change time TOYOTA SIENNA 2007 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SIENNA, Model: TOYOTA SIENNA 2007Pages: 3000, PDF Size: 52.26 MB
Page 259 of 3000
AUDIO / VISUAL – AUDIO AND VISUAL SYSTEMAV – 7
AV
(f) File names
(1) Only files with an extension of ".mp3" or ".wma"
can be recognized and played as MP3 or WMA
files.
(2) Save MP3 or WMA files with an extension of
".mp3" or ".wma".
NOTICE:
If saving non-MP3 or non-WMA files with an
extension of ".mp3" or ".wma", those files
are wrongly recognized as MP3 or WMA files
and played. A loud noise may occur and
damage to the speaker may result.
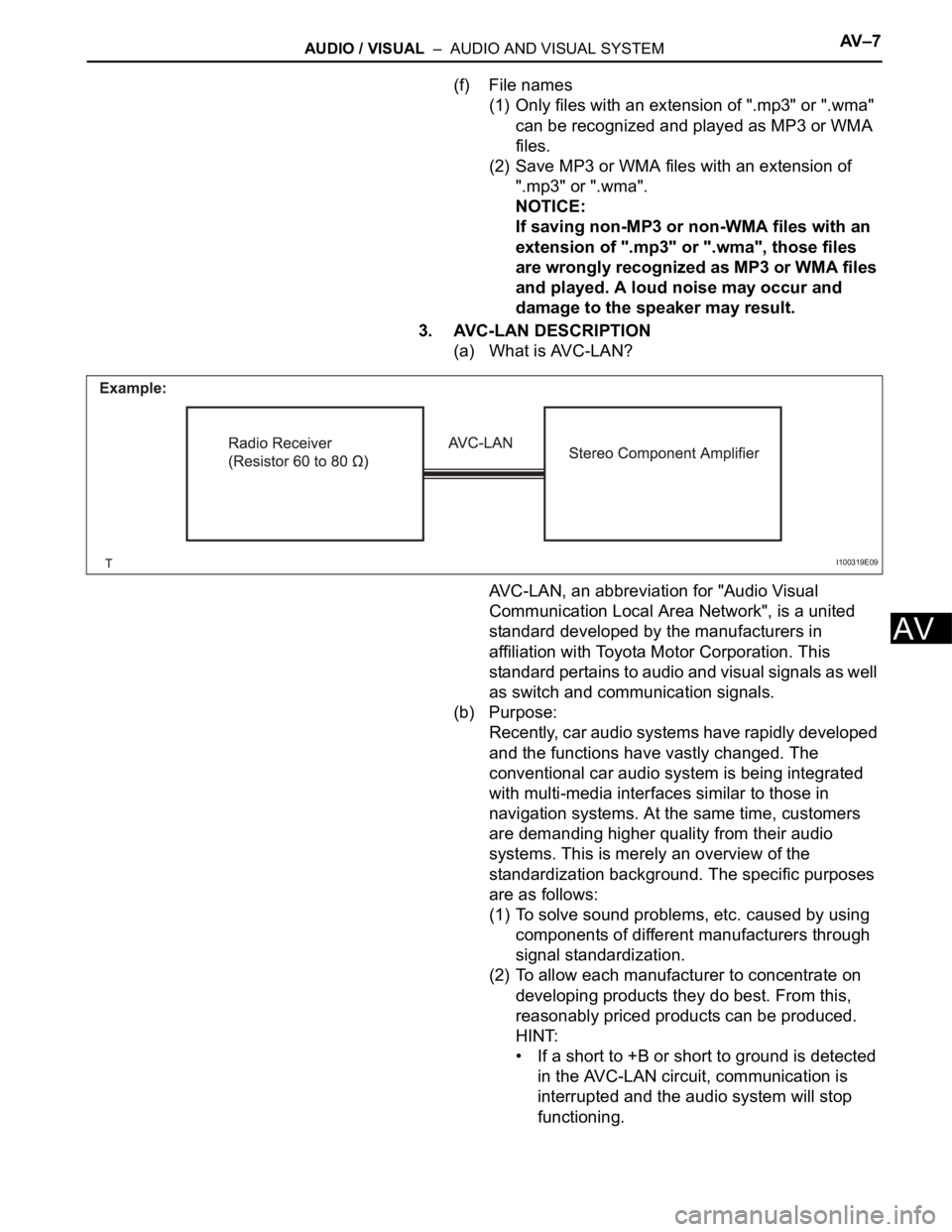
3. AVC-LAN DESCRIPTION
(a) What is AVC-LAN?
