charging SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2008, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 4 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Vo l u m e 1
Precautions............................................................... 00-iPrecautions ............................................................ 00-1
General Information ................ ................................... 0-i
General Information ............................................... 0A-1
Maintenance and Lubricatio n ................................. 0B-1
Engine ......................................................................... 1-i Precautions .............................................................. 1-1
Engine General Information and Diagnosis ........... 1A-1
Aux. Emission Control Devices .............................. 1B-1
Engine Electrical Devices....................................... 1C-1
Engine Mechanical ................................................. 1D-1
Engine Lubrication System .................................... 1E-1
Engine Cooling System .......................................... 1F-1
Fuel System ...........................................................1G-1
Ignition System....................................................... 1H-1
Starting System ....................................................... 1I-1
Charging System.....................................................1J-1
Exhaust System ..................................................... 1K-1
Suspension ................................................................. 2-i Precautions .............................................................. 2-1
Suspension General Diagnosis .............................. 2A-1
Front Suspension ................................................... 2B-1
Rear Suspension................ .................................... 2C-1
Wheels and Tires ................................................... 2D-1
Driveline / Axle ........................................................... 3-i Precautions .............................................................. 3-1
Drive Shaft / Axle ................................................... 3A-1
Brakes ......................................................................... 4-i Precautions .............................................................. 4-1
Brake Control System and Diagnosis .................... 4A-1
Front Brakes........................................................... 4B-1
Rear Brakes ........................................................... 4C-1
Parking Brake......................................................... 4D-1
ABS ........................................................................ 4E-1
Electronic Stability Program ................................... 4F-1
Vo l u m e 2
Precautions ............................................................... 00-iPrecautions ............................................................ 00-1
Transmission / Transaxle .... ...................................... 5-i
Precautions .............................................................. 5-1
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle ........................ 5A-1
Manual Transmission/Transaxle ............................ 5B-1
Clutch .....................................................................5C-1
Steering ....................................................................... 6-i Precautions .............................................................. 6-1
Steering General Diagnosis ................................... 6A-1
Steering Wheel and Column .................................. 6B-1
Power Assisted Steering System ...........................6C-1
HVAC ........................................................................... 7-i Precautions .............................................................. 7-1
Heater and Ventilation............................................ 7A-1
Air Conditioning System ......................................... 7B-1
Restraint ...................................................................... 8-i Precautions .............................................................. 8-1
Seat Belts ............................................................... 8A-1
Air Bag System ...................................................... 8B-1
Body, Cab and Accessories .... .................................. 9-i
Precautions .............................................................. 9-1
Wiring Systems ...................................................... 9A-1
Lighting Systems .................................................... 9B-1
Instrumentation / Driver Info. / Horn .......................9C-1
Wipers / Washers ...................................................9D-1
Glass / Windows / Mirrors ...................................... 9E-1
Security and Locks ................................................. 9F-1
Seats ..................................................................... 9G-1
Interior Trim ............................................................9H-1
Hood / Fenders / Doors .......................................... 9J-1
Body Structure ....................................................... 9K-1
Paint / Coatings ...................................................... 9L-1
Exterior Trim .......................................................... 9M-1
