check engine YAMAHA WR 250F 2009 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: YAMAHA, Model Year: 2009, Model line: WR 250F, Model: YAMAHA WR 250F 2009Pages: 224, PDF Size: 13.93 MB
Page 77 of 224
3-24
CHASSIS
CLEANING THE FRONT FORK OIL
SEAL AND DUST SEAL
1. Remove:•Protector
• Dust seal "1"
Use a thin screw driver, and be care-
ful not to damage the inner fork tube
and dust seal.
2. Clean:
• Dust seal "a"
•Oil seal "b"
• Clean the dust seal and oil seal af-ter every run.
• Apply the lithium soap base grease on the inner tube.
RELIEVING THE FRONT FORK
INTERNAL PRESSURE
If the front fork initial movement feels
stiff during a run, relieve the front fork
internal pressure.
1. Elevate the front wheel by placing
a suitable stand under the engine.
2. Remove the air bleed screw "1"
and release the internal pressure
from the front fork.
3. Install:
• Air bleed screw ADJUSTING THE FRONT FORK
REBOUND DAMPING FORCE
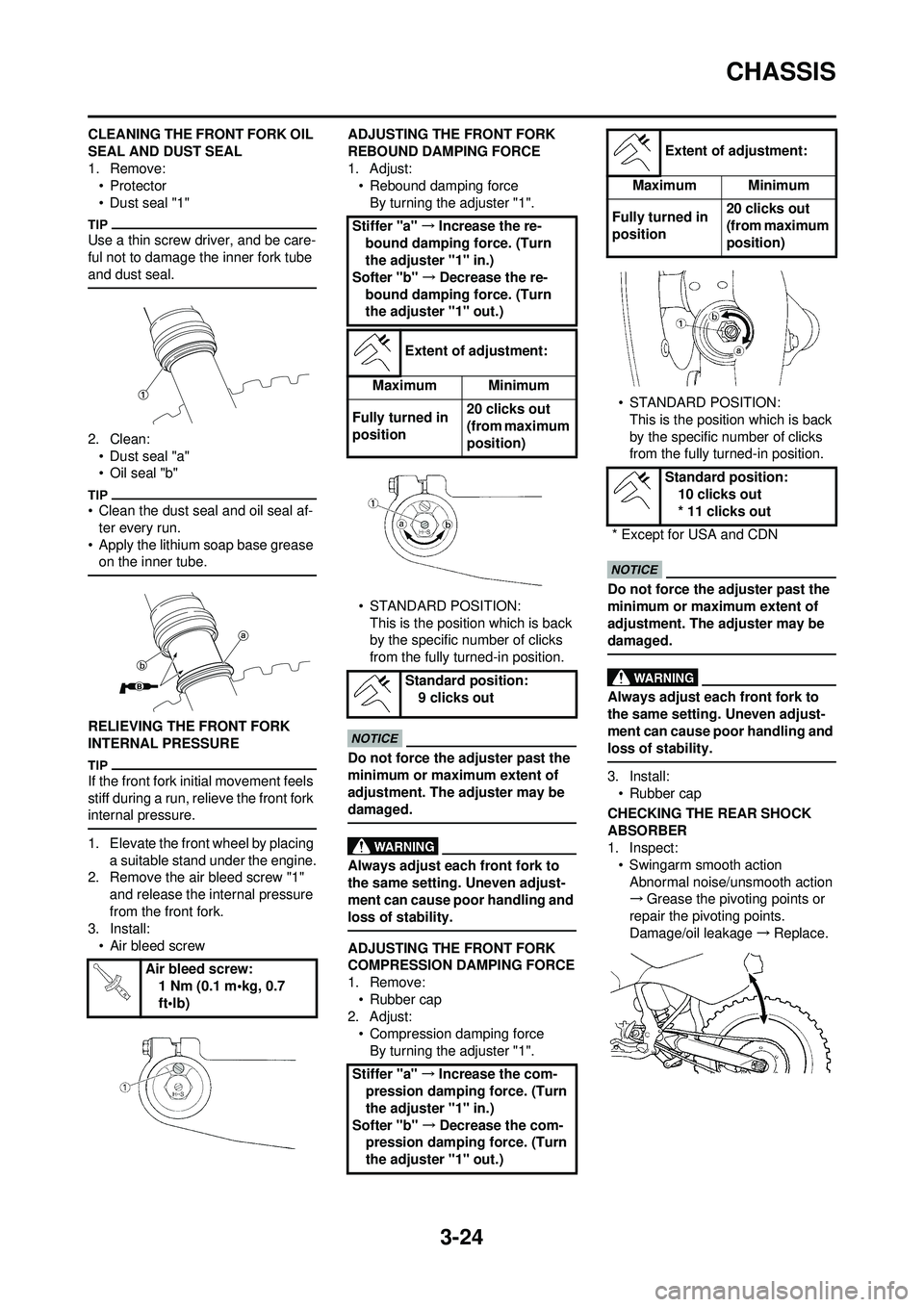
1. Adjust:
• Rebound damping force
By turning the adjuster "1".
• STANDARD POSITION: This is the position which is back
by the specific number of clicks
from the fully turned-in position.
Do not force the adjuster past the
minimum or maximum extent of
adjustment. The adjuster may be
damaged.
Always adjust each front fork to
the same setting. Uneven adjust-
ment can cause poor handling and
loss of stability.
ADJUSTING THE FRONT FORK
COMPRESSION DAMPING FORCE
1. Remove:• Rubber cap
2. Adjust:
• Compression damping forceBy turning the adjuster "1". • STANDARD POSITION:
This is the position which is back
by the specific number of clicks
from the fully turned-in position.
Do not force the adjuster past the
minimum or maximum extent of
adjustment. The adjuster may be
damaged.
Always adjust each front fork to
the same setting. Uneven adjust-
ment can cause poor handling and
loss of stability.
3. Install:• Rubber cap
CHECKING THE REAR SHOCK
ABSORBER
1. Inspect: • Swingarm smooth actionAbnormal noise/unsmooth action
→ Grease the pivoting points or
repair the pivoting points.
Damage/oil leakage →Replace.
Air bleed screw: 1 Nm (0.1 m•kg, 0.7
ft•lb)
Stiffer "a" →Increase the re-
bound damping force. (Turn
the adjuster "1" in.)
Softer "b" → Decrease the re-
bound damping force. (Turn
the adjuster "1" out.)
Extent of adjustment:
Maximum Minimum
Fully turned in
position 20 clicks out
(from maximum
position)
Standard position: 9 clicks out
Stiffer "a" →Increase the com-
pression damping force. (Turn
the adjuster "1" in.)
Softer "b" → Decrease the com-
pression damping force. (Turn
the adjuster "1" out.)
Extent of adjustment:
Maximum Minimum
Fully turned in
position 20 clicks out
(from maximum
position)
Standard position: 10 clicks out
* 11 clicks out
* Except for USA and CDN
Page 80 of 224
3-27
CHASSIS
2. Inspect:• Bearing free playExist play →Replace.
CHECKING AND ADJUSTING THE
STEERING HEAD
1. Place a stand under the engine to raise the front wheel off the
ground. WARNING! Securely
support the vehicle so that
there is no danger of it falling
over.
