check engine YAMAHA WR 250F 2017 Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: YAMAHA, Model Year: 2017, Model line: WR 250F, Model: YAMAHA WR 250F 2017Pages: 432, PDF Size: 14.14 MB
Page 394 of 432

FUEL PUMP SYSTEM
9-58
EAS2GBB380TROUBLESHOOTING
The fuel pump fails to operate.
TIP
Before troubleshooting, remove the following part(s):
1. Seat
2. Side cover (left/right)
3. Air scoop (left/right)
4. Fuel tank
1. Check the fuse.
Refer to “CHECKING THE FUSES”
on page 9-68.NG
Replace the fuse(s).
OK
2. Check the battery.
Refer to “CHECKING AND
CHARGING THE BATTERY” on
page 9-69.NG
• Clean the battery terminals.
• Recharge or replace the battery.
OK
3. Check the engine stop switch.
Refer to “CHECKING THE
SWITCHES” on page 9-64.NG
Replace the engine stop switch.
OK
4. Check fuel pressure.
Refer to “CHECKING THE FUEL
PRESSURE” on page 8-5.NG
Replace the fuel pump.
OK
5. Check the fuel pump system wire
harness connections.
Refer to “CIRCUIT DIAGRAM” on
page 9-56.NG
Properly connect or repair the fuel pump
system’s wiring.
OK
Replace the ECU.
Page 407 of 432

ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
9-71
TIP
Voltage should be measured 30 minutes after
the engine is stopped.
b. Connect a charger and ammeter to the bat-
tery and start charging.
TIP
Set the charging voltage to 16–17 V. If the set-
ting is lower, charging will be insufficient. If too
high, the battery will be over-charged.
c. Make sure that the current is higher than the
standard charging current written on the bat-
tery.
TIP
If the current is lower than the standard charg-
ing current written on the battery, set the charg-
ing voltage adjust dial at 20–24 V and monitor
the amperage for 3–5 minutes to check the bat-
tery.
d. Adjust the voltage so that the current is at
the standard charging level.
e. Set the time according to the charging time
suitable for the open-circuit voltage.
f. If charging requires more than 5 hours, it is
advisable to check the charging current after
a lapse of 5 hours. If there is any change in
the amperage, readjust the voltage to obtain
the standard charging current.
g. Measure the battery open-circuit voltage af-
ter leaving the battery unused for more than
30 minutes.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
Charging method using a constant volt-
age charger
a. Measure the open-circuit voltage prior to
charging.
TIP
Voltage should be measured 30 minutes after
the engine is stopped.
b. Connect a charger and ammeter to the bat-
tery and start charging.c. Make sure that the current is higher than the
standard charging current written on the bat-
tery.
TIP
If the current is lower than the standard charg-
ing current written on the battery, this type of
battery charger cannot charge the VRLA (Valve
Regulated Lead Acid) battery. A variable volt-
age charger is recommended.
d. Charge the battery until the battery’s charg-
ing voltage is 15 V.
TIP
Set the charging time at 20 hours (maximum).
e. Measure the battery open-circuit voltage af-
ter leaving the battery unused for more than
30 minutes.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
6. Install:
• Battery
7. Connect:
• Battery leads
(to the battery terminals)
ECA
NOTICE
First, connect the positive battery lead “1”,
and then the negative battery lead “2”.
8. Check:
• Battery terminals
Dirt Clean with a wire brush.
Loose connection Connect properly.
9. Lubricate:
• Battery terminals • Standard charging current is reached
Battery is good.
• Standard charging current is not reached
Replace the battery.
12.8 V or more --- Charging is complete.
12.7 V or less --- Recharging is required.
Under 12.0 V --- Replace the battery.
12.8 V or more --- Charging is complete.
12.7 V or less --- Recharging is required.
Under 12.0 V --- Replace the battery.
Recommended lubricant
Dielectric grease
2
1
Page 409 of 432

ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
9-73
Radiator fan motor relay
EAS2GBB387CHECKING THE DIODE
1. Check:
•Diode
Out of specification Replace.
TIP
The pocket tester and the analog pocket tester
readings are shown in the following table.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Disconnect the diode from the wire harness.b. Connect the pocket tester ( 1) to the di-
ode coupler as shown.
c. Check the diode for continuity.
d. Check the diode for no continuity.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
EAS2GBB388CHECKING THE IGNITION SPARK GAP
1. Check:
• Ignition spark gap
Out of specification Perform the ignition
system troubleshooting, starting with step 4.