Control Systems ....................................................... 10-i Precautions ............................................................ 10-1
Body Electrical Control Sy stem ............................ 10B-1
Immobilizer Control System .................................10C-1
Keyless Start System ........................................... 10E-1
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 49 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Table of Contents 1-v
Ignition Timing Inspection ................................... 1H-8
Specifications ....................................................... 1H-9
Tightening Torque Specifications ........................ 1H-9
Special Tools and Equipmen t ............................. 1H-9
Special Tool ........................................................ 1H-9
Starting System ................. ........................ 1I-1
Schematic and Routing Diagram ......................... 1I-1
Cranking System Circuit Diagram ........................ 1I-1
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............. 1I-1
Cranking System Symptom Diagnosis ................. 1I-1
Cranking System Test.......................................... 1I-3
Repair Instructions ............................................... 1I-4 Starting Motor Dismounting and Remounting ...... 1I-4
Starting Motor Components ................................. 1I-5
Starting Motor Inspection ..................................... 1I-6
Specifications ........................................................ 1I-9
Cranking System Specifications........................... 1I-9
Tightening Torque Specifications ......................... 1I-9
Special Tools and Equipment .............................. 1I-9
Recommended Service Material .......................... 1I-9
Charging System ............ .......................... 1J-1
General Description ......... .................................... 1J-1
Battery Description ...............................................1J-1
Generator Descripti on ..........................................1J-2
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............ 1J-4 Battery Inspection ................................................1J-4
Generator Symptom Diagnosis ............................1J-4 Generator Test (Undercharged Battery
Check) ............................................................... 1J-5
Generator Test (Overcharg ed Battery Check) .... 1J-6
Repair Instructions ........... ................................... 1J-6
Jump Starting in Case of Emergency.................. 1J-6
Battery Dismounting and Remounting ................ 1J-7
Water Pump / Generator Drive Belt Tension Inspection and Adjustment ................................ 1J-7
Water Pump / Generator Drive Belt Removal and Installation .................................................. 1J-8
Generator Unit Co mponents ............................... 1J-9
Generator Dismounting a nd Remounting............ 1J-9
Generator Components........ ............................. 1J-10
Generator Insp ection......................................... 1J-11
Specifications ..................................................... 1J-13 Charging System Specifications ....................... 1J-13
Tightening Torque Specifications ...................... 1J-13
Exhaust System .............. ......................... 1K-1
General Description .............................................1K-1
Exhaust System Description ............................... 1K-1
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............1K-1 Exhaust System Check ....................................... 1K-1
Repair Instructions ........... ...................................1K-2
Exhaust System Components ............................. 1K-2
Exhaust Manifold Removal and Installation ........ 1K-3
Exhaust Pipe and Muffler Removal and Installation ......................................................... 1K-4
Specifications .................... ...................................1K-5
Tightening Torque Specifications ........................ 1K-5
Page 61 of 1496
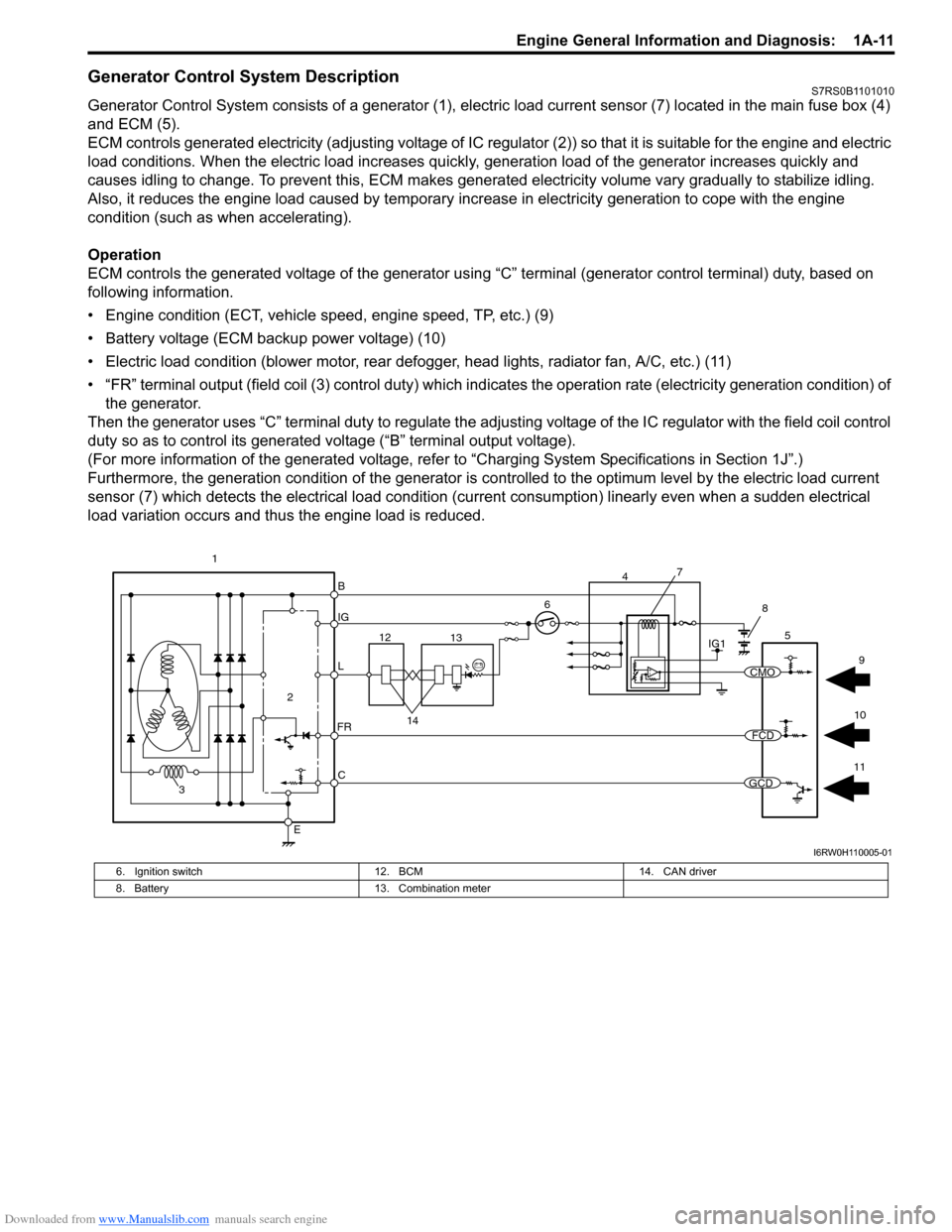
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-11
Generator Control System DescriptionS7RS0B1101010
Generator Control System consists of a generator (1), electric load current sensor (7) located in the main fuse box (4)
and ECM (5).
ECM controls generated electricity (adjusting voltage of IC regulator (2)) so that it is suitable for the engine and electric
load conditions. When the electric load increases quickly, generation load of the generator increases quickly and
causes idling to change. To prevent this, ECM makes generated electricity volume vary gradually to stabilize idling.
Also, it reduces the engine load caused by temporary incr ease in electricity generation to cope with the engine
condition (such as when accelerating).
Operation
ECM controls the generated voltage of the generator using “C” terminal (generator control terminal) duty, based on
following information.
• Engine condition (ECT, vehicle speed, engine speed, TP, etc.) (9)
• Battery voltage (ECM backup power voltage) (10)
• Electric load condition (blower motor, rear defogger, head lights, radiator fan, A/C, etc.) (11)
• “FR” terminal output (field coil (3) cont rol duty) which indicates the operation rate (electricity generation condition) of
the generator.