2. Check: • Steering stem
Grasp the bottom of the forks and
gently rock the fork assembly
back and forth.
Free play →Adjust steering head.
3. Check: • Steering smooth action
Turn the handlebar lock to lock.
Unsmooth action →Adjust steer-
ing ring nut.
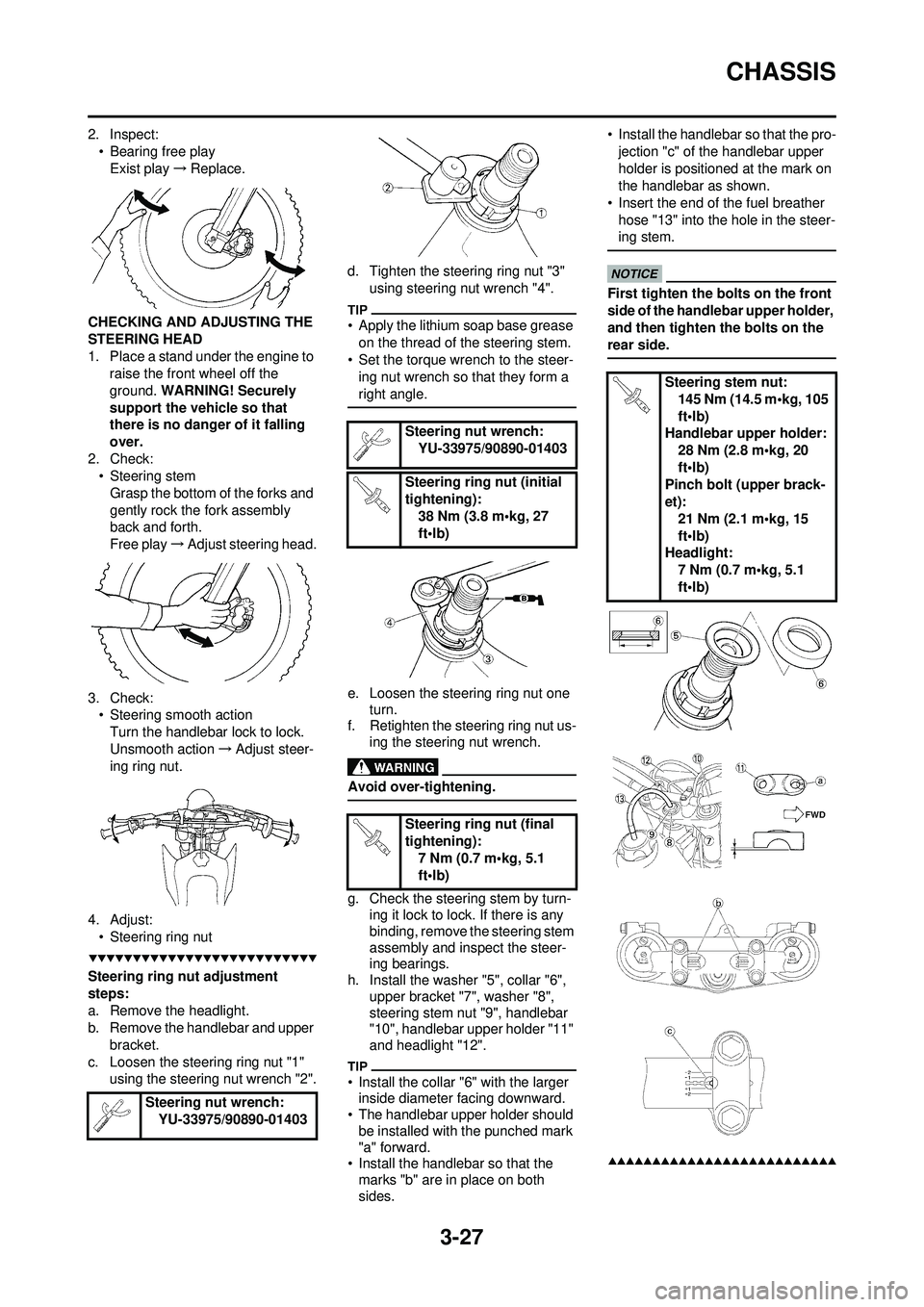
4. Adjust: • Steering ring nut
Steering ring nut adjustment
steps:
a. Remove the headlight.
b. Remove the handlebar and upper
bracket.
c. Loosen the steering ring nut "1" using the steering nut wrench "2". d. Tighten the steering ring nut "3"
using steering nut wrench "4".
• Apply the lithium soap base grease on the thread of the steering stem.
• Set the torque wrench to the steer-
ing nut wrench so that they form a
right angle.
e. Loosen the steering ring nut one turn.
f. Retighten the steering ring nut us-
ing the steering nut wrench.
Avoid over-tightening.
g. Check the steering stem by turn-ing it lock to lock. If there is any
binding, remove the steering stem
assembly and inspect the steer-
ing bearings.
h. Install the washer "5", collar "6", upper bracket "7", washer "8",
steering stem nut "9", handlebar
"10", handlebar upper holder "11"
and headlight "12".
• Install the collar "6" with the larger inside diameter facing downward.
• The handlebar upper holder should be installed with the punched mark
"a" forward.
• Install the handlebar so that the
marks "b" are in place on both
sides. • Install the handlebar so that the pro-
jection "c" of the handlebar upper
holder is positioned at the mark on
the handlebar as shown.
• Insert the end of the fuel breather hose "13" into the hole in the steer-
ing stem.
First tighten the bolts on the front
side of the handlebar upper holder,
and then tighten the bolts on the
rear side.
