SUZUKI SX4 2010 1.G Owners Manual
Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2010, Model line: SX4, Model: SUZUKI SX4 2010 1.GPages: 297, PDF Size: 4.51 MB
Page 231 of 297

7-26
INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE
80J23-03E
D. Construction Code
This letter code is used to indicate
the type of ply construction in the
tire. The letter “R” means radial
ply tire construction, the letter “D”
means diagonal or bias ply con-
struction, and the letter “B” means
belted-bias ply construction.
E. Rim Diameter
This two-digit number is the wheel
or rim diameter in inches.Tire Inflation Pressure
Tire inflation pressure should be
checked when the tire is cold. “Cold
tire inflation pressure” is the pressure
in a tire that has been driven less than
1 mile (1.6 km) or has been standing
for three hours or more.
80JS025
The front and rear tire pressure speci-
fications for your vehicle are shown
below and are listed on the Tire and
Loading Information Label, which is
located on the driver’s door lock pillar.
The Tire and Loading Information
Label contains the following informa-
tion: Seating Capacity
Maximum Allowed Combined
Weight of Occupants and Cargo
Original Tire Size
Recommended Cold Tire Inflation
Pressure of Original Tires
Size of Compact Spare Tire
Recommended Cold Tire Inflation
Pressure of Compact Spare Tire
WARNING
Your SUZUKI is equipped with
tires which are all the same type
and size. This is important to
ensure proper steering and han-
dling of the vehicle. Never mix
tires of different size or type on
the four wheels of your vehicle.
Mixing tires could cause you to
lose control while driving which
may lead to an accident. The size
and type of tires used should be
only those approved by SUZUKI
Motor Corporation as standard or
optional equipment for your vehi-
cle.
Recommended Cold Tire Inflation
Pressures
Front Tires230 kPa
33 psi
Rear Tires230 kPa
33 psi
Compact Spare Tire420 kPa
60 psi
Page 232 of 297

7-27INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE
80J23-03E
NOTE:
The tire inflation pressure will change
due to changes in atmospheric pres-
sure, temperature or tire temperature
when driving. To reduce the chance that
the low tire pressure warning light will
come on due to normal changes in tem-
perature and atmospheric pressure, it is
important to check and adjust the tire
pressures when the tires are cold. Tires
that appear to be at the specified pres-
sure when checked after driving, when
the tires are warm, could have pressure
below the specification when the tires
cool down. Also, tires that are inflated to
the specified pressure in a warm
garage may have pressure below the
specification when the vehicle is driven
outside in very cold temperature. If you
adjust the tire pressure in a garage that
is warmer than the outside tempera-
ture, you should add 1 psi to the recom-
mended cold tire inflation pressure for
every 10°F difference between garage
temperature and outside temperature.Measuring Air Pressure
Use the following steps to achieve
proper tire inflation:
1) Identify the recommended tire pres-
sure on the vehicle’s Tire and Load-
ing Information Label or in the
owner’s manual.
2) Remove the valve cap from the tire
valve stem.
3) Using a reliable pressure gauge,
measure the tire inflation pressure
by pressing the tire gauge firmly
onto the valve to get a pressure
measurement. Remember that
inflation pressures should be
checked when the tires are “cold”,
meaning before they have been
driven one mile or after sitting for
three hours or more allowing the tire
to cool to ambient air temperature.
4) If the air pressure is too high, slowly
release the air by pressing on the
tire valve stem with the edge of the
tire gauge until you reach the cor-
rect pressure.
5) If the air pressure is too low, fill the
tire with air at a service station until
it reaches the recommended pres-
sure.
6) Make sure all tires have the same
air pressure (unless the owner’s
manual indicates otherwise).
WARNING
Air pressures should be
checked when the tires are cold
or you may get inaccurate read-
ings.
Check the inflation pressure
from time to time while inflating
the tire gradually, until the spec-
ified pressure is obtained.
Never underinflate or overin-
flate the tires.
Underinflation can cause
unusual handling characteristics
or can cause the rim to slip on
the tire bead, resulting in an acci-
dent or damage to the tire or rim.
Underinflation can also cause
tires to overheat, leading to tire
failure.
Overinflation can cause the tire
to burst, resulting in personal
injury.
Overinflation can also cause
unusual handling characteristics
which may result in an accident.
