lock TOYOTA CELICA 1987 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 1987, Model line: CELICA, Model: TOYOTA CELICA 1987Pages: 346, PDF Size: 35.13 MB
Page 6 of 346
IN-4 Identification Information,
INTRODUCTION - General Repair Instructions
IDENTIFICATION INFORMATION
ENGINE SERIAL NUMBER
The engine serial number is stamped on the right side of the
cylinder block.
Seal Lock Adhesive
GENERAL REPAIR INSTRUCTIONS
1. Use fender, seat and floor covers to keep the vehicle clean
and prevent damage.
2.
3. During disassembly, keep parts in order to facilitate
reassembly.
Observe the following:
(a)
(b) Before performing electrical work, disconnect ‘the
negative (-1 cable from the battery terminal.
If it is necessary to disconnect the battery for inspec-
tion or repair, always disconnect the cable from the
negative (-) terminal which is grounded to the vehi-
cle body.
(c) To prevent damage to the battery terminal post,
loosen the terminal nut and raise the cable straight up
without twisting or prying it.
(d) Clean the battery terminal posts and cable terminals
with a shop rag. Do not scrape them with a file or
other abrasive object.
(e)
(f) Install the cable terminal to the battery post with the
nut loose, and tighten the nut after installation. Do
not use a hammer to tap the terminal onto the post.
Be sure the cover for the positive (+I terminal is pro-
perly in place.
4.
5. Check hose and wiring connectors to make sure that they
are secure and correct.
Non-reusable parts
(a)’ Always replace cotter pins gaskets, O-rings, oil seals,
etc. with new ones.
(b) Non-reusable parts are indicated in the component
illustrations by the “+” symbol.
6. Precoated Parts
Precoated parts are the bolts, nuts, etc. which are coated
with a seal lock adhesive at the factory.
(a) If a precoated part is retightened, loosened or caused
to move in any way, it must be recoated with the
specified adhesive.
Page 7 of 346

INTRODUCTION - General Repair Instructions
IN-S
(b) Recoating of Precoated Parts
(1) Clean off the old adhesive from the part’s
threads.
(2) Dry with compressed air.
(3) Apply the specified seal lock adhesive to the
part’s threads.
(c) Precoated parts are indicated in the component
illustrations by the “*” symbol.
7. When necessary, use a sealer or gaskets to prevent leaks.
8. Carefully observe all specifications for bolt torques.
Always use a torque wrench.
9. Use of special service tools (SST) and special service
materials (SSM) may be required, depending on the nature
of the repair. Be sure to use SST and SSM where specified
and follow the proper work procedure. A list of SST and
SSM can be found at the back of this manual.
10. When replacing fuses, be sure the new fuse is the correct
amperage. DO NOT exceed the fuse amp rating or use one
of a lower rating.
11. Care must be taken when jacking up and supporting the
vehicle. Be sure to lift and support the vehicle at the
proper locations.
(a) If the vehicle is to be jacked up only at the front or
rear end, be sure to block the wheels in order to
ensure safety.
(b) After the vehicle is jacked up, be sure to support it on
stands. It is extremely dangerous to do any work on
the vehicle raised on a jack alone, even for a small job
that can be finished quickly.
WRONG
CORRECT 12. Observe the following precautions to avoid damaging the
parts:
(a) Do not open the cover or the case of the ECU unless
absolutely necessary. (If the IC terminals are touched,
the IC may be destroyed by static electricity.)
(b) Be careful not to drop electrical components, such as
sensors or relays. If they are dropped on a hard floor,
they should be replaced and not reused.
(c) When disconnecting vacuum hoses, pull on the end
of the hose, not the middle.
(d) When separating electrical connectors, pull on the
connector itself, not the wires.
Page 23 of 346

. COOLING SYSTEM - Description
co;3
RESERVOIR TANK
The reservoir tank is used to catch coolant
which overflows the cooling systein as a result of
volumetric expansion when the coolant is heated.
The coolant in the reservoir tank returns to the
radiator when the coolant temperature drops, thus
keeping the radiator full at all times and avoiding
needless coolant loss. Check the reservoir tank
level to learn if the coolant needs to be rep-
lenished.