Refer to “TROUBLESHOOTING” on page 9-
4.
TIP
If the ignition spark gap is within specification,
the ignition system circuit is operating normally.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Remove the spark plug cap from the spark
plug.
b. Connect the ignition checker “1” as shown.
c. Push the engine stop switch.
d. Measure the ignition spark gap “a”.
1. Positive battery terminal
2. Negative battery terminal
3. Positive tester probe
4. Negative tester probe
Result
Continuity
(between “3” to “4”)
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
No continuity
Tester positive lead Sky blue
“1”
Tester negative lead Green/
Black “2”
Continuity
Tester positive lead Green/
Black “2”
Tester negative lead Sky blue
“1”
No continuity
Tester positive lead Red “3”
Tester negative lead Red/Blue
“4”
Continuity
Tester positive lead Red/Blue
“4”
Tester negative lead Red “3”
1 23
4
P/L
R/L
R/W
Br,R/W
Minimum ignition spark gap
6.0 mm (0.24 in)
Ignition checker
90890-06754
Oppama pet–4000 spark checker
YM-34487
2. Spark plug cap
2
1
4
3
R Sb
G/B R/L
Page 410 of 432
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
9-74
e. Crank the engine by pushing the start switch
and gradually increase the spark gap until a
misfire occurs.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
EAS2GBB389CHECKING THE SPARK PLUG CAP
1. Remove:
• Spark plug cap
(from the spark plug lead)
2. Check:
• Spark plug cap resistance
Out of specification Replace.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Connect the pocket tester ( 1k) to the
spark plug cap.
b. Measure the spark plug cap resistance.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
EAS2GBB390CHECKING THE IGNITION COIL
1. Disconnect:
• Ignition coil terminal