Then the generator uses “C” terminal duty to regulate the adju sting voltage of the IC regulator with the field coil control
duty so as to control its generated voltage (“B” terminal output voltage).
(For more information of the generated voltage, refer to “Charging System Specifications in Section 1J”.)
Furthermore, the generation condition of the generator is co ntrolled to the optimum level by the electric load current
sensor (7) which detects the electrical load condition (cur rent consumption) linearly even when a sudden electrical
load variation occurs and thus the engine load is reduced.
B
IG
L
C
E
6
2
3
FR
5
12 13
14
1IG1
7
4
8
11
10 9
CMO
FCD
GCD
I6RW0H110005-01
6. Ignition switch
12. BCM 14. CAN driver
8. Battery 13. Combination meter
Page 284 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1C-12 Engine Electrical Devices:
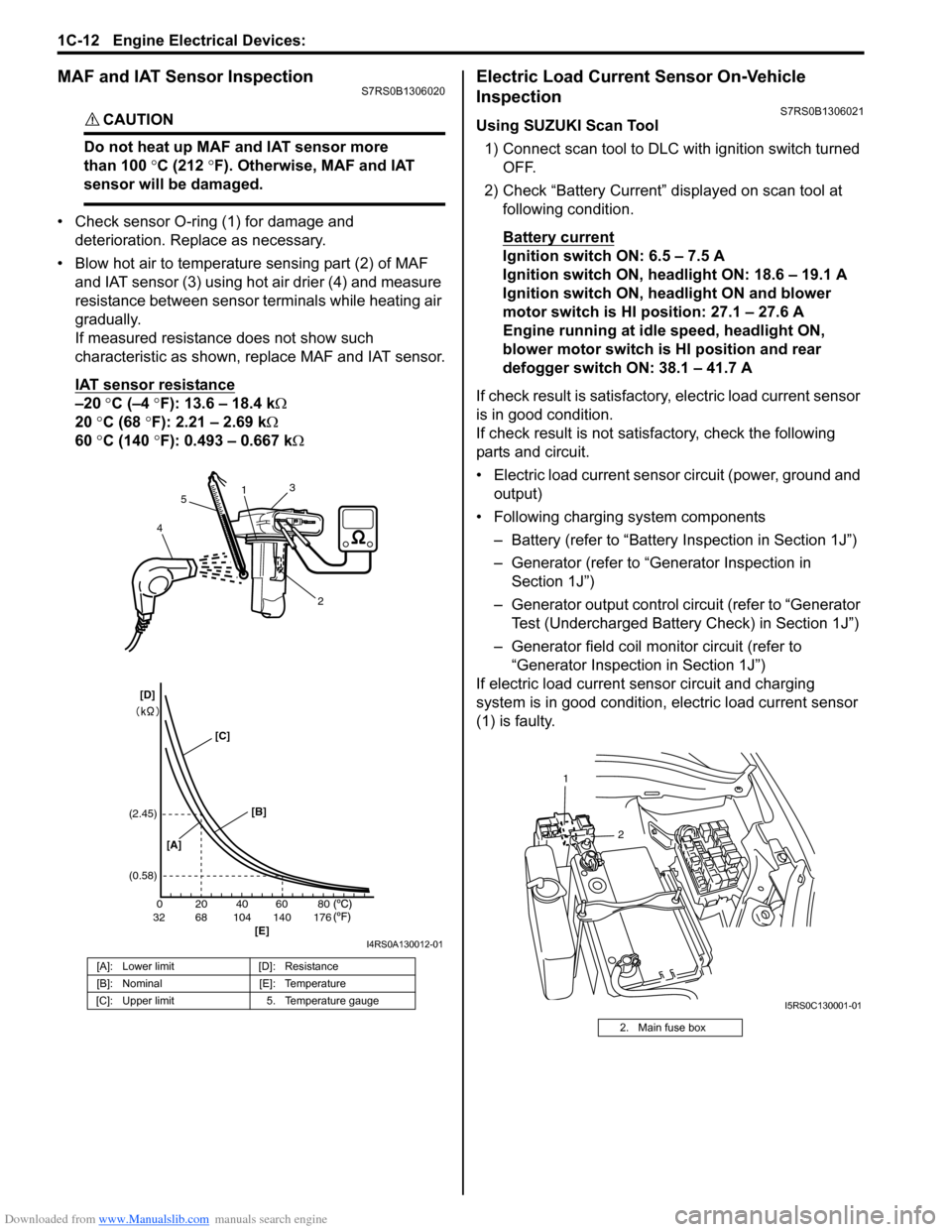
MAF and IAT Sensor InspectionS7RS0B1306020
CAUTION!
Do not heat up MAF and IAT sensor more
than 100 °C (212 °F). Otherwise, MAF and IAT
sensor will be damaged.
• Check sensor O-ring (1) for damage and deterioration. Replace as necessary.
• Blow hot air to temperature sensing part (2) of MAF and IAT sensor (3) using hot air drier (4) and measure
resistance between sensor terminals while heating air
gradually.
If measured resistance does not show such
characteristic as shown, replace MAF and IAT sensor.