Steering nut wrench: YU-33975/90890-01403
Steering nut wrench:YU-33975/90890-01403
Steering ring nut (initial
tightening): 38 Nm (3.8 m•kg, 27
ft•lb)
Steering ring nut (final
tightening): 7 Nm (0.7 m•kg, 5.1
ft•lb)
Steering stem nut:145 Nm (14.5 m•kg, 105
ft•lb)
Handlebar upper holder:
28 Nm (2.8 m•kg, 20
ft•lb)
Pinch bolt (upper brack-
et): 21 Nm (2.1 m•kg, 15
ft•lb)
Headlight:
7 Nm (0.7 m•kg, 5.1
ft•lb)
Page 82 of 224
3-29
ELECTRICAL
ELECTRICAL
CHECKING THE SPARK PLUG
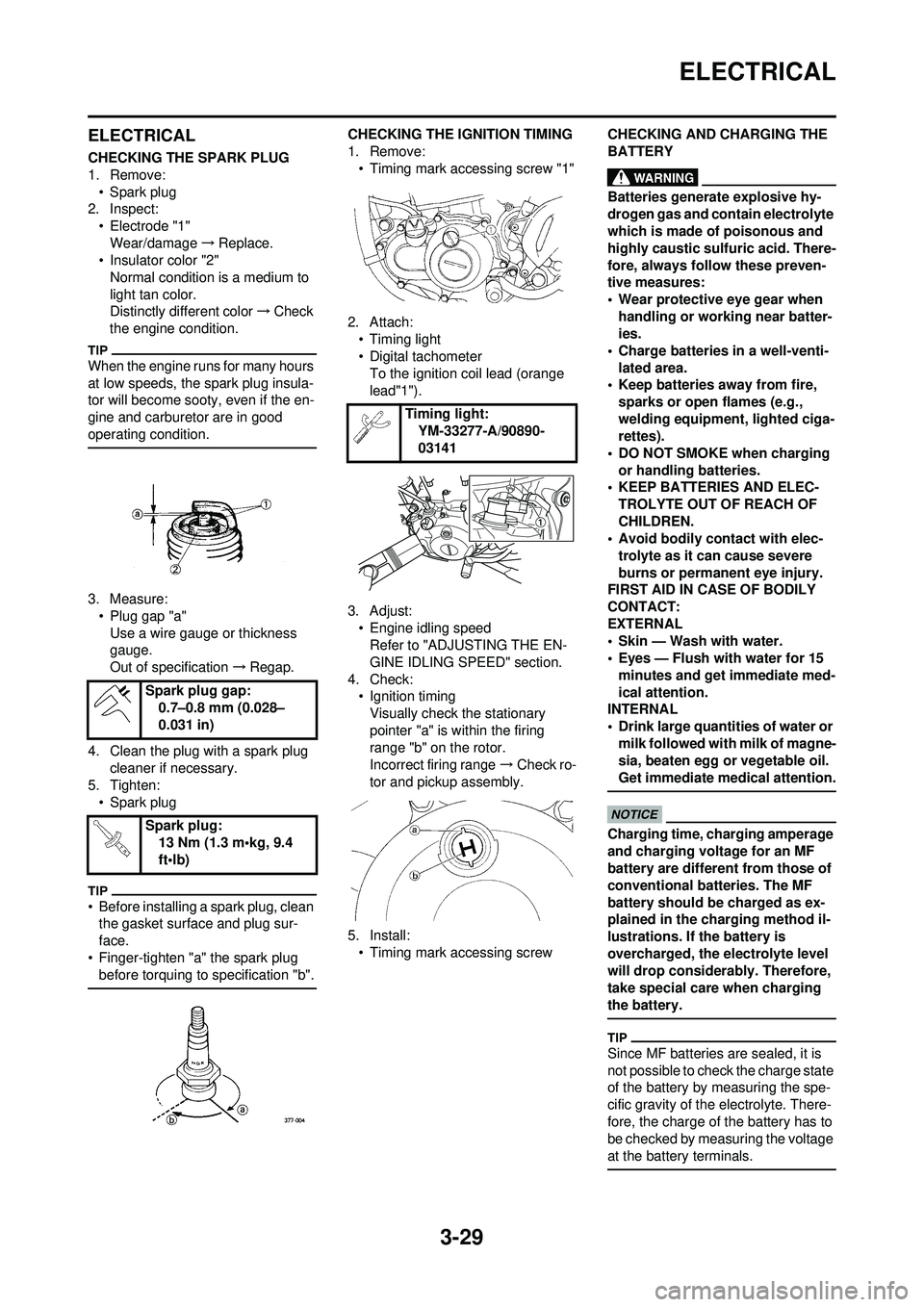
1. Remove:• Spark plug
2. Inspect:
• Electrode "1"Wear/damage →Replace.
• Insulator color "2"
Normal condition is a medium to
light tan color.
Distinctly different color →Check
the engine condition.
When the engine runs for many hours
at low speeds, the spark plug insula-
tor will become sooty, even if the en-
gine and carburetor are in good
operating condition.
3. Measure: • Plug gap "a"Use a wire gauge or thickness
gauge.
Out of specification →Regap.
4. Clean the plug with a spark plug cleaner if necessary.
5. Tighten: • Spark plug
• Before installing a spark plug, clean the gasket surface and plug sur-
face.
• Finger-tighten "a" the spark plug before torquing to specification "b".
CHECKING THE IGNITION TIMING
1. Remove:
• Timing mark accessing screw "1"
2. Attach: • Timing light
• Digital tachometerTo the ignition coil lead (orange
lead"1").
3. Adjust: • Engine idling speedRefer to "ADJUSTING THE EN-
GINE IDLING SPEED" section.
4. Check: • Ignition timing
Visually check the stationary
pointer "a" is within the firing
range "b" on the rotor.
Incorrect firing range →Check ro-
tor and pickup assembly.
5. Install: • Timing mark accessing screw CHECKING AND CHARGING THE
BATTERY
Batteries generate explosive hy-
drogen gas and contain electrolyte
which is made of poisonous and
highly caustic sulfuric acid. There-
fore, always follow these preven-
tive measures:
• Wear protective eye gear when
handling or working near batter-
ies.
• Charge batteries in a well-venti- lated area.
• Keep batteries away from fire,
sparks or open flames (e.g.,
welding equipment, lighted ciga-
rettes).
• DO NOT SMOKE when charging or handling batteries.
• KEEP BATTERIES AND ELEC-
TROLYTE OUT OF REACH OF
CHILDREN.
• Avoid bodily contact with elec-
trolyte as it can cause severe
burns or permanent eye injury.
FIRST AID IN CASE OF BODILY
CONTACT:
EXTERNAL
• Skin — Wash with water.
• Eyes — Flush with water for 15
minutes and get immediate med-
ical attention.
INTERNAL
• Drink large quantities of water or
milk followed with milk of magne-
sia, beaten egg or vegetable oil.
Get immediate medical attention.
Charging time, charging amperage
and charging voltage for an MF
battery are different from those of
conventional batteries. The MF
battery should be charged as ex-
plained in the charging method il-
lustrations. If the battery is
overcharged, the electrolyte level
will drop considerably. Therefore,
take special care when charging
the battery.
Since MF batteries are sealed, it is
not possible to check the charge state
of the battery by measuring the spe-
cific gravity of the electrolyte. There-
fore, the charge of the battery has to
be checked by measuring the voltage
at the battery terminals.
Spark plug gap: 0.7–0.8 mm (0.028–
0.031 in)
Spark plug: 13 Nm (1.3 m•kg, 9.4
ft•lb)
Timing light:YM-33277-A/90890-
03141
Page 88 of 224
4-1
ENGINE (Except for Canada)
TUNING
ENGINE (Except for Canada)
CARBURETOR SETTING
• The air/fuel mixture will vary de-pending on atmospheric conditions.
Therefore, it is necessary to take
into consideration the air pressure,
ambient temperature, humidity,
etc., when adjusting the carburetor.
• Perform a test run to check for prop- er engine performance (e.g., throt-
tle response) and spark plug(-s)
discoloration or fouling. Use these
readings to determine the best pos-
sible carburetor setting.
It is recommended to keep a record of
all carburetor settings and external
conditions (e.g., atmospheric condi-
tions, track/surface conditions, lap
times) to make future carburetor set-
ting easier.
• The carburetor is a part of the fuel line. Therefore, be sure to in-
stall it in a wellventilated area,
away from flammable objects
and any sources of fire.