Page 233 of 297

7-28
INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE
80J23-03E
Tire Inspection
Inspect your vehicle’s tires at least
once a month by performing the fol-
lowing checks:
1) Measure the air pressure with a tire
gauge. Adjust the pressure if nec-
essary. Remember to check the
spare tire, too. Refer to the “Mea-
suring Air Pressure” section.
54G136
(1) Tread wear indicator
(2) Indicator location mark
2) Check that the depth of the tread
groove is more than 1.6 mm (0.06
in.). To help you check this, the tires
have molded-in tread wear indica-
tors in the grooves. When the indi-
cators appear on the tread surface,
the remaining depth of the tread is1.6 mm (0.06 in.) or less and the
tire should be replaced.
3) Check for abnormal wear, cracks
and damage. Any tires with cracks
or other damage should be
replaced. If any tires show abnor-
mal wear, have them inspected by
your SUZUKI dealer.
4) Check for loose wheel nuts.
5) Check that there are no nails,
stones or other objects sticking into
the tires.
WARNING
Hitting curbs and running over
rocks can damage tires and affect
wheel alignment. Be sure to have
tires and wheel alignment
checked periodically by your
SUZUKI dealer.
WARNING
Your SUZUKI is equipped with
tires which are all the same type
and size. This is important to
ensure proper steering and han-
dling of the vehicle. Never mix
tires of different size or type on
the four wheels of your vehicle.
The size and type of tires used
should be only those approved by
SUZUKI Motor Corporation as
standard or optional equipment
for your vehicle.
CAUTION
For intelligent All Wheel Drive (i-
AWD) models, replacing a tire
with one of a different size, or
using different brands among the
four tires can result in damage to
the drive train.
Page 234 of 297

7-29INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE
80J23-03E
Uniform Tire Quality Grading
The U.S. National Highway Traffic
Safety Administration has developed a
grading system for evaluating the per-
formance of passenger car tires. The
following information will help you
understand the grading system, which
applies to vehicles sold in the U.S.
Consult your SUZUKI dealer or tire
retailer for help in choosing the correct
replacement tires for your vehicle.
Quality grades can be found where
applicable on the tire sidewall between
tread shoulder and maximum section
width. For example:
Treadwear 200 Traction AA Tempera-
ture A
DOT Quality Grades
Treadwear
Traction AA A B C
Temperature A B C
All Passenger Car Tires Must Conform
To Federal Safety Requirements in
Addition To These GradesTreadwear
The treadwear grade is a comparative
rating based on the wear rate of the tire
when tested under controlled condi-
tions on a specified government test
course. For example, a tire graded 150
would wear one and one-half (1 1/2)
times as well on the government course
as a tire graded 100. The relative per-
formance of tires depends upon the
actual conditions of their use, however
and may depart significantly from the
norm due to variations in driving habits,
service practices and differences in
road characteristics and climate.
Traction – AA, A, B, C
The traction grades, from highest to
lowest, are AA, A, B and C. Those
grades represent the tire’s ability to
stop on wet pavement as measured
under controlled conditions on speci-
fied government test surfaces of
asphalt and concrete. A tire marked C
may have poor traction performance.
WARNING
Replacing the wheels and tires
equipped on your vehicle with
certain combinations of aftermar-
ket wheels and tires can signifi-
cantly change the steering and
handling characteristics of your
vehicle. Oversized tires may also
rub against the fender over
bumps, causing vehicle damage
or tire failure. Therefore, use only
those wheel and tire combina-
tions approved by SUZUKI Motor
Corporation as standard or
optional equipment for your vehi-
cle. For information regarding the
specified tires, refer to the Tire
Information Label located on the
driver’s side door pillar or the
“SPECIFICATIONS” section.
CAUTION
Replacing the original tires with
tires of a different size may result
in false speedometer or odometer
readings. Check with your
SUZUKI dealer before purchas-
ing replacement tires that differ in
size from the original tires.
WARNING
The traction grade assigned to
this tire is based on straight-
ahead braking traction tests, and
does not include acceleration,
cornering, hydroplaning or peak
traction characteristics.