WATER PUMP
The water pump is used for forced circulation of
coolant through the cooling system. It is mounted
on the front of the cylinder block and driven by a
V-ribbed belt,
THERMOSTAT I The cooling system is composed of the water
jacket (inside the cylinder block and cylinder head),
radiator, water pump, thermostat, cooling fan,
hoses and other components.
Coolant which is heated in the water
jacket is
pumped to the radiator, through which a cooling
fan blows air to cool the coolant as it passes
through. Coolant which has been cooled is then
sent back to the engine by the water pump, where
it cools the engine.
The water jacket is a network of channels in the
shell of the cylinder block and cylinder head
through which coolant passes. It is designed to
provide adequate cooling of the cylinders are com-
bustion chambers which become the hottest dur-
ing engine operation.
F(/ “ IATOR
The radiator performs the function of cooling
the coolant which has passed through the water
jacket and become hot, and is mounted in the front
of the vehicle. The radiator consists of an upper
tank and ‘lower tank, and a core which connects
the two tanks. The upper tank contains the inlet for
coolant from the water jacket and the filter inlet. It
also has a hose attached through which excess
coolant or steam can flow. The lower tank contains
the outlet for coolant and the drain cock. The core
contains many tubes through which coolant flows
from the upper tank to the lower tank as well as
cooling fins which radiate heat away from the coo-
lant in the tubes. The air sucked through the radia-
tor by cooling fan, as well as the wind generated
by the vehicle’s travel, passes through the radia-
tor, cooling it. Models with automatic transmission
incrl*-le an automatic transmission fluid cooler built
in:.
.le lower tank of the radiator.
RADIATOR CAP
The radiator cap is a pressure type can which
seals the radiator, resulting in pressurization of the
radiator as the coolant expands. The pressuriza-
tion prevents the coolant from boiling even when
the coolant temperature exceeds 100°C. A relief
valve (pressurization valve) and a vacuum valve
(negative pressure valve) are built into the radiator
zap. The relief valve opens and lets steam escape
:hrough the overflow pipe when the pressure
3enerated inside the cooling system exceeds the
imit (coolant temperature:
110 - 1 20°C, (230
- 248”F), pressure; 0.3 - 1 .O kg/cmz, (4.3 - 14.2
)si, 29.4 - 98.1 kPa). The vacuum valve opens to
3ljeviate the vacuum which develops in the coolant
system after the engine is stopped and the coolant
emperature drops. The valve’s opening allows the
)ressure in the cooling system to return to the
Qclant in the reservoir tank. The thermostat has a wax type and is mounted
in the. water outlet housing. The thermostat
includes a type of automatic valve operated by
fluctuations in the coolant temperature. This valve
closes when the coolant temperature drops, pre-
venting the circulation of coolant through the
engine and thus permitting the engine to warm up
rapidly. The valve opens when the coolant tem-
perature has risen, allowing the circulation of coo-
lant. Wax inside the thermostat expands when
heated and contracts when cooled. Heating the
wax thus generates pressure which overpowers
the force of the spring which keeps the valve
closed, thus opening the valve. When the wax
cools, its contraction causes the force of the
spring to take effect once more, closing the valve.
The thermostat in this engine operates at a tem-
perature of 88”C(19O”F).
I
I
Page 24 of 346

co-4 CQOLING SYSTEM - Troubleshootmg
TROUBLESHOOTING
, Problem
Engine overheats Possible cause
Alternator drive belt loose or missing
Dirt, leaves or insects in radiator or
condenser
Hoses, water pump, water outlet
housing, radiator, heater, core plugs
or head gasket leakage
Thermostat faulty
Ignition timing
retarded
Fluid coupling faulty
Radiator hose plugged or rotted
Water pump faulty
Radiator plugged or cap faulty
Cylinder head or block cracked or
phwd Remedy
Adjust or replace belt
Clean radiator or condenser
Repair as necessary
Check thermostat
Set timing
Replace fluid coupling
Replace hose
Replace water pump
Check radiator
Repair as necessary Page
CH-4
CO-8
EM-l 7
CO-6
CO-6
co-9
Page 25 of 346
COOLING SYSTEM i Check and Replacement of Engine Coolant
co-5
._
CHECK AND REPLACEMENT OF
ENGINE COOLANT
1. CHECK ENGINE COOLANT LEVEL AT RESERVE TANK
The coolant level should be between the “LOW” and
“FULL” lines.