AVC-LAN, an abbreviation for "Audio Visual
Communication Local Area Network", is a united
standard developed by the manufacturers in
affiliation with Toyota Motor Corporation. This
standard pertains to audio and visual signals as well
as switch and communication signals.
(b) Purpose:
Recently, car audio systems have rapidly developed
and the functions have vastly changed. The
conventional car audio system is being integrated
with multi-media interfaces similar to those in
navigation systems. At the same time, customers
are demanding higher quality from their audio
systems. This is merely an overview of the
standardization background. The specific purposes
are as follows:
(1) To solve sound problems, etc. caused by using
components of different manufacturers through
signal standardization.
(2) To allow each manufacturer to concentrate on
developing products they do best. From this,
reasonably priced products can be produced.
HINT:
• If a short to +B or short to ground is detected
in the AVC-LAN circuit, communication is
interrupted and the audio system will stop
functioning.
I100319E09
Page 275 of 3000

NS–14NAVIGATION – NAVIGATION SYSTEM
NS
(b) Purpose:
Recently, car audio systems have rapidly developed
and the functions have vastly changed. The
conventional car audio system is being integrated
with multi-media interfaces similar to those in
navigation systems. At the same time, customers
are demanding higher quality from their audio
systems. This is merely an overview of the
standardization background. The specific purposes
are as follows:
(1) To solve sound problems, etc. caused by using
components of different manufacturers through
signal standardization.
(2) To allow each manufacturer to concentrate on
developing products they do best. From this,
reasonably priced products can be produced.
HINT:
• If a short to +B or short to ground is detected
in the AVC-LAN circuit, communication is
interrupted and the audio system will stop
functioning.
• If an audio system is equipped with a
navigation system, the multi-display unit acts
as the master unit.
If the navigation system is not equipped, the
audio head unit acts as the master unit
instead. If the radio and navigation assembly
is equipped, it is the master unit.
• The radio and navigation assembly contains
a resistor that is necessary to enable
communication on the different AVC-LAN
circuits.
• The car audio system with an AVC-LAN
circuit has a diagnostic function.
• Each component has a specified number (3-
digit) called a physical address. Each function
has a number (2-digit) called a logical
address.
7. Communication system outline
(a) Components of the navigation system communicate
with each other via the AVC-LAN.
(b) The radio and navigation assembly has enough
resistance (60 to 80
) necessary for
communication.
(c) If a short circuit or open circuit occurs in the AVC-
LAN circuit, communication is interrupted and the
navigation system will stop functioning.
8. Diagnostic function outline
(a) The audio system has a diagnostic function (the
result is indicated on the master unit).
(b) A 3-digit hexadecimal component code (physical
address) is allocated to each component on the
AVC-LAN. Using this code, the component in the
diagnostic function can be displayed.
Page 354 of 3000

ES–282GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
• Vehicle was driven in the city area (or on free-
way) for 10 minutes or more.
(b) Monitor Conditions
(1) Turn the ignition switch off and wait for 6 hours.
HINT:
Do not start the engine until checking Readiness
Monitor status. If the engine is started, the step
described above must be repeated.
(c) Monitor Status
(1) Connect an intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(3) Turn the tester or scan tool ON.
(4) Check the Readiness Monitor status displayed
on the tester or scan tool.
If the status does not switch to COMPL
(complete), restart the engine, make sure that
the preconditions have been met, and then
perform the Monitor Conditions again.
4. A/F SENSOR AND HO2S MONITORS
(a) Preconditions
The monitor will not run unless:
• 2 minutes or more have elapsed since the engine
was started.
• The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is 75
C
(167
F) or more.
• Cumulative driving time at a vehicle speed of 30
mph (48 km/h) or more exceeds 6 minutes.
• Air-fuel ratio feedback control is performed.
• Fuel-cut control is performed for 8 seconds or
more (for the Rear HO2 Sensor Monitor).
(b) Drive Pattern for front A/F sensor and HO2 sensor.
(1) Connect an intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(3) Turn the tester ON.
(4) Clear the DTCs.
(5) Start the engine, and warm it up until the ECT
reaches 75
C (167F) or higher.
(6) Drive the vehicle at 38 mph (60 km/h) or more
for at least 10 minutes.
(7) Change the transmission to the 2nd gear.
(8) Accelerate the vehicle to 40 mph (64 km/h) or
more by depressing the accelerator pedal for at
least 10 seconds (Procedure "A").
