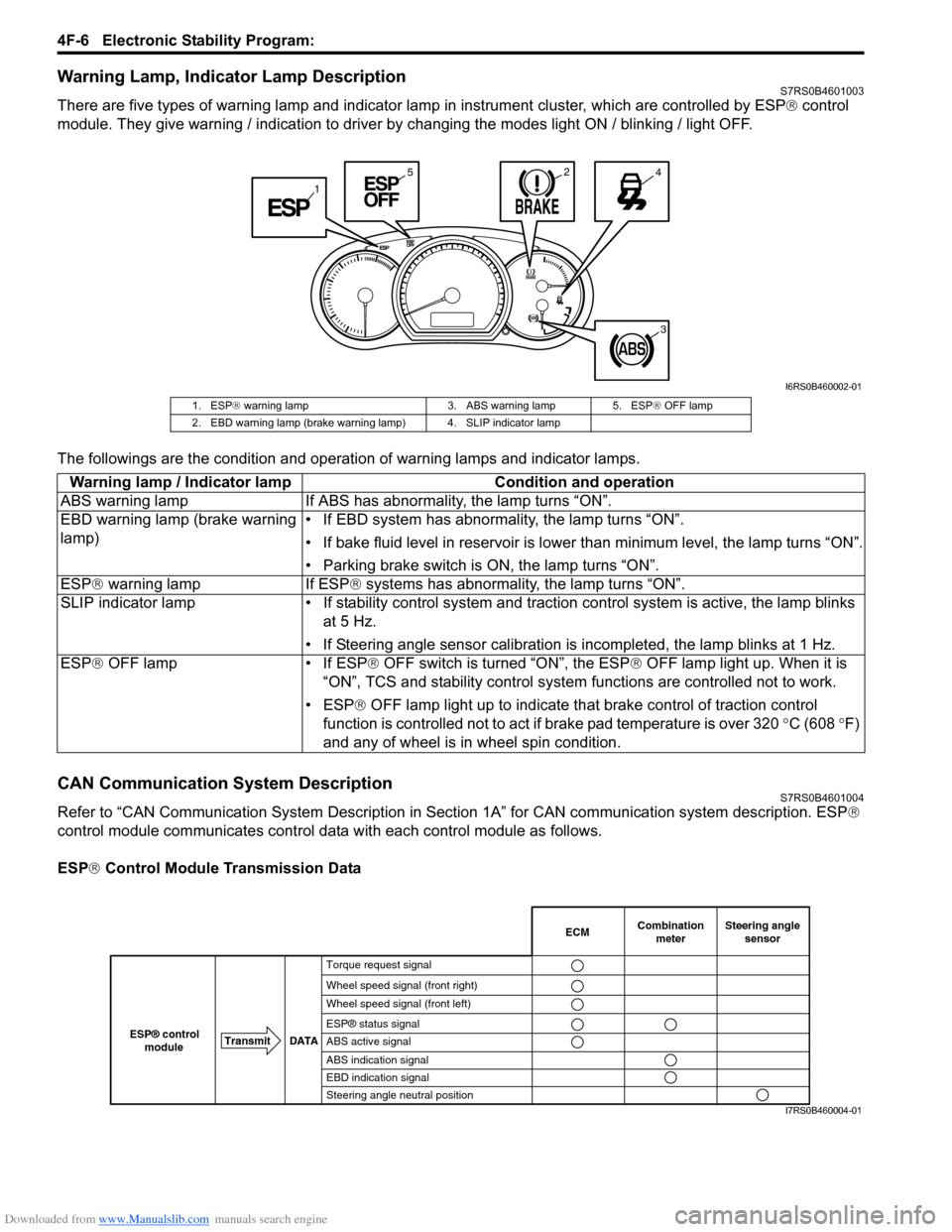
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4F-6 Electronic Stability Program:
Warning Lamp, Indicator Lamp DescriptionS7RS0B4601003
There are five types of warning lamp and indicator lamp in instrument cluster, which are controlled by ESP ® control
module. They give warning / indication to driver by changing the modes light ON / blinking / light OFF.
The followings are the condition and operation of warning lamps and indicator lamps.
CAN Communication System DescriptionS7RS0B4601004
Refer to “CAN Communication System Description in Section 1A” for CAN communication system description. ESP ®
control module communicates control data with each control module as follows.
ESP ® Control Module Transmission Data
1
245
3
I6RS0B460002-01
1. ESP ® warning lamp 3. ABS warning lamp 5. ESP ® OFF lamp
2. EBD warning lamp (brake warning lamp) 4. SLIP indicator lamp
Warning lamp / Indicator lamp Condition and operation
ABS warning lamp If ABS has abnor mality, the lamp turns “ON”.
EBD warning lamp (brake warning
lamp) • If EBD system has abnormality, the lamp turns “ON”.
• If bake fluid level in reservoir is lower
than minimum level, the lamp turns “ON”.
• Parking brake switch is ON, the lamp turns “ON”.