IAT sensor resistance
–20 °C (–4 °F): 13.6 – 18.4 k Ω
20 °C (68 °F): 2.21 – 2.69 k Ω
60 °C (140 °F): 0.493 – 0.667 k Ω
Electric Load Current Sensor On-Vehicle
Inspection
S7RS0B1306021
Using SUZUKI Scan Tool
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned OFF.
2) Check “Battery Current” displayed on scan tool at following condition.
Battery current
Ignition switch ON: 6.5 – 7.5 A
Ignition switch ON, headlight ON: 18.6 – 19.1 A
Ignition switch ON, headlight ON and blower
motor switch is HI position: 27.1 – 27.6 A
Engine running at idle speed, headlight ON,
blower motor switch is HI position and rear
defogger switch ON: 38.1 – 41.7 A
If check result is satisfactory, electric load current sensor
is in good condition.
If check result is not satisf actory, check the following
parts and circuit.
• Electric load current sensor circuit (power, ground and output)
• Following charging system components
– Battery (refer to “Battery Inspection in Section 1J”)
– Generator (refer to “Generator Inspection in Section 1J”)
– Generator output control ci rcuit (refer to “Generator
Test (Undercharged Battery Check) in Section 1J”)
– Generator field coil monitor circuit (refer to “Generator Inspection in Section 1J”)
If electric load current sensor circuit and charging
system is in good condition, electric load current sensor
(1) is faulty.
[A]: Lower limit [D]: Resistance
[B]: Nominal [E]: Temperature
[C]: Upper limit 5. Temperature gauge
200
6832104 140 17640 60 80
(2.45)
(0.58)
1
2
3
4 5
[A] [B]
[E]
[C]
[D]
I4RS0A130012-01
2. Main fuse box
2
1
I5RS0C130001-01
Page 285 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Electrical Devices: 1C-13
Without Using SUZUKI Scan Tool1) Measure sensor voltage between “C37-23” terminal of ECM connector and vehicle body ground referring
to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits in Section 1A”.
If check result is satisfactory, electric load current
sensor is in good condition.
If check result is not satisfactory, check the following
parts and circuit.
• Electric load current sensor circuit (power, ground and output)
• Following charging system components – Battery (refer to “Battery Inspection in Section
1J”)
– Generator (refer to “Generator Inspection in Section 1J”)
– Generator output control circuit (refer to “Generator Test (Undercharged Battery Check)
in Section 1J”)
– Generator field coil monitor circuit (refer to “Generator Inspection in Section 1J”) If electric load current sensor circuit and charging
system is in good condition,
electric load current sensor
(1) is faulty.
Specifications
Tightening Torque SpecificationsS7RS0B1307001
Reference:
For the tightening torque of fastener not specified in this section, refer to “Fasteners Information in Section 0A”.
2. Main fuse box
2
1
I5RS0C130001-01
Fastening part
Tightening torque
Note
N ⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
ECM mounting bolt 8 0.8 6.0 �)
APP sensor assembly nut 5.5 0.55 4.0 �)
ECT sensor 15 1.5 11.0 �)
Heated oxygen sensor 45 4.5 32.5 �)
CMP sensor bolt 10 1.0 7.5 �)
CKP sensor bolt 10 1.0 7.5 �)
Knock sensor 22 2.2 16.0 �)
MAF and IAT sensor screw 1.5 0.15 1.1 �)
Page 411 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Charging System: 1J-1
Engine
Charging System
General Description
Battery DescriptionS7RS0B1A01001
The battery has three major functions in the electrical
system.
• It is a source of electrical energy for cranking the engine.
• It acts as a voltage stabilizer for the electrical system.
• It can, for a limited time, provide energy when the electrical load exceeds the output of the generator.
Carrier and Hold-Down
The battery carrier should be in good condition so that it
will support the battery securely and keep it level. Before
installing the battery, the ba ttery carrier and hold-down
clamp should be clean and free from corrosion and
make certain there are no parts in carrier.
To prevent the battery from shaking in its carrier, the
hold-down bolts should be tight enough but not over-
tightened.
Electrolyte Freezing
The freezing point of electrolyte depends on its specific
gravity. Since freezing may ruin a battery, it should be
protected against freezing by keeping it in a fully
charged condition. If a battery is frozen accidentally, it
should not be charged until it is warmed.