Page 235 of 297
7-30
INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE
80J23-03E
Temperature – A, B, C
The temperature grades are A (the
highest), B and C, representing the
tire’s resistance to the generation of
heat and its ability to dissipate heat
when tested under controlled condi-
tions on a specified indoor laboratory
test wheel. Sustained high tempera-
ture can cause the material of the tire
to degenerate and reduce tire life, and
excessive temperature can lead to
sudden tire failure. The grade C corre-
sponds to a level of performance
which all passenger car tires must
meet under the Federal Motor Vehicle
Safety Standard No. 109. Grades B
and A represent higher levels of per-
formance on the laboratory test wheel
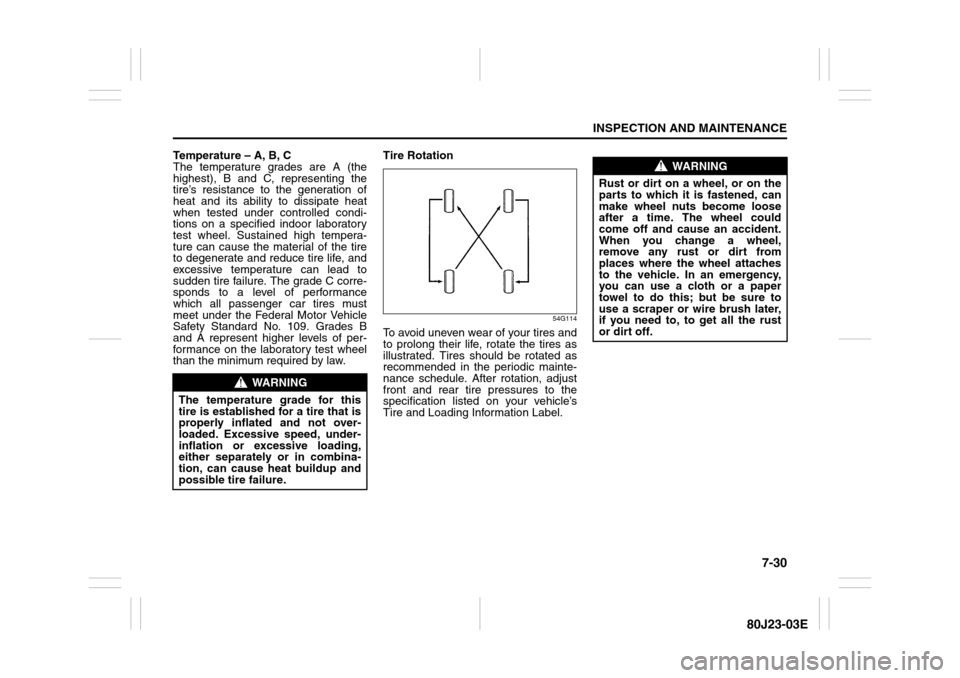
than the minimum required by law.Tire Rotation
54G114
To avoid uneven wear of your tires and
to prolong their life, rotate the tires as
illustrated. Tires should be rotated as
recommended in the periodic mainte-
nance schedule. After rotation, adjust
front and rear tire pressures to the
specification listed on your vehicle’s
Tire and Loading Information Label.
WARNING
The temperature grade for this
tire is established for a tire that is
properly inflated and not over-
loaded. Excessive speed, under-
inflation or excessive loading,
either separately or in combina-
tion, can cause heat buildup and
possible tire failure.
WARNING
Rust or dirt on a wheel, or on the
parts to which it is fastened, can
make wheel nuts become loose
after a time. The wheel could
come off and cause an accident.
When you change a wheel,
remove any rust or dirt from
places where the wheel attaches
to the vehicle. In an emergency,
you can use a cloth or a paper
towel to do this; but be sure to
use a scraper or wire brush later,
if you need to, to get all the rust
or dirt off.
