TOYOTA SEQUOIA 2008 2.G Owners Manual
Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2008, Model line: SEQUOIA, Model: TOYOTA SEQUOIA 2008 2.GPages: 596, PDF Size: 12.93 MB
Page 191 of 596

191
2-4. Using other
driving systems
2
When driving
■Automatically canceling vehicle-to-vehicle distance control
Vehicle-to-vehicle distance control driving is automatically canceled in the
following situations.
●Vehicle speed falls below 25 mph (40 km/h)
● VSC is activated
● The sensor cannot operate correctly because it is covered in some way.
*
●The windshield wipers are operating at high or low speed.*
●The operation cannot be switched for 5 seconds or more after operating
the front wheel drive control switch or the center differential lock switch.
*: Vehicle-to-vehicle distance control driving must be reset by pressing the
ON-OFF button again.
If vehicle-to-vehicle distance control driving is automatically canceled for any
other reason, there may be a malfunction in the system. Contact your Toyota
dealer.
■ Automatically cancelling constant speed control
The set speed is automatically canceled in the following situations.
●Actual vehicle speed is more than 10 mph (16 km/h) below the preset
vehicle speed
At this time, the memorized set speed is not retained.
● Vehicle speed falls below 25 mph (40 km/h)
● VSC is activated
● The operation cannot be switched for 5 seconds or more after operating
the front wheel drive control switch or the center differential lock switch.
■ Vehicle-to-vehicle distance settings
Select a distance from the table below. Note that the distances shown corre-
spond to a vehicle speed of 55 mph (90 km/h). Vehicle-to-vehicle distance
increases/decreases in accordance with vehicle speed.
Distance optionsVehicle-to-vehicle distance
Long Approximately 245 ft. (75 m)
Medium Approximately 165 ft. (50 m) Short Approximately 100 ft. (30 m)
Page 192 of 596

192 2-4. Using other driving systems
■Laser radar sensor
■ Certification
Always keep the sensor clean to ensure
that the vehicle-to-vehicle distance con-
trol operates properly. (Some obstruc-
tions, such as snow, ice or plastic objects,
cannot be detected by the obstruction
sensor.)
Dynamic laser cruise control is canceled
if an obstruction is detected.
This product is a class l laser product complied with 21C.F.R part 1040.10
and 1040.11.
Page 193 of 596

193
2-4. Using other
driving systems
2
When driving
CAUTION
■To avoid bodily injury
●Do not look into the aperture window.
● Use of controls or adjustment or performance of procedures other than
those specified herein may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
■ Before using dynamic laser cruise control
Do not overly rely on vehicle-to-vehicle distance control.
Be aware of the set vehicle speed. If automatic deceleration/acceleration is
not appropriate, adjust the vehicle speed, as well as the distance between
your vehicle and vehicles ahead by applying the brakes, etc.
■ To avoid inadvertent cruise control activation
Turn off the system when not in use.
■ Situations unsuitable for dynamic laser cruise control
Do not use dynamic laser cruise control in any of the following situations.
Doing so may result in inappropriate control of speed and could cause seri-
ous or fatal accident.
●In heavy traffic
● On roads with sharp bends
● On winding roads
● On slippery roads, such as those covered with rain, ice or snow
● Where there are sudden changes between sharp up and down gradients
● At entrances to expressways
● When weather conditions are bad enough that they may prevent the sen-
sors from functioning correctly (fog, snow, sandstorm, etc.)
● Where buzzer can be heard often
■ When the laser radar sensor may not be correctly detecting the vehicle
ahead
Apply the brakes as necessary when any of the following types of vehicles
are in front of you.
As the sensor may not be able to correctly detect these types of vehicles,
the proximity alarm ( P. 514) will not be activated, and an accident may
result.
Page 194 of 596

194 2-4. Using other driving systems
CAUTION
■When the laser radar sensor may not be correctly detecting the vehicle
ahead
● Vehicles that cut in suddenly
● Vehicles traveling at low speeds
● Vehicles that are not moving
● Vehicles with small rear ends (trailers with no load on board etc.)
● Motorcycles traveling in the same lane
■ Conditions under which the vehicle -to-vehicle distance control may
not function correctly
Apply the brakes as necessary in the following conditions as the laser radar
sensor may not be able to correctly detect vehicles ahead, and an accident
may result.
● When water or snow thrown up by the surrounding vehicles hinders the
functioning of the sensor
● When your vehicle is pointing upwards (caused by a heavy load in the lug-
gage compartment, etc.)
● When the road curves or when the lanes are narrow
● When steering wheel operation or your position in the lane is unstable
● When towing a trailer
■ To ensure the laser rada r sensor functions correctly
Do not do the following to the sensor as doing so may cause the sensor not
to function correctly and could result in an accident.
● Stick or attach anything to them
● Leave them dirty
● Disassemble, subject them to strong shocks
● Modify or paint them
● Replace them with non-genuine parts
Page 195 of 596