Sulfation
If the battery is allowed to stand for a long period in
discharged condition, the lead sulfate becomes
converted into a hard, cryst alline substance, which will
not easily turn back to the active material again during
the subsequent recharging. “Sulfation” means the result
as well as the process of that reaction. Such a battery
can be revived by very slow charging and may be
restored to usable condition but its capacity is lower than
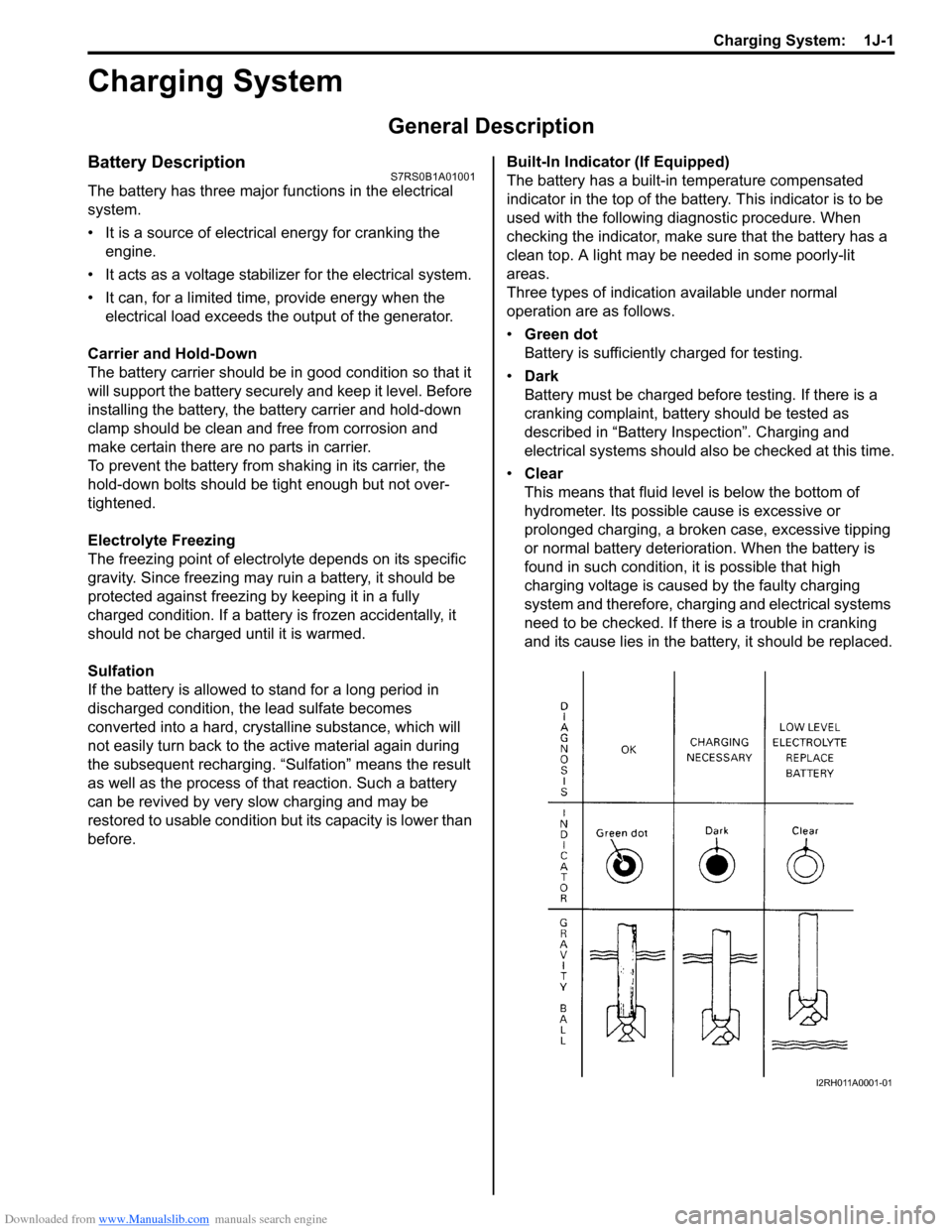
before. Built-In Indicator (If Equipped)
The battery has a built-in temperature compensated
indicator in the top of the battery. This indicator is to be
used with the following diagnostic procedure. When
checking the indicator, make sure that the battery has a
clean top. A light may be needed in some poorly-lit
areas.
Three types of indication available under normal
operation are as follows.
•
Green dot
Battery is sufficiently charged for testing.
• Dark
Battery must be charged before testing. If there is a
cranking complaint, battery should be tested as
described in “Battery Inspection”. Charging and
electrical systems should also be checked at this time.
• Clear
This means that fluid level is below the bottom of
hydrometer. Its possible cause is excessive or
prolonged charging, a broken case, excessive tipping
or normal battery deteriorat ion. When the battery is
found in such condition, it is possible that high
charging voltage is caused by the faulty charging
system and therefore, charging and electrical systems
need to be checked. If there is a trouble in cranking
and its cause lies in the battery, it should be replaced.