Page 236 of 297
7-31INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE
80J23-03E
Compact Spare Tire (if equipped)
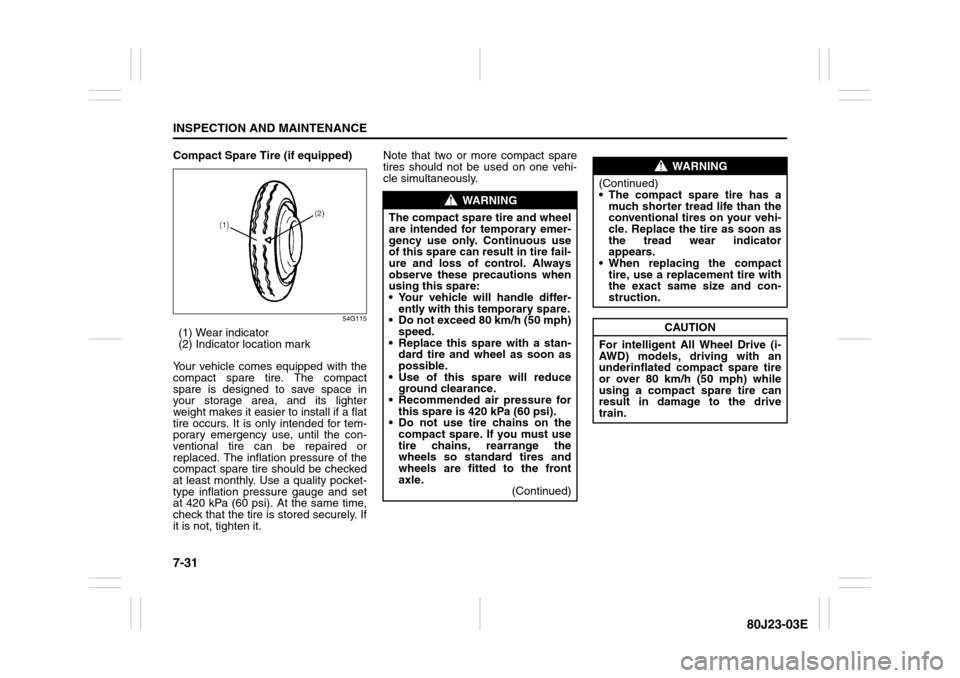
54G115
(1) Wear indicator
(2) Indicator location mark
Your vehicle comes equipped with the
compact spare tire. The compact
spare is designed to save space in
your storage area, and its lighter
weight makes it easier to install if a flat
tire occurs. It is only intended for tem-
porary emergency use, until the con-
ventional tire can be repaired or
replaced. The inflation pressure of the
compact spare tire should be checked
at least monthly. Use a quality pocket-
type inflation pressure gauge and set
at 420 kPa (60 psi). At the same time,
check that the tire is stored securely. If
it is not, tighten it.Note that two or more compact spare
tires should not be used on one vehi-
cle simultaneously.
WARNING
The compact spare tire and wheel
are intended for temporary emer-
gency use only. Continuous use
of this spare can result in tire fail-
ure and loss of control. Always
observe these precautions when
using this spare:
Your vehicle will handle differ-
ently with this temporary spare.
Do not exceed 80 km/h (50 mph)
speed.
Replace this spare with a stan-
dard tire and wheel as soon as
possible.
Use of this spare will reduce
ground clearance.
Recommended air pressure for
this spare is 420 kPa (60 psi).
Do not use tire chains on the
compact spare. If you must use
tire chains, rearrange the
wheels so standard tires and
wheels are fitted to the front
axle.
(Continued)
WARNING
(Continued)
The compact spare tire has a
much shorter tread life than the
conventional tires on your vehi-
cle. Replace the tire as soon as
the tread wear indicator
appears.
When replacing the compact
tire, use a replacement tire with
the exact same size and con-
struction.
CAUTION
For intelligent All Wheel Drive (i-
AWD) models, driving with an
underinflated compact spare tire
or over 80 km/h (50 mph) while
using a compact spare tire can
result in damage to the drive
train.
Page 237 of 297

7-32
INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE
80J23-03E
Snow Tires
Your vehicle is equipped with all-sea-
son tires which are designed for use in
summer and most winter conditions.
For improved traction in severe winter
conditions, SUZUKI recommends
mounting radial snow tires on all four
wheels. Snow tires must be the same
size as the standard tires. Also be sure
to use the tires of the same type and
brand on all four wheels of your vehi-
cle.GLOSSARY OF TIRE TERMINOL-
OGY
Accessory Weight – the combined
weight (in excess of those standard
items which may be replaced) of CVT,
power steering, power brakes, power
windows, power seats, radio, and
heater, to the extent that these items
are available as factory-installed
equipment (whether installed or not).
Cold Tire Inflation Pressure – the pres-
sure in a tire that has been driven less
than 1 mile or has been standing for
three hours or more.
Curb Weight – the weight of a motor
vehicle with standard equipment
including the maximum capacity of
fuel, oil, and coolant, and, if so
equipped, air conditioning and addi-
tional weight optional engine.