If low, check for leaks and add coolant up to the “FULL”
line. .,>‘
2. CHECK ENGINE COOLANT QUALITY
There should not be any excessive deposits of rust or
scales around the radiator cap or radiator filler hole, and
the coolant should also be free from oil.
lf excessively dirty, replace the coolant.
3. REPLACE ENGINE COOLANT
(a) Remove the radiator cap.
(b) Drain the coolant from radiator and engine drain
cocks.(Engine drain is at right rear of cylinder block.)
(cl Close the drain cocks.
(d) Fill system with coolant.
Use a good brand of. ethylene-glycol base coolant, mixed
according to manufactuer’s directions.
Capacity:
MA
w/ Heater or air conditioner
M/T 8.1 liters (8.5 US qts. 7.1 Imp. qts)
A/T 8.0 liters (8.5 US qts, 7.0 Imp. qts)
w/o Heater or air conditioner
M/T 7.5 liters (7.9 US qts, 6.6
Imp. qts)
A/T 7.4 liters (7.8 US qts, 6.5 Imp. qts)
MS
w/ Heater or air conditioner
GCC Countries*
8.5 liters (9.0 US qts, 7.5 Imp. qts)
Others
7.8 liters (8.2 US qts, 6.7 Imp. qts)
w/o Heater or air conditioner
GCC Countries*
7.8 liters (8.2 US qts, 6.7 Imp. qts)
Others
7.1 liters (7.5 US qts, 6.2 Imp. qts)
(e) Install the radiator cap.
(f) Start the engine and check for leaks.
(g) Recheck the coolant level and refill as necessary.
l GCC Countries: Saudi Arabia, Sultanate of Oman,
Bahrain, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Kuwait.
Page 29 of 346

COOLING SYSTEM - Radiator
-,... ~‘e:,.,,’ _,
CLEANING OF RADIATOR _ ---w..w- -...,.
Using water or steam cleaner, remove mud and dirt from
the radiator core.
CAUTION: If using’ high-pressure, type cleaner, be
careful not to deform the fins of the radiator core. Keep
a distance of more than 40 - 50 cm (15.75 - 19.69 in.)
between the radiator core and cleaner nozzle when
the cleaner nozzle pressure is 30 - 35 kg/cm2 (427 -
1
498 psi, 2,942 - 3,432 kPa1.
I lNSPECTlON.OF RADIATOR
t 1. CHECK RADIATOR CAP
Using a radiator cap tester, pump tester until relief valve
opens. Check that valve opens between 0.75 kg/cm2
(10.7 psi, 74 kPa) and 1.05 kg/cm2 (14.9 psi, 103 kPa).
Check that pressure gauge does not drop rapidly when
pressure on cap is below 0.6 kg/cm2 (8.5 psi, 59 kPa).
!J If either check is not within limits, replace cap.
1 2. CHECK COOLING SYSTEM FOR LEAKS
(a) Fill the radiator with coolant and attach a radiator cap
tester.
(b) Warm up the engine.
(c) Pump it to 1.2 kg/cm2 117.1 psi, 118 kPa), check
that pressure does not drop.
If the pressure drops, check for leaks from the hoses,
radiator or water pump. If no external
leaks are found,
check the heater core, cylinder block
and head.
Page 33 of 346
COGLING SYSTEM - Radiator’ .