I2RH011A0001-01
Page 412 of 1496
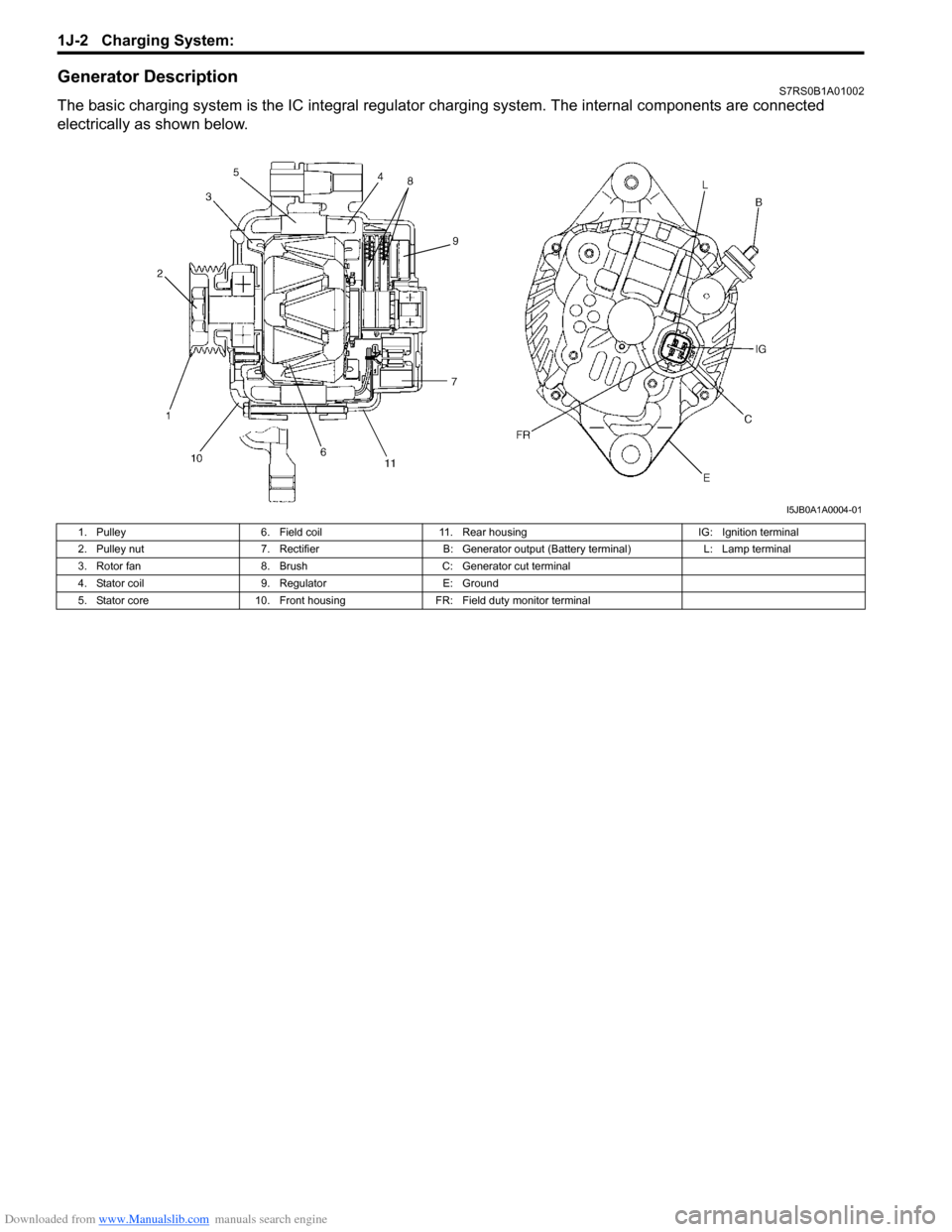
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1J-2 Charging System:
Generator DescriptionS7RS0B1A01002
The basic charging system is the IC integral regulator charging system. The internal co mponents are connected
electrically as shown below.
I5JB0A1A0004-01
1. Pulley 6. Field coil11. Rear housing IG: Ignition terminal
2. Pulley nut 7. RectifierB: Generator output (Battery terminal) L: Lamp terminal
3. Rotor fan 8. BrushC: Generator cut terminal
4. Stator coil 9. RegulatorE: Ground
5. Stator core 10. Front housing FR: Field duty monitor terminal
Page 413 of 1496
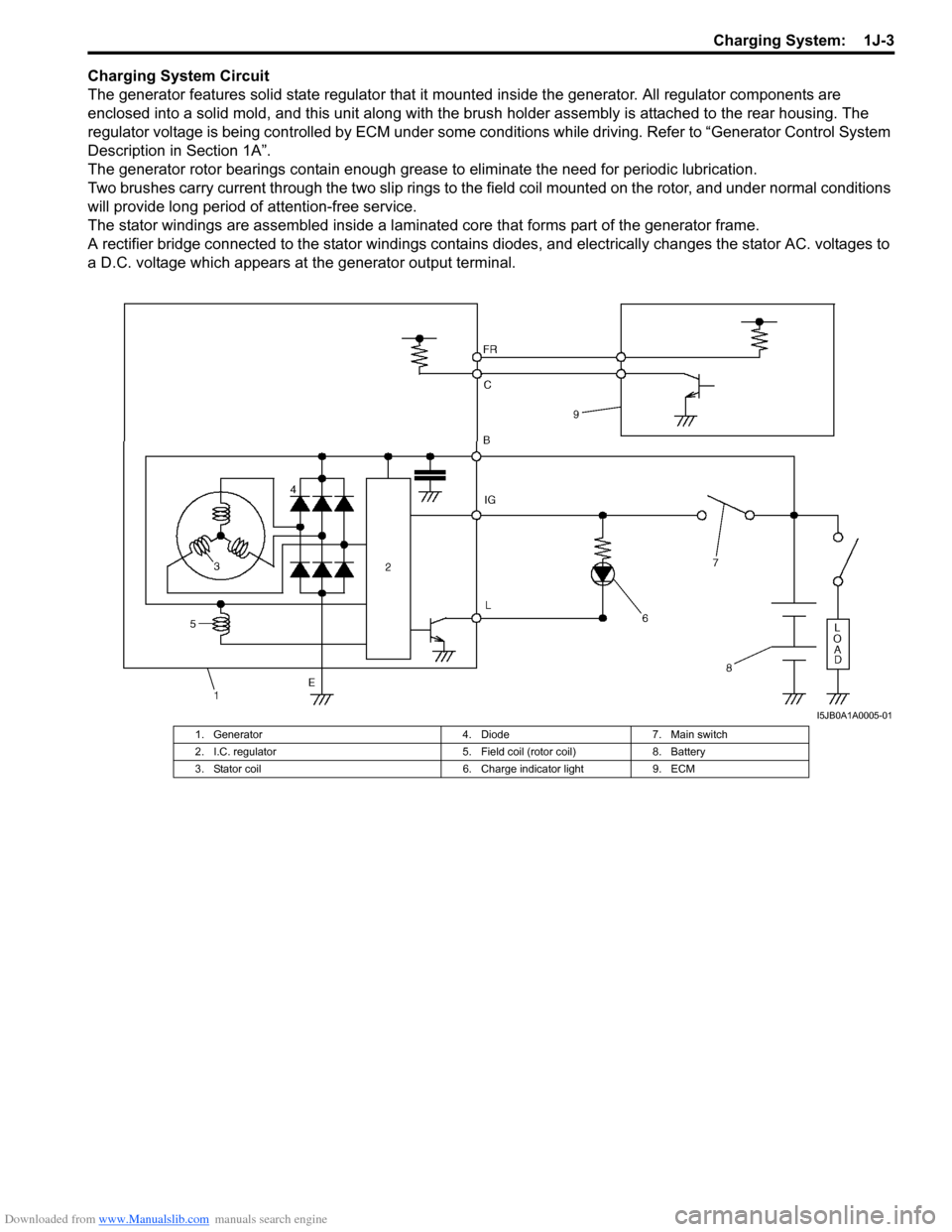
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Charging System: 1J-3
Charging System Circuit
The generator features solid state regulator that it mounted inside the generator. All regulator components are
enclosed into a solid mold, and this unit along with the brus h holder assembly is attached to the rear housing. The
regulator voltage is being controlled by ECM under some cond itions while driving. Refer to “Generator Control System
Description in Section 1A”.
The generator rotor bearings contain enough grease to eliminate the need for periodic lubrication.
Two brushes carry current through the two slip rings to the field coil mounted on the rotor, and under normal conditions
will provide long period of attention-free service.
The stator windings are assembled inside a laminate d core that forms part of the generator frame.
A rectifier bridge connected to the stator windings contains diodes, and electrically changes the stator AC. voltages to
a D.C. voltage which appears at the generator output terminal.
I5JB0A1A0005-01
1. Generator 4. Diode7. Main switch
2. I.C. regulator 5. Field coil (rotor coil)8. Battery
3. Stator coil 6. Charge indicator light9. ECM
Page 414 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1J-4 Charging System:
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Battery InspectionS7RS0B1A04001
Common Causes of Failure
A battery is not designed to last indefinitely; however, with proper care, it will provide many years of service. If the
battery performs satisfactorily during te st but fails to operate properly for no apparent reason, the following are some
factors that may point to the cause of trouble:
• Accessories left on overnight or for an extended period without the generator operating.
• Slow average driving speeds for short periods.
• Electrical load exceeding generator output partic ularly with addition of aftermarket equipment.
• Defects in charging system such as high resistance, s lipping drive belt, loose generator output terminal, faulty
generator or voltage regulator, Refer to “Generator Symptom Diagnosis”.
• Battery abuse, including failure to keep battery cable terminals clean and tight or loose battery hold down.
• Mechanical problems in electrical sys tem such as shorted or pinched wires.
Visual Inspection
Check for obvious damage, such as cracked or broken case or cover, that could permit loss of electrolyte. If obvious
damage is noted, replace battery. Determine cause of damage and correct as needed.
Generator Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B1A04002
CAUTION!
• Do not mistake polarities of “IG” terminal and “L” terminal.
• Do not create short circuit between “IG” and “L” terminals. Always connect these terminals through a lamp.
• Do not connect any load between “L” and “E” terminals.
• When connecting charger or booster battery to vehicle battery, refer to “Jump Starting in Case of Emergency”.
Trouble in charging system will show up as one or more of the following conditions:
1) Faulty indicator lamp operation.
2) An undercharged battery as evidenced by slow cranking or indicator dark.
3) An overcharged battery as evidenced by ex cessive spewing of electrolyte from vents.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Noisy generator Loose drive belt Adjust or replace drive belt.
Loose drive belt pulley Tighten by specified torque.
Loose mounting bolts Tighten by specified torque.
Worn or dirty bearings Replace.
Defective diode or stator Replace.
Charge light does not
light with ignition ON and
engine off Fuse blown
Replace fuse and check for shorted circuit.
Indicator lamp (LED) faulty Replace combination meter.
Wiring connection loose Tighten loose connection.
IC regulator or field coil faulty Replace.
Poor contact between brush and slip
ring Repair or replace.
Charge light does not go
out with engine running
(battery requires frequent
recharging) Drive belt loose or worn
Adjust or replace drive belt.
IC regulator or generator faulty Replace.
Wiring faulty Repair wiring.
