ecu wiring TOYOTA SIENNA 2007 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SIENNA, Model: TOYOTA SIENNA 2007Pages: 3000, PDF Size: 52.26 MB
Page 55 of 3000

INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMSIN–43
IN
(d) HIGH ELECTRICAL LOAD METHOD: When a
malfunction seems to occur when electrical load is
excessive.
(1) Turn on the heater blower, headlight, rear
window defogger and all other electrical loads.
Check if the malfunction reoccurs.
5. DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
Look for output Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) (from the
DTC checks) in the appropriate section's Diagnostic Trouble
Code Chart. Use the chart to determine the trouble area and
the proper inspection procedure. A description of each of the
chart's columns is shown in the table below.
6. PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE
When a "Normal" code is output during a DTC check but
the problem still occurs, use the Problem Symptoms
Table. The suspected areas (circuits or parts) for each
problem symptoms are in the table. The suspected areas
are listed in order of probability. A description of each of
the chart's columns is shown in the table below.
HINT:
In some cases, the problem is not detected by the
diagnostic system even though a problem symptom
occurs. It is possible that the problem is occurring
outside the detection range of the diagnostic system, or
that the problem occurs in a completely different system.
7. CIRCUIT INSPECTION
A description of the main areas of each circuit inspection
is shown in the table below.
B107149
Item Description
DTC No. Indicates the diagnostic trouble code
Detection Item Indicates the system or details of the problem
Trouble Area Indicates the suspect areas of the problem
See Page Indicates the page where the inspection procedures for each circuit is
to be found, or gives instruction for checking and repairs.
Item Description
Problem Symptom -
Circuit Inspection, Inspection Order Indicates the order in which the circuits need to be checked
Circuit or Part Name Indicates the circuit or part which needs to be checked
See Page Indicates the page where the flowchart for each circuit is located
Item Description
Circuit Description The major role, operation of the circuit and its component parts are
explained.
Diagnostic Trouble Code No. and Detection item Indicates the diagnostic trouble codes, diagnostic trouble code
settings and suspected areas for a problem
Wiring diagram This shows a wiring diagram of the circuit.
Use this diagram together with ELECTRICAL WIRING DIAGRAM to
thoroughly understand the circuit.
Wire colors are indicated by an alphabetical code. B = Black, L = Blue,
R = Red, BR = Brown, LG = Light Green, V = Violet, G = Green, O =
Orange, W = White, GR = Gray, P = Pink, Y = Yellow, SB = Sky Blue
The first letter indicates the basic wire color and the second letter