• Never look into the carburetor in- take. Flames may shoot out from
the pipe if the engine backfires
while it is being started. Gasoline
may be discharged from the ac-
celerator pump nozzle when the
carburetor has been removed.
• The carburetor is extremely sen-sitive to foreign matter (dirt,
sand, water, etc.). During instal-
lation, do not allow foreign mat-
ter to get into the carburetor.
• Always handle the carburetor and its components carefully.
Even slight scratches, bends or
damage to carburetor parts may
prevent the carburetor from
functioning correctly. Carefully
perform all servicing with the ap-
propriate tools and without ap-
plying excessive force.
• When the engine is stopped or when riding at no load, do not
open and close the throttle un-
necessarily. Otherwise, too
much fuel may be discharged,
starting may become difficult or
the engine may not run well. • After installing the carburetor,
check that the throttle operates
correctly and opens and closes
smoothly.
ATMOSPHERIC CONDITIONS AND
CARBURETOR SETTINGS
The air density (i.e., concentration of
oxygen in the air) determines the rich-
ness or leanness of the air/fuel mix-
ture.
• Higher temperature expands the air with its resultant reduced density.
• Higher humidity reduces the
amount of oxygen in the air by so
much of the water vapor in the
same air.
• Lower atmospheric pressure (at a high altitude) reduces the density of
the air.
EFFECT OF SETTING PARTS IN
RELATION TO THROTTLE VALVE
OPENING
A. Closed
B. Fully open
1. Pilot jet
2. Throttle valve cutaway
3. Jet needle
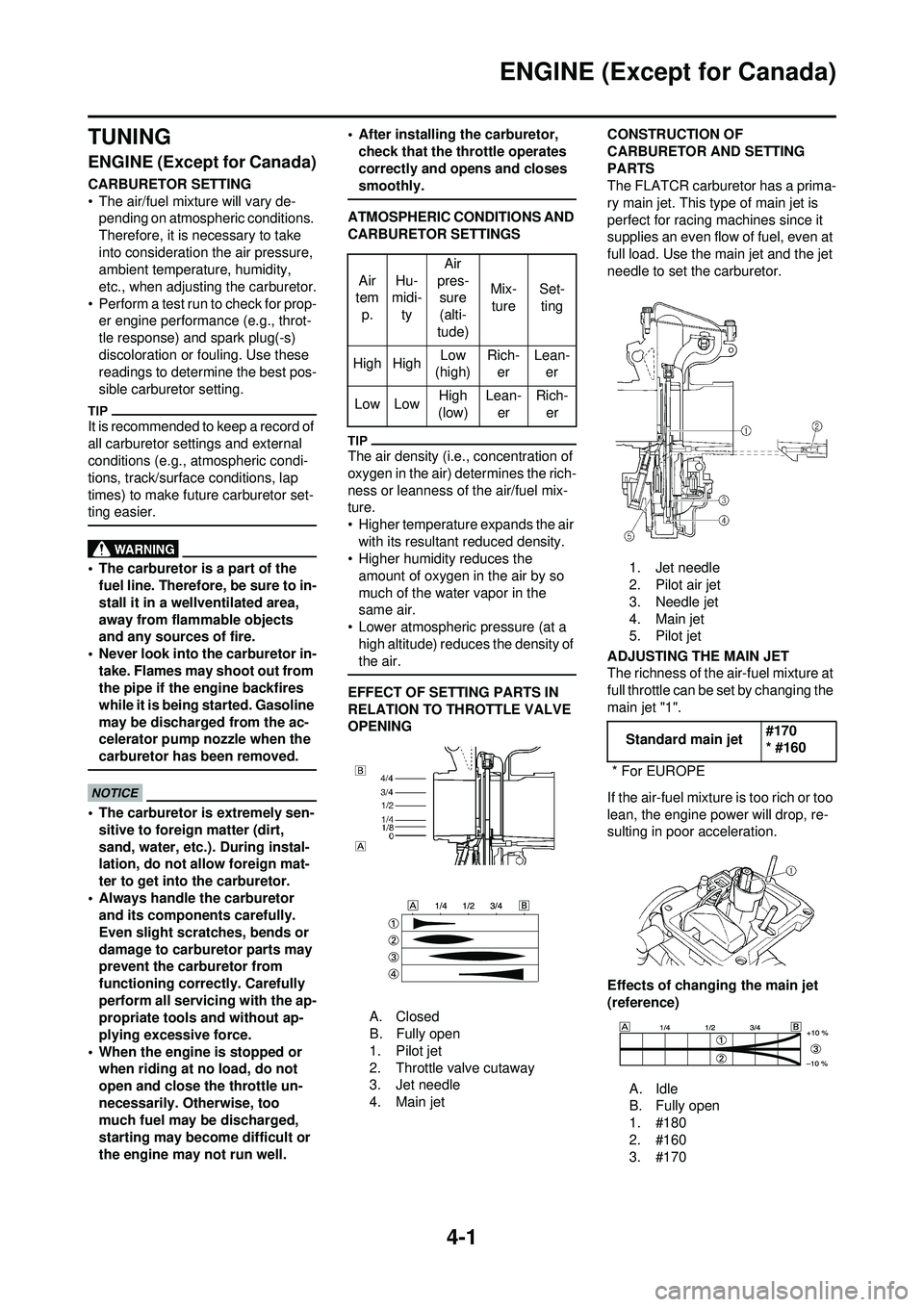
4. Main jet CONSTRUCTION OF
CARBURETOR AND SETTING
PARTS
The FLATCR carburetor has a prima-
ry main jet. This type of main jet is
perfect for racing machines since it
supplies an even flow of fuel, even at
full load. Use the main jet and the jet
needle to set the carburetor.
1. Jet needle
2. Pilot air jet
3. Needle jet
4. Main jet
5. Pilot jet
ADJUSTING THE MAIN JET
The richness of the air-fuel mixture at
full throttle can be set by changing the
main jet "1".
If the air-fuel mixture is too rich or too
lean, the engine power will drop, re-
sulting in poor acceleration.