(9) Soon after performing procedure "A" above,
release the accelerator pedal for at least 4
seconds without depressing the brake pedal, in
order to execute fuel-cut control (Procedure "B").
(10) Allow the vehicle to decelerate until the vehicle
speed declines to less than 6 mph (10 km/h)
(Procedure "C").
(11) Repeat procedures from "A" through "C" above
at least 3 times in one driving cycle.
Page 395 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–89
ES
3) After above conditions 1) and 2) are met, the OCV is forcibly activated 63 times or more.
DTCs P0011 and P0021 (Advanced Cam Timing) are detected with 1 trip detection logic.
DTCs P0012 and P0022 (Retarded Cam Timing) are detected with 2 trip detection logic.
These DTCs indicate that the VVT controller cannot operate properly due to OCV malfunctions or the
presence of foreign objects in the OCV.
The monitor will not run unless the following conditions are met:
- The engine is warm (the engine coolant temperature is 75
C [167F] or more).
- The vehicle has been driven at more than 40 mph (64 km/h) for 3 minutes.
- The engine has idled for 3 minutes.
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
P0011, P0021:
P0012, P0022:
If the difference between the target and actual camshaft timings is greater than the specified value, the
ECM operates the VVT actuator.
Then, the ECM monitors the camshaft timing change for 5 seconds.
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0010 (See page ES-77).
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
Related DTCsP0011: Advanced intake camshaft timing (bank 1)
P0012: Retarded intake camshaft timing (bank 1)
P0021: Advanced intake camshaft timing (bank 2)
P0022: Retarded intake camshaft timing (bank 2)
Required sensors / components (Main) VVT OCV, VVT Actuator
Required sensors / components (Related) Crankshaft position sensor, Camshaft position sensor, ECT sensor
Frequency of operation Once per driving cycles
Duration Less than 10 seconds
MIL operationP0011 and P0021: Immediate
P0012 and P0022: 2 driving cycles
Sequence operation None
The monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not
presentP0100, P0101, P0102, P0103 (MAF Sensor), P0115, P0116, P0117, P0118 (ECT
Sensor), P0125 (Insufficient ECT for Closed Loop), P0335 (CKP Sensor), P0340
(CMP Sensor), P0351, P0352, P0353, P0354, P0355, P0356 (Ignitor)
Battery voltage 11 V or more
Engine RPM 500 to 4000 rpm
ECT 75 to 100
C (167 to 212F)
Duration of actual valve timing and target valve timing More than 5
CA (Crankshaft angle)
Valve timing No change in advanced valve timing
Duration of actual valve timing and target valve timing More than 5
CA (Crankshaft angle)
Valve timing No change in retarded valve timing
Abnormal bankAdvanced timing over
(Valve timing is out of specified range)Retarded timing over
(Valve timing is out of specified range)
Bank 1 P0011 P0012
Bank 2 P0021 P0022
Page 445 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–139
ES
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
All:
After engine stop:
After cold engine start:
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
After engine stop:
After cold engine start:
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0110 (See page ES-126).
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Turn the tester on.
(d) Enter the following menus: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED
OBD II / DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES.
Required Sensors / Components (Main) Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor
Required Sensors / Components (Sub) -
Frequency of Operation Once per driving cycle
Duration 5 hours
MIL Operation 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
Monitor runs whenever following DTCs are not present None
Time after engine start 10 seconds or more
Battery voltage 10.5 V or more
ECT sensor OK
ECT change since engine stopped Less than 180
C (356F)
ECT before engine stop 70
C (158F) or more
Time that MAF is low before engine stop 70 minutes
Accumulated MAF amount before engine stop 3774 g or more
Key-off duration 30 minutes
Key-off duration 5 hours
Time after engine start 10 seconds or more
ECT sensor OK
ECT 70
C (158F) or more
Accumulated MAF amount 3774 g or more
One of the following conditions 1 or 2 is met: -
1. Duration while engine load is low 120 seconds or more
2. Duration while engine load is high 10 seconds or more
IAT change Less than 1
C (2F)
IAT change Less than 1
C (2F)
1CHECK ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO DTC P0111)
Page 454 of 3000

ES–1482GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
All:
ECT sensor cold start monitor:
ECT sensor soak monitor:
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
ECT sensor cold start monitor:
ECT sensor soak monitor:
COMPONENT OPERATING RANGE
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
• If any of DTC P0115, P0117, P0118 or P0125 are set simultaneously with DTC P0116, the ECT sensor
may have an open or a short circuit. Troubleshoot those DTCs first.
• Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition
information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame
data can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, whether the engine
was warmed up or not, whether the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the
time of a malfunction.
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Turn the tester on.
(d) Enter the following menus: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED II
/ DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES.
(e) Read the DTC.
Monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not present. P0100, P0102, P0103 (MAF Sensor)
Battery voltage 10.5 V or more
Time after engine start 1 second or more
ECT at engine start Less than 60
C (140F)
IAT sensor circuit OK
Soak time 5 hours or more
Accumulated MAF 1421.2 g or more
Engine Running
Fuel cut OFF
Difference between ECT at engine start and IAT Less than 40
C (72F)
Battery voltage 10.5 V or more
Engine Running
Soak time 5 hours or more
ECT at engine start 60
C (140F) or more
Accumulated MAF 3298.1 g or more
ECT sensor value change Less than 5
C (9F)
ECT sensor value change Less than 5
C (9F)
Engine coolant temperature Varies with actual engine coolant temperature
1CHECK ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO DTC P0166)
Page 482 of 3000
ES–1762GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
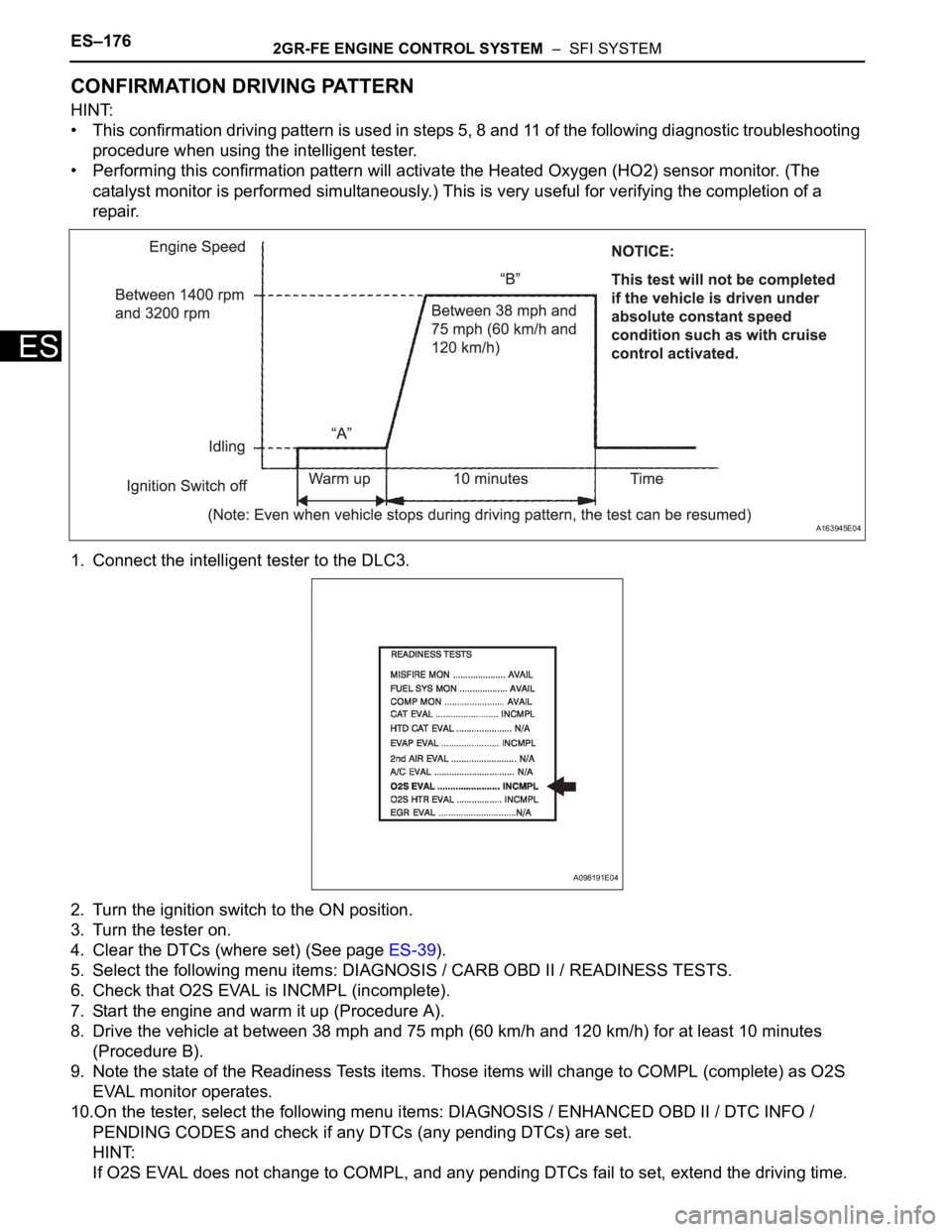
CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
HINT:
• This confirmation driving pattern is used in steps 5, 8 and 11 of the following diagnostic troubleshooting
procedure when using the intelligent tester.