indicates the color of the stripe.
Page 62 of 3000
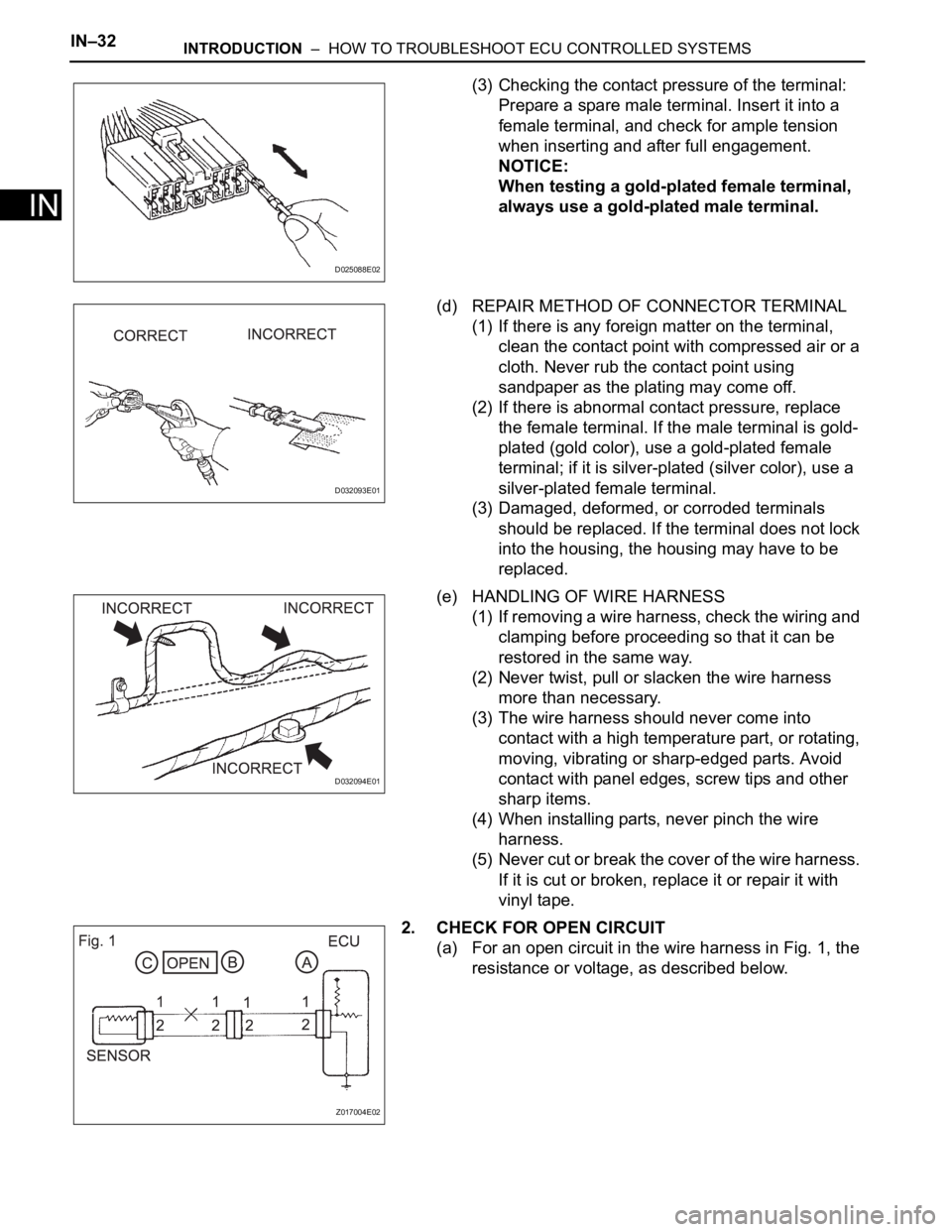
IN–32INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
IN
(3) Checking the contact pressure of the terminal:
Prepare a spare male terminal. Insert it into a
female terminal, and check for ample tension
when inserting and after full engagement.
NOTICE:
When testing a gold-plated female terminal,
always use a gold-plated male terminal.
(d) REPAIR METHOD OF CONNECTOR TERMINAL
(1) If there is any foreign matter on the terminal,
clean the contact point with compressed air or a
cloth. Never rub the contact point using
sandpaper as the plating may come off.
(2) If there is abnormal contact pressure, replace
the female terminal. If the male terminal is gold-
plated (gold color), use a gold-plated female
terminal; if it is silver-plated (silver color), use a
silver-plated female terminal.
(3) Damaged, deformed, or corroded terminals
should be replaced. If the terminal does not lock
into the housing, the housing may have to be
replaced.
(e) HANDLING OF WIRE HARNESS
(1) If removing a wire harness, check the wiring and
clamping before proceeding so that it can be
restored in the same way.
(2) Never twist, pull or slacken the wire harness
more than necessary.
(3) The wire harness should never come into
contact with a high temperature part, or rotating,
moving, vibrating or sharp-edged parts. Avoid
contact with panel edges, screw tips and other
sharp items.
(4) When installing parts, never pinch the wire
harness.
(5) Never cut or break the cover of the wire harness.
If it is cut or broken, replace it or repair it with
vinyl tape.
2. CHECK FOR OPEN CIRCUIT
(a) For an open circuit in the wire harness in Fig. 1, the
resistance or voltage, as described below.
D025088E02
D032093E01
D032094E01
Z017004E02
Page 73 of 3000

INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMSIN–43
IN
(d) HIGH ELECTRICAL LOAD METHOD: When a
malfunction seems to occur when electrical load is
excessive.
(1) Turn on the heater blower, headlight, rear
window defogger and all other electrical loads.
Check if the malfunction reoccurs.
5. DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
Look for output Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) (from the
DTC checks) in the appropriate section's Diagnostic Trouble
Code Chart. Use the chart to determine the trouble area and
the proper inspection procedure. A description of each of the
chart's columns is shown in the table below.
6. PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE
When a "Normal" code is output during a DTC check but
the problem still occurs, use the Problem Symptoms
Table. The suspected areas (circuits or parts) for each
problem symptoms are in the table. The suspected areas
are listed in order of probability. A description of each of
the chart's columns is shown in the table below.