Intended Outboard Sidewall – (1) the
sidewall that contains a whitewall,
bears white lettering or bears manu-
facturer, brand, and/or model name
molding that is higher or deeper than
the same molding on the other side-
wall of the tire, or (2) the outward fac-
ing sidewall of an asymmetrical tire
that has a particular side that must
always face outward when mounted
on a vehicle.Maximum Inflation Pressure – the max-
imum cold inflation pressure a tire is
designed to support in normal service.
Maximum Loaded Vehicle Weight –
the sum of curb weight, accessory
weight, vehicle capacity weight (total
load capacity), and production options
weight.
Normal Occupant Weight – 68 kilo-
grams times the number of occupants
specified in the second column of
Table 1 (shown below).
Occupant distribution – distribution of
occupants in a vehicle as specified in
the third column of Table 1 (shown
below).
Production Options Weight – the com-
bined weight of those installed regular
production options weighing over 2.3
kilograms in excess of those standard
items which they replace, not previ-
ously considered in curb weight or
accessory weight, including heavy
duty brakes, ride levelers, roof rack,
heavy duty battery, and special trim.
Recommended Inflation Pressure –
the cold tire inflation pressure recom-
mended by a manufacturer.
Rim – metal support for a tire or tire
and tube assembly upon which the tire
beads are seated.
Page 238 of 297
7-33INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE
80J23-03E
Vehicle Capacity Weight – the rated
cargo and luggage load plus 68 kilo-
grams (150 lbs) times the vehicle’s
designated seating capacity.
Vehicle Maximum Load on the Tire –
the load on an individual tire that is
determined by distributing to each axle
its share of the maximum loaded vehi-
cle weight and dividing by two.
Vehicle Normal Load on the Tire – the
load on an individual tire that is deter-
mined by distributing to each axle its
share of the curb weight, accessory
weight, and normal occupant weight
(distributed in accordance with Table 1
shown below) and dividing by 2.
TABLE 1 – Occupant Loading and
Distribution For Vehicle Normal
Load For Various Designated Seat-
ing CapacitiesVehicle Loading
Your vehicle was designed for specific
load capacities. The load capacities of
your vehicle are indicated by the
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR),
the Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR,
front and rear), and the total load
capacity, the seating capacity, and the
cargo load capacity. The GVWR and
GAWR (front and rear) are listed on
the Safety Certification Label which is
located below the driver’s side door
latch striker. The total load capacity
and seating capacity are listed on the
Tire and Loading Information Label
which is located below the Safety Cer-
tification Label. The cargo load capac-
ity can be determined as described
below.
Cargo Load Capacity – Maximum
weight of cargo and luggage that the
vehicle can safely carry. Cargo load
capacity is the difference between the
total load capacity of the vehicle and
the total combined weight of all vehicle
occupants. Refer to “Steps for Deter-
mining Correct Load Limit” for details
on how to determine cargo load
capacity.GVWR – Maximum permissible overall
weight of the fully loaded vehicle
(including all the occupants, accesso-
ries and cargo plus the trailer tongue
weight if towing a trailer).
GAWR – (Front and Rear) Maximum
permissible weight on an individual
axle.
Seating Capacity – Maximum number
of occupants the vehicle is designed to
carry.
NOTE:
Even though the number of occupants
is within the seating capacity, you still
must make sure that you do not
exceed the total load capacity of the
vehicle.
Total Load Capacity – Maximum per-
missible weight a vehicle can carry
including the weight of all the occu-
pants, accessories, cargo, plus trailer
tongue weight (if towing a trailer).
The weight of any accessories already
installed on your vehicle at the time of
purchase, or that you or the dealer
install after purchase, must be sub-
tracted from the total load capacity to
determine how much capacity remains
available for occupants, cargo, and
trailer tongue weight (if towing a Designated
seating
capacity,
number of
occupantsVehicle nor-
mal load,
number of
occupants
Occupant
distribution
in a nor-
mally loaded
vehicle
2 through 4 2 2 in front5 through 10
32 in front,
1 in second
seat
Page 239 of 297

7-34
INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE
80J23-03E
trailer). Contact your dealer for further
information.
Actual weight of the loaded vehicle
and actual loads at the front and rear
axles can only be determined by
weighing the vehicle using a vehicle
scale. To measure the weight and
load, try making your vehicle to a high-
way weighing station, shipping com-
pany or inspection station for trucks,
etc. Compare these weights to the
GVWR and GAWR (front and rear)
listed on the Safety Certification Label.