ESP ® warning lamp If ESP ® systems has abnormality, the lamp turns “ON”.
SLIP indicator lamp • If stability cont rol system and traction control system is active, the lamp blinks
at 5 Hz.
• If Steering angle sensor calibration is incompleted, the lamp blinks at 1 Hz.
ESP ® OFF lamp • If ESP ® OFF switch is turned “ON”, the ESP ® OFF lamp light up. When it is
“ON”, TCS and stability control system functions are controlled not to work.
• ESP® OFF lamp light up to indicate th at brake control of traction control
function is controlled not to act if brake pad temperature is over 320 °C (608 °F)
and any of wheel is in wheel spin condition.
Combination
meter
Transmit DATA
ESP® control
moduleECMSteering angle sensor
Torque request signal
Wheel speed signal (front right)
Wheel speed signal (front left)
ESP® status signal
ABS active signal
ABS indication signal
EBD indication signal
Steering angle neutral position
I7RS0B460004-01
Page 670 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5A-26 Automatic Transmission/Transaxle:
TRANSAXLE RANGE
Transaxle range detected by signal fed from
transmission range sensor.
D RANGE SIGNAL
ON: Signal which TCM require ECM to increase idle
speed
OFF: Signal which TCM does not require ECM to
increase idle speed
THROTTLE POSITION (%)
Throttle opening ratio computed by CAN signal from
ECM.
BRAKE SWITCH
Inputted signal from brake light switch on pedal bracket.
ON: Brake pedal depressed
OFF: Brake pedal released
TORQUE REDUCTION SIGNAL
ON: Signal which TCM require ECM to reduce output
torque at shifting gear
OFF: Signal which TCM does not require ECM to reduce
output torque
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE ( °C, °F)
Engine coolant temperature computed by CAN signal
from ECM. AIR CONDITIONER SIGNAL
ON: Signal which inform that air conditioner compressor
is turned ON.
OFF: Signal which inform that air conditioner
compressor is not turned ON.
ENGINE TORQUE SIGNAL (N
⋅m)
Engine torque computed by duty pulse signal outputted
from ECM.
SLIP RPM (RPM)
This parameter indicates slip ping rotation in the torque
converter (difference between input shaft rotation and
engine rotation)
MIL REQUEST
ON: Signal which TCM requires combination meter to
turn on malfunction indicator lamp.
OFF: Signal which TCM does not require combination
meter to turn on malf unction indicator lamp.
FUEL CUT FLAG
ON: Signal which inform that fuel cut is operating.
OFF: Signal which inform that fuel cut is not operating.
A/T Basic CheckS7RS0B5104010
This check is important for troubleshooting when TCM has detected no DTC and no abnormality has been noted in
“Visual Inspection”. Fo llow the flow carefully.
Step Action YesNo
1 Was “A/T System Check” preformed? Go to Step 2.Go to “A/T System
Check”.
2 Perform “Road Test”.
Is it OK? Go to Step 3.
Proceed to
“Troubleshooting” in
“Road Test”.
3 Perform “Manual Road Test”.
Is it OK? Go to Step 4.
Proceed to
“Troubleshooting” in
“Manual Road Test”.
4 Perform “Engine Brake Test”.
Is it OK? Go to Step 5.
Proceed to
“Troubleshooting” in
“Engine Brake Test”.
5 Perform “Stall Test”.
Is it OK? Go to Step 6.
Proceed to
“Troubleshooting” in
“Stall Test”.
6 Perform “Time Lag Test”.
Is it OK? Go to Step 7.
Proceed to
“Troubleshooting” in
“Time Lag Test”.
7 Perform “Line Pressure Test”.
Is it OK? Go to Step 8.
Proceed to
“Troubleshooting” in
“Line Pressure Test”.
8 Proceed to “Trouble Diag nosis 1” in “A/T Symptom
Diagnosis”.
Is trouble identified? Repair or replace faulty
parts.
Go to Step 9.
Page 958 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 7B-10 Air Conditioning System: Manual Type
Abnormal Noise from Tension Pulley
Abnormal Noise from A/C Evaporator
Abnormal Noise from Blower Motor
A/C System Performance InspectionS7RS0B7214003
1) Confirm that vehicle and environmental conditions are as follows.
• Vehicle is put indoors.
• Ambient temperature is within 25 – 35 °C (77 – 95
° F).
• Relative humidity is within 30 – 70%.
• There is no wind indoors.
• HVAC unit is normal.
• Blower motor is normal.
• There is no air leakage from air ducts.
• Condenser fins are clean.
• Air filter in HVAC unit is not clogged with dirt and
dust.
• Battery voltage is about 12 V.
• Radiator cooling fan operates normally.