HINT:
In some cases, the problem is not detected by the
diagnostic system even though a problem symptom
occurs. It is possible that the problem is occurring
outside the detection range of the diagnostic system, or
that the problem occurs in a completely different system.
7. CIRCUIT INSPECTION
A description of the main areas of each circuit inspection
is shown in the table below.
B107149
Item Description
DTC No. Indicates the diagnostic trouble code
Detection Item Indicates the system or details of the problem
Trouble Area Indicates the suspect areas of the problem
See Page Indicates the page where the inspection procedures for each circuit is
to be found, or gives instruction for checking and repairs.
Item Description
Problem Symptom -
Circuit Inspection, Inspection Order Indicates the order in which the circuits need to be checked
Circuit or Part Name Indicates the circuit or part which needs to be checked
See Page Indicates the page where the flowchart for each circuit is located
Item Description
Circuit Description The major role, operation of the circuit and its component parts are
explained.
Diagnostic Trouble Code No. and Detection item Indicates the diagnostic trouble codes, diagnostic trouble code
settings and suspected areas for a problem
Wiring diagram This shows a wiring diagram of the circuit.
Use this diagram together with ELECTRICAL WIRING DIAGRAM to
thoroughly understand the circuit.
Wire colors are indicated by an alphabetical code. B = Black, L = Blue,
R = Red, BR = Brown, LG = Light Green, V = Violet, G = Green, O =
Orange, W = White, GR = Gray, P = Pink, Y = Yellow, SB = Sky Blue
The first letter indicates the basic wire color and the second letter
indicates the color of the stripe.
Page 413 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–107
ES
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
All:
P0016 and P0018:
P0017 and P0019:
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
P0016 and P0018:
P0017 and P0019:
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0335 (See page ES-222).
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition
information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data
can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, whether the engine was
warmed up or not, whether the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the time of
a malfunction.
Related DTCsP0016: Deviation in crankshaft position sensor signal and camshaft position sensor
signal (Bank 1)
P0017: Deviation in crankshaft position sensor signal and camshaft position sensor
signal (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
P0018: Deviation in crankshaft position sensor signal and camshaft position sensor
signal (Bank 2)
P0019: Deviation in crankshaft position sensor signal and camshaft position sensor
signal (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
Required Sensors / Components (Main)P0016 and P0018: VVT actuator
P0017 and P0019: Timing chain/belt
Required Sensors / Components (Related)P0016 and P0018: Camshaft position sensor, Crankshaft position sensor
P0017 and P0019: None
Frequency of Operation Once per driving cycle
Duration Less than 60 seconds
MIL Operation 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
The monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not
presentP0011, P0012 (VVT System 1-Advance, Retard), P0021, P0022 (VVT System 2-
Adavance, Retard), P0115, P0116, P0117, P0118 (ECT Sensor)
Engine RPM 500 to 1000 rpm
VVT feedback mode Executing
VVT Maximum advanced position
Engine RPM 500 to 1000 rpm
One of the following conditions is met: Condition 1 or 2
1. VVT learning value at maximum retarded valve
timingLess than 18.5
CA
2. VVT learning value at maximum retarded valve
timingMore than 43.5
CA
One of the following conditions is met: Condition 1 or 2
1. VVT learning value Less than 77
CA
2. VVT learning value More than 102
CA
Page 496 of 3000

ES–1902GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
Fuel-trim:
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
Fuel trim:
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P2195 (See page ES-359).
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
For use of the intelligent tester only:
Malfunctioning areas can be identified by performing the A/F CONTROL function provided in the ACTIVE
TEST. The A/F CONTROL function can help to determine whether the Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor, Heated
Oxygen (HO2) sensor and other potential trouble areas are malfunctioning.
The following instructions describe how to conduct the A/F CONTROL operation using the intelligent
tester.
1. Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
2. Start the engine and turn the tester on.
3. Warm up the engine at an engine speed of 2500 rpm for approximately 90 seconds.
4. Select the following menu items on the tester: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED OBD II / ACTIVE TEST / A/F
CONTROL.
5. Perform the A/F CONTROL operation with the engine in an idling condition (press the RIGHT or LEFT
button to change the fuel injection volume).