(from the sub wire harness)
• Spark plug cap
(from the ignition coil)
2. Check:
• Primary coil resistance
Out of specification Replace.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
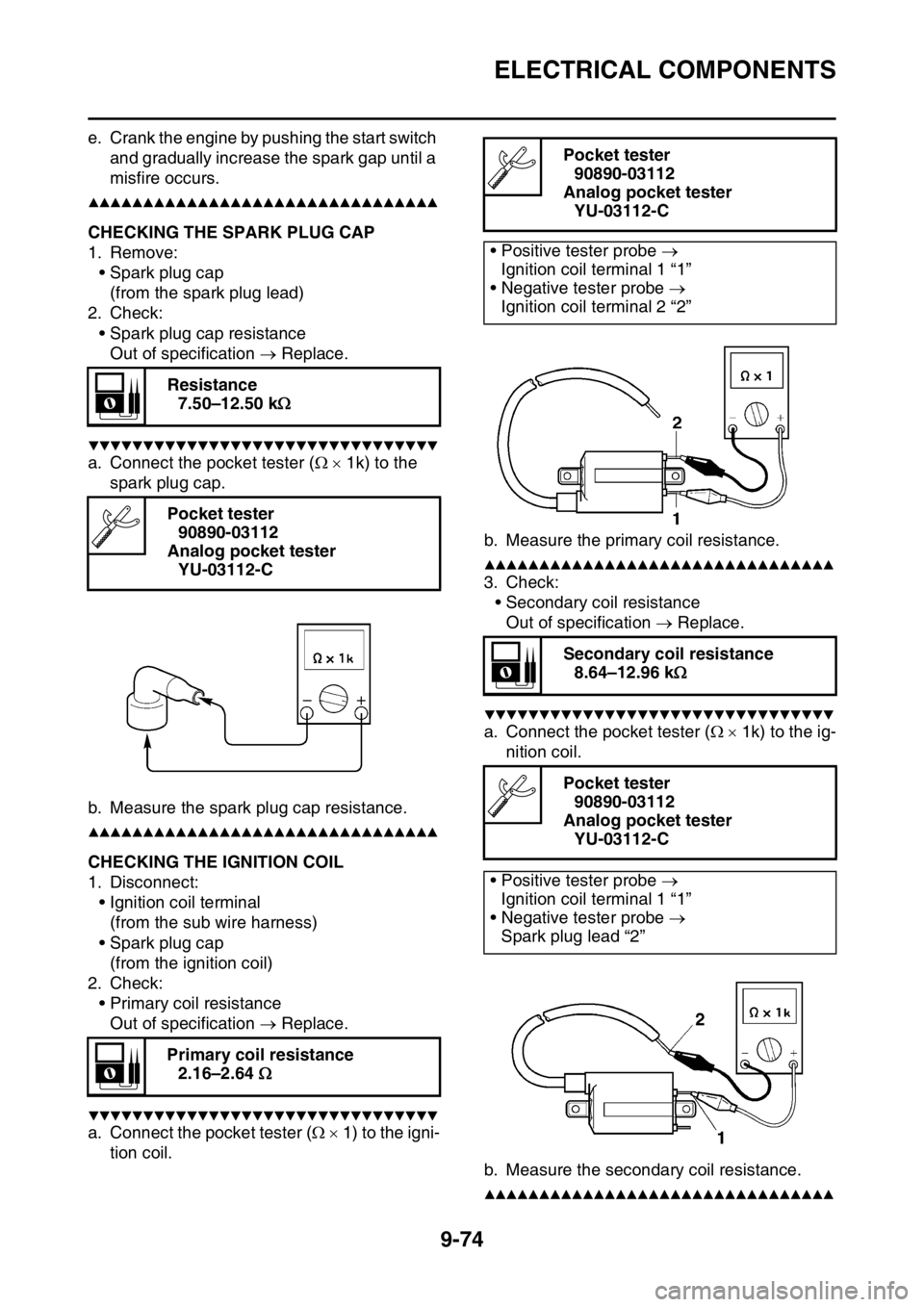
a. Connect the pocket tester ( 1) to the igni-
tion coil.b. Measure the primary coil resistance.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
3. Check:
• Secondary coil resistance
Out of specification Replace.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Connect the pocket tester ( 1k) to the ig-
nition coil.
b. Measure the secondary coil resistance.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
Resistance
7.50–12.50 k
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
Primary coil resistance
2.16–2.64
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
• Positive tester probe
Ignition coil terminal 1 “1”
• Negative tester probe
Ignition coil terminal 2 “2”
Secondary coil resistance
8.64–12.96 k
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
• Positive tester probe
Ignition coil terminal 1 “1”
• Negative tester probe
Spark plug lead “2”
Page 413 of 432
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
9-77
c. Start the engine and let it run at approxi-
mately 5000 r/min.
d. Measure the charging voltage.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
EAS2GBB395CHECKING THE SPEED SENSOR
1. Check:
• Speed sensor output voltage
Out of specification Replace.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
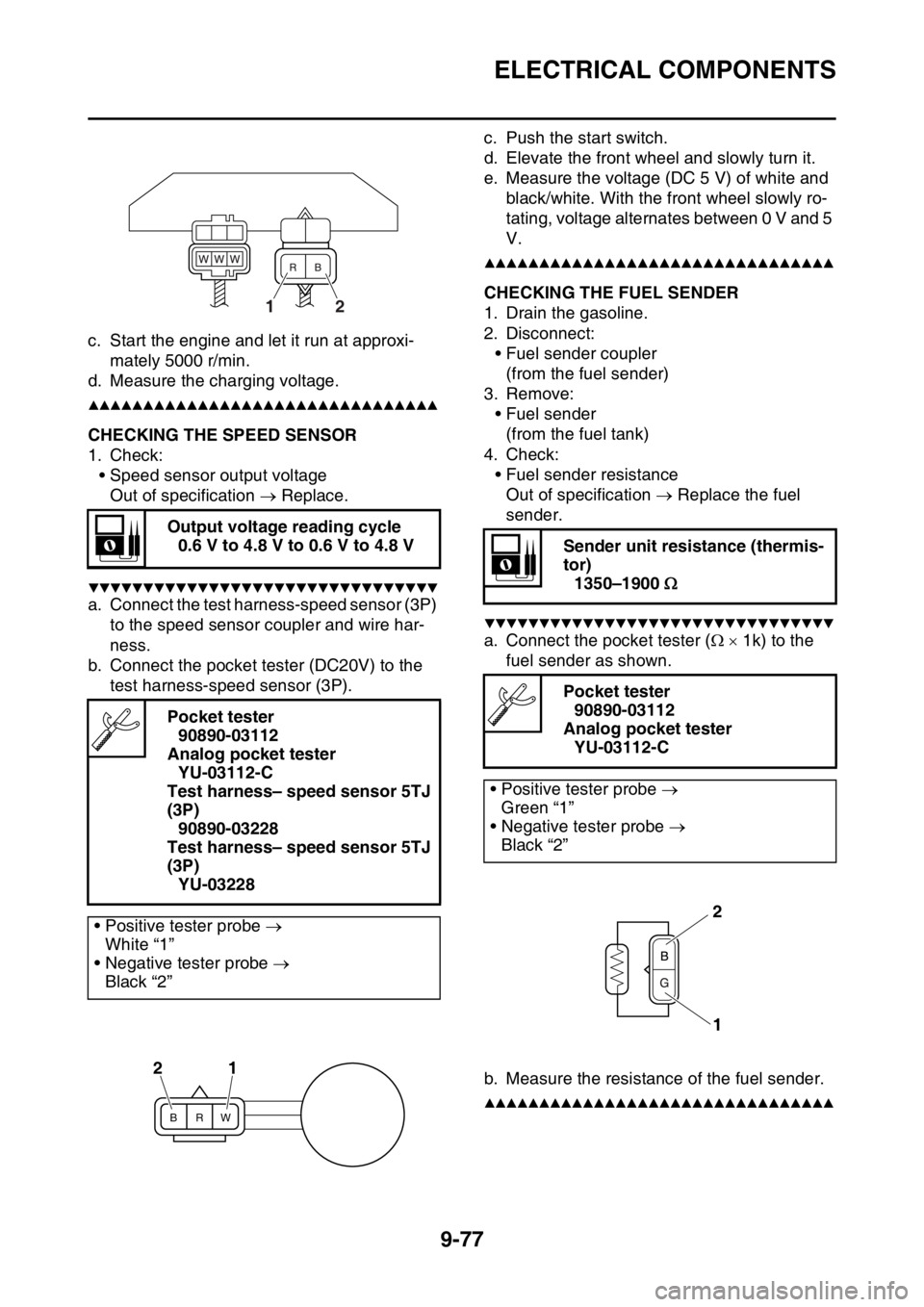
a. Connect the test harness-speed sensor (3P)
to the speed sensor coupler and wire har-
ness.
b. Connect the pocket tester (DC20V) to the
test harness-speed sensor (3P).c. Push the start switch.