__ co- 1.3::
.-
1 SST
r
i
Tank Plate
Punch I
I
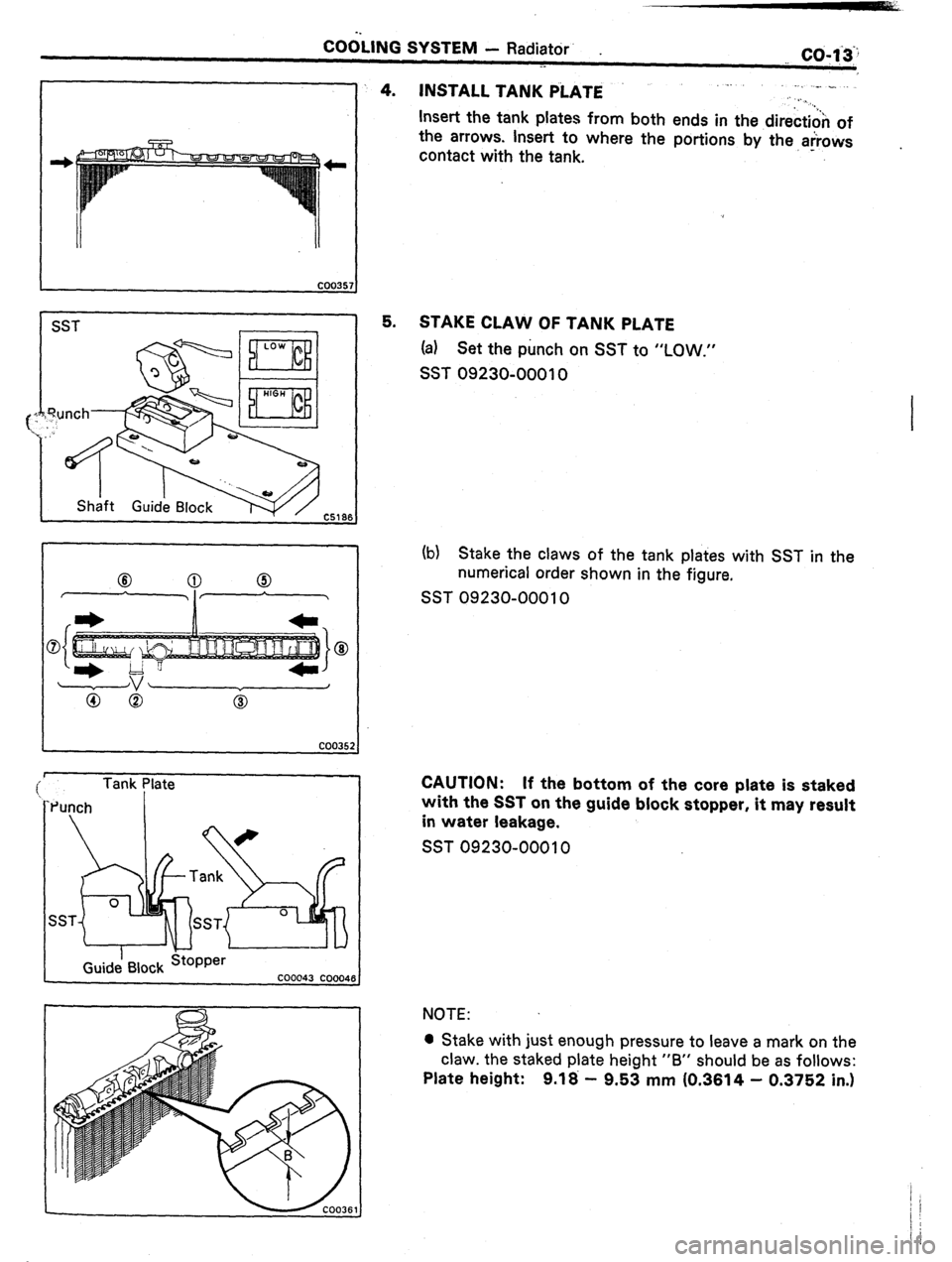
4. INSTALL TANK PiATE .
., _. .,
. ._
Insert the tank plates from both ends in the direction of
the arrows. Insert to where the portions by the arrows
contact with the tank. - .
5. STAKE CLAW OF TANK PLATE
(a) Set the punch on SST to “LOW.”
SST 09230-00010
(b) Stake the claws of the tank plates with SST in the
numerical order shown in the figure.
SST 09230-00010
CAUTION: If the bottom of the core plate is staked
with the SST on the guide block stopper, it may result
in water leakage.