6. Monitor the voltage outputs of the A/F and HO2 sensors (AFS B1S1 and O2S B1S2 or AFS B2S1 and
O2S B2S2) displayed on the tester.
HINT:
• The A/F CONTROL operation lowers the fuel injection volume by 12.5% or increases the injection
volume by 25%.
• Each sensor reacts in accordance with increases and decreases in the fuel injection volume.
Standard voltage
The monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not
presentP0010, P0020 (VVT VSV1, 2), P0011, P0012 (VVT System-Advance, Retard),
P0021, P0022 (VVT System 2-Adavance, Retard), P0031, P0032, P0051, P0052 (A/
F Sensor Heater Sensor 1), P0100, P0101, P0102, P0103 (MAF Sensor), P0115,
P0116, P0117, P0118 (ECT Sensor), P0120, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0220, P0222,
P0223, P2135 (TP Sensor), P0125 (Insufficient ECT for Closed Loop), P0335 (CKP
Sensor), P0340 (CMP Sensor), P0351, P0352, P0353, P0354, P0356 (Ignitor),
P0500 (VSS)
Fuel system status Closed-loop
Battery voltage 11 V or more
Either of the following conditions is met Condition 1 or 2
1. Engine RPM Less than 1100 rpm
2. Intake air amount per revolution 0.22 g/rev or more
Catalyst monitor Not executed
EVAP purge-cut Executing
Either of the following conditions is met Condition 1 or 2
1. Average between short-term fuel trim and long-term
fuel trim35% or more at 80
C (176F) of ECT
2. Average between short-term fuel trim and long-term
fuel trim-35% or less at 80
C (176F) of ECT
Tester Display (Sensor) Injection Volumes Status Voltages
AFS B1S1 or AFS B2S1 (A/F) +25% Rich Less than 3.0
Page 635 of 3000

ES–3422GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
*: System guard set when following conditions met
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
P2111 (Throttle actuator stuck open):
P2112 (Throttle actuator stuck closed):
FA I L - S A F E
When either of these DTCs, as well as other DTCs relating to ETCS (Electronic Throttle Control System)
malfunctions, is set, the ECM enters fail-safe mode. During fail-safe mode, the ECM cuts the current to
the throttle actuator off, and the throttle valve is returned to a 6
throttle angle by the return spring. The
ECM then adjusts the engine output by controlling the fuel injection (intermittent fuel-cut) and ignition
timing, in accordance with the accelerator pedal opening angle, to allow the vehicle to continue at a
minimal speed.
If the accelerator pedal is depressed slowly, the vehicle can be driven slowly.
Fail-safe mode continues until a pass condition is detected, and the ignition switch is then turned off.
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P2102 (See page ES-331).
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition
information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data
can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, whether the engine was
warmed up or not, whether the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the time of
a malfunction.
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Turn the tester on.
(d) Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS /
ENHANCED OBD II / DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES.
(e) Read the DTCs.
Result
Throttle actuator open duty-cycle 80% or more
Throttle actuator ON
Throttle actuator duty calculation Executing
Throttle position sensor Fail determined
Throttle actuator current-cut operation Not executing
Throttle actuator power supply 4 V or more
Throttle actuator Fail determined
TP sensor voltage change No change
TP sensor voltage change No change
1CHECK ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO DTC P2111 OR P2112)
Display (DTC Output) Proceed to
P2111 or P2112 A
P2111 or P2112 and other DTCs B
Page 642 of 3000
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–349
ES
FAIL-SAFE
When this DTC, as well as other DTCs relating to ETCS (Electronic Throttle Control System)
malfunctions, is set, the ECM enters fail-safe mode. During fail-safe mode, the ECM cuts the current to
the throttle actuator off, and the throttle valve is returned to a 6
throttle angle by the return spring. The
ECM then adjusts the engine output by controlling the fuel injection (intermittent fuel-cut) and ignition
timing, in accordance with the accelerator pedal opening angle, to allow the vehicle to continue at a
minimal speed. If the accelerator pedal is depressed slowly, the vehicle can be driven slowly.
Fail-safe mode continues until a pass condition is detected, and the ignition switch is then turned off.
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P2102 (See page ES-331).
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition
information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data
can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, whether the engine was
warmed up or not, whether the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the time of
a malfunction.
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Turn the tester on.
(d) Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS /
ENHANCED OBD II / DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES.
(e) Read the DTCs.