195
2-4. Using other
driving systems
2
When driving
NOTICE
■Handling the laser radar sensor
Observe the following to ensure the cruise control system can function effec-
tively.
●Keep the sensor clean at all times.
Clean the sensor with a soft cloth so you do not mark or damage them.
● Do not subject the sensor or surrounding area to a strong impact.
If the sensor moves even slightly off position, the system may malfunction.
If the sensor or surrounding area is subject to a strong impact, always
have the area inspected and adjusted by a Toyota dealer.
● Do not disassemble the sensor.
● Do not attach accessories or stickers to the sensor, surrounding area.
Page 196 of 596

196
2-4. Using other driving systems
Intuitive parking assist (if equipped)
The intuitive parking assist is designed to inform you of the approxi-
mate distance between your vehicle and an obstruction by indicator
and buzzer when parking the veh icle. This system uses sensors to
detect obstructions.
This system works when the engine switch is in the ON position and
the shift lever is not in P.
Back and rear corner sensors work only when the shift lever is in
R.
Front corner sensors work when:
● The shift lever is in R
● The shift lever is not in P or R and vehicle speed is approximate
6 mph (10 km/h) or less.
Back sensors
Rear corner sensors
Front corner sensors
Page 197 of 596
197
2-4. Using other
driving systems
2
When driving
The distance and buzzer
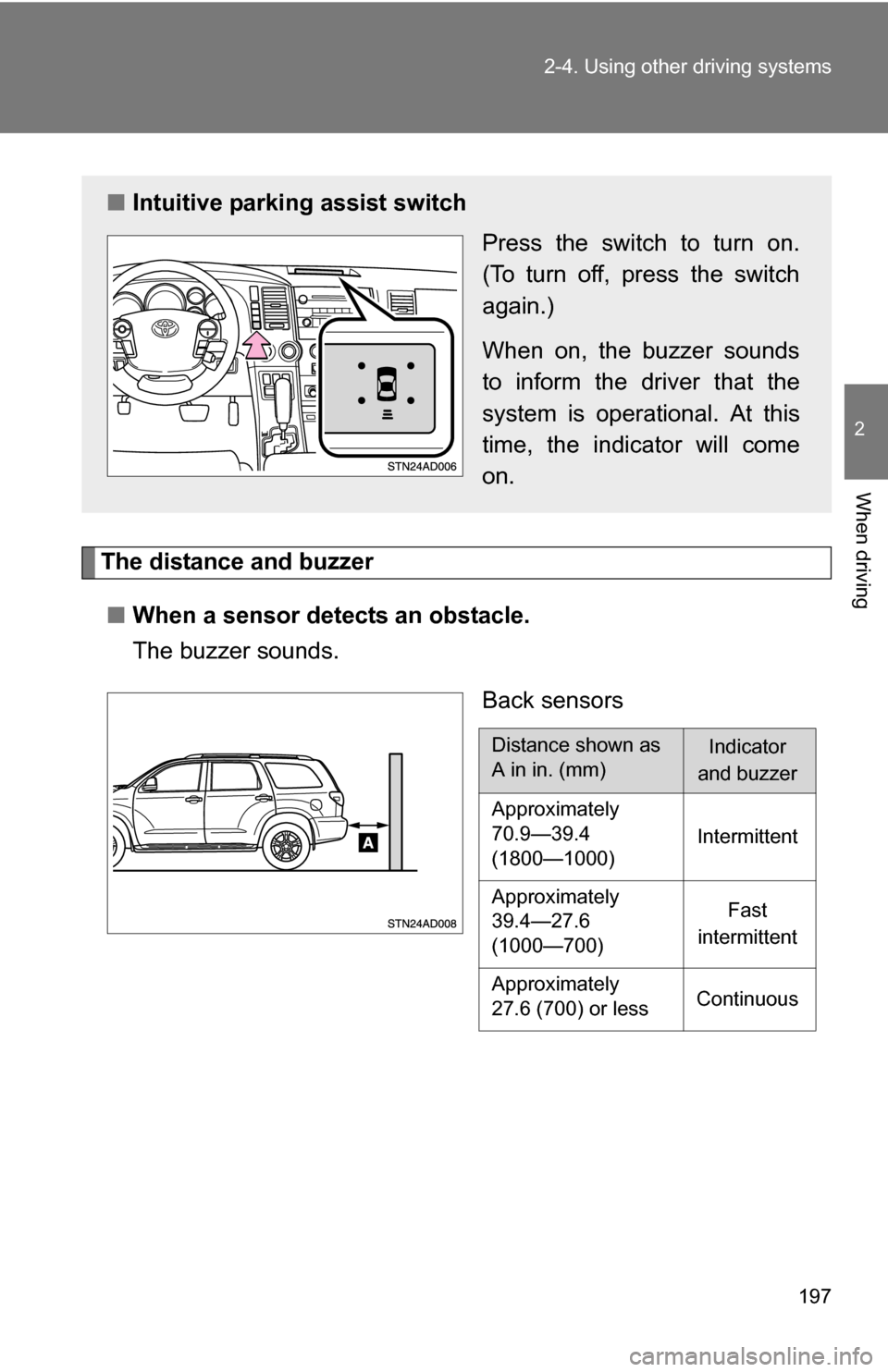
■ When a sensor detects an obstacle.
The buzzer sounds.
Back sensors
■Intuitive parking assist switch
Press the switch to turn on.
(To turn off, press the switch
again.)
When on, the buzzer sounds
to inform the driver that the
system is operational. At this
time, the indicator will come
on.
Distance shown as
A in in. (mm)Indicator
and buzzer
Approximately
70.9—39.4
(1800—1000) Intermittent
Approximately
39.4—27.6
(1000—700) Fast
intermittent
Approximately
27.6 (700) or less Continuous
Page 198 of 596
198 2-4. Using other driving systems
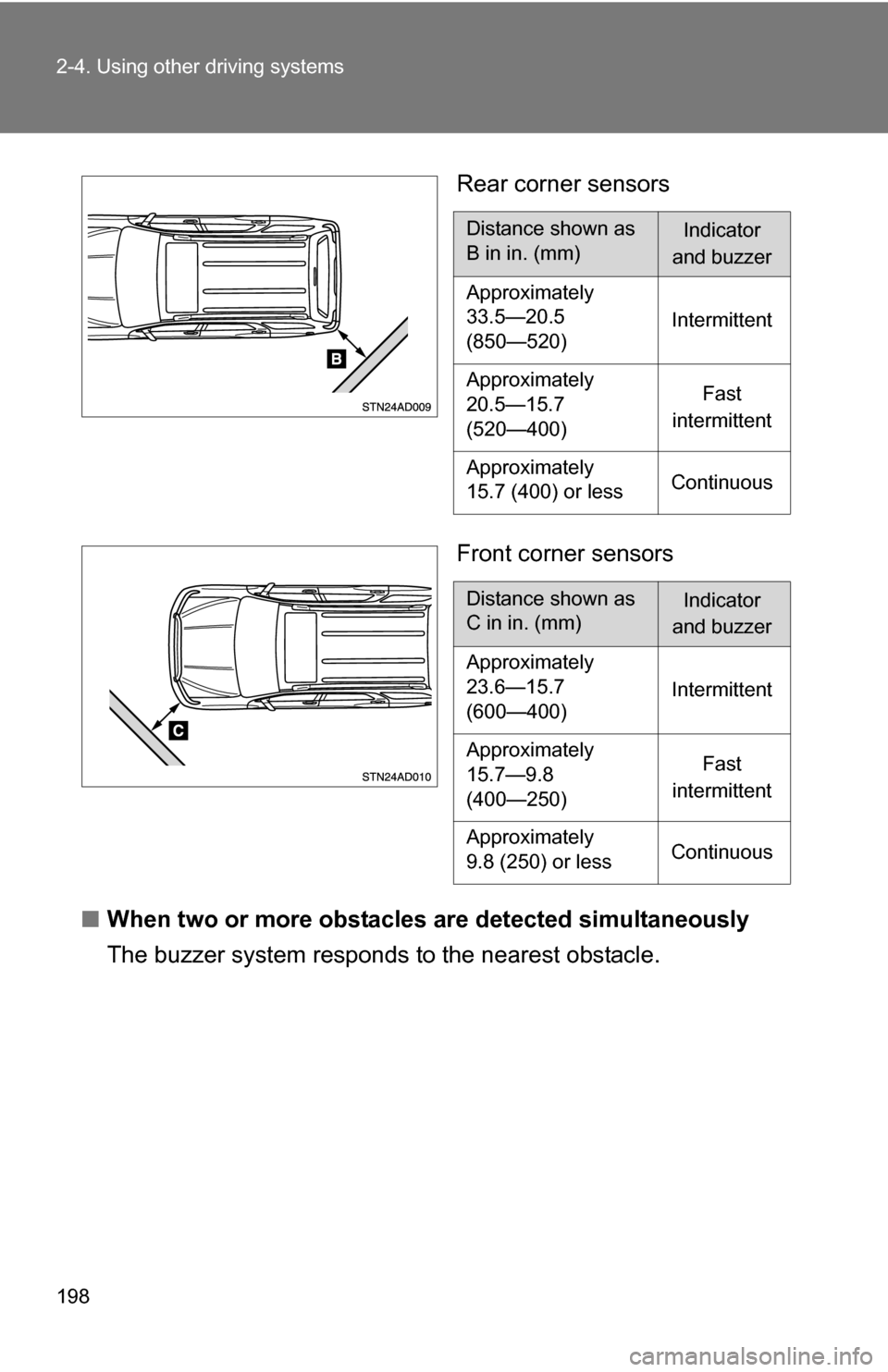
Rear corner sensors
Front corner sensors
■ When two or more obstacles are detected simultaneously
The buzzer system respond s to the nearest obstacle.
Distance shown as
B in in. (mm)Indicator
and buzzer
Approximately
33.5—20.5
(850—520) Intermittent
Approximately
20.5—15.7
(520—400) Fast
intermittent
Approximately
15.7 (400) or less Continuous
Distance shown as
C in in. (mm)Indicator
and buzzer
Approximately
23.6—15.7
(600—400) Intermittent
Approximately
15.7—9.8
(400—250) Fast
intermittent
Approximately
9.8 (250) or less Continuous
Page 199 of 596