If the gross vehicle weight or the load
on either axle exceeds these ratings,
you must remove enough weight to
bring the load down to the rated
capacity.Steps for Determining Correct Load
Limit
1) Locate the statement “The com-
bined weight of occupants and
cargo should never exceed XXX kg
or XXX lbs” on your vehicle’s plac-
ard.
2) Determine the combined weight of
the driver and passengers that will
be riding in your vehicle.
3) Subtract the combined weight of
the driver and passengers from
XXX kg or XXX lbs.
4) The resulting figure equals the
available amount of cargo and lug-
gage load capacity. For example, if
the “XXX” amount equals 1400 lbs
and there will be five 150 lb passen-
gers in your vehicle, the amount of
available cargo and luggage load
capacity is 650 lbs (1400 – 750 (5 x
150) = 650 lbs).
5) Determine the combined weight of
luggage and cargo being loaded on
the vehicle. That weight may not
safely exceed the available cargo
and luggage load capacity calcu-
lated in Step 4.
6) If your vehicle will be towing a
trailer, load from your trailer will be
transferred to your vehicle. Consult
this manual to determine how this
reduces the available cargo and lug-
gage load capacity of your vehicle.
WARNING
Never overload your vehicle. Over-
loading your vehicle can cause
damage to your tires and lead to
poor steering and braking which
can result in an accident. The
gross vehicle weight (sum of the
weights of the loaded vehicle,
driver and passengers) must
never exceed the Gross Vehicle
Weight Rating (GVWR) listed on
the Safety Certification Label. In
addition, never distribute a load so
that the weight on either the front
or rear axle exceeds the Gross
Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) listed
on the Safety Certification Label.
WARNING
Always distribute cargo evenly.
To avoid personal injury or
damage to your vehicle, always
secure cargo to prevent it from
shifting if the vehicle moves
suddenly.
Place heavier objects on the
floor and as far forward in the
cargo area as possible. Never
pile cargo higher than the top of
the seatbacks.
Page 240 of 297

7-35INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE
80J23-03E
Vehicle Loading Example
As an example, suppose that the Tire
and Loading Information label on your
vehicle indicates that your vehicle’s
total load capacity is 950 lbs. If you
were to drive your vehicle with one
passenger, and the total combined
weight of you and your passenger was
350 lbs, then the cargo and luggage
capacity of your vehicle would be 600
lbs (950 – 350 = 600 lbs).
If you later added 2 more passengers,
having a combined weight of 325 lbs,
the cargo and luggage capacity of
your vehicle would be reduced from
600 lbs to 275 lbs (600 – 325 = 275
lbs). As you can see, as the number
and combined weight of vehicle occu-
pants increase, the vehicle’s cargo
and luggage capacity decreases.
Suppose again, that you were to take
a trip in your vehicle with the same
three passengers described above,
and you decided to tow a trailer having
a trailer tongue weight of 75 lbs. The
cargo and luggage capacity would be
reduced again, to 200 lbs (275 – 75 =
200 lbs).Determining Compatibility of Tire
and Vehicle Load Limits
The tires on your vehicle, when they
are inflated to the recommended tire
inflation pressure, have a load-carry-
ing capacity that is greater than the
load that will be on the tires when the
vehicle is at its GVWR or GAWR limit.
Never use replacement tires that have
a load-carrying capacity less than the
original tires on your vehicle. Tire load-
carrying capacity information is
molded into the tire sidewall typically
shown as “Max. Load”. Use of replace-
ment tires with a lower load-carrying
capacity than the original tires, or fail-
ure to keep the tires inflated to recom-
mended tire pressure, may reduce the
GVWR or GAWR limit of your vehicle.
NOTE:
Use of replacement tires with a higher
load-carrying capacity than the origi-
nal tires, or using a tire inflation pres-
sure higher than the recommended
tire inflation pressure, will not increase
the GVWR or GAWR limit of your vehi-
cle.
Battery
60A269
WARNING
Batteries produce flammable hydro-
gen gas. Keep flames and sparks
away from the battery or an explosion
may occur. Never smoke when work-
ing near the battery.
WARNING
When checking or servicing the bat-
tery, disconnect the negative cable.
Be careful not to cause a short circuit
by allowing metal objects to contact
the battery posts and the vehicle at
the same time.EXAMPLE