Effects of changing the main jet
(reference)
A. Idle
B. Fully open
1. #180
2. #160
3. #170
Air
tem
p. Hu-
midi-
ty Air
pres- sure
(alti-
tude) Mix-
ture Set-
ting
High High Low
(high) Rich-
er Lean-
er
Low Low High
(low) Lean-
er Rich-
er
Standard main jet #170
* #160
* For EUROPE
Page 91 of 224
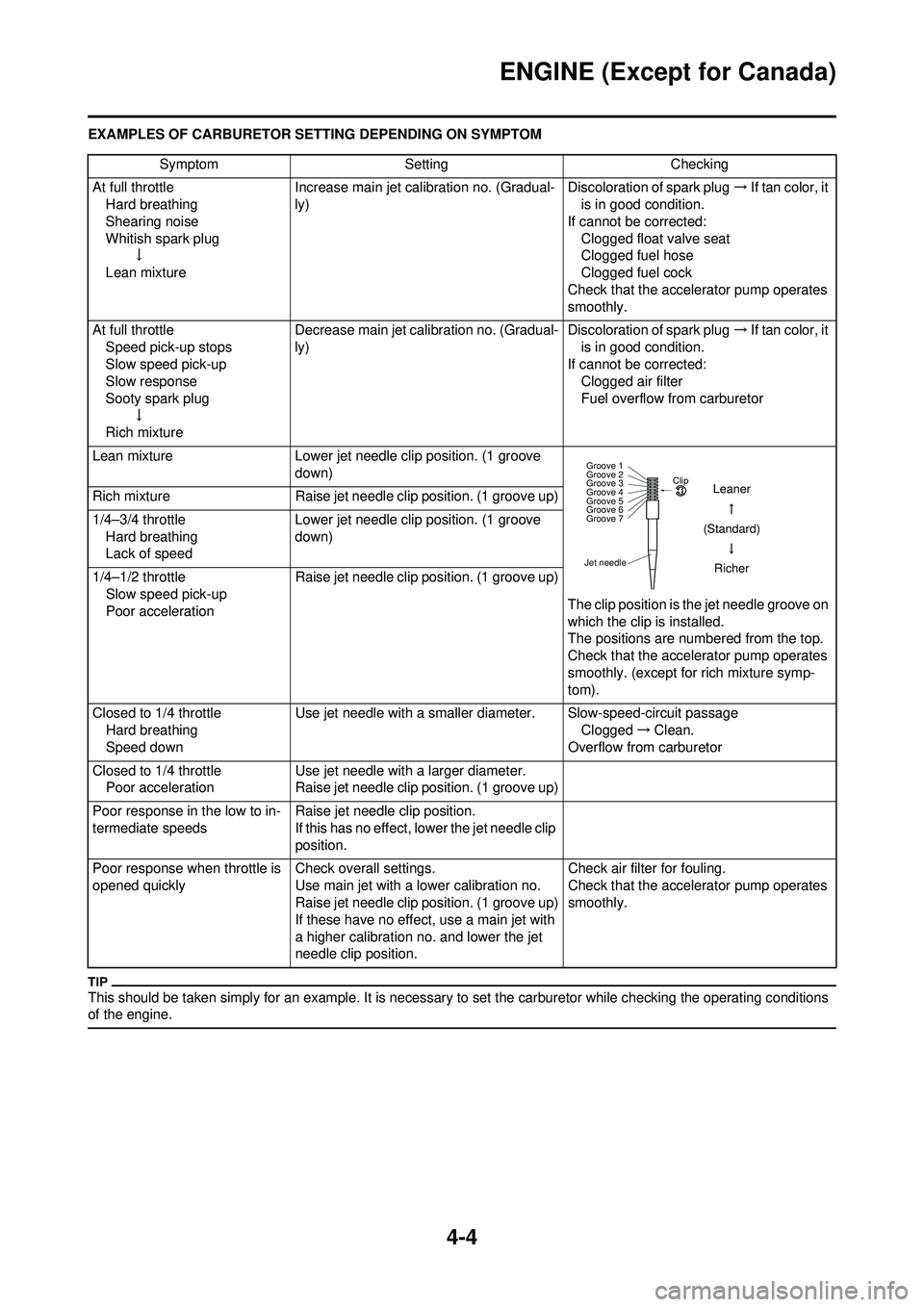
4-4
ENGINE (Except for Canada)
EXAMPLES OF CARBURETOR SETTING DEPENDING ON SYMPTOM
This should be taken simply for an example. It is necessary to set the carburetor while checking the operating conditions
of the engine.
SymptomSetting Checking
At full throttle Hard breathing
Shearing noise
Whitish spark plug ↓
Lean mixture Increase main jet calibration no. (Gradual-
ly)
Discoloration of spark plug
→If tan color, it
is in good condition.
If cannot be corrected: Clogged float valve seat
Clogged fuel hose
Clogged fuel cock
Check that the accelerator pump operates
smoothly.
At full throttle Speed pick-up stops
Slow speed pick-up
Slow response
Sooty spark plug ↓
Rich mixture Decrease main jet calibration no. (Gradual-
ly)
Discoloration of spark plug
→If tan color, it
is in good condition.
If cannot be corrected: Clogged air filter
Fuel overflow from carburetor
Lean mixture Lower jet needle clip position. (1 groove
down)
The clip position is the jet needle groove on
which the clip is installed.
The positions are numbered from the top.
Check that the accelerator pump operates
smoothly. (except for rich mixture symp-
tom).
Rich mixture
Raise jet needle clip position. (1 groove up)
1/4–3/4 throttle Hard breathing
Lack of speed Lower jet needle clip position. (1 groove
down)
1/4–1/2 throttle Slow speed pick-up
Poor acceleration Raise jet needle clip position. (1 groove up)
Closed to 1/4 throttle Hard breathing
Speed down Use jet needle with a smaller diameter. Slow-speed-circuit passage
Clogged→Clean.
Overflow from carburetor
Closed to 1/4 throttle Poor acceleration Use jet needle with a larger diameter.
Raise jet needle clip position. (1 groove up)
Poor response in the low to in-
termediate speeds Raise jet needle clip position.
If this has no effect, lower the jet needle clip
position.
Poor response when throttle is
opened quickly Check overall settings.
Use main jet with a lower calibration no.
Raise jet needle clip position. (1 groove up)
If these have no effect, use a main jet with
a higher calibration no. and lower the jet
needle clip position. Check air filter for fouling.
Check that the accelerator pump operates
smoothly.