SST 09230-00010
NOTE:
l Stake with just enough pressure to leave a mark on the
claw. the staked plate height “B” should be as follows:
Plate height: 9.18 - 9.53 mm (0.3614 - 0.3752 in.)
Page 43 of 346
EFI SYSTEM - inspection Precautions
FI-9
FM066
FlOO95 FlOO91
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM
1.
2.
3. Before removing EFI wiring connectors, terminals, etc.,
first disconnect-the power-by either turning the ignition
switch OFF or disconnecting the battery terminals.
When installing a battery, be especially careful not to
incorrectly connect the positive and negative cables.
Do not permit parts to receive a severe impact during
removal or installation. Handle all EEI parts carefully.
especially the ECU.
4. Do not be careless during troubleshooting as there are
numerous transistor circuits and even slight terminal con-
tact can cause further troubles.
5.
6. Do not open the ECU cover.
When inspecting during rainy weather, take care to pre-
vent entry of water. Also, when washing the engine com-
.partment, prevent water from getting on the EFI parts and
wiring connectors.
7. Parts should be replaced as an assembly.
8. Care is required when pulling out the inserting wiring con-
nectors.
(a) Release the lock and pull out the connector, pulling
on the connectors. .
(b) Fully insert the connector and insure that it is locked.
9. When inspecting a connector with a circuit tester.
(a) Carefully take out the water-proofing rubber if it is a
water-proof type connector.
Page 46 of 346

1-12 EFI SYSTEM - Troubleshooting’
FlO48
TROUBLESH~~TI~~G
. .
TROUBLESHOOTING HlhJTS
1. Engine troubles are usually not caused by the EFI system.
When troubleshooting, always first check the condition of
the other systems.
(a) Electronic source
0 Battery
0 Fusible links
0 Fuses
(b) Body ground
(cl Fuel supply
0 Fuel leakage
0 Fuel filter
0 Fuel pump
(d) Ignition system
0 Spark plug
0 High-tension cord
l Distributor (7M-GE) or cam position sensor (7M-
GTE)
0 Igniter and ignition coil
(e) Air induction system
0 Vacuum leaks
(f) Emission control system
0 PCV system
0 EGR system (w/ EGR)
(g) Others
l Ignition timing (ESA system)
0 Idle speed (ISC system)
-r