Result
HINT:
If any DTCs other than P2119 are output, troubleshoot
those DTCs first.
B
A
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Turn the tester on.
(d) Clear the DTCs (See page ES-39).
(e) Allow the engine to idle for 15 seconds.
CAUTION:
Perform the procedures "A" and "B" below with
great care. Failure to do so may result in the vehicle
unexpectedly rolling away.
1CHECK ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO DTC P2119)
Display (DTC Output) Proceed to
P2119 A
P2119 and other DTCs B
GO TO DTC CHART (See page ES-56)
2CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P2119)
Page 848 of 3000

MULTIPLEX COMMUNICATION – MULTIPLEX COMMUNICATION SYSTEMMP–5
MP
TERMINALS OF ECU
1. MULTIPLEX NETWORK GATEWAY ECU
(a) Disconnect the G4 ECU connector.
(b) Measure the voltage between the specified
terminals on the wire harness side connector.
If the result is not as specified, there may be a
malfunction on the wire harness side.
(c) Measure the resistance between the specified
terminals on the wire harness side connector.
If the result is not as specified, there may be a
malfunction on the wire harness side.
C129903E02
Terminal No.
(Symbols)Wiring Color Terminal Description Condition Specified Condition
G4-1 (IG) - Body ground B-R - Body ground Power supply (IG) Ignition switch: ON 11 to 14 V
G4-2 (ACC) - Body ground P - Body ground Power source (ACC) Ignition switch: ACC 11 to 14 V
G4-10 (BATT) - Body
groundW-L - Body ground Power supply (Battery) Always 11 to 14 V
Terminal No.
(Symbols)Wiring Color Terminal Description Condition Specified Condition
G4-3 (MPD1) - Body
groundR-G - Body ground MPX line Always 10 k
or higher
G4-12 (MPD2) - Body