Jet needleClip
Groove 7 Groove 6
Groove 5
Groove 4
Groove 3
Groove 2
Groove 1
Leaner
(Standard) Richer
Page 97 of 224
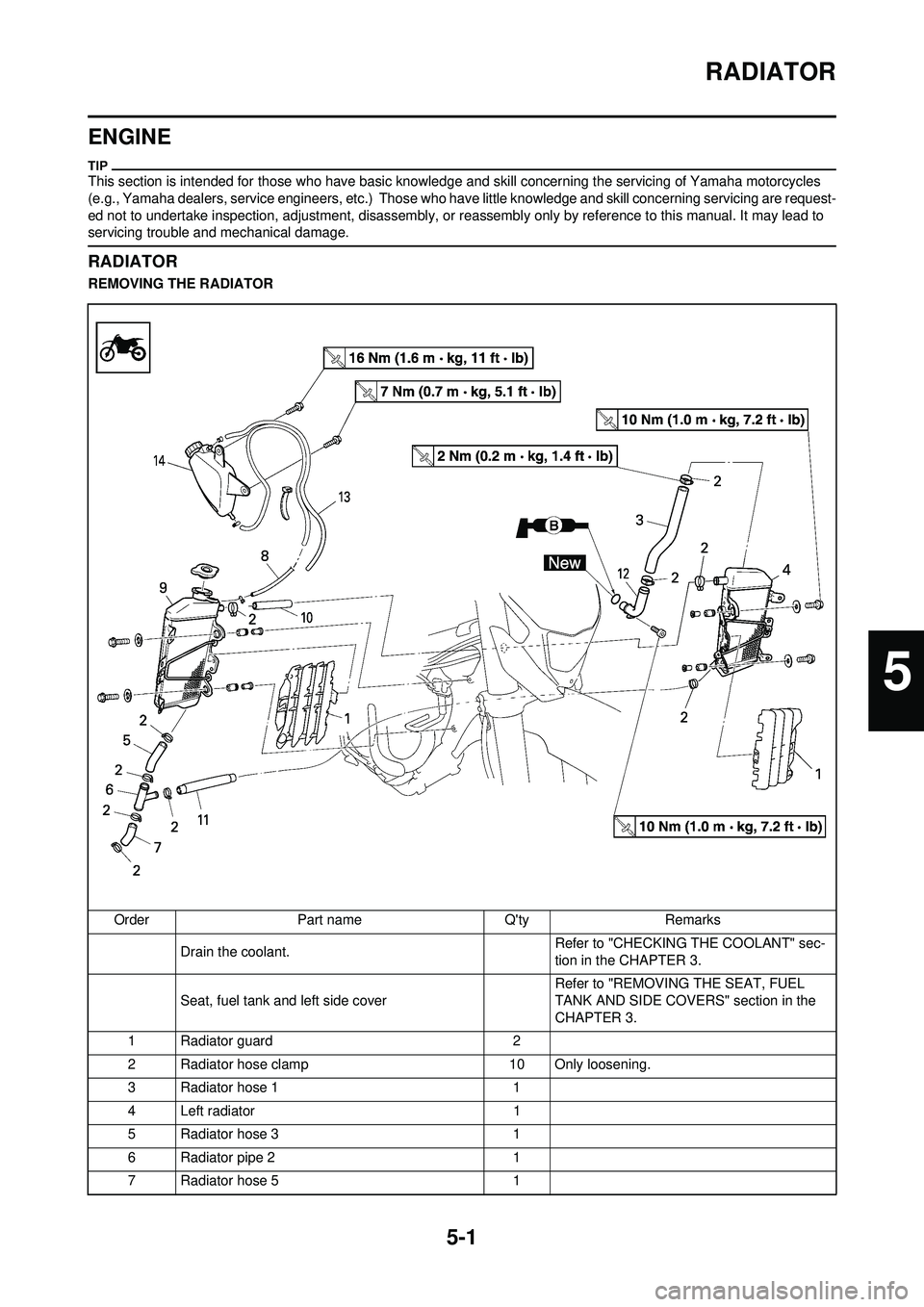
5-1
RADIATOR
ENGINE
This section is intended for those who have basic knowledge and skill concerning the servicing of Yamaha motorcycles
(e.g., Yamaha dealers, service engineers, etc.) Those who have little knowledge and skill concerning servicing are request-
ed not to undertake inspection, adjustment, disassembly, or reassembly only by reference to this manual. It may lead to
servicing trouble and mechanical damage.
RADIATOR
REMOVING THE RADIATOROrder Part name Q'ty Remarks Drain the coolant. Refer to "CHECKING THE COOLANT" sec-
tion in the CHAPTER 3.
Seat, fuel tank and left side cover Refer to "REMOVING THE SEAT, FUEL
TANK AND SIDE COVERS" section in the
CHAPTER 3.
1 Radiator guard 2
2 Radiator hose clamp 10 Only loosening.
3 Radiator hose 1 1
4 Left radiator 1
5 Radiator hose 3 1
6 Radiator pipe 2 1
7 Radiator hose 5 1
5
Page 99 of 224
5-3
RADIATOR
HANDLING NOTE
Do not remove the radiator cap
when the engine and radiator are
hot. Scalding hot fluid and steam
may be blown out under pressure,
which could cause serious injury.
When the engine has cooled, open
the radiator cap by the following
procedure:
Place a thick rag, like a towel, over
the radiator cap, slowly rotate the
cap counterclockwise to the de-
tent. This procedure allows any re-
sidual pressure to escape. When
the hissing sound has stopped,
press down on the cap while turn-
ing counterclockwise and remove
it.
CHECKING THE RADIATOR
1. Inspect:• Radiator core "1"Obstruction →Blow out with com-
pressed air through rear of the ra-
diator.
Bent fin →Repair/replace.
INSTALLING THE RADIATOR
1. Install: • O-ring "1"
• Radiator pipe 1 "2"
• Bolt (radiator pipe) "3"
Apply the lithium soap base grease
on the O-ring.
2. Install:• Catch tank hose "1"
• Radiator hose 2 "2"
• Radiator hose 3 "3"
• Radiator pipe 2 "4"
• Radiator hose 5 "5"
• Radiator hose 4 "6"To right radiator "7".
3. Install: • Right radiator "1"
• Bolt (right radiator) "2"
• Radiator hose 5 "3"
Refer to "CABLE ROUTING DIA-
GRAM" section in the CHAPTER
2.
4. Install: • Left radiator "1"
• Bolt (left radiator) "2"
• Radiator hose 1 "3"
Refer to "CABLE ROUTING DIA-
GRAM" section in the CHAPTER
2. 5. Tighten:
• Radiator hose clamp "4"
6. Install: • Radiator guard "1"
First fit the inner hook portion "a" and
then the outer one "b" onto the radia-
tor.
7. Install:• Catch tank "1"
• Bolt (catch tank) "2"
• Bolt (catch tank) "3"
• Catch tank hose "4"
• Catch tank breather hose "5"Refer to "CABLE ROUTING DIA-
GRAM" section in the CHAPTER
2.
Bolt (radiator pipe):
10 Nm (1.0 m•kg, 7.2
ft•lb)
Bolt (right radiator):10 Nm (1.0 m•kg, 7.2
ft•lb)
Bolt (left radiator): 10 Nm (1.0 m•kg, 7.2
ft•lb)
Radiator hose 1: 2 Nm (0.2 m•kg, 1.4
ft•lb)
Radiator hose clamp:2 Nm (0.2 m•kg, 1.4
ft•lb)
Bolt (catch tank): 7 Nm (0.7 m•kg, 5.1
ft•lb)
Bolt (catch tank): 16 Nm (1.6 m•kg, 11
ft•lb)
Page 103 of 224
5-7
CARBURETOR
HANDLING NOTE
Do not loosen the screw (throttle
position sensor) "1" except when
changing the throttle position sen-
sor due to failure because it will
cause a drop in engine perfor-
mance.
REMOVING THE PILOT SCREW
(For EUROPE)
1. Remove:• Pilot screw "1"
To optimize the fuel flow at a small
throttle opening, each machine's pilot
screw has been individually set at the
factory. Before removing the pilot
screw, turn it in fully and count the
number of turns. Record this number
as the factory-set number of turns
out.
CHECKING THE CARBURETOR
1. Inspect:• Carburetor body
Contamination →Clean.
• Use a petroleum based solvent for
cleaning. Blow out all passages and
jets with compressed air.
• Never use a wire.
2. Inspect: •Main jet "1"
• Pilot jet "2"
• Needle jet "3"
• Starter jet "4"
• Pilot air jet "5"
•Leak jet "6"
• Main air jet "7"Damage →Replace.