• Performing this confirmation pattern will activate the Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor monitor. (The
catalyst monitor is performed simultaneously.) This is very useful for verifying the completion of a
repair.
1. Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
2. Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
3. Turn the tester on.
4. Clear the DTCs (where set) (See page ES-39).
5. Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS / CARB OBD II / READINESS TESTS.
6. Check that O2S EVAL is INCMPL (incomplete).
7. Start the engine and warm it up (Procedure A).
8. Drive the vehicle at between 38 mph and 75 mph (60 km/h and 120 km/h) for at least 10 minutes
(Procedure B).
9. Note the state of the Readiness Tests items. Those items will change to COMPL (complete) as O2S
EVAL monitor operates.
10.On the tester, select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED OBD II / DTC INFO /
PENDING CODES and check if any DTCs (any pending DTCs) are set.
HINT:
If O2S EVAL does not change to COMPL, and any pending DTCs fail to set, extend the driving time.
A163945E04
A098191E04
Page 494 of 3000

ES–1882GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
DESCRIPTION
The fuel trim is related to the feedback compensation value, not to the basic injection time. The fuel trim
consists of both the short-term and long-term fuel trims.
The short-term fuel trim is fuel compensation that is used to constantly maintain the air-fuel ratio at
stoichiometric levels. The signal from the Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor indicates whether the air-fuel ratio is
rich or lean compared to the stoichiometric ratio. This triggers a reduction in the fuel injection volume if the
air-fuel ratio is rich and an increase in the fuel injection volume if it is lean.
Factors such as individual engine differences, wear over time and changes in operating environment
cause short-term fuel trim to vary from the central value. The long-term fuel trim, which controls overall
fuel compensation, compensates for long-term deviations in the fuel trim from the central value caused by
the short-term fuel trim compensation.
If both the short-term and long-term fuel trims are lean or rich beyond predetermined values, it is
interpreted as a malfunction, and the ECM illuminates the MIL and sets a DTC.
HINT:
• When DTC P0171 or P0174 is set, the actual air-fuel ratio is on the lean side. When DTC P0172 or
P0175 is set, the actual air-fuel ratio is on the rich side.
• If the vehicle runs out of fuel, the air-fuel ratio is lean and DTC P0171 or P0174 may be set. The MIL is
then illuminated.
DTC P0171 System Too Lean (Bank 1)
DTC P0172 System Too Rich (Bank 1)
DTC P0174 System Too Lean (Bank 2)
DTC P0175 System Too Rich (Bank 2)
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0171
P0174With warm engine and stable air-fuel ratio feedback,
fuel trim considerably in error to lean side (2 trip
detection logic)• Intake system
• Injector blockage
• Mass Air Flow (MAF) meter
• Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor
• Fuel pressure
• Gas leakage from exhaust system
• Open or short in A/F sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
circuit
• A/F sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
• A/F sensor heater (bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
• A/F sensor heater relay
• A/F sensor heater and A/F sensor heater relay
circuits
• PCV valve and hose
• PCV hose connections
•ECM
P0172
P0175With warm engine and stable air-fuel ratio feedback,
fuel trim considerably in error to rich side (2 trip
detection logic)• Injector leakage or blockage
• MAF meter
• ECT sensor
• Ignition system
• Fuel pressure
• Gas leakage from exhaust system
• Open or short in A/F sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
circuit
• A/F sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
• A/F sensor heater (bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
• A/F sensor heater relay
• A/F sensor heater and A/F sensor heater relay
circuits
•ECM
Page 540 of 3000

ES–2342GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
DESCRIPTION
The intake camshaft's Variable Valve Timing (VVT) sensor (G signal) consists of a magnet and MRE
(Magneto Resistance Element).