Page 415 of 1496
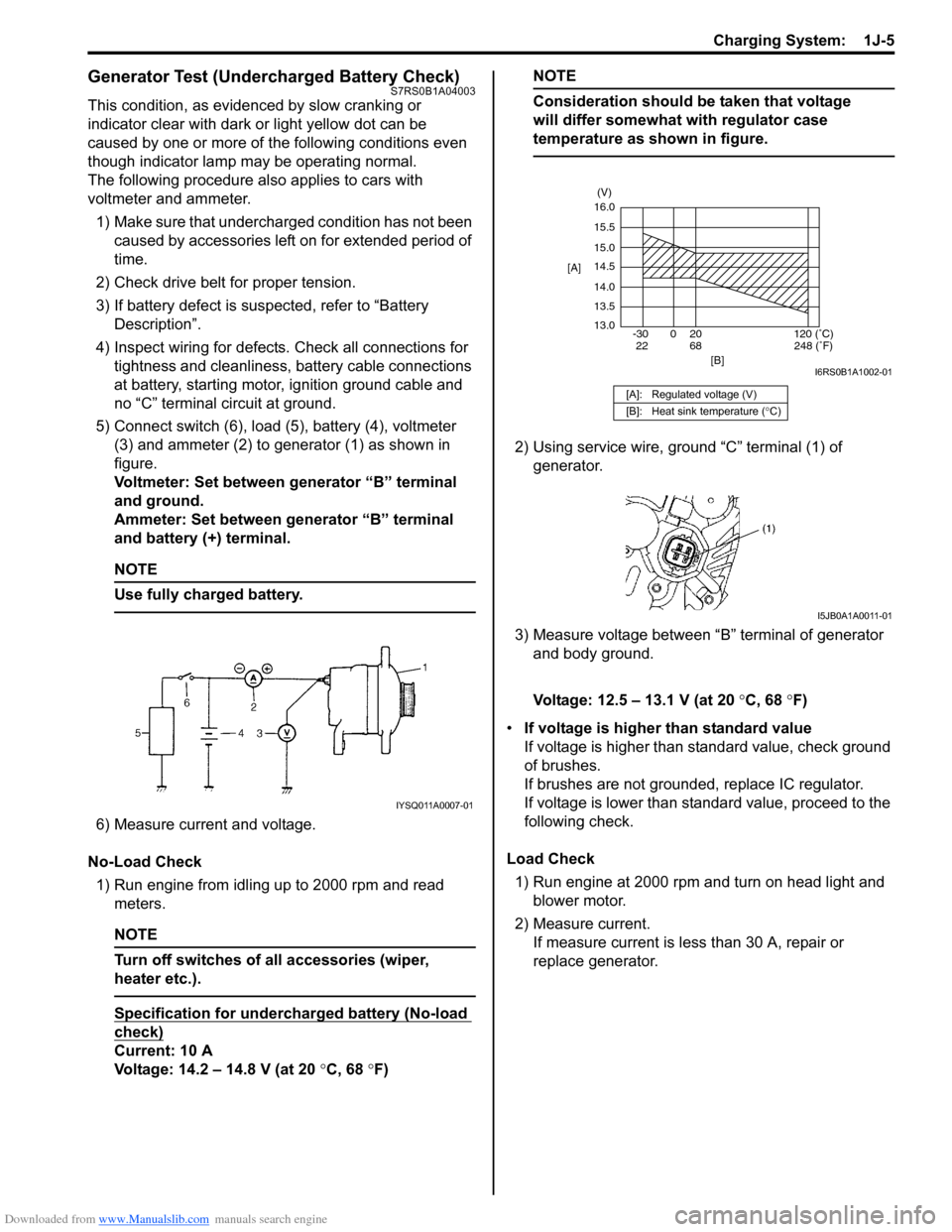
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Charging System: 1J-5
Generator Test (Undercharged Battery Check)S7RS0B1A04003
This condition, as evidenced by slow cranking or
indicator clear with dark or light yellow dot can be
caused by one or more of the following conditions even
though indicator lamp may be operating normal.
The following procedure also applies to cars with
voltmeter and ammeter.1) Make sure that undercharged condition has not been caused by accessories left on for extended period of
time.
2) Check drive belt for proper tension.
3) If battery defect is suspected, refer to “Battery Description”.
4) Inspect wiring for defects. Check all connections for tightness and cleanliness, battery cable connections
at battery, starting motor, ignition ground cable and
no “C” terminal circuit at ground.
5) Connect switch (6), load (5), battery (4), voltmeter (3) and ammeter (2) to generator (1) as shown in
figure.
Voltmeter: Set between generator “B” terminal
and ground.
Ammeter: Set between generator “B” terminal
and battery (+) terminal.
NOTE
Use fully charged battery.
6) Measure current and voltage.
No-Load Check 1) Run engine from idling up to 2000 rpm and read meters.
NOTE
Turn off switches of all accessories (wiper,
heater etc.).
Specification for undercharged battery (No-load
check)
Current: 10 A
Voltage: 14.2 – 14.8 V (at 20 °C, 68 °F)
NOTE
Consideration should be taken that voltage
will differ somewhat with regulator case
temperature as shown in figure.
2) Using service wire, ground “C” terminal (1) of
generator.
3) Measure voltage between “B” terminal of generator and body ground.
Voltage: 12.5 – 13.1 V (at 20 °C, 68 °F)
• If voltage is higher than standard value
If voltage is higher than standard value, check ground
of brushes.
If brushes are not grounded, replace IC regulator.
If voltage is lower than standard value, proceed to the
following check.
Load Check 1) Run engine at 2000 rpm and turn on head light and blower motor.
2) Measure current. If measure current is less than 30 A, repair or
replace generator.
IYSQ011A0007-01
[A]: Regulated voltage (V)
[B]: Heat sink temperature ( °C)
16.0
15.5
15.0
14.5
14.0
13.5
13.0
-30 0 20
[A]
[B]
68
22120 (˚C)
248 (˚F)
(V)
I6RS0B1A1002-01
I5JB0A1A0011-01