d. Elevate the front wheel and slowly turn it.
e. Measure the voltage (DC 5 V) of white and
black/white. With the front wheel slowly ro-
tating, voltage alternates between 0 V and 5
V.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
EAS2GBB396CHECKING THE FUEL SENDER
1. Drain the gasoline.
2. Disconnect:
• Fuel sender coupler
(from the fuel sender)
3. Remove:
• Fuel sender
(from the fuel tank)
4. Check:
• Fuel sender resistance
Out of specification Replace the fuel
sender.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Connect the pocket tester ( 1k) to the
fuel sender as shown.
b. Measure the resistance of the fuel sender.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
Output voltage reading cycle
0.6 V to 4.8 V to 0.6 V to 4.8 V
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
Test harness– speed sensor 5TJ
(3P)
90890-03228
Test harness– speed sensor 5TJ
(3P)
YU-03228
• Positive tester probe
White “1”
• Negative tester probe
Black “2”
12
BRW
21
Sender unit resistance (thermis-
tor)
1350–1900
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
• Positive tester probe
Green “1”
• Negative tester probe
Black “2”
1
2
Page 416 of 432
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
9-80
EAS2GBB401CHECKING THE THROTTLE POSITION
SENSOR INPUT VOLTAGE
1. Check:
• Throttle position sensor input voltage
Out of specification Replace the ECU.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
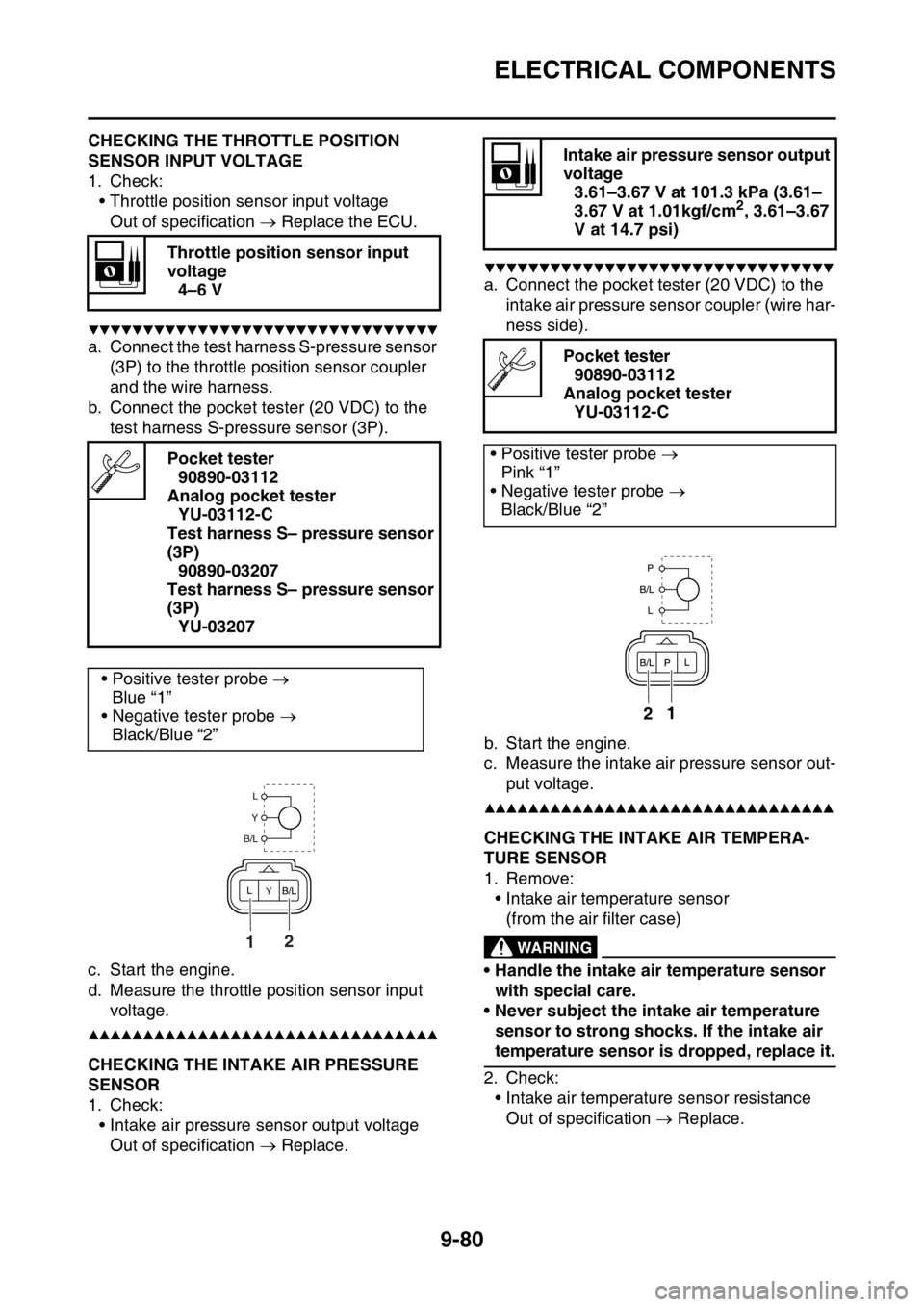
a. Connect the test harness S-pressure sensor
(3P) to the throttle position sensor coupler
and the wire harness.
b. Connect the pocket tester (20 VDC) to the
test harness S-pressure sensor (3P).
c. Start the engine.
d. Measure the throttle position sensor input