groundR-L - Body ground MPX line Always 10 k
or higher
G4-24 (GND) - Body
groundW-B - Body ground Ground Always Below 1
Page 850 of 3000
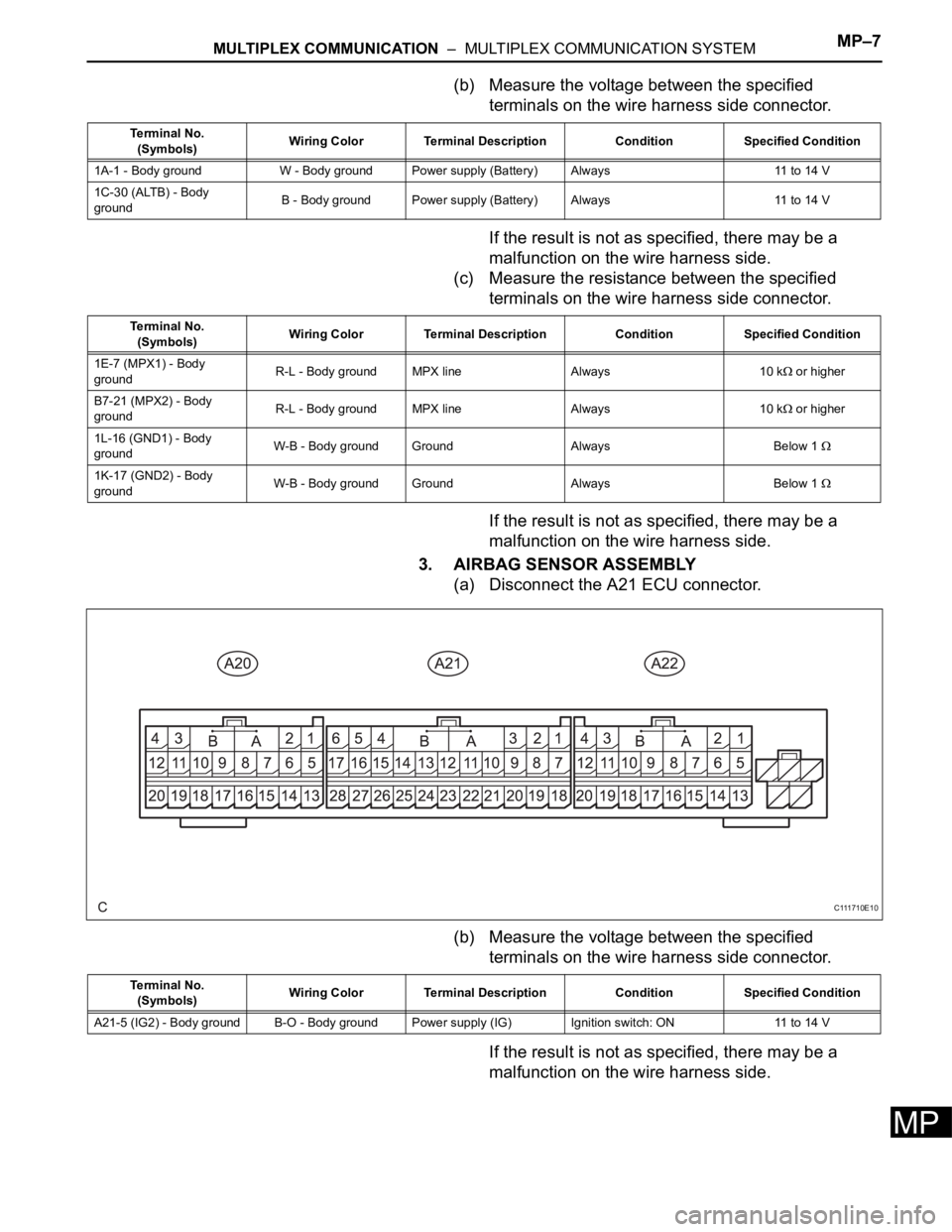
MULTIPLEX COMMUNICATION – MULTIPLEX COMMUNICATION SYSTEMMP–7
MP
(b) Measure the voltage between the specified
terminals on the wire harness side connector.
If the result is not as specified, there may be a
malfunction on the wire harness side.
(c) Measure the resistance between the specified
terminals on the wire harness side connector.
If the result is not as specified, there may be a
malfunction on the wire harness side.
3. AIRBAG SENSOR ASSEMBLY
(a) Disconnect the A21 ECU connector.
(b) Measure the voltage between the specified
terminals on the wire harness side connector.
If the result is not as specified, there may be a
malfunction on the wire harness side.
Terminal No.
(Symbols)Wiring Color Terminal Description Condition Specified Condition
1A-1 - Body ground W - Body ground Power supply (Battery) Always 11 to 14 V
1C-30 (ALTB) - Body
groundB - Body ground Power supply (Battery) Always 11 to 14 V
Terminal No.
(Symbols)Wiring Color Terminal Description Condition Specified Condition
1E-7 (MPX1) - Body
groundR-L - Body ground MPX line Always 10 k
or higher
B7-21 (MPX2) - Body
groundR-L - Body ground MPX line Always 10 k
or higher
1L-16 (GND1) - Body
groundW-B - Body ground Ground Always Below 1
1K-17 (GND2) - Body
groundW-B - Body ground Ground Always Below 1
C111710E10
Terminal No.
(Symbols)Wiring Color Terminal Description Condition Specified Condition
A21-5 (IG2) - Body ground B-O - Body ground Power supply (IG) Ignition switch: ON 11 to 14 V
Page 851 of 3000
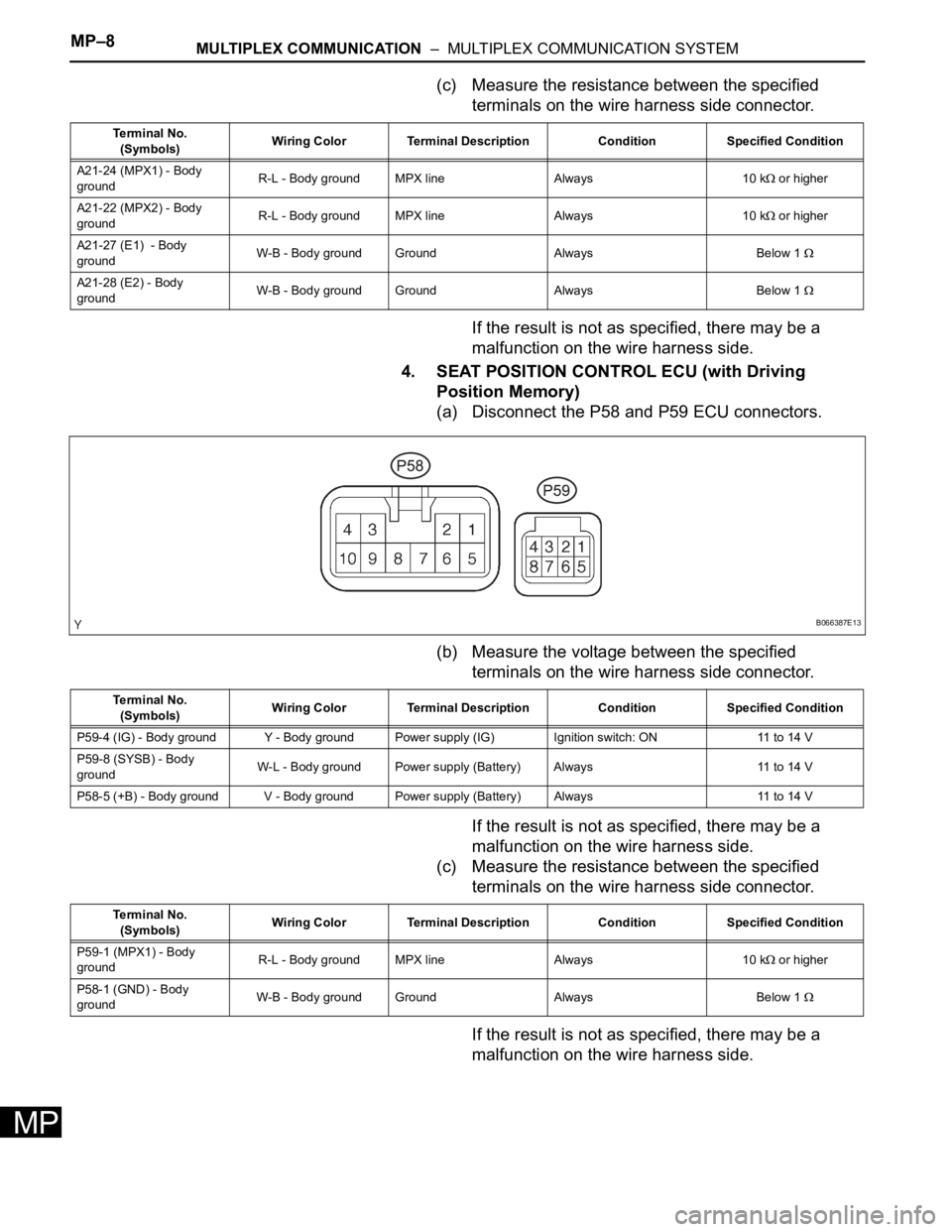