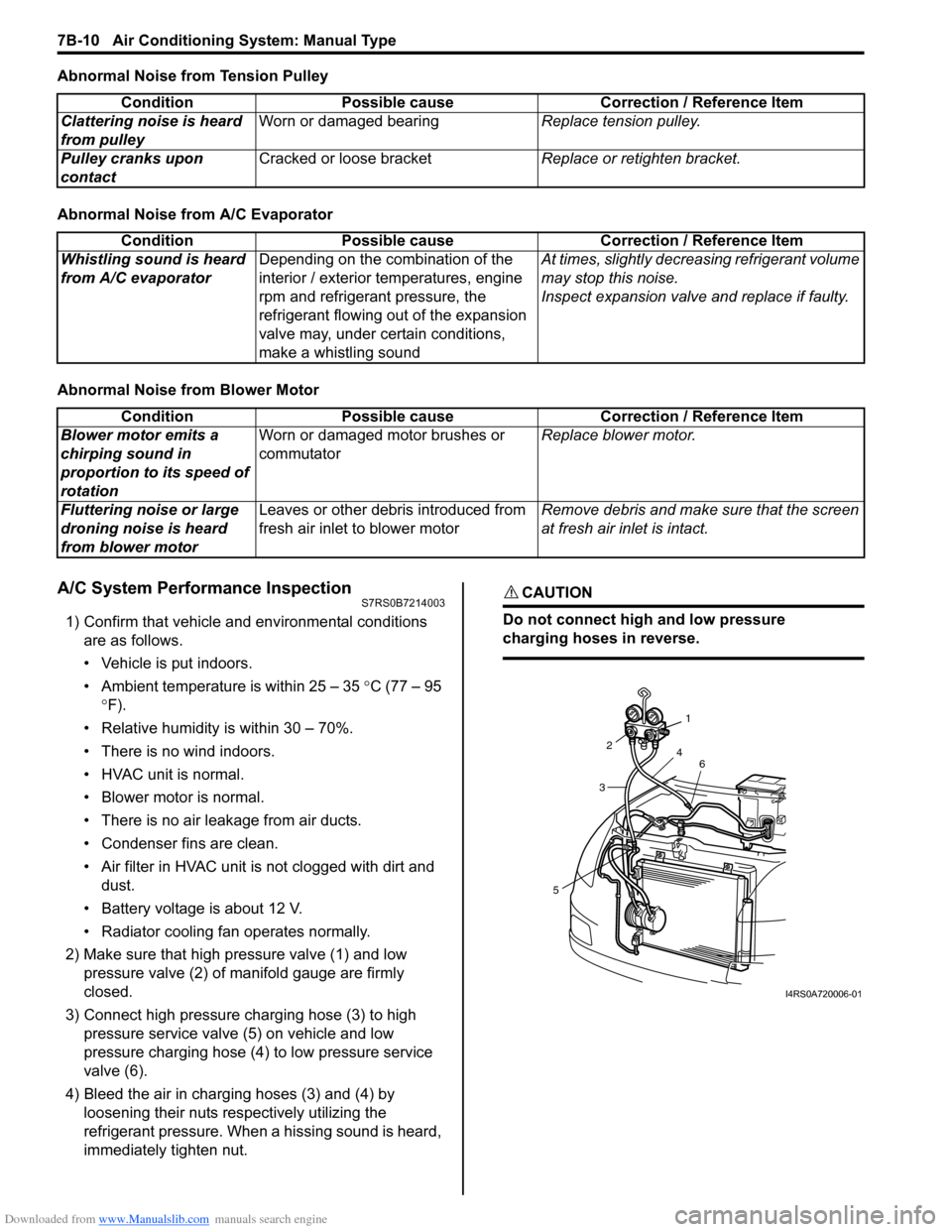
2) Make sure that high pressure valve (1) and low pressure valve (2) of manifold gauge are firmly
closed.
3) Connect high pressure charging hose (3) to high pressure service valve (5) on vehicle and low
pressure charging hose (4) to low pressure service
valve (6).
4) Bleed the air in charging hoses (3) and (4) by loosening their nuts respectively utilizing the
refrigerant pressure. When a hissing sound is heard,
immediately tighten nut.
CAUTION!
Do not connect high and low pressure
charging hoses in reverse.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Clattering noise is heard
from pulley Worn or damaged bearing
Replace tension pulley.
Pulley cranks upon
contact Cracked or loose bracket
Replace or retighten bracket.
ConditionPossible cause Correction / Reference Item
Whistling sound is heard
from A/C evaporator Depending on the combination of the
interior / exterior temperatures, engine
rpm and refrigerant pressure, the
refrigerant flowing out of the expansion
valve may, under certain conditions,
make a whistling sound At times, slightly decrea
sing refrigerant volume
may stop this noise.
Inspect expansion valve and replace if faulty.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Blower motor emits a
chirping sound in
proportion to its speed of
rotation Worn or damaged motor brushes or
commutator
Replace blower motor.
Fluttering noise or large
droning noise is heard
from blower motor Leaves or other debris introduced from
fresh air inlet to blower motor
Remove debris and make sure that the screen
at fresh air inlet is intact.
53
2
1
4 6
I4RS0A720006-01