voltage.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
EAS2GBB402CHECKING THE INTAKE AIR PRESSURE
SENSOR
1. Check:
• Intake air pressure sensor output voltage
Out of specification Replace.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Connect the pocket tester (20 VDC) to the
intake air pressure sensor coupler (wire har-
ness side).
b. Start the engine.
c. Measure the intake air pressure sensor out-
put voltage.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
EAS2GBB403CHECKING THE INTAKE AIR TEMPERA-
TURE SENSOR
1. Remove:
• Intake air temperature sensor
(from the air filter case)
EWA
WARNING
• Handle the intake air temperature sensor
with special care.
• Never subject the intake air temperature
sensor to strong shocks. If the intake air
temperature sensor is dropped, replace it.
2. Check:
• Intake air temperature sensor resistance
Out of specification Replace. Throttle position sensor input
voltage
4–6 V
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
Test harness S– pressure sensor
(3P)
90890-03207
Test harness S– pressure sensor
(3P)
YU-03207
• Positive tester probe
Blue “1”
• Negative tester probe
Black/Blue “2”
21
Intake air pressure sensor output
voltage
3.61–3.67 V at 101.3 kPa (3.61–
3.67 V at 1.01kgf/cm
2, 3.61–3.67
V at 14.7 psi)
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
• Positive tester probe
Pink “1”
• Negative tester probe
Black/Blue “2”
12
Page 420 of 432

TROUBLESHOOTING
10-1
EAS2GBB405
TROUBLESHOOTING
EAS2GBB406GENERAL INFORMATION
TIP
The following guide for troubleshooting does
not cover all the possible causes of trouble. It
should be helpful, however, as a guide to basic
troubleshooting. Refer to the relative procedure
in this manual for checks, adjustments, and re-
placement of parts.