MP–8MULTIPLEX COMMUNICATION – MULTIPLEX COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
MP
(c) Measure the resistance between the specified
terminals on the wire harness side connector.
If the result is not as specified, there may be a
malfunction on the wire harness side.
4. SEAT POSITION CONTROL ECU (with Driving
Position Memory)
(a) Disconnect the P58 and P59 ECU connectors.
(b) Measure the voltage between the specified
terminals on the wire harness side connector.
If the result is not as specified, there may be a
malfunction on the wire harness side.
(c) Measure the resistance between the specified
terminals on the wire harness side connector.
If the result is not as specified, there may be a
malfunction on the wire harness side.
Te r m i n a l N o .
(Symbols)Wiring Color Terminal Description Condition Specified Condition
A21-24 (MPX1) - Body
groundR-L - Body ground MPX line Always 10 k
or higher
A21-22 (MPX2) - Body
groundR-L - Body ground MPX line Always 10 k
or higher
A21-27 (E1) - Body
groundW-B - Body ground Ground Always Below 1
A21-28 (E2) - Body
groundW-B - Body ground Ground Always Below 1
B066387E13
Te r m i n a l N o .
(Symbols)Wiring Color Terminal Description Condition Specified Condition
P59-4 (IG) - Body ground Y - Body ground Power supply (IG) Ignition switch: ON 11 to 14 V
P59-8 (SYSB) - Body
groundW-L - Body ground Power supply (Battery) Always 11 to 14 V
P58-5 (+B) - Body ground V - Body ground Power supply (Battery) Always 11 to 14 V
Te r m i n a l N o .
(Symbols)Wiring Color Terminal Description Condition Specified Condition
P59-1 (MPX1) - Body
groundR-L - Body ground MPX line Always 10 k
or higher
P58-1 (GND) - Body
groundW-B - Body ground Ground Always Below 1