199
2-4. Using other
driving systems
2
When driving
Sensors that operate and detection range
The following diagrams show the se nsor detection range. Note that
sensors may not be able to detect obstacles that are extremely close
to the vehicle.
■ Detection range of the sensors
Back sensors
Rear corner sensors
Front corner sensors
Perceptible area
A. Approx. 70.9 in. (1800 mm)
B. Approx. 33.5 in. (850 mm)
C. Approx. 23.6 in. (600 mm)
The diagram shows the detection range of the sensors. Note that the sen-
sors may not be able to detect obstacles that are extremely close to the vehi-
cle.
The range of the sensors may change depending on the shape of the object
etc.
Page 200 of 596

200 2-4. Using other driving systems
■Sensor detection information
●Certain vehicle conditions and the surrounding environment may affect
the ability of a sensor to correctly detect an obstacle. Particular instances
where this may occur are listed below.
• There is dirt, snow or ice on a sensor.
• A sensor is frozen.
• A sensor is covered in any way.
• The vehicle is leaning considerably to one side.
• On an extremely bumpy road, on an incline, on gravel, or on grass.
• The vicinity of the vehicle is noisy due to vehicle horns, motorcycle
engines, air brakes of large vehicles, or other loud noises producing
ultrasonic waves.
• There is another vehicle equipped with parking assist sensors in the vicinity.
• A sensor is coated with a sheet of spray or heavy rain.
• The vehicle is equipped with a fender pole or radio antenna.
• A bumper or sensor receives a strong impact.
• The vehicle is approaching a tall or right-angled curb.
• In harsh sunlight or intense cold weather.
• The area directly under the bumpers is not detected. Objects lower than the sensors or thin stakes etc. may be detected ini-
tially, but as they draw closer, they may cease to be detected.
• A towing hitch is mounted to the vehicle.
• A non-genuine Toyota suspension (lowered suspension etc.) is installed.
• When attaching a two-way radio antenna.
• When a towing eyelet is mounted on your vehicle.
• When the bumper is damaged.
In addition to the examples above, there are instances in which, because of
their shapes, signs and other objects may be judged by a sensor to be closer
than they are.
● The shape of the obstacle may prevent a sensor from detecting it. Pay
particular attention to the following obstacles:
• Wires, fences, ropes, etc.
• Cotton, snow and other materials that absorb radio waves
• Sharply-angled objects