Contamination →Clean.
• Use a petroleum based solvent for
cleaning. Blow out all passages and
jets with compressed air.
• Never use a wire.
CHECKING THE NEEDLE VALVE
1. Inspect: • Needle valve "1"
• Valve seat "2"
Grooved wear "a" →Replace.
Dust "b" →Clean.
•Filter "c" Clogged →Clean.
CHECKING THE THROTTLE
VALVE
1. Check: • Free movement
Stick →Repair or replace.
Insert the throttle valve "1" into the
carburetor body, and check for free
movement.
CHECKING THE JET NEEDLE
1. Inspect:
•Jet needle "1"Bends/wear →Replace.
• Clip groove Free play exists/wear →Replace.
MEASURING AND ADJUSTING
THE FLOAT HEIGHT
1. Measure: • Float height "a"
Out of specification →Adjust.
Measurement and adjustment
steps:
a. Hold the carburetor in an upside
down position.
• Slowly tilt the carburetor in the op-posite direction, then take the mea-
surement when the needle valve
aligns with the float arm.
• If the carburetor is level, the weight
of the float will push in the needle
valve, resulting in an incorrect mea-
surement.
b. Measure the distance between the mating surface of the float
chamber and top of the float using
a vernier calipers.
The float arm should be resting on the
needle valve, but not compressing
the needle valve.
c. If the float height is not within specification, inspect the valve
seat and needle valve.
d. If either is worn, replace them
both.
Float height:8.0 mm (0.31 in)
Page 113 of 224
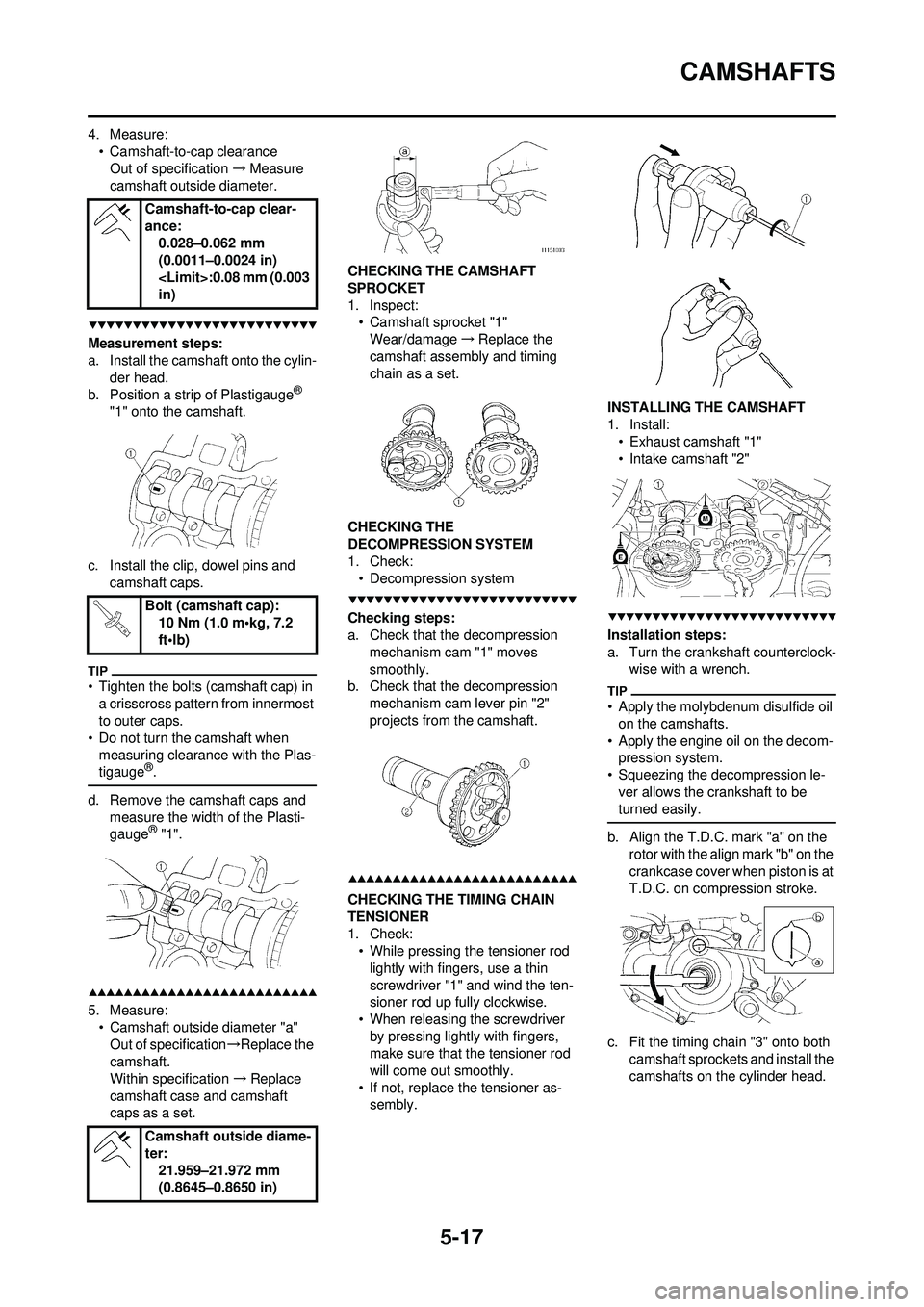
5-17
CAMSHAFTS
4. Measure:• Camshaft-to-cap clearanceOut of specification →Measure
camshaft outside diameter.
Measurement steps:
a. Install the camshaft onto the cylin-
der head.
b. Position a strip of Plastigauge
®
"1" onto the camshaft.
c. Install the clip, dowel pins and camshaft caps.
• Tighten the bolts (camshaft cap) in a crisscross pattern from innermost
to outer caps.
• Do not turn the camshaft when measuring clearance with the Plas-
tigauge
®.
d. Remove the camshaft caps and measure the width of the Plasti-
gauge
® "1".
5. Measure:• Camshaft outside diameter "a"Out of specification →Replace the
camshaft.
Within specification →Replace
camshaft case and camshaft
caps as a set. CHECKING THE CAMSHAFT
SPROCKET
1. Inspect:
• Camshaft sprocket "1"
Wear/damage →Replace the
camshaft assembly and timing
chain as a set.
CHECKING THE
DECOMPRESSION SYSTEM
1. Check: • Decompression system
Checking steps:
a. Check that the decompression mechanism cam "1" moves
smoothly.
b. Check that the decompression
mechanism cam lever pin "2"
projects from the camshaft.
CHECKING THE TIMING CHAIN
TENSIONER
1. Check:• While pressing the tensioner rod
lightly with fingers, use a thin
screwdriver "1" and wind the ten-
sioner rod up fully clockwise.
• When releasing the screwdriver by pressing lightly with fingers,
make sure that the tensioner rod
will come out smoothly.