2. The most frequent cause of problems is simply a bad don-
tact in wiring connectors. Always make sure that connec-
tions are secure.
When inspecting the connector, pay particular attention to
the following points:
(a) Check to see that the terminals are not bent.
(b) Check to see that the connector is pushed in com-
pletely and locked.
(c) Check to see that there is no signal change when the
connector is slightly tapped or wiggled.
3. Sufficiently troubleshoot for other causes before replac-
ing the ECU. The ECU is of high quality and it is expensive.
Page 63 of 346
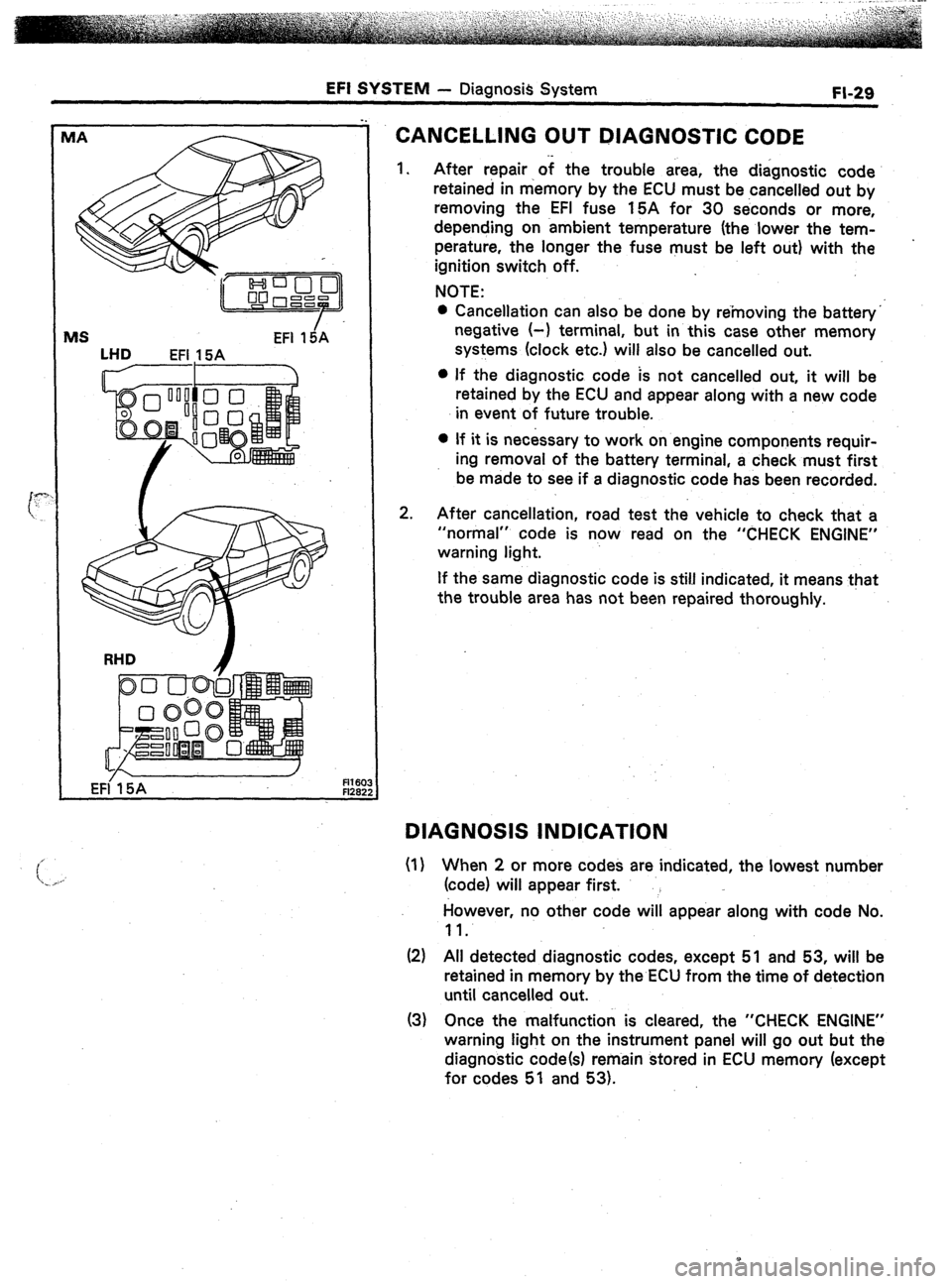
EFI SYSTEM - Diagnosis System FI-29
MS EFI 15iA
LHD
EFI 15A
EFI 15A
R16C
FI26:
CANCELLING OUT DIAGNOSTIC CODE
1.
2. After repair of the trouble area, the diagnostic code
retained in memory by the ECU must be cancelled out by
removing the EFI fuse 15A for 30 seconds or more,
depending on ambient temperature (the lower the tem-
perature, the longer the fuse must be left out) with the
ignition switch off.
NOTE:
l Cancellation can also be done by removing the battery”
negative (-1 terminal, but in this case other memory
systems (clock etc.) will also be cancelled out.
l If the diagnostic code is not cancelled out, it will be
retained by the ECU and appear along with a new code
in event of future trouble.
l If it is necessary to work on engine components requir-
ing removal of the battery terminal, a check must first
be made to see if a diagnostic code has been recorded.
After cancellation, road test the vehicle to check that a
“normal” code is now read on the “CHECK ENGINE”
warning light.
If the same diagnostic code is still indicated, it means that
the trouble area has not been repaired thoroughly.
DIAGNOSIS INDICATION
(I) When 2 or more codes are indicated, the lowest number
(code) will appear first.
However, no other code will appear along with code No.
11.
(2) All detected diagnostic codes, except 51 and 53, will be
retained in memory by the ECU from the time of detection
until cancelled out.
(3) Once the malfunction is cleared, the “CHECK ENGINE”
warning light on the instrument panel will go out but the
diagnostic code(s) remain stored in ECU memory (except
for codes 51 and 53).