The VVT camshaft drive gear has a sensor plate with 3 teeth on its outer circumference. When the gear
rotates, changes occur in the air gaps between the sensor plate and MRE, which affects the magnetic
field. As a result, the resistance of the MRE material fluctuates. The VVT sensor converts the gear
rotation data to pulse signals, uses the pulse signals to determine the camshaft angle, and sends it to the
ECM.
The crankshaft angle sensor plate has 34 teeth. The pickup coil generates 34 signals for each engine
revolution. Based on combination of the G signal and NE signal, the ECM detects the crankshaft angle.
Then the ECM uses this data to control fuel injection time and injection timing. Also, based on the NE
signal, the ECM detects the engine speed.
Reference: Inspection using an oscilloscope
DTC P0340Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit (Bank 1
or Single Sensor)
DTC P0342Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit Low
Input (Bank 1 or Single Sensor)
DTC P0343Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit High
Input (Bank 1 or Single Sensor)
DTC P0345 Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit (Bank 2)
DTC P0347Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit Low
Input (Bank 2)
DTC P0348Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit High
Input (Bank 2)
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0340
P0345• Input voltage to ECM remains 0.3 V or less, or 4.7
V or higher for more than 5 seconds, when 2 or
more seconds have elapsed after turning ignition
switch ON (2 trip detection logic)
• No VVT sensor signal to ECM during cranking (1
trip detection logic)• Open or short in VVT sensor circuit for intake
camshaft
• VVT sensor for intake camshaft
• Camshaft timing gear for intake camshaft
• Jumped tooth of timing chain for intake camshaft
•ECM
P0342
P0347Output voltage of VVT sensor is 0.3 V or less for 5
seconds (1 trip detection logic)• Open or short in VVT sensor circuit for intake
camshaft
• VVT sensor for intake camshaft
• Camshaft timing gear for intake camshaft
• Jumped tooth of timing chain for intake camshaft
•ECM
P0343
P0348Output voltage of VVT sensor is 4.7 V or more for 5
seconds (1 trip detection logic)• Open or short in VVT sensor circuit for intake
camshaft
• VVT sensor for intake camshaft
• Camshaft timing gear for intake camshaft
• Jumped tooth of timing chain for intake camshaft
•ECM
Page 561 of 3000

ES–2682GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ESKey-off monitor sequence 1 to 8
1. Atmospheric pressure measurement
2. First reference pressure measurement
3. EVAP canister vent valve close stuck check
4. Vacuum introduction
5. EVAP canister purge valve close stuck check
6. Second reference pressure measurement
7. Leak check
8. Atmospheric pressure measurement
Time after key-off 5 or 7 or 9.5 hours
EVAP pressure sensor malfunction (P0450, P0451,
P0452, P0453)Not detected
EVAP canister purge valve Not operated by scan tool
EVAP canister vent valve Not operated by scan tool
EVAP leak detection pump Not operated by scan tool
Both of the following conditions 1 and 2 are met before
key-off-
1. Duration that vehicle driven 5 minutes or more
2. EVAP purge operation Performed
ECT 4.4 to 35
C (40 to 95F)
IAT 4.4 to 35
C (40 to 95F)
Next sequence is run if the following condition is met: -
Atmospheric pressure change Less than 0.3 kPa (2.25 mmHg) in 1 second
Next sequence is run if all of the following conditions
are met:Conditions 1, 2 and 3
1. EVAP pressure just after reference pressure
measurement-1 kPa (-7.5 mmHg) or less
2. Reference pressure -4.85 to -1.057 kPa (-36.384 to -7.929 mmHg)
3. Reference pressure Saturated within 1 minute
Next sequence is run if the following condition is met: -
EVAP pressure change after vent valve is ON 0.3 kPa (2.25 mmHg) or more
Next sequence is run if the following condition is met: -
EVAP pressure Saturated within 15 minutes
Next sequence is run if the following condition is met: -
EVAP pressure change after purge valve is open 0.3 kPa (2.25 mmHg) or more
Next sequence is run if all of the following conditions
are met:Conditions 1, 2, 3 and 4
1. EVAP pressure just after reference pressure
measurement-1 kPa (-7.5 mmHg) or less
2. Reference pressure -4.85 to -1.057 kPa (-36.384 to -7.929 mmHg)
3. Reference pressure Saturated
4. Difference between first reference pressure and
second reference pressureLess than 0.7 kPa (5.25 mmHg)
Next sequence is run if the following condition is met -
EVAP pressure when vacuum introduction was
completeLower than second reference pressure
EVAP monitor is complete if the following condition is
met:-