• If not, replace the tensioner as- sembly. INSTALLING THE CAMSHAFT
1. Install:
• Exhaust camshaft "1"
• Intake camshaft "2"
Installation steps:
a. Turn the crankshaft counterclock- wise with a wrench.
• Apply the molybdenum disulfide oil
on the camshafts.
• Apply the engine oil on the decom- pression system.
• Squeezing the decompression le- ver allows the crankshaft to be
turned easily.
b. Align the T.D.C. mark "a" on the rotor with the align mark "b" on the
crankcase cover when piston is at
T.D.C. on compression stroke.
c. Fit the timing chain "3" onto both camshaft sprockets and install the
camshafts on the cylinder head.
Camshaft-to-cap clear-
ance:
0.028–0.062 mm
(0.0011–0.0024 in)
in)
Bolt (camshaft cap): 10 Nm (1.0 m•kg, 7.2
ft•lb)
Camshaft outside diame-
ter: 21.959–21.972 mm
(0.8645–0.8650 in)
Page 120 of 224
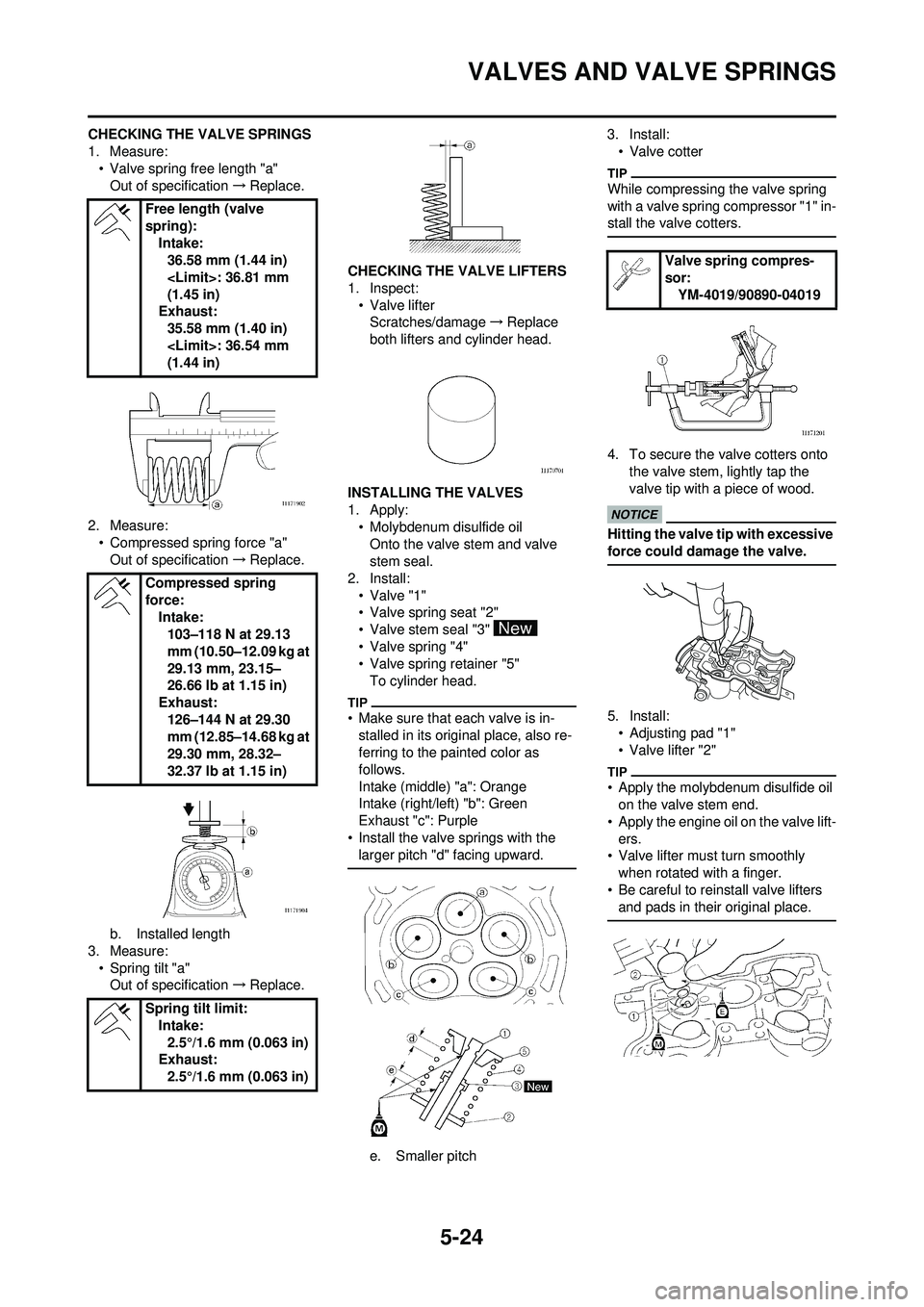
5-24
VALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS
CHECKING THE VALVE SPRINGS
1. Measure:• Valve spring free length "a"Out of specification →Replace.
2. Measure: • Compressed spring force "a"Out of specification →Replace.
b. Installed length
3. Measure: • Spring tilt "a"Out of specification →Replace. CHECKING THE VALVE LIFTERS
1. Inspect:
• Valve lifterScratches/damage →Replace
both lifters and cylinder head.
INSTALLING THE VALVES
1. Apply: • Molybdenum disulfide oilOnto the valve stem and valve
stem seal.
2. Install: •Valve "1"
• Valve spring seat "2"
• Valve stem seal "3"
• Valve spring "4"
• Valve spring retainer "5"To cylinder head.
• Make sure that each valve is in-stalled in its original place, also re-
ferring to the painted color as
follows.
Intake (middle) "a": Orange
Intake (right/left) "b": Green
Exhaust "c": Purple
• Install the valve springs with the larger pitch "d" facing upward.
e. Smaller pitch 3. Install:
• Valve cotter
While compressing the valve spring
with a valve spring compressor "1" in-
stall the valve cotters.
4. To secure the valve cotters onto the valve stem, lightly tap the
valve tip with a piece of wood.
Hitting the valve tip with excessive
force could damage the valve.
5. Install:• Adjusting pad "1"
• Valve lifter "2"
• Apply the molybdenum disulfide oil on the valve stem end.
• Apply the engine oil on the valve lift- ers.
• Valve lifter must turn smoothly
when rotated with a finger.
• Be careful to reinstall valve lifters and pads in their original place.
Free length (valve
spring):
Intake:36.58 mm (1.44 in)
(1.45 in)
Exhaust:
35.58 mm (1.40 in)
(1.44 in)
Compressed spring
force: Intake:103–118 N at 29.13
mm (10.50–12.09 kg at
29.13 mm, 23.15–
26.66 lb at 1.15 in)
Exhaust: 126–144 N at 29.30
mm (12.85–14.68 kg at
29.30 mm, 28.32–
32.37 lb at 1.15 in)
Spring tilt limit: Intake:2.5°/1.6 mm (0.063 in)
Exhaust:
2.5°/1.6 mm (0.063 in)
Valve spring compres-
sor: YM-4019/90890-04019