EAS2GBB407STARTING FAILURES
Engine
1. Cylinder and cylinder head
• Loose spark plug
• Loose cylinder head or cylinder
• Damaged cylinder head gasket
• Damaged cylinder gasket
• Worn or damaged cylinder
• Incorrect valve clearance
• Improperly sealed valve
• Incorrect valve-to-valve-seat contact
• Incorrect valve timing
• Faulty valve spring
• Seized valve
2. Piston and piston ring(s)
• Improperly installed piston ring
• Damaged, worn or fatigued piston ring
• Seized piston ring
• Seized or damaged piston
3. Air filter
• Improperly installed air filter
• Clogged air filter element
4. Crankcase and crankshaft
• Improperly assembled crankcase
• Seized crankshaft
Fuel system
1. Fuel tank
• Empty fuel tank
• Clogged fuel tank breather hose
• Deteriorated or contaminated fuel
• Clogged or damaged fuel hose
2. Fuel pump
• Faulty fuel pump
3. Throttle body
• Deteriorated or contaminated fuel
• Sucked-in airElectrical system
1. Battery
• Discharged battery
• Faulty battery
2. Fuse
• Blown, damaged or incorrect fuse
• Improperly installed fuse
3. Spark plug
• Incorrect spark plug gap
• Incorrect spark plug heat range
• Fouled spark plug
• Worn or damaged electrode
• Worn or damaged insulator
4. Ignition coil
• Cracked or broken ignition coil body
• Broken or shorted primary or secondary
coils
5. Ignition system
• Faulty ECU
• Faulty crankshaft position sensor
• Broken generator rotor woodruff key
6. Switches and wiring
• Faulty ECU
• Faulty engine stop switch
• Broken or shorted wiring
• Faulty neutral switch
• Improperly grounded circuit
• Loose connections
7. Starting system
• Faulty starter motor
• Faulty starter relay
• Faulty starting circuit cut-off relay
• Faulty starter clutch
EAS2GBB408INCORRECT ENGINE IDLING SPEED
Engine
1. Cylinder and cylinder head
• Incorrect valve clearance
• Damaged valve train components
2. Air filter
• Clogged air filter element
Fuel system
1. Throttle body
• Damaged or loose throttle body joint
• Improperly synchronized throttle bodies
• Improper throttle cable free play
• Flooded throttle body
Page 425 of 432

LIST OF SELF-DIAGNOSTIC AND FAIL-SAFE ACTIONS
10-6
SENSOR OPERATION TABLE
Diag-
nostic
code
No.Item Display Procedure
01 Throttle position sensor sig-
nal
• Fully closed position
• Fully opened position• 11–14
• 109–116• Check with throttle valve
fully closed.
• Check with throttle valve
fully open.
03 Intake air pressure Displays the intake air pres-
sure.Operate the throttle while
pushing the start switch. (If
the display value changes,
the performance is OK.)
05 Intake air temperature Displays the intake air tem-
perature.Compare the actually mea-
sured intake air tempera-
ture with the Yamaha
diagnostic tool display val-
ue.
06 Coolant temperature When engine is cold: Dis-
plays temperature closer to
air temperature.
When engine is hot: Displays
current coolant temperature.Compare the actually mea-
sured coolant temperature
with the Yamaha diagnostic
tool display value.
07 Vehicle speed pulses Vehicle speed pulse
0–999Check that the number in-
creases when the front
wheel is rotated. The num-
ber is cumulative and does
not reset each time the
wheel is stopped.
08 Lean angle sensor
• Upright
• OverturnedDisplays the output voltage.
• 0.4–1.4
• 3.7–4.4Remove the lean angle
sensor, and incline it more
than 45 degrees.
09 Monitor voltage Displays the fuel system volt-
age.
• Approximately 12.0 (V)—
21 Neutral switch
• Gear in neutral
• Gear not in neutral•ON
•OFFOperate the shift pedal.
60 EEPROM fault code display
• No fault
• CO adjustment value
• Setting tool adjustment
values 0–8 for fuel injec-
tion amount or ignition tim-
ing•00
•01
•07—
61 Malfunction history ( )
code display *1
• There is no history.
• There is some history.•00
• Other: Displays the fault